At PSI, several projects are dedicated to important research questions concerning the Sars-CoV-2 coronavirus and the resulting diseases. We provide information on activities and projects, for example on investigations of lung tissue, on the production of proteins and antibodies or on ideas for new research on Covid-19.
Useful links
Award for the Best Poster at the 8th Annual World ADC
PSI Founder Fellow Philipp Spycher from the Group of Pharmacology at the Laboratory Center For Radiopharmaceutical Sciences (CRS) received the Award for the Best Poster at the 8th Annual World ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) conference San Diego (USA) from 20 to 22 September 2017. The poster on his latest work "Enzymatic (dual) site-specific conjugation of engineered and native antibodies" was highlighted as an exceptional poster with the highest impact in the field and Philipp was given the opportunity for a short-fire presentation in front of the whole plenum.
X-ray and neutron imaging for palaeontologists and archaeologists
Federica Marone illuminates objects with high-intensity X-ray beams, Eberhard Lehmann with neutrons. Both have used their methods to give palaeontologists and archaeologists a new view into the past.
Commissioning and first performance studies of the new CMS pixel detector
In the previous months the new CMS pixel detector was brought into operation. The detector was moved from PSI to CERN and installed in February, followed by an intensive period of commissioning and calibration. This process mostly involved the adjustment of many operational parameters which influence the detector performance, e.g.
Dr. Goran Lovric receives 2nd best abstract prize at the 34th SSAI Congress
Goran Lovric, a Postdoc at TOMCAT and CIBM, received the Best abstract 2nd Prize at the 34th congress of the Scandinavian Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care (SSAI) in Malmö (Sweden), 6-8th of September 2017. He presented the latest results of his work, entitled Spatial distribution of ventilator induced lung injury at the acinar level. An in-vivo synchrotron phase-contrast microscopy study in BALB/c mice.
ATHOS Conceptual Design Report (CDR)
The ATHOS Conceptual Design Report has recently been completed and describes the ATHOS project in detail. The CDR starts with a summary of the characteristics of the ATHOS undulator line. Especially the design parameters of the different ATHOS operation modes are explained and illustrated by simulation results. The core part of the report is a description of all key components, i.e. from the electron bunch extraction kicker down to the ATHOS experimental stations.Download the full report Athos CDR .
ATHOS Conceptual Design Report (CDR)
The ATHOS Conceptual Design Report has recently been completed and describes the ATHOS project in detail. The CDR starts with a summary of the characteristics of the ATHOS undulator line. Especially the design parameters of the different ATHOS operation modes are explained and illustrated by simulation results. The core part of the report is a description of all key components, i.e. from the electron bunch extraction kicker down to the ATHOS experimental stations.
Sorption of trivalent lanthanides and actinides onto montmorillonite
The credibility of long-term safety assessments of radioactive waste repositories may be greatly enhanced by a molecular level understanding of the sorption processes onto individual minerals present in the near- and far-fields. A study conducted at LES in collaboration with the Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf used extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopies (TRLFS) to elucidate the uptake mechanism of trivalent lanthanides and actinides (Ln/AnIII) by the clay mineral montmorillonite.The excellent agreement between the thermodynamic model parameters obtained by fitting the macroscopic data, and the spectroscopically identified mechanisms, demonstrates the mature state of the 2SPNE SC/CE sorption model developed at LES for predicting and quantifying the retention of Ln/AnIII elements by montmorillonite-rich clay rocks.
The hard worker from Val Mesolcina
For Aldo Antognini, physics and conviviality are in the bloodPSI researcher Aldo Antognini has received more than 2.2 million Swiss francs from the EU for his latest experiment. He wants to find out how magnetism is distributed in the proton. The particle physicist will be able to apply not only his scientific and technical talents, but his social flair as well.
