Shifting away from nuclear energy, expanding solar and wind power, generating energy from biomass, reducing energy consumption. Switzerland is committed to becoming climate-neutral by 2050. An ambitious goal, which has become more urgent than ever due to the increasingly challenging geopolitical situation. How can a sustainable and resilient energy supply for Switzerland be established over the coming years? What's the optimal way to use renewable energy sources? What new technologies are especially promising? At PSI, researchers are seeking answers to these crucial questions.
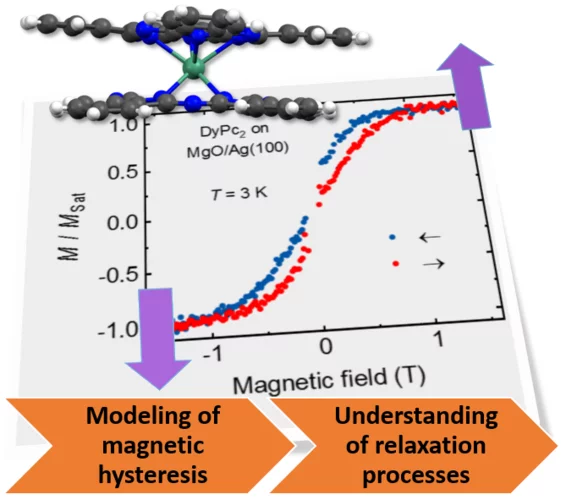
Understanding the Superior Stability of Single-Molecule Magnets on an Oxide Film
A research team centered at the X-Treme beam line at the Swiss Light Source has demonstrated that spin-phonon coupling plays a major role in enhancing the magnetic stability of so-called lanthanide phthalocyanine double decker single-molecule magnets. This understanding is important in order to employ such molecules in future spintronics applications.
Welcome Carla Jennifer Huber
We warmly welcome Carla Huber as a PhD student in the Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry. She joined the Analytical Chemistry group on 1 October 2019.
Carla Huber studied Chemistry at the ETH Zurich, with a focus on organic chemistry. For her master thesis, she investigated solvent effects on the binding of lysine and arginine to proline rich cyclic receptors.
At PSI, Carla Huber will investigate the preservation, stability and potential contamination of molecular markers in snow and ice through analysis of snow pit and simultaneous long-term atmospheric aerosol samples from the same site using state-of-the-art high-resolution organic mass spectrometry.
Award by NPSS
The IEEE Nuclear Plasma Science Society has recently awarded Dr. Paolo Craievich, leader of the group «RF-system 2» in GFA, with the Particle Accelerator Science Technology award for his exceptional contributions to accelerator science and technology. https://www.frib.msu.edu/events/2019/napac19/awards.html
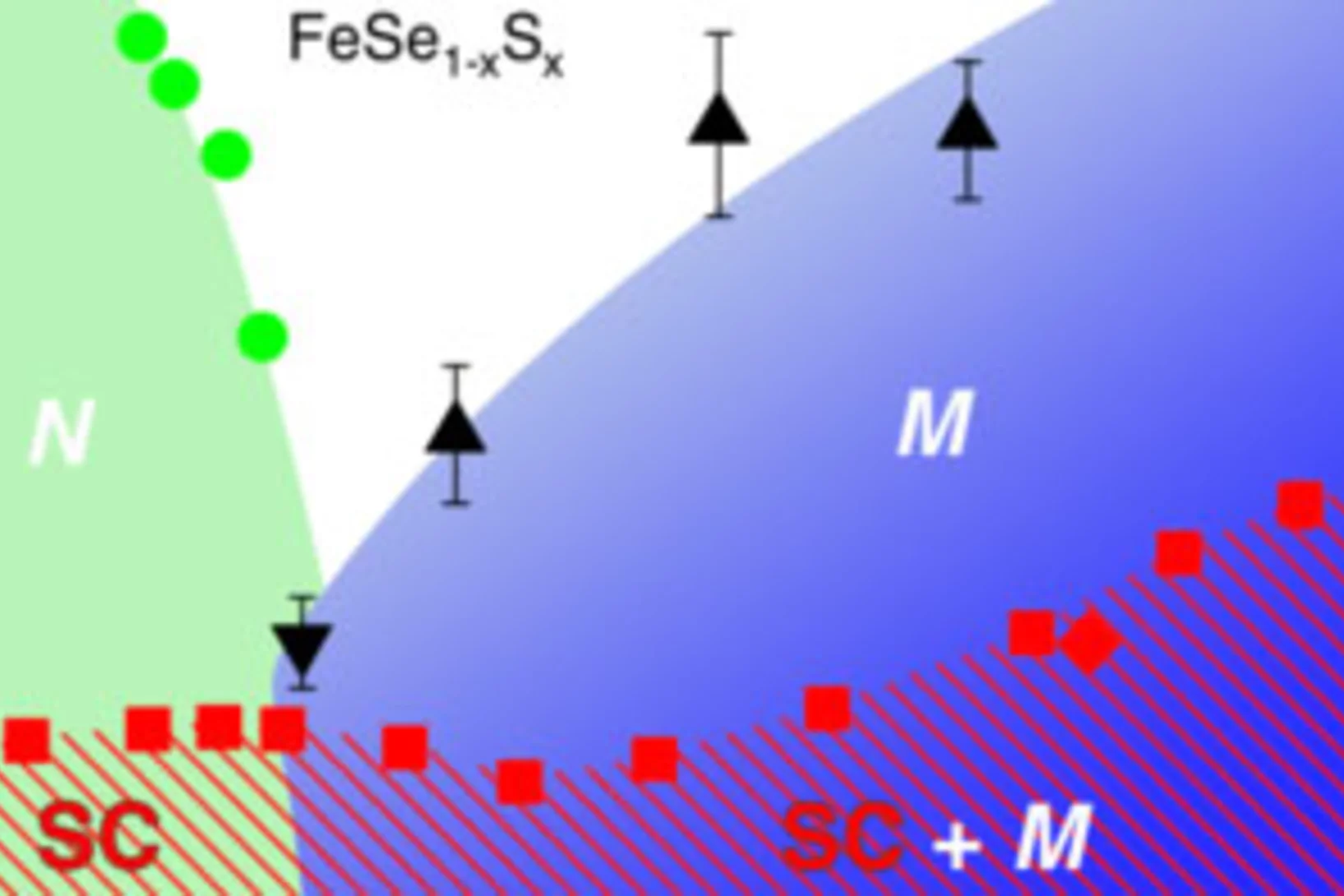
Extended Magnetic Dome Induced by Low Pressures in Superconducting FeSe(1 − x)Sx
We report muon spin rotation and magnetization measurements under pressure on Fe1+δSe1−xSx with x ≈ 0.11. Above p ≈ 0.6 GPa we find a microscopic coexistence of superconductivity with an extended dome of long range magnetic order that spans a pressure range between previously reported separated magnetic phases.
