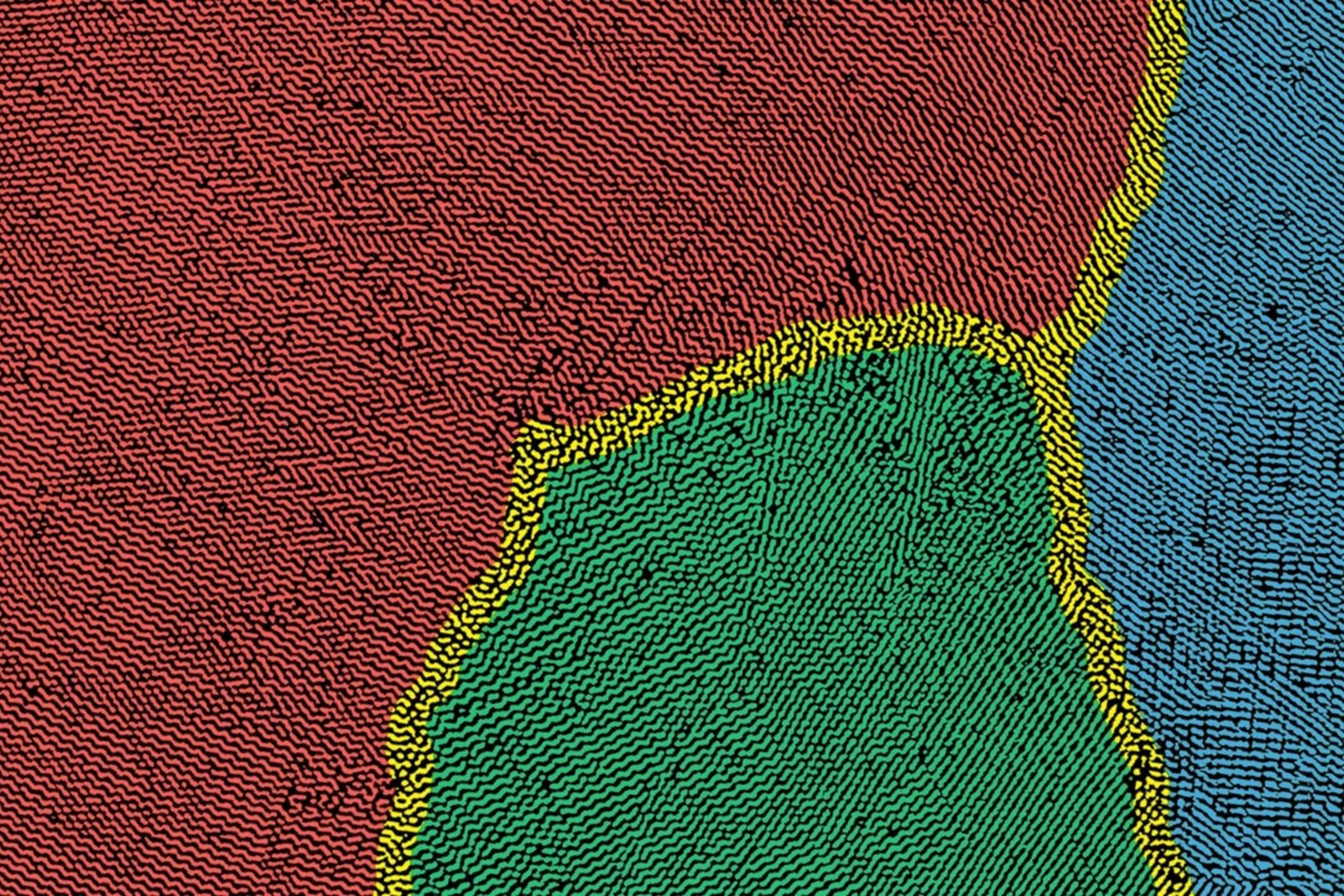
Nanoimaging Reveals Topological Textures in Nanoscale Crystalline Networks
X-ray nano-tomography reveals collective behavior in synthetic self-assembled nanostructures. The new method opens opportunities for the synthesis of photonic and plasmonic materials with improved long-range ordering.
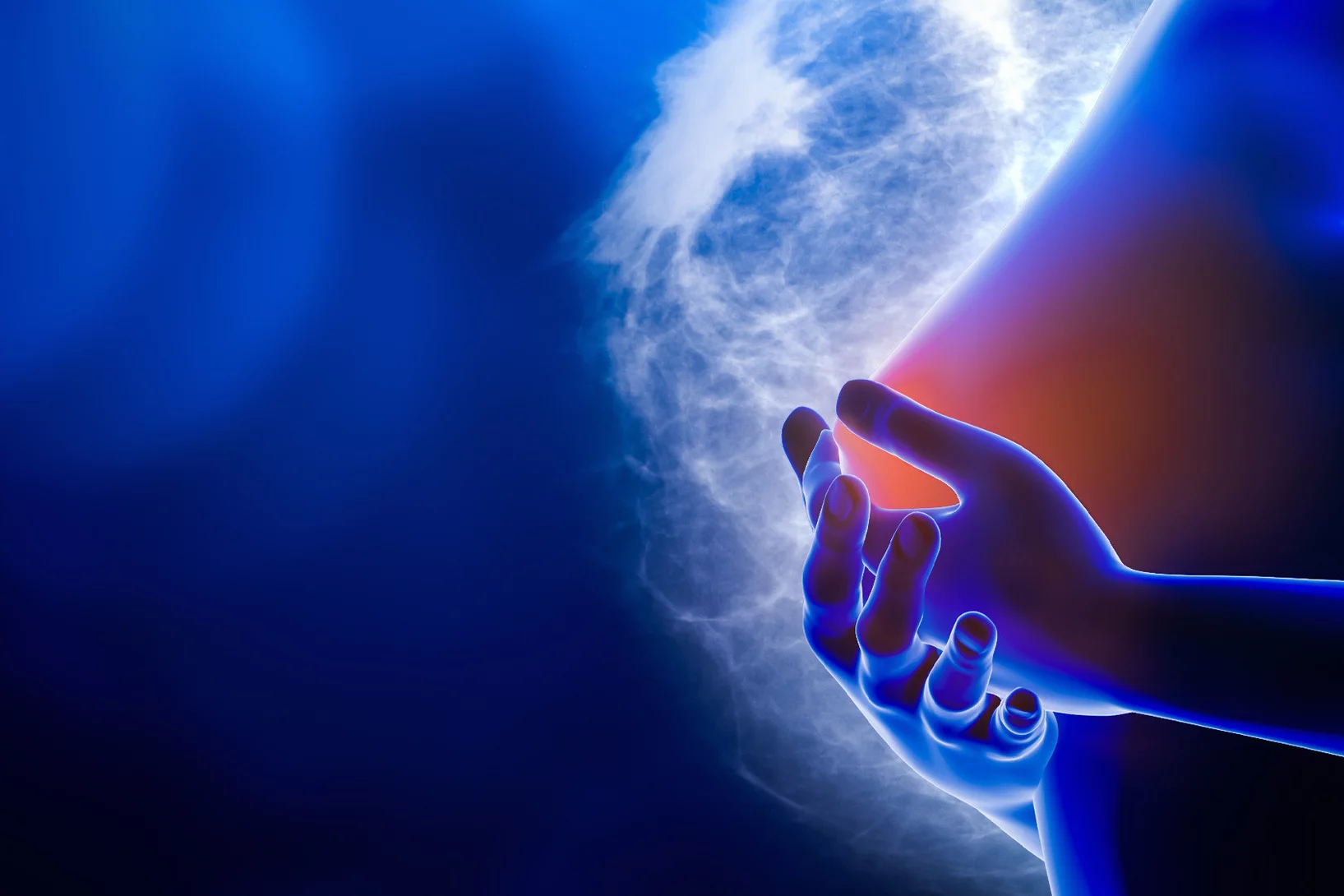
Breast cancer classification using AI
Researchers at PSI and MIT are developing a new approach, which combines imaging and artificial intelligence to improve the staging of breast cancer.
