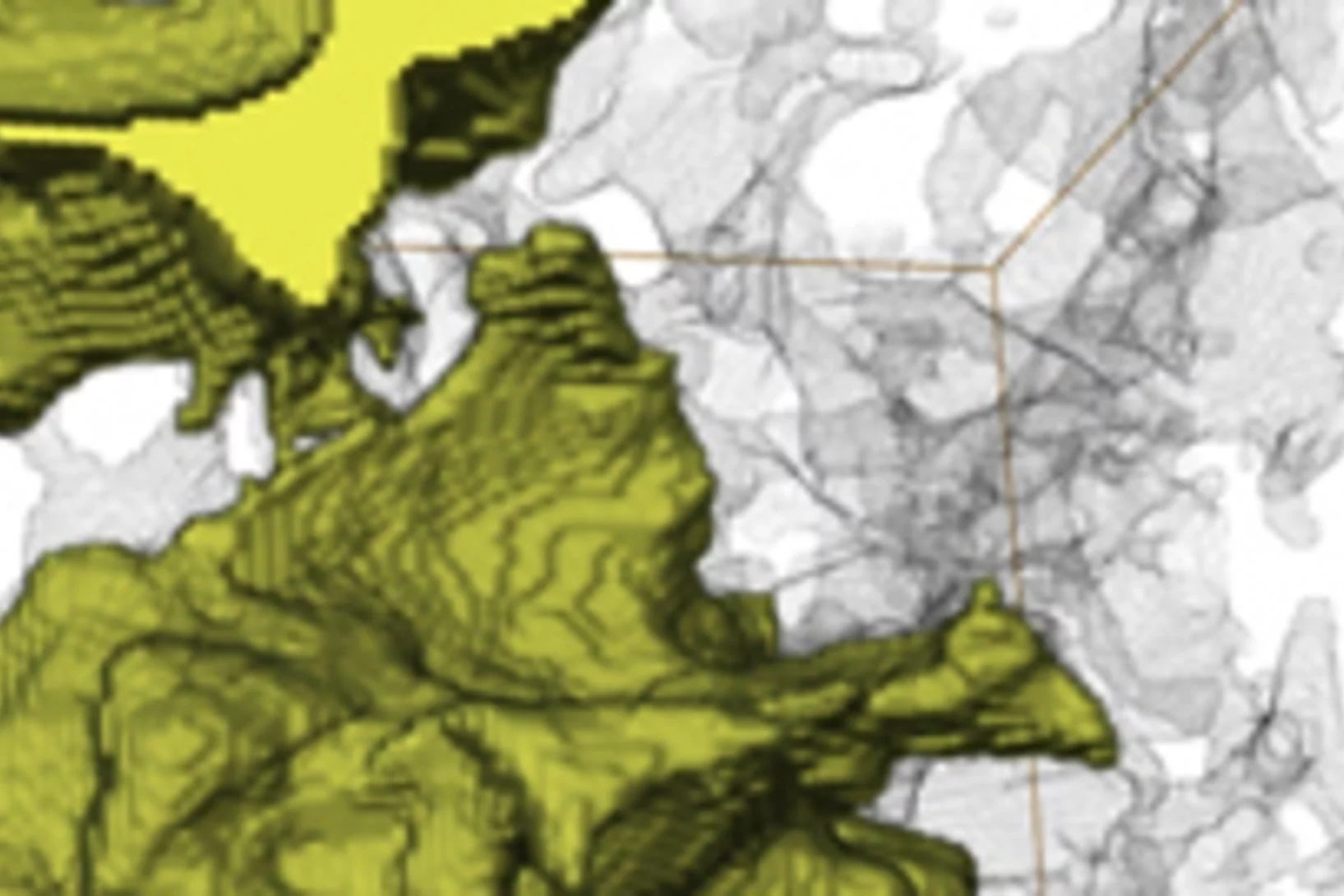
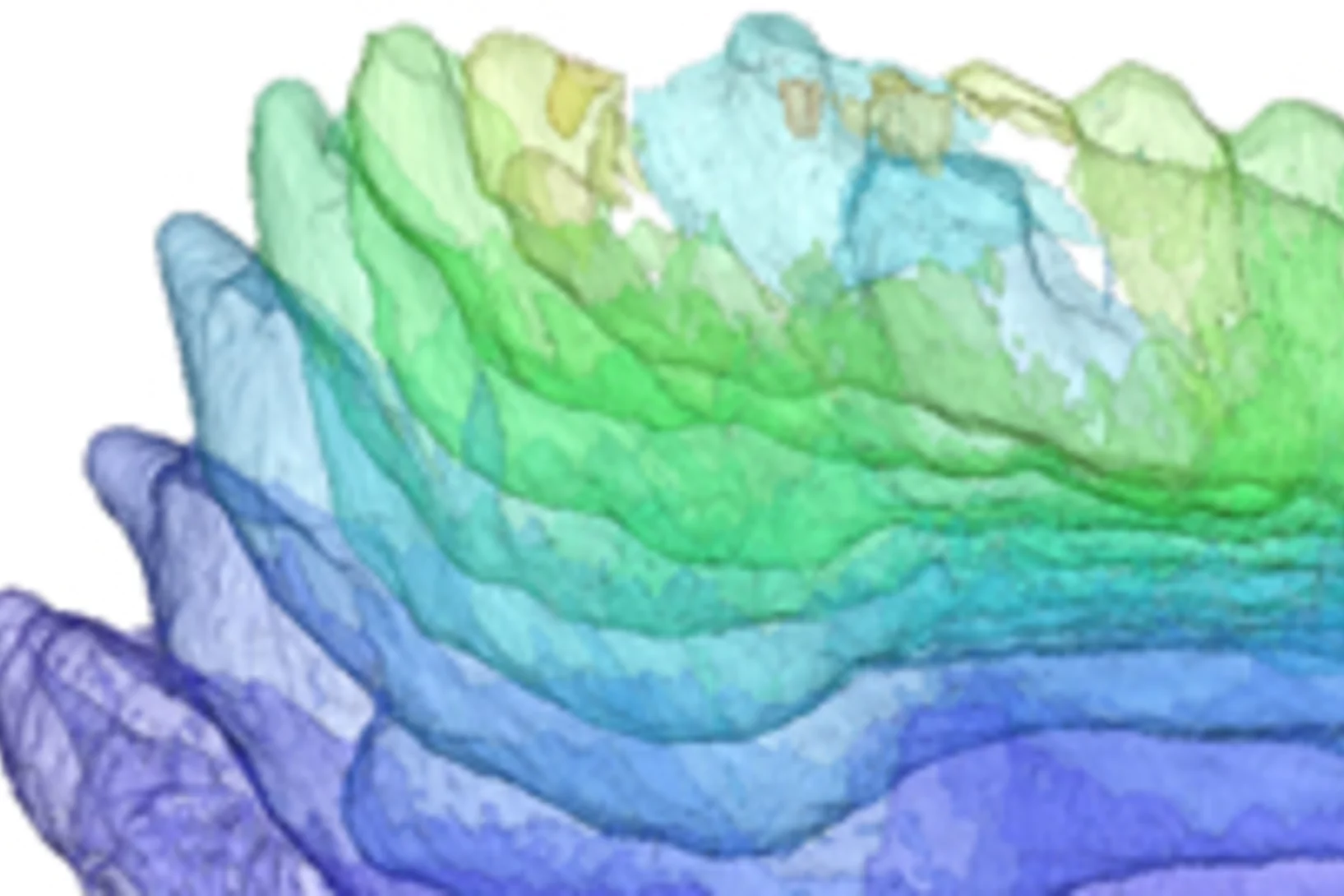
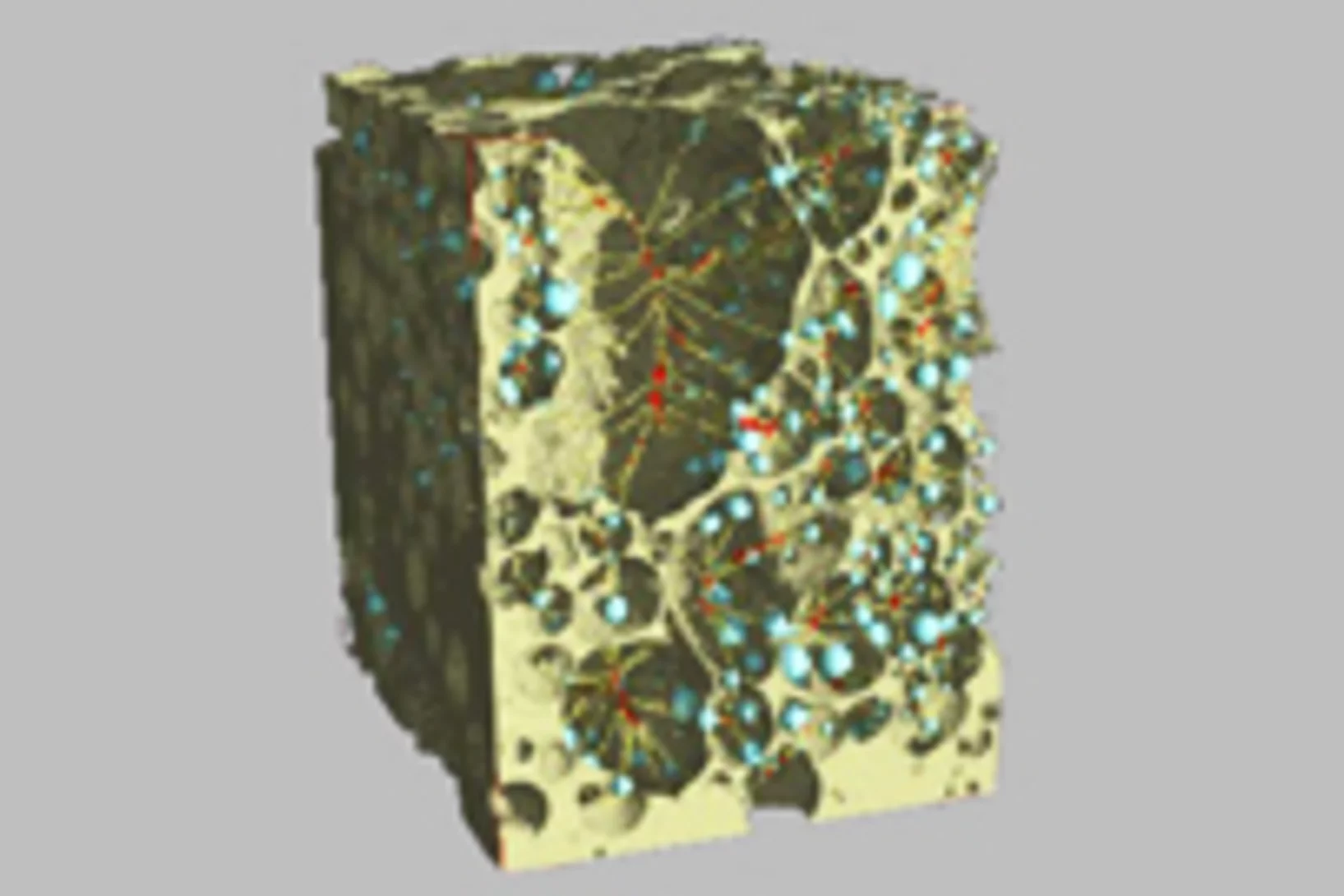
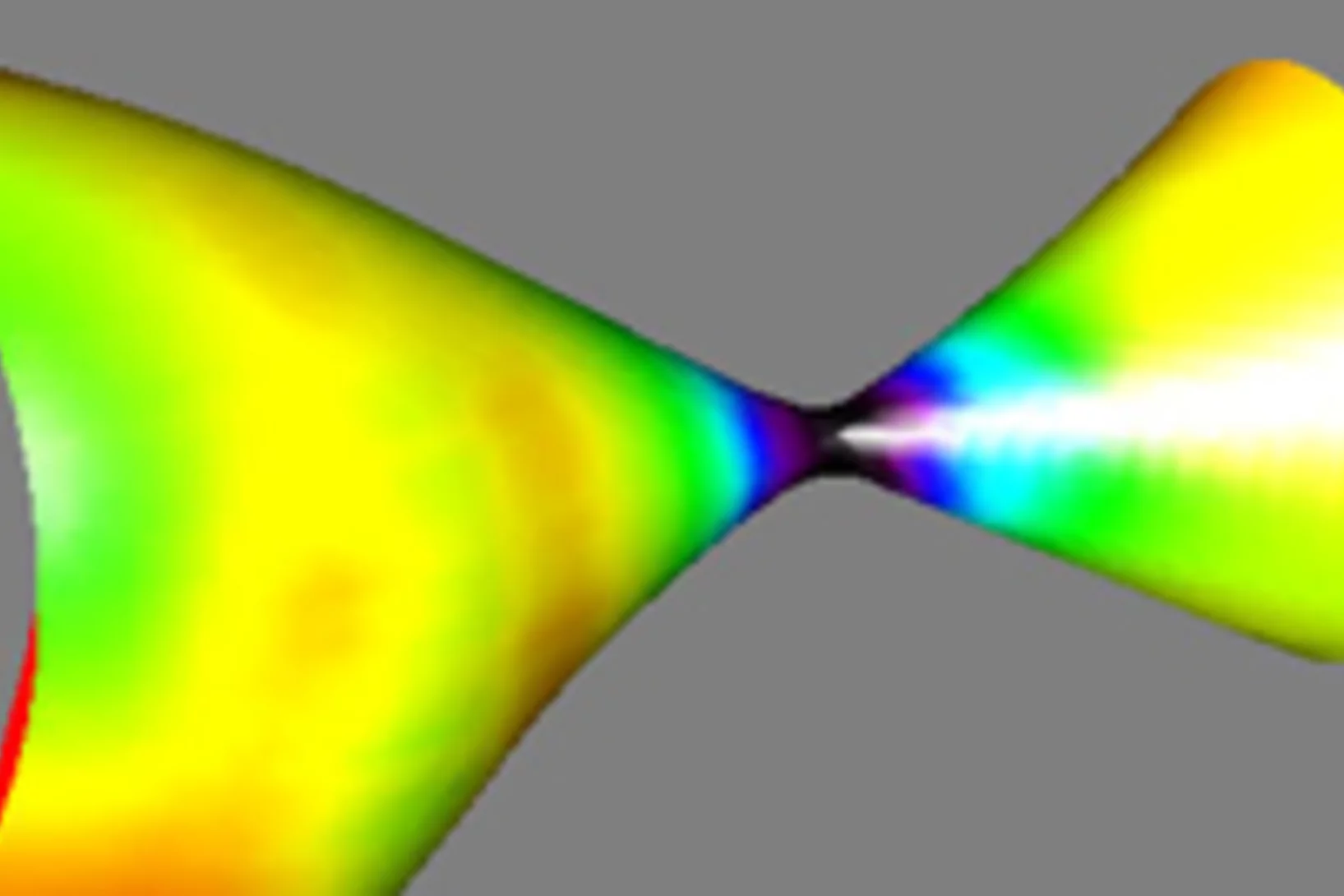
PSI Thesis Medal goes to Dr. Matias Kagias
The PSI Thesis Medal is awarded every second year to the best PhD thesis performed at the Paul Scherrer Institut. Matias received the prize for his excellent thesis entitled "Direct Self-Imaging Methods for X-ray Differential Phase and Scattering Imaging". Congratulations!
Une lentille virtuelle améliore la microscopie à rayons X