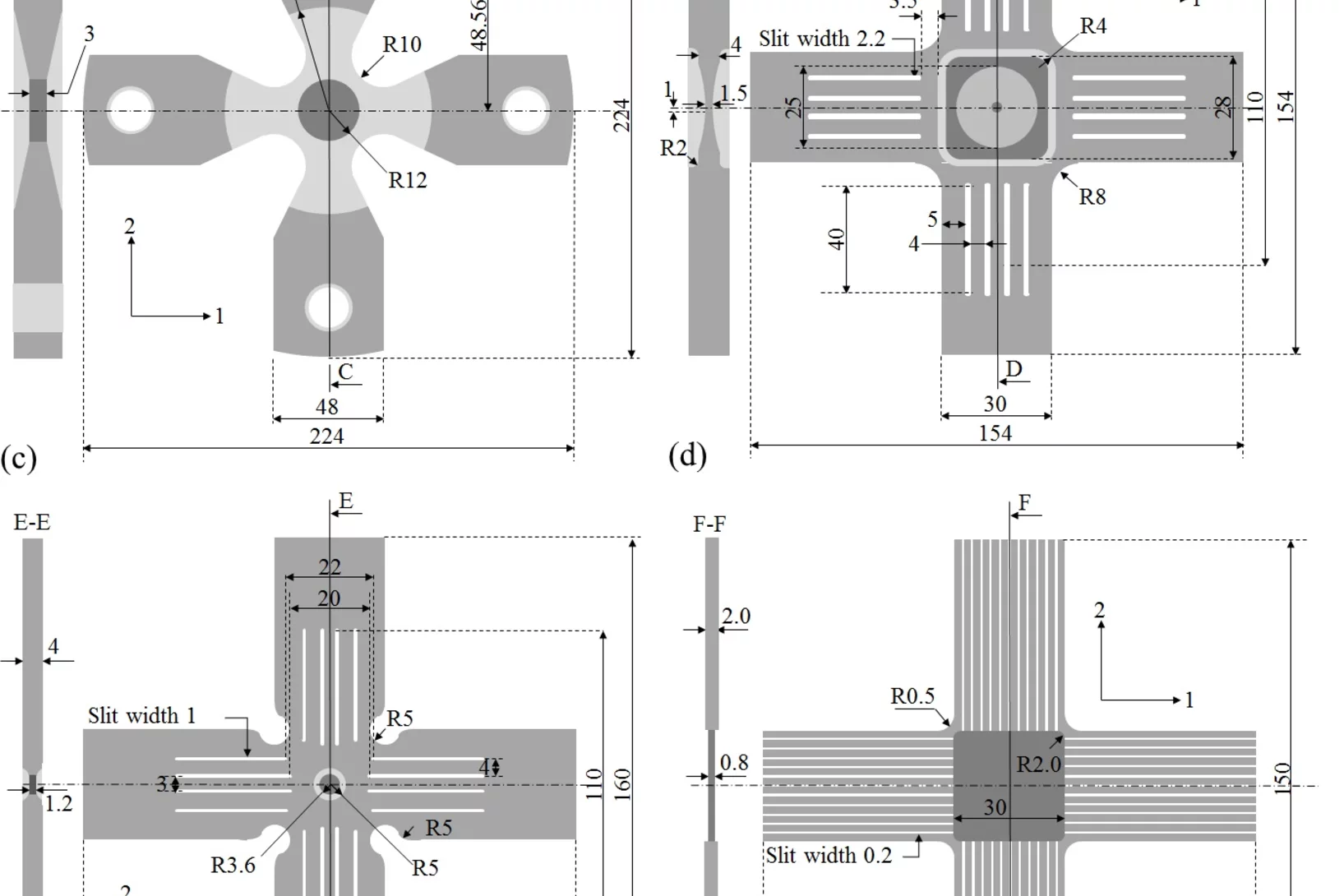
Composite laminated cruciform design for multiaxial testing of metals
Multiaxial mechanical testing of sheet metals is far from trivial, which is mainly related to issues with sample design and fabrication. PSI scientists have developed a new methodology to produce cruciform shaped samples from thin sheet metals based on a novel bottom-up approach. A proof-of-principle experiment based on polymer lamination of an aluminum thin sheet demonstrates the effectiveness of this new approach.
New Sample and Task Management Software
The AHL accounts, according to internal as well as external regulations, nuclear materials and moderators. For the detection and control of nuclear fuel samples and monitoring with respect to criticality safety, AHL developed a new sample and task management software (IPV).
Hector Dejea presented a talk at the conference Functional Imaging and Modelling of the Heart (FIMH2017) in Toronto
Hector Dejea (PhD student at ETH and TOMCAT) just attended the biennial FIMH conference in Toronto (Canada), which aims to integrate the state-of-the-art scientific advances in the fields cardiovascular imaging, image analysis and heart modelling fields.
