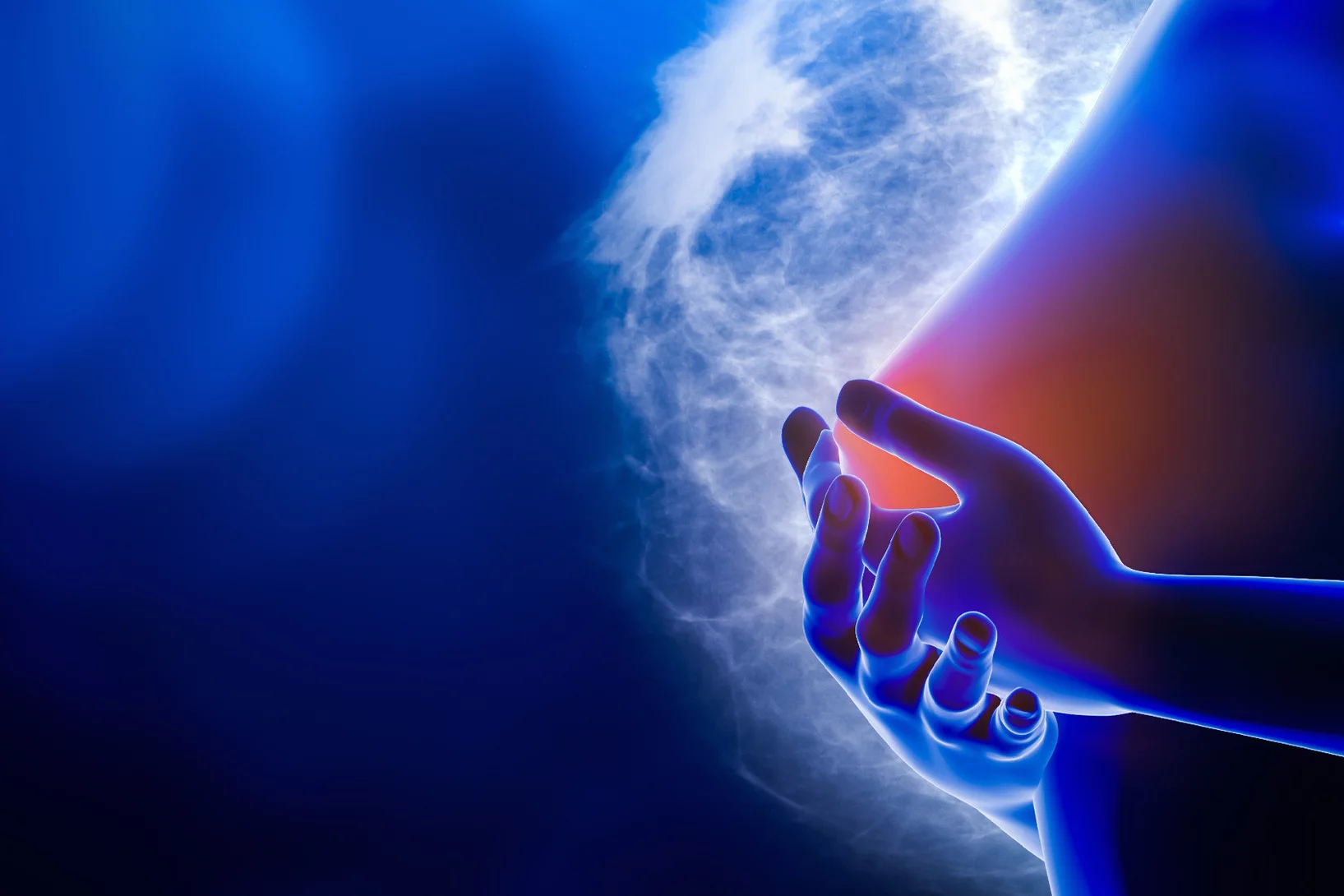
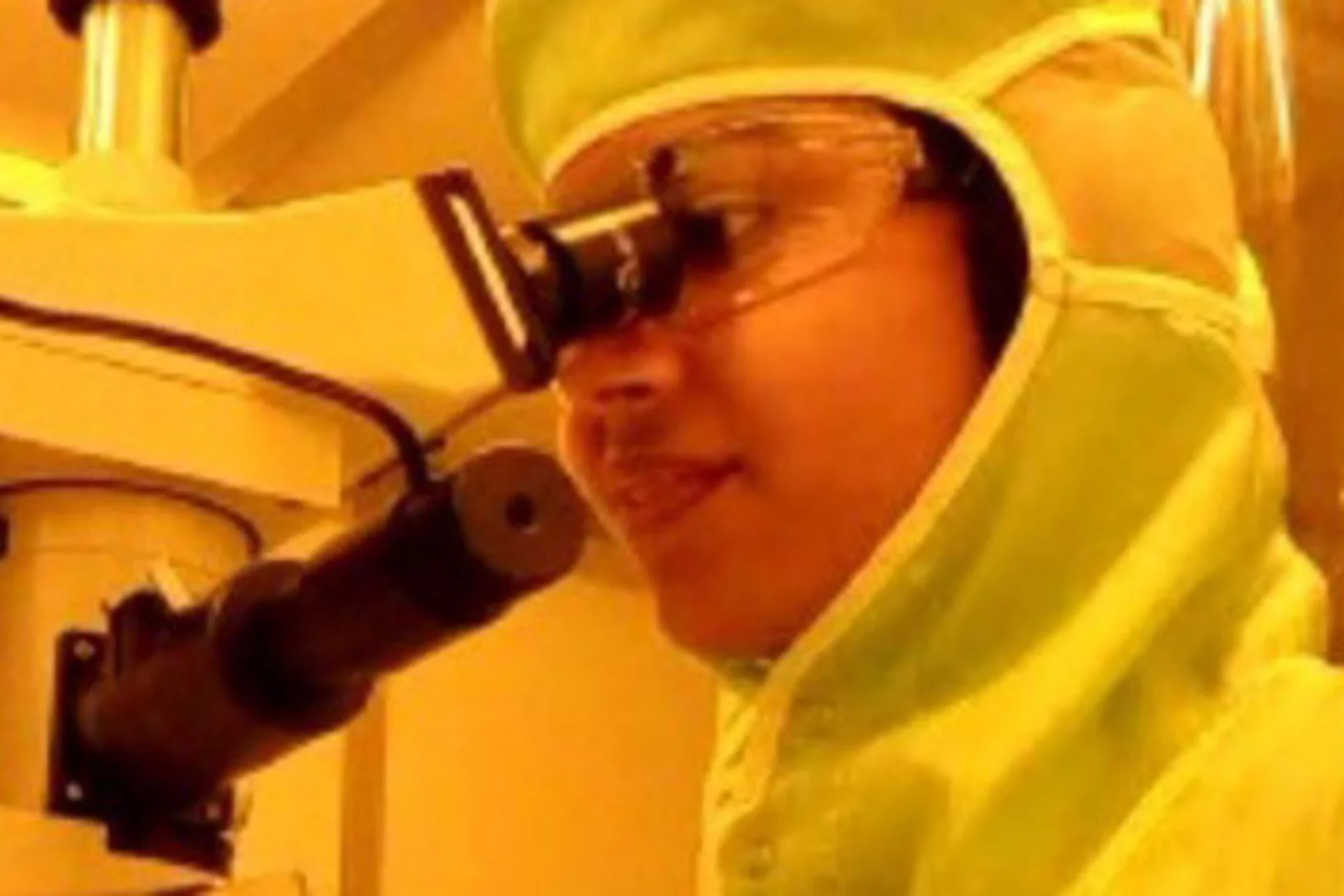
Breast cancer classification using AI
Researchers at PSI and MIT are developing a new approach, which combines imaging and artificial intelligence to improve the staging of breast cancer.
Protein droplets likely don’t cause Parkinson’s
Study deepens our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases linked to protein aggregation.
EMBO workshop on Nuclear Mechano-Genomics
The EMBO-workshop on Nuclear Mechano-Genomics taking place from April 16 to April 19, 2024 in Sardinia, Italy, was a great success.
Enabling early detection of cancer
PSI researchers develop a fundamentally new method for early detection of cancer.
Reprogramming tissue mechanically
