Abandon de l’énergie nucléaire, développement de l’énergie solaire et éolienne, production d’énergie à partir de la biomasse, réduction de la consommation d’énergie. D’ici 2050, la Suisse doit atteindre la neutralité climatique. Un objectif ambitieux, rendu plus urgent que jamais par une situation géopolitique de plus en plus difficile. Comment faire pour mettre en place ces prochaines années un approvisionnement énergétique durable et résistant pour la Suisse? Comment les énergies renouvelables peuvent-elles être utilisées de manière optimale? Quelles sont les nouvelles technologies les plus prometteuses? Au PSI, des chercheurs s’efforcent de trouver des réponses à ces questions décisives.
Virtual Collaboration Meeting
During the Corona crisis, meetings are only possible online. The Mu3 collaboration met today virtually with more than 20 people from three different countries.
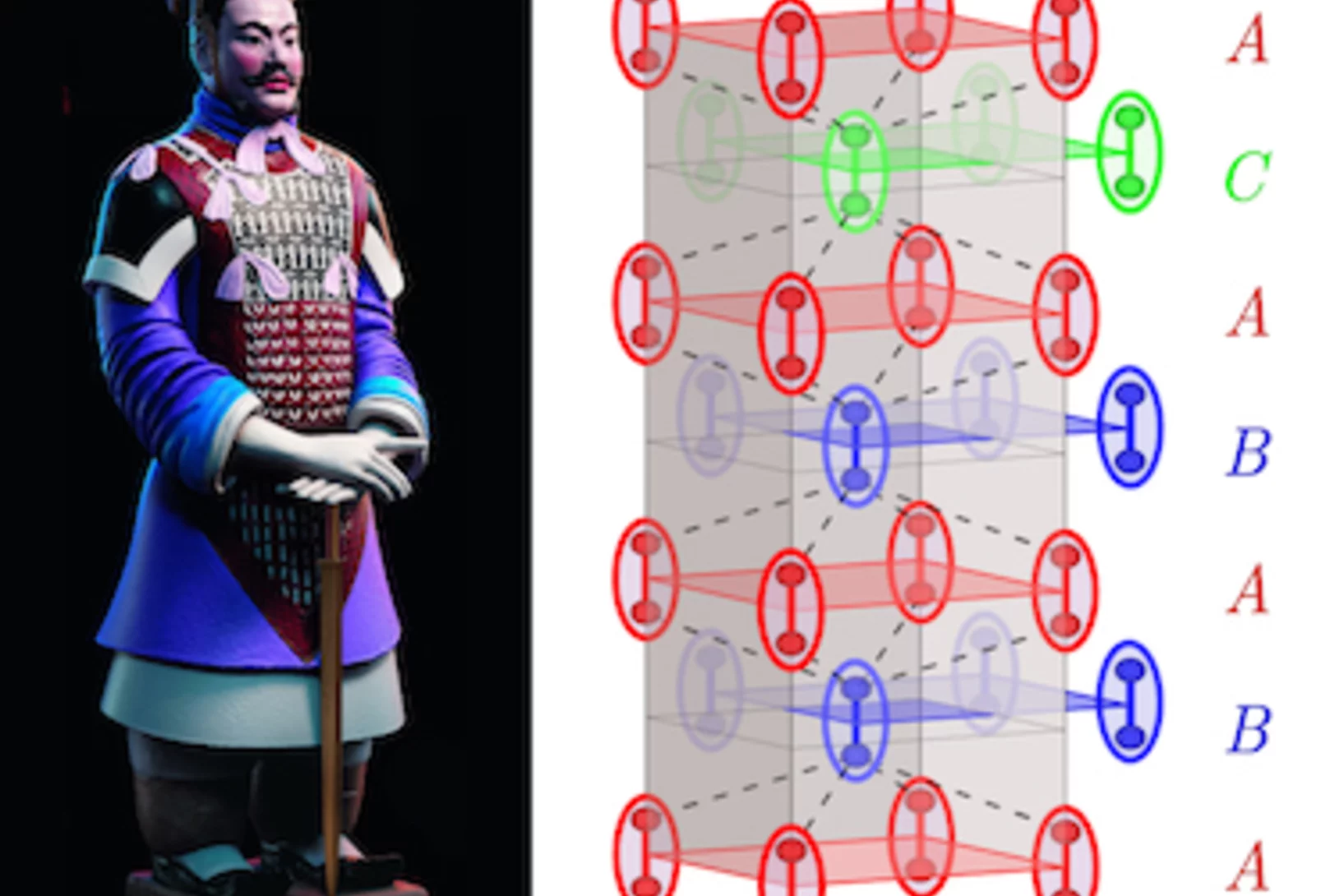
Understanding Quantum Critical Magnetism in Han Purple
The ancient purple pigment used to paint the terracotta warriors, BaCuSi2O6, is also a quantum magnetic material which consists of stacked Cu2+ bilayers hosting spin dimers. Magnetometry and NMR experiments have revealed puzzling critical phenomena at the quantum phase transition (QPT) caused by an applied magnetic field, which suggest that the universal behaviour of the system is not three- but only two-dimensional. By performing high-resolution neutron spectroscopy measurements .....
