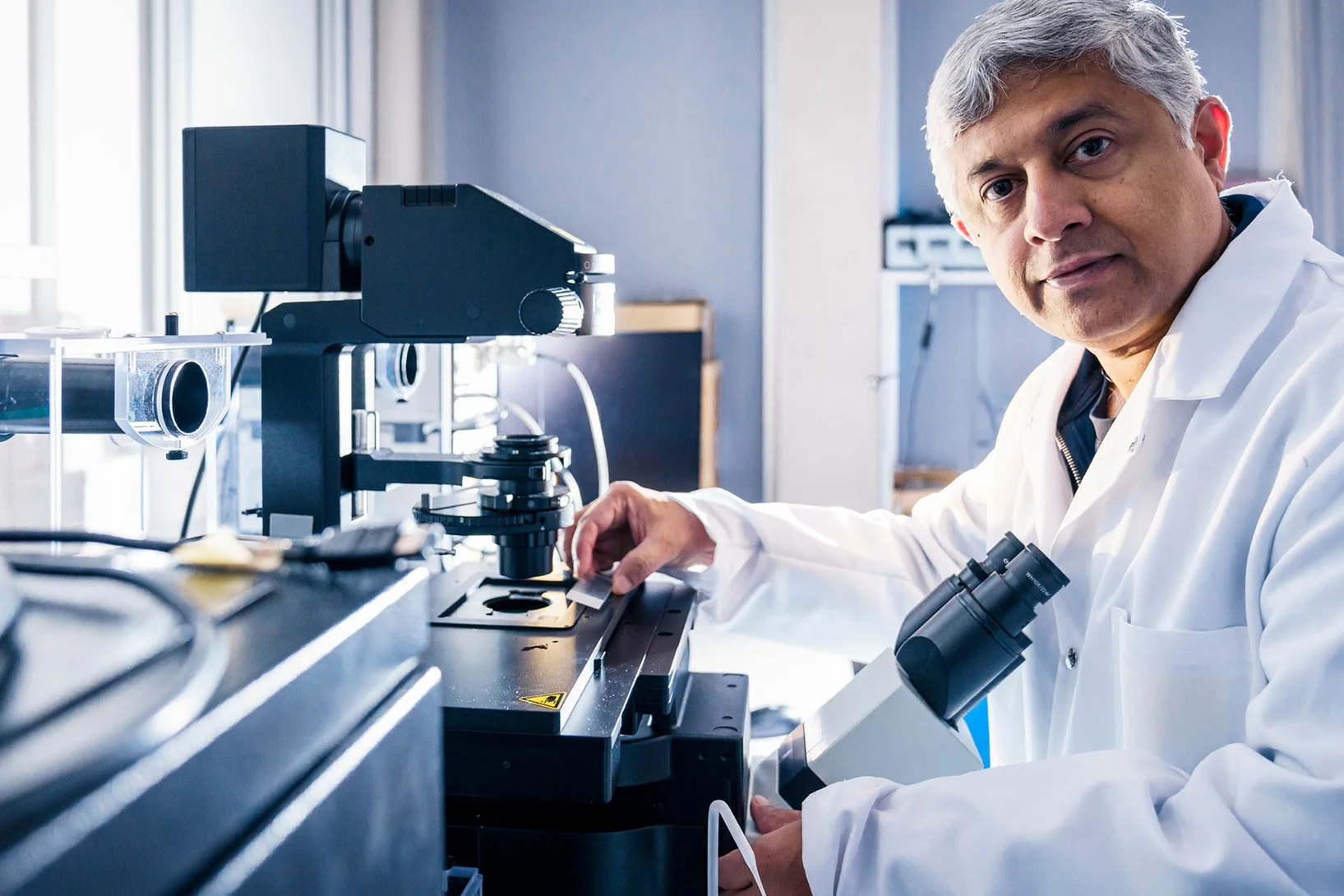
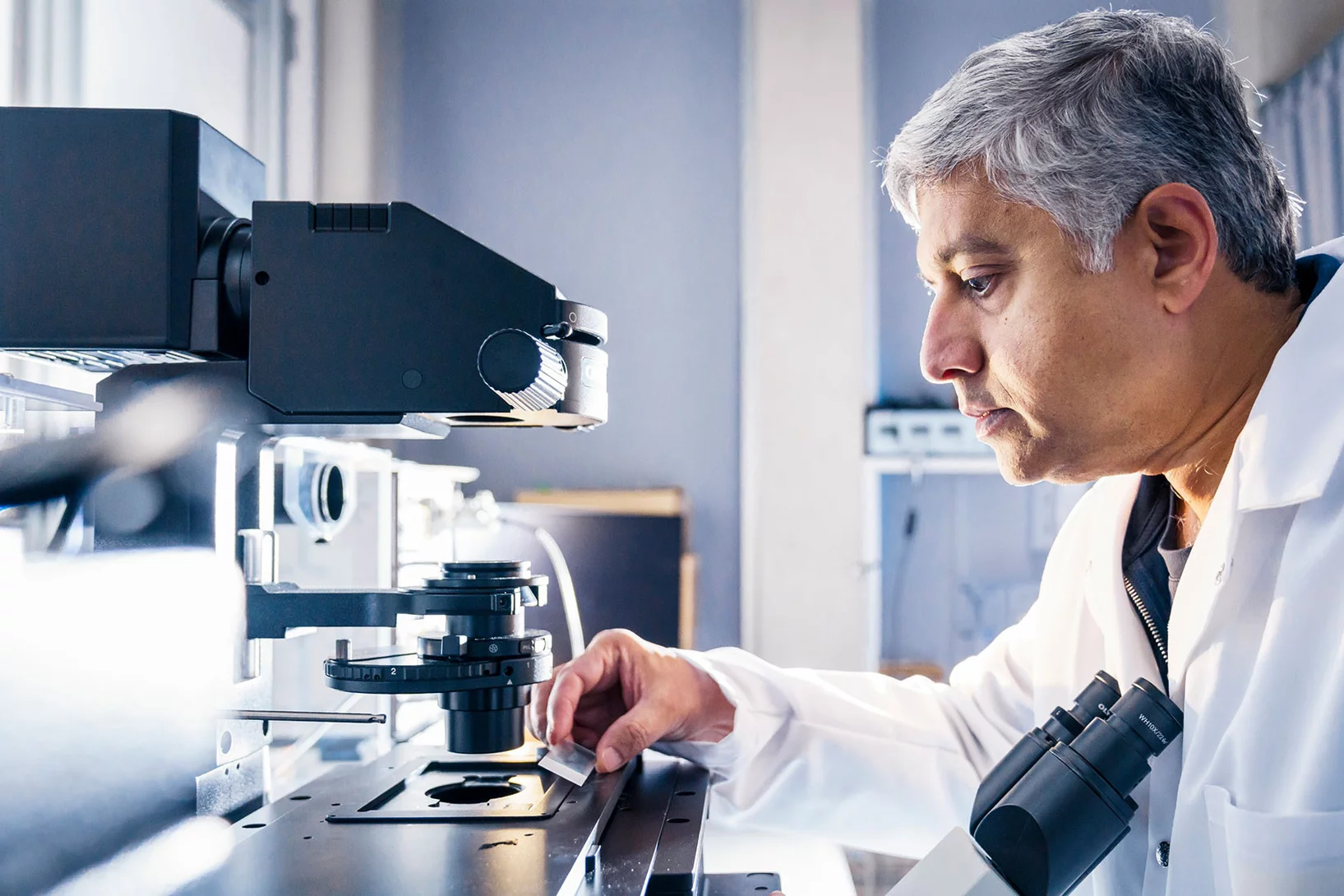
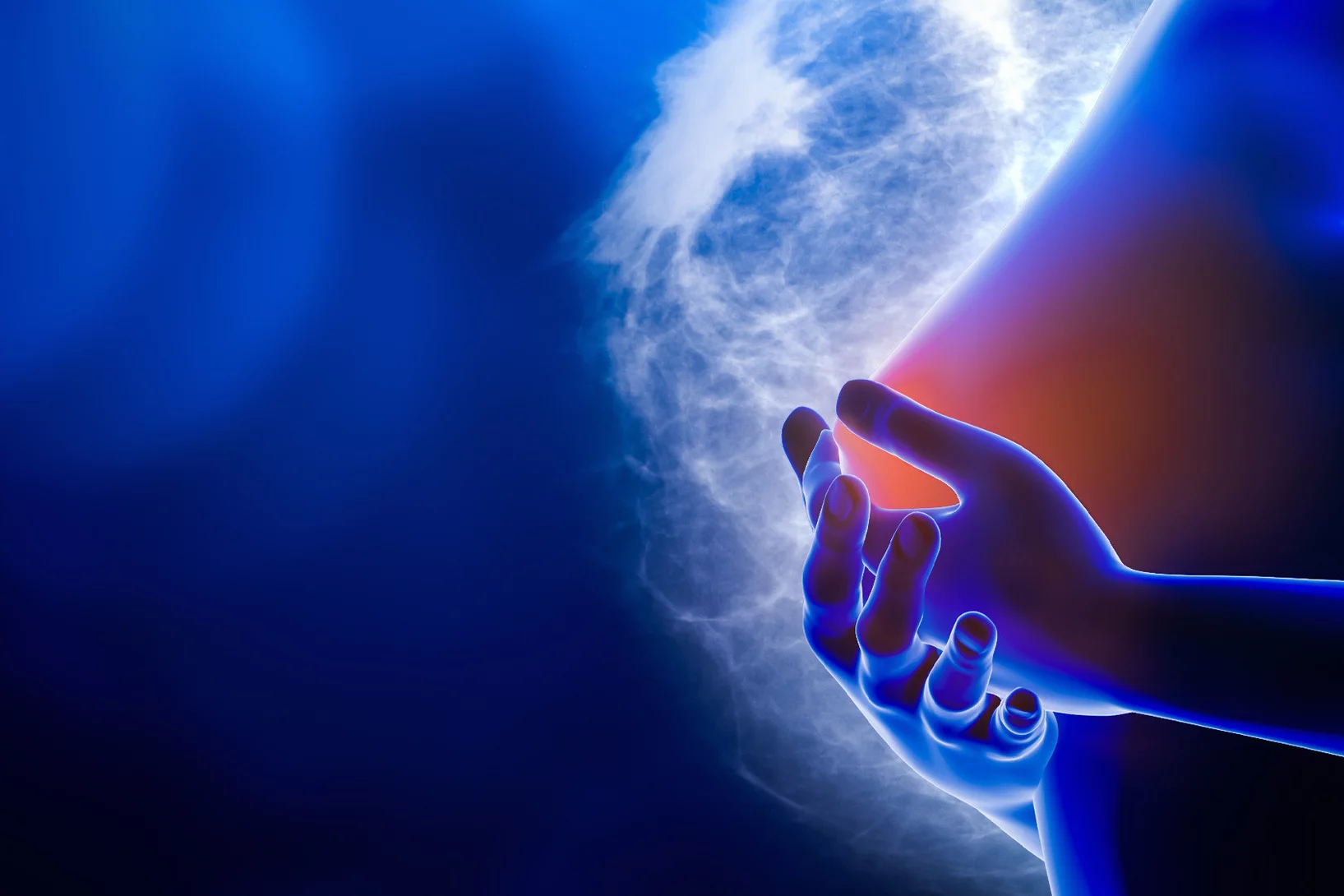
Breast cancer classification using AI
Researchers at PSI and MIT are developing a new approach, which combines imaging and artificial intelligence to improve the staging of breast cancer.
Protein droplets likely don’t cause Parkinson’s
Study deepens our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases linked to protein aggregation.
EMBO workshop on Nuclear Mechano-Genomics
The EMBO-workshop on Nuclear Mechano-Genomics taking place from April 16 to April 19, 2024 in Sardinia, Italy, was a great success.