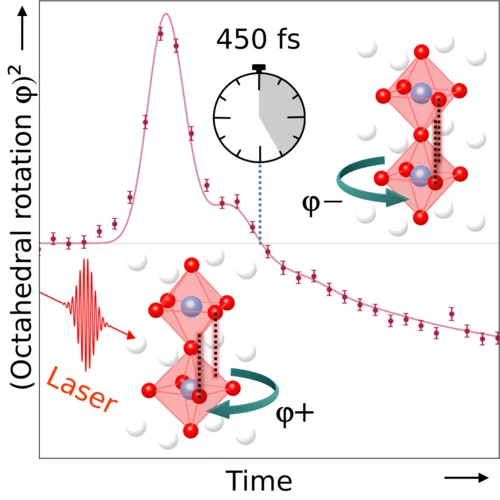
Ultrafast Transient Increase of Oxygen Octahedral Rotations in a Perovskite
Via femtosecond x-ray diffraction, we observe an ultrafast increase of the octahedral rotation angle in the perovskite EuTiO3 after ultrafast laser excitation. This is opposite to what is expected from an increase in temperature. We ascribe this increase to an effective change of ionic sizes that transforms directly into a change of the Goldschmidt tolerance factor. Rotating oxygen octahedra at will opens up the possibility to control electronic and magnetic properties of perovskites on ultrafast timescales.
Cancer cells under attack
At PSI, cancer patients receive a therapy that is unique in Switzerland. Bombardment with protons wipes out cancer cells – and does so more precisely than with any other form of irradiation.
Chemielaboranten-Ausflug zur Ilmac-Messe 2019
Wir Lernende Laboranten Fachrichtung Chemie reisen mit unserm Berufsbildner an die ILMAC, der führenden Schweizer Fachmesse für Labor- und Prozesstechnologie in Basel.
Visit of ESS Council to Switzerland
On 24 September the Paul Scherrer Institut was the venue of a meeting between the top supervisory board of the European Spallation Source ESS to be built in Lund, Sweden, and representatives of the Swiss government from SERI. The chair and the vice chair of the ESS Council, Beatrix Vierkorn-Rudolph and Kurt Clausen, respectively came to Switzerland to discuss the Swiss In-Kind Contributions to the largest spallation neutron source under construction in Sweden.
Lehrlingslager 2019
In diesem Jahr führte es uns nach Hottwil/Böttstein, wo wir 2 sehr lehrreiche und interessante Wochen mit viel Spass und harter Arbeit verbracht haben.
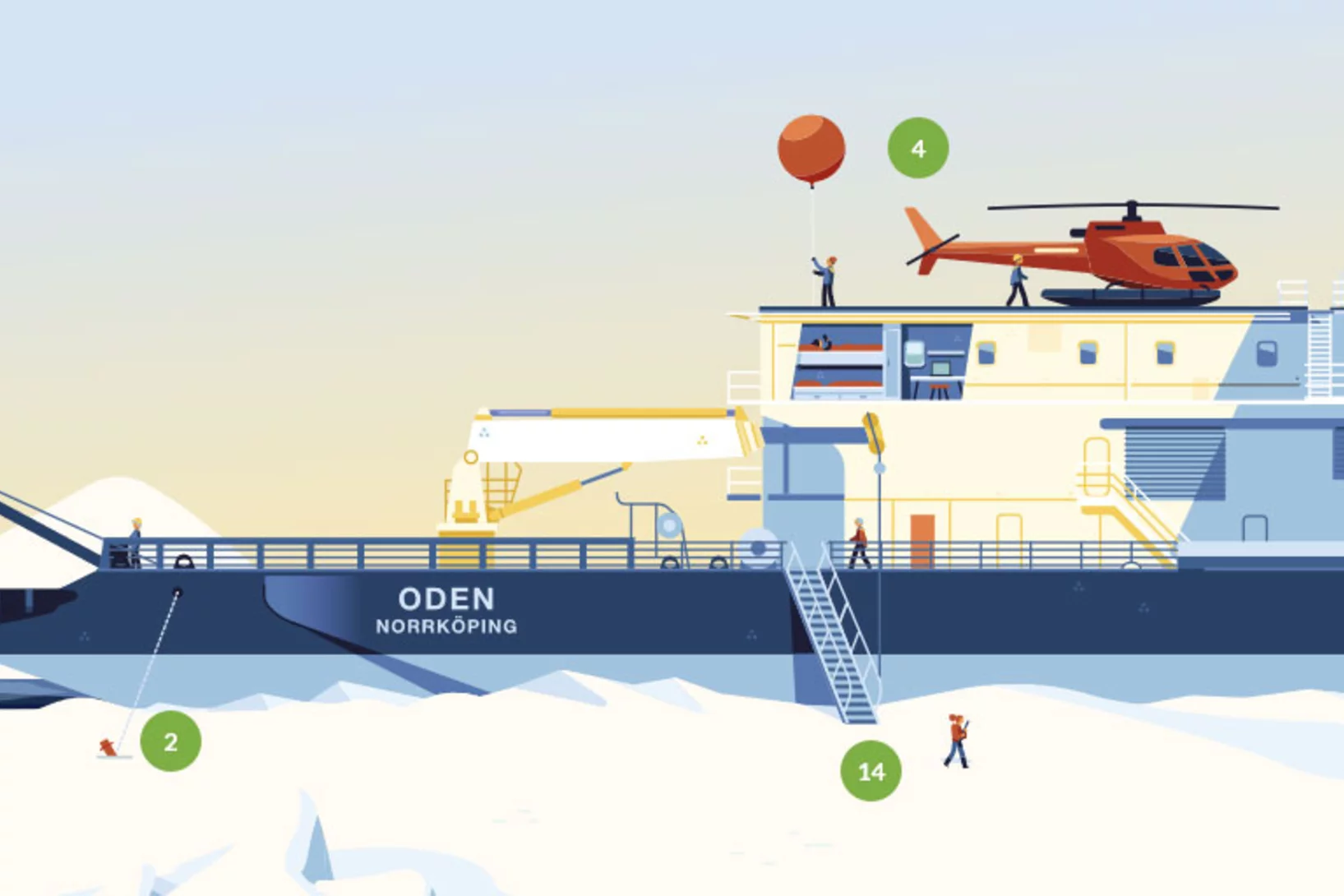
Thirteen months in the Arctic
A PSI research project investigating atmospheric chemistry will be on board the icebreaker Polarstern on 20th September 2019. Researcher Julia Schmale talks about the upcoming expedition and her role in it.