Scientists at PSI have used mechanical stimuli to turn connective tissue cells into stem-cell-like cells and transplanted these into damaged skin tissue. This speeds up the regeneration of the skin and the healing of wounds.
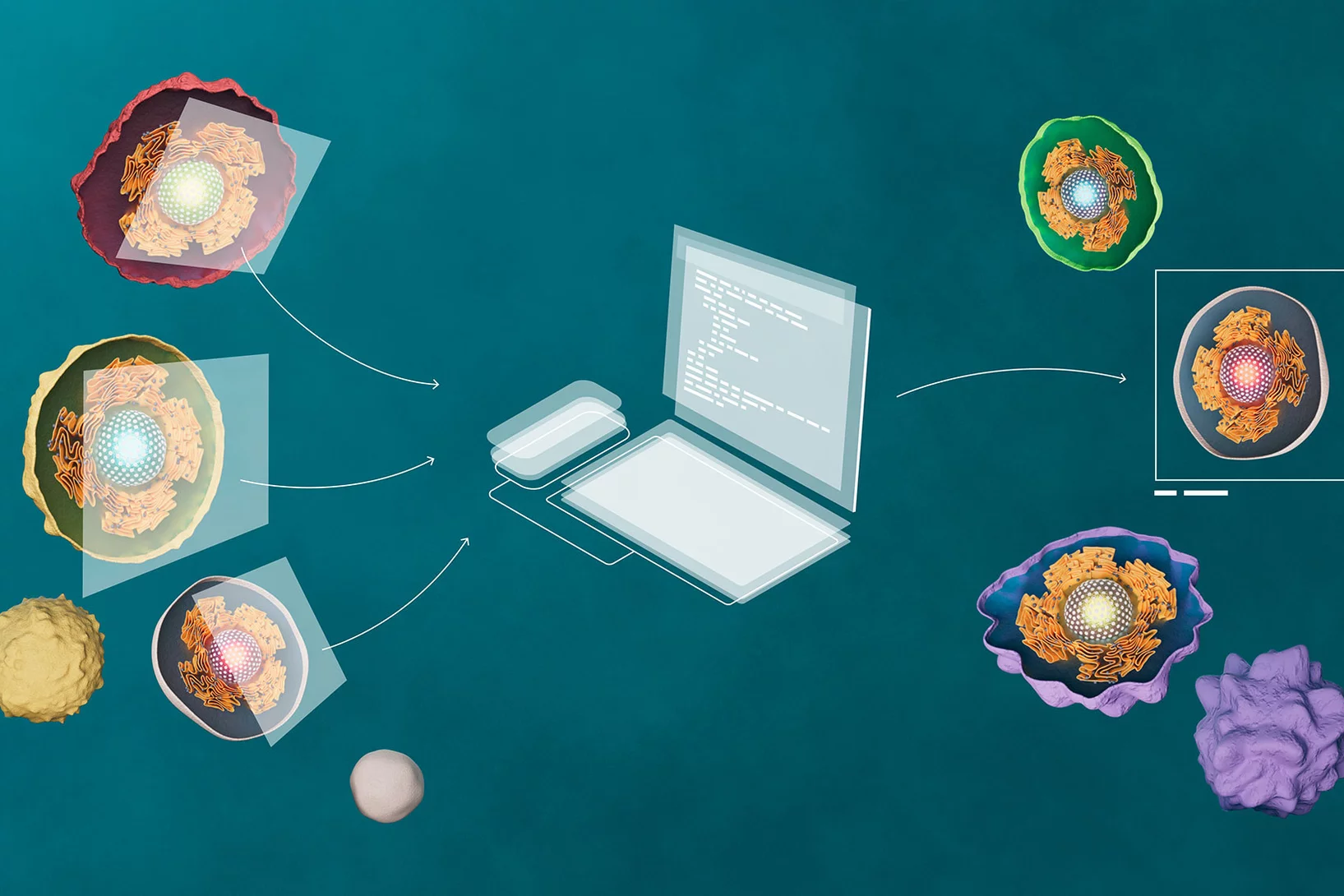
Grasping diseases by the roots
PSI researchers take pictures of cell nuclei using modern high-resolution imaging techniques, employ learning algorithms to comb through these data, and thus can more reliably identify anomalies.
More than just a support structure
Each cell in the human body contains a cytoskeleton. Contrary to what the name suggests, the cytoskeleton is far more than just a support structure.
Deciphering the secrets of the brain
A place for cutting-edge research: PSI researchers to receive comprehensive funding from the US NIH for their brain research.
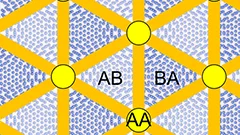
Controlling topological states in bilayer graphene
