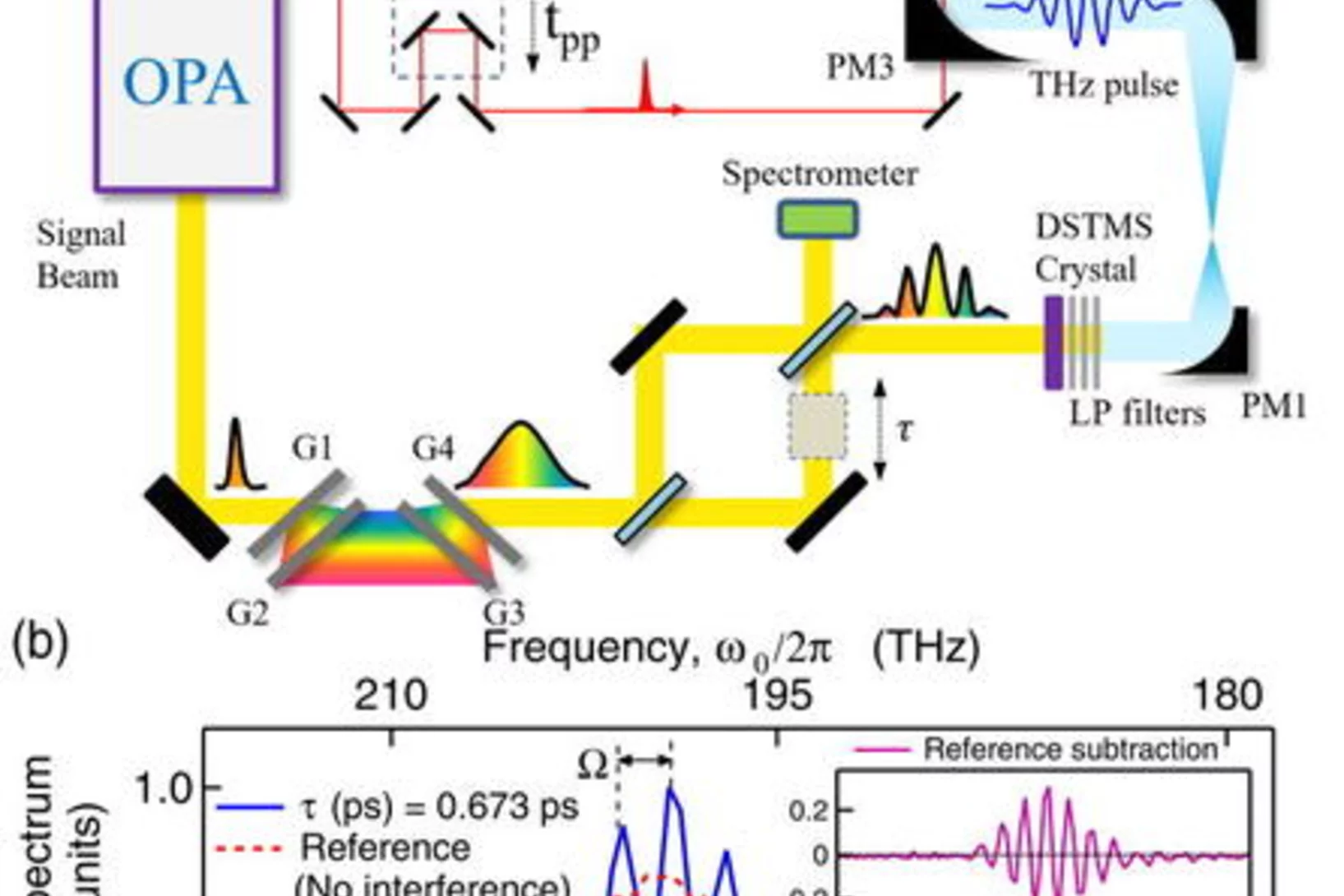
Narrow-band and tunable intense terahertz pulses for mode-selective coherent phonon excitation
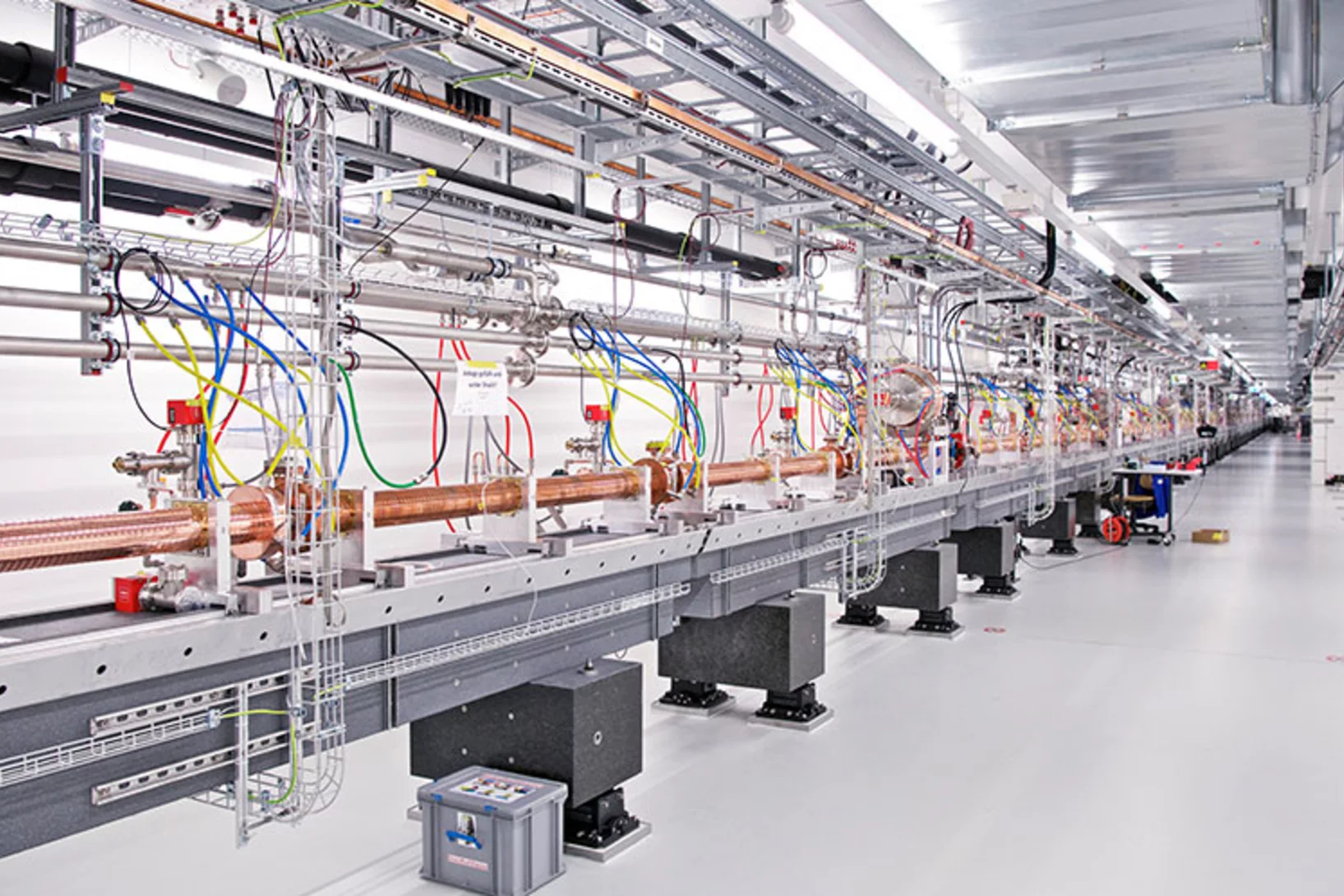
We generate frequency-tunable narrow-band intense fields in the terahertz (THz) range by optical rectification of a temporally modulated near-infrared laser pumping a nonlinear organic crystal.
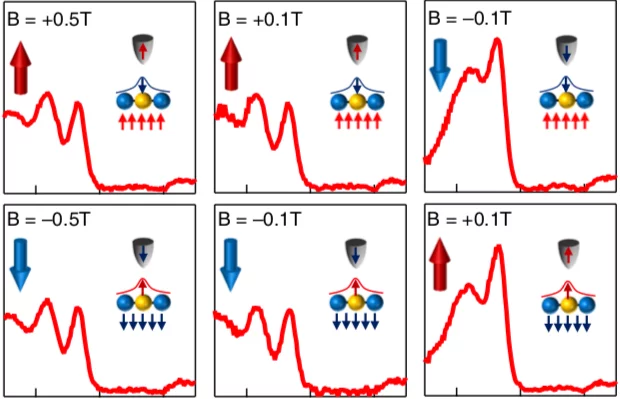
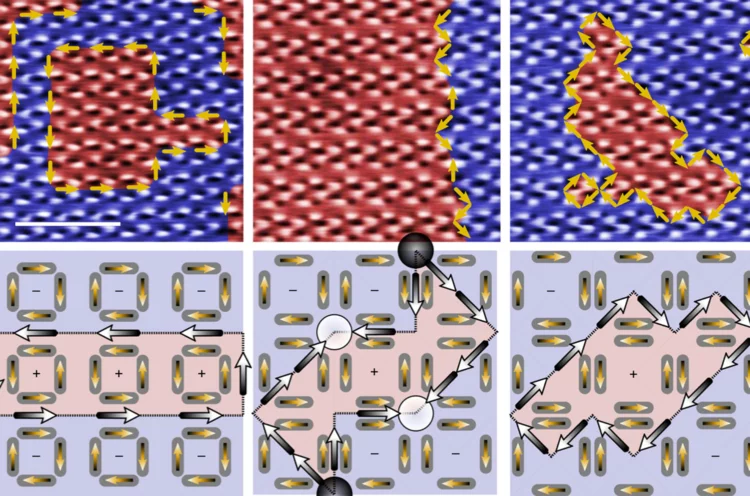
Spin-orbit quantum impurity in a topological magnet