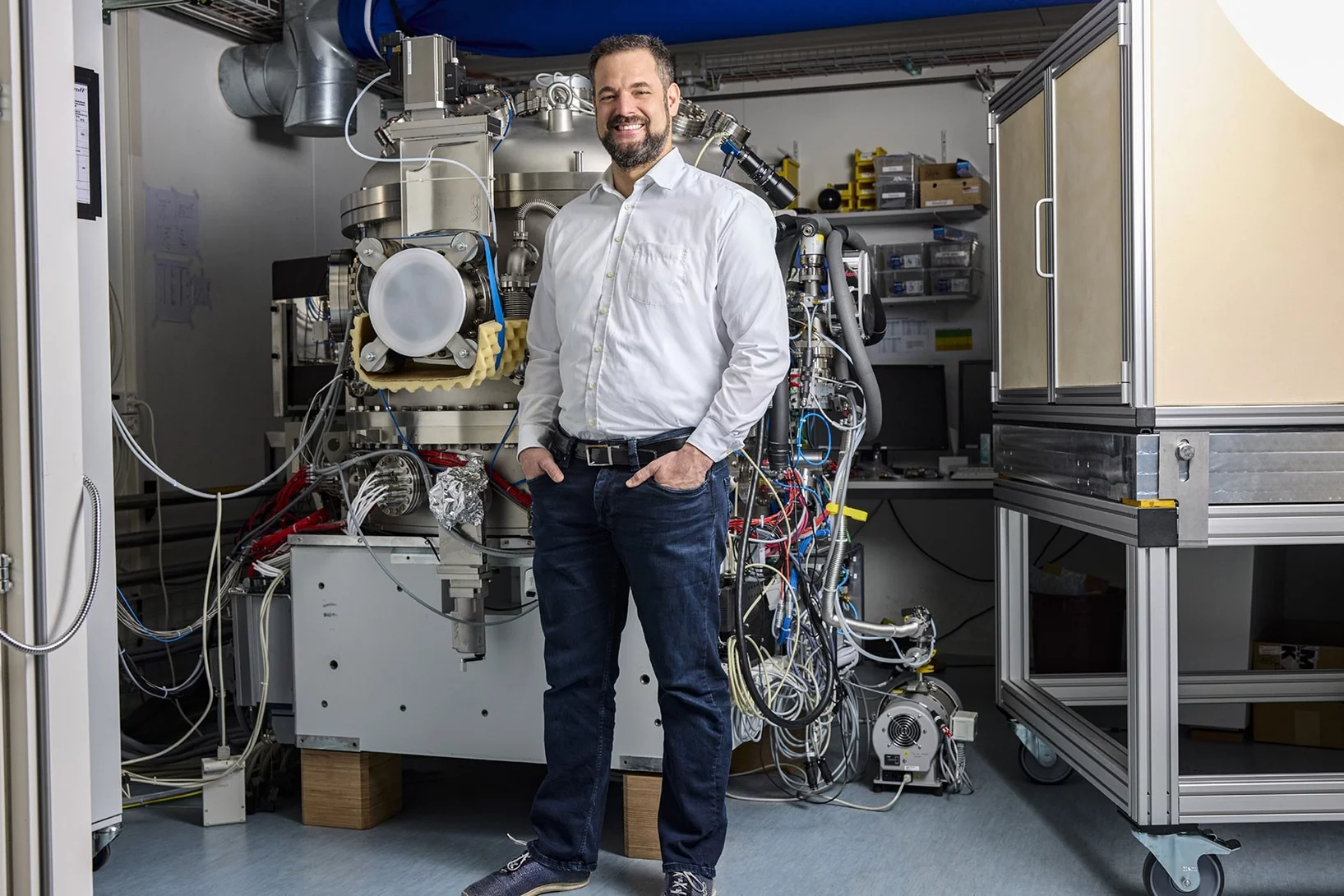
Enabling early detection of cancer
PSI researchers develop a fundamentally new method for early detection of cancer.
Reprogramming tissue mechanically
Scientists at PSI have used mechanical stimuli to turn connective tissue cells into stem-cell-like cells and transplanted these into damaged skin tissue. This speeds up the regeneration of the skin and the healing of wounds.