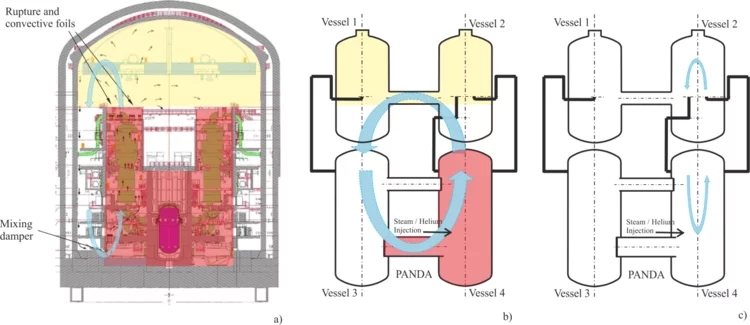
PANDA Large-scale Experiments addressing Complex Natural Circulation in a PWR two-room type containment
In nuclear safety analyses, the assessment of hydrogen release, distribution, and mitigation in the containment has high relevance, because under certain postulated scenarios, combustible mixture could form and hydrogen explosions could damage safety systems.
Safety analyses is carried out using advanced computational tools that have been assessed and validated through a variety of the analyses based experiments representative of the phenomena postulated in the containment and obtained in highly instrumented thermal-hydraulics facilities.
The OECD/NEA HYMERES project (www.psi.ch/en/teg/projects) was carried out to create an experimental database consisting in 24 PANDA tests and 9 MISTRA (CEA, France) tests devoted to phenomena with high relevance in nuclear safety. In two PANDA tests identified as HP6_1 and HP6_2) was investigated the effect of complex natural circulation in a PWR two-room type containment, on the hydrogen distribution, during postulated accidents [1]. The PANDA test specifications have been determined based on scoping analyses with the GOTHIC and APROS advanced computational tools [2].
Herbstliches Beer & Dine
Luc Van Loon und Christopher Chen präsentieren ihre Biere.
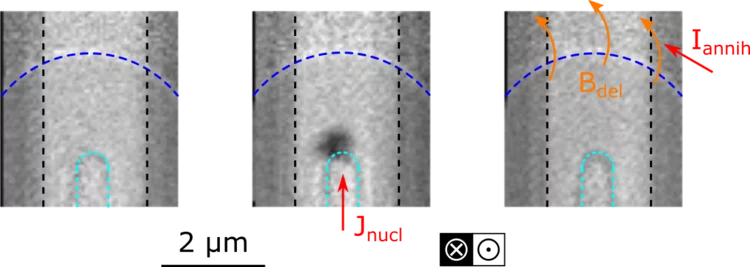
Nano-engineered contact for the zero-field nucleation of magnetic skyrmions
Researchers in a joint collaboration between the PolLux endstation of the Swiss Light Source and the University of Leeds have achieved the reliable and reproducible electrical nucleation of magnetic skyrmions from a nano-engineered point contact structure, investigating the physical mechanisms driving the nucleation process.
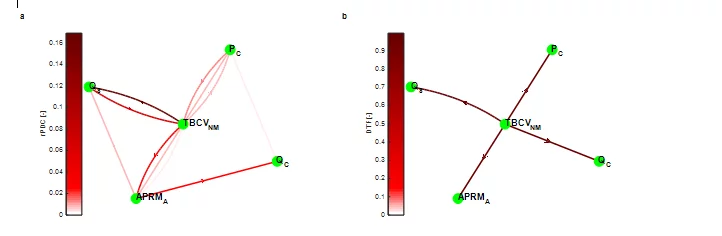
Identifying a disturbance root-cause from ... noise!
