Cuprate Trilogy
In a trio of recent papers, a research group from the University of Zürich has made a number of new discoveries about the nature of cuprates' electronic structure and orbital composition. The results have important implications for superconductivity and pseudogaps in cuprates, and even the existence of type-II Dirac fermions in oxides.
SwissFEL's First Call for Proposals
The first SwissFEL call for proposals took place, deadline for submission was the 15th of September. In this first call for proposals SwissFEL received overwhelming interest from the user community. A total of 47 proposals were submitted for the SwissFEL Alvra experimental station and 26 for the Bernina experimental station. The Proposal Review committee PRC took place on 18-19 October 2018.
Why the Little Ice Age ended in the middle of the 19th century
In the first half of the 19th century, a series of large volcanic eruptions in the tropics led to a temporary global cooling of Earth's climate. That Alpine glaciers grew and subsequently receded again during the final phase of the so-called Little Ice Age was due to a natural process. This has now been proven by PSI researchers on the basis of ice cores.
Discrete Hall contribution of magnetic skyrmions
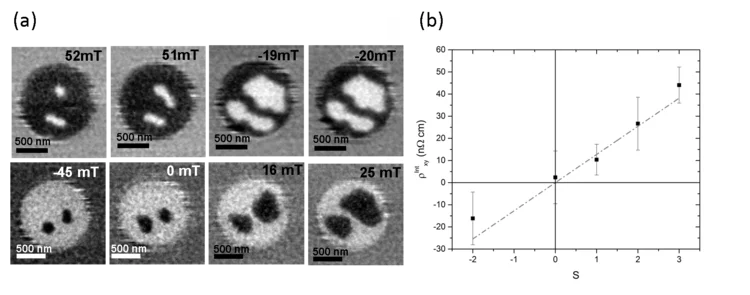
The reliable electrical detection of magnetic skyrmions is of fundamental importance for the application of such topological magnetic quasi-particles for data storage devices. Researchers in a joint collaboration between the University of Leeds and the PolLux endstation have investigated the electrical detection of isolated magnetic skyrmions in applications-relevant nanostructured devices, observing the presence of a strong skyrmion-dependent contribution to the Hall resistivity.