Parameters of topological channels created in twisted bilayer graphene can be controlled by lithium atoms intercalation.
Hairy cells: How cilia’s motor works
Understanding this motion may help to tackle health problems that affect cilia, which range from fertility issues to lung disease and COVID-19.
Imaging biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease
Artificial intelligence pinpoints cells indicative of Alzheimer’s disease based on DNA packing in mouse brain images, shows study in Nature Communications
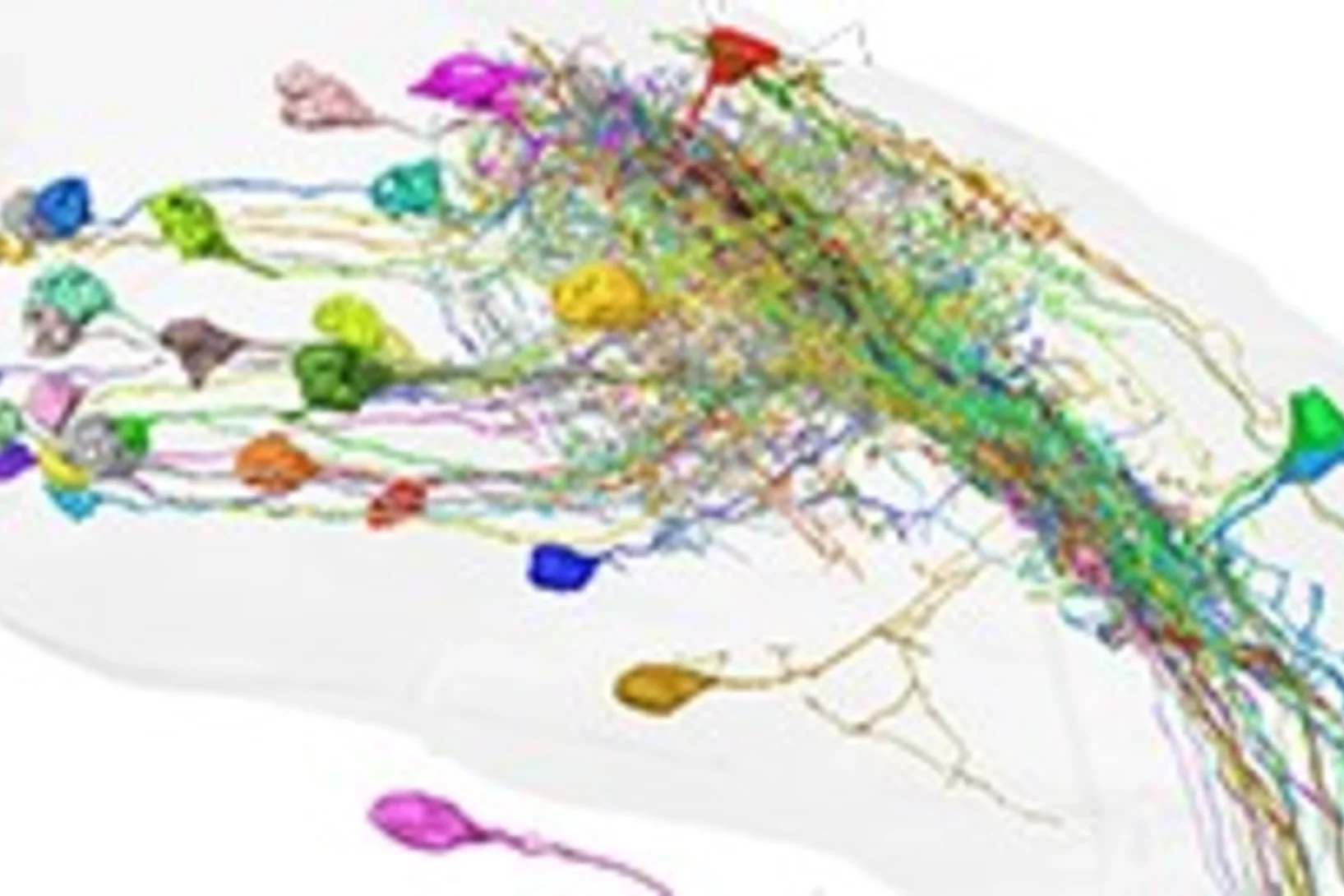
Automated synapse-level reconstruction of neural circuits in the larval zebrafish brain
Researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Biological Intelligence, Google Inc. and the Paul Scherrer Institute published a new method and data resource that makes connectomic analyses of the entire larval zebrafish brain possible.