MuPix8, our first large sensor, has arrived
We have just received first samples of the MuPix8 chip from the foundry. This is our first large (20mm x 10mm) pixel sensor prototype and a big step on the way to building the Mu3e tracking detector. The prototype will now be thoroughly tested in the labs in Karlsruhe and Heidelberg and will also soon see first beam at DESY in Hamburg, PSI and MAMI in Mainz.
Dr. Nan Xu awarded SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics
The SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics, sponsored by IBM, has been awarded to Dr. Nan Xu for his excellent work on topological quantum states. Dr. Nan Xu is a joint postdoc of Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
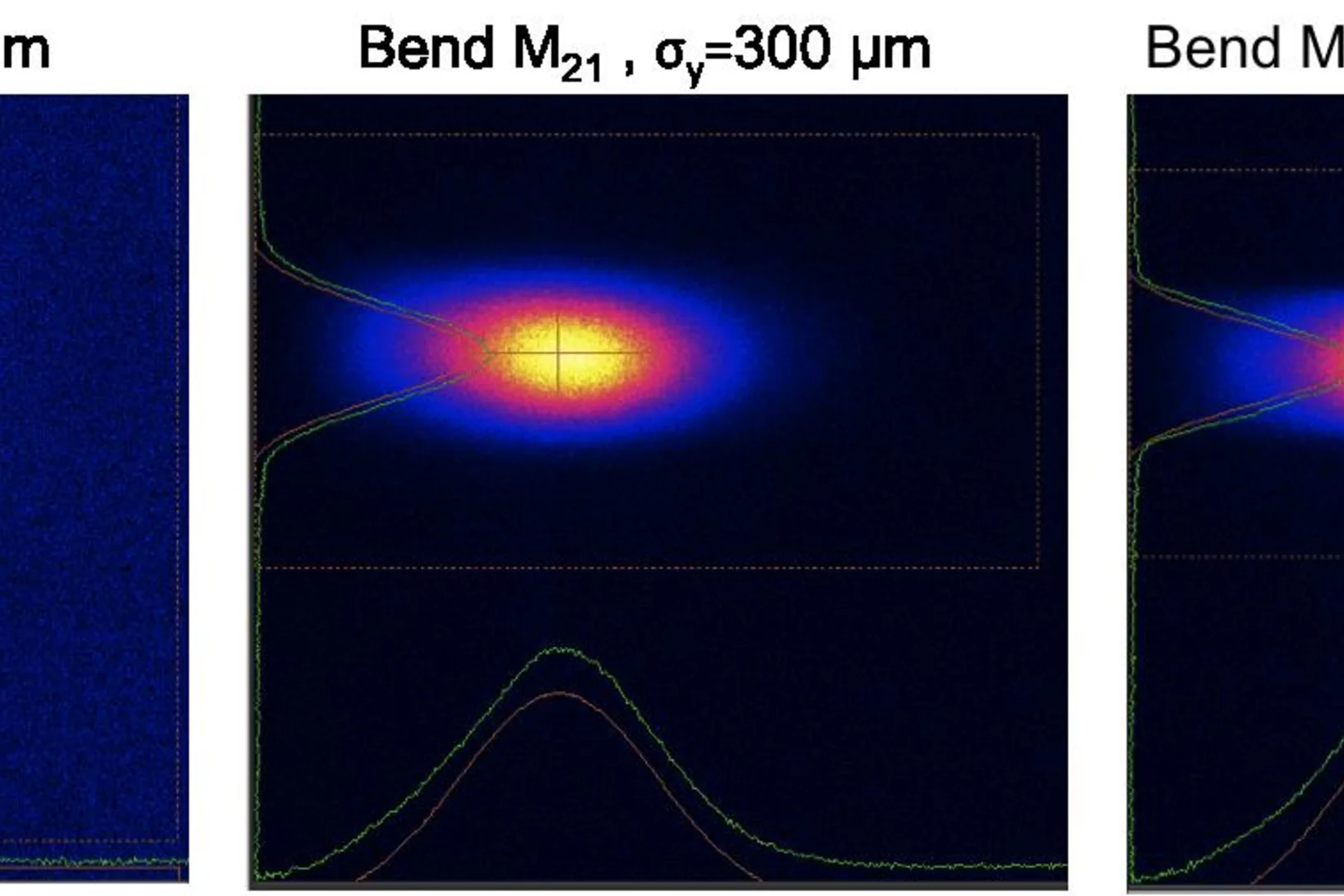
First beam in optics hutch
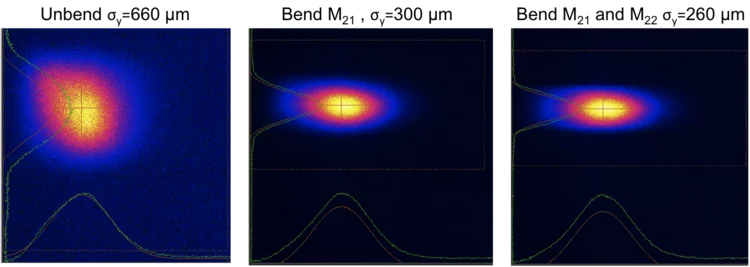
On August 31st, 2017, SwissFEL reached the next milestone by sending the first X-rays into the Optics Hutch. The Aramis undulators of SwissFEL produced SASE-radiation with 1.2 nm wavelength. The beam entered the Aramis-beamline along the pink beam path of Bernina via two vertical offset mirrors and was detected on the diagnostic photon screen at the end of the Optics Hutch. A stable and well shaped beam with a diameter of 1.5 mm was observed. With the bendable offset mirrors we were able to manipulate the profile to enlarge and reduce the vertical its size from 660 µm (rms) down to 260 µm (rms) without introducing distortions. The gas based intensity and position monitor in the frontend could be calibrated and determined a pulse energy of approximately 5 µJ. We are now looking forward to the next commissioning time in October to commission the monochromatic beam path of Bernina and the second branchline Alvra.
First beam in optics hutch
On August 31st, 2017, SwissFEL reached the next milestone by sending the first X-rays into the Optics Hutch. The Aramis undulators of SwissFEL produced SASE-radiation with 1.2 nm wavelength.
Swiss Neutron Scattering Prize