Observation of the out-of-plane magnetization in a mesoscopic ferromagnetic structure superjacent to a superconductor
The geometry of magnetic flux penetration in a high temperature superconductor at a buried interface was imaged using element-specific x-ray excited luminescence. We performed low tem- perature observation of the flux penetration in YBa2Cu3O7–δ (YBCO) at a buried interface by imaging of the perpendicular magnetization component in square Permalloy (Py) mesostructures patterned superjacent to a YBCO film.
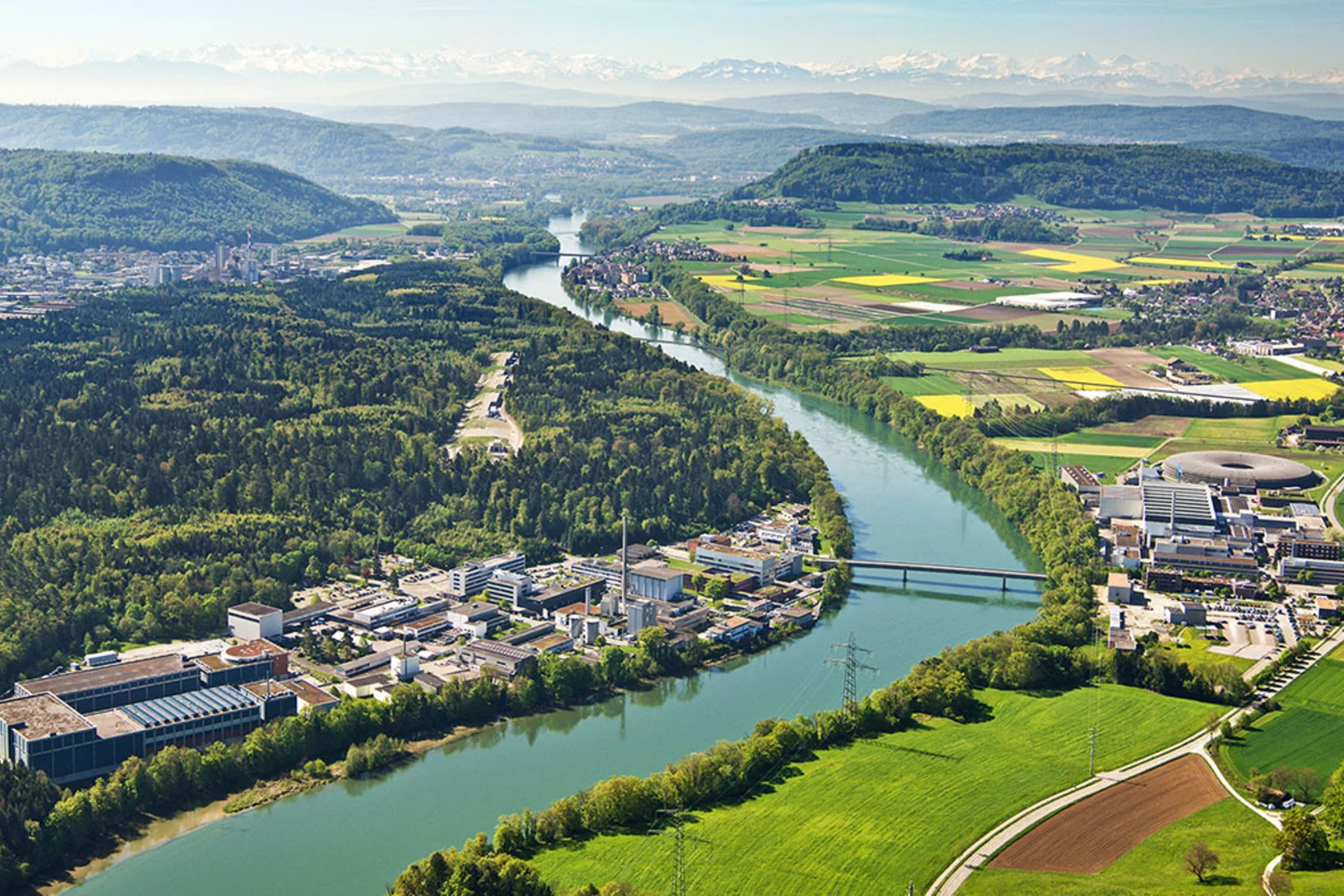
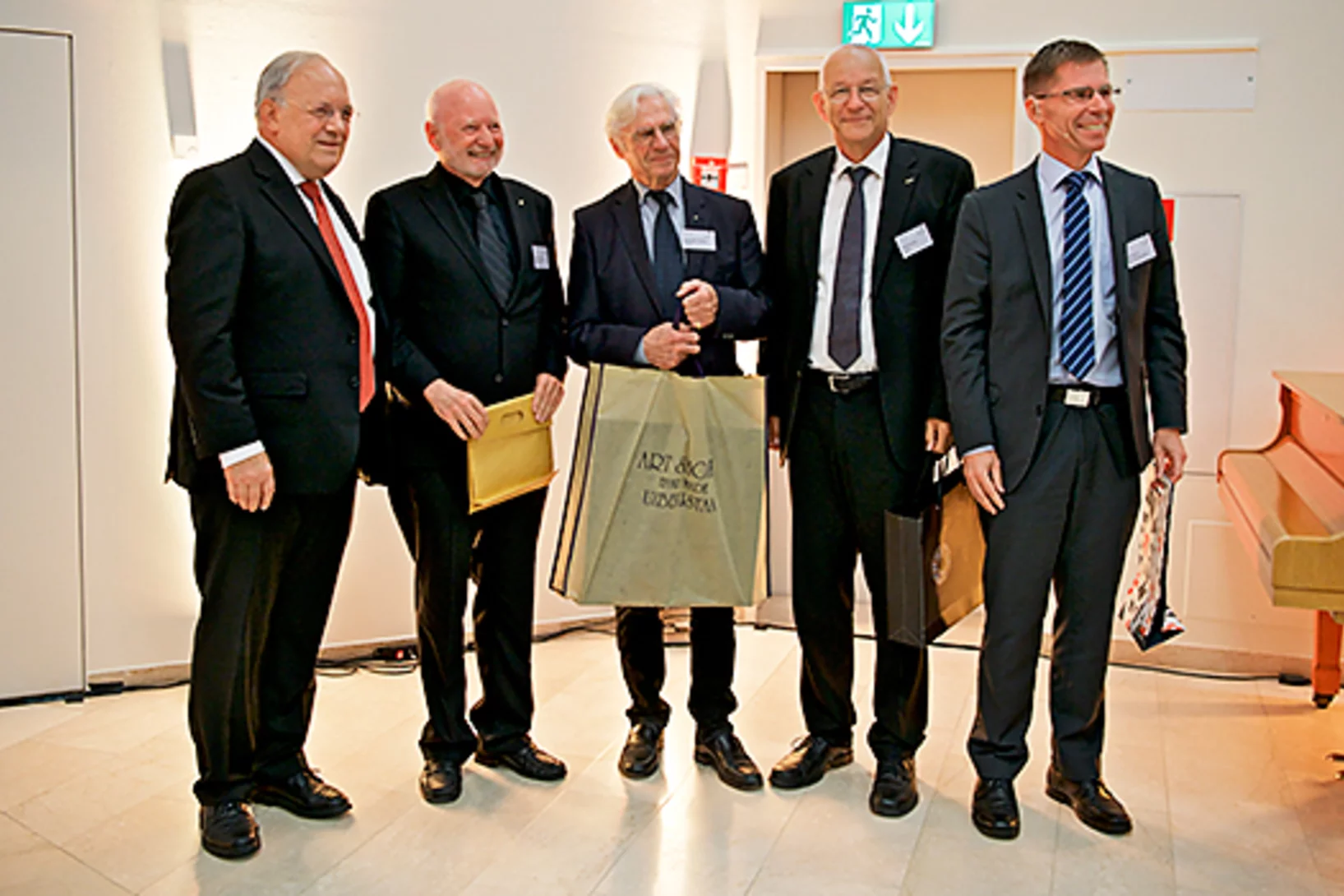
30 years Paul Scherrer Institute PSI
Ceremony with invited guests from politics, business and sciencePSI held its 30 Years of PSI ceremony. The PSI showed guests what it has achieved over the past three decades, with results that could be of benefit to everyone in Switzerland.
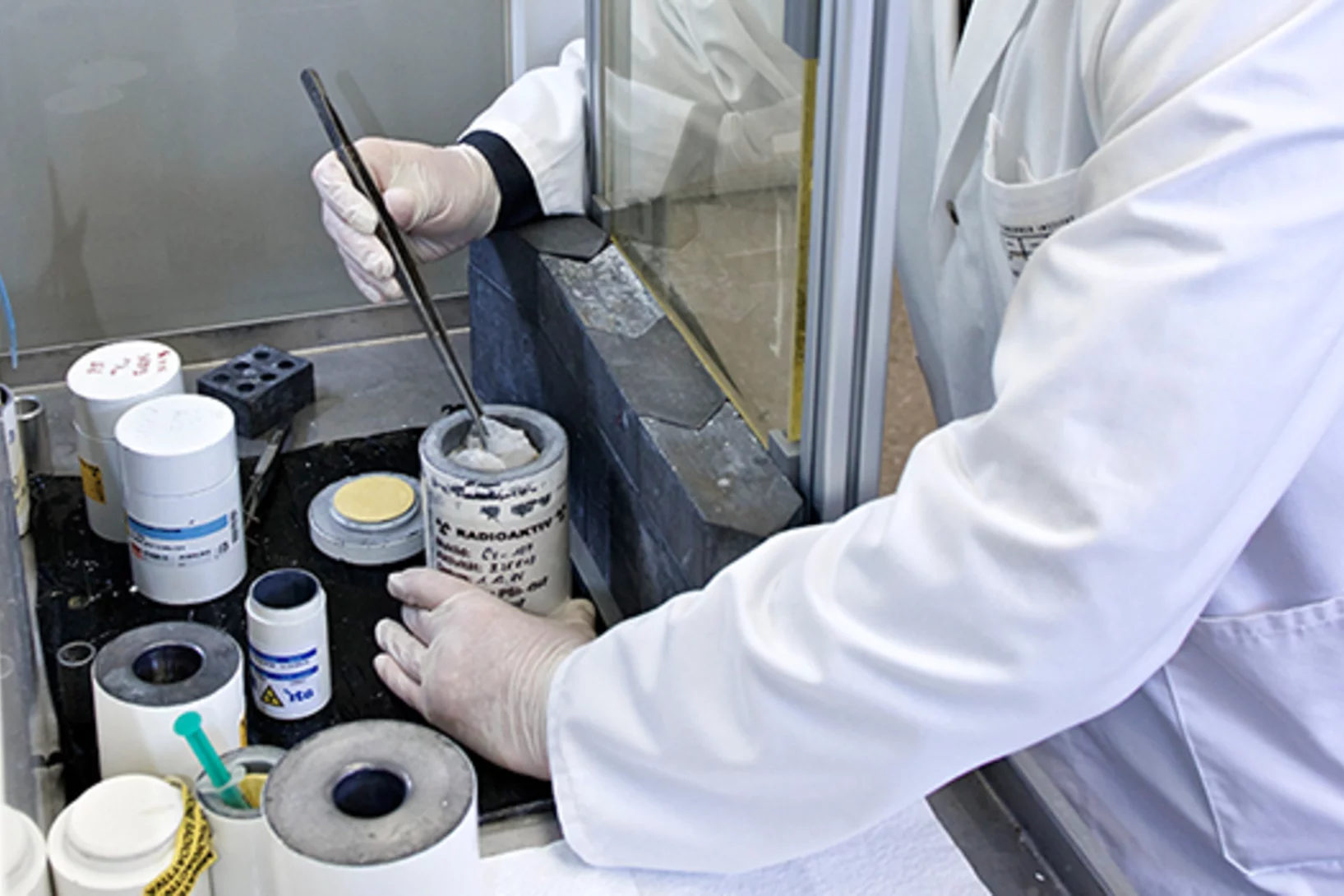
Licence agreement with Swiss pharma firm for development of a cancer drug
A radioactive agent, developed at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI to fight an especially malignant form of thyroid cancer, has the potential to become a blockbuster drug. Due to its structure, it might also be able to dock onto cells of other tumours and destroy them with its radiation. The Lausanne-based biopharmaceutical company Debiopharm wants to further develop the PSI agent to the point where it is approved as a drug. Debiopharm and PSI have now created the contractual basis for this.