Den «Funken im Griff»
Eine andere Variante Mantel-Thermoelemente abisolieren zu können.
Unterstützung während Corona
Auf dieser Seite finden sich hilfreiche Tools und Links für Familien und andere Personen, die Betreuungsarbeit und Home-Office während Corona verbinden.
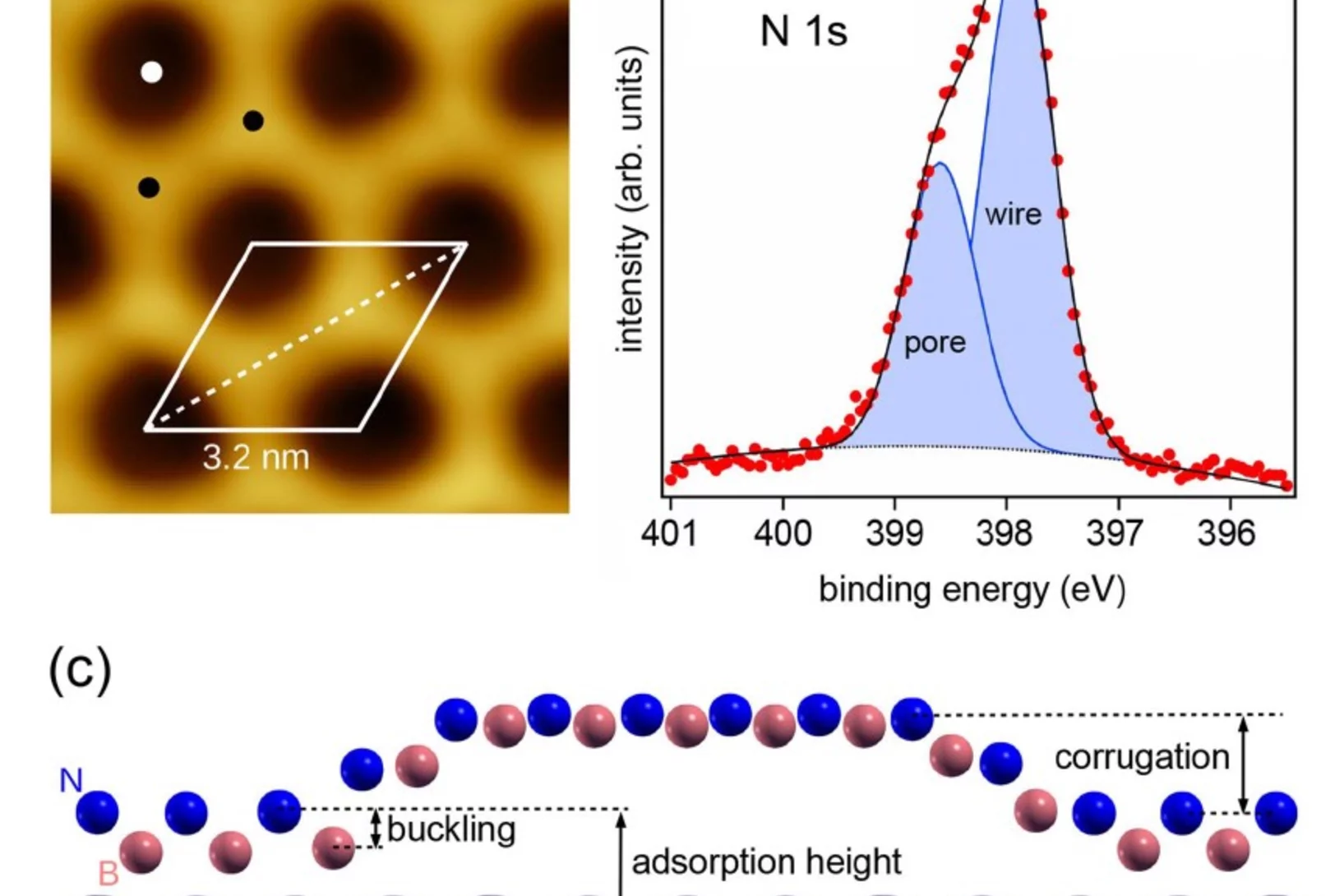
2D Materials
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) “nanomesh”, a two-dimensional insulating monolayer, grown on the (111) surface of rhodium exhibits an intriguing hexagonal corrugation pattern with a lattice constant of 3.2 nm.