Une nouvelle méthode développée par des chercheurs du PSI permet d’améliorer encore les radiographies de matériaux. Pour ce faire, les chercheurs ont déplacé une lentille optique et réalisé chaque fois une image individuelle. A partir de là, ils ont calculé une image globale à l’aide d’algorithmes informatiques.
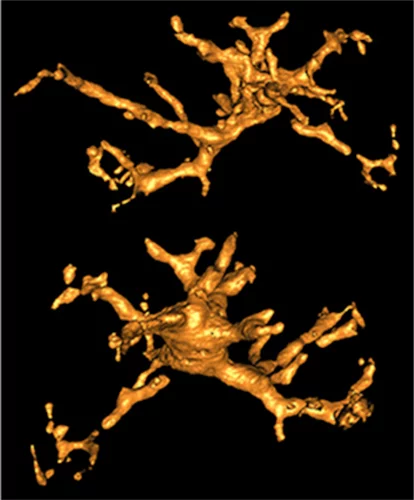
Soft-tissue evidence for homeothermy and crypsis in a Jurassic ichthyosaur
Synchrotron-based X-ray tomographic microscopy of melanophores (skin pigment cells) of an amazingly well preserved 180 million years old ichtyosaur (extinct marine reptile similar to whales) contributed in a multidisciplinary investigation to the new findings published today in Nature.