This time, it's all bio: SwissFEL makes protein structures visible
For the development of new medicinal agents, accurate knowledge of proteins is crucial. In a pilot experiment, researchers have now, for the first time, used the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of PSI for the examination of protein crystals.
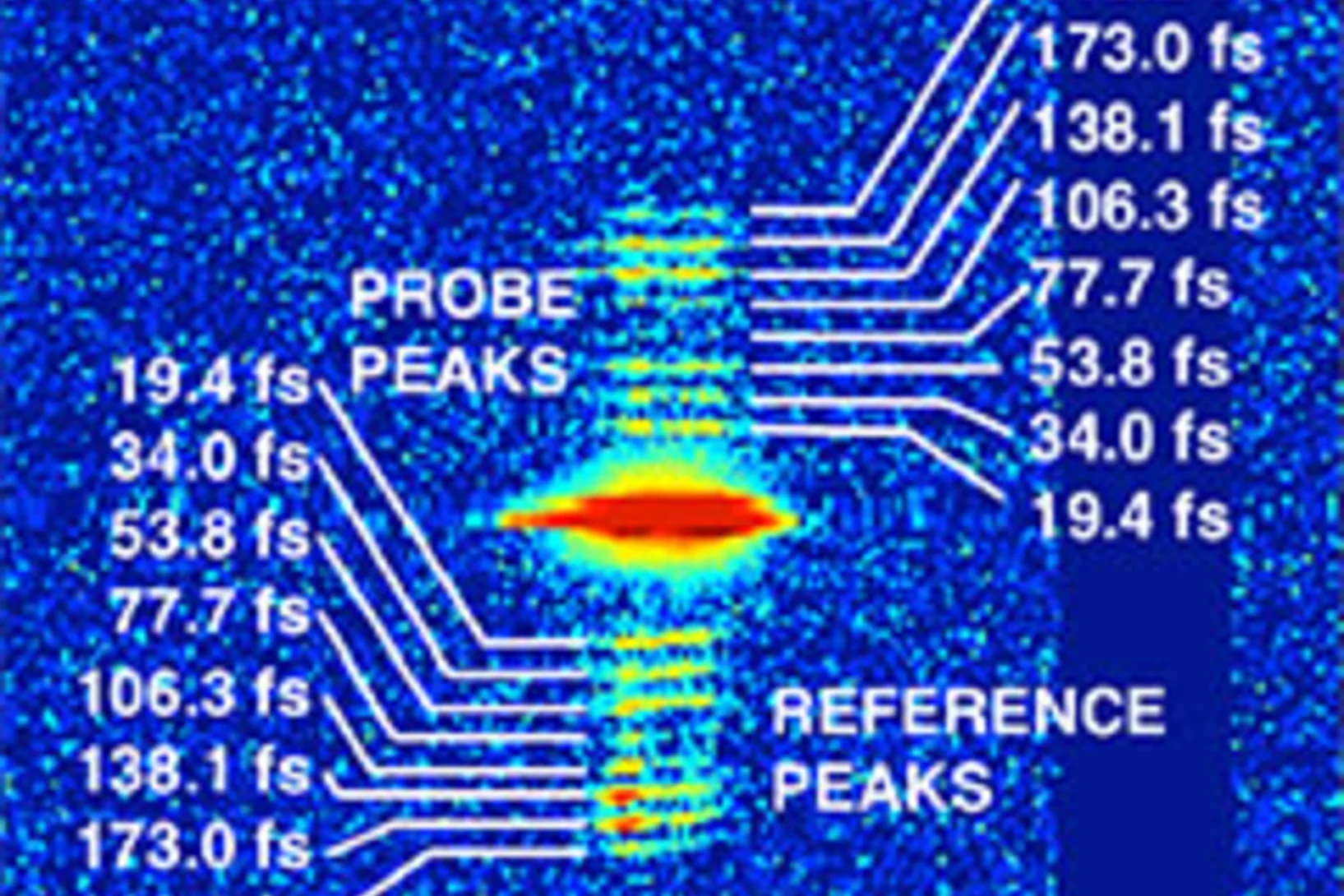
Demonstration of femtosecond X-ray pump X-ray probe diffraction on protein crystals
Our experiments, published in the September issue of Structural Dynamics, demonstrate the feasibility of time-resolved pump-multiprobe X-ray diffraction experiments on protein crystals using a split-and-delay setup which was temporarily installed at the LCLS X-ray Free Electron Laser.