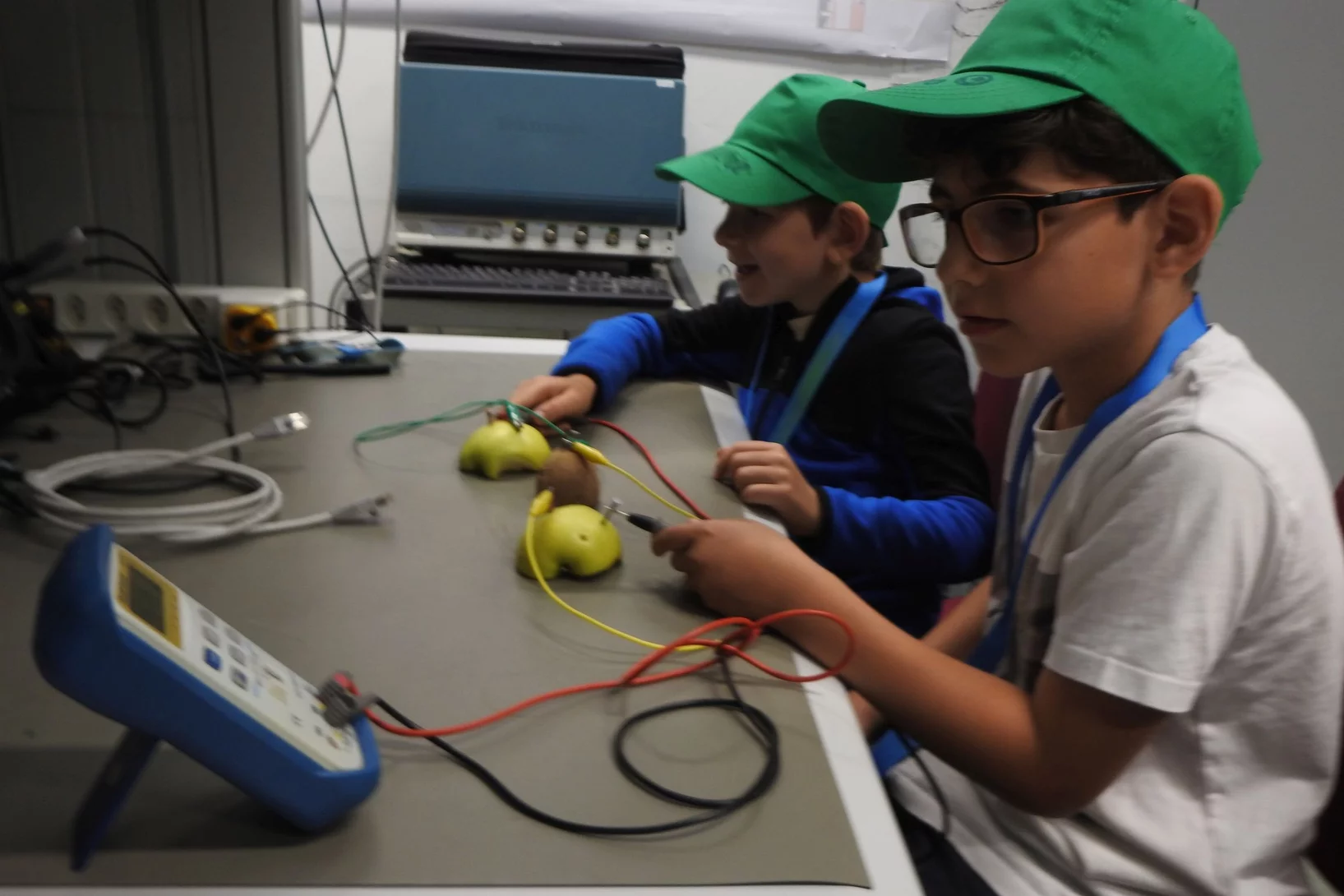
Feriencamp 2024
Spannende Aktivitäten + Experimente = PSI-Feriencamp
Mealplanner - Wo wird unser Mittagessen festgelegt?
Eine Applikation, ohne welche wir nicht wüssten, was es denn heute zum Mittagessen gibt.