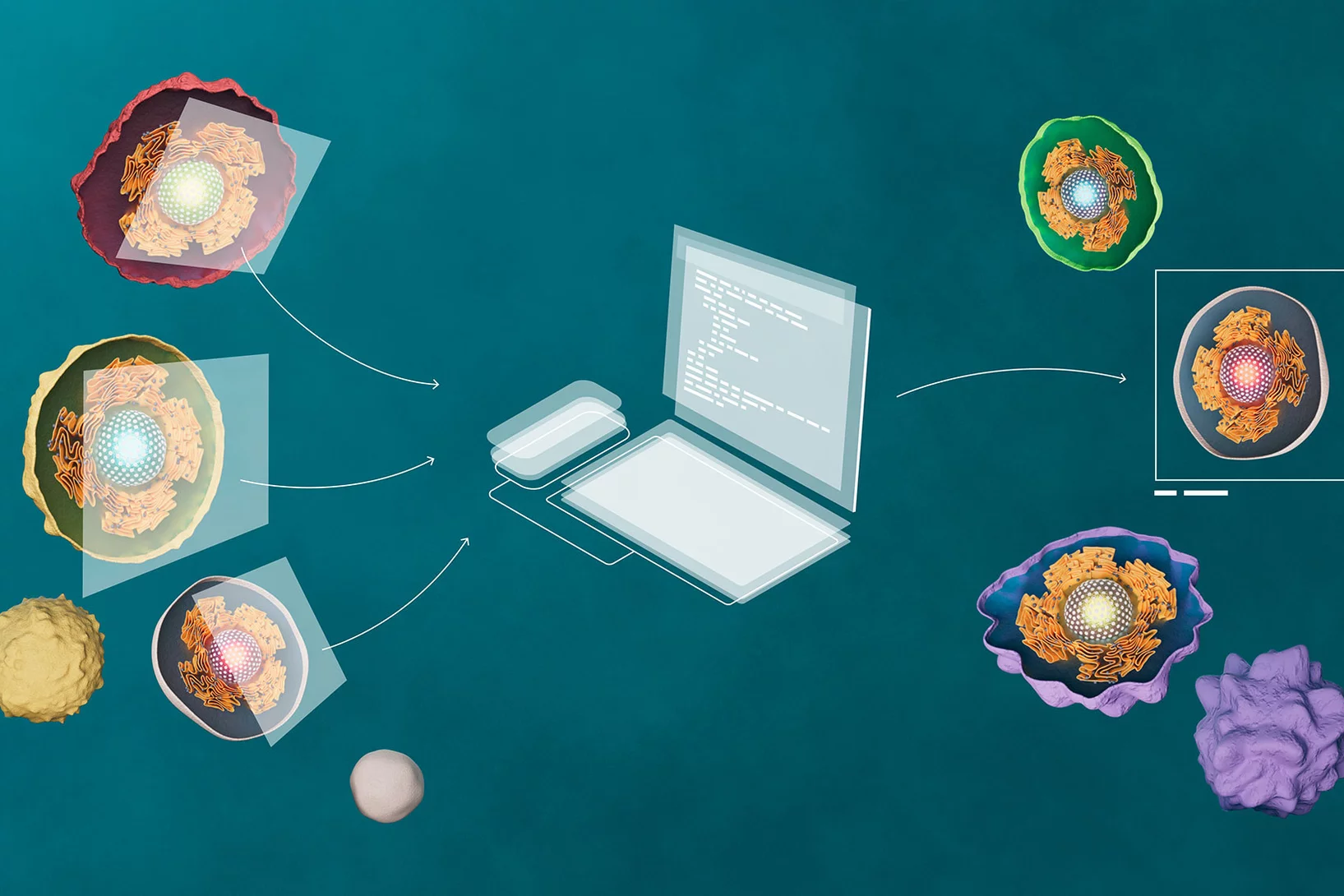
Grasping diseases by the roots
PSI researchers take pictures of cell nuclei using modern high-resolution imaging techniques, employ learning algorithms to comb through these data, and thus can more reliably identify anomalies.