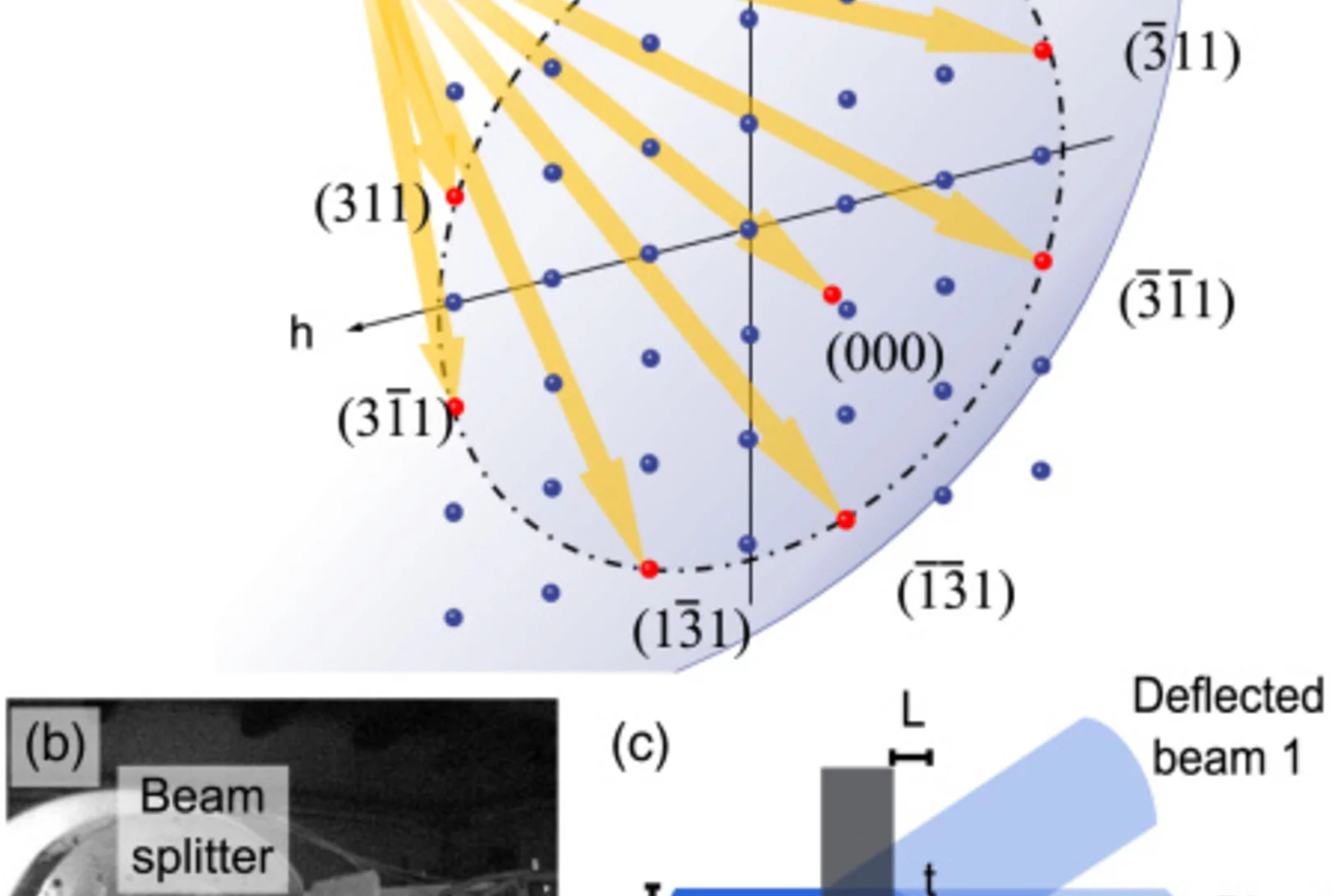
TOMCAT paper on hard X-ray multi-projection imaging published
The TOMCAT team in collaboration with scientists from CFEL, MaxIV and ESRF developed a method for hard X-ray multi-projection imaging, using a single crystal to split the beam into multiple beams with different directions.
La spin-off du PSI GratXray remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017
Une spin-off du PSI remporte le Swiss Technology Award 2017: la jeune entreprise GratXray développe une nouvelle méthode de diagnostic précoce du cancer du sein.
New TOMCAT paper: The GigaFRoST camera and readout system
The PSI in-house developed GigaFRoST high-speed camera and readout system is available for fast imaging experiments at the TOMCAT beamline, opening up exciting new possibilities for the observation of fast dynamic phenomena with X-ray tomography.
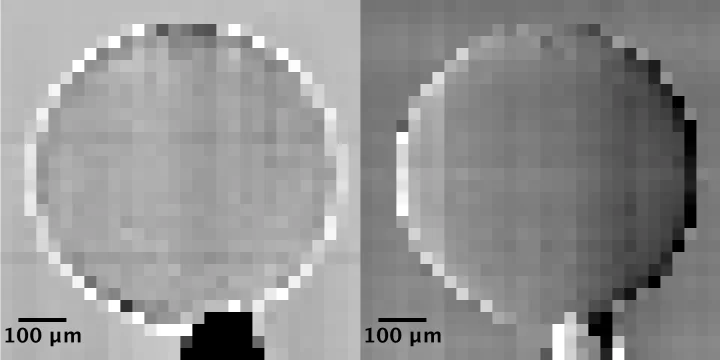
Single shot grating interferometry demonstrated using direct conversion detection
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute's Swiss Light Source in Villigen, Switzerland, have developed an X-ray grating interferometry setup which does not require an analyzer grating, by directly detecting the fringes generated by the phase grating with a high resolution detector. The 25um pitch GOTTHARD microstrip detector utilizes a direct conversion sensor in which the charge generated from a single absorbed photon is collected by more than one channel. Therefore it is possible to interpolate to achieve a position resolution finer than the strip pitch.
Watching lithium move in battery materials
In order to understand limitations in current battery materials and systematically engineer better ones, it is helpful to be able to directly visualize the lithium dynamics in materials during battery charge and discharge. Researchers at ETH Zurich and Paul Scherrer Institute have demonstrated a way to do this.