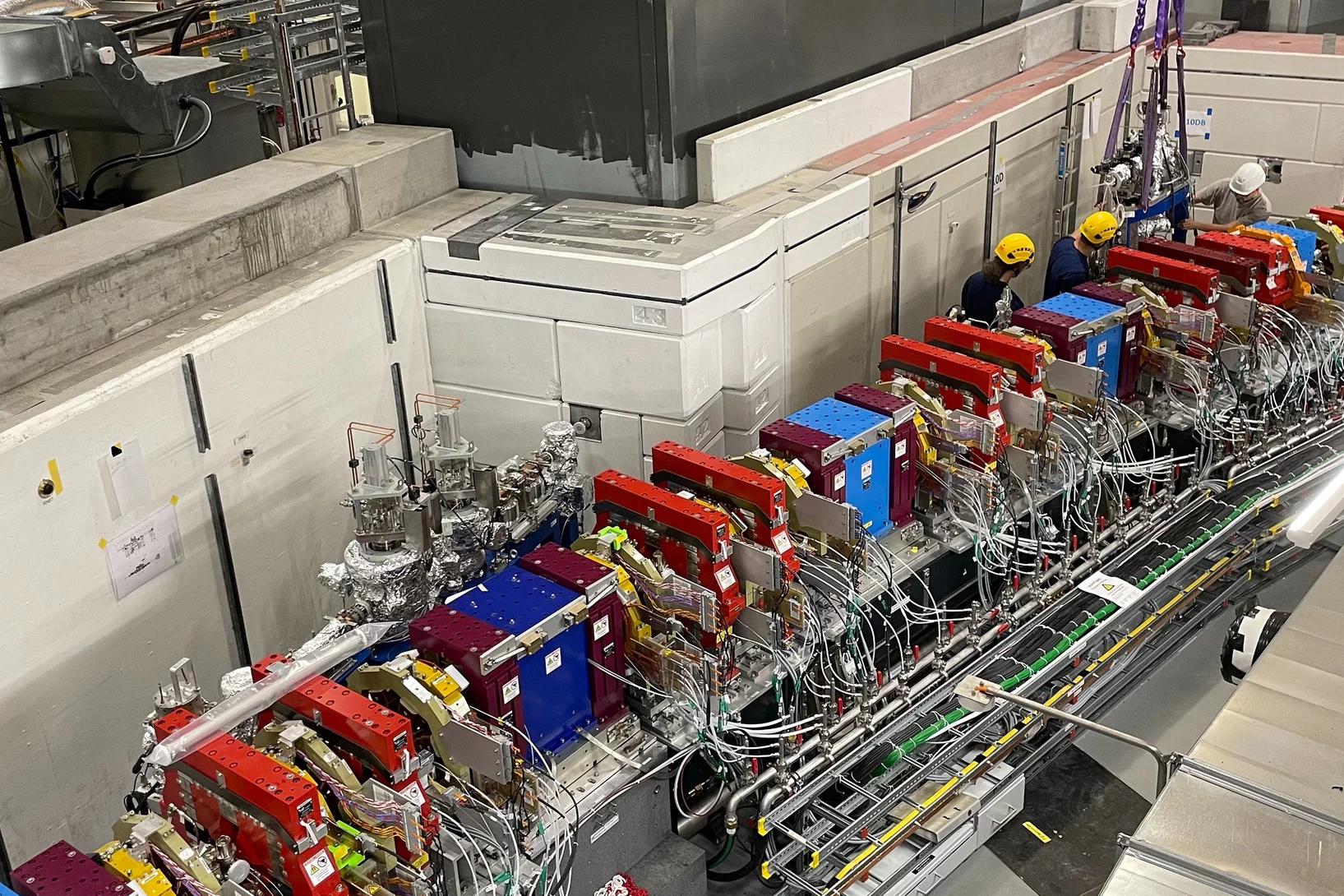
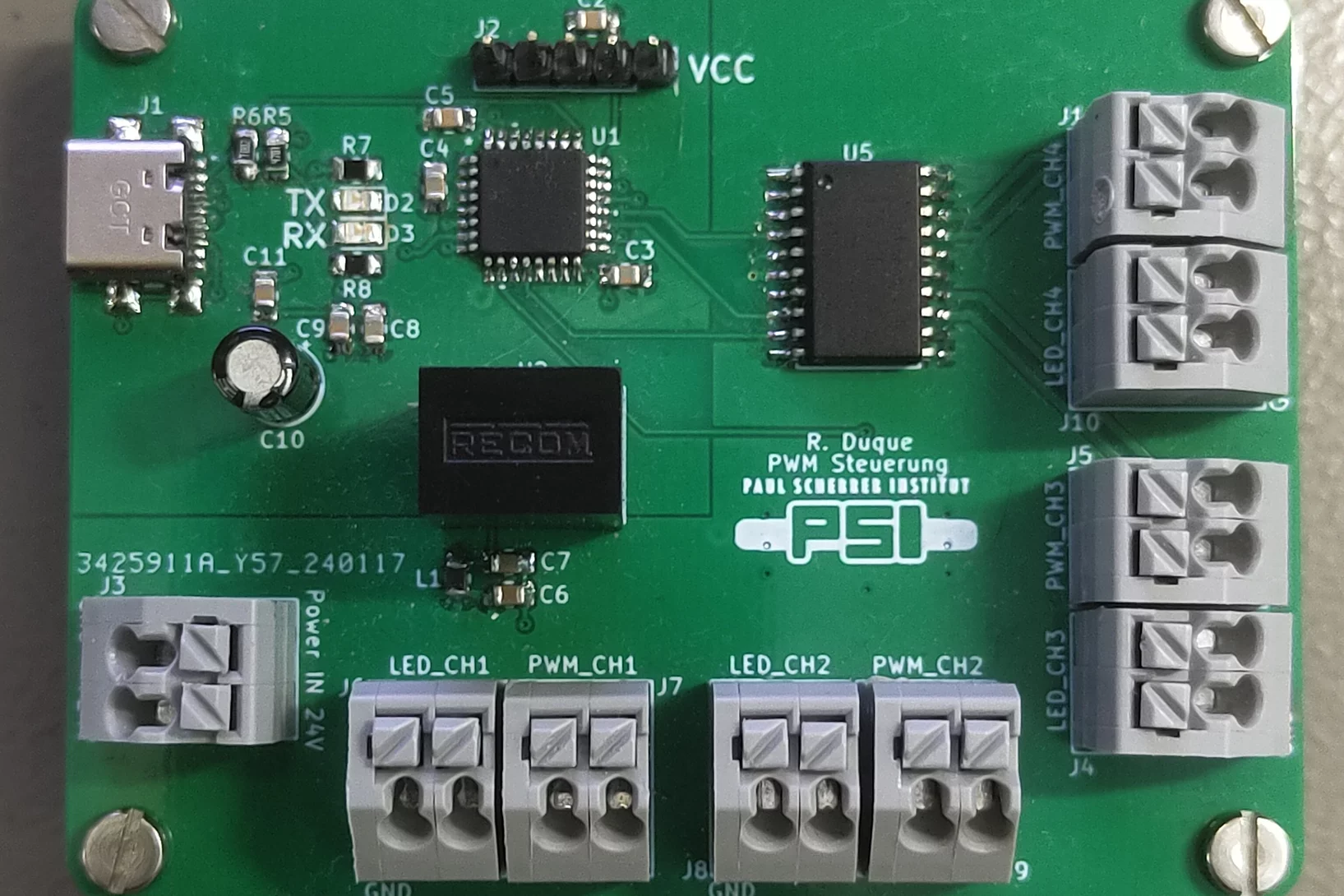
Fourth Data Challenge
The Mu3e data challenges aim at establishing the data processing and storage procedures as well as the online monitoring tools. To this end, we use simulated data to test all involved systems and further develop the code. In the forth edition, we aimed at incorporating the farm FPGAs, GPU selection and advanced subdetector monitoring tools.
