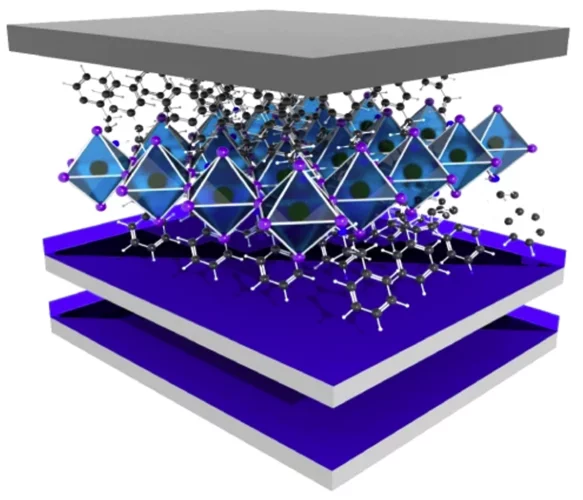
Lighting up the appealing world of hybrid perovskites
Researchers from Italy, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institut, successfully used the macromolecular crystallography beamline X06DA-PXIII at the Swiss Light Source to characterize promising perovkites materials used in solar cells and other photodetector devices.
Opening the door to X-ray quantum optics
The 'perfect' X-ray beam-splitter: Researchers at SwissFEL have an ingenious solution to produce coherent copies of pulses, facilitating a realm of new X-ray techniques.
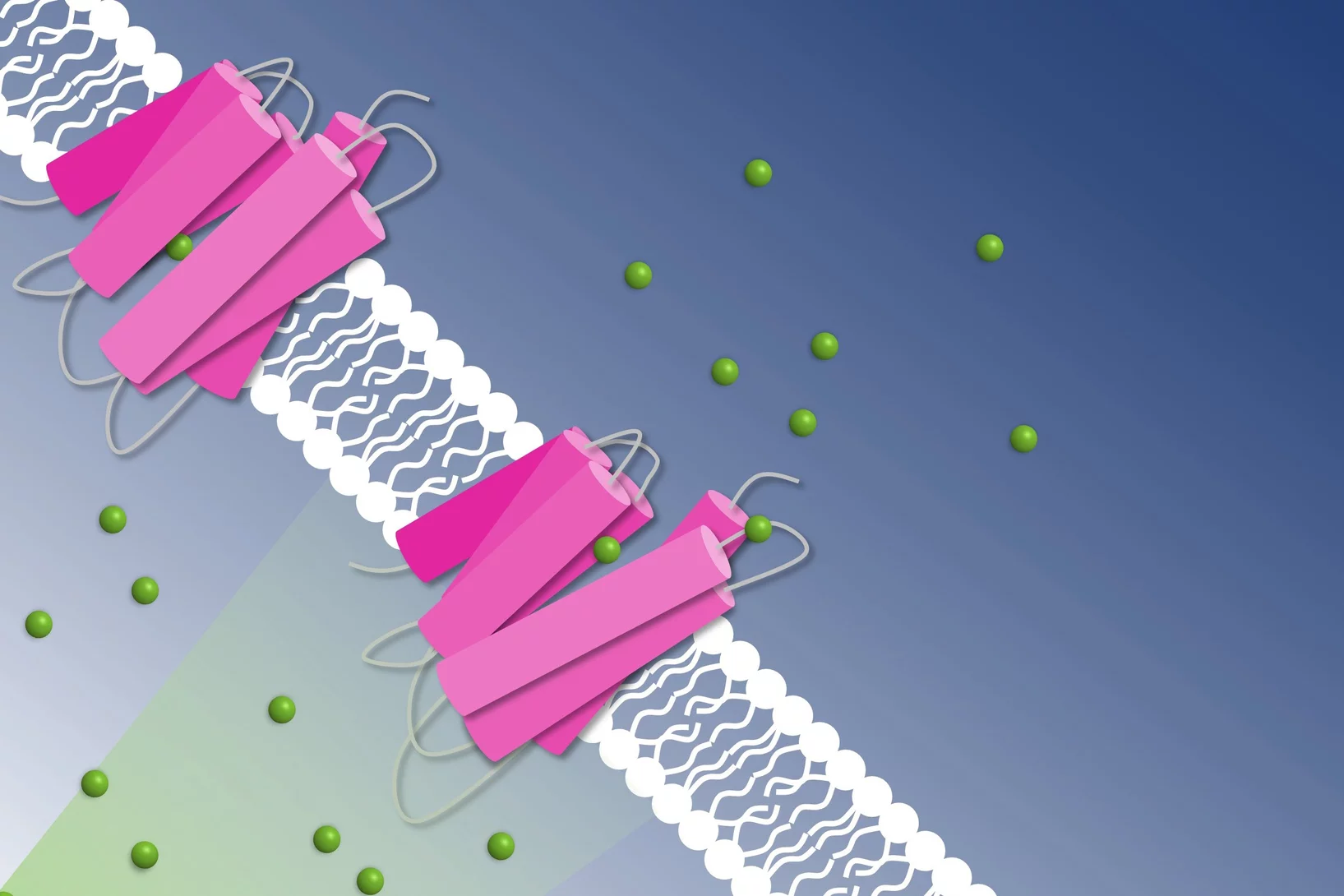
How to get chloride ions into the cell
A molecular movie shot at PSI reveals the mechanism of a light-driven chloride pump
Simulant material could aid in Fukushima cleanup
A new simulation of the most dangerous radioactive debris from the Fukushima nuclear power plant will help with clean-up efforts.
EU XFEL Young Scientist Award for Camila Bacellar
Camila Bacellar, beamline scientist and group leader of the Alvra endstation at SwissFEL, has received the European XFEL Young Scientist Award. The award recognises the contribution of young scientists to research at the European XFEL.
New, better coronavirus rapid test
The test identifies different virus variants and improves disease prognosis.
Towards compact quantum computers, thanks to topology
In pursuit of particularly stable quantum bits, researchers have closely examined the electron distribution in two semiconductors.
