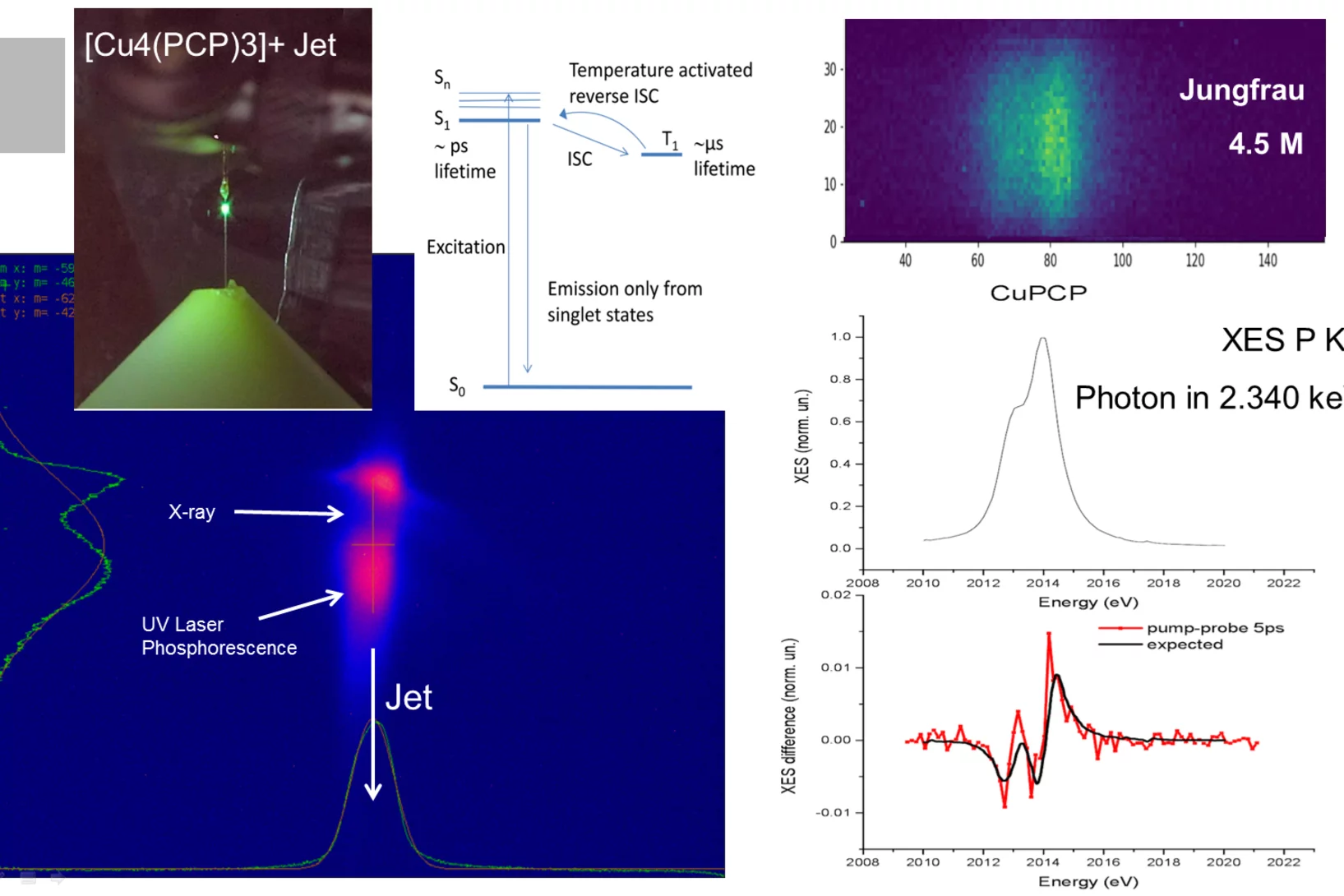
Tender X-rays show how one of nature’s strongest bonds breaks
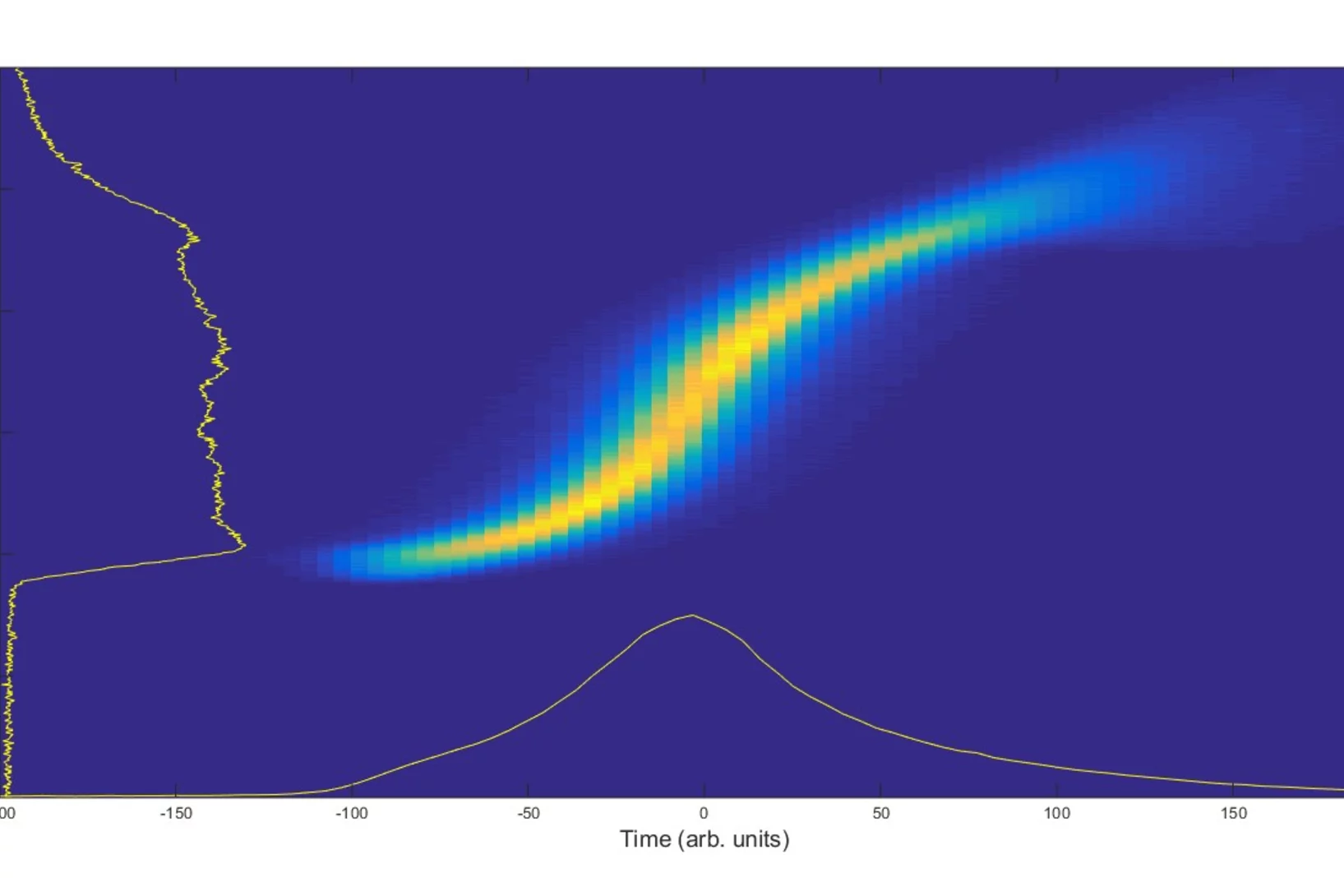
Short flashes of an unusual kind of X-ray light at SwissFEL and SLS bring scientists closer to developing better catalysts to transform the greenhouse gas methane into a less harmful chemical.
How to get chloride ions into the cell
A molecular movie shot at PSI reveals the mechanism of a light-driven chloride pump
EU XFEL Young Scientist Award for Camila Bacellar
Camila Bacellar, beamline scientist and group leader of the Alvra endstation at SwissFEL, has received the European XFEL Young Scientist Award. The award recognises the contribution of young scientists to research at the European XFEL.
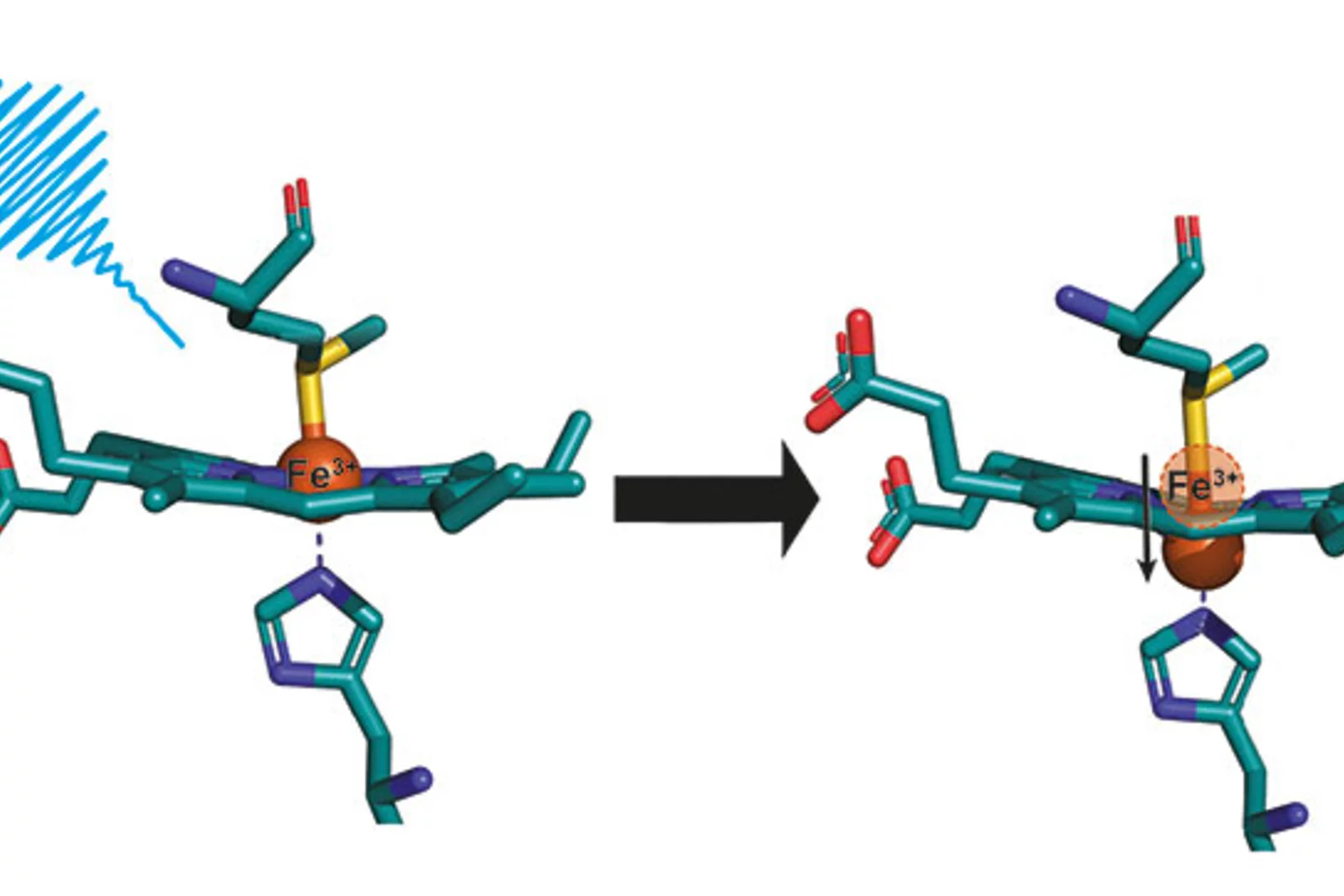
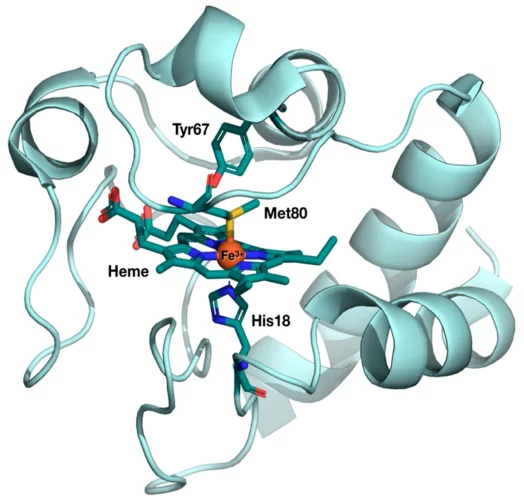
A protein's unexpected "doming"
Researchers have coaxed a secret out of the vital protein cytochrome c that it kept well-hidden up to now. Measurements at the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL reveal structural changes that science had previously ruled out for this kind of biomolecule.
Advances in de novo protein structure determination using long-wavelength native-SAD phasing at SwissFEL