Viviane Lutz-Bueno was awarded the Swiss Neutron Scattering Prize of the Swiss Neutron Scattering Society, at the Joint Annual Meeting of the Swiss and Austrian Physical Society, for her PhD thesis Effects of formulation and flow on the structure of micellar aggregates carried out at ETH Zürich. Viviane is currently a postdoctoral fellow at the CXS group at PSI, developing scanning SAXS analysis methods.
Custom-tailoring better metallic materials
Using the large research facilities at PSI, Helena Van Swygenhoven-Moens examines the inner workings of metals. The watch industry needs small, robust springs and engineers are interested in turbine blades made of stress resistant materials.
Complementary Response of Static Spin-Stripe Order and Superconductivity to Nonmagnetic Impurities in Cuprates
We report muon-spin rotation and neutron-scattering experiments on nonmagnetic Zn impurity effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity of the La214 cuprates. Remarkably, it was found that, for samples with hole doping x ≈ 1/8, the spin-stripe ordering temperature Tso decreases linearly with Zn doping y and disappears at y ≈ 4%, demonstrating a high sensitivity of static spin-stripe order to impurities within a CuO2 plane.
A new RIXS analyzer scheme based on transmission zone plates
PSI scientists have developed a new type of X-ray optics that allows for analyzing the emission in resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) experiments. The new approach combines the energy dispersion with imaging capabilities. In a collaborative effort with research groups from Göttingen and Hamburg, two new classes of RIXS experiments, energy mapping and RIXS imaging, have been demonstrated.
More than just spilling the beans
Because of their high nitrogen content, spent coffee grounds are a popular garden fertilizer. Recycled in this manner, they already contribute to an environmentally friendly waste management. But they have the potential to deliver much more: a new procedure developed at the PSI allows high quality methane to be formed from spent coffee grounds. PSI researchers involved in a pilot project carried out in cooperation with the Swiss food producer Nestlé were able to show that spent coffee grounds left over during the production of instant coffee can be efficiently re-used elsewhere.