Direct observation of crack formation mechanisms with operando Laser Powder Bed Fusion X-ray radiography
Operando high-speed X-ray radiography experiments reveal the cracking mechanism during 3D laser printing of a Ni superalloy.
Millions in funding for brain and quantum research
The European Research Council approves PSI projects for the development of a quantum computer and brain research worth about 5 million euros.
Semiconductors reach the quantum world
Boosted with superconductivity: Semiconductor technology can get a new twist by exploiting quantum effects in superconductors.
Priority access call for work on combating COVID-19 continues
On January 30th, 2020, the WHO declared the recent outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), a public health emergency of international concern. It declared that there is an urgent need to improve our understanding of the newly identified virus and its possible future evolution as well as to contain the spread; to develop precise diagnostics and treatment, and to improve the public health response and patient care.
The COVID priority access call continues and is still open in 2022.
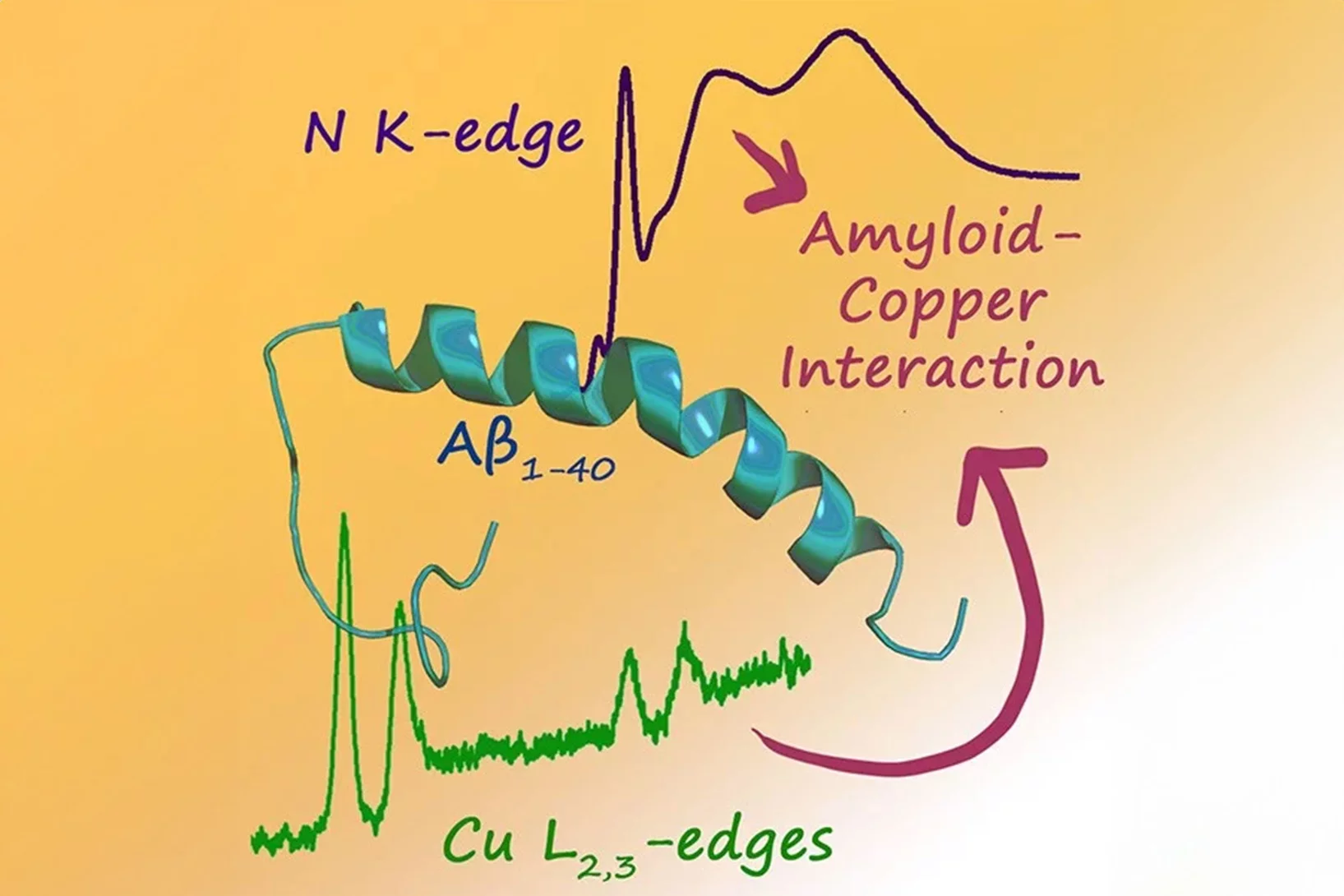
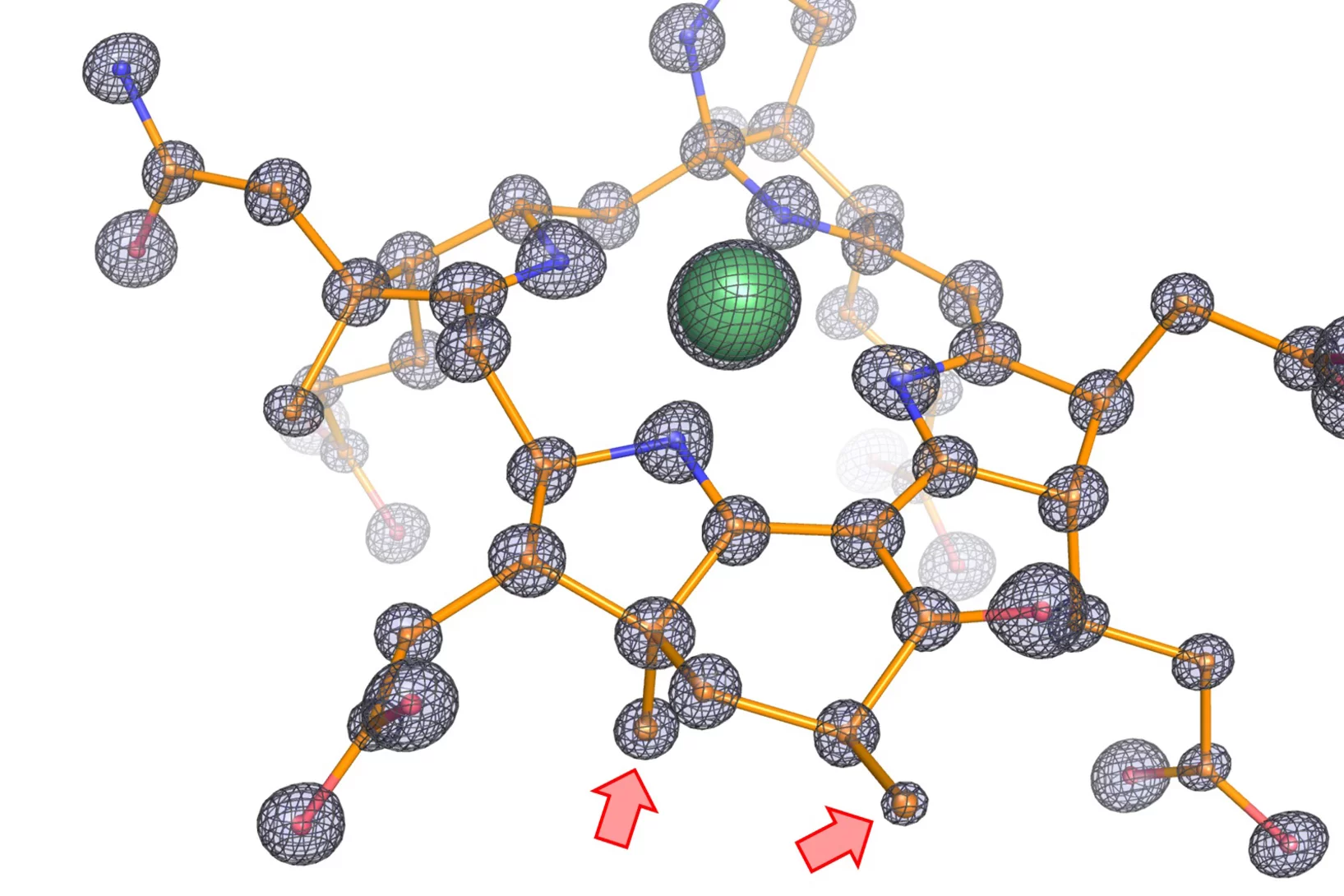
Fingerprint of Copper in Peptides Linked to Alzheimer's Disease
In an interdisciplinary project, researchers from the Laboratory of Nanoscale Biology in BIO and the Laboratory for Condensed Matter in PSD have revealed the reaction between the nitrogen atoms of the amyloid-beta peptide and copper/zinc ions by using soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Ground-breaking technology development recognised
PSI researchers win the international Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation for 3D mapping of nanoscopic details in macroscopic specimens, such as bone.
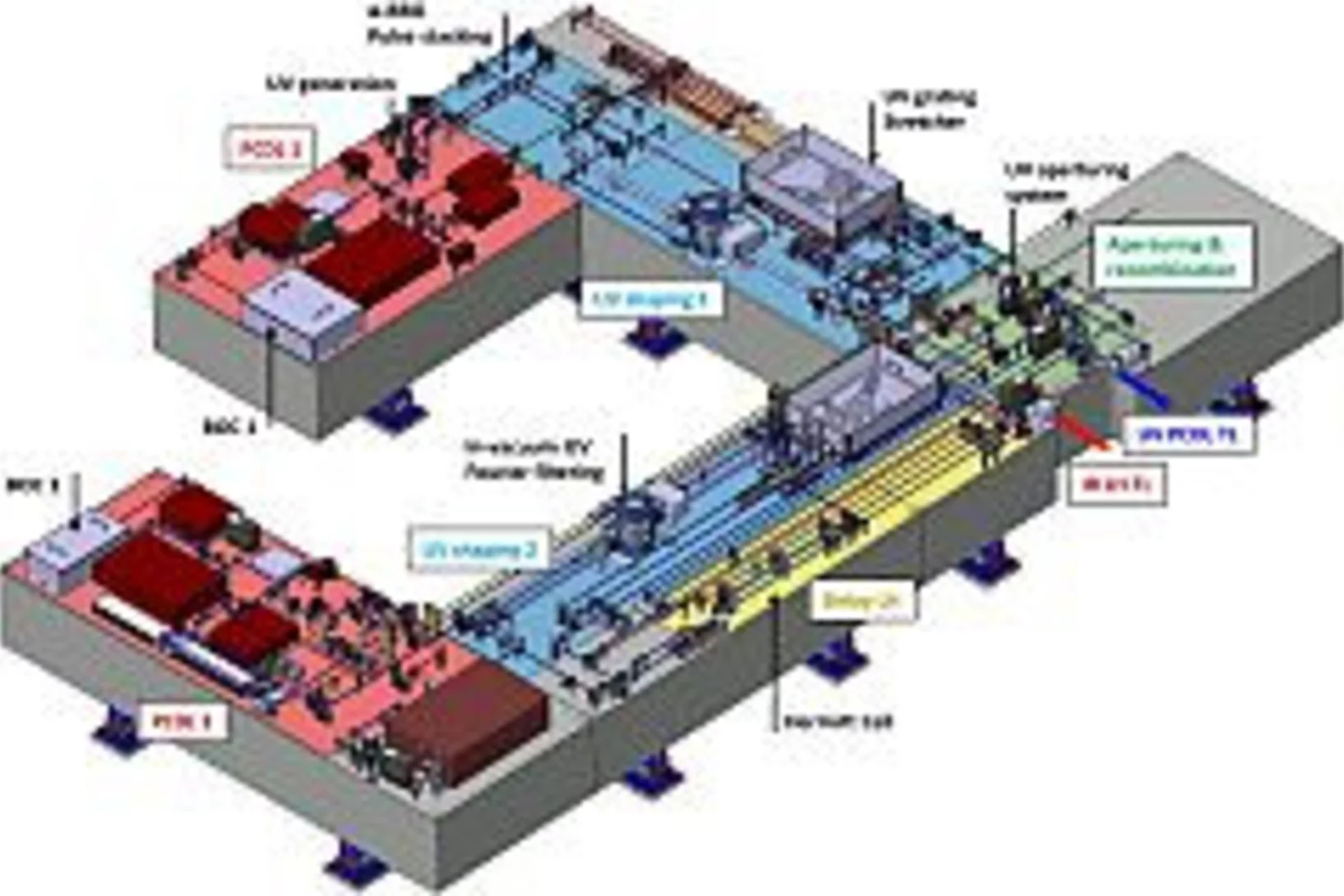
Overview of SwissFEL dual-photocathode laser capabilities and perspectives for exotic FEL modes
SwissFEL is a compact, high-brilliance, soft and hard X-ray Free Electron Laser (FEL) facility laser composed of two parallel beam lines seeded by a common linear accelerator (LINAC), and a two-bunch photo-injector. For the injector, an innovative dual-photocathode laser scheme has been developed based on state-of-the-art Ytterbium