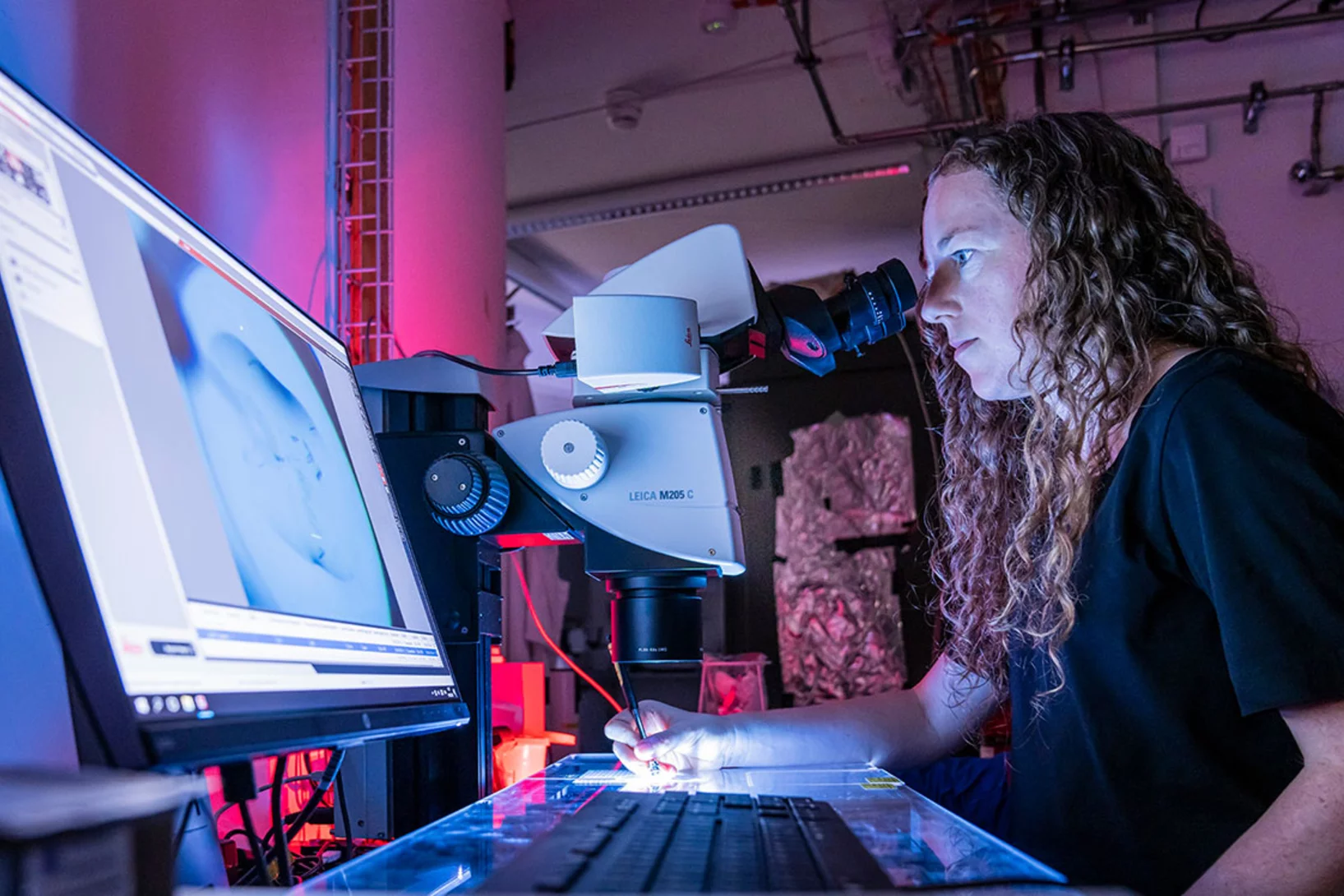
Quantum states induced by single-atomic impurities are at the frontier of physics and material science. While such states have been reported in high-temperature superconductors and dilute magnetic semiconductors, they are unexplored in topological magnets which can feature spin-orbit tunability. Here we use spin-polarized scanning tunneling microscopy/ spectroscopy (STM/S) to study the engineered quantum impurity in a topological magnet Co3Sn2S2. We find