Abschlussfeiern an den Berufs- und Berufsmaturitätsschulen 2024
Die erfolgreichen Abschlüsse wurden an den Berufs- und Berufsmaturitätsschulen gefeiert. Wir sind stolz auf unsere Lernenden und ihre tollen Leistungen!
Protein droplets likely don’t cause Parkinson’s
Study deepens our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases linked to protein aggregation.
Heizungsteuerung 2024
Neue Steuerung für Chemie-Experimente
Installation of the first two front ends for the SLS2.0 completed
At the Swiss Light Source SLS of the Paul Scherrer Institute, another important step has been taken towards the completion of the SLS 2.0 upgrade project.
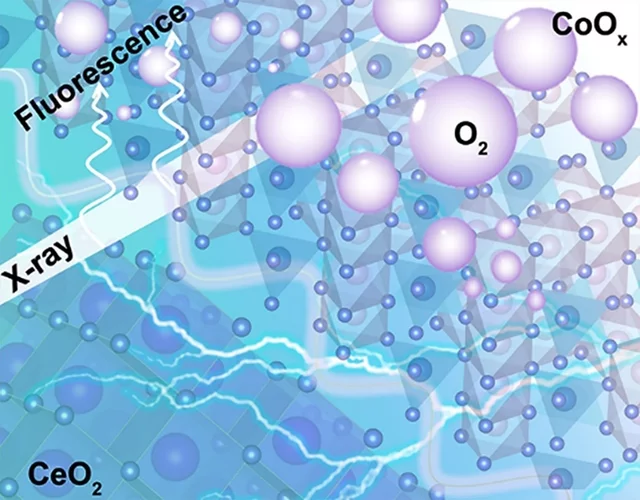
Insights into the superior oxygen evolution reaction activity of CoOx/CeO2 composite electrocatalyst
CeO2 significantly enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of CoOx, although the mechanism behind this synergy is still unclear. Here, operando hard X-ray absorption spectroscopy (hXAS) is applied to monitor the Co-K edge and Ce L3 edge in CoOx/CeO2 to shed light on the evolution of Co and Ce oxidation states during OER. In addition, ex situ soft XAS (sXAS) characterizations provide information on the irreversible surface-specific transformations of the Co L3 edge as well as the O K edge.
PSI-UCL-Surrey workshop on silicon and germanium based quantum devices
A team of PSI scientists as well as collaborators from UCL and the University of Surrey met at the Fondazione Monte Verità to discuss results and trace the roadmap for future research into quantum devices based on silicon and germanium.
Proxima Fusion moves to Park Innovaare
Proxima Fusion and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have signed a framework agreement to develop high-temperature superconductor magnet technology (HTS).
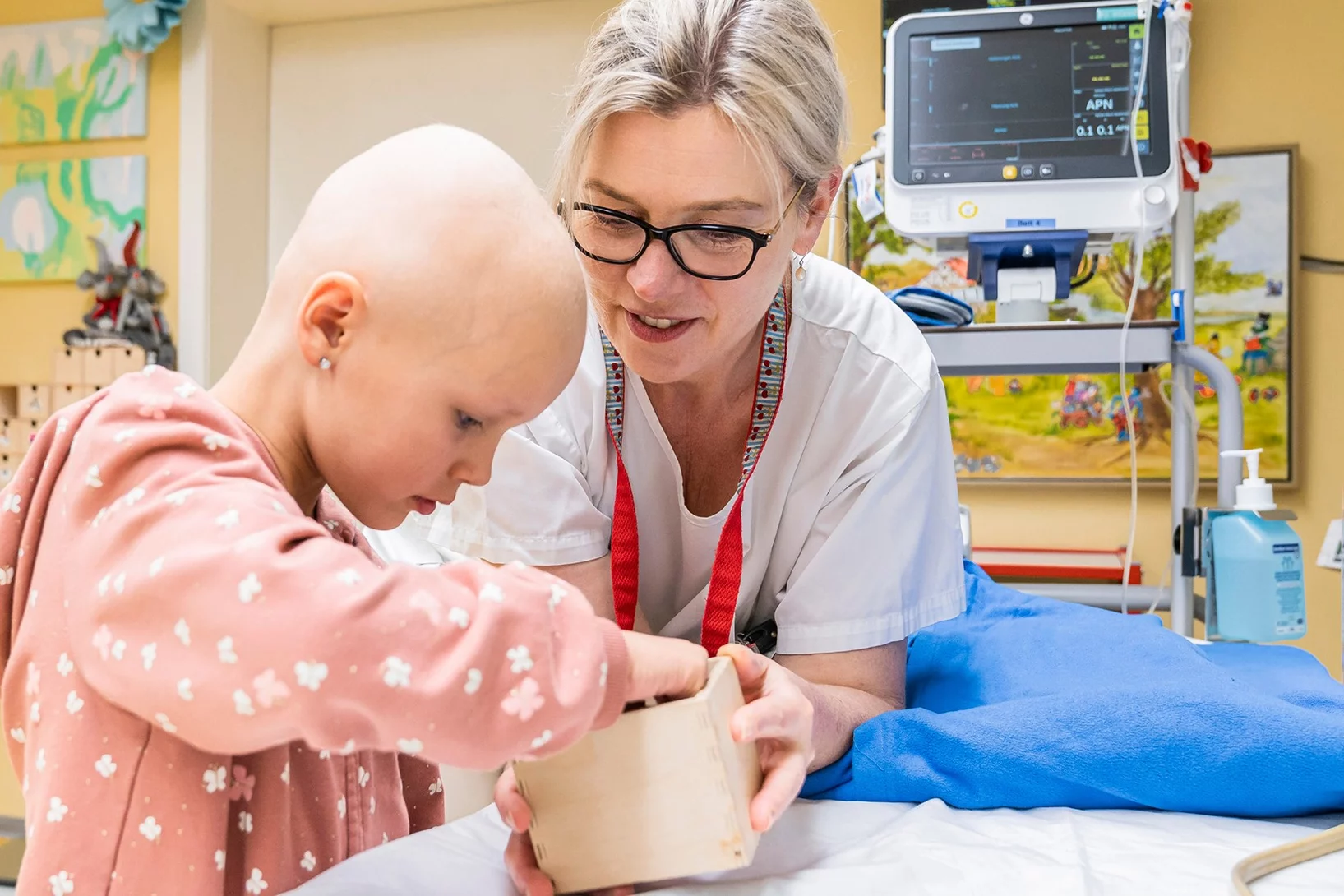
Joining forces to cure children
The close collaboration between PSI and the University Children’s Hospital Zurich for the benefit of children with cancer began 20 years ago.