femtosecond laser systems. We just published an overview of the the SwissFEL Photo Cathode Drive Lasers (PCDL) performance, pulse shaping capabilities as well as the versatility of the systems, which allow many different modes of operation of SwissFEL [1]. The full control over the SwissFEL electron bunch properties via the unique architecture of the PCDL will enable in the future the advent of more advanced FEL modes; these modes are, but not restricted to, the generation of single or trains of sub-fs FEL pulses, multi-color FEL and finally the generation of fully coherent X-ray pulses via laser-based seeding.
Glycation of collagen: Quantifying rates
Collagen is abundant in the connective tissue of human beings, e.g. in tendons, ligament and cornea. Glycation of collagen distorts its structure, renders the extracellular matrix stiff and brittle and at the same time lowers the degradation susceptibility thereby preventing renewal. Based on models and with parameters determined from experimental data, we describe the glycation of type 1 collagen in bovine pericardium derived bio-tissues upon incubation in glucose and ribose. We hope that this contributes to a better quantitative understanding of the effects of diabetes on collagen.
Ultrafast control of quantum materials
Using light to fundamentally change the properties of solids
New active agent against parasites
PSI researchers identify potential active agent against several unicellular parasites – including the pathogens that cause malaria and toxoplasmosis.
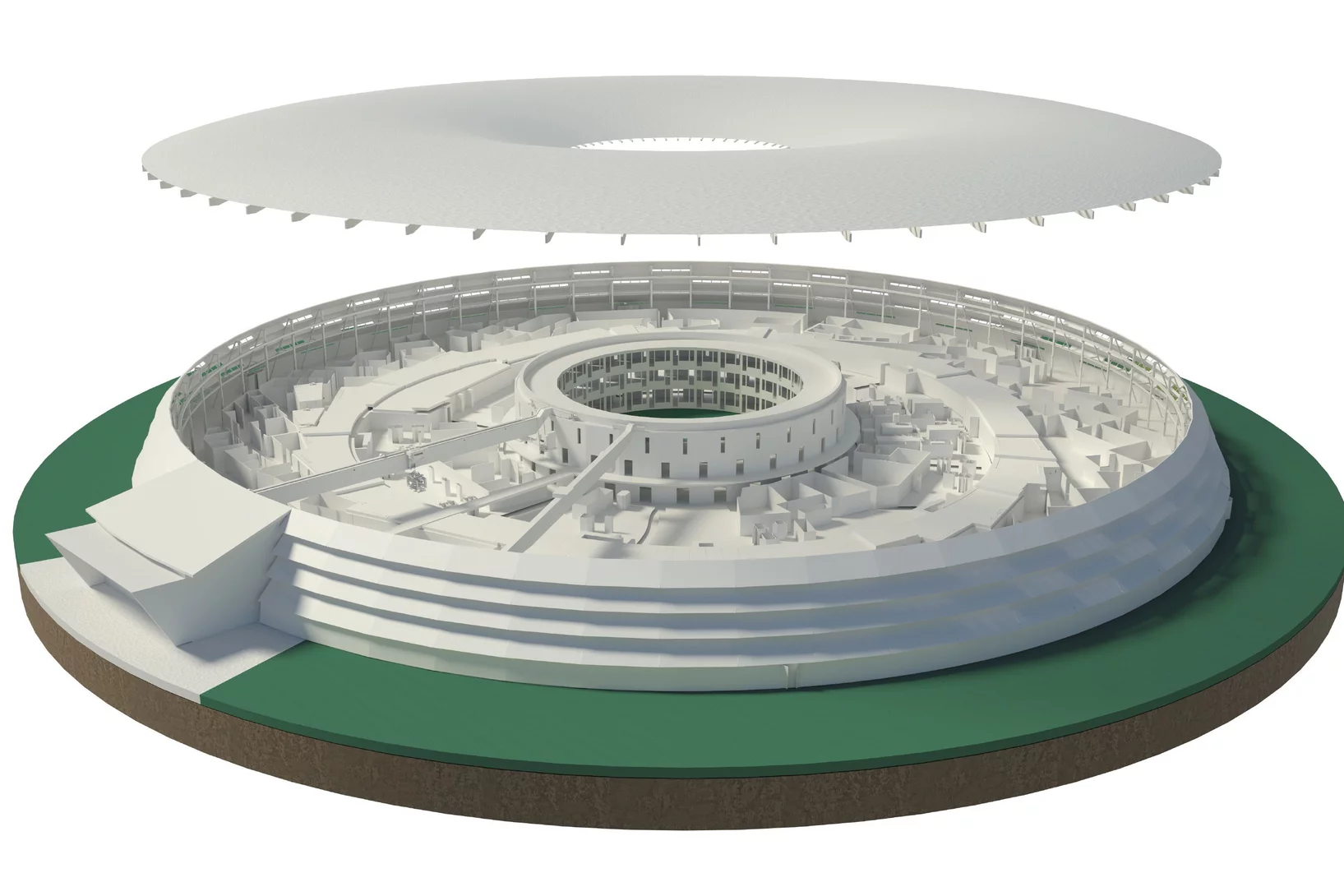
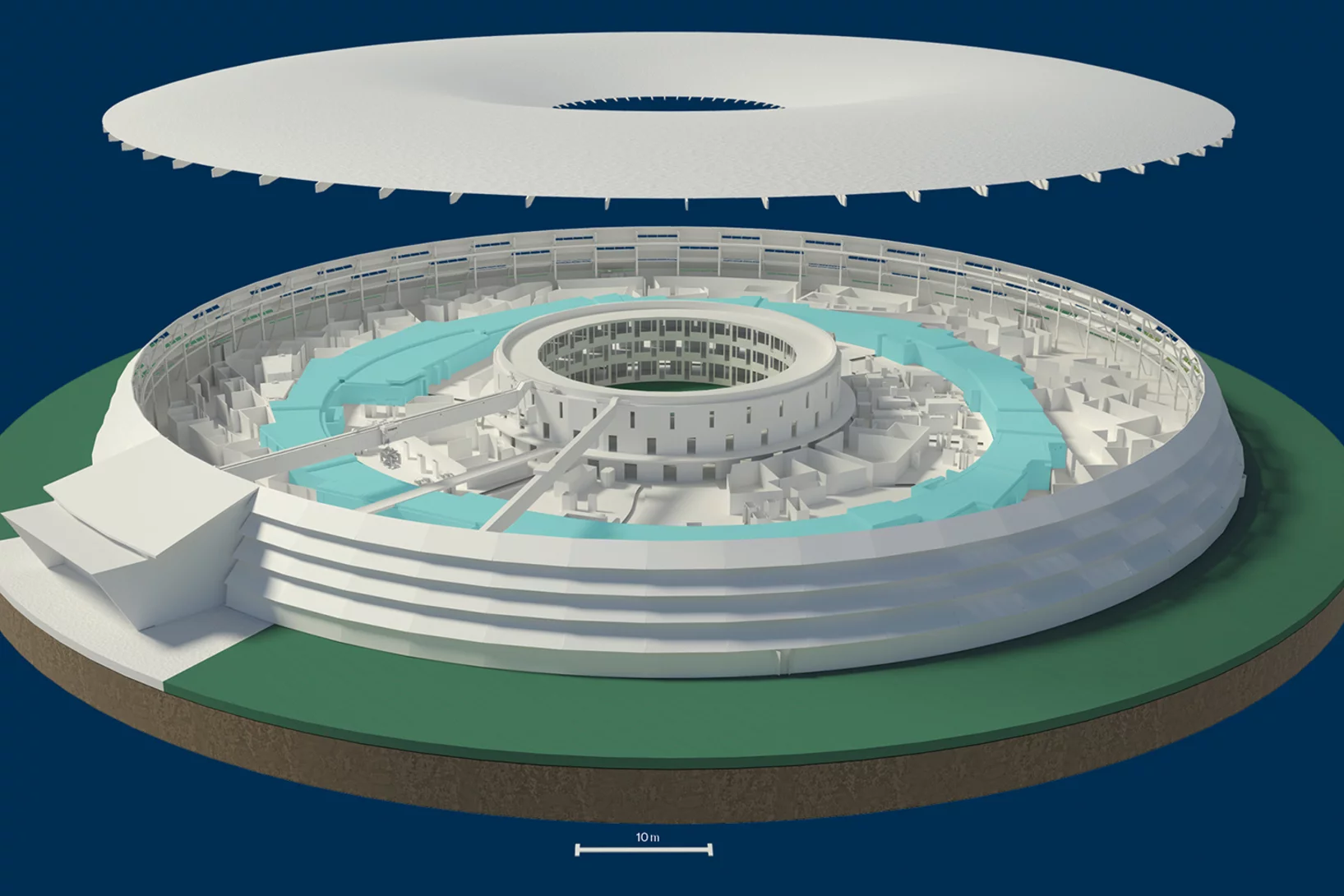
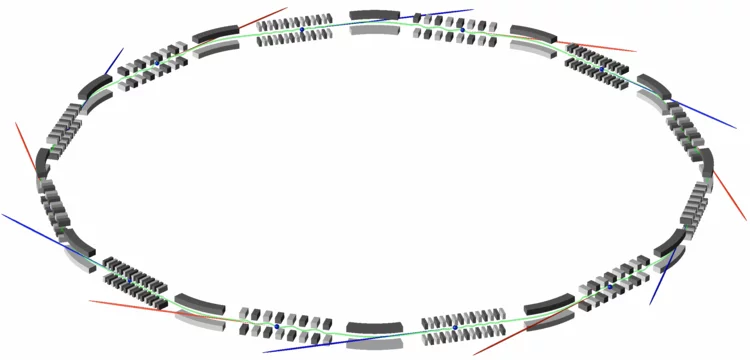
3D view: Swiss Light Source SLS
Linear accelerator, booster ring, storage ring: our 3D graphic of the Swiss Light Source shows the inside of the facility and how it serves research.
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos is awarded ICO prize
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, beamline scientist at the cSAXS beamline, is the 2019 recipient of the International Commission for Optics (ICO) Prize. The distinction was awarded in the EOSAM conference in Rome.
X-ray microscopy with 1000 tomograms per second
A team at the Swiss Light Source SLS have set a new record using an imaging method called tomoscopy.