that each substituted In impurity introduces a striking localized bound state.
«Forschung online erleben»: Mittendrin statt nur dabei
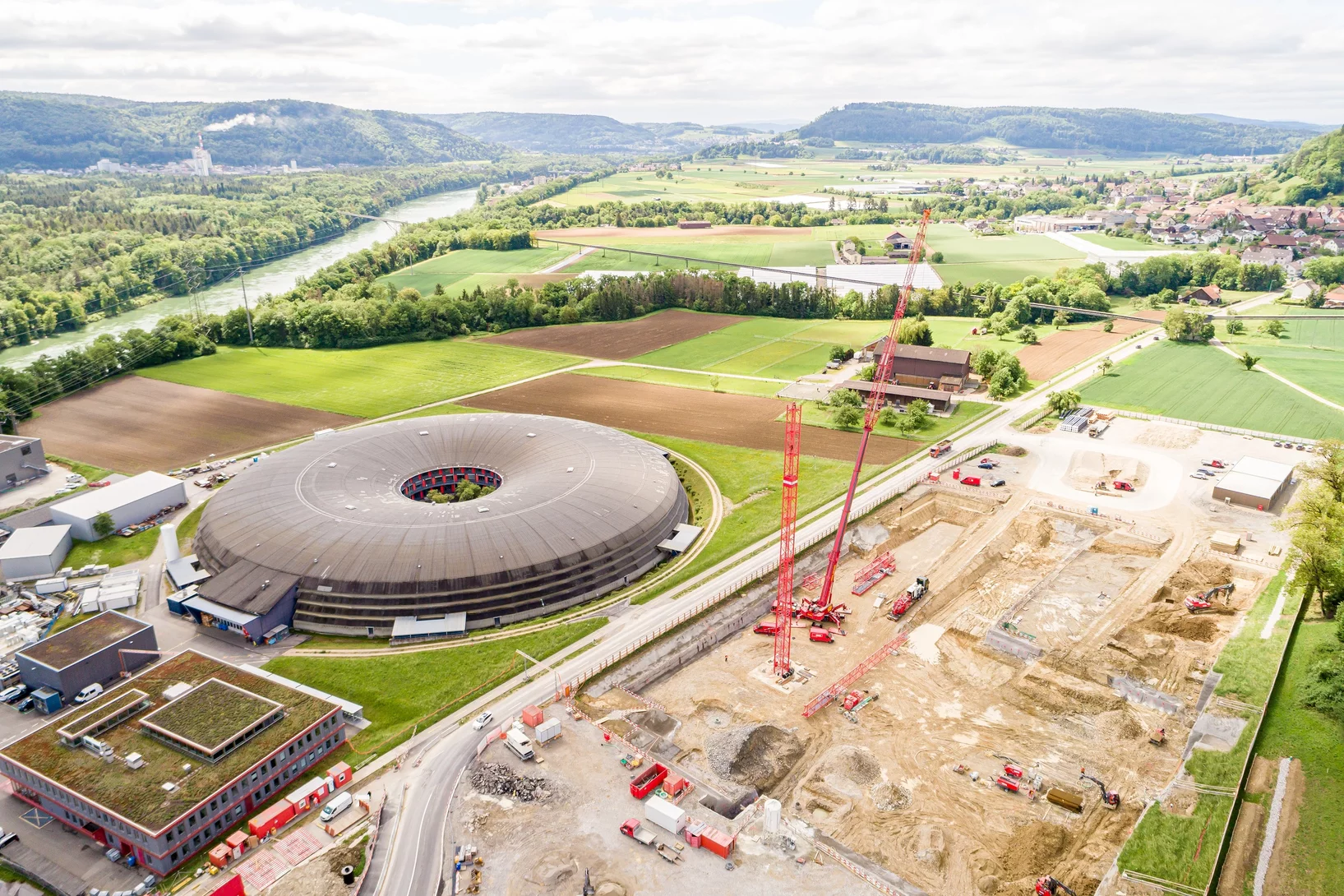
Erstmals Live-Rundgang durch eine Grossforschungsanlage per Video-Stream. Am 9. September haben Interessierte exklusiv die Möglichkeit, sich von Experten des PSI durch den neuen Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL führen zu lassen und zu erfahren, welche Rätsel der Materie und der Natur sich damit lösen lassen.