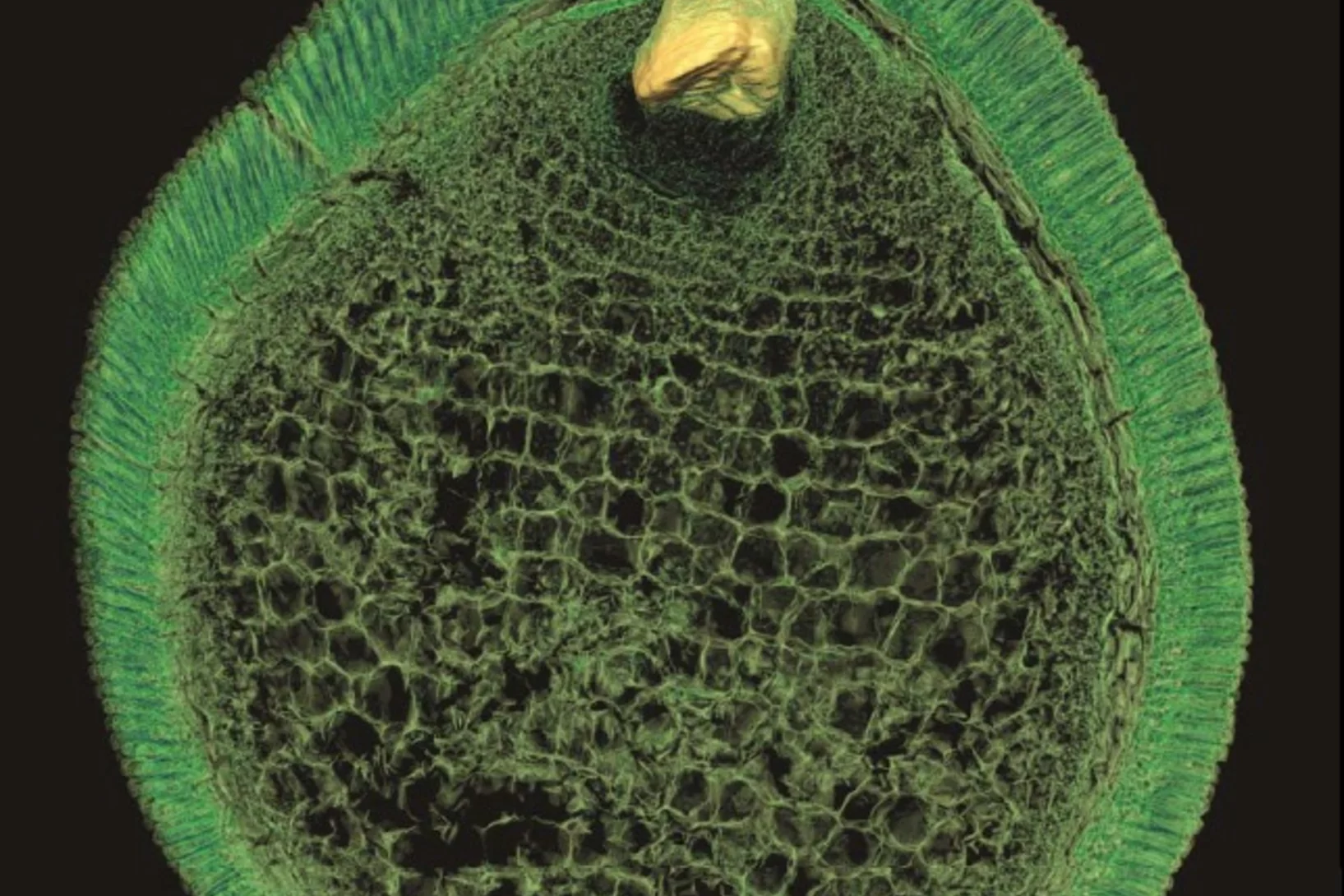
Preserved Embryos Illustrate Seed Dormancy in Early Angiosperms
The discovery of exceptionally well-preserved, tiny fossil seeds dating back to the Early Cretaceous corroborates that flowering plants were small opportunistic colonizers at that time, according to a new Yale-led study.
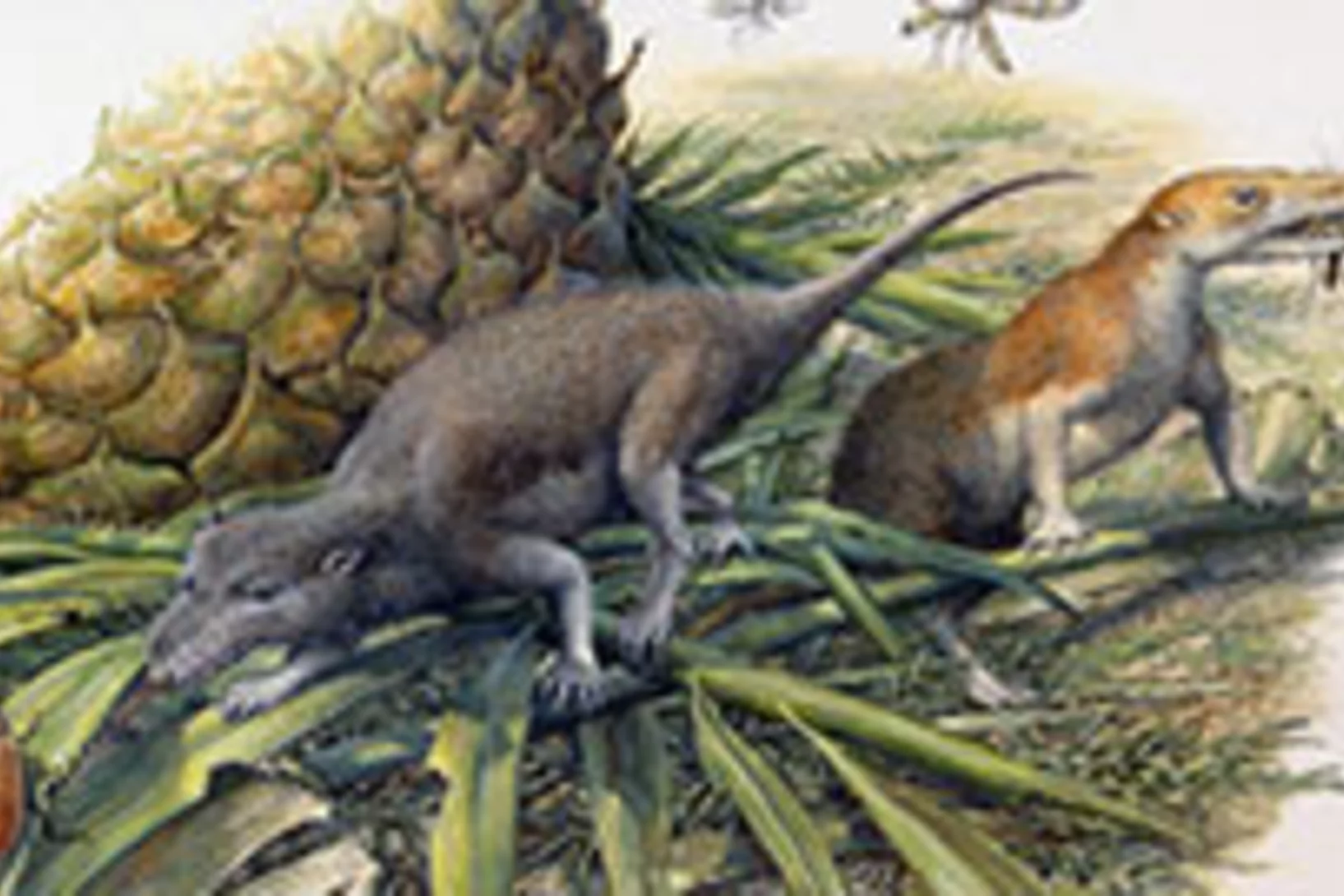
Côté menu, les premiers mammifères avaient déjà leurs préférences
De toutes nouvelles analyses de petits mammifères fossiles livrent de nouveaux éléments sur la connaissance du menu de nos plus lointains ancêtres. Les résultats permettent de comprendre comment sont apparues certaines caractéristiques typiques des mammifères actuels. Ces conclusions reposent sur des analyses, qui ont été réalisées à la Source de Lumière Suisse (SLS) de l’Institut Paul Scherrer, au moyen de la tomographie par rayons X.