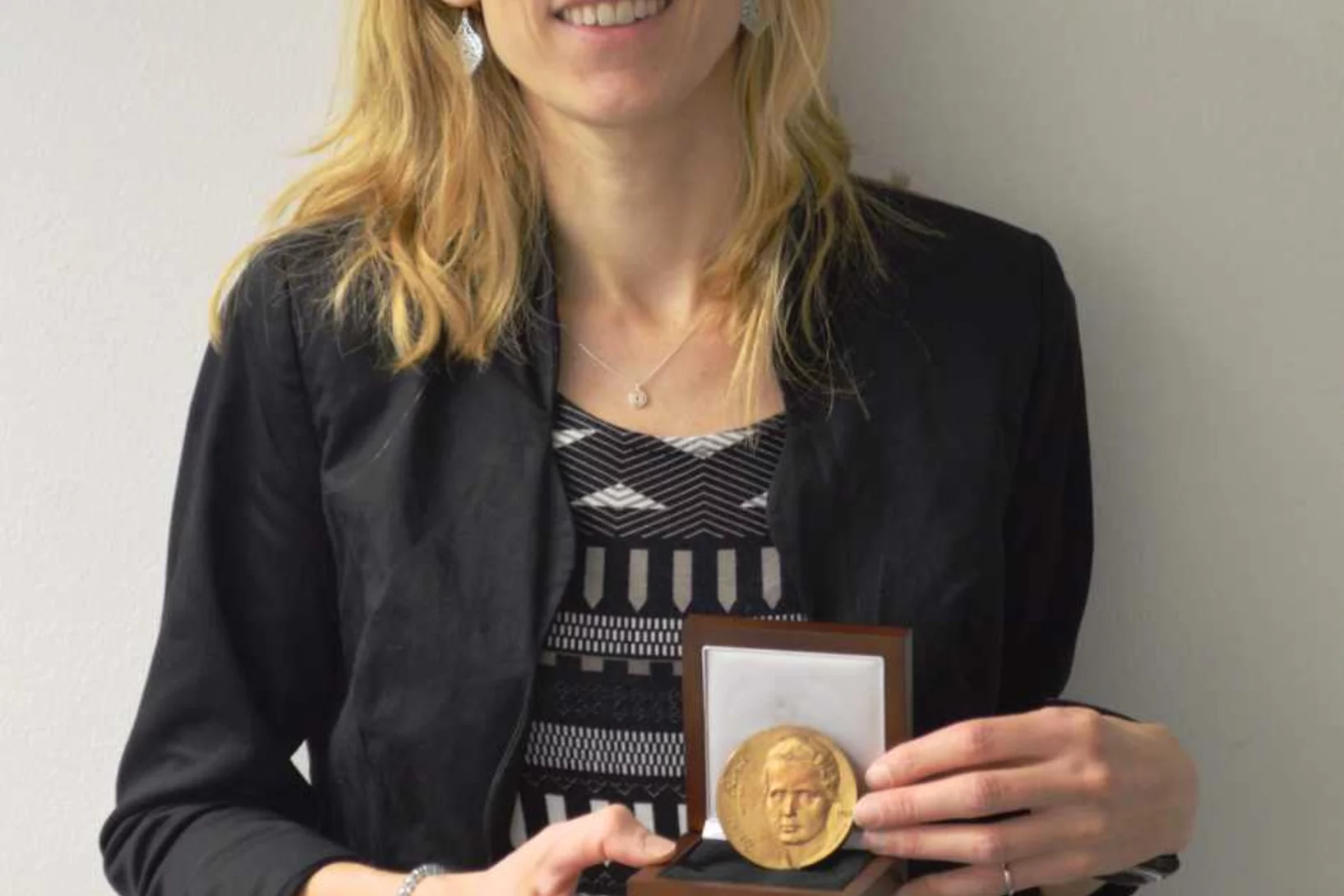
Cristina Müller (CRS) receives the Marie Curie Award
The Marie Curie Award, the most prestigious price by the European Association of Nuclear Medicine, has been awarded in 2018 for the project "Terbium-161 for PSMA-Targeted Radionuclide Therapy of Prostate Cancer", lead by Christina Müller in collaboration with Nick van der Meulen (LRC/NES) EANM-Website(link is external).
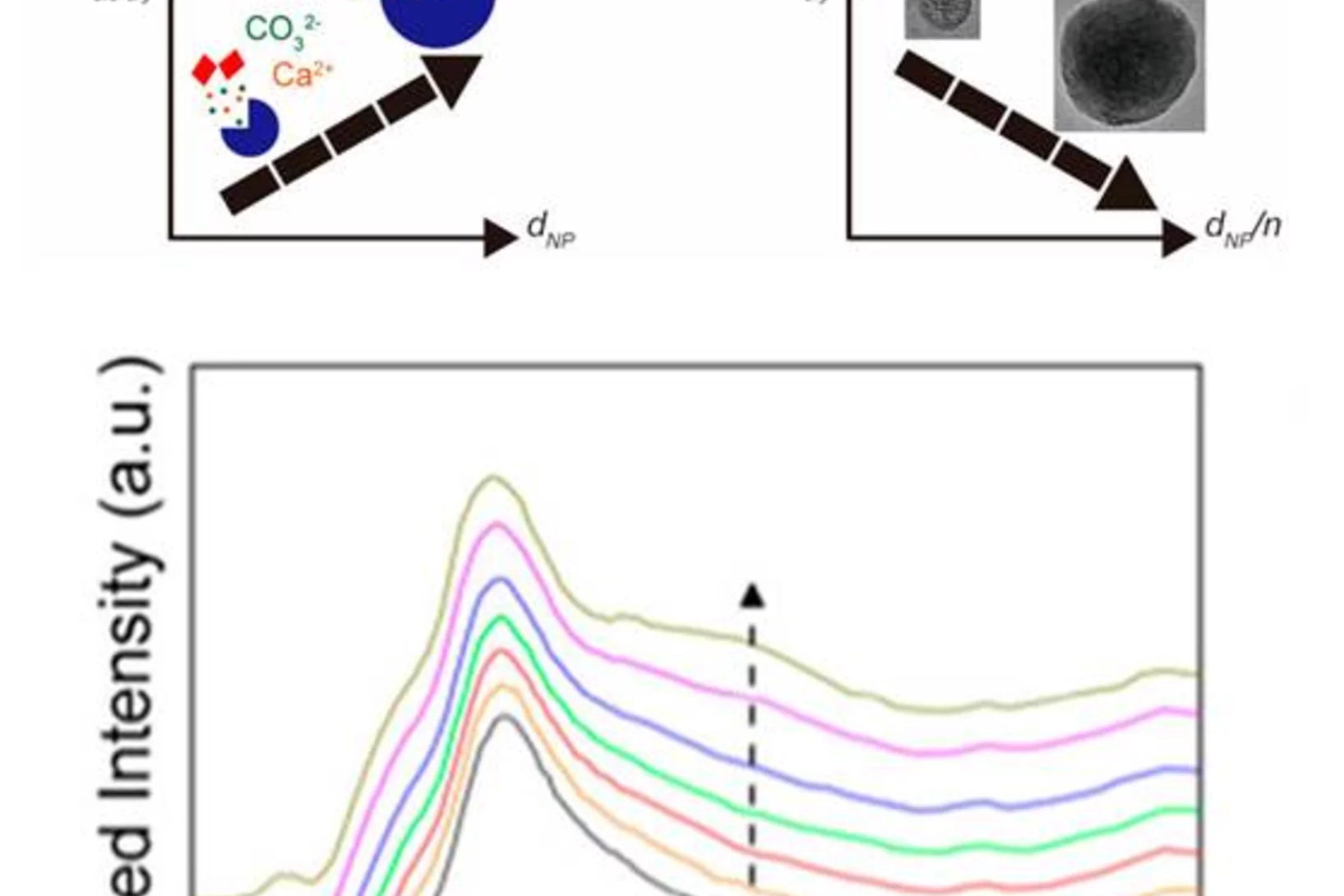
Amorphous CaCO3: Influence of the Formation Time on Its Degree of Hydration and Stability
Carbonate minerals serve as reservoir for CO2 in the global CO2 cycle, as biomineral in animal skeletons and shells of marine animals, and are used in carbon capturing techniques. Moreover, they serve as an important model system in crystallization studies, and have important commercial applications, for example as fillers. Researchers from EPFL and PSI developed a new methodology to study the crystallization of CaCO3 that offers both high temporal and spatial resolution, which is the key challenge in elucidating early stages of crystallization. Using X-ray absorption spectroscopy and other techniques it could be demonstrated that the degree of hydration of amorphous CaCO3 increases during its growth. As a result of the increasing degree of hydration, the stability of the resulting amorphous particles against solid-state crystallization decreases.