A question of binding
At PSI, researchers are screening molecule fragments to see if these bind to important proteins of the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and thus have the potential to disable it. They are hoping the many individual pieces of information will yield an answer as to what an effective drug might look like.
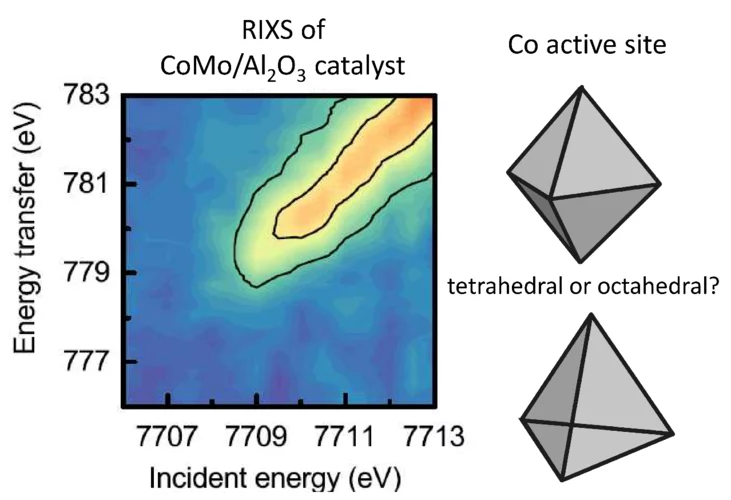
The structure of active sites of CoMo/Al2O3 catalysts determined by RIXS spectroscopy.
A fundamental understanding of the active sites in technical CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts is crucial to improve the production of clean transportation fuels by hydrodesulfurization (HDS), which removes sulfur from fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide, resulting from fossil fuel combustion, is one of the main causes for acid rain. In situ X-ray spectroscopic experiments at the SuperXAS beamline of the SLS provided insight in the structure and number of active sites (“Co−Mo−S”) in sulfided CoMo/ Al2O3 catalysts. When the Co to Mo ratio is less than 0.1, cobalt forms isolated sites on the MoS2 phase, where the cobalt promoter atoms are in centrosymmetric octahedral coordination with six-sulfur ligands.
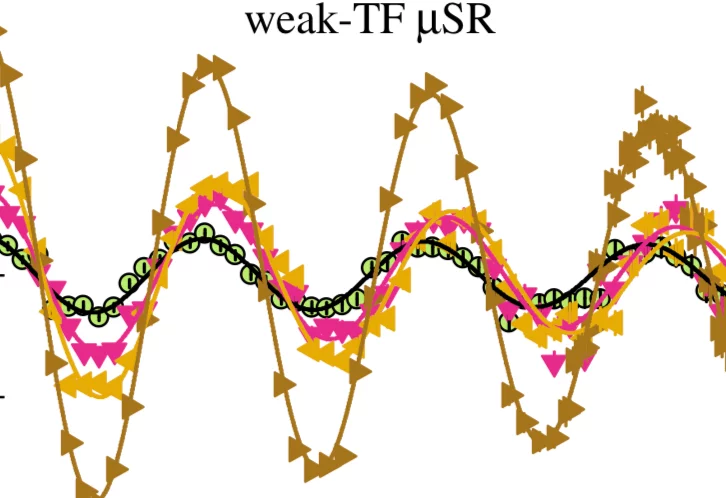
Using Uniaxial Stress to Probe the Relationship between Competing Superconducting States in a Cuprate with Spin-stripe Order
We report muon spin rotation and magnetic susceptibility experiments on in-plane stress effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity in the cuprate system La2−xBaxCuO4 with x = 0.115. An extremely low uniaxial stress of ∼0.1 GPa induces a substantial decrease in the magnetic volume fraction and a dramatic rise in the onset of 3D superconductivity, from ∼10 to 32 K.