An international team of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute and members of the LeadXpro and Heptares pharmaceutical companies led by Karol Nass (Alvra group, SwissFEL) demonstrated a significant advancement in de novo protein structure determination at X-ray free-electron lasers. Their article, published recently in IUCrJ (DOI: 10.1107/S2052252520011379), describes structure determination of a membrane protein and an important drug target (A2A adenosine receptor) by native single-wavelength anomalous diffraction (native-SAD) at SwissFEL with up to ten fold reduction in the required number of indexed images.
Unraveling the structural dynamics of Heme proteins at SwissFEL
The results from the very first user experiment at SwissFEL have just been published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The measurements probed the electron transport properties of the cytochrome c protein, which is found in cellular mitochondria. The measurements show that when the Fe atom at the centre of the protein undergoes electronic excitation, for example when it gains or loses and electron, the active centre of the protein undergoes a doming structural rearrangement. This result raises interesting questions about how this structural change is involved in the electron transfer properties of cytochrome c.
Elucidating the mechanism of a light-driven sodium pump
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded for the first time in recording a light-driven sodium pump from bacterial cells in action. The findings promise progress in developing new methods in neurobiology. The researchers used the new X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL for their investigations.
In search of the lighting material of the future
At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, researchers have gained insights into a promising material for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). This new understanding at the atomic level will help to develop new lighting materials that have higher light output and also are cost-efficient to manufacture.
First serial femtosecond crystallography experiment using SwissFEL’s large bandwidth X-ray pulses
The typical mode of operation at XFEL facilities uses the so-called self-amplified spontaneous emission (SASE) process to generate the short, bright X-ray pulses. This mode of operation is stochastic in nature, causing some variance in intensity and spectrum on a shot-to-shot basis, which makes certain types of crystallographic measurements much more challenging.