Felix Berg successfully defends his Ph.D. thesis on the Compact Muon Beam Line (CMBL) for Mu3e
Felix Berg has developed a full simulation of the high intensity, compact muon beam line for Mu3e. Beam tests he performed in the piE5 area have validated his simulations and established the beam setup for phase I of Mu3e. He has successfully defended his thesis at ETH Zürich.
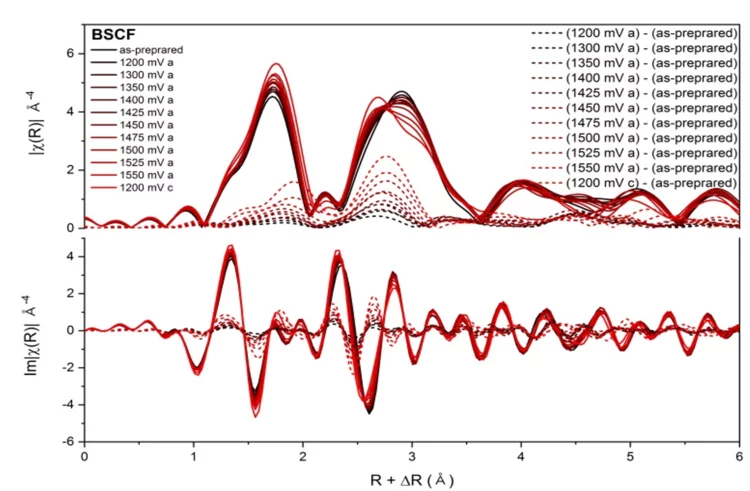
Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER)
Perovskite oxides
Time-resolved XAS is exploited to capture the dynamic local electronic and geometric structure of perovskite oxides under operando conditions.
Single-shot Monitoring of Ultrafast Processes via X-ray Streaking at a Free Electron Laser
The advent of x-ray free electron lasers has extended the unique capabilities of resonant x-ray spectroscopy techniques to ultrafast time scales. Here, in collaboration between researchers from PSI, Sorbonne Universités, HASYLAB/DESY, Synchrotron SOLEIL, CNRS, and Uppsala University, we report on a novel experimental method that allows retrieving with a single x-ray pulse the time evolution of an ultrafast process, not only at a few discrete time delays, but continuously over an extended time window.
In Situ Serial Crystallography 2 Workshop at the SLS
A workshop dedicated to the presentation of the in meso in situ serial crystallography (IMISX) method (Huang et al. 2015, 2016 ActaD) for the X-ray structure determination of membrane proteins is organised at the Swiss Light Source at PSI for the second time. It will be held between November 27 and 29, 2017.
Chemical Imaging to Spy on Malaria Parasites
Unique insights into the adolescence and metabolism of a Malaria parasite in a human red blood cell are obtained by a new chemical imaging methodology – in situ correlative X-ray fluorescence microscopy and soft X-ray tomography.
Equilibrium Skyrmion Lattice Ground State in a Polar Easy-plane Magnet
The skyrmion lattice state (SkL), a crystal built of mesoscopic spin vortices, gains its stability via thermal fluctuations in all bulk skyrmion host materials known to date. Therefore, its existence is limited to a narrow temperature region below the paramagnetic state. This stability range can drastically increase in systems with restricted geometries, such as thin films, interfaces and nanowires.
Testing the Limits for the Patients' Benefit
Proton therapy is already a success story at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI but researchers remain dedicated to making treatment faster and safer.
Welcome Huanyu Yang
Join me in welcoming Huanyu Yang, our new PhD student in Markus Ammann’s group.
He has a Bachelor degree in Physics and obtained his Master from the University of Rome, “La Sapienza”. The title of his dissertation was “Optical pump-terahertz probe on semiconductors” and the project task was to study the electro-optical properties of several semiconductors by constructing the time-domain and time-resolved spectroscopy with a laser (pulse duration <100 fs), both at equilibrium state and dynamical state.