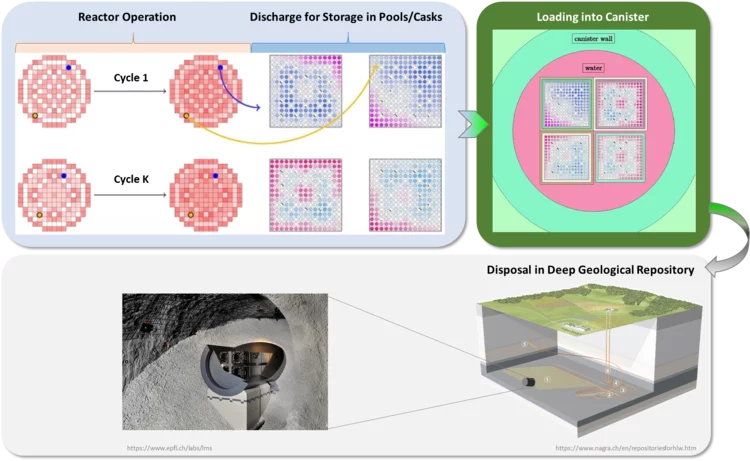
Used Nuclear Fuel: from Better Characterization to Better Optimization
A safe, economical and environmental friendly disposal of used nuclear fuel represents an essential objective of relevance for all. This guides the approach under development at the laboratory for reactor physics and thermal-hydraulics. Establish higher resolution simulation methods to gain more detailed knowledge on the content of each single nuclear fuel rod ever irradiated in a reactor. Thereafter, use this knowledge to explore optimization approaches that could potentially enlarge the range of disposal options allowing to fulfill the highest level of safety standards while reducing economical costs and geological footprints at the same time.
Scientists develop a new kind of qubit based on the concept of Schrödinger’s cat
Scientists in the Applied Physics department of Yale University – one of the leading authors, Alexander Grimm, has in the meantime relocated to PSI – have developed a new device that combines the Schrödinger’s cat concept of superposition (a physical system existing in two states at once) with the ability to fix some of the trickiest errors in a quantum computation.
Park Innovaare: The new building is proceeding according to plan
Since the ground-breaking ceremony for the Park Innovaare last November, the construction of the new Innovation Park has been progressing at a rapid pace. Research and industry will work closely together there to bring innovations to market. The new building should be ready for occupancy by the end of 2023.
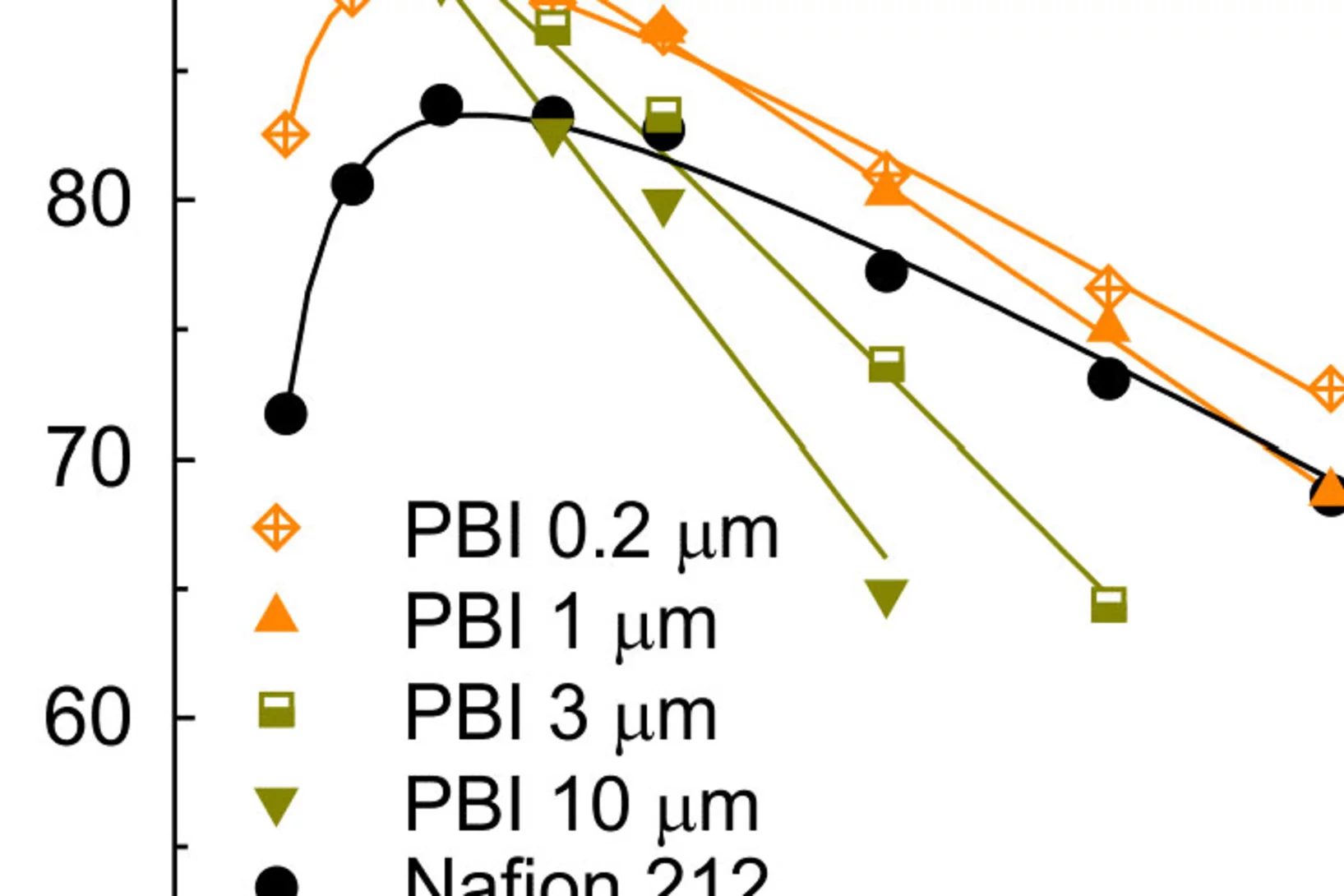
Bilayer Composite Membrane for the Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
The vanadium redox flow battery (VRFB) is designed for grid-scale energy storage applications. Ion-exchange membranes are performance and cost relevant components of redox flow batteries. Currently used materials are largely ‘borrowed’ from other applications that have different functional requirements. For next generation VRFBs, it would be desirable to develop membrane materials based on low-cost porous separators with low resistance and high transport selectivity to minimize vanadium-ion and electrolyte crossover.
