Open Quantum Institute launch
Dr. Cornelius Hempel, head of the Ion Trap Quantum Computation group at LNQ’s ETHZ-PSI Quantum Computing Hub, spoke to SRF to explain how quantum computers work and how future versions of these devices can be used to solve some of the big problems of our time.
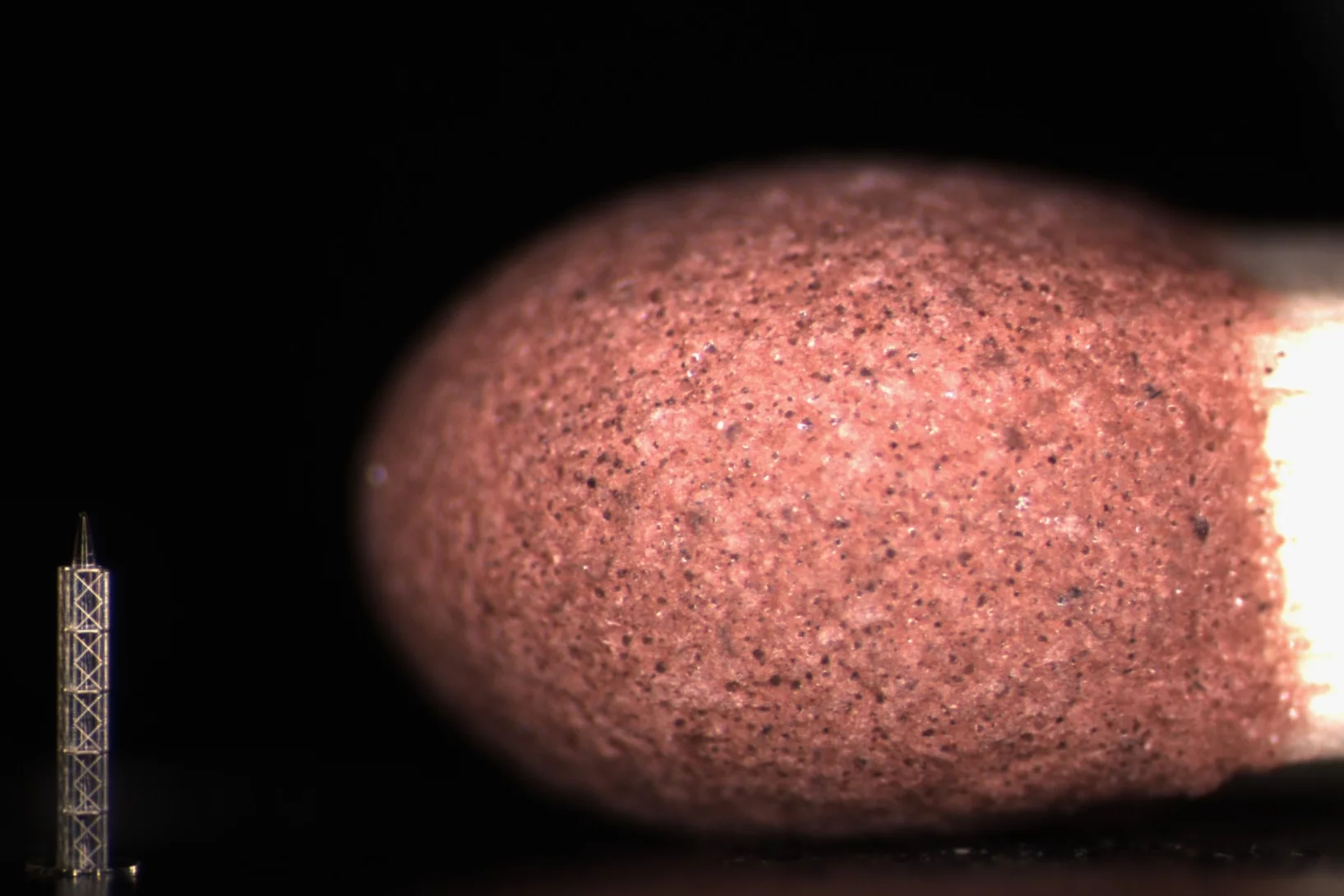
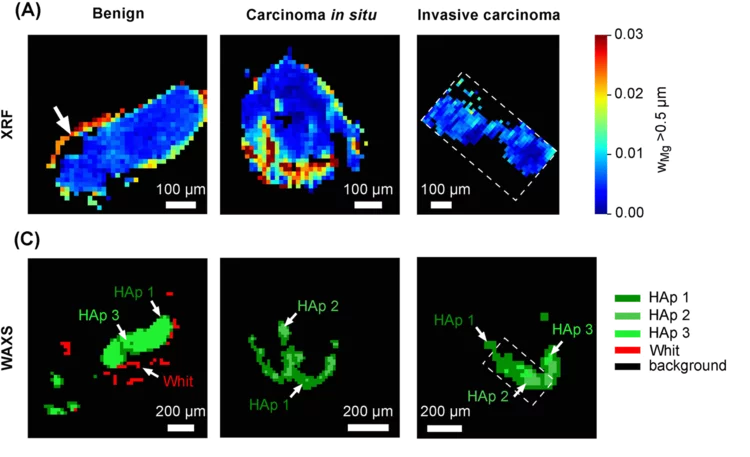
Whitlockite in mammary microcalcifications is not associated with breast cancer
Microcalcifications, small deposits of calcium-containing minerals that form in breast tissue, are often, but not always, a warning sign of breast cancer. The relationship between microcalcifications and cancer has not been fully understood thus far. Researchers discovered now that the relationship between microcalcifications and tumors seems to be linked to the presence of a particular mineral called whitlockite, which is rich in magnesium and is found in microcalcifications only in the absence of tumors.
SLS 2.0: “Dark time” during the upgrade
The SLS is shutting down temporarily as it undergoes a major upgrade.
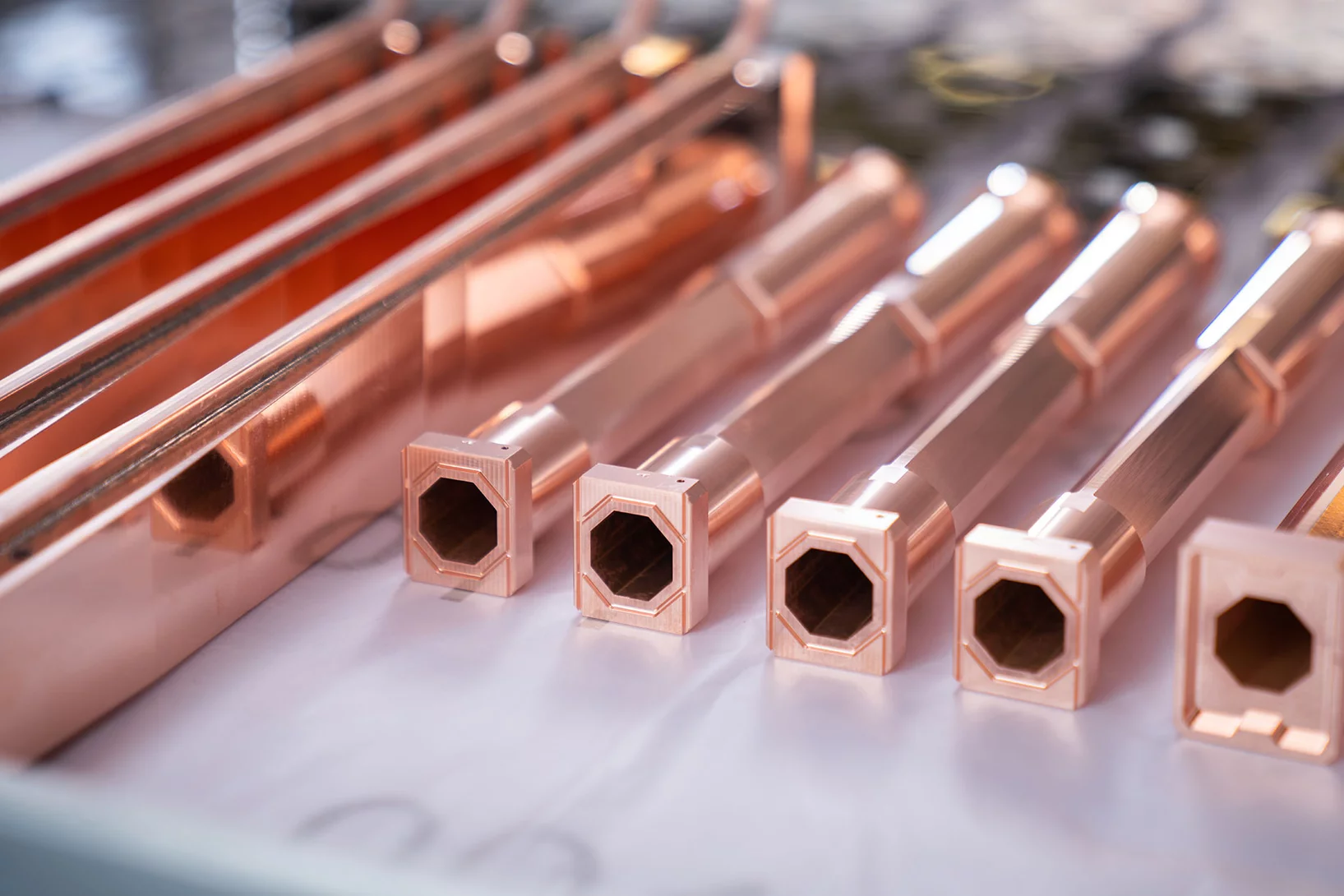
3D insights into an innovative manufacturing process
3D printing for creating complex shapes
Unveiling ultra-thin electron liquids in silicon
Soft X-rays enable scientists to visualise non-invasively the electronic properties of ultra-thin dopant layers buried within semiconductor wafers.
“Molecular chains could be useful for the electronics of the future”
Christian Wäckerlin talks about fundamental research into novel nanowires and their potential applications.
Earlier detection of breast cancer
3D X-rays can improve breast cancer screening.
A metal alloy like a sponge
Once the vacuum chambers for the SLS 2.0 upgrade are the right shape, they still need a special surface coating.
A six-metre high oven
The most complicated vacuum chambers for the SLS 2.0 upgrade are being built in the PSI workshop.
Progress of the X06DA-PXIII beamline upgrade: First light in the optics hutch
On June 7, 2023, the PXIII project team successfully shone the first light into the optics hutch at the upgraded X06DA-PXIII beamline. It is an essential first step for testing new hardware and software solutions that will be implemented at SLS2.0.
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
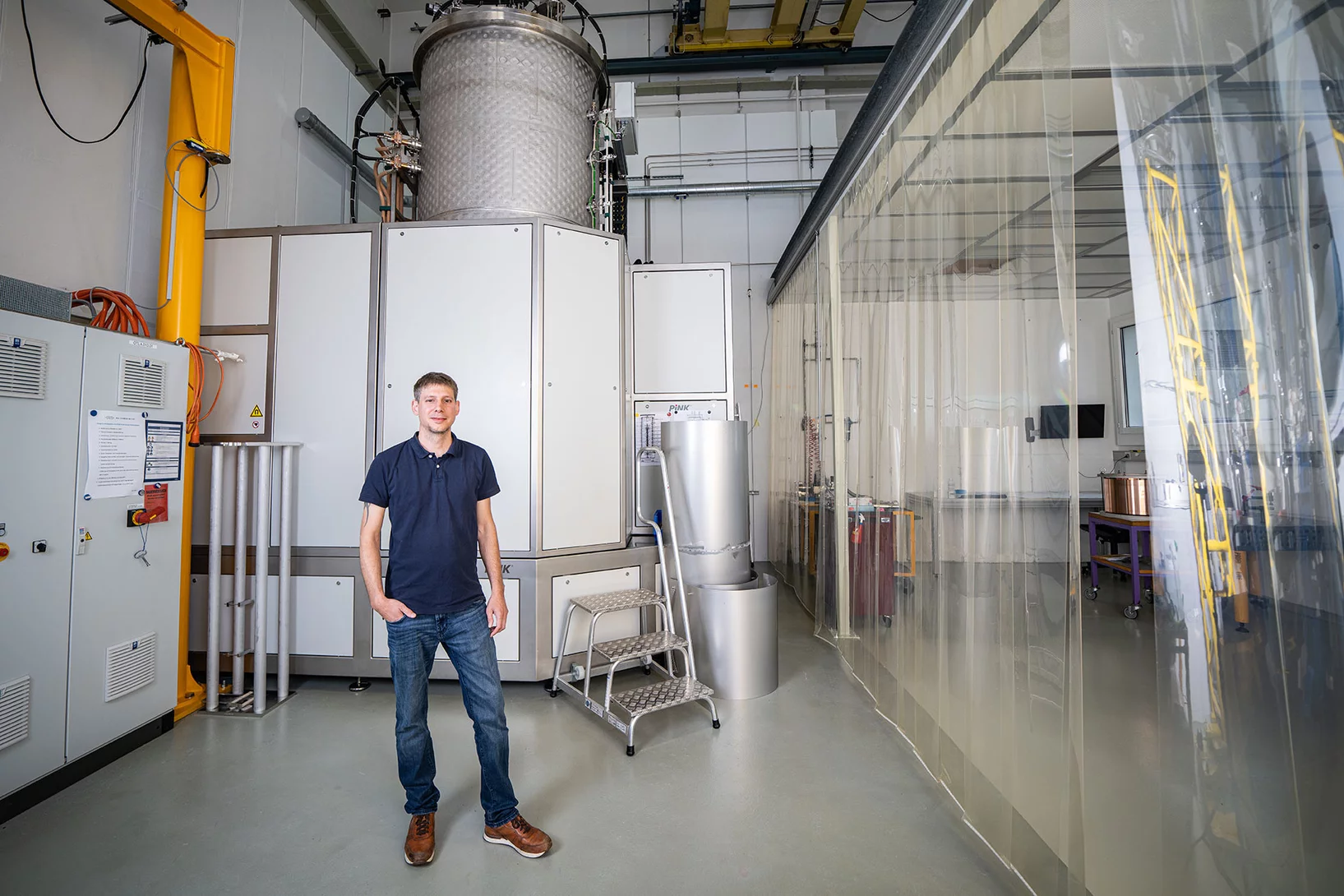
500 vacuum chambers for the new ring
Making the tube through which the electrons will race after the SLS 2.0 upgrade.
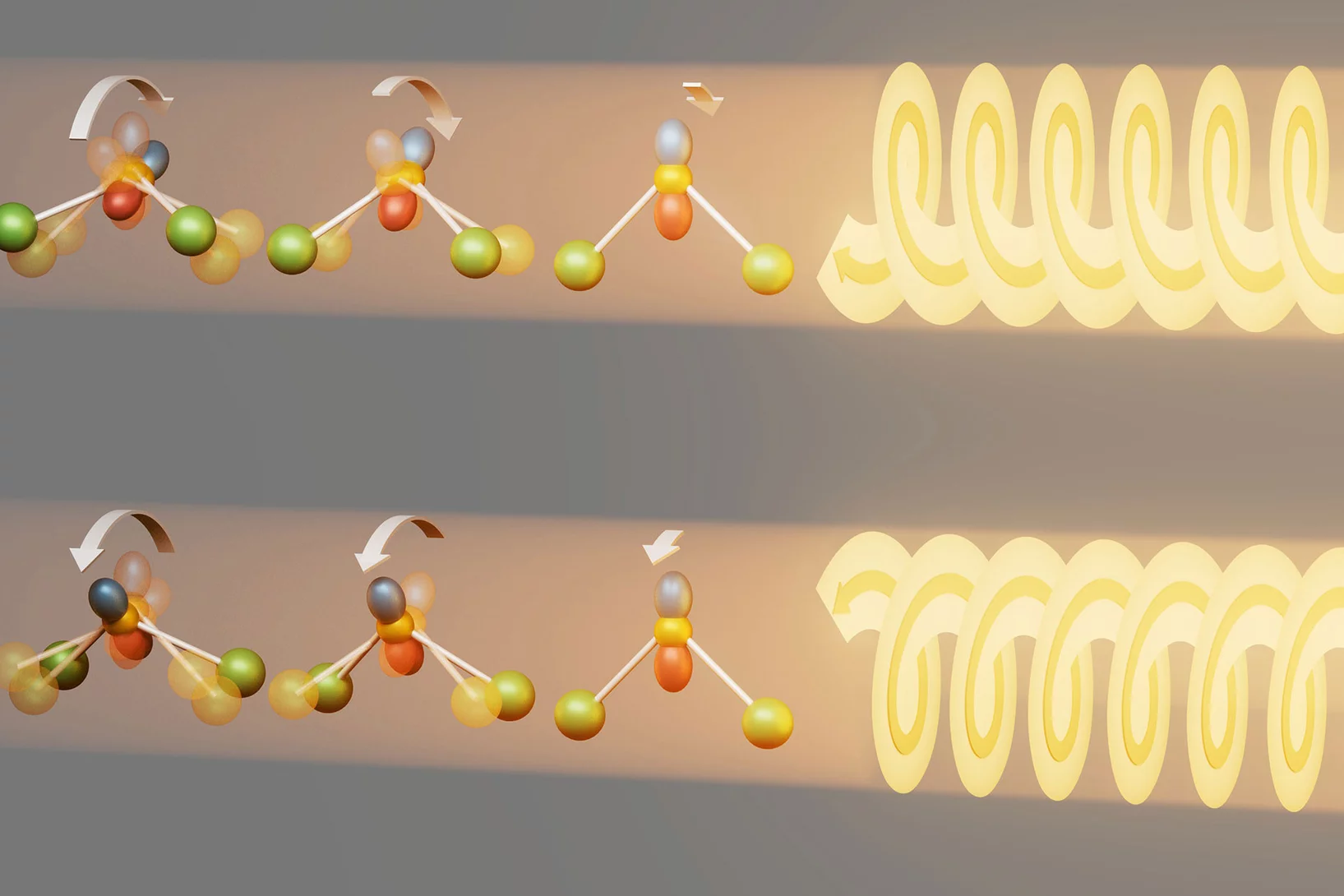
Mirror, mirror on the wall…
…. Now we know there are chiral phonons for sure
PSI researchers use extreme UV light to produce tiny structures for information technology.
Synchrotron light can be used in follow-up after a heart transplant to determine whether the body may be rejecting the new organ.
An algorithm for sharper protein films
A newly developed algorithm allows measurements performed at X-ray free-electron lasers to be evaluated more efficiently.
Dr Christian Wäckerlin is appointed as assistant professor at EPFL
Dr Christian Wäckerlin (*1983), currently Research and Teaching Associate at EPFL and Project Leader at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), as Assistant Professor of Physics in the School of Basic Sciences. Christian Wäckerlin’s research focuses on nanoscience and quantum engineering.
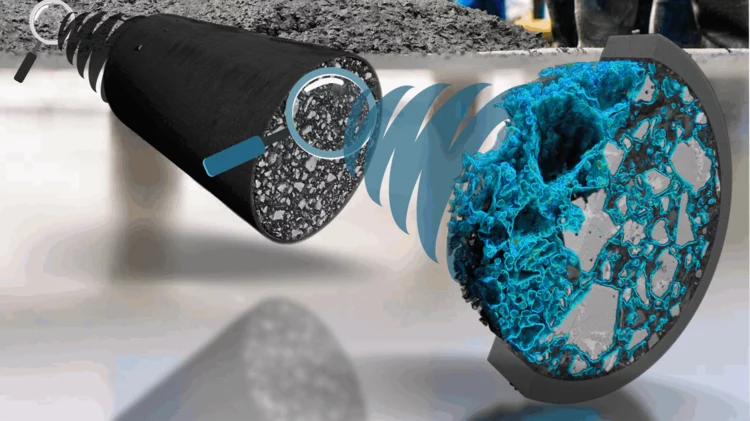
A deep look into hydration of cement
Researchers led by the University of Málaga show the Portland cement early age hydration with microscopic detail and high contrast between the components. This knowledge may contribute to more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes.
Apochromatic X-ray focusing
A team of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institut, the University of Basel and DESY have demonstrated the first-ever realization of apochromatic X-ray focusing using a tailored combination of a refractive lens and a Fresnel zone plate. This innovative approach enables the correction of the chromatic aberration suffered by both refractive and diffractive lenses over a wide range of X-ray energies. This groundbreaking development in X-ray optics have been just published in the scientific journal Light: Science & Applications.
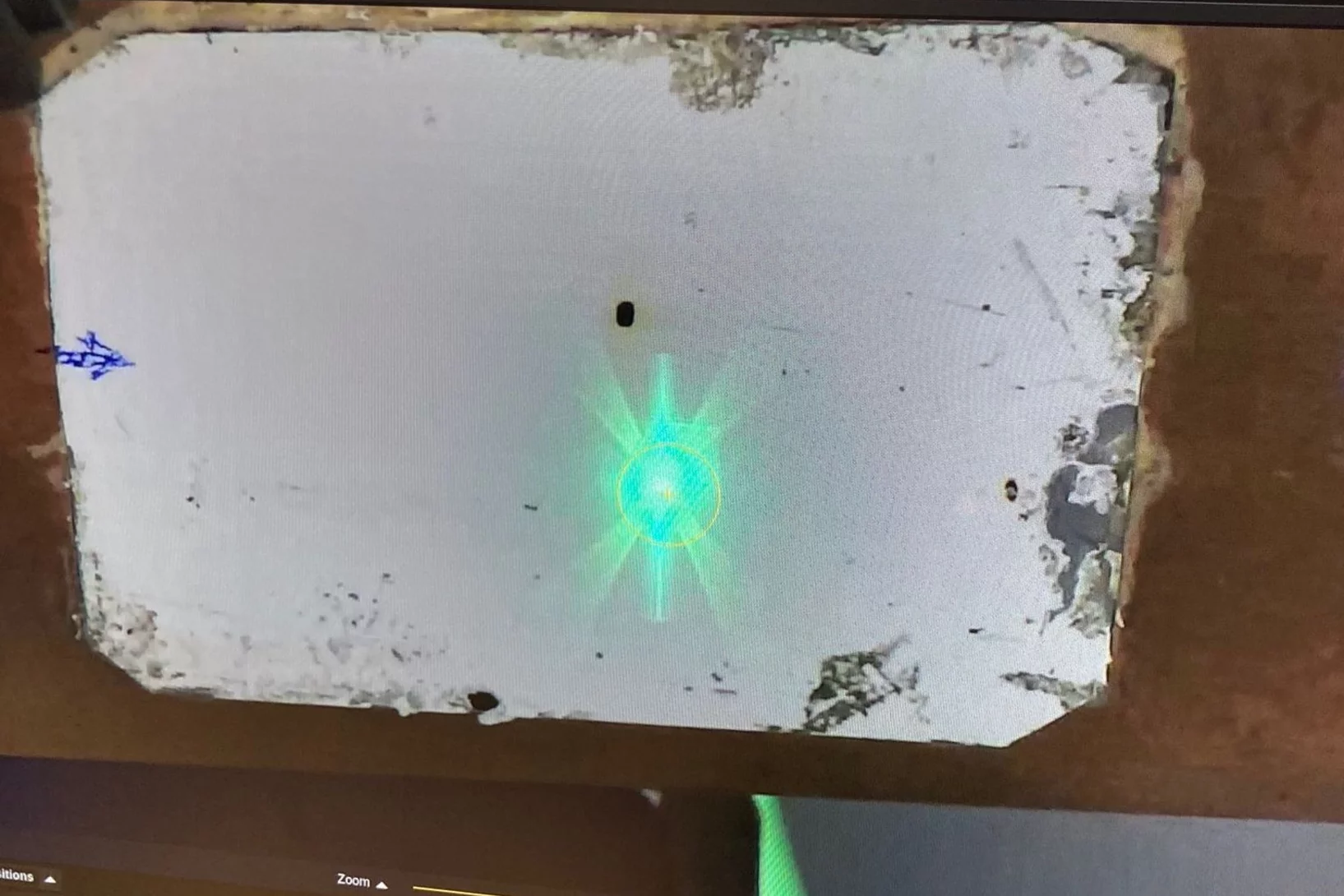
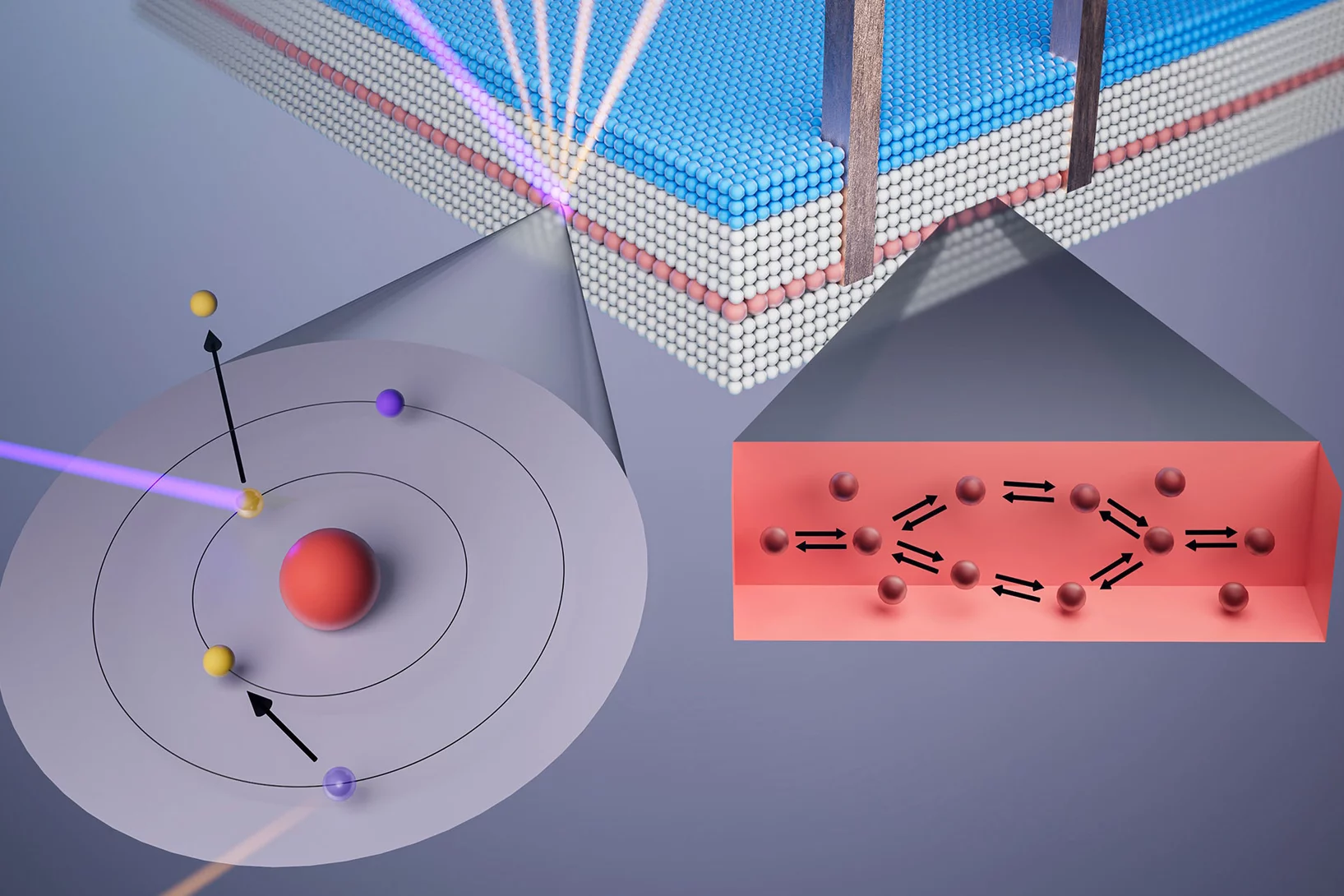
Quality control of future transistors: Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
X-ray imaging after heart transplantations
Synchrotron light can be used in follow-up after a heart transplant to determine whether the body may be rejecting the new organ.
The Hercules School visits PSI
20 international students visited PSI as part of the renowned Hercules School to learn about our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities.
How football-shaped molecules occur in the universe
An international research team reveals how fullerene is formed in the universe.
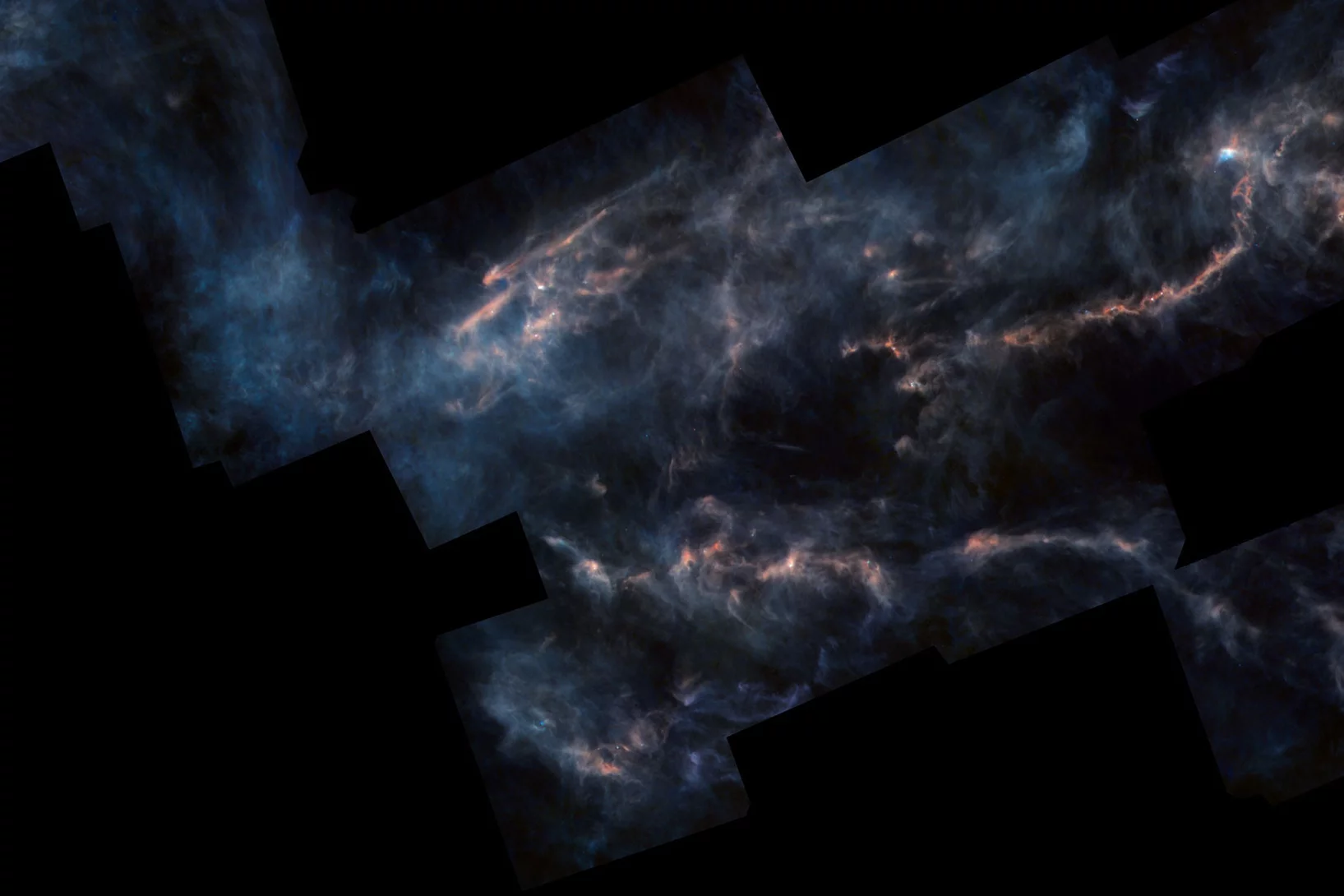
A star is born
Swiss Light Source SLS reveals complex chemistry inside ‘stellar nurseries’
Using light to switch drugs on and off
PSI researchers record a molecular film of a cancer drug fitted with a photoswitch. This opens new insights for drug developers.
IEEE Early Career Award 2022
For contributions to the development of detectors for XFELs and specifically for their verification, characterization, and calibration
Swiss PIC to support Swiss photonics industry
The technology transfer centre Swiss PIC will be located in the Park Innovaare.
Manuel Guizar-Sicairos appointed as Associate Professor at EPF Lausanne and head of the Computational X-ray Imaging group at PSI
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, currently Senior Scientist at PSI, was appointed as Associate Professor of Physics in EPF Lausanne and head of the Computational X-ray Imaging group in PSI.
3.1 million in funding for new research projects at PSI
The PSI scientists Zurab Guguchia and Kirsten Schnorr are to receive grants totalling CHF 3.1 million from the Swiss National Science Foundation for ground-breaking projects.
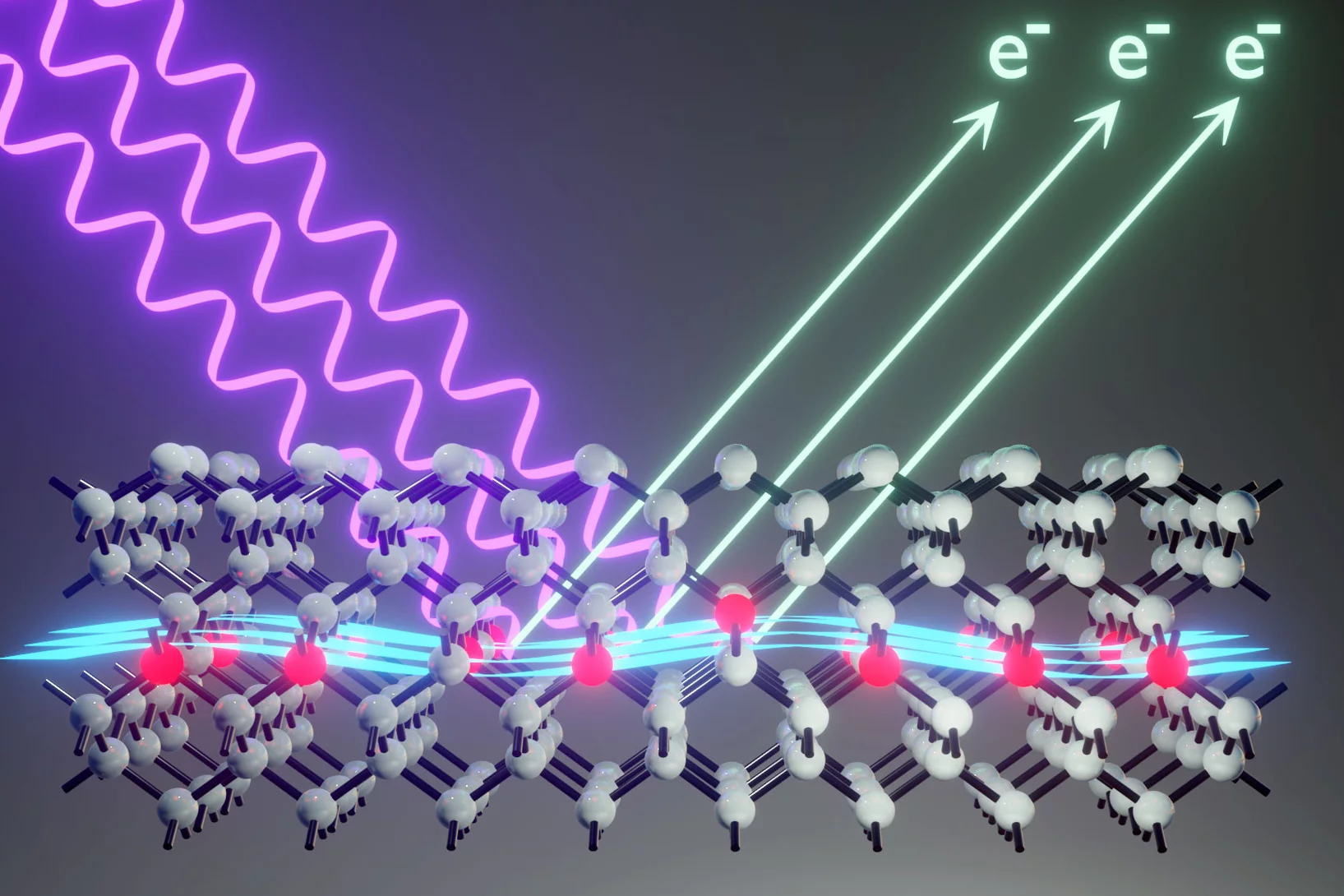
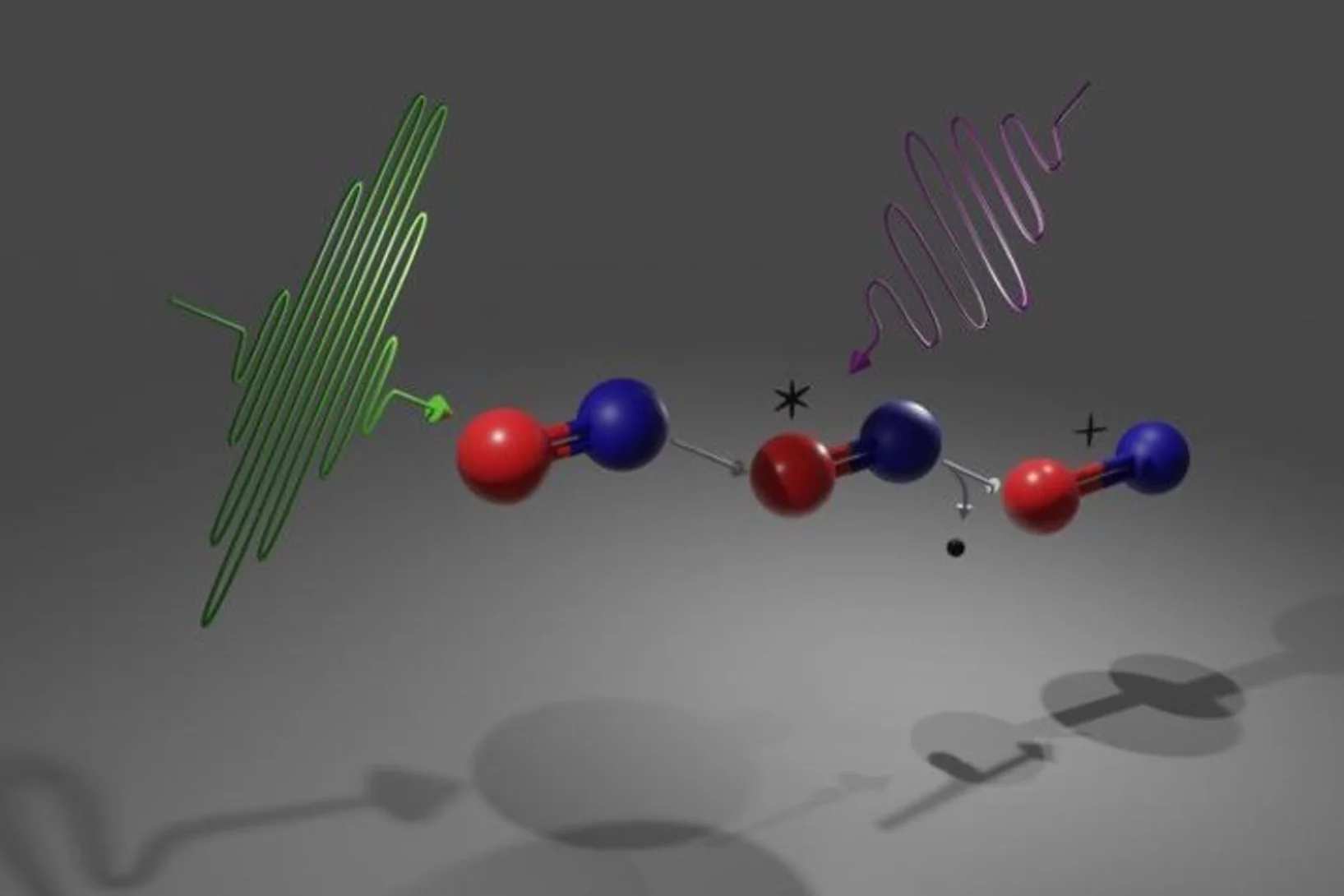
Tracking chemical bond changes with element selectivity and in real time
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy probes the chemical environment in a molecule at a specific atomic site. Now the concept is extended with a site selective trigger to follow chemical bond changes as they occur on the femtosecond time scale.
New materials for the computer of the future
Researchers are identifying and studying material compounds whose unique properties could lead to the development of novel types of chip.