Paul Scherrer Institute and Apollo Health Ventures Launch Focal Biosciences
Newly established Focal Biosciences will focus on bringing together leading experts and scientific discoveries to harness cellular reprogramming in the fight against common age-related diseases.
Millions in funding for brain and quantum research
The European Research Council approves PSI projects for the development of a quantum computer and brain research worth about 5 million euros.
Biased signalling for better drugs
A dream drug would provide a targeted therapeutic effect without side effects. Biased signalling could make this a reality. Publishing in PNAS, PSI researchers present a platform for biased signalling-based drug discovery.
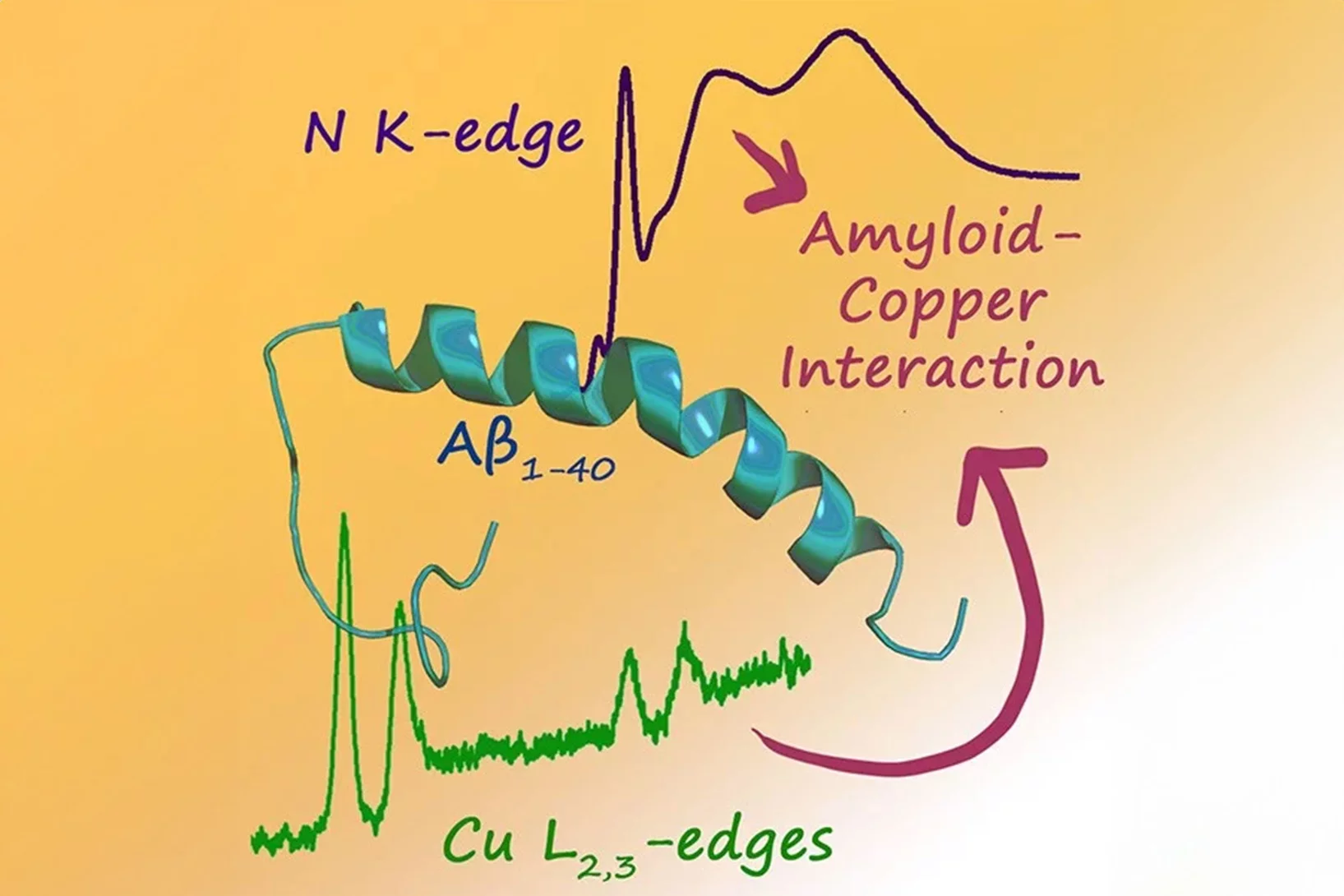
Fingerprint of Copper in Peptides Linked to Alzheimer's Disease
In an interdisciplinary project, researchers from the Laboratory of Nanoscale Biology in BIO and the Laboratory for Condensed Matter in PSD have revealed the reaction between the nitrogen atoms of the amyloid-beta peptide and copper/zinc ions by using soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy.