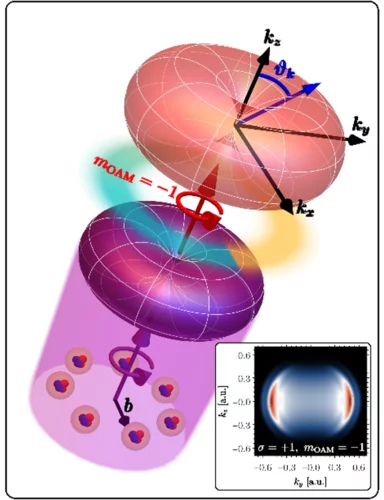
Photoelectric Effect with a Twist
In a joint research effort, an international team of scientists lead by Prof. Giovanni de Ninno (University of Nova Gorica, Elettra Sincrotrone Trieste) now demonstrated that an OAM-dependent dichroic effect can be observed on photoelectrons. The photoelectrons are released from a sample of He atoms that is excited by the strong extreme ultraviolet light pulses from the FERMI free electron laser, whereas the orbtial momentum is imprinted with an intense infrared laser pulse. The X-ray Optics and Applications group of PSI supported the team with their experience in the creation of OAM beams and during the experiments.
Lehrabschlussfeier 2020
Stolz, mit viel Freunde und dem "nötigen Abstand" durften wir am Freitag, 14. August 25 neue Berufsleute feiern. Sie schlossen ihre Berufslehre mit einem tollen Noten-Durchschnitt und einer Höchstnote von 5.9 ab. Wir gratulieren herzlich und sind sehr stolz auf sie!
«We're making SLS fit for the future»
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to get an upgrade to make excellent research possible in the coming decades as well. Hans Braun, SLS 2.0 project leader, talks about this undertaking in an interview.
Einführungswoche 2020
Unter erschwerten Bedingungen haben wir gestartet ...
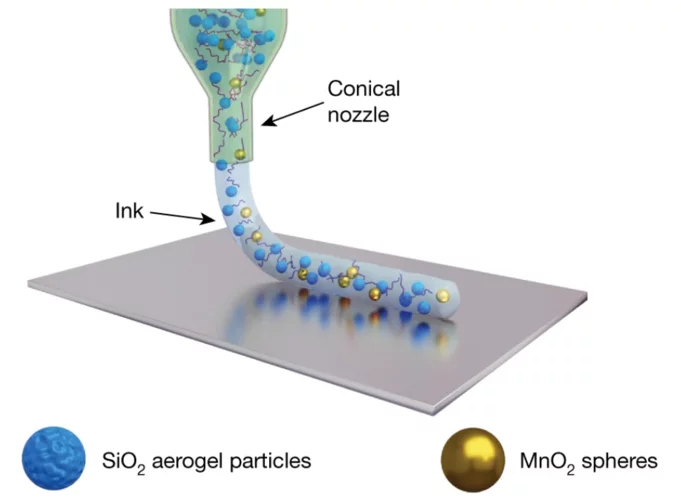
3D printing silica aerogels at the micrometer scale
A group of EMPA and ETH Zürich researchers have developed a new method to directly write ink made of silica aerogels in 3D. Thanks to X-ray phase contrast tomography at the TOMCAT beamline they characterized the resulting printed material with different compositions. Their results were published in Nature on August 18, 2020.
3D printing silica aerogels at the micrometer scale
A group of EMPA and ETH Zürich researchers have developed a new method to directly write ink made of silica aerogels in 3D. Thanks to X-ray phase contrast tomography at the TOMCAT beamline they characterized the resulting printed material with different compositions. Their results were published in Nature on August 18, 2020.
Novel optics enable better X-ray Free Electron Laser experiments
Our research on multifocus off-axis zone plates was accepted in “Optica”, the highest impact journal of the Optical Society of America. In the paper we report on different ways to combine focusing and beam-splitting functionalities in one single optical element.
Global Fit to Modified Neutrino Couplings and the Cabibbo-Angle Anomaly
Recently, discrepancies of up to 4σ between the different determinations of the Cabibbo angle were observed. In this context, we point out that this “Cabibbo-angle anomaly” can be explained by lepton flavor universality violating new physics in the neutrino sector. However, modified neutrino couplings to standard model gauge bosons also affect many other observables sensitive to lepton flavor universality violation, which have to be taken into account in order to assess the viability of this explanation.
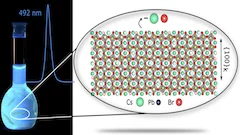
X-rays illuminate the particle atomic structure of cyan light emitting 6-monolayers CsPbBr3 nanoplatelets by Total Scattering
A cyan light (492 nm) emitting colloidal suspension of CsPbBr3 nanoplatelets in a flask, together with the high-quality XRPD Total Scattering pattern of the suspension measured at the X04SA-MS beamline and the full-nanoparticle structure thereby inferred.