Do you want to use the summer break to advance your career?
Are you wondering what you can do over the summer to enhance your career prospects and improve your employability? Look no further, this blog post has some ideas to spark your curiosity, motivation and enthusiasm, and advance your career at the same time:
Lehrberufe à la Carte 2024
700 Personen besuchten Berufsbildungsevent des PSI Paul Scherrer Instituts
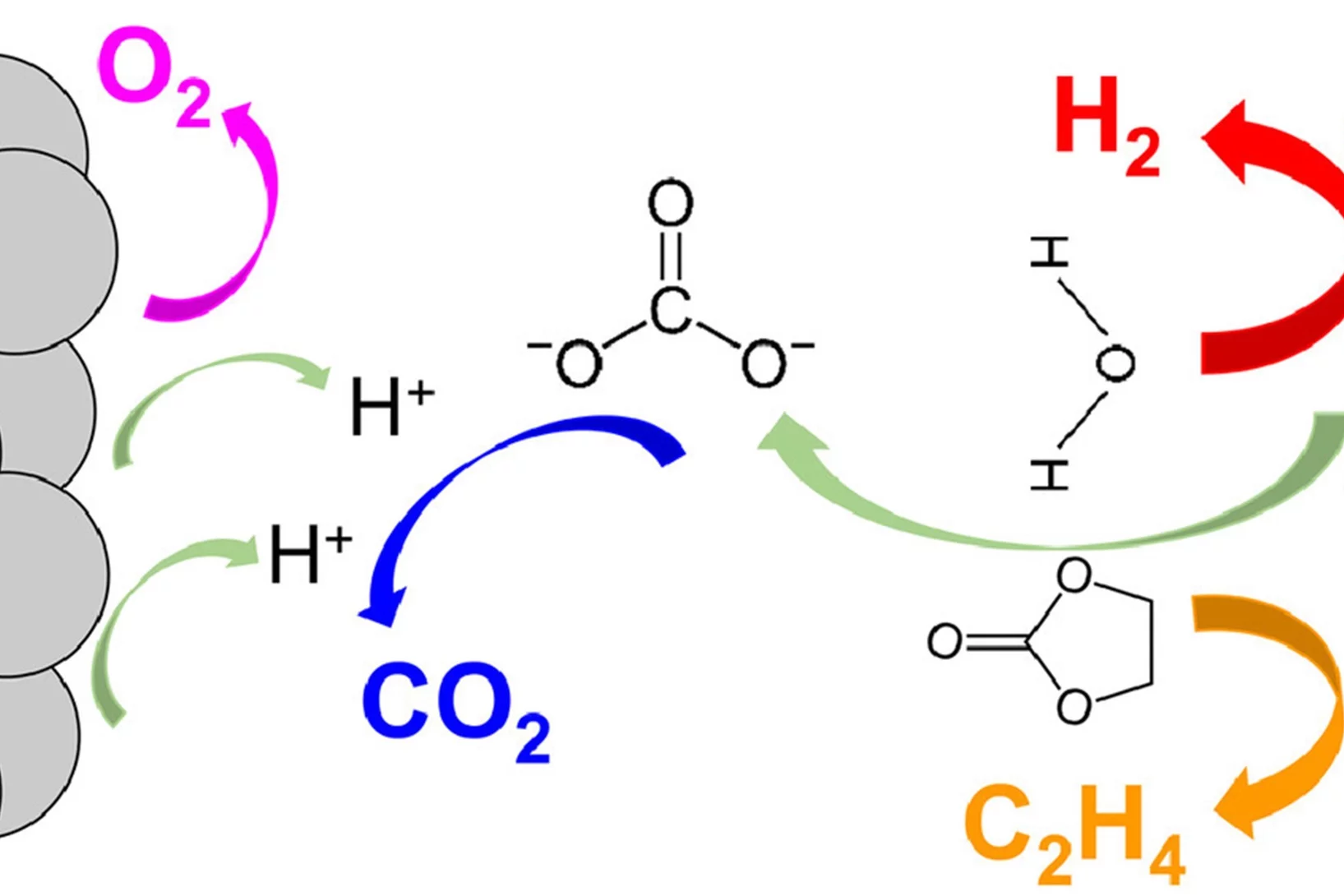
Real-Time Insights into Sodium-Ion Battery Chemistry
Identification of gaseous decomposition products from irreversible side-reactions enables understanding of inner working of rechargeable batteries. Unlike for Li-ion batteries, the knowledge of the gas-evolution processes in Na-ion batteries is limited. Our study revealed that Na-ion cells develop a less stable solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) compared to Li-ion cells due to higher solubility of SEI constituents in Na-electrolytes.
A new Fusion Collaboration
Munich-based Proxima Fusion and PSI have signed a framework agreement.
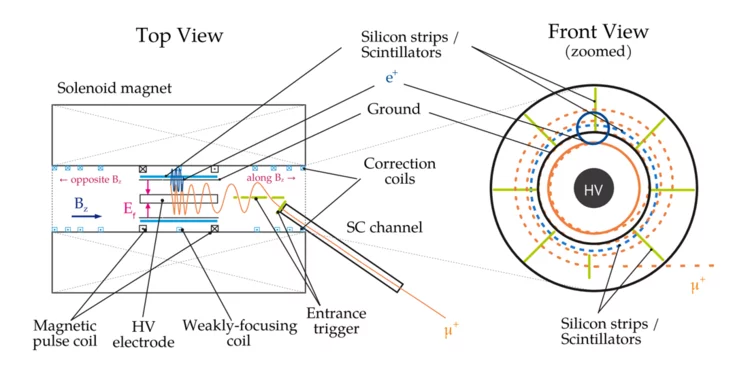
Anomalous spin precession systematic effects in the search for a muon EDM using the frozen-spin technique
In the paper, the international muEDM collaboration at PSI discusses systematic effects of the most sensitive measurement of the muon's electric dipole moment (EDM). Scientists from Europe are developing a prototype experiment using the frozen-spin technique (FST) to achieve unprecedented sensitivity. The FST meticulously aligns a magnetic field with a perpendicular electric field so that the muon's spin orientation always follows its momentum. This enhances the sensitivity to the muon EDM by about 3 orders of magnitude compared to the best result from the muon g-2 experiment at Brookhaven National Lab.