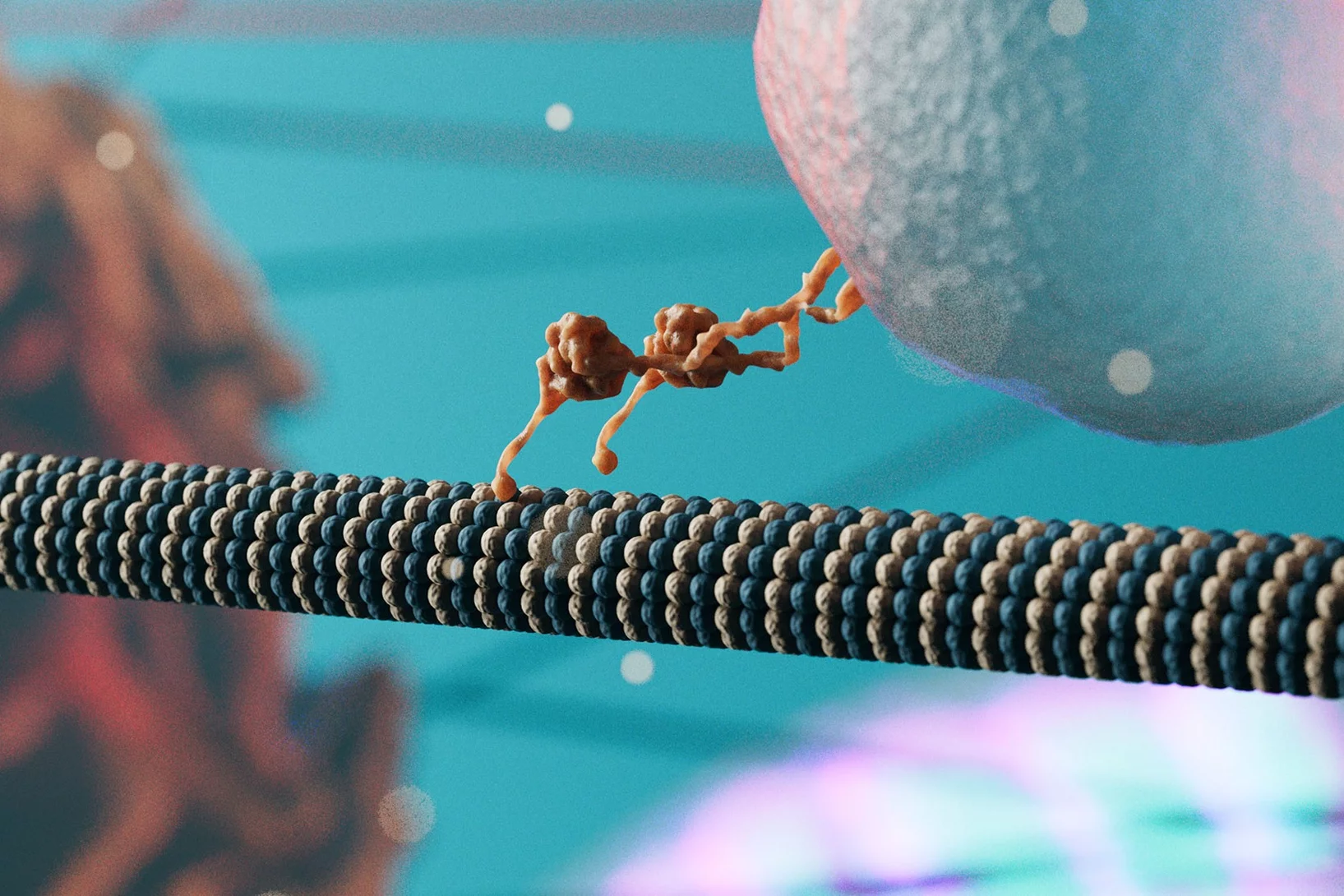
More than just a support structure
Each cell in the human body contains a cytoskeleton. Contrary to what the name suggests, the cytoskeleton is far more than just a support structure.
Deciphering the secrets of the brain
A place for cutting-edge research: PSI researchers to receive comprehensive funding from the US NIH for their brain research.
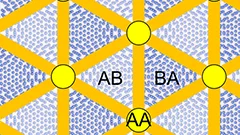
Controlling topological states in bilayer graphene
Parameters of topological channels created in twisted bilayer graphene can be controlled by lithium atoms intercalation.