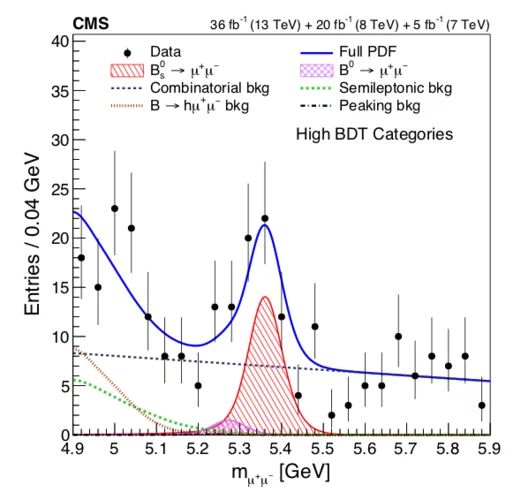
Measurement of properties of Bs0 → μ+μ− decays and search for B0 → μ+μ− with the CMS experiment
Results are reported for the B0s → μ+μ− branching fraction and effective lifetime and from a search for the decay B0 → μ+μ−. The analysis uses a data sample of proton-proton collisions accumulated by the CMS experiment in 2011, 2012, and 2016, with center-of-mass energies (integrated luminosities) of 7TeV (5fb−1), 8TeV (20fb−1),and 13TeV (36fb−1).
Swiss BIC of CERN Technologies calls for innovative ideas – deadline 30th April
For the third time, Switzerland Innovation Park Innovaare in Villigen/AG is hosting the call for proposals for high-tech business ideas that incorporate accelerator technologies into their products.
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
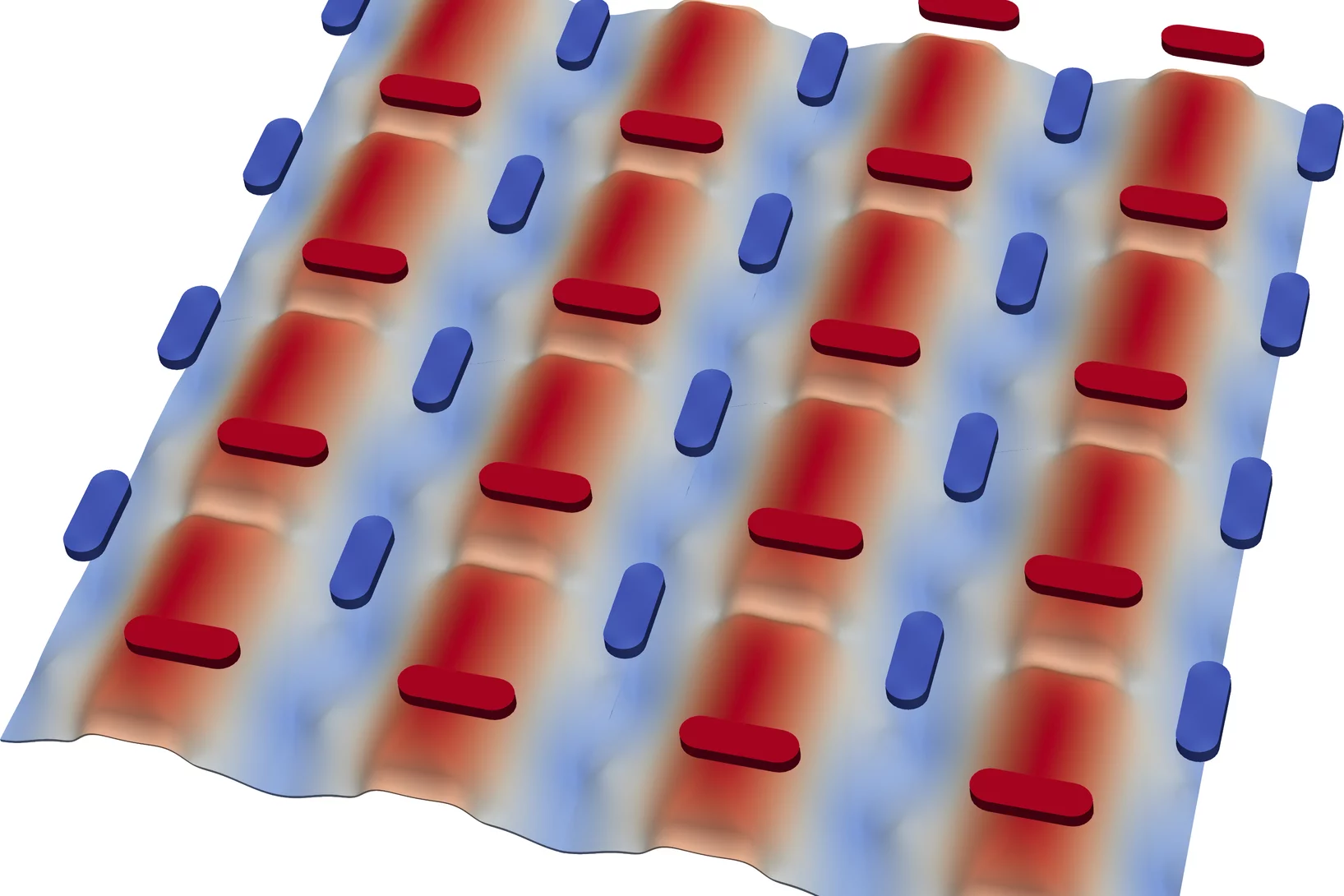
Tailoring Spin-Wave Channels in an Artificial Spin Ice
Magnonic crystals are periodic magnetic structures, which are attracting great interest because of their potential use in low-power information technology based on spin waves, or magnons. Artificial spin ices have been recently studied as reconfigurable magnonic crystals, but