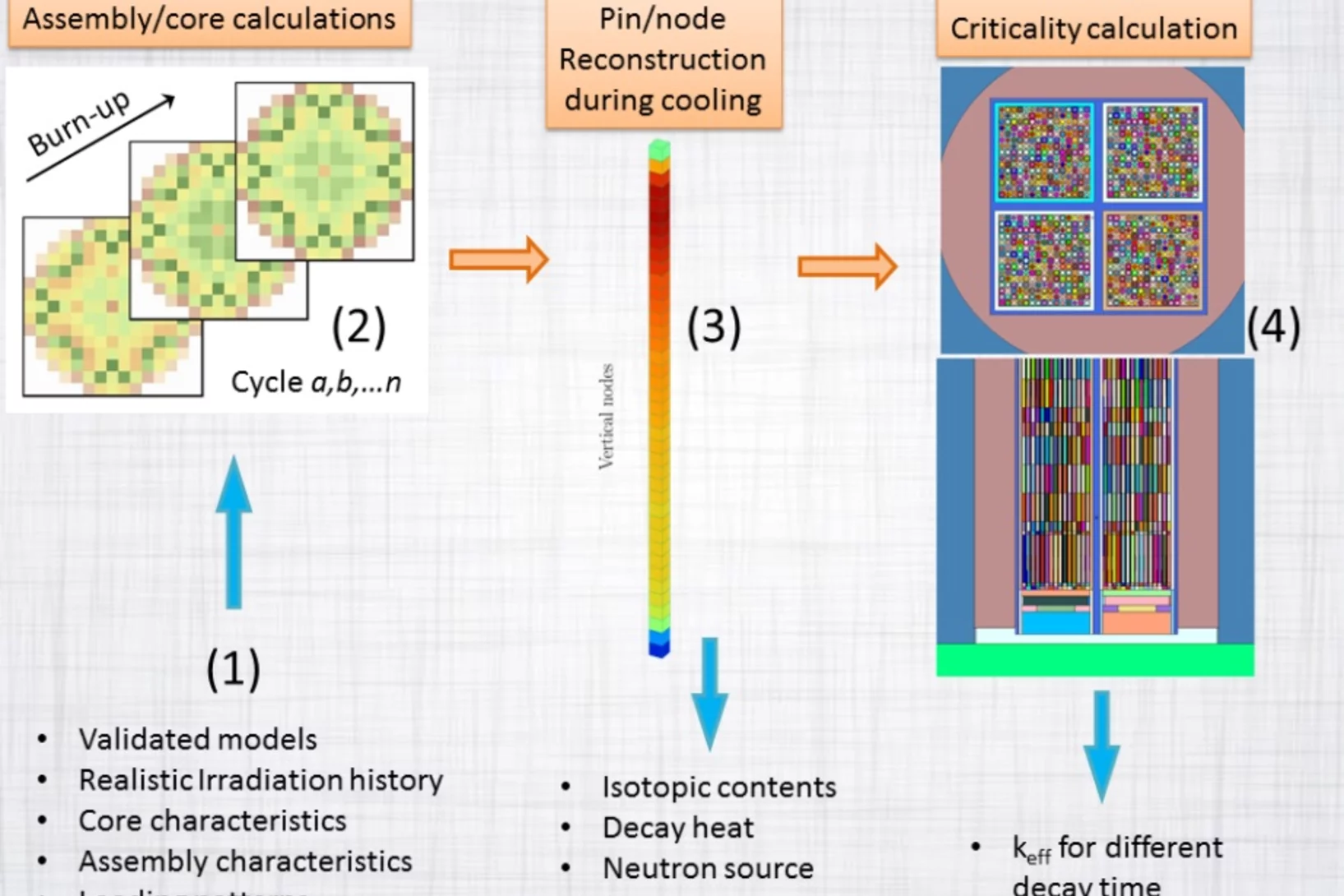
Consistent criticality and radiation studies of Swiss spent nuclear fuel: The CS2M approach
Spent fuel management is becoming one of the major concerns in many countries with a nuclear program. The radiation aspect as well as the safe and economical part of the long-term storage of the spent nuclear fuel has to be evaluated with a high degree of confidence. To assist such project from the neutronic simulation side, a new method is proposed to systematically calculate at the same time canister loading curves and radiation sources, based on the inventory information from an in-core fuel management system.
From researcher to entrepreneur
Towards new shores: At the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, enterprising researchers are venturing into the unknown. They're leaving their safe haven to become successful entrepreneurs. The journey from PSI to one's own spin-off takes courage. To keep the voyage from getting too stormy, PSI supports its business founders as they navigate through rough waters, and maintains these connections over many years.
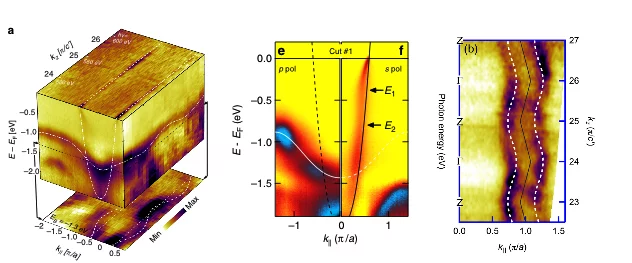
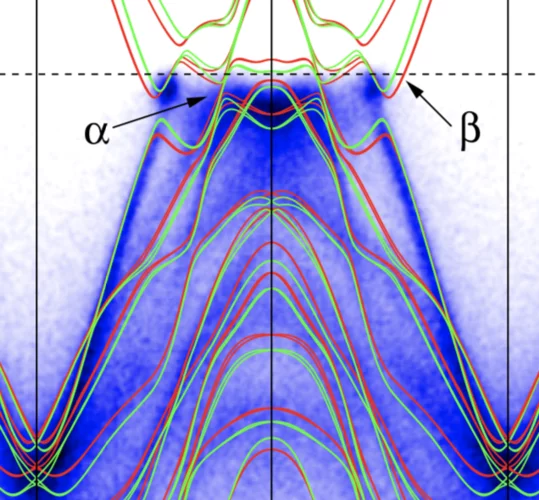
Evidence of a Coulomb-Interaction-Induced Lifshitz Transition and Robust Hybrid Weyl Semimetal in Td-MoTe2
Using soft x-ray angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy we probed the bulk electronic structure of Td-MoTe2. We found that on-site Coulomb interaction leads to a Lifshitz transition, which is essential for a precise description of the electronic structure. A hybrid Weyl semimetal state with a pair of energy bands touching at both type-I and type-II Weyl nodes is indicated by comparing the experimental data with theoretical calculations.