Nuclear reactors are complex systems with inherent stochastic behaviour. In simple words, the behaviour of various reactor processes are continuously fluctuating over their mean values, even under normal operation and steady-state conditions. The detailed and systematic analysis of this noisy behaviour can reveal valuable information about the operating status of the studied nuclear reactor. More importantly, designed modifications of the reactor’s operation or even unexpected deviations from the normal performance can be identified using advanced signal analysis techniques. The STARS program, at the Laboratory for Reactor Physics and Thermal-Hydraulics (LRT) in PSI, based on a tight collaboration with the Swiss nuclear industry, has developed a well-established signal analysis methodology, being continuously improved since more than two decades. The latest enhancements of the PSI signal analysis methodology allow a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms that drive the reactor’s operation, and can provide better insight on the root-cause of possible disturbances or malfunctions. Recently, the latest STARS activities in advanced signal analysis techniques were culminated by an international recognition through a special distinction from the AIP Chaos Journal.
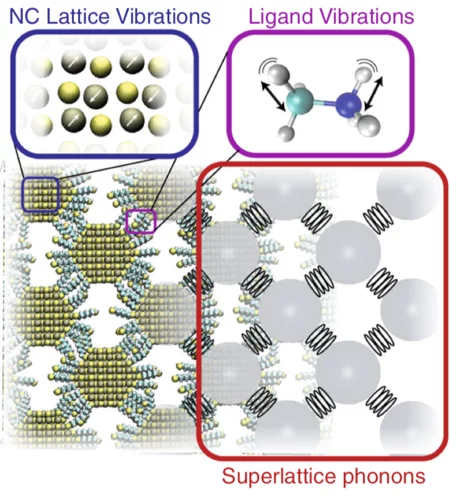
Nanocrystal superlattices as phonon-engineered solids and acoustic metamaterials
Phonon engineering of solids enables the creation of materials with tailored heat-transfer properties, controlled elastic and acoustic vibration propagation, and custom phonon-electron and phonon-photon interactions. These can be leveraged for energy transport, harvesting, or isolation applications and in the creation of novel phonon-based devices, including photoacoustic systems and phonon-communication networks.
LIN Engineers participate in the DENIM conference
LIN Engineers Manuel Lehmann, Sven Schütz, Dieter Graf and Peter Keller attended the 8th annual Design and Engineering of Neutron Instruments Meeting (DENIM VIII). DENIM is world’s largest conference on Neutron Instrument Engineering and is an important avenue for our engineers to share and exchange their knowledge with other international experts. This allows us to continuously develop and maintain neutron instruments for SINQ that push the current state-of-the-art.
New 6M€ European grant awarded to ExPaNDS to drive open access data
A new 6M€ grant is being launched for the Photon and Neutron Data Services (ExPaNDS) to come together and work under the European Open Science Cloud (EOSC). This ambitious project will create enormous opportunities for scientific communities, and through their findings for humankind worldwide. It aims to publish and map the data behind the thousands of successful published scientific papers generated by Europe’s Photon and Neutron Research Infrastructures (PaN RIs) – which every year create petabytes of data – and make it available to all.
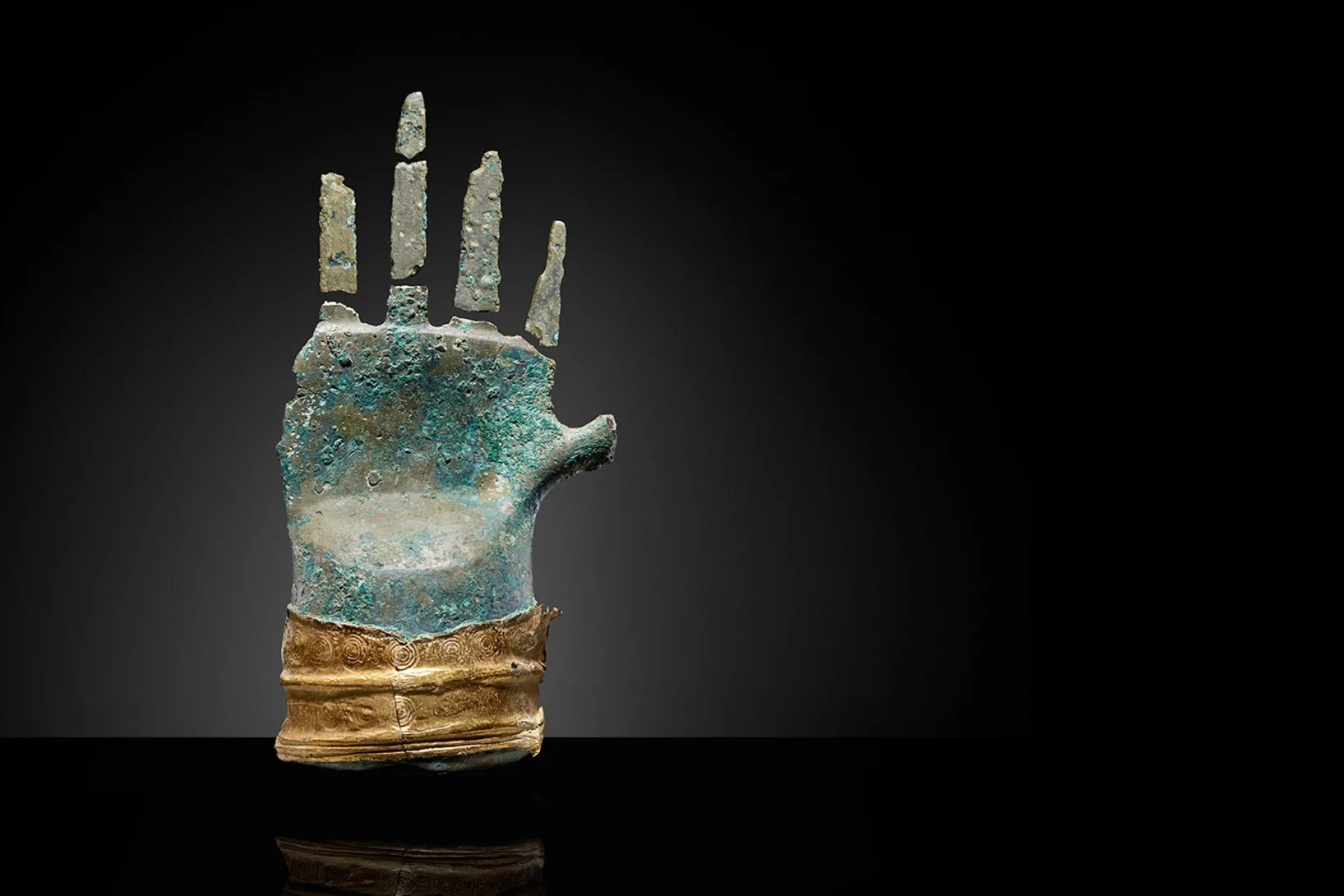
A hand like no other
A 3,500-year-old bronze sculpture is being examined at PSI's SINQ neutron source. This will enable conservators to get a unique view into the interior of the sensational find – and gain insights into how it was made.