achieving the required combination of magnetic state reconfigurability and desired magnon dispersions remains challenging. Here, researchers propose a hybrid system that makes use of a magnetic thin film underlayer to couple and strengthen the interaction between the artificial spin ice’s nanoelements though spin waves. Moreover, the magnetic state of the artificial spin ice gives rise to directional spin wave channels in the underlayer. This hybrid system opens a new direction for band structure engineering in reconfigurable magnonic crystals.
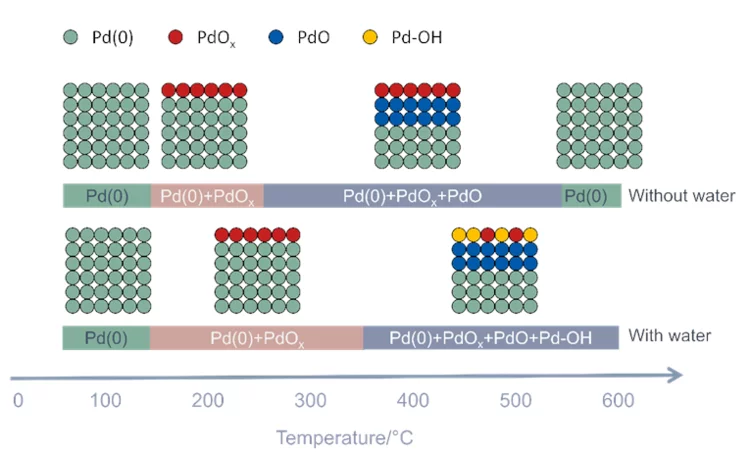
Role of water on the structure of palladium for methane complete oxidation
The mechanism of methane oxidation in the presence of water has been investigated in situ by means of APXPS.
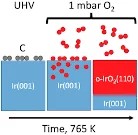
Kinetics of the Thermal Oxidation of Ir(100) Studied by APXPS
The thermal oxidation of single-crystalline Ir(100) films toward rutile IrO2(110) has been investigated in situ by means of APXPS.
Brennstoffzellenexponat im PSI forum
Anfang dieses Jahres haben die Physiklaboranten des 3. Lehrjahres das Brennstoffzellen Exponat im PSI forum repariert und auf den neusten Stand gebracht.