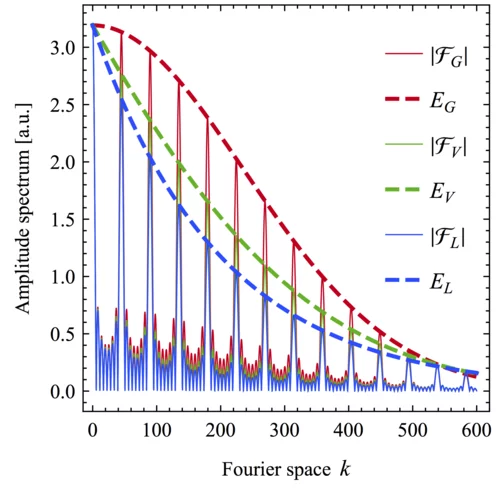
Efficient analysis method for multiplet lines in Fourier space
In his first paper as lead author, LMN PhD student Adrian Beckert and co-authors demonstrate an algorithm which takes advantage of peak multiplicity to retrieve line shape information. The results were published in Optics Express and are relevant to a wide range of topics, ranging from neutron-scattering to spectroscopy of rare-earth doped solids.
Relation between microscopic interactions and macroscopic properties in ferroics
The driving force in materials to spontaneously form states with magnetic or electric order is of fundamental importance for basic research and device technology. The macroscopic properties and functionalities of these ferroics depend on the size, distribution and morphology of domains; that is, of regions across which such uniform order is maintained. Typically, extrinsic factors such as strain profiles, grain size or annealing procedures control the size and shape of the domains, whereas intrinsic parameters are often difficult to extract due to the complexity of a processed material. Here, we achieve this separation ...
Coronavirus advice: Ventilate, ventilate, ventilate!
SARS-CoV-2 might be transmitted via aerosols, that is, through the air. Researchers point this out in the journal Clinical Infectious Diseases. André Prévôt from PSI co-signed the publication. In this interview, he explains which precautionary measures he recommends.
Phase contrast microtomography reveals nanoparticle accumulation in zebrafish
Metal-based nanoparticles are a promising tool in medicine – as a contrast agent, transporter of active substances, or to thermally kill tumor cells. Up to now, it has been hardly possible to study their distribution inside an organism. Researchers at the University of Basel in collaboration with the TOMCAT team have used phase contrast X-ray tomographic microscopy to take high-resolution captures of the nanoparticle aggregation inside zebrafish embryos.
The study was published in the journal Small and featured on the cover of its current issue.
From the lab to the market: deep tech entrepreneurs talk about their journey
Although Switzerland is championed as a world leader at innovation, it is less celebrated for its start-up culture. Does the country have what it takes to produce, finance and nurture the technology of the future? A new documentary explores that question. Our spin-off Gaia Membranes talks about their experiences as a swiss startup.
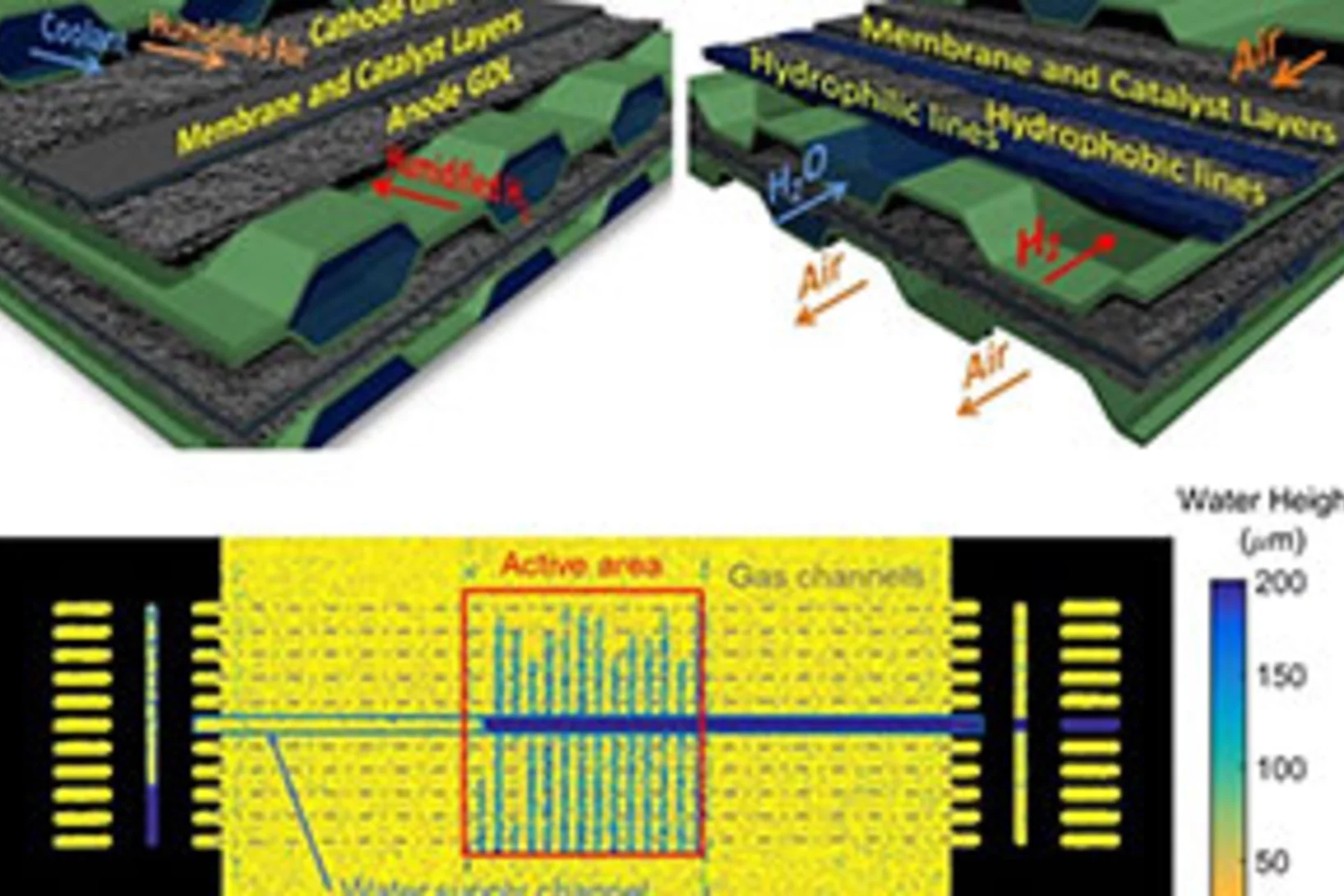
How to increase the power density of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells with evaporative cooling
A system of evaporative cooling for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells (PEFCs) has been developed at PSI, based entirely on one simple, yet effective change of one of the fuel cell components. Our team at the Electrochemistry Laboratory has demonstrated how this single change allows to operate a cell without the need of bulky and costly external humidifiers. Additionally, the proposed design has the potential to increase the power density of a PEFC stack by up to 35% due to the sparing of the space usually dedicated to the convective coolant circulation.