The paper addresses systematic effects that could mimic an EDM signal when E- and B-fields are not perfectly aligned, adjusted, or stable over time. While most effects cancel out when reversing the magnetic field, some residual effects the specifications for the fields' uniformity, stability, and orientation,
which are challenging but achievable.
Cooperation in reactor research
Copenhagen Atomics and the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have entered into a collaboration agreement on a thorium molten salt critical experiment.
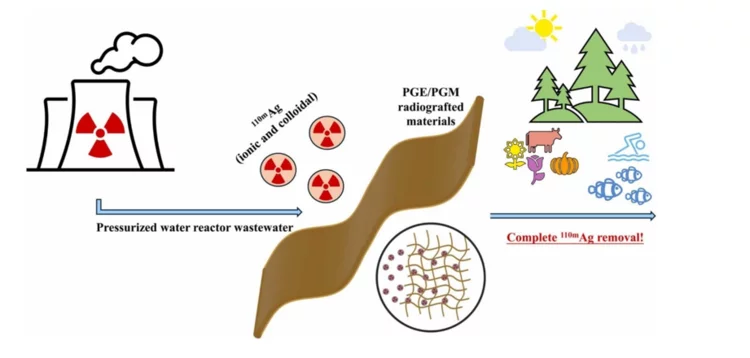
Removal of ionic and colloidal 110 mAg from radioactive wastewater using radiografted chelating adsorbents
Nuclear power plays a crucial role in a sustainable future due to its ability to generate large amounts of low-carbon electricity, which is essential for mitigating climate change. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear energy produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, helping to reduce the overall carbon footprint of power generation. However, the main concern is the inevitable accumulation of nuclear waste, and this needs to be properly addressed. With the anticipated increase in the number of operating nuclear power plants around the world it is essential to develop new materials and technologies for nuclear waste management. In our latest study we have developed and tested new radiografted materials as potential 110mAg adsorbents. This silver radionuclide is a very elusive contaminant in the pressurized water reactors (PWR) and represents a major problem for normal operation. Additionally, 110mAg possess a significant danger to the environment, if not removed completely from the PWR wastewater.
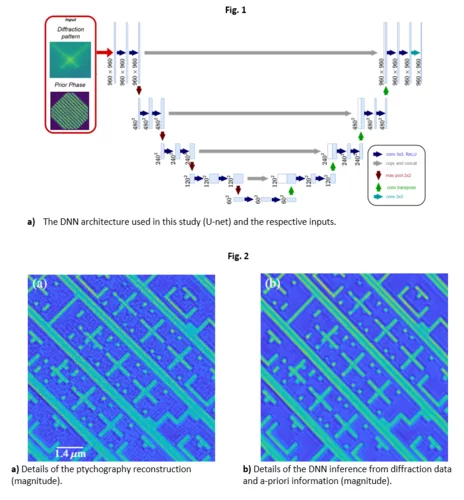
Towards fast ptychography image reconstruction of EUV masks by deep neural networks
In this study, we explore and demonstrate a rapid method for actinic patterned EUV mask inspection based on a deep neural network (DNN) architecture which exploits a-priori information of the photomask sample. We aim to achieve fast, high-quality image reconstruction of an EUV mask by using comparatively few diffraction patterns in a formalism consistent with the ptychography approach.
We tested our prior-primed DNN method on both synthetic and experimental data, demonstrating that the sample can be reconstructed fast and with high fidelity, allowing us to map out the mask defects down to a size of about 40 nm.
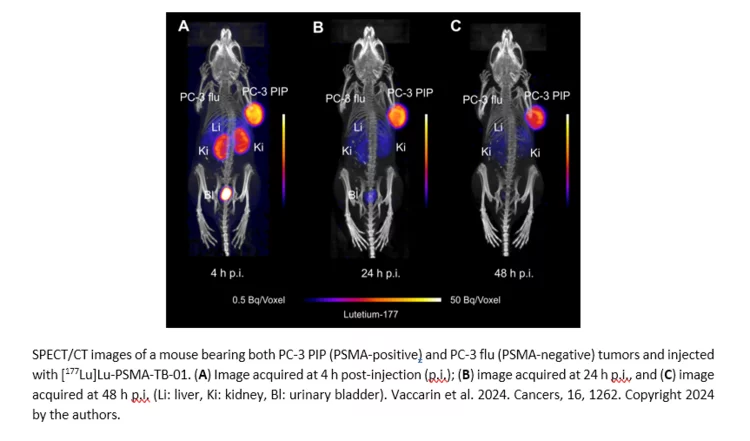
Design and Preclinical Evaluation of a Novel Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Radioligand Modified with a Transthyretin Binder
Radioligands targeting the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) are currently used in the clinics to treat patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Continuous investigations are, nevertheless, conducted to design new small molecule-based radioligands and improve their respective pharmacokinetic properties. Various strategies have been devised to reasonably prolong the blood circulation, which would result into enhanced tumor accumulation and radiation dose delivered to eliminate the cancer cells. The goal of this study was to investigate the influence of the incorporation of a transthyretin binder (TB-01) in the tumor uptake of the resultant PSMA-targeted radioligand.
Slipping a note to a neighbour: the cellular way
Study reveals how drug molecules bind in channels between neighbouring cells, changing intercellular communication.
International collaboration lays the foundation for future AI for materials via the OPTIMADE standard
Artificial intelligence (AI) is accelerating the development of new materials. A prerequisite for AI in materials research is large-scale use and exchange of data on materials, which is facilitated by a broad international standard. A major international collaboration including researchers from the LMS laboratory now presents an extended version of the OPTIMADE standard.
Observation of Mermin-Wagner behavior in LaFeO3/SrTiO3 superlattices
Two-dimensional magnetic materials can exhibit new magnetic properties due to the enhanced spin fluctuations that arise in reduced dimension. However, the suppression of the long-range magnetic order in two dimensions due to long-wavelength spin fluctuations, as suggested by the Mermin-Wagner theorem, has been questioned for finite-size laboratory samples. Here we study ...