Pourquoi le Covid-19 frappe si durement les personnes âgées
Plus on est âgé, plus le risque de mourir d’une infection au coronavirus est élevé. G. V. Shivashankar, chef d’un groupe de recherche au PSI et professeur à l’ETH Zurich, vient de présenter une thèse surprenante dans le cadre d’une publication dans la revue «Nature Reviews»: la rigidité des cellules jouerait un rôle décisif dans l’évolution de la maladie. Dans cet entretien, il explique pourquoi.
«Dans la lutte contre le virus, chaque jour compte»
La pratique de la recherche au PSI a changé depuis le début de la pandémie de coronavirus, mais elle n’est pas à l’arrêt. Gabriel Aeppli, chef de la division de recherche Sciences photoniques au PSI, évoque la menace particulière que représente le Covid-19, de même que la manière dont des chercheurs du PSI étudieront ce nouveau virus à la SLS et l’étudieront sans doute bientôt au SwissFEL également.
La recherche prioritaire se poursuit
En raison de la pandémie de Covid-19, l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI a restreint son activité et, conformément aux directives du Conseil fédéral, la plupart des collaborateurs font du télétravail. Les installations et les projets de recherche indispensables, en revanche, continuent à fonctionner toujours dans le respect de l’ensemble des mesures de sécurité requises.
«Notre objectif est de comprendre comment fonctionne ce virus»
Malgré la pandémie de Covid-19, la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS est toujours en service et, en cette période difficile, il se pourrait bien que l’on en ait urgemment besoin. Oliver Bunk, chef du Laboratoire de macromolécules et de bio-imagerie, nous explique pourquoi.
«La stratégie et le réseautage revêtent une importance énorme»
Gebhard Schertler dirige la division de recherche Biologie et Chimie au PSI et est professeur de biologie structurale à l’ETH Zurich. Il décrit le type de recherche menée au PSI sur le coronavirus et souligne l’importance de la coopération avec des chercheurs d’autres institutions.
«La SLS est actuellement quelque chose de très spécial dans toute l’Europe»