Protein distancing
PSI researchers have developed a new method to attach proteins to the surface of virus-like particles.
SGS award for Pooja Thakkar
Pooja Thakkar received the Shoulders-Gray-Spindt award at the 34th Vacuum Nanoelectronics Conference for her paper "Voltage-controlled three-electron-beam interference by a three-element Boersch phase shifter with top and bottom shielding electrodes"
On-demand sample delivery article highlighted in "Applied Physics Letters"
An article on the on-demand sample delivery and protein crystallography using acoustic levitation has been selected in an Applied Physics Letters collection of papers on technology and application of acoustic tweezers.
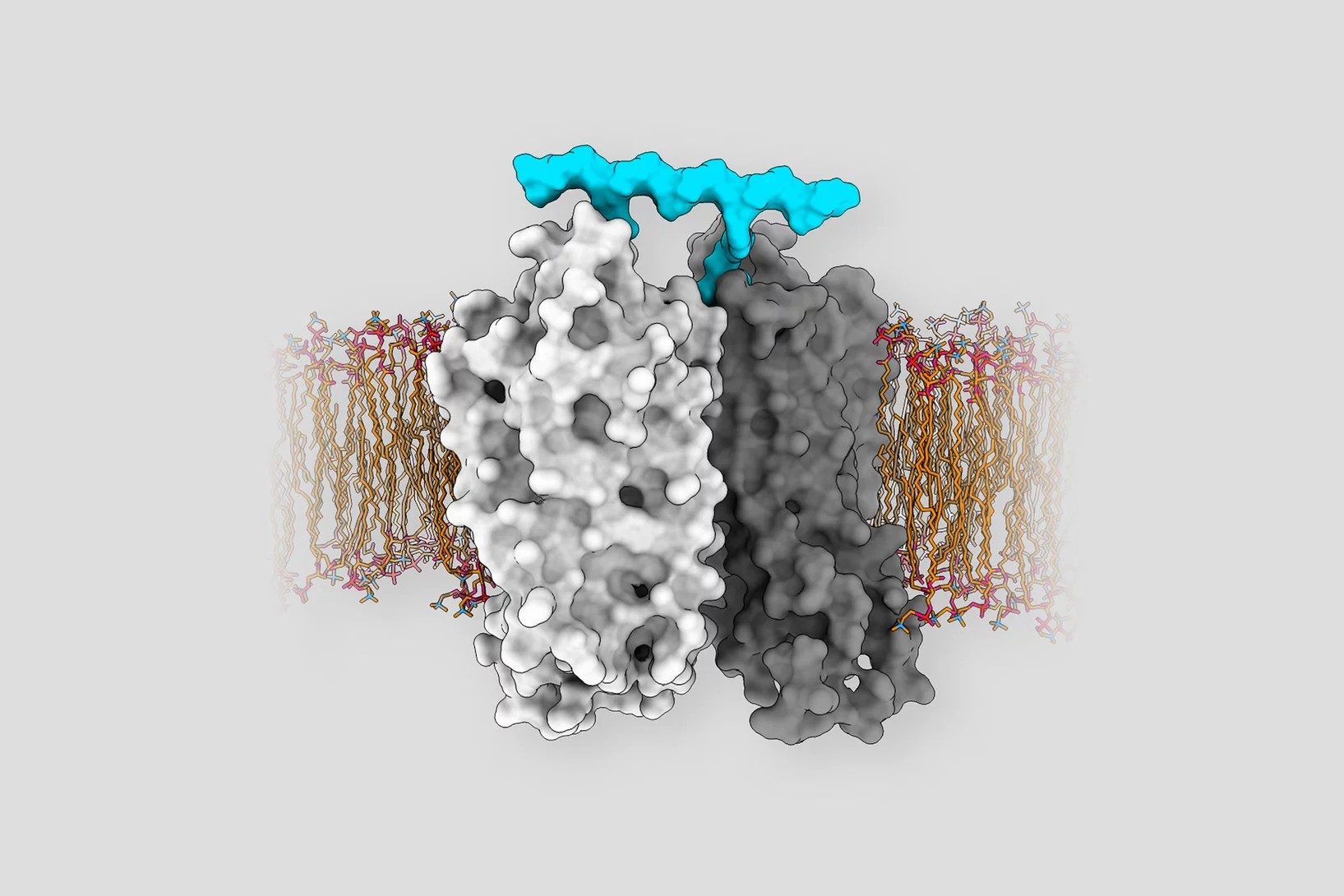
Catching Alzheimer's Toxin
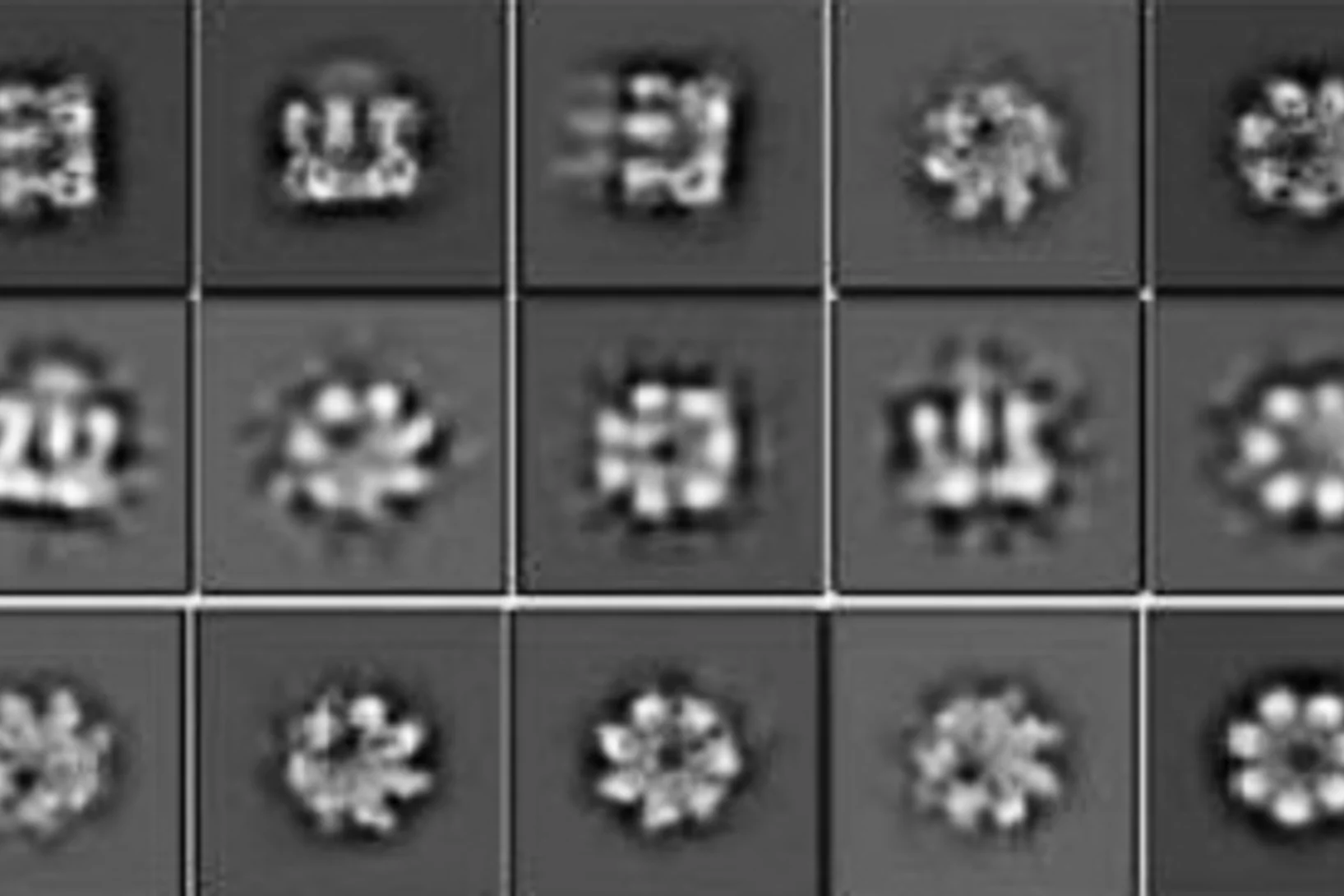
Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy of a functional Aβ42 pore equivalent, created by fusing Aβ42 to the oligomerizing, soluble domain of the α-hemolysin toxin, offers new insights into structure and function of proteins forming amyloid aggregates in Alzheimer’s disease.