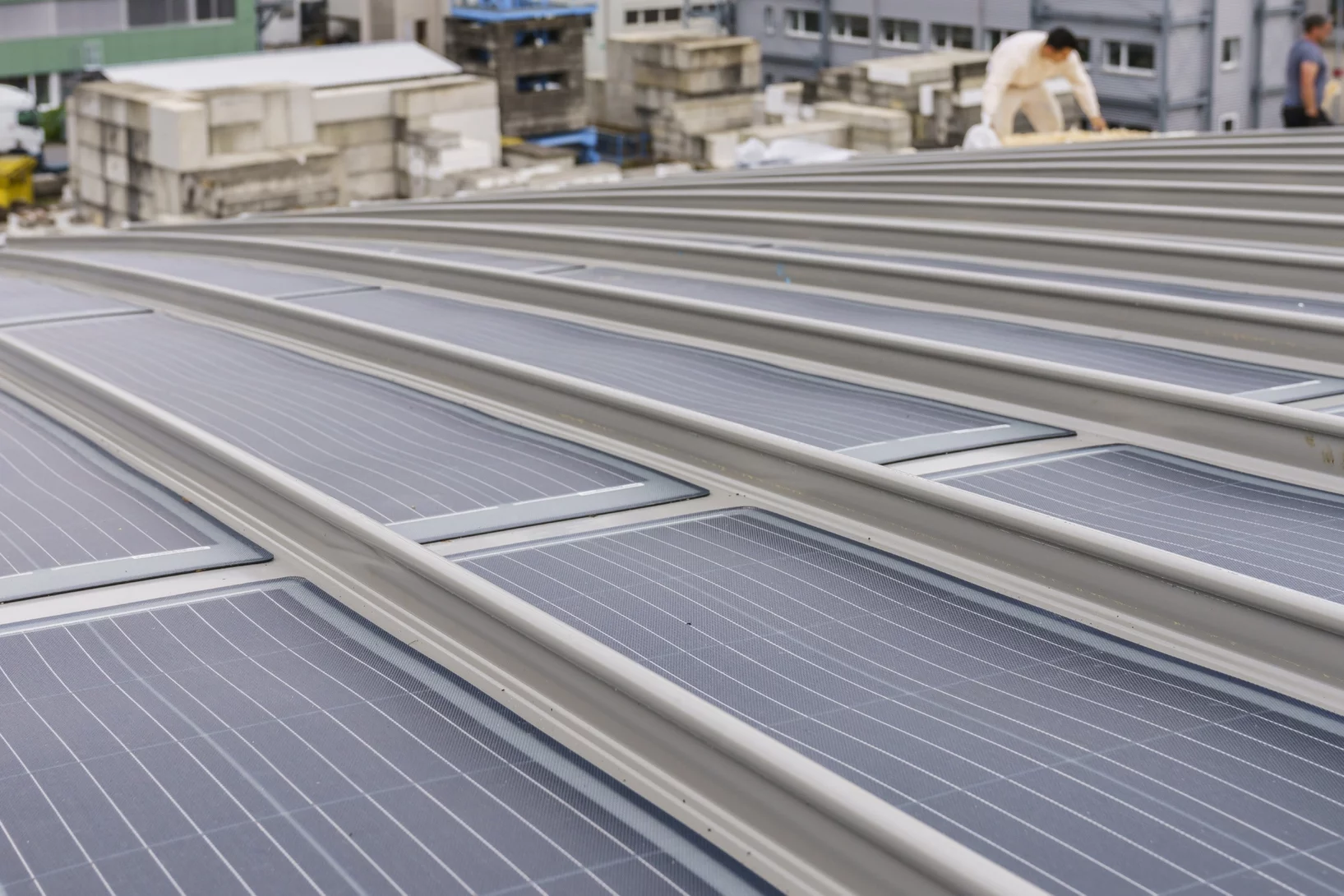
Aluminium and solar
The SLS building is currently getting a new roof.
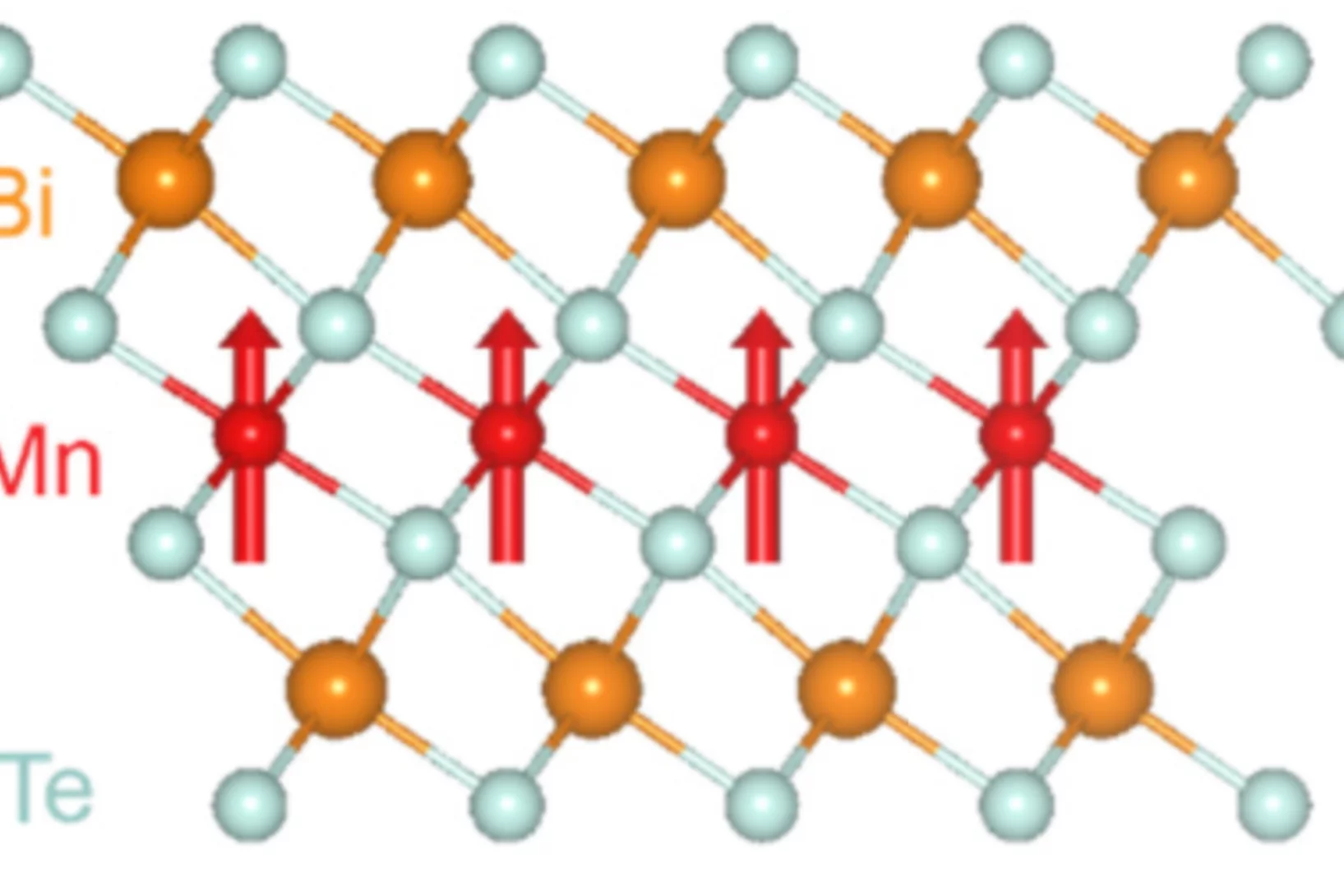
Coexistence of Superconductivity and Antiferromagnetism in Topological Magnet MnBi2Te4 Films
The interface of two materials can harbor unexpected emergent phenomena. One example is interface-induced superconductivity. In this work, we employ molecular beam epitaxy to grow a series of heterostructures formed by stacking together two nonsuperconducting antiferromagnetic materials, an intrinsic antiferromagnetic topological insulator MnBi2Te4 and an antiferromagnetic iron chalcogenide FeTe.