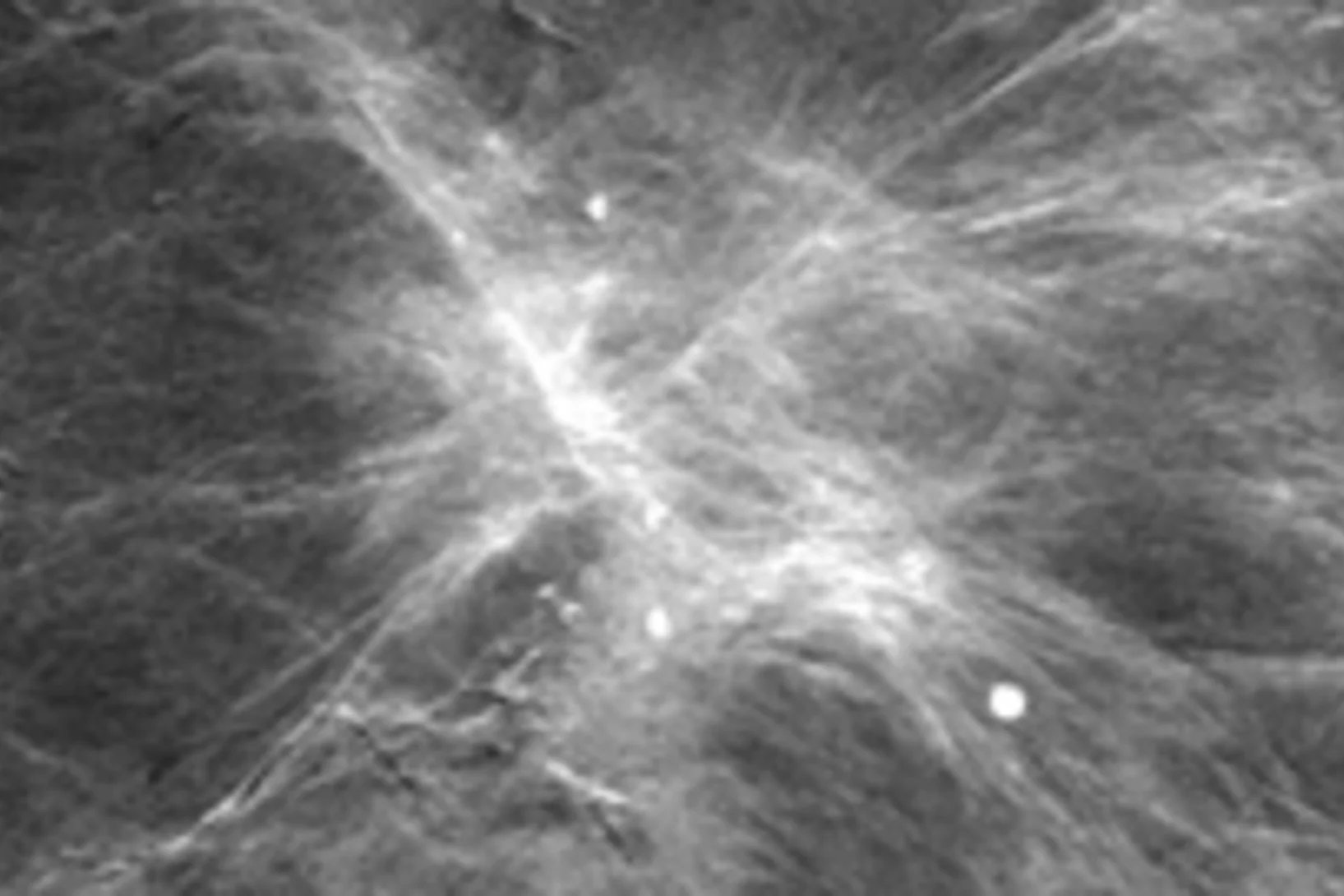
Le contraste de phase améliore la mammographie
Grâce à l'imagerie par contraste de phase, des chercheurs de l’EPF Zurich, de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) et de l’hôpital cantonal de Baden ont réussi à obtenir des mammographies, grâce auxquelles il est possible de procéder à une évaluation plus précise des cancers et des précancers du sein. Ce procédé pourrait contribuer à une utilisation plus ciblée des biopsies, et à l’amélioration des examens de suivi.
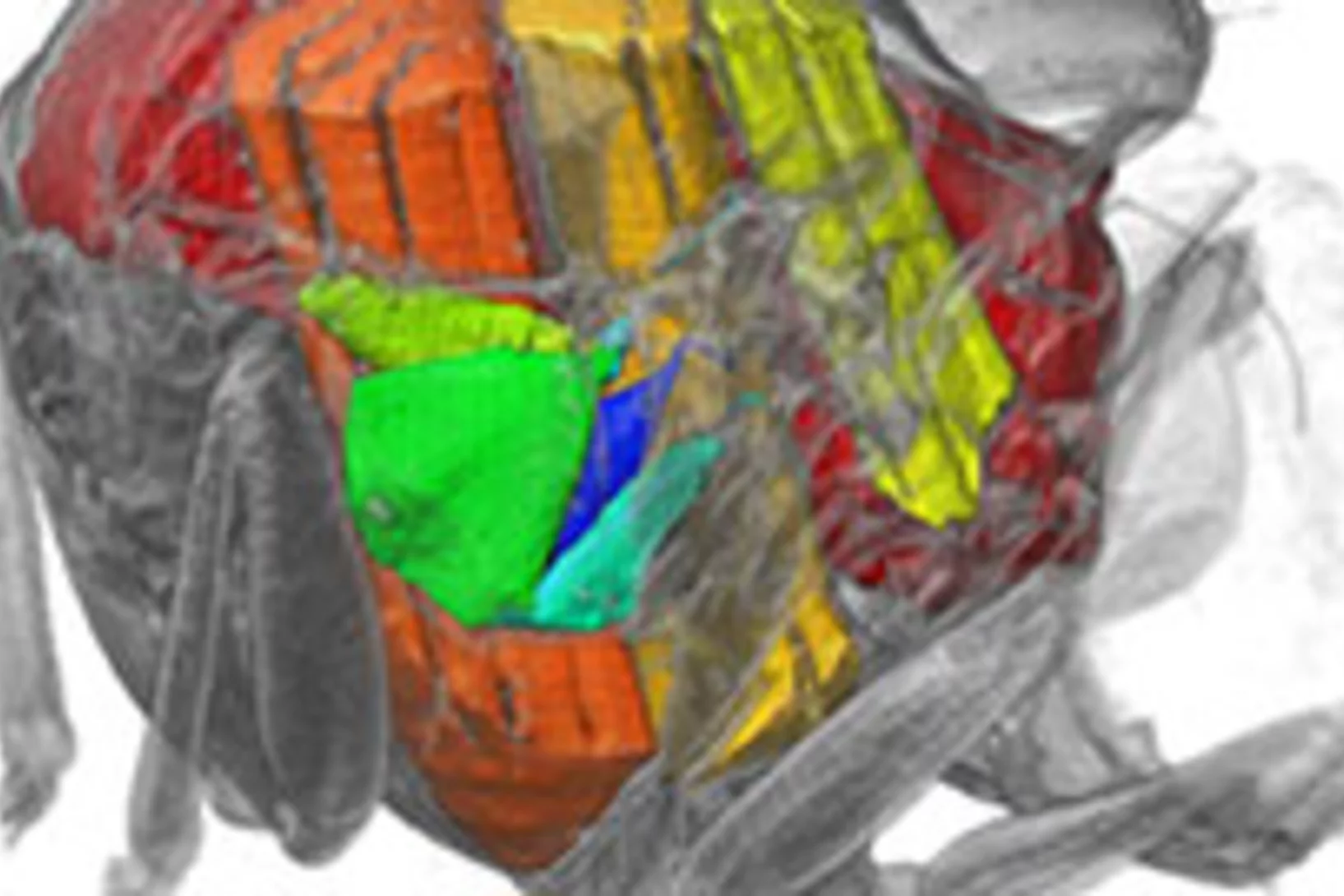
Un film en 3D montre ce qui se passe à l’intérieur d’insectes en plein vol
Grâce aux rayons X produits par la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS, des prises de vue inédites des muscles que les mouches utilisent pour voler (muscles alaires) ont pu être réalisées, à haute vitesse et en 3D. Une équipe de scientifiques de l’Université d’Oxford, de l’Imperial College de Londres et de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) a développé un procédé de prise de vue tomographique révolutionnaire. Grâce à lui, ils ont pu filmer ce qui se passe à l’intérieur d’insectes en plein vol. Ces films permettent de découvrir en profondeur l’un des mécanismes naturels les plus complexes, et montrent que les déformations structurelles sont la clé pour comprendre la manière dont la mouche contrôle son battement d’aile.
Neues Diagnoseverfahren bei Brustkrebs vielversprechend
Ein neues Mammografie-Verfahren könnte laut einer soeben veröffentlichten Studie einen deutlichen Mehrwert für die Diagnose von Brustkrebs in der medizinischen Praxis bringen. Die am PSI in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Brustzentrum des Kantonsspitals Baden und dem Industriepartner Philips entwickelte Methode macht bereits kleinste Gewebeveränderungen besser sichtbar. Dies könnte potenziell die Früherkennung von Brustkrebs verbessern. Zukünftig sollen Studien an Frauen mit einer Brustkrebserkrankung den Mehrwert der Methode endgültig belegen.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.
Mit Röntgenstrahlen der Lebensdauer von Lithium-Ionen-Akkus auf der Spur
Mithilfe von Röntgen-Tomographie haben Forschende die Vorgänge in Materialien von Batterie-Elektroden detailliert untersuchen können. Anhand hochaufgelöster 3D-Filme zeigen sie auf, weshalb die Lebensdauer der Energiespeicher begrenzt ist.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.