En cette période de pandémie, la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS est l’une des rares sources de rayonnement synchrotron à être encore en service en Europe. Mirjam van Daalen, cheffe d’état-major de la division de recherche Sciences photoniques, souligne dans cet entretien à quel point la collaboration internationale est importante à l’heure actuelle.
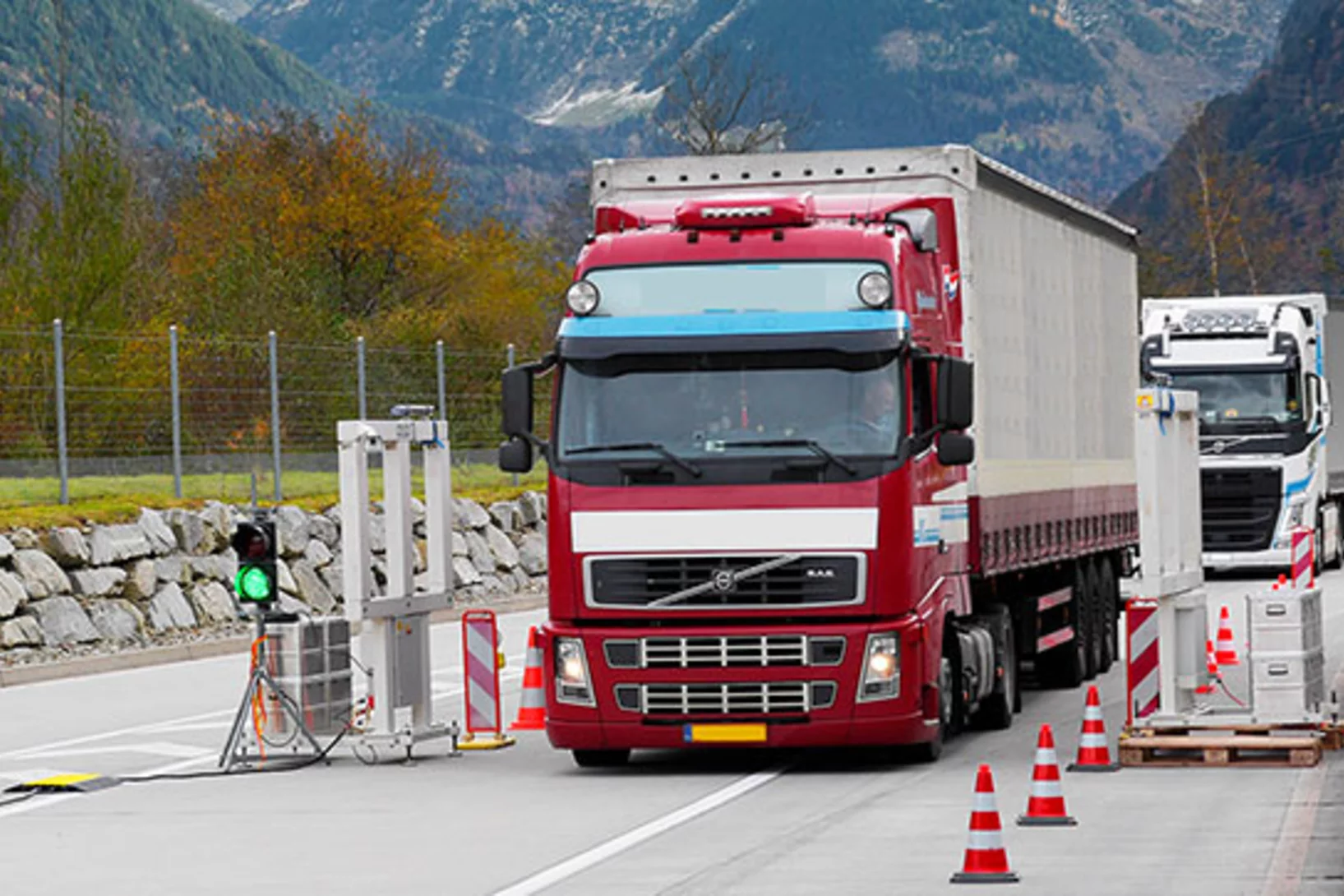
Détecter les sources radioactives dans le transport de marchandises
Le PSI opère régulièrement des contrôles de radioactivité sur des camions à l’aide d’un portique de détection mobile, sur mandat de l’Office fédéral de la santé publique. Sa mission: détecter les sources de radiation orphelines.
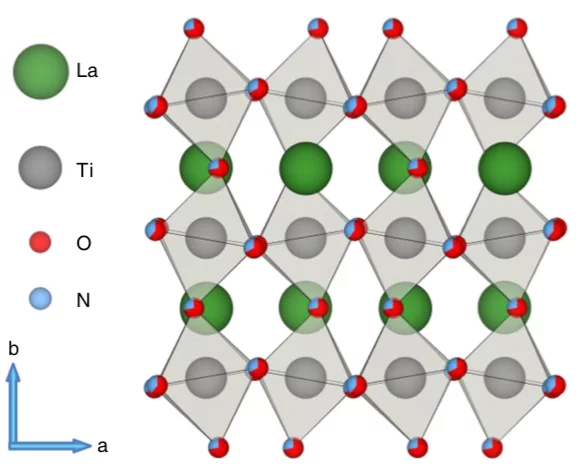
Examining the surface evolution of LaTiOxNy an oxynitride solar water splitting photocatalyst
LaTiOxNy oxynitride thin films are employed to study the surface modifications at the solid- liquid interface that occur during photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. Neutron reflectometry and grazing incidence x-ray absorption spectroscopy were utilised to distinguish between the surface and bulk signals, with a surface sensitivity of 3 nm.
Microcalcifications in breast tissue: Paving the way for future diagnostic solutions?
Microcalcifications are a common sign in mammography. For example, in 90% of ductal carcinoma in situ microcalcifications are the first and unique sign indicating the presence of the lesion. Nevertheless, up to around 50% of the resulting biopsies reveal a benign lesion, a 'false positive'. Researchers were able to show now that breast microcalcifications detected in tumors have specific chemical and crystalline features different from those observed in benign samples. Moreover, microcalcifications detected in tumors but located outside the lesion show malignant features too. This indicates that cancer influences the surrounding tissue even if it exhibits apparently healthy morphological features. These results indicate that the biochemical differences between benign and malignant microcalcifications can be potentially identified by light-based tools, able to investigate microcalcifications inside the breast without performing biopsies.