At PSI, Huanyu Yang will be studying the hydrogen bonding structure at solid and aqueous interfaces with X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
Stresses and Strains in cruciform samples deformed in tension
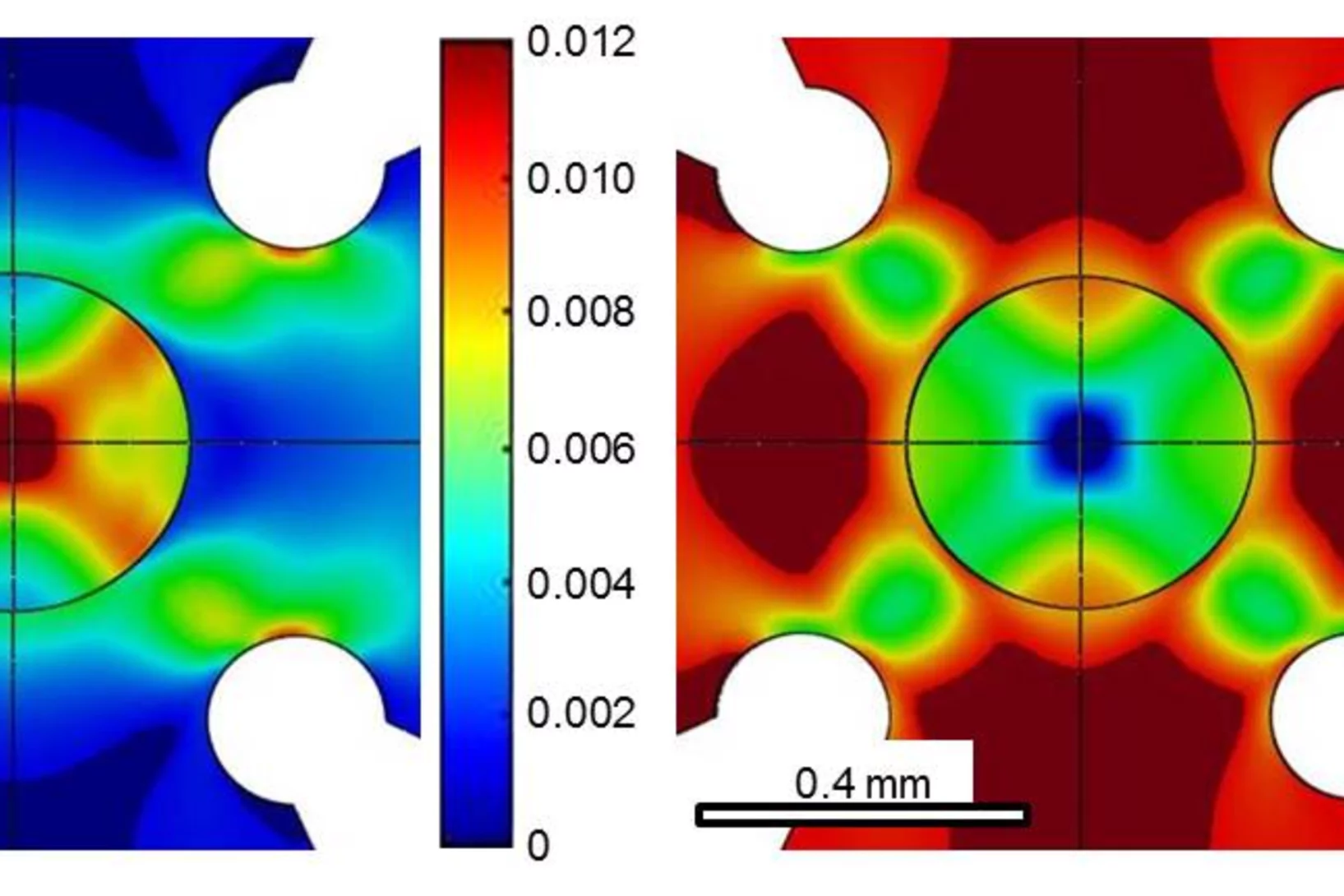
Cruciform experiments are very useful to study non-proportional strain path change behavior of engineering metals and alloys. This work studies the stress response of 6 prominently used cruciform geometries deformed under tension. Results show that for most of the cruciform samples, the gauge stresses are non-linearly coupled to the applied forces in both arms. Cruciform geometries based on the ISO standard are able to decouple these stresses but negligible gauge plastic strains are reached prior to failure.
Understanding the Enhanced Magnetic Response of Aminocholesterol Doped Lanthanide-Ion-Chelating Phospholipid Bicelles
Cholesterol (Chol-OH) and its conjugates are powerful molecules for engineering the physicochemical and magnetic properties of phospholipid bilayers in bicelles.