Can aerosols stop global warming?
Injecting particles into the stratosphere to cool the earth? In our interview, PSI researcher Markus Ammann comments critically on the controversial subject of solar geoengineering.
leadXpro and Golgi Neurosciences Work on GPR65 Modulators
leadXpro, a spin-off company of PSI active in the field of biotechnology, and Golgi Neurosciences, a biotech incubator based in Milan, have announced a partnership to develop therapies for neurodegenerative diseases. They are working on positive and negative modulators of the GPR65 receptor, which plays a role in neuroinflammation, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, fibrosis, cancer, and inflammatory bowel disease.
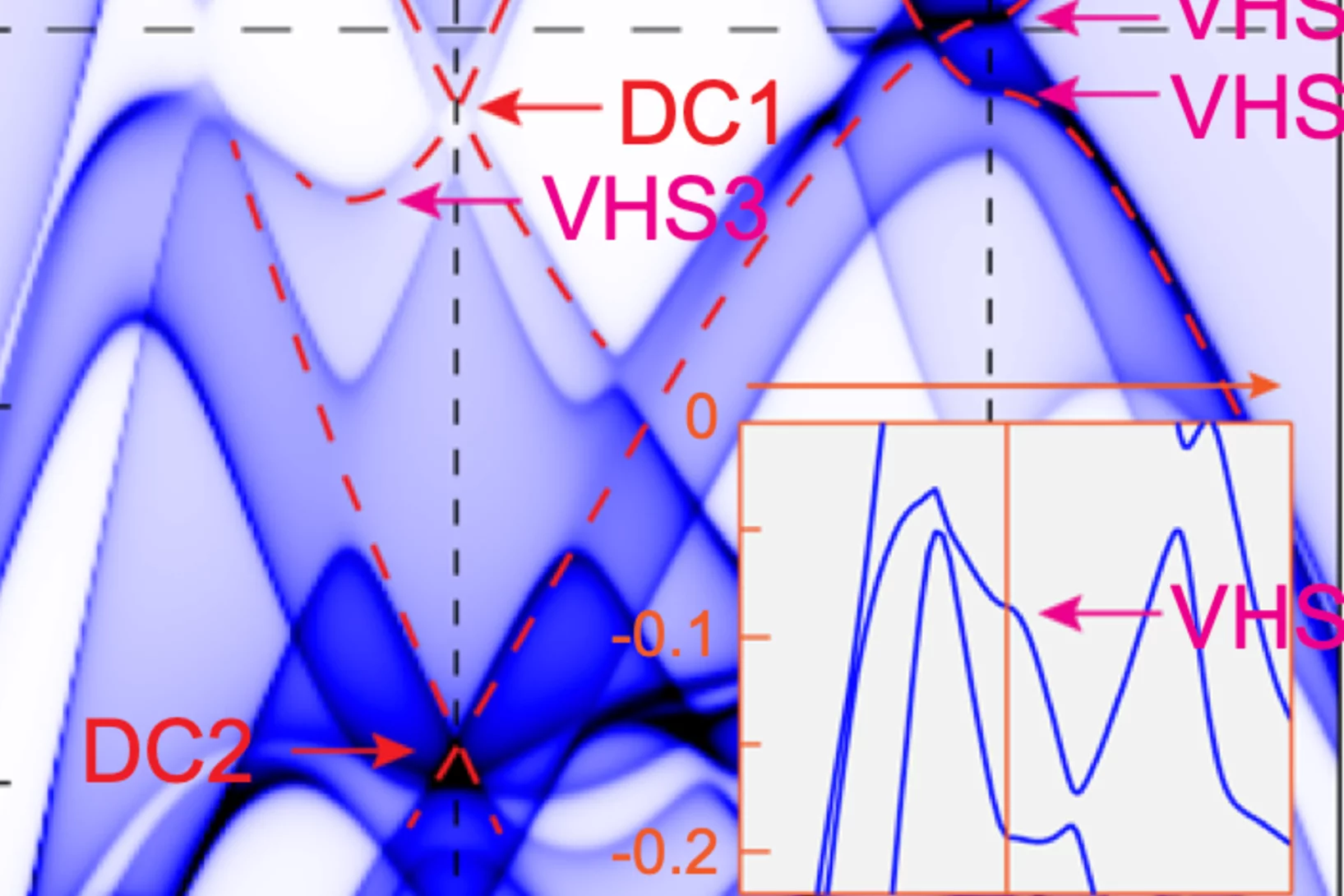
Phonon promoted charge density wave in topological kagome metal ScV6Sn6
Charge density wave (CDW) orders in vanadium-based kagome metals have recently received tremendous attention, yet their origin remains a topic of debate. The discovery of ScV6Sn6, a bilayer kagome metal featuring an intriguing √3 × √3 × √3 CDW order, offers a novel platform to explore the underlying mechanism behind the unconventional CDW. Here we combine ...