Marc Janoschek appointed new head of LDM
Dr Marc Janoschek has been appointed new head of the NUM Laboratory for Scientific Developments and Novel Materials LDM. He will take office on November 15, 2018. Marc studied Physics at TU Munich and did his PhD at PSI and TUM on "Neutron Scattering on Chiral Magnets". After that he went to the University of California in San Diego as Feodor-Lynen Fellow. Since 2011 he is head of "Neutron research" in the "Condensed Matter and Magnet Science" group in Los Alamos. For his research Marc has been awarded the Wolfram Prandl Prize and the Los Alamos Fellow Prize for Outstanding Research. We wish Marc success and satisfaction for his new duties and wish to thank cordially Peter Keller, who led the LDM ad interim since March 2018.
Jay Slowik and Ru-Jin Huang win prestigious Schmauss award
Award conferred by the Gesellschaft für Aerosolforschung (GAeF) during the International Aerosol Conference in St. Louis, MO, USA
Collaboration meeting in Liverpool
The Mu3e collaboration met for three days at the University of Liverpool to discuss integration and assembly of the experiment and recent progress for all subdetectors.
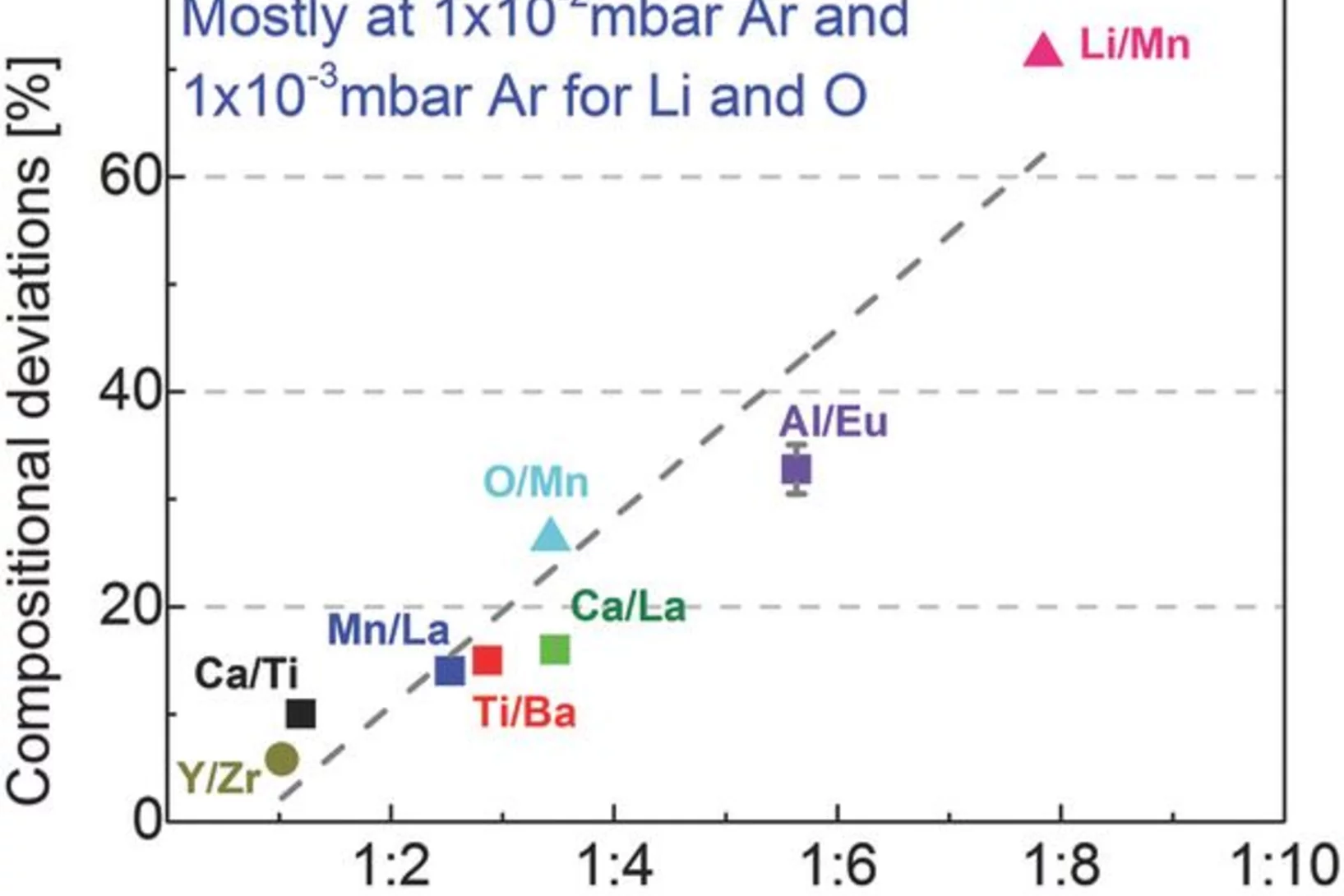
Influence of Plume Properties on Thin Film Composition in Pulsed Laser Deposition
Despite the apparent simplicity of pulsed laser deposition, consistent deposition of thin films with the desired thickness, composition, crystallinity, and quality still remains challenging. This article explores the influence of process parameters with respect to film thickness and composition, two key aspects for thin films which have a very strong effect on film properties, possible applications, and characterization.
Influence of Plume Properties on Thin Film Composition in Pulsed Laser Deposition
Despite the apparent simplicity of pulsed laser deposition, consistent deposition of thin films with the desired thickness, composition, crystallinity, and quality still remains challenging. This article explores the influence of process parameters with respect to film thickness and composition, two key aspects for thin films which have a very strong effect on film properties, possible applications, and characterization.
Bernina status first summer shutdown
The summer shutdown was used to install more missing hardware. With the new components the Bernina instrument will be already very close to the full design capabilities when the exciting time of user experiments will begin in 2019.
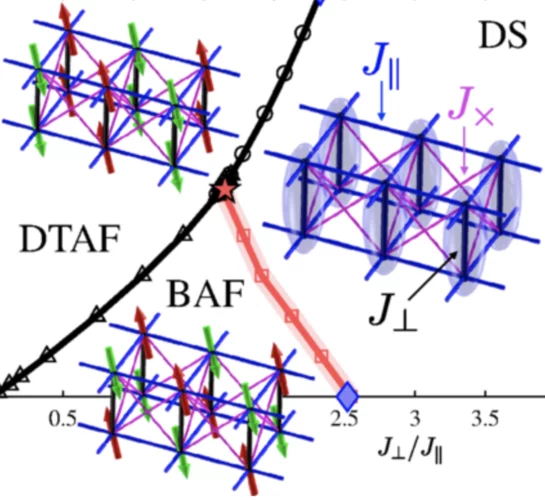
Thermal Critical Points and Quantum Critical End Point in the Frustrated Bilayer Heisenberg Antiferromagnet
We consider the finite-temperature phase diagram of the S=1/2 frustrated Heisenberg bilayer. Although this two-dimensional system may show magnetic order only at zero temperature, we demonstrate the presence of a line of finite-temperature critical points related to the line of first-order transitions between the dimer-singlet and -triplet regimes.