Towards X-ray Transient Grating Spectroscopy at SwissFEL
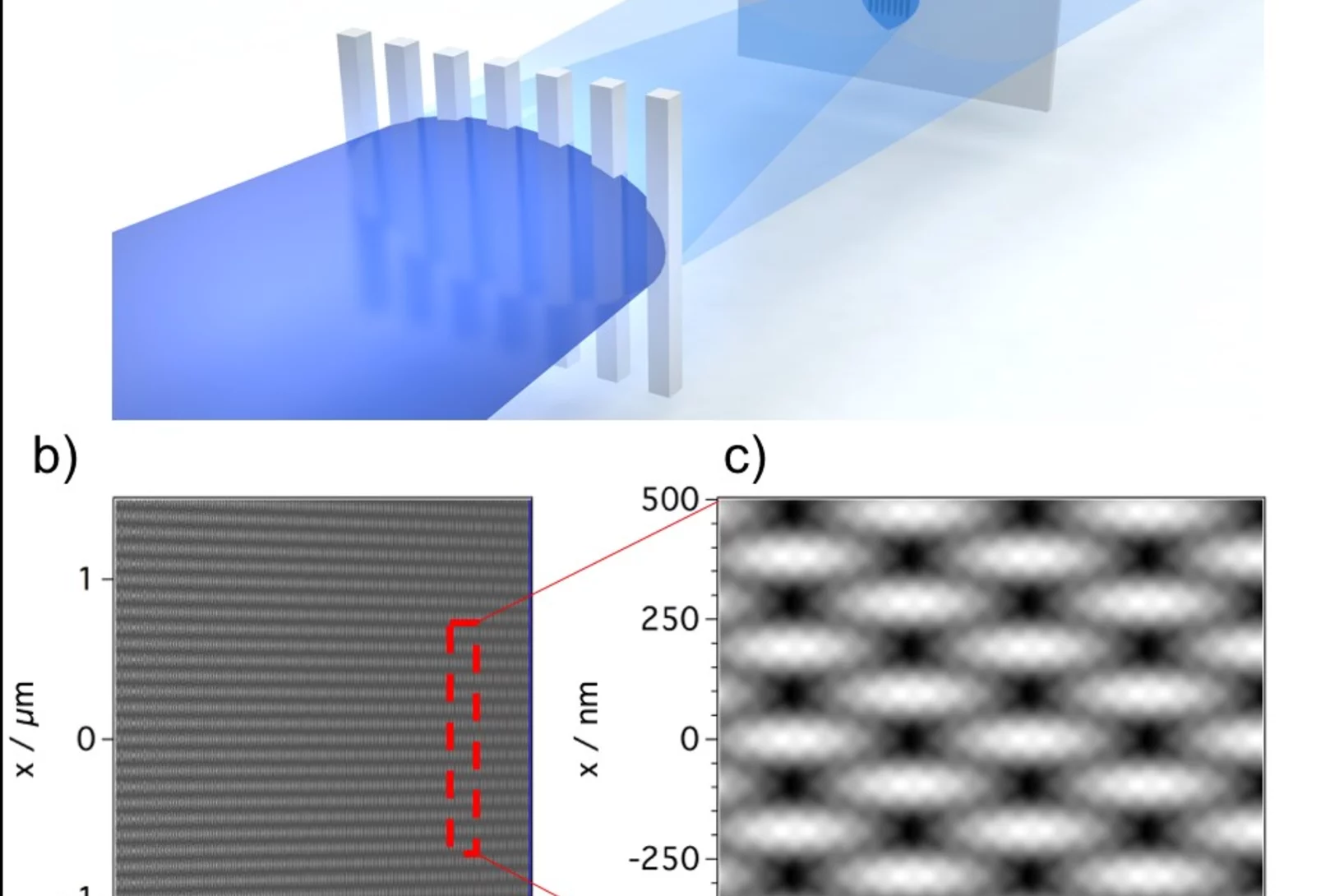
The high brilliance of new X-ray sources such as X-ray Free Electron Laser opens the way to non-linear spectroscopies. These techniques can probe ultrafast matter dynamics that would otherwise be inaccessible. One of these techniques, Transient Grating, involves the creation of a transient excitation grating by crossing X-ray beams on the sample. Scientists at PSI have realized a demonstration of such crossing by using an innovative approach well suited for the hard X-ray regime.
First femtosecond protein pump-probe measurements at SwissFEL
A major milestone in the commissioning of SwissFEL has been reached: the first pump-probe experiments on proteins have been successfully carried out. Crystals of several retinal-binding proteins were delivered in a viscous jet system and a femtosecond laser was used to start the isomerization reaction. Microsecond to sub-picosecond snapshots were then collected, catching the retinal proteins shortly after isomerization of the chromophore.
Demonstration of femtosecond X-ray pump X-ray probe diffraction on protein crystals
Our experiments, published in the September issue of Structural Dynamics, demonstrate the feasibility of time-resolved pump-multiprobe X-ray diffraction experiments on protein crystals using a split-and-delay setup which was temporarily installed at the LCLS X-ray Free Electron Laser.