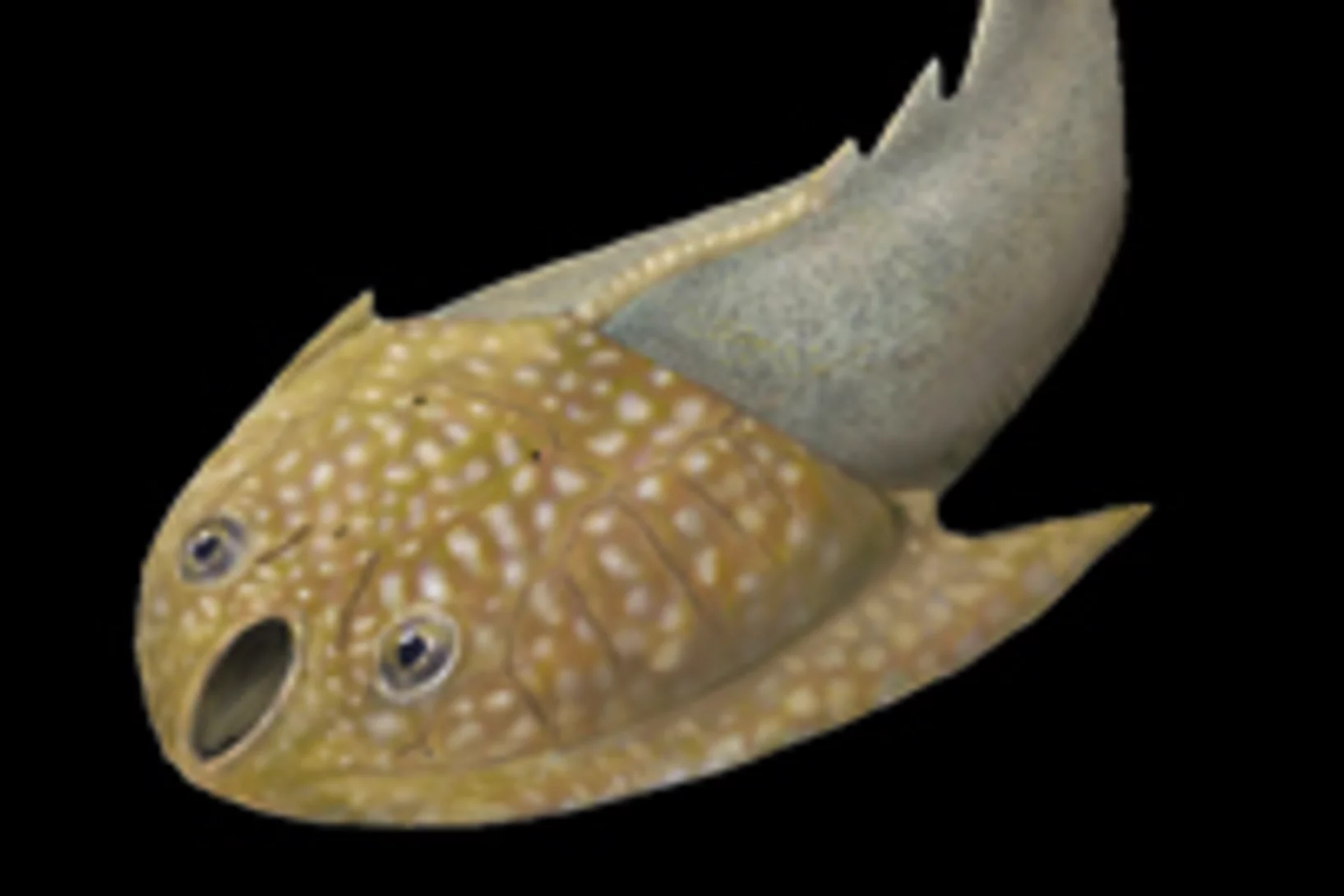
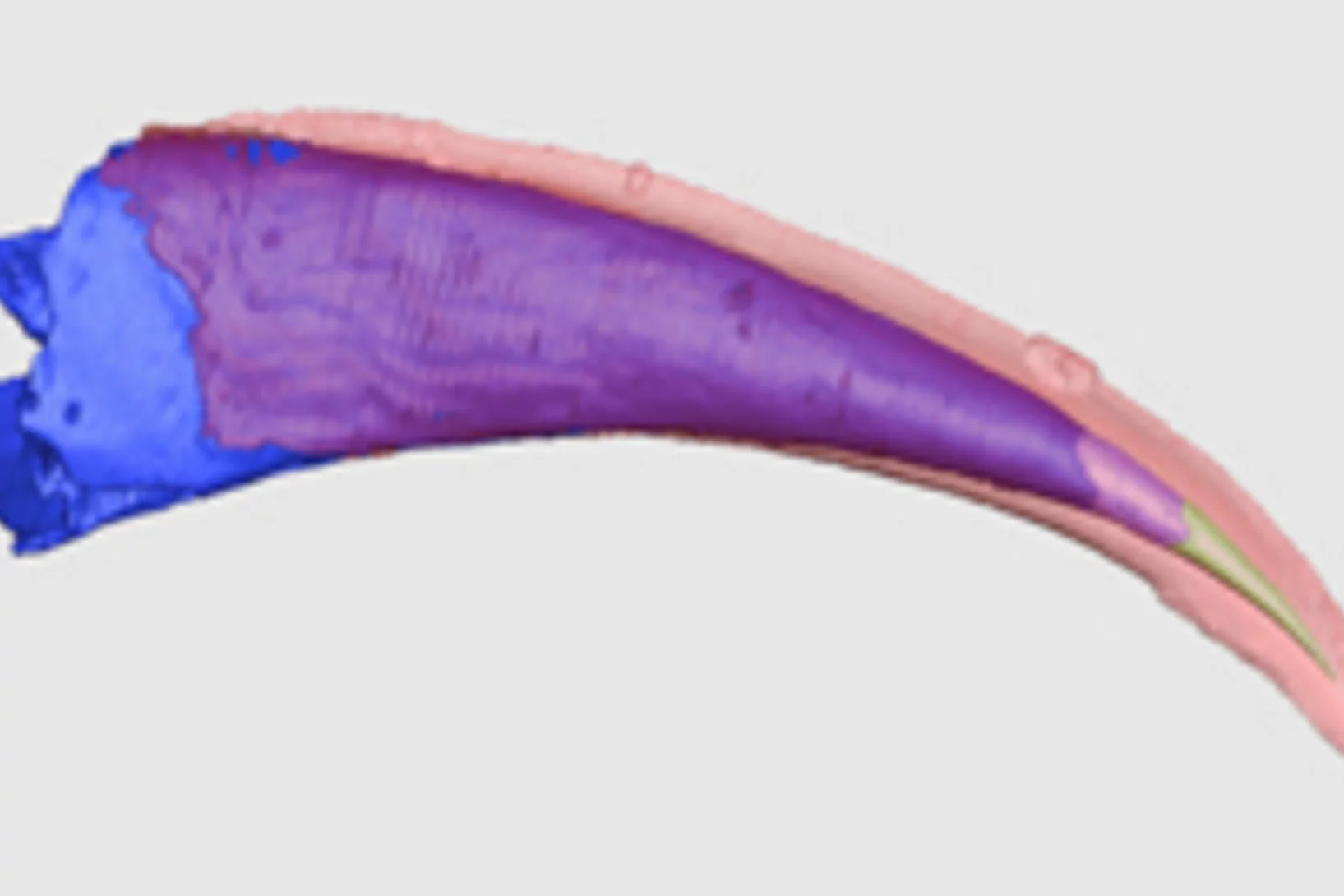
Die Ursprünge der ersten Fische mit Zähnen
Mit Hilfe von Röntgenlicht aus der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz des PSI ist es Paläontologen der Universität Bristol gelungen, ein Rätsel um den Ursprung der ersten Wirbeltiere mit harten Körperteilen zu lösen. Sie haben gezeigt, dass die Zähne altertümlicher Fische (der sogenannten Conodonten) unabhängig von den Zähnen und Kiefern heutiger Wirbeltiere entstanden sind. Die Zähne dieser Wirbeltiere haben sich vielmehr aus einem Panzer entwickelt, der dem Schutz vor den Conodonten, den ersten Raubtieren, diente.
Tout circule : nouvelles possibilités d’observation du comportement des fluides dans les roches poreuses
Grâce à la tomographie computerisé (CT) à rayons X il est possible pour la première fois d’observer directement la circulation du pétrole et de l’eau dans la roche à en 3D, avec une résolution temporelle jamais atteinte jusqu’ici. Cette nouvelle approche, et les informations qu’elle permet d’obtenir, contribuent à mieux comprendre comment différents fluides peuvent se refouler réciproquement dans des matériaux poreux.
L’origine de nos dents du point de vue de l’évolution
Jusqu’à présent, la question de savoir si les premiers vertébrés possédant une mâchoire avaient des dents ou non était sujette à controverse. Mais une équipe de chercheurs internationaux a récemment démontré que le poisson Compagopiscis, un des premiers poissons ayant vécu sur Terre, en possédait. Cela permet d’en déduire que dans l’évolution, les dents sont apparues conjointement avec la mâchoire, ou du moins peu après. Le projet s’est fait sous la direction des chercheurs de l’Université de Bristol (Angleterre), les recherches décisives ont été réalisées au SLS.
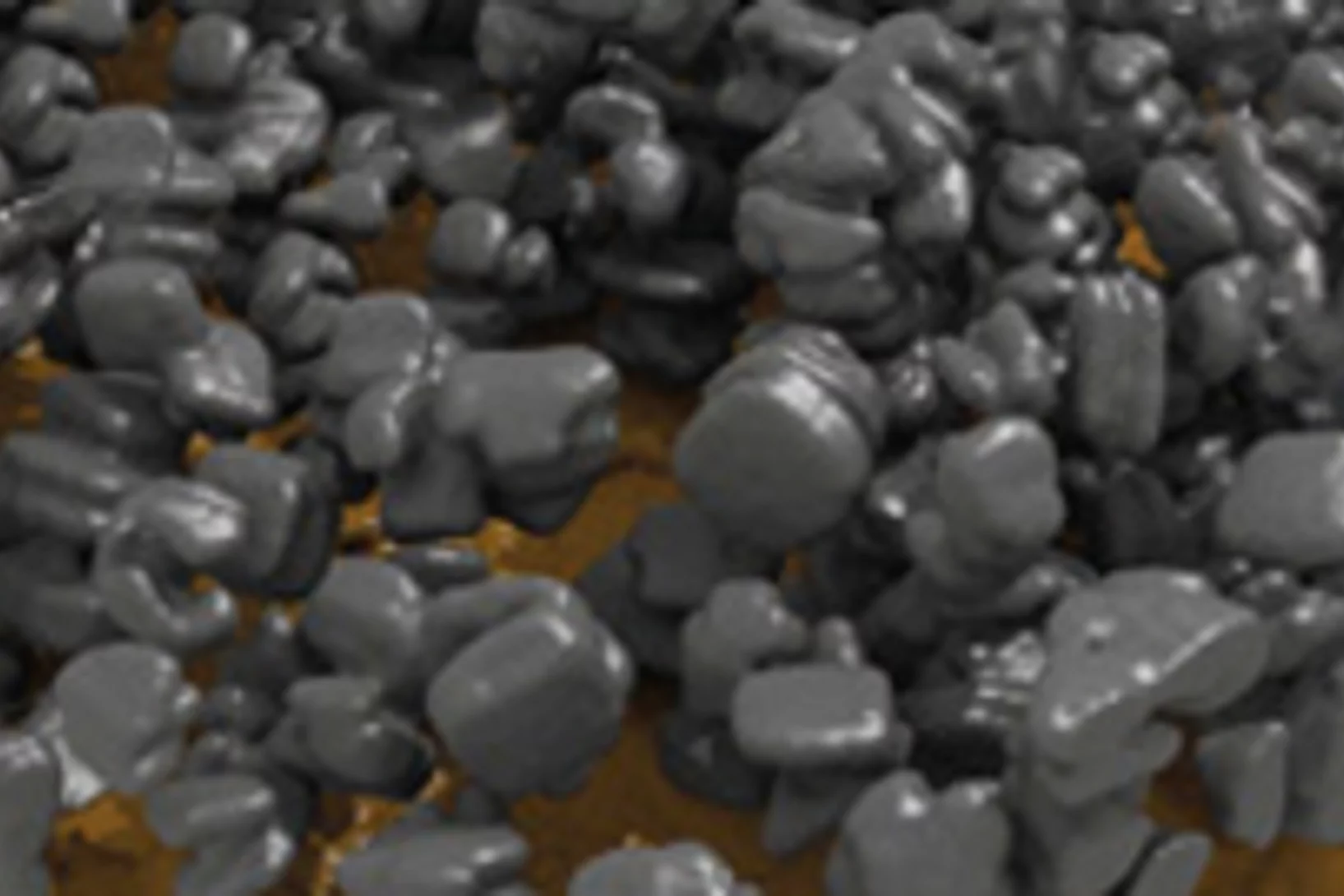
Röntgenlicht liefert Einblicke in die Ursachen von Vulkanausbrüchen
Experimente am Paul Scherrer Institut bieten Einblicke in Vorgänge in vulkanischen Materialien, die darüber entscheiden wie heftig ein Vulkan ausbricht. Dabei haben Forschende ein Stück vulkanisches Material so aufgeheizt, dass darin Bedingungen entstanden, wie sie am Beginn eines Vulkanausbruchs herrschen. Sie nutzten dann Röntgenlicht aus der SLS, um in Echtzeit zu verfolgen, was in dem Gestein passiert, während es schmilzt.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.Sur le site web de l’Université McGill une présentation est disponible en français :Mieux comprendre les éruptions volcaniques
ERC Grant for the development of a new imaging method with high potential clinical impact
Marco Stampanoni, Assistant Professor for X-ray microscopy at the ETH Zürich and Head of the 'X-ray Tomography Group' of the SLS has been recently awarded one of the coveted European Research Council (ERC) Starting Grant for the project PhaseX: 'Phase contrast X-ray imaging for medicine'. Marco Stampanoni's project will be supported by the ERC with 1.5 million euros for the next 5 years. The highly competitive ERC Starting Grants are reserved for outstanding young research talents.
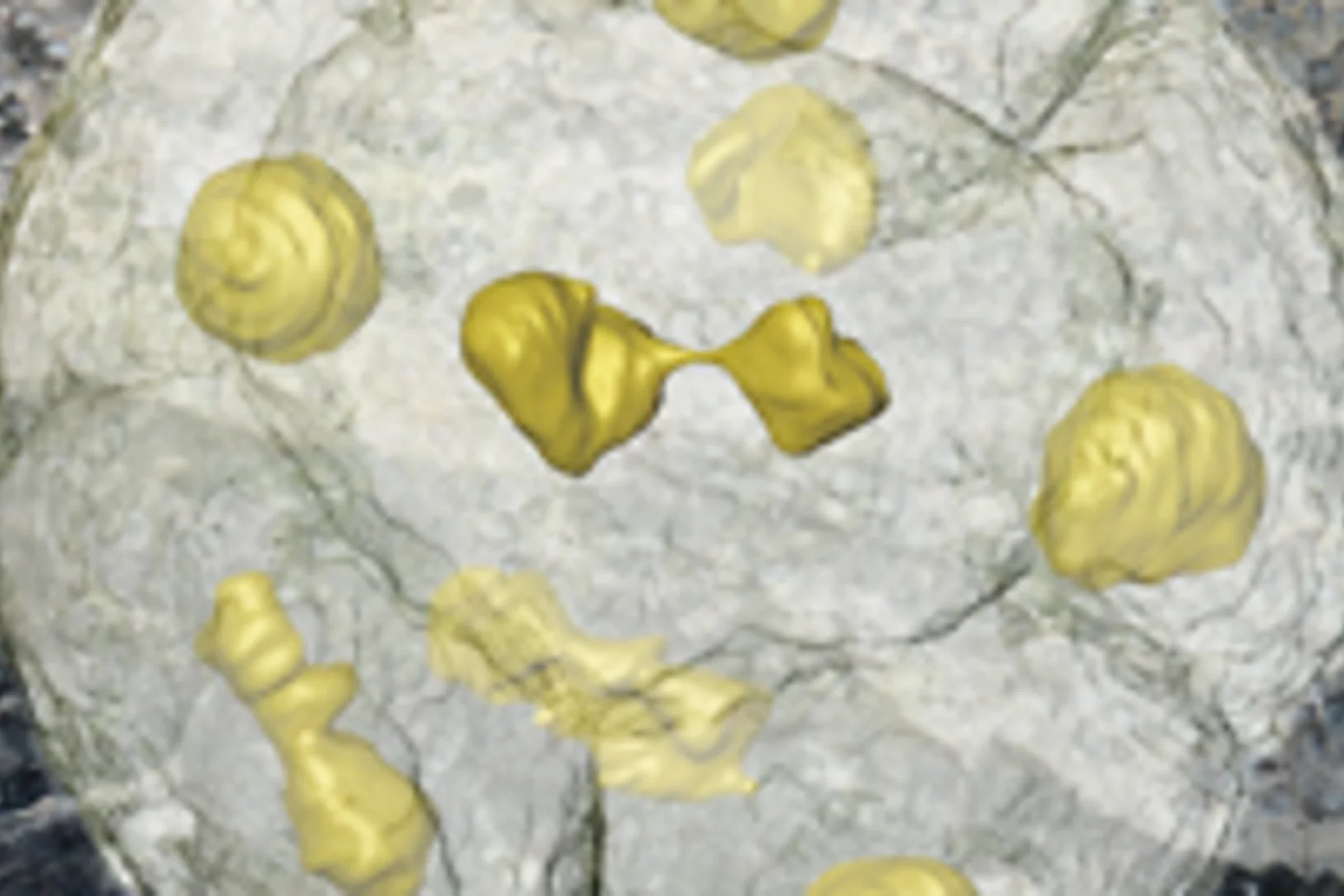
Les plaques amyloïdes de l’Alzheimer en 3D
Des chercheurs ont réussi à générer des images tridimensionnelles détaillées de la distribution des plaques amyloïdes dans le cerveau de souris atteintes de la maladie d’Alzheimer. La nouvelle technique utilisée pour ces travaux de recherche a permis le développement d’une méthode d’analyse extrêmement puissante qui permettra de mieux comprendre la maladie. Les résultats étaient obtenus dans le cadre d’un projet commun de deux équipes de chercheurs à une de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) et de l’EPF Zurich, l’autre de l’École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
Fossile Vorläufer der ersten Tiere