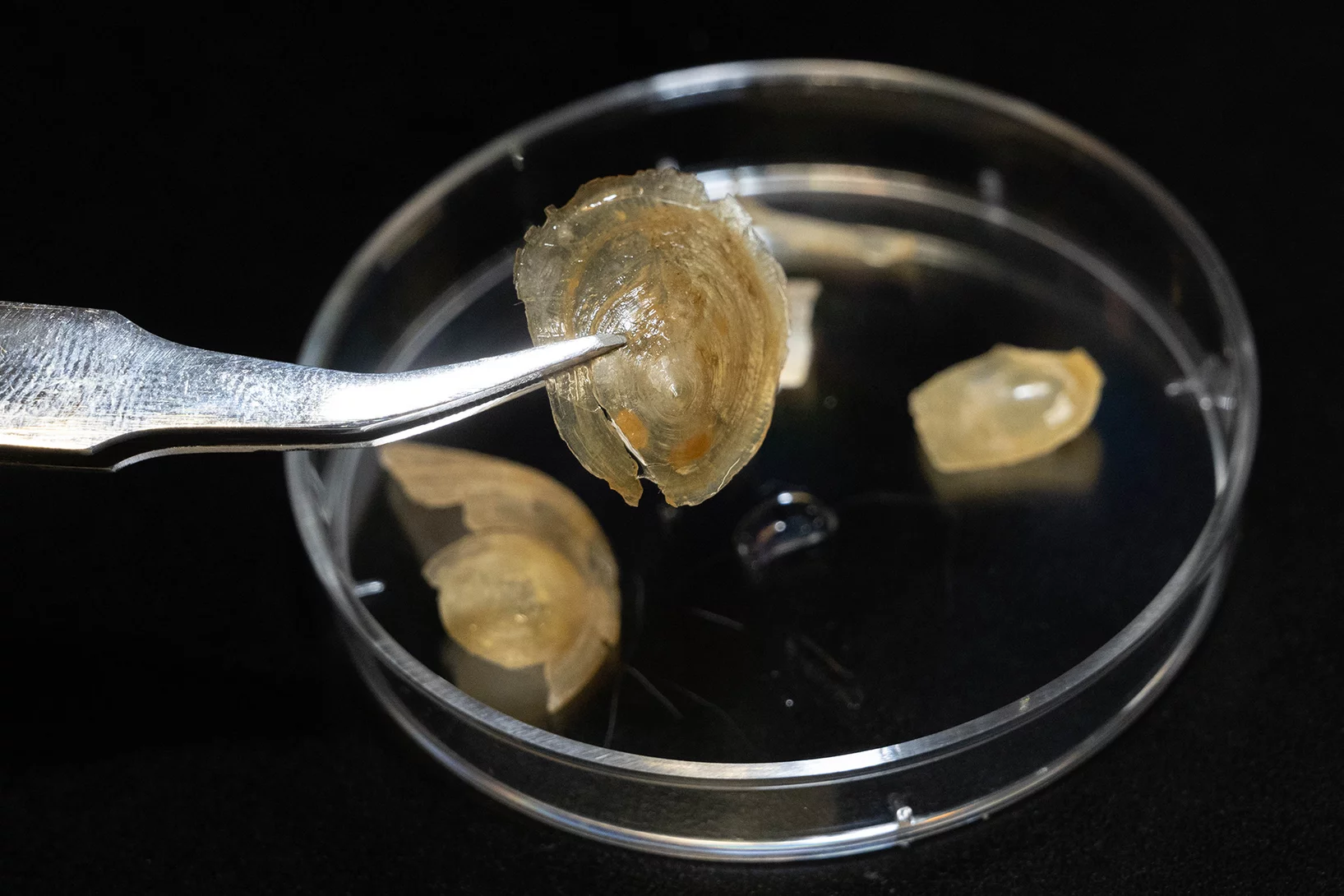
The mystery of the flexible shell
Why the shell of a marine animal is soft in water but hard in air.
Exploring the practical benefits of exotic materials
Niels Schröter receives an award from the Swiss Physical Society (SPG).
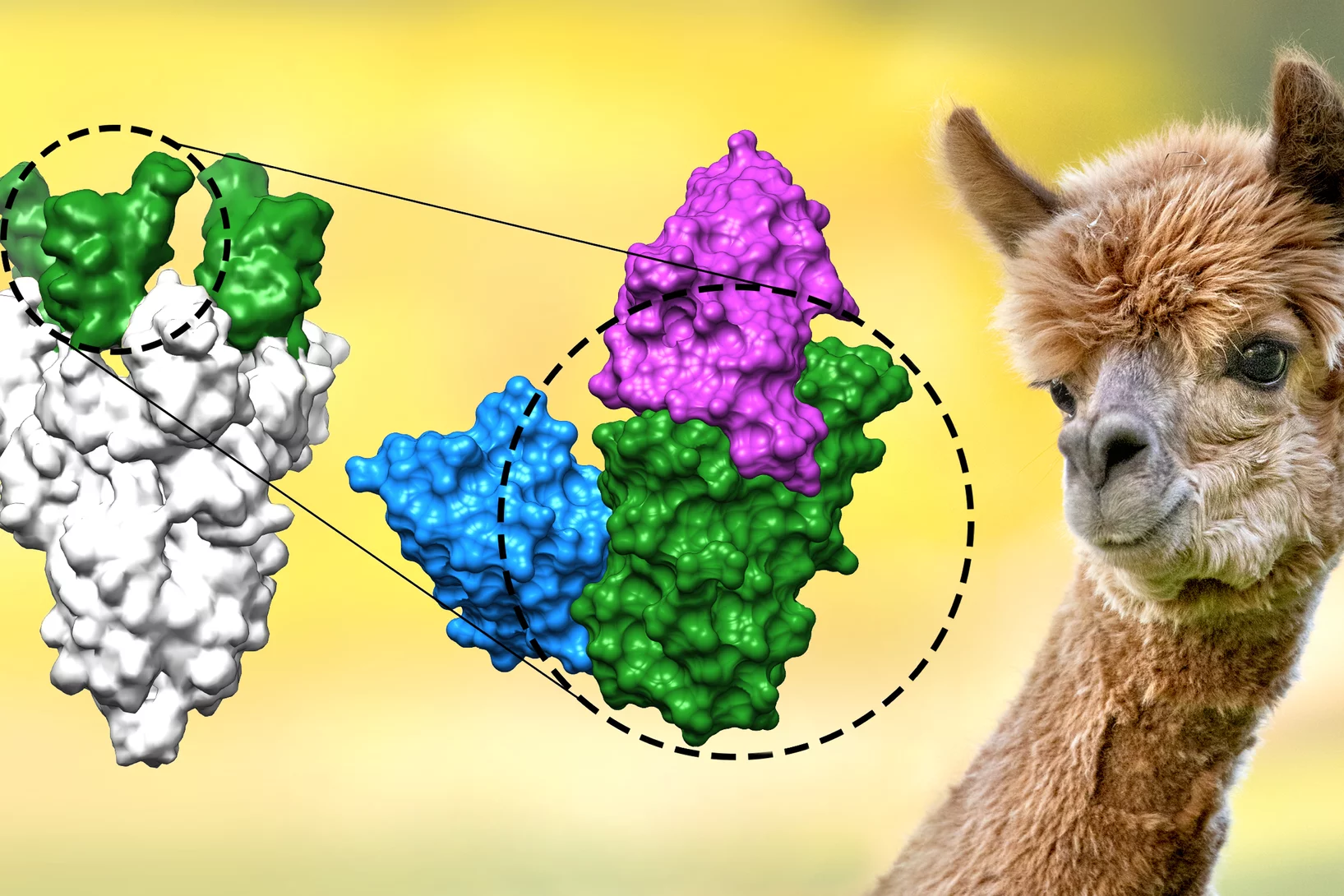
Nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2
In a study published in EMBO Journal, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany, developed nanobodies that efficiently block the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. The high resolution structural characterization was performed at the X10SA crystallography beamline at the Swiss Light Source.