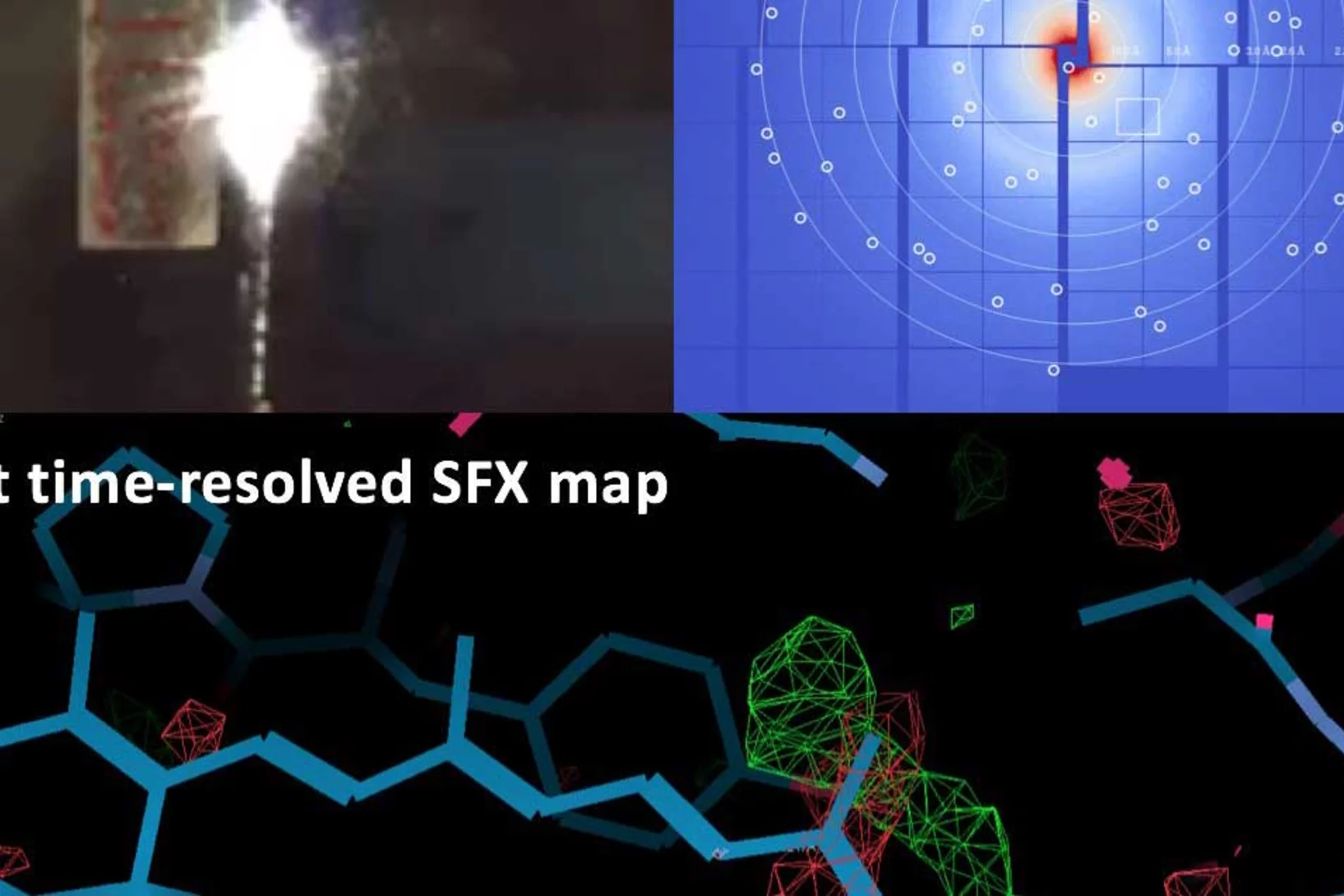
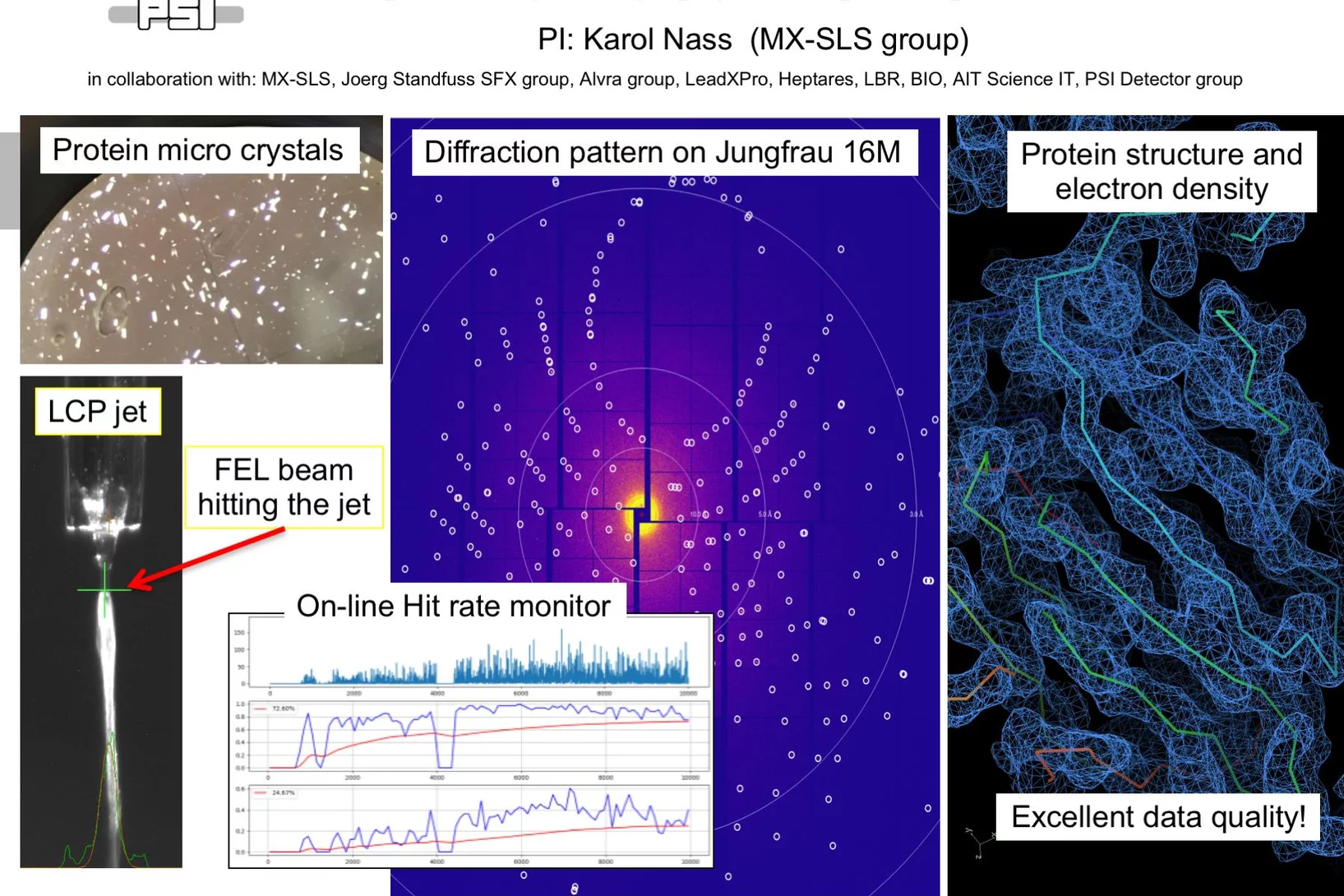
First serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at SwissFEL
On the 7th to 12th of August 2018, a collaborative group of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute and members of the LeadXpro and Heptares pharmaceutical companies led by Karol Nass (PSI macromolecular crystallography MX-SLS group) performed the first serial femtosecond crystallography (SFX) pilot user experiment at the SwissFEL X-ray free electron laser (XFEL).
Biological light sensor filmed in action
Using X-ray laser technology, a team led by researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI has recorded one of the fastest processes in biology. In doing so, they produced a molecular movie that reveals how the light sensor retinal is activated in a protein molecule. Such reactions occur in numerous organisms. The movie shows for the first time how a protein efficiently controls the reaction of the embedded light sensor.
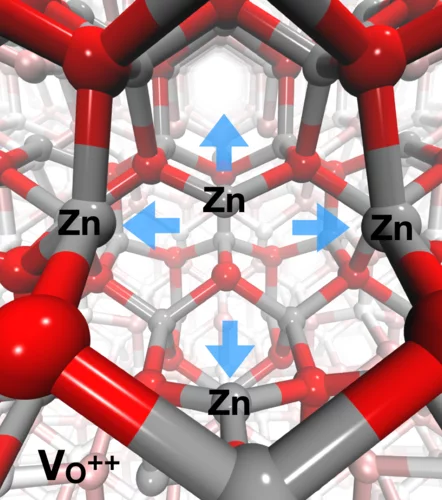
Identification of hole trapping sites in ZnO nanomaterials
Members of the Alvra group led an investigation into the fate of charge carrier dynamics in metal oxide semiconductor nanomaterials. The experiments were performed at the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne, IL, USA) and used a PSI-designed von Hamos geometry X-ray emission spectrometer that was constructed for the experiment to perform resonant XES measurements on a solution of 32 nm diameter ZnO nanoparticles photo-excited with 3.2 eV (355 nm) short laser pulses. The measurement showed that the hole-trapping takes place within less than 100 ps and the trapping site in the ZnO crystal lattice is at oxygen vacancies in the lattice. The trapping of the hole results in a local structural distortion, where the four neighbouring Zn atoms move away from the vacancy. The measurement demonstrated the strength of the RXES technique's ability to probe both the electronic and geometric structure of materials and the results were recently published in Nature Communications.
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra: UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline.
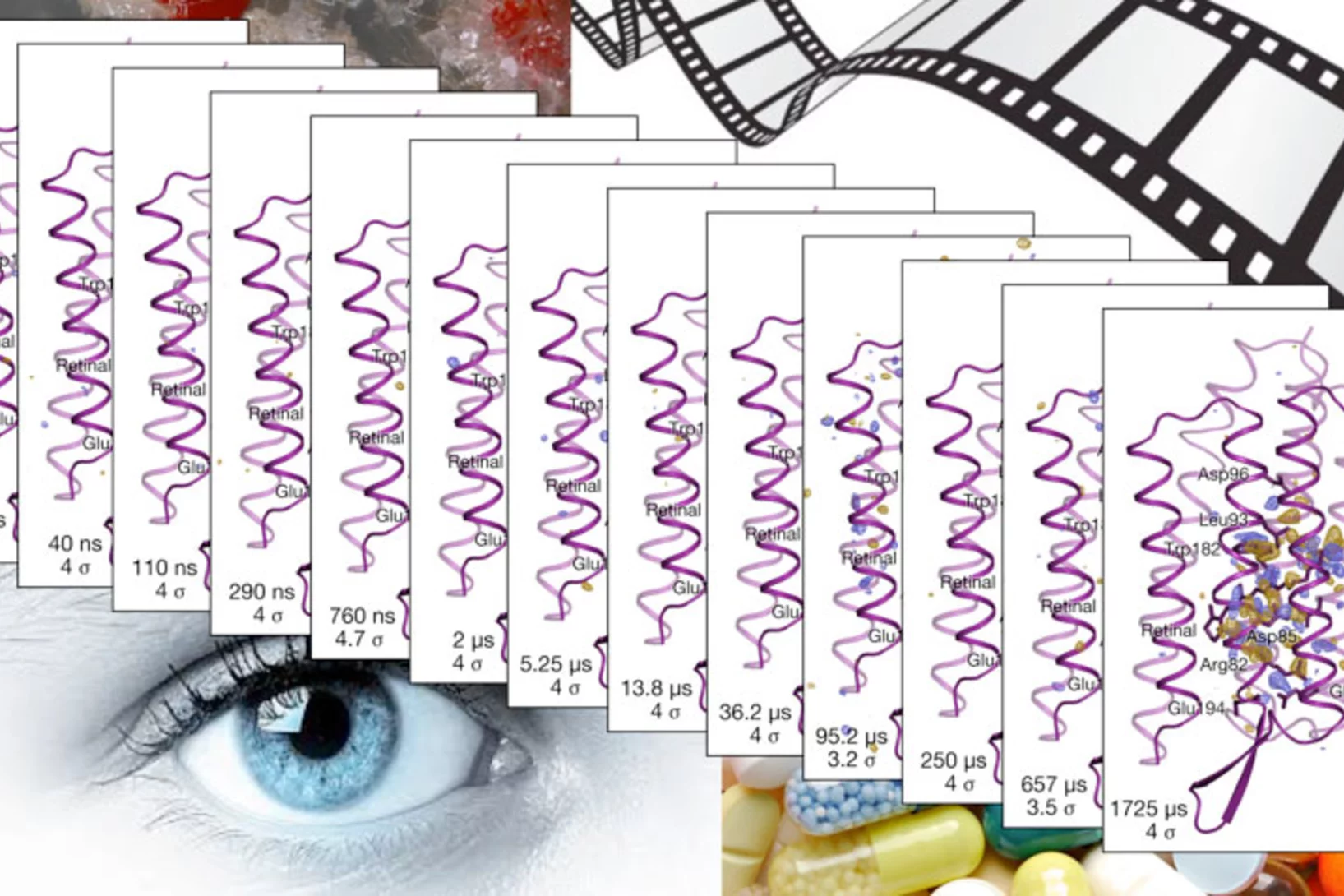
A three-dimensional movie of structural changes in bacteriorhodopsin
Snapshots of bacteriorhodopsinBacteriorhodopsin is a membrane protein that harvests the energy content from light to transport protons out of the cell against a transmembrane potential. Nango et al. used timeresolved serial femtosecond crystallography at an x-ray free electron laser to provide 13 structural snapshots of the conformational changes that occur in the nanoseconds to milliseconds after photoactivation. These changes begin at the active site, propagate toward the extracellular side of the protein, and mediate internal protonation exchanges that achieve proton transport.
Together, not alone
Decoding biomolecules at SwissFEL and SLSProteins are a coveted but stubborn research object. A method developed for x-ray free-electron lasers and PSI’s future SwissFEL should now help researchers to make good headway in this field. It involves x-raying many small, identical protein samples consecutively at short intervals, thereby avoiding the main problem that protein research has faced thus far: producing samples in a sufficient size.
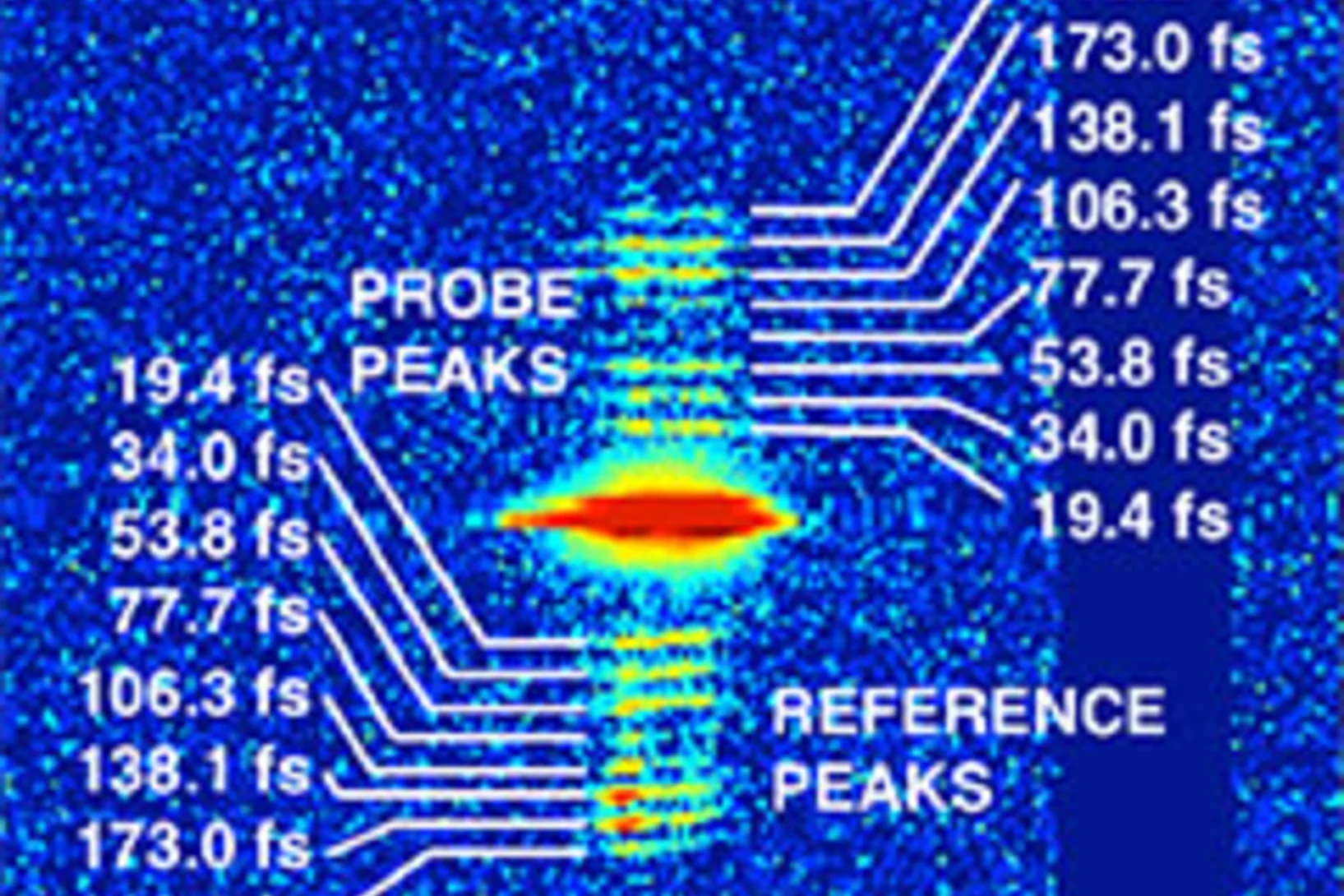
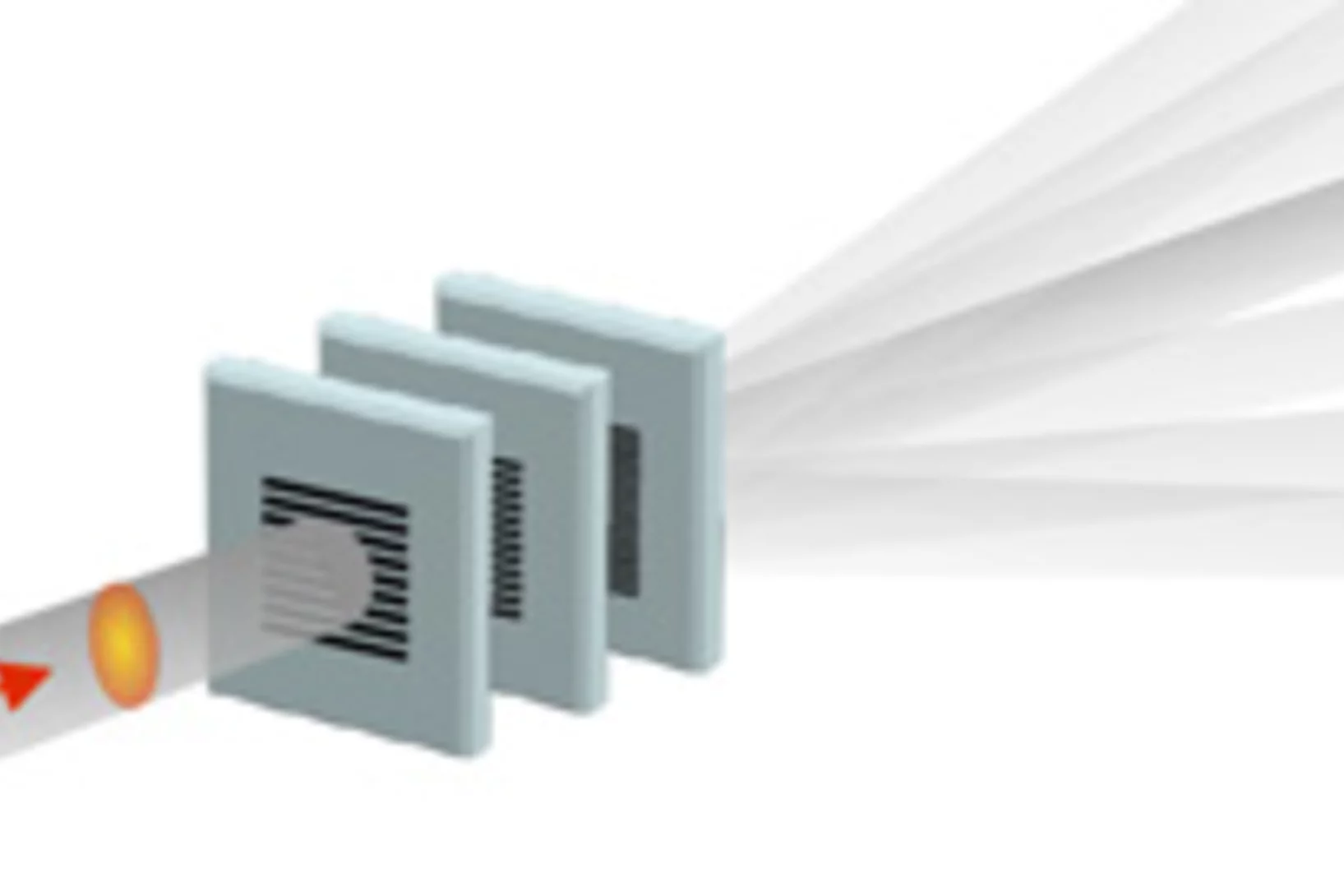
Split x-ray flash shows rapid processes
SwissFEL, PSI’s x-ray laser, is to render the individual steps of very rapid processes visible. A new method will facilitate especially precise experiments: the individual x-ray flashes are split into several parts that arrive at the object under examination one by one. The principle of the method harks back to the ideas of the earliest high-speed photography.