Einzellige Organismen, die vor über einer halben Milliarde Jahre gelebt haben und deren Fossilien in China gefunden wurden, sind wohl die unmittelbaren Vorläufer der frühesten Tiere. Die amöbenartigen Einzeller haben sich in einer Weise in zwei, vier, acht usw. Zellen geteilt, wie es heute tierische (und menschliche) Embryonen tun. Die Forscher glauben, dass diese Organismen einem der ersten Schritte vom Einzeller zum Vielzeller in der Entwicklung richtiger Tiere entsprechen.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Unseren frühen Vorfahren in den Kopf (und in die Nase) geschaut
Der Umbau des Gehirns und der Sinnesorgane dürfte den Erfolg der Wirbeltiere, eines der grossen Rätsel der Evolutionsbiologie, erklären à so die Aussage einer Arbeit, die heute im Wissenschaftsjournal Nature erschienen ist. Die Forschenden konnten das Rätsel durch Untersuchungen des Gehirns eines 400 Millionen Jahre alten versteinerten Fisches à eines evolutionären Bindeglieds zwischen den heute lebenden kiefertragenden Wirbeltieren und den Kieferlosen.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.
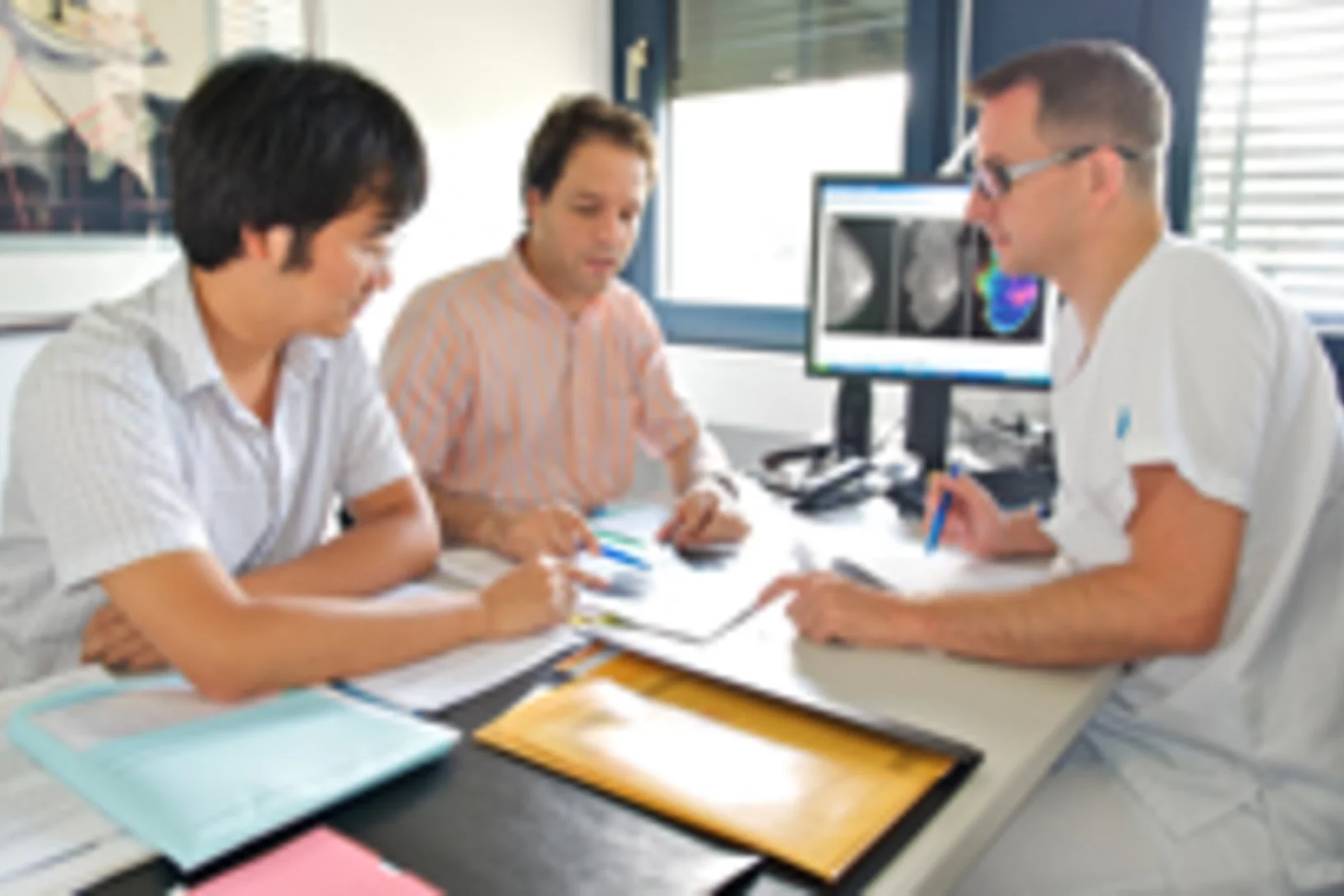
Expérimentation d’une nouvelle méthode pour le dépistage du cancer dans les tissus mammaires
L’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI a développé une nouvelle méthode pour le diagnostic du cancer du sein et a réalisé pour la première fois, en collaboration avec l’hôpital cantonal de Baden AG, des tests sur des tissus humains non conservés. Cette nouvelle méthode permet de révéler des structures invisibles par les techniques de mammographie traditionnelle. Les scientifiques du département de recherche de l’entreprise Philips étudient actuellement l’utilisation de ce procédé dans la pratique médicale.
Universelles Gesetz für Veränderungen in Werkstoffen gefunden
In vielen wichtigen Werkstoffen findet man mehrere Phasen. Wird ein solcher Werkstoff erwärmt, können Atome von der einen Phase zur anderen wandern, so dass sich die Verteilung der Phasen ändert à und damit oft die Eigenschaften des Werkstoffs. Nun haben Forschende für einen wichtigen Fall einer solchen Veränderung gezeigt, dass es eine universelle Gesetzmässigkeit gibt, die den Vorgang beschreibt. Und zwar für alle Werkstoffklassen.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.
Un nouveau procédé de radiographie permet de différencier ce qui, auparavant, avait la même apparence
Sur les images créées au moyen du procédé de contraste de phase, il est possible de distinguer des tissus (muscles, cartilages, tendons ou tumeurs des parties molles) qui présentent pratiquement le même aspect sur des radiographies classiques. Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer et de l’Académie Chinoise des Sciences ont perfectionné le procédé de manière à rendre son utilisation plus simple à l’avenir. Cette nouvelle méthode pourrait permettre d’identifier des tumeurs ou de visualiser des objets dangereux placés dans des bagages.