Finite-temperature critical points and quantum critical end point in a 2D magnet
The Mermin–Wagner theorem has long told us that in two dimensions a continuous symmetry can be broken, allowing a finite order parameter, only at zero temperature. Now PSI theorist Bruce Normand, working with colleagues in Aachen, Amsterdam, Lausanne and Paris, has circumvented this rule. The team was considering the thermodynamics
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
Cu-SSZ13
The combination of time-resolved XAS and transient experiments enables to capture an inhibition effect by NH3 on the rate-limiting re-oxidation of CuI at low temperature.
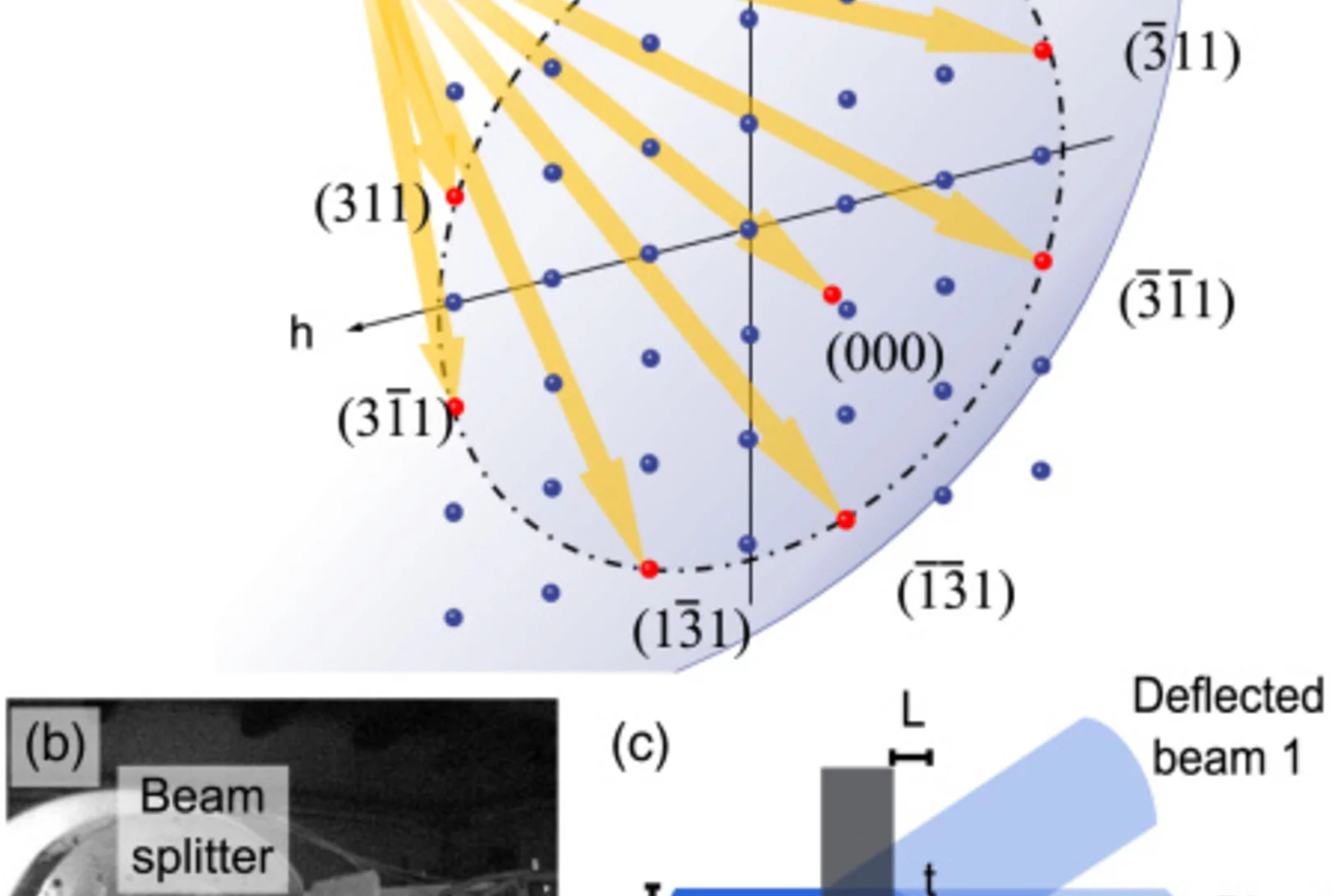
TOMCAT paper on hard X-ray multi-projection imaging published
The TOMCAT team in collaboration with scientists from CFEL, MaxIV and ESRF developed a method for hard X-ray multi-projection imaging, using a single crystal to split the beam into multiple beams with different directions.
Disordered skyrmion phase stabilized by magnetic frustration in a chiral magnet
Magnetic skyrmions are vortex-like topological spin textures often observed to form a triangular-lattice skyrmion crystal in structurally chiral magnets with the Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction. Recently, β-Mn structure-type Co-Zn-Mn alloys were identified as a new class of chiral magnet to host such skyrmion crystal phases, while β-Mn itself is known as hosting an elemental geometrically frustrated spin liquid.
SNI Honorary Membership for Jens Gobrecht
At this year's annual meeting of the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI) Jens Gobrecht, the former Head of LMN, received the SNI Honorary Membership.
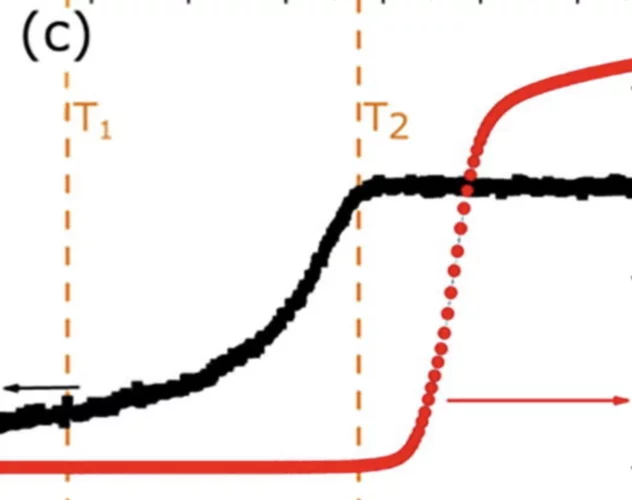
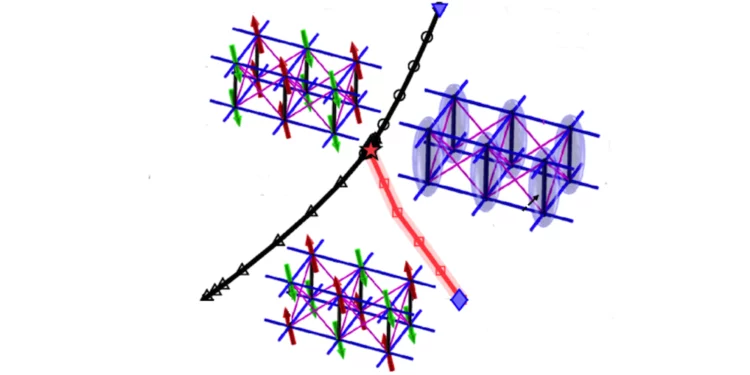
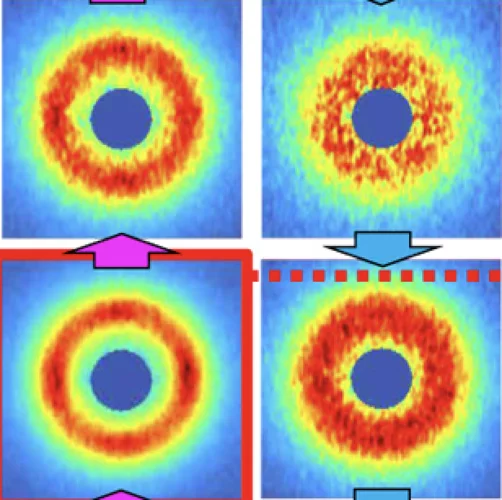
Quantum magnets under pressure
The demonstration that applied pressure can substantially change – rather than merely tweak – the properties of a metal–organic quantum magnet indicates a route to designing quantum materials with tailored properties.