"This is incredibly ambitious"
Every three years, the World Energy Council explores possible developments of the global energy system under different scenarios. Tom Kober, head of the Energy Economics Group in PSI’s Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis and one of the lead authors of the study, explains what the individual scenarios mean and how global warming could be mitigated.
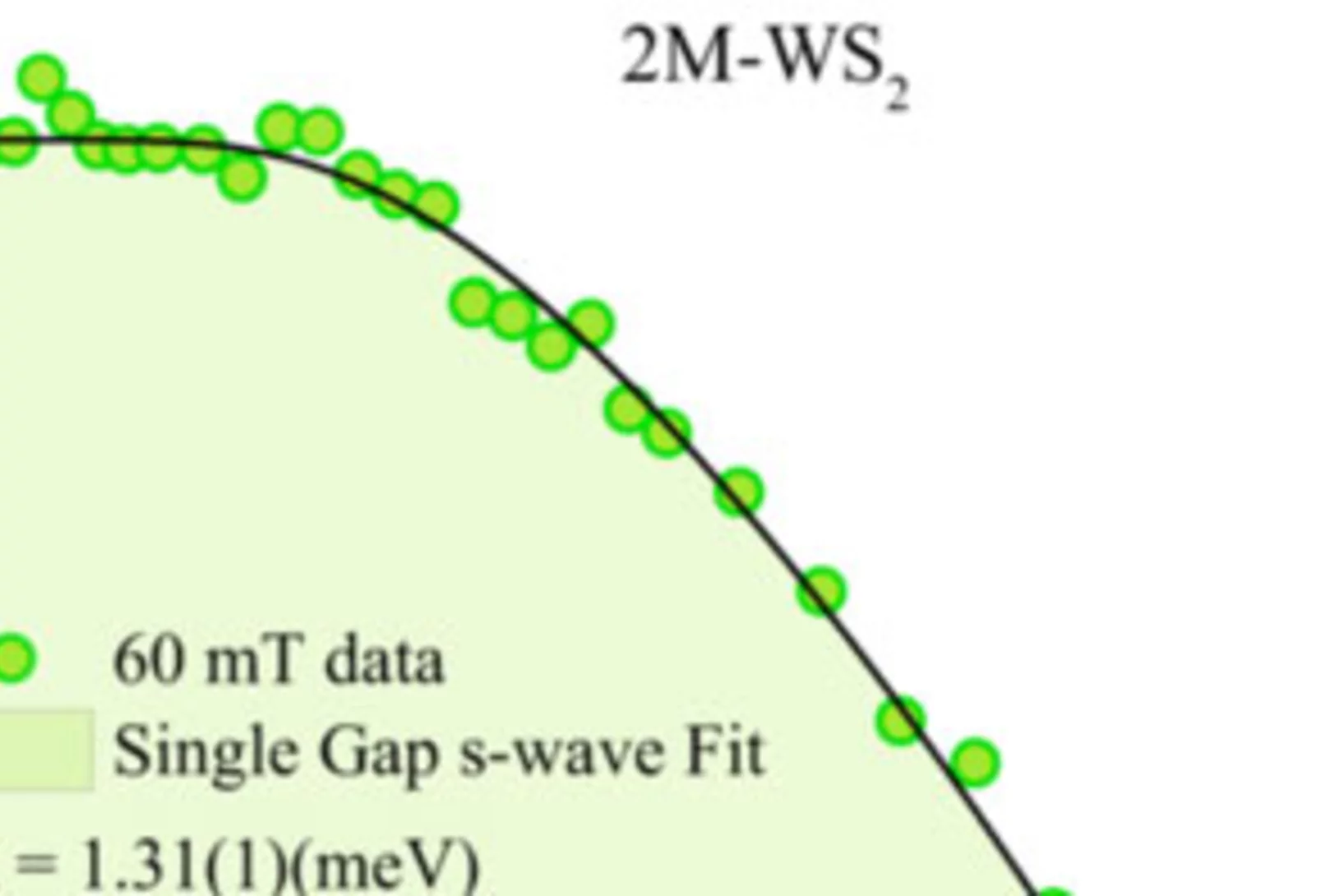
Nodeless superconductivity and its evolution with pressure in the layered dirac semimetal 2M-WS2
Recently, the transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) system 2M-WS2 has been identified as a Dirac semimetal exhibiting both superconductivity with the highest Tc ~ 8.5 K among all the TMD materials and topological surface states. Here we report on muon spin rotation (μSR) and density functional theory studies of microscopic SC properties and the electronic structure in 2M-WS2 at ambient and under hydrostatic pressures (pmax = 1.9 GPa).