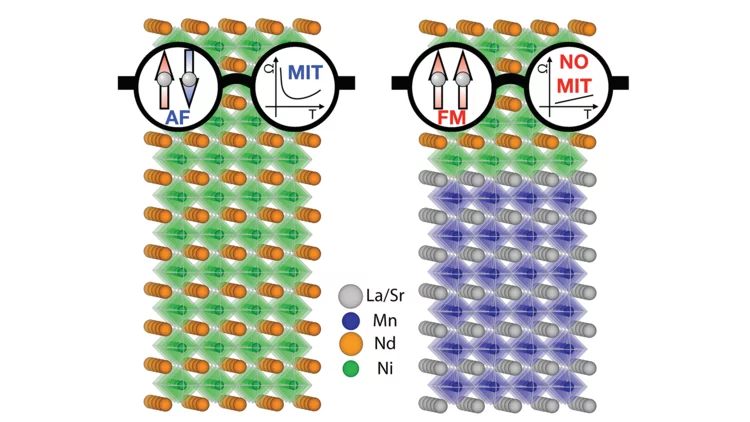
Creating novel quantum phases via the heterostructure engineering
Within this synergetic collaboration, PSI scientists have investigated the correlation between magnetic and electronic ordering in NdNiO3 by tuning its properties through proximity to a ferromagnetic manganite layer. The main outcome is that the stray magnetic field from the manganite layer causes a novel ferromagnetic-metallic (FM-M) phase in NNO. This work demonstrates the utilization of heterostructure engineering for creating novel quantum phases.
First light at Furka: The experiments can begin
The path to experiments that are unique in the world is now open.
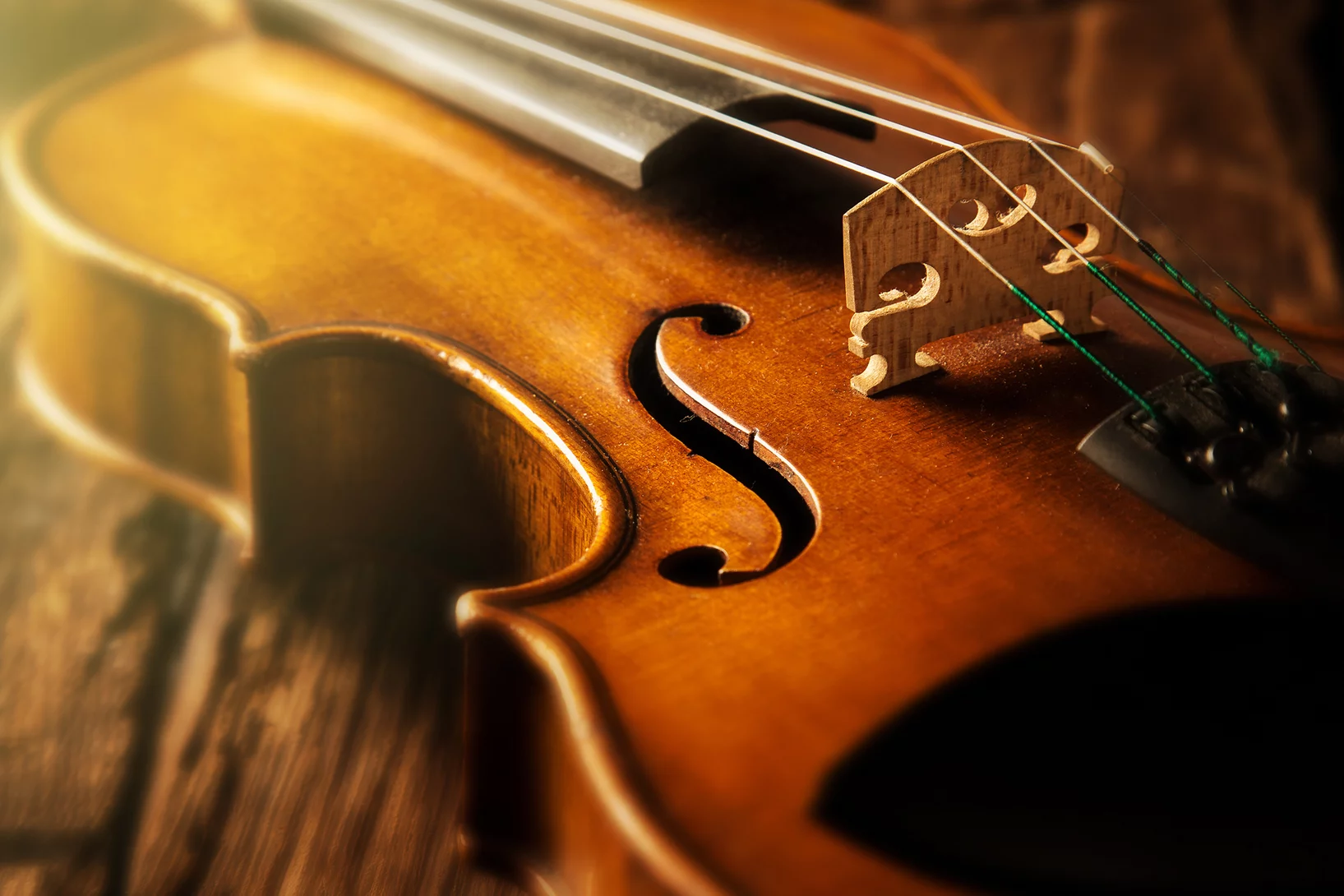
Secret of Stradivarius violins revealed
As an international team of researchers discovered, the old Italian masters Stradivari and Guarneri relied on unexpected chemical additives in making violins.