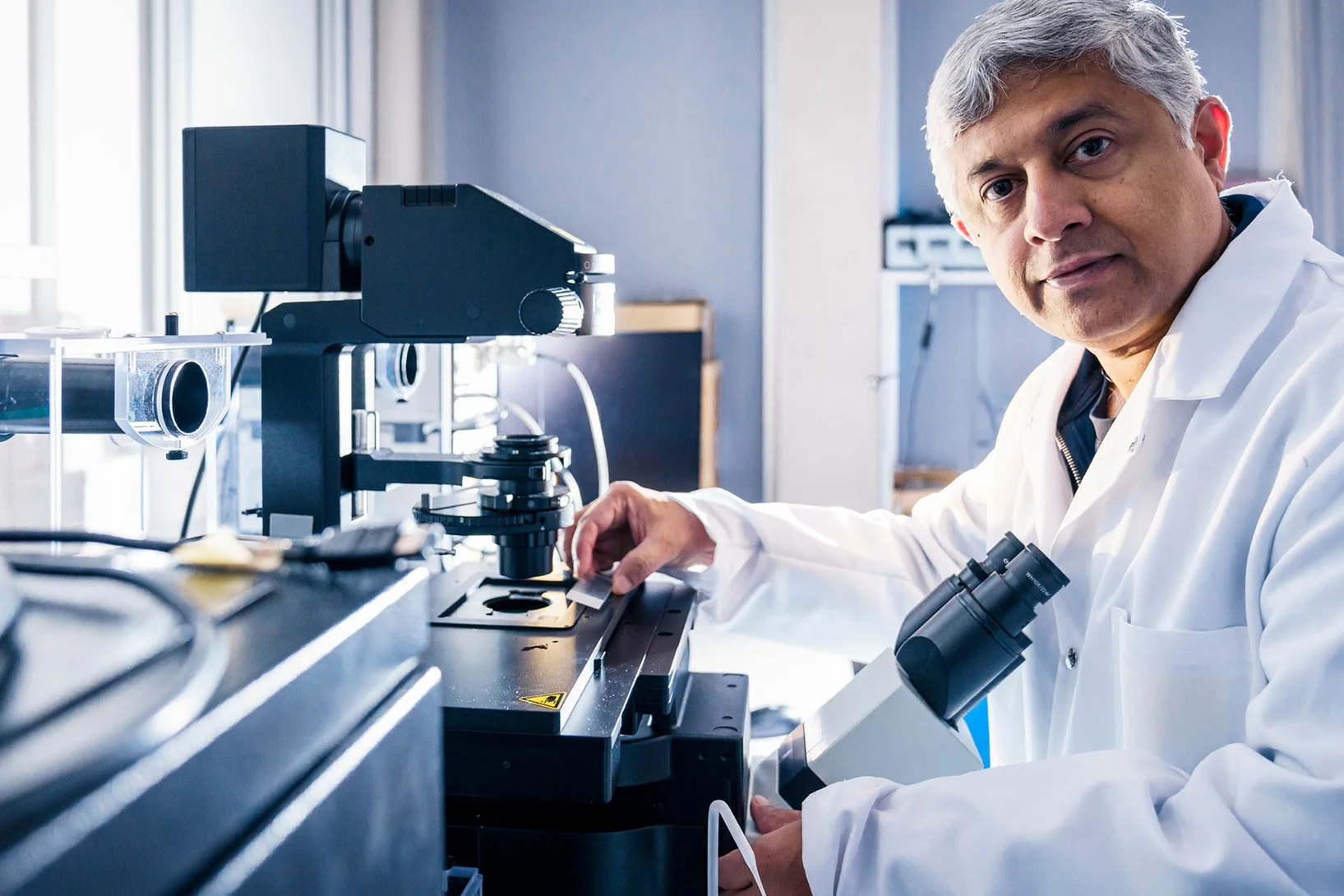
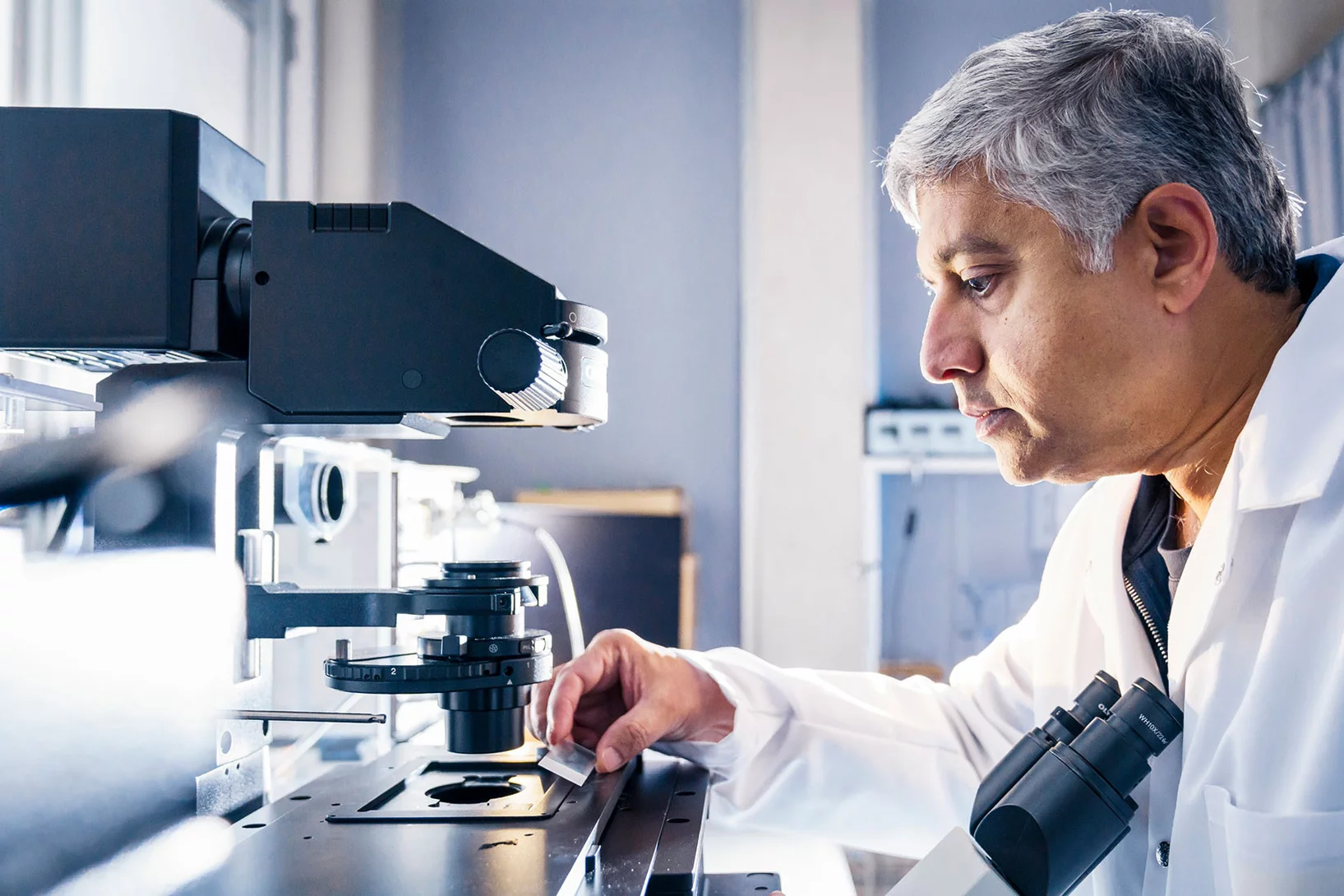
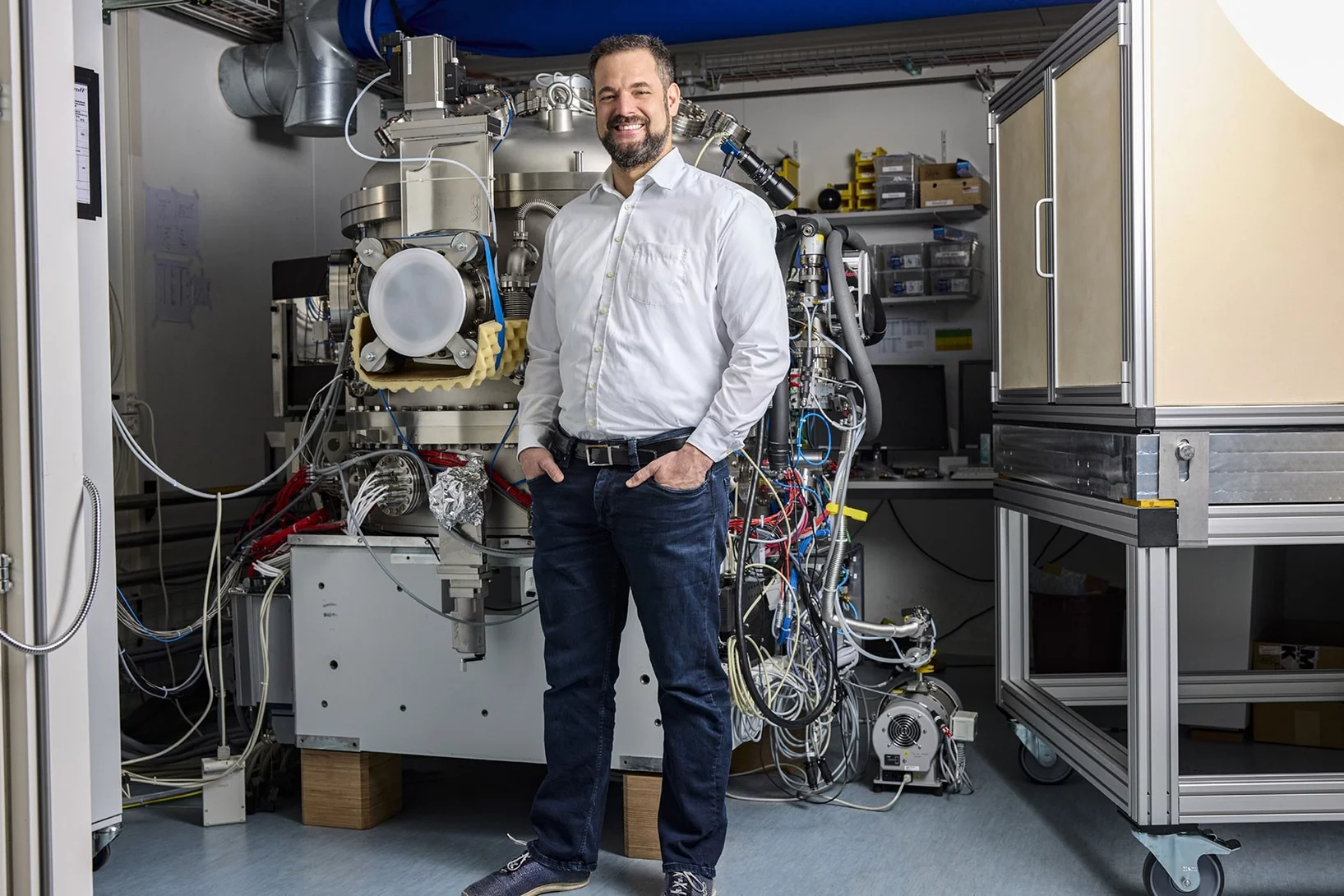
"Ultimately, we aim to understand how diseases start in single cells"
Imaging and sequencing techniques combined with machine learning offer researchers countless opportunities to look inside cells with greater precision than ever before. G.V. Shivashankar, lab head at PSI, describes how such information can be used to find answers to pressing questions.
Why Covid-19 hits older people especially hard
The older you are, the higher the risk of dying from a coronavirus infection. G. V. Shivashankar, a group leader at PSI and professor at ETH Zurich, now presents an unusual thesis in a publication in Nature Reviews: that the stiffness of cells might play a decisive role in the course of the disease. In this interview, he explains why.