Information for CHRISP users
Because of the present coronavirus situation, preparations for the startup of the proton accelerator HIPA are currently suspended since March 16. At that point in time, there were still about 8 weeks to finalize the shutdown work.
Home Office der Lernenden Chemielaboranten während Coronavirus
Mit den folgenden Beiträgen wollen wir Ihnen zeigen, welche Projekte die Chemielaboranten während dem Home Office erarbeitet haben. Zudem wollen wir Ihnen auch veranschaulichen, dass Chemie überall in unserem Alltag anzutreffen ist.
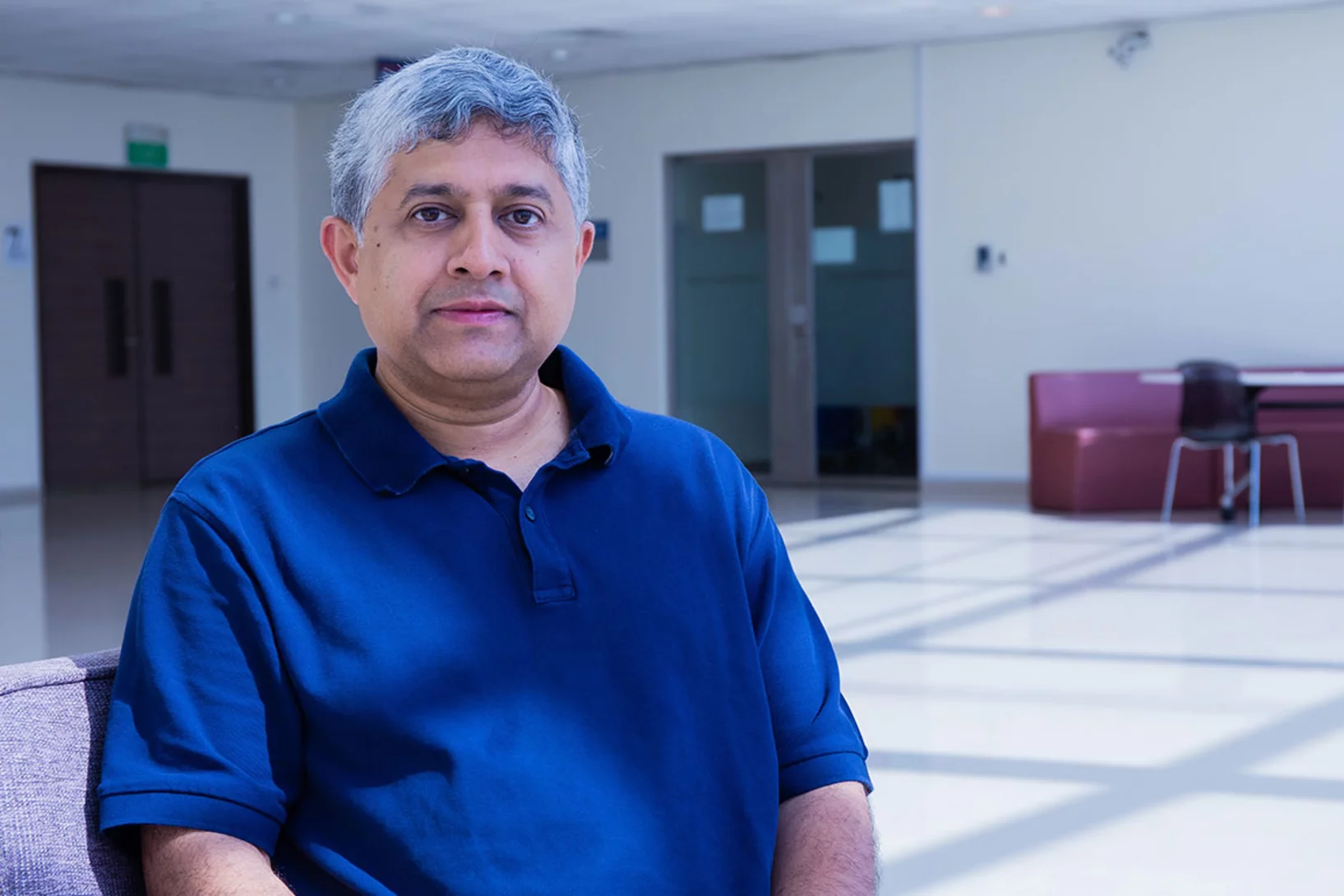
Le professeur Christian Rüