Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
At the imaging Photoelectron Photoion Coincidence (iPEPICO) endstation of the VUV beamline evidence of H-atom tunneling was shown.
Structure of concrete disease
solved
When bridges, dam walls and other structures made of concrete are streaked with dark cracks after a few decades, the culprit is the so-called the concrete disease. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa have now solved the structure of the material produced in these cracks at atomic level - and have thereby discovered a previously unknown crystalline arrangement of the atoms.
X-ray research in the UFO
At first glance, the Swiss Light Source SLS stands out as a striking building. The inside reveals a setting of cutting-edge research. A journey through a world where electrons race a slalom course and X-rays help decode proteins.
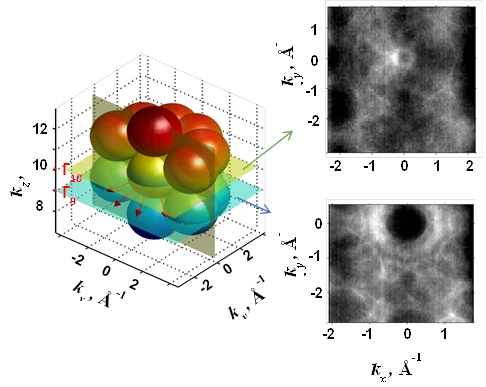
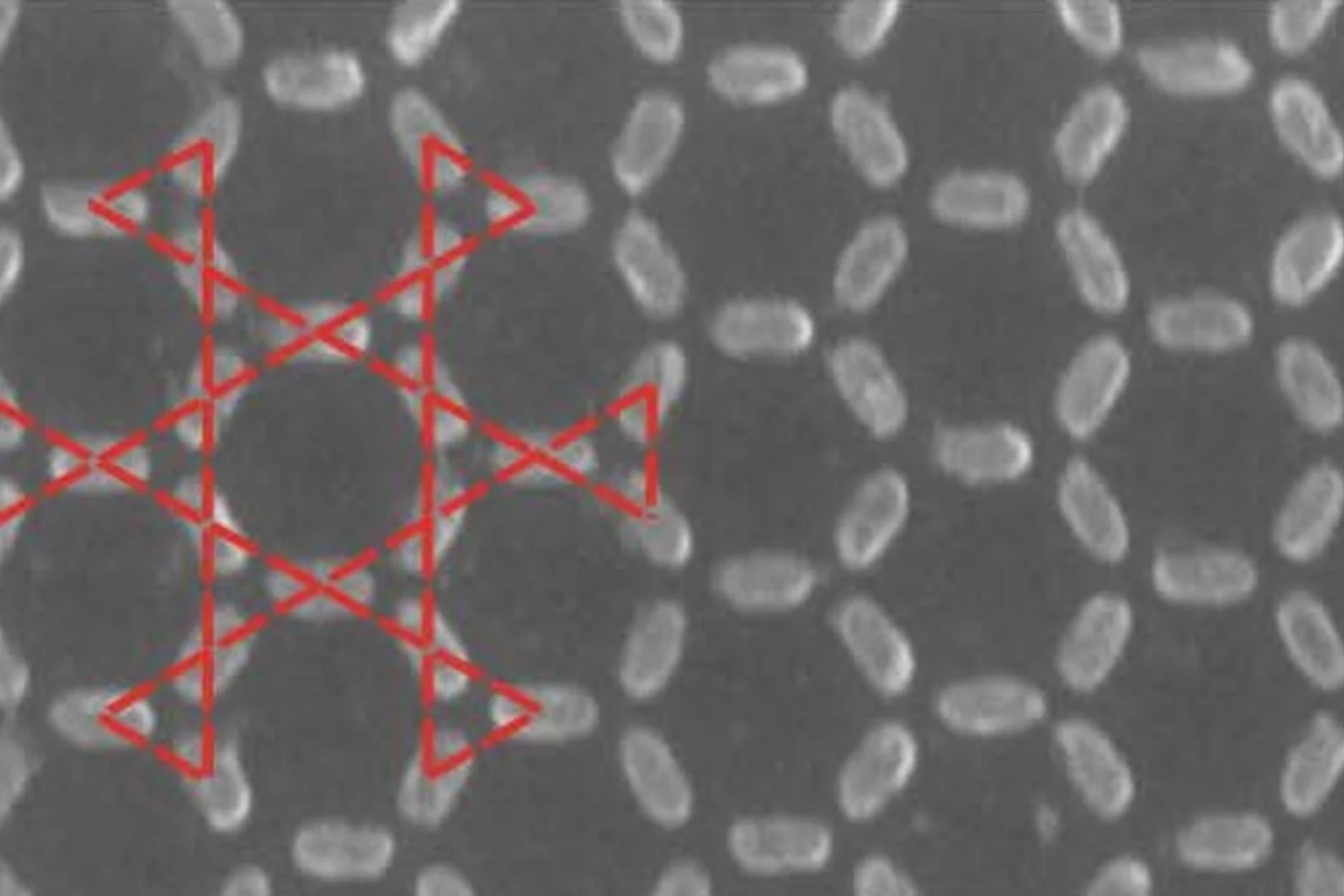
Fermi states and anisotropy of Brillouin zone scattering in the decagonal Al–Ni–Co quasicrystal
Quasicrystals (QCs) are intermetallic alloys where excellent long-range order coexists with lack of translational symmetry in one or more dimensions. These materials have a high potential in application as a material for a solar cells, hydrogen storage applications, heat insulating layers, and others.
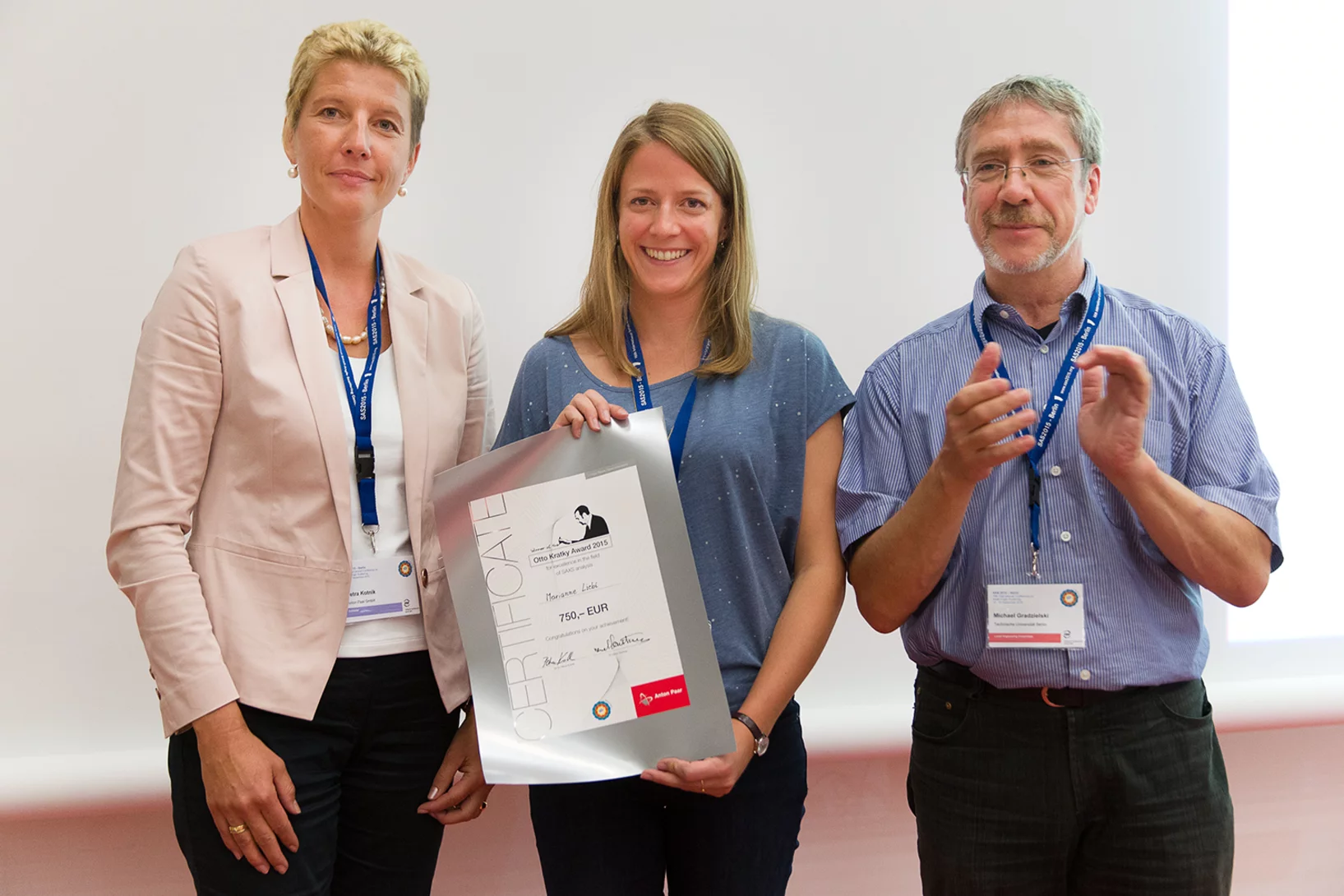
2015 Otto Kratky award
Marianne Liebi was awarded the 2015 Otto Kratky award by the Helmholtz-Centre Berlin for excellence in the field of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis. The award was bestowed in the last SAS2015 conference in Berlin. Marianne is a postdoctoral fellow in the coherent X-ray scattering group (CXS) in PSI, carrying out research in scanning SAXS measurement and analysis in 2D and 3D. Image credit ©HZB/Michael Setzpfandt
Tiny magnets mimic steam, water and ice
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) created a synthetic material out of 1 billion tiny magnets. Astonishingly, it now appears that the magnetic properties of this so-called metamaterial change with the temperature, so that it can take on different states; just like water has a gaseous, liquid and a solid state.
The key to charging a lithium-ion battery rapidly
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are very durable and can be charged relatively quickly. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), ETH Zurich and Japanese car manufacturer Toyota reveal the reasons for these properties in a new study. The findings were made possible thanks to measurements using a new method at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) at PSI.
In search of the smallest bit
For increasingly compact storage media, magnetic areas – the memory bits – also need to become smaller and smaller. But just how small can a magnet be? Frithjof Nolting and his colleagues at the Paul Scherrer Institute investigate the surprising phenomena in the field of nanomagnetism.
In Situ Serial Crystallography Workshop at the SLS
The Macromolecular Crystallography group at SLS is organizing a three days workshop on in situ serial crystallography (http://indico.psi.ch/event/issx) between November 17 and 19, 2015. It will be dedicated in the presentation of a novel method facilitating the structure determination of membrane proteins, which are highly important pharmaceutical targets but are difficult to handle using 'classical' crystallographic tools. Designed for 20 Ph.D. students, postdocs and young scientists from both academia and industry, the workshop will consist of introductory lectures, followed by hands-on practicals on in meso or lipidic cubic phase (LCP) crystallization, on in situ serial crystallography data collection using a micro-sized beam and on data processing.
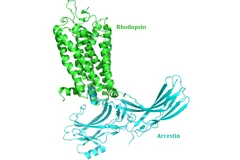
New insight into receptor signalling
A team of 72 investigators across 25 institutions including researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institut obtained the X-ray structure of a rhodopsinàarrestin complex, which represents a major milestone in the area of G-protein-coupled-receptor (GPCR), a protein family recognized in the award of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Element-Specific X-Ray Phase Tomography of 3D Structures at the Nanoscale
Recent advances in fabrication techniques to create mesoscopic 3D structures have led to significant developments in a variety of fields including biology, photonics, and magnetism. Further progress in these areas benefits from their full quantitative and structural characterization.
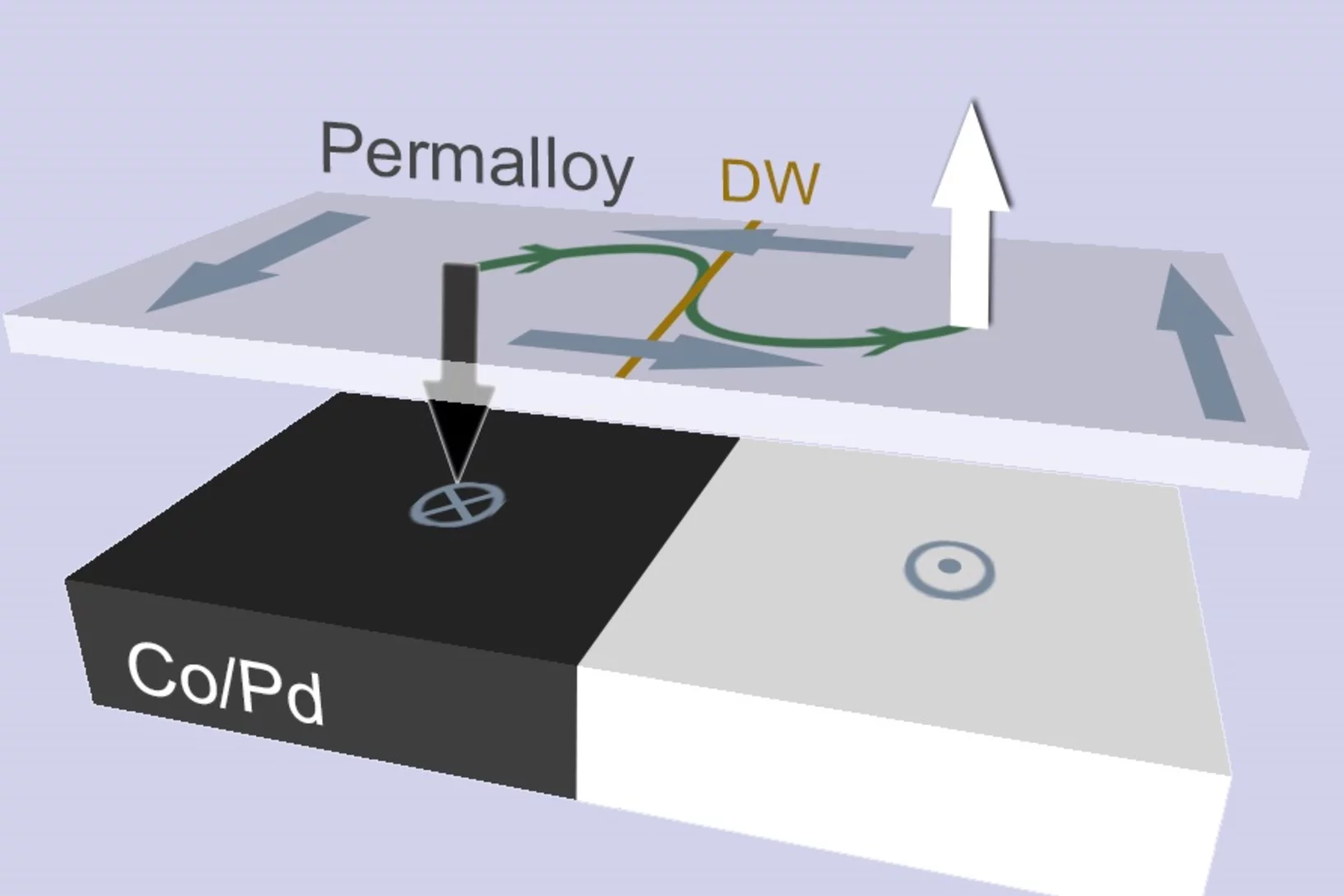
Nanoscale switch for vortex polarization mediated by Bloch core formation in magnetic hybrid systems
Vortices are fundamental magnetic topological structures characterized by a curling magnetization around a highly stable nanometric core.
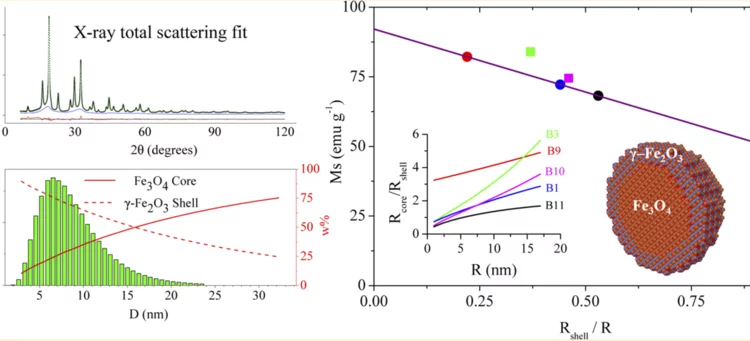
Correlating the Core-Shell Composition and the Surface Structure to the Magnetic Properties for Magnetite-Maghemite Nanoparticles in the 5-15 nm Range
Very small superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles were characterized by innovative synchrotron X-ray total scattering methods and Debye function analysis, developed at the X04SA Materials Science beamline of SLS.
Seven nanometres for the electronics of the future
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute have succeeded in creating regular patterns in a semiconductor material that are sixteen times smaller than in today’s computer chips. As a result, they have taken an important step closer towards even smaller computer components. Industry envisages structures on this scale as the standard for the year 2028.
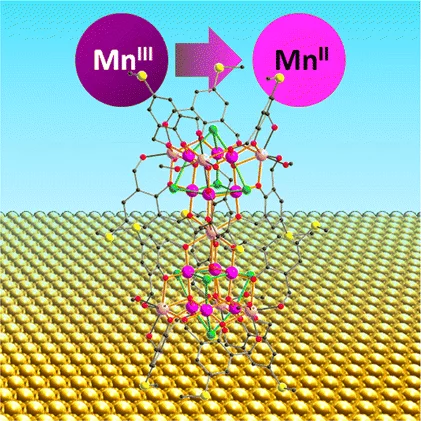
Reduction of Mn19 Coordination Clusters on a Gold Surface
The surface-induced changes of the oxidation state and magnetic properties of Mn ion clusters have been probed by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism.
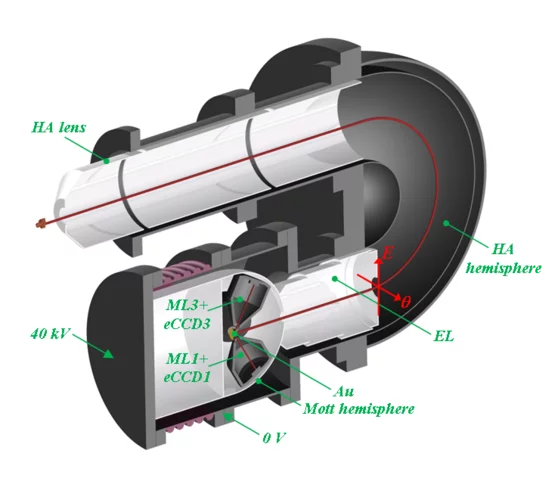
Concept of a multichannel spin-resolving electron analyzer based on Mott scattering
The spin of electron plays a crucial role in many physical phenomena, ranging from the obvious example of magnetism, via novel materials for spintronics applications, to high-temperature superconductivity. Spin- and angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy (SARPES) gives the most direct access to the spin aspects of the electronic structure, but the one-channel detection principle of all presently available SARPES spectrometers severely limits their efficiency. A team of Swiss and Russian scientists has developed a revolutionary concept of a multichannel electron spin detector based on Mott scattering as the spin selective process and imaging-type electron optics.
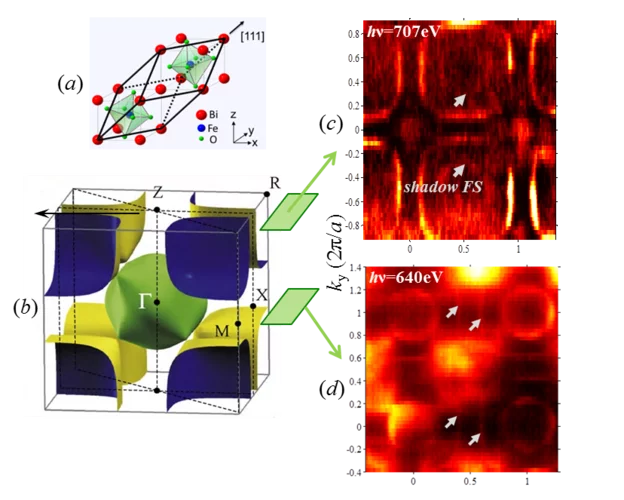
Fermi Surface of Three-Dimensional La1−xSrxMnO3 Explored by Soft-X-Ray ARPES: Rhombohedral Lattice Distortion and its Effect on Magnetoresistance
A research team led by scientists from the Swiss Light Source has for the first time established three-dimensional (3D) electronic structure of the perovskite compound La1−xSrxMnO3 connected with its colossal magnetoresistance. Instrumental for this study has been the use of the new experimental technique of soft-x-ray ARPES, available at the ADRESS beamline, with its intrinsically sharp definition of 3D electron momentum.
Together, not alone
Decoding biomolecules at SwissFEL and SLSProteins are a coveted but stubborn research object. A method developed for x-ray free-electron lasers and PSI’s future SwissFEL should now help researchers to make good headway in this field. It involves x-raying many small, identical protein samples consecutively at short intervals, thereby avoiding the main problem that protein research has faced thus far: producing samples in a sufficient size.
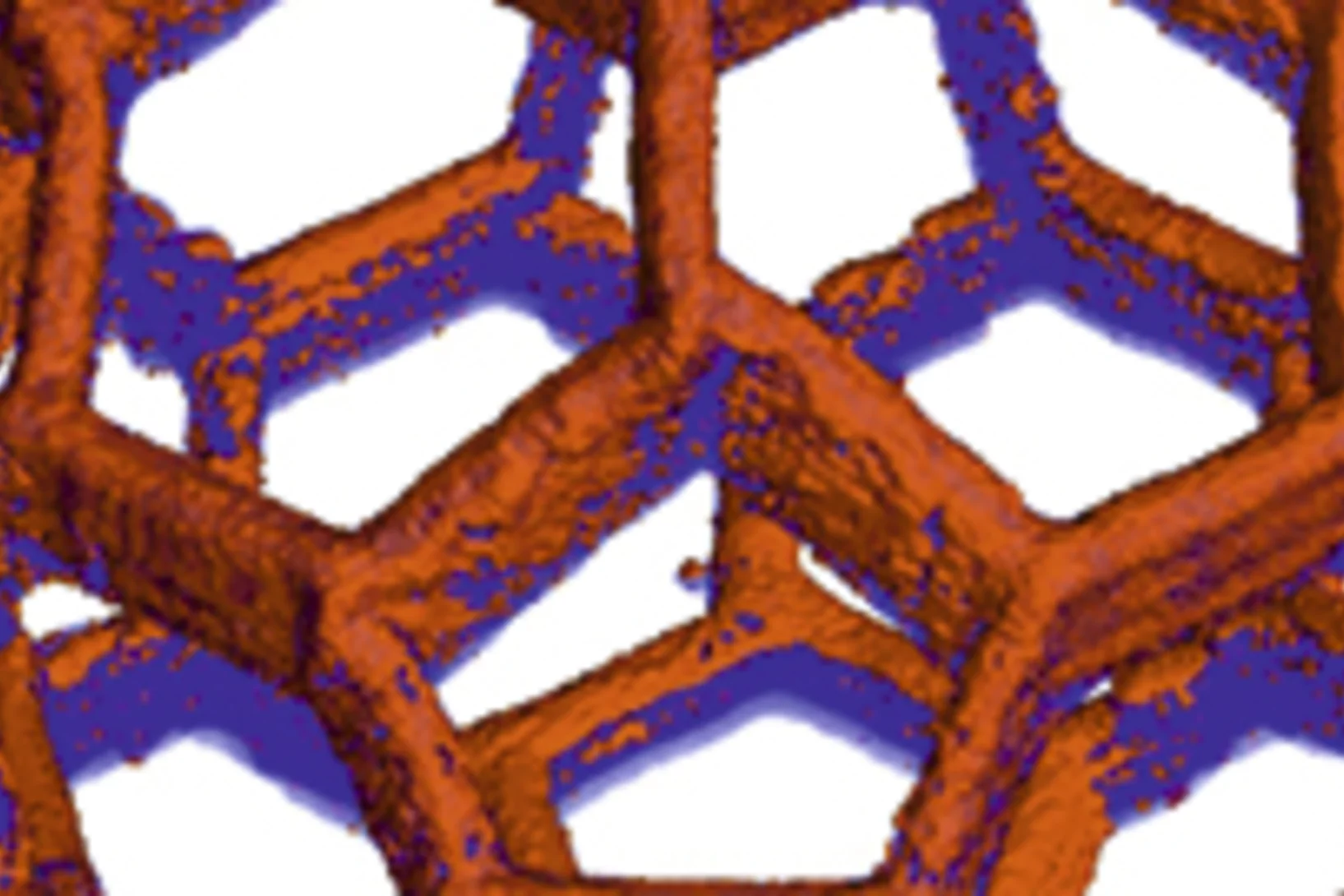
From inside an eggshell
Tiny cavities inside eggshells supply the materials that stimulate and control the shell’s growth. Using a novel imaging technique, researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), ETH Zurich and the Dutch FOM Institute AMOLF have succeeded in depicting these voids in 3D for the first time. In doing so, they lift an old limitation of tomographic images and hope that one day medicine will also benefit from their method.
Research geared towards the future
Interview with Gabriel AeppliGabriel Aeppli has been head of synchrotron radiation and nanotechnology research at PSI since 2014. Previously, the Swiss-born scientist set up a leading research centre for nanotechnology in London. In this interview, Aeppli explains how the research approaches of the future can be implemented at PSI's large research facilities and talks about his view of Switzerland.
Multiresolution X-ray tomography, getting a clear view of the interior
Researchers at PSI have developed a technique that combines tomography measurements at different resolution levels to allow quantitative interpretation for nanoscale tomography on an interior region of interest of the sample. In collaboration with researchers of the institute AMOLF in the Netherlands and ETH Zurich in Switzerland they showcase their technique by studying the porous structure within a section of an avian eggshell. The detailed measurements of the interior of the sample allowed the researchers to quantify the ordering and distribution of an intricate network of pores within the shell.
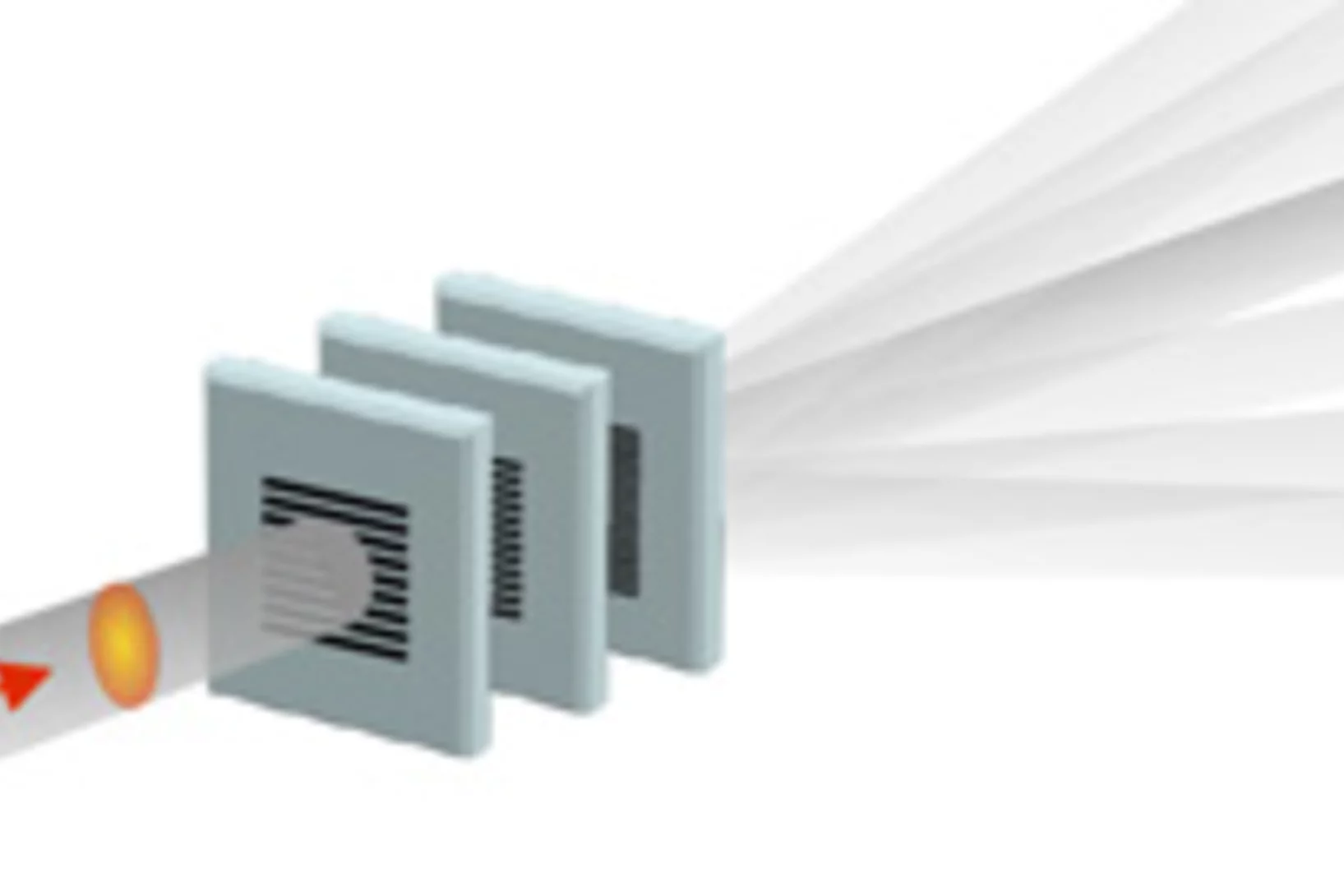
Split x-ray flash shows rapid processes
SwissFEL, PSI’s x-ray laser, is to render the individual steps of very rapid processes visible. A new method will facilitate especially precise experiments: the individual x-ray flashes are split into several parts that arrive at the object under examination one by one. The principle of the method harks back to the ideas of the earliest high-speed photography.
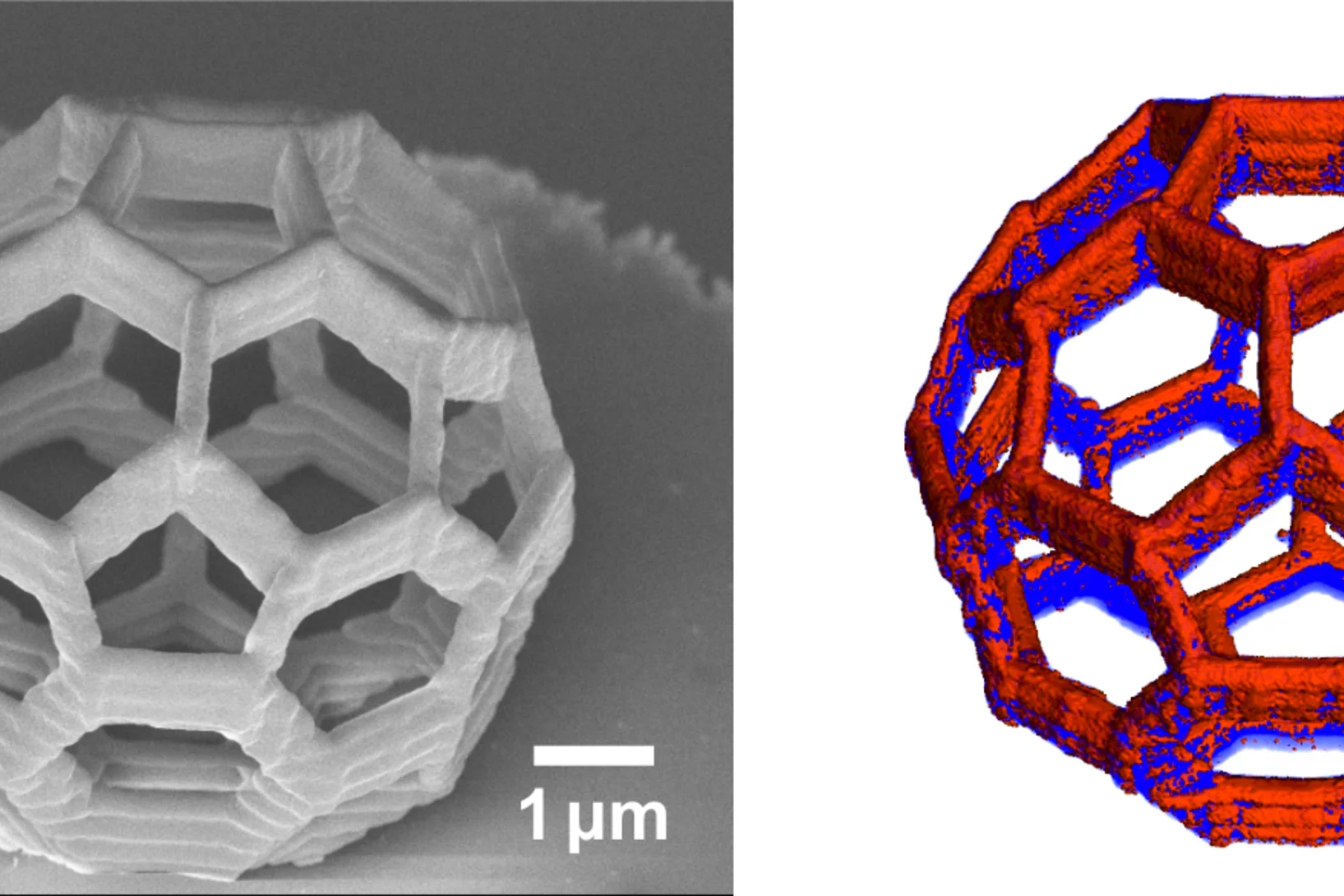
Nanometres in 3D
Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute and ETH Zurich have created 3D images of tiny objects showing details down to 25 nanometres. In addition to the shape, the scientists determined how particular chemical elements were distributed in their sample and whether these elements were in a chemical compound or in their pure state.
Prepared for the SwissFEL
For many years, PSI researchers have been testing experimental methods that will provide insights into novel materials for electronic devices. Using a special trick to make the Swiss Light Source (SLS) at PSI generate light with similar properties to that of PSI’s x-ray laser SwissFEL, the researchers were able to demonstrate that the experiments planned for SwissFEL are possible and they are now building an experimental station at SwissFEL.
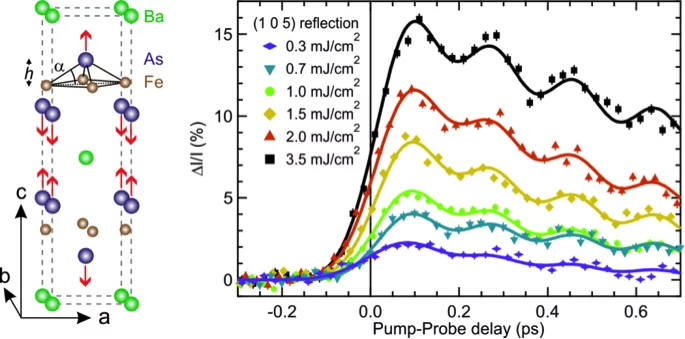
Ultrafast structural dynamics of the Fe-pnictide parent compound BaFe2As2
Understanding the interplay of the various degrees of freedom such as the electrons, spins and lattice is essential for many complex materials, including the high-temperature superconductors.