Antoaneta Damyanova successfully defends her Ph.D. thesis on the Mu3e SciFi detector
Antoaneta Damyanova developed the scintillating fiber detector from fiber characterization to prototype construction and evaluation, SiPM array perfromance studies, and mechanical integration. She has successfully defended her thesis at Geneva University.
Aarg. Berufsschau ab'19
Vom 3. – 8. September 2019 fand in Wettingen die Aargauische Berufsschau ab'19 statt. Auch das PSI war wieder mit einem Stand vertreten und hat unsere Berufe und das iLab vorgestellt.
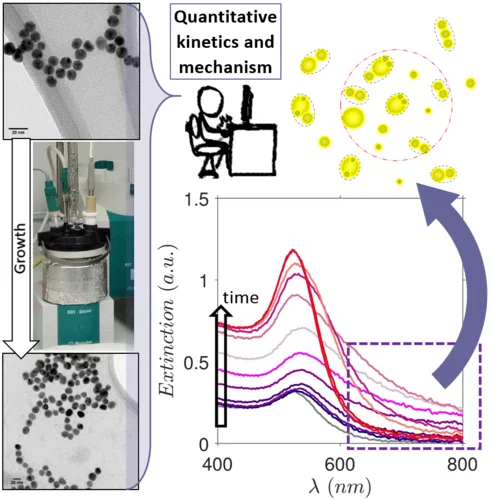
Kinetics and Mechanism of Metal Nanoparticle Growth via Optical Extinction Spectroscopy and Computational Modeling: The Curious Case of Colloidal Gold
An overarching computational framework unifying several optical theories to describe the temporal volution of gold nanoparticles (GNPs) during a seeded growth process is presented. To achieve this, we sed the inexpensive and widely available optical extinction spectroscopy, to obtain quantitative kinetic data. In situ spectra collected over a wide set of experimental conditions were regressed using the hysical model, calculating light extinction by ensembles of GNPs during the growth process. This model rovides temporal information on the size, shape, and concentration of the particles, and any electromagnetic interactions between them. Consequently, we were able to describe the mechanism of GNP growth and divide the process into distinct genesis periods. We provide explanations for several longstanding mysteries, e.g., the phenomena responsible for the purple-greyish hue during the early stages of GNP growth, the complex interactions between nucleation, growth and aggregation events, and a clear distinction between agglomeration and electromagnetic interactions. The presented theoretical formalism has been developed in a generic fashion so that it can readily be adapted to other nanoparticulate formation scenarios such as the genesis of various metal nanoparticles.
Silicon as a semiconductor: silicon carbide would be much more efficient
In power electronics, semiconductors are based on the element silicon – but the energy efficiency of silicon carbide would be much higher.
A floating lab
To investigate Arctic water, ice, and air, 40 scientists cruised to the North Pole on the icebreaker Oden in the summer of 2018. Two atmospheric researchers from PSI were on board.
Dr. Jinqiu Xu joins the X-ray Tomography Group as Post Doc
Dr. Jinqiu Xu will work with the team developing X-ray phase contrast CT for breast cancer diagnosis. Before coming to PSI, she worked on CT reconstruction from incomplete data at Capital Normal University (Beijing, China).
Welcome Tatjana Sarah Münster
We warmly welcome Tatjana Münster as a PhD student in the Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry. She joined the Analytical Chemistry group on 1 September 2019.
Tatjana Münster studied Earth Sciences with a focus on palaeoclimatology, sedimentology, palaeoenvironmental, dynamics, and isotope geochemistry. She received her BSc from the Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz and her MSc from the Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg.
At PSI, Tatjana Münster will characterize the performance of a new ICP-TOF mass spectrometer for trace element analysis in ice cores, obtain a trace element record using this instrument from an Alpine ice core, and reconstruct the history of Saharan dust transports and heavy metal pollution from metallurgy over the last 2000 years.
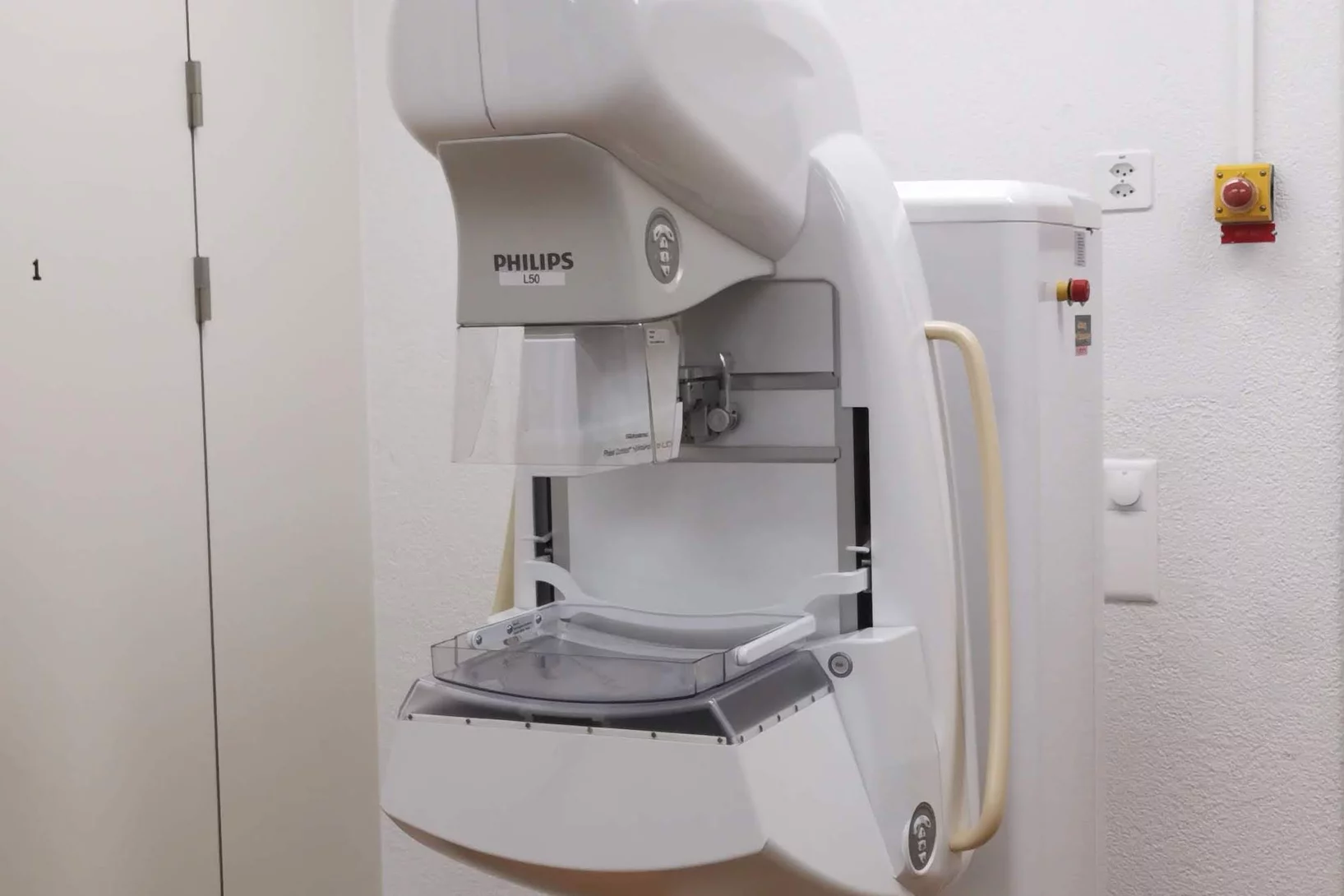
Towards clinical grating-interferometry mammography
The team of X-ray tomography group has developed the word-first clinical grating-interferometry mammography system in collaboration with Philips Research Hamburg, Kantonsspital Baden and Universitätspital Zurich. The novel imaging method shines a light on more accurate breast cancer detection. The prototype is installed at Universitätspital Zurich for clinical trial.
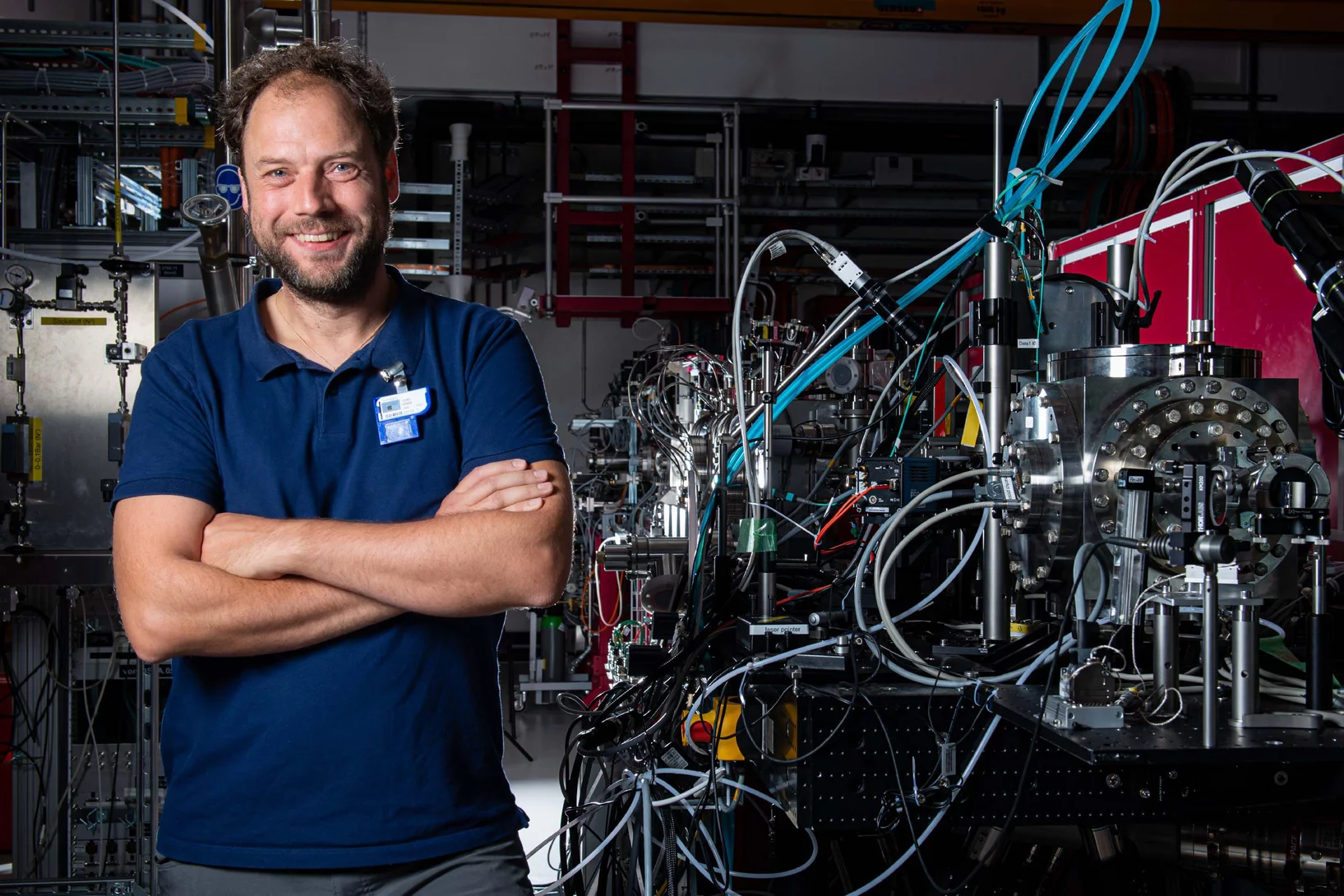
Research and tinkering – SwissFEL in 2019
The newest large research facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute, SwissFEL, has been completed. In January 2019 it began regular operation. Henrik Lemke, head of the SwissFEL Bernina research group, gives an interim report.