The Swiss Federal Interim Storage Facility
In medicine, industry, and research as well as in power generation radioactive waste occurs. In Switzerland, there are currently two central interim storage facilities. The Federal interim storage facility for waste stemming from medicine, industry and research is located on the grounds of PSI.
Founding Partners Sign Charter Establishing Neutron Source Consortium LENS
On September 12 representatives of eight European research infrastructures including SINQ at PSI signed the Charter of the League of advanced European Neutron Sources (LENS) at the International Conference of Research Infrastructures, ICRI2018 in Vienna. The signing ceremony marks the establishment of a new strategic consortium of European neutron source facilities with the aim, according to the charter, to “facilitate any form of discussion and decision-making process that has the potential to strengthen European neutron science via enhanced collaboration among the facilities”. The founding partners in the consortium include both European and national facilities in France, Germany, Sweden, Hungary, the United Kingdom, Norway and Switzerland. Other qualifying facilities are invited to join at any time.
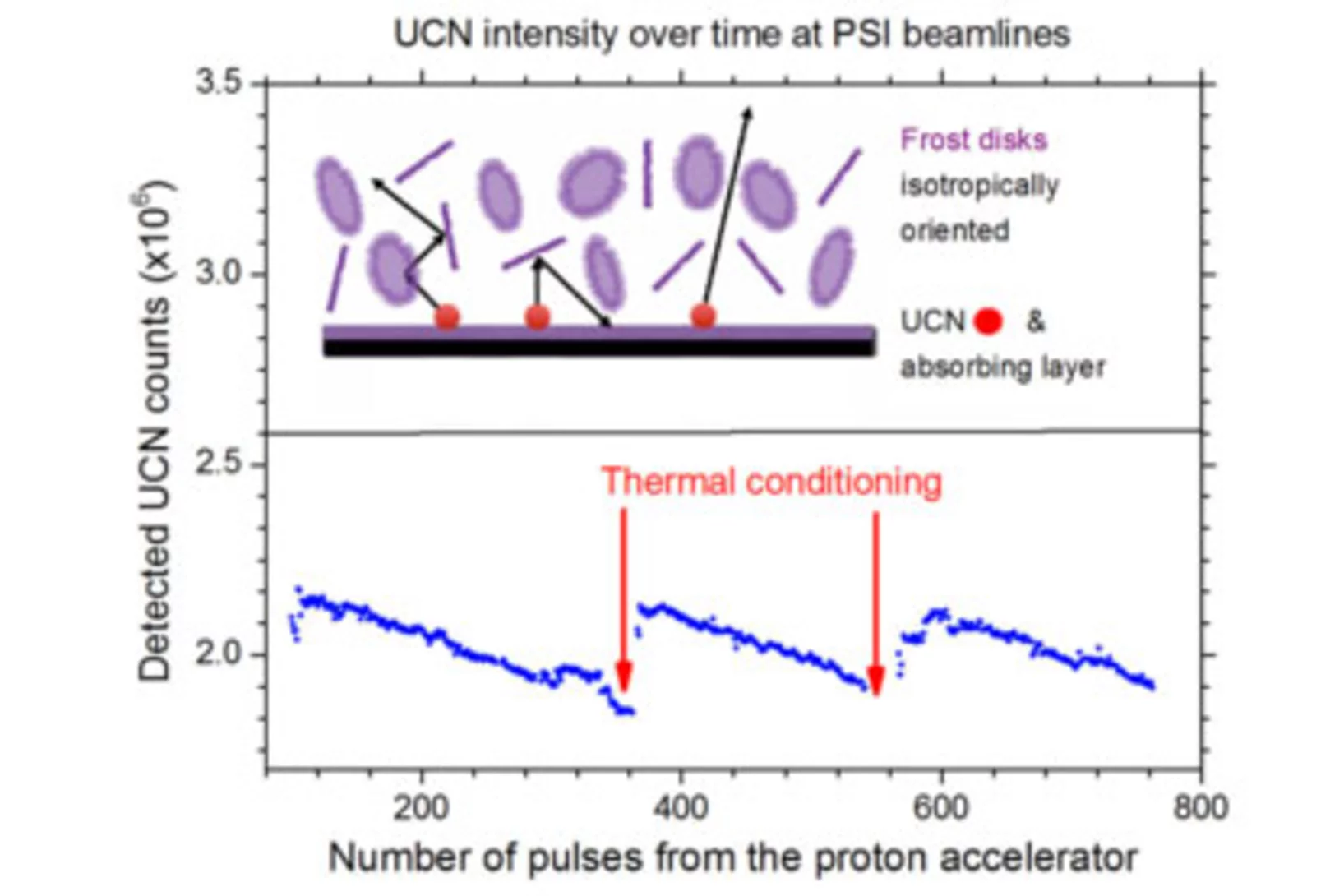
Solid deuterium surface degradation at ultracold neutron sources
Solid deuterium (sD2) is used as an efficient converter to produce ultracold neutrons (UCN). Itis known that the sD2 must be sufficiently cold, of high purity and mostly in its ortho-state in order to guarantee long lifetimes of UCN in the solid from which they are extracted into vacuum.












![Crystallographic structure of [CuF2(H2O)2]2pyrazine below (left) and above the structural phase transition observed at 18 kbar. The images show calculated spin-density distributions of the ground state, with spins up and down represented in cyan and green, respectively. (Image adapted from [1].)](/sites/default/files/styles/teaser_grid_3_2_scale_xl/public/import/num/News20180914PressureEN/Pressure.png.webp?itok=TwuZCxxZ)