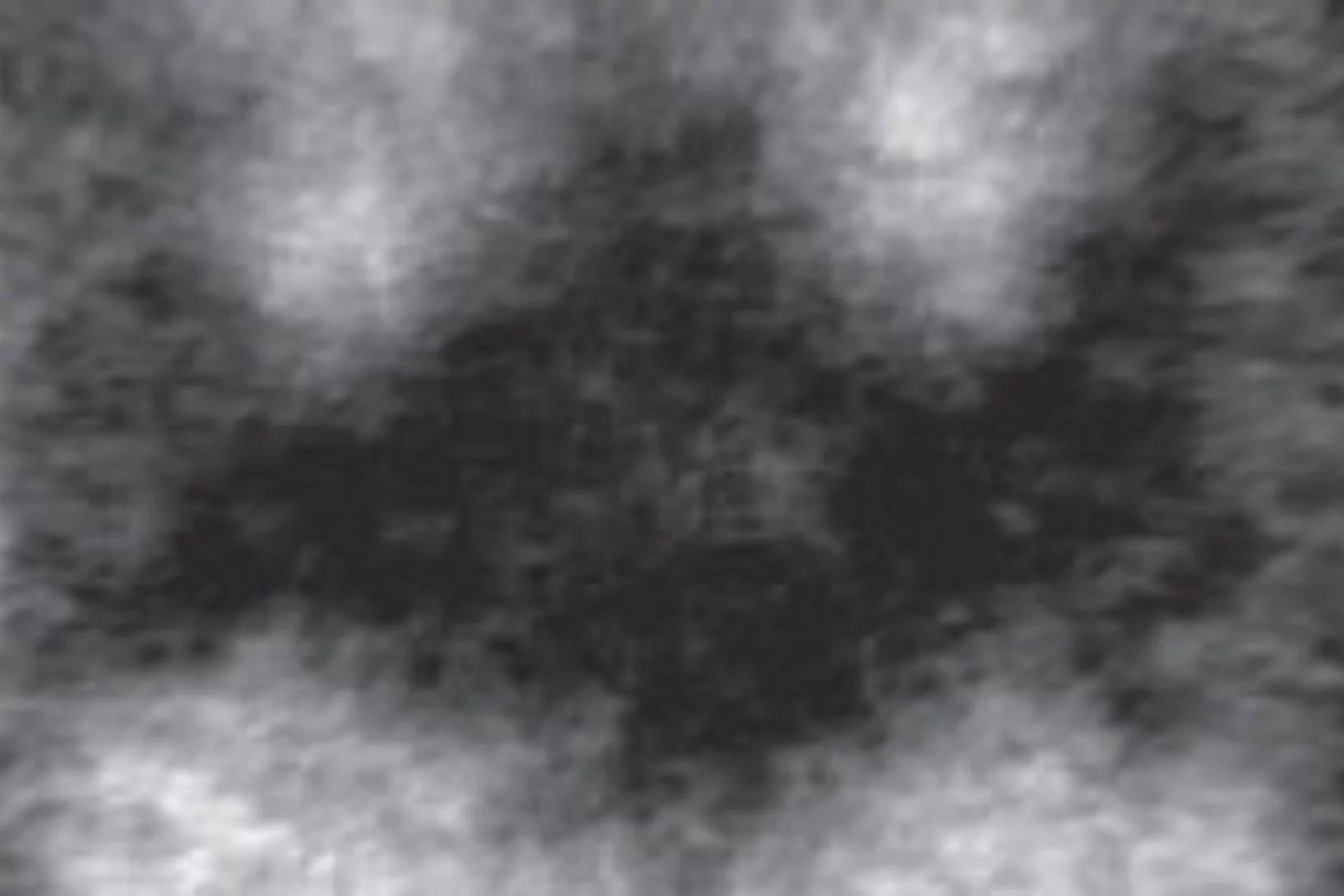
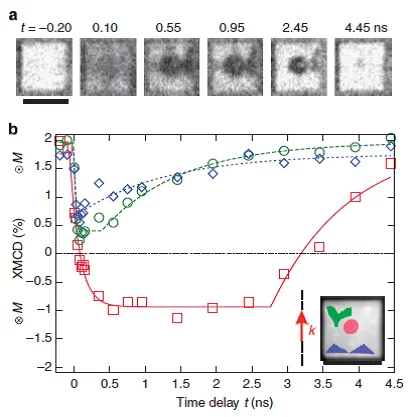
Batman lights the way to compact data storage
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have succeeded in switching tiny, magnetic structures using laser light and tracking the change over time. In the process, a nanometre-sized area bizarrely reminiscent of the Batman logo appeared. The research results could render data storage on hard drives faster, more compact and more efficient.
Nanoscale sub-100 picosecond all-optical magnetization switching in GdFeCo microstructure
Ultrafast magnetization reversal driven by femtosecond laser pulses has been shown to be a promising way to write information. Seeking to improve the recording density has raised intriguing fundamental questions about the feasibility of combining ultrafast temporal resolution with sub-wavelength spatial resolution for magnetic recording. Here we report on the experimental demonstration of nanoscale sub-100 ps all-optical magnetization switching, providing a path to sub-wavelength magnetic recording.