Understanding the physics in new metals
Together with international colleagues, PSI researchers have now been able to make correlated metals more readily usable for applications in superconductivity, data processing, and quantum computers.
Synchrotron movies
Prof Philip Willmott, the author of the book 'Introduction to Synchrotron Radiation: techniques and applications' (second edition, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 2019. ISBN: 9781119280392), makes the scripts for the simulations and animations available to the public.
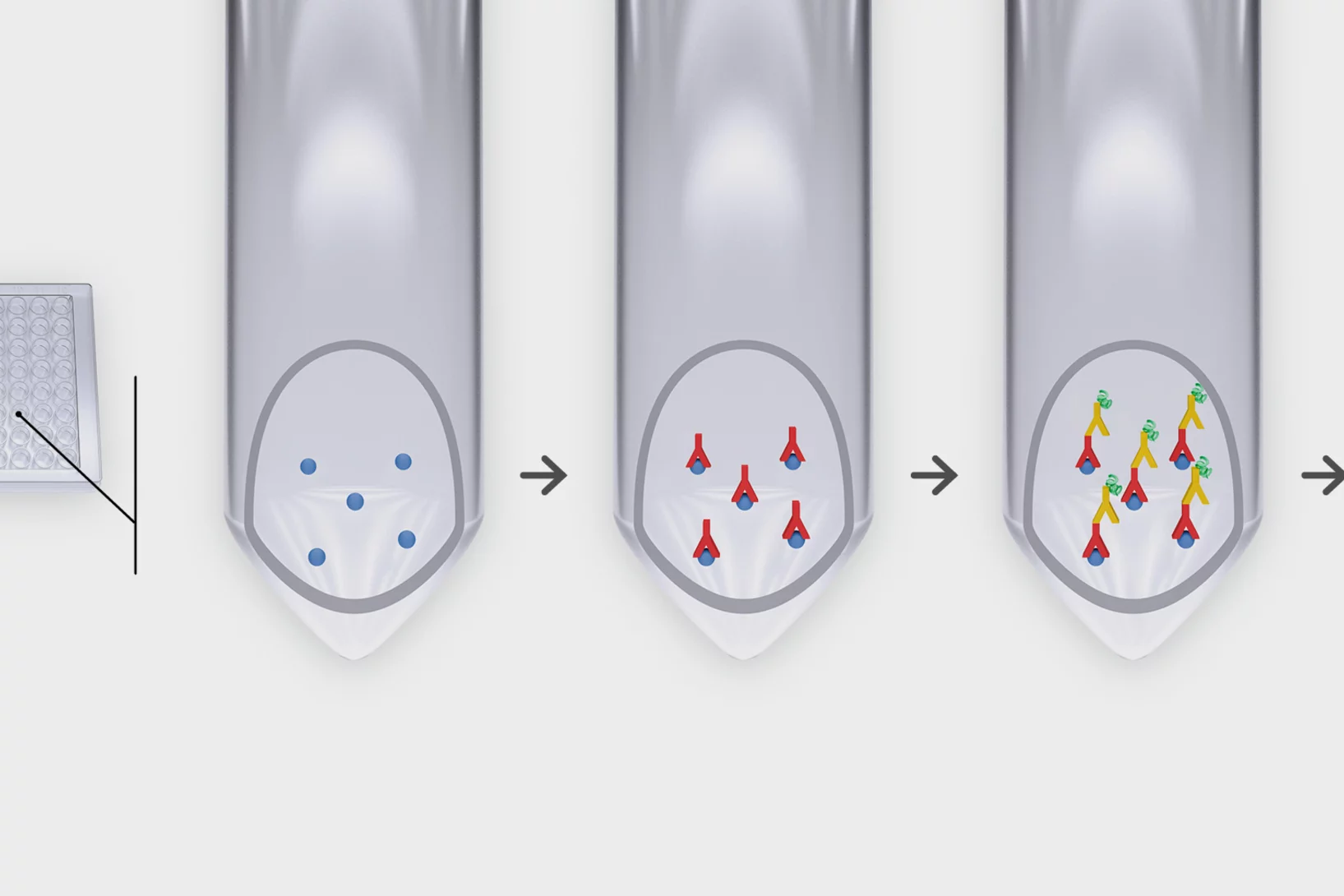
Tracking down unreported Coronavirus cases
The University Hospital of Zurich uses proteins made at PSI for Europe’s first large-scale serology study on coronavirus prevalence in Switzerland.
How ethane-consuming archaea pick up their favorite dish
Scientists decode the structure of the enzyme responsible for the ethane fixation by – beside others – using the SLS.