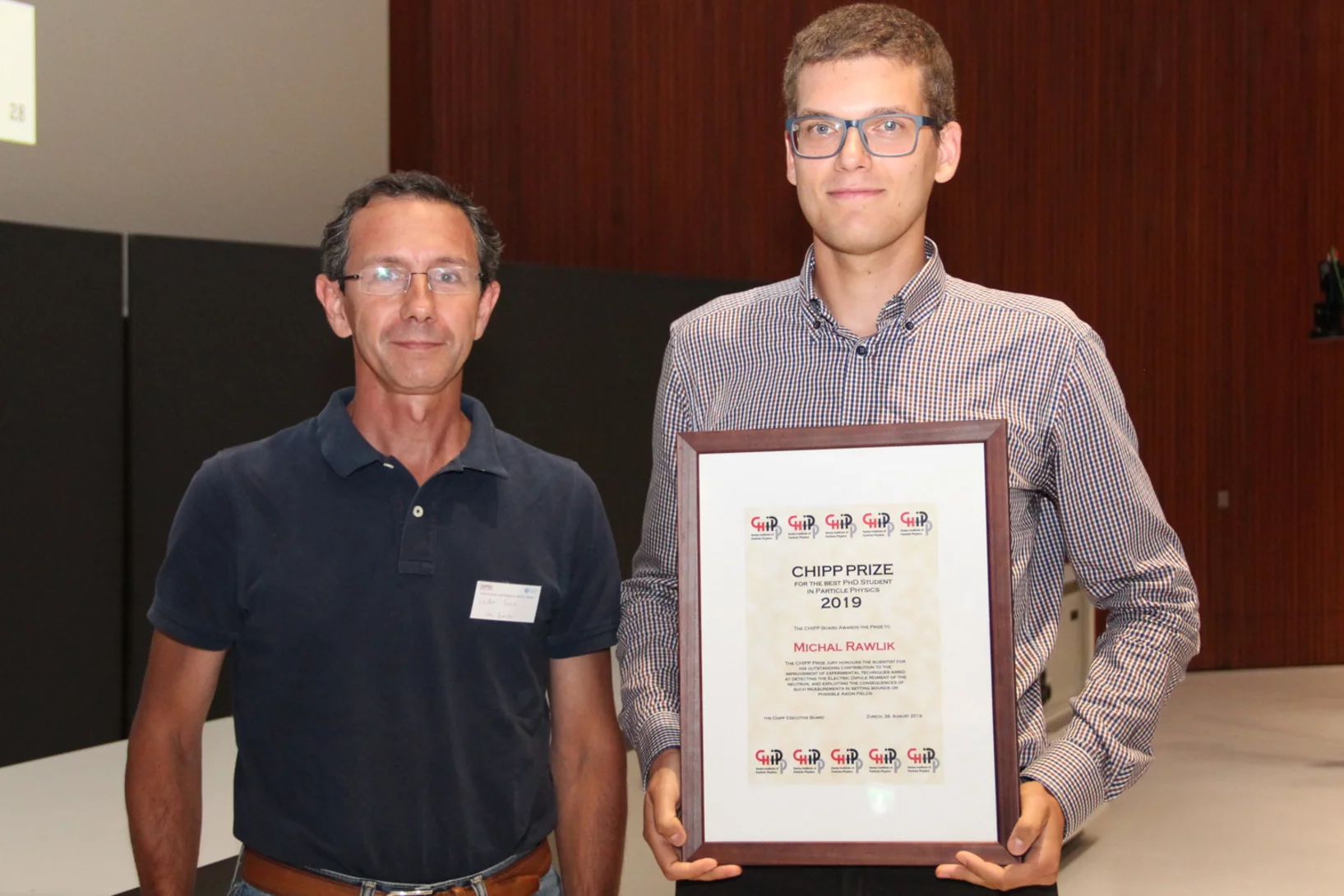
Michał Rawlik awarded the CHIPP Prize 2019
PSI researcher Dr. Michał Rawlik has been awarded the CHIPP Prize 2019 "for his outstanding contribution to the improvement of experimental techniques aimed at detecting the Electric Dipole Moment of the neutron, and exploiting the consequences of such measurements in setting bounds on possible Axion fields".