Methylbismuth: First observation of an organometallic biradical reactive intermediate
Open shell organometallic bismuth are promising agents for catalytic applications, but difficult to characterize due to their high reactivity. The simplest methylbismuth (Bi-CH3), a biradical species, was in-situ synthesized and spectroscopically characterized for the first time. Electronic and thermochemical properties could be obtained, which will guide future synthetic applications.
4 times compression factor for tomographic data feasible
In a recent study, TOMCAT has shown that lossy compression by a factor of at least 3 to 4 of raw acquisitions generally does not affect the reconstruction quality and that higher factors (six to eight times) can be achieved for tomographic volumes with a high signal-to-noise ratio as it is the case for phase-retrieved datasets. This finding is relevant to current challenges on large tomography data management and storage especially at synchrotron facilities. The results of this study was published in Journal of Synchrotron Radiation.
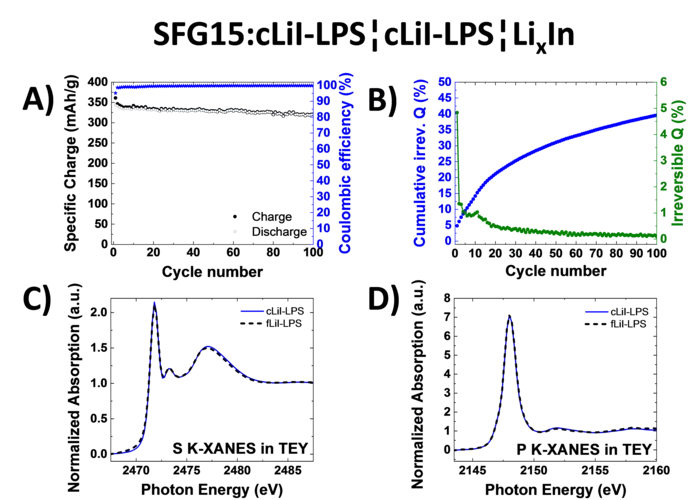
Study of Graphite Cycling in Sulfide Solid Electrolytes
Nowadays, most of the commercial Li-ion batteries employ graphite as the active material in negative electrodes. In the race for the next-generation Li-ion batteries, tremendous research efforts in academia and industry are carried out to replace the current flammable liquid electrolyte with a solid electrolyte, which could improve both, the batteries safety and energy density. Our study investigates two different sulfide-based solid electrolytes, 0.75Li2S-0.25P2S5 (LPS) and 0.3LiI-0.7(0.75Li2S-0.25P2S5), in combination with graphite and discloses the stability of the graphite-solid electrolyte interface. Optimizing the electrode morphology is the key to enhance the rate capability of all-solid-state cells. Using the special tender X-ray range allows chemical characterization of sulfur, phosphor and iodine.
Covid-19 research: Anti-viral strategy with double effect
Frankfurt scientists identify a possible weakness of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. They carried out part of their measurements at PSI's Swiss Light Source SLS. The research results are published this week in the scientific journal Nature.
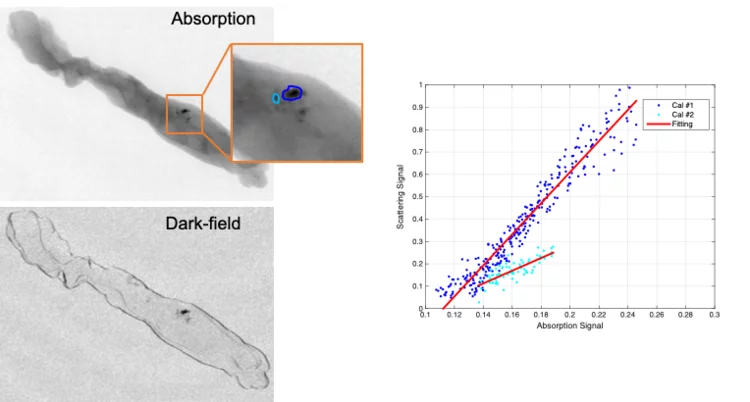
Looking into the hints of early breast cancer detection
Microcalcifications are the most important indicator in the diagnosis of early breast cancer. The team of X-ray tomography group, in collaboration with Kantonsspital Baden, has carried out a reader study to characterize microcalcifications non-invasively using grating interferometry. This study reveals a potential way to discriminate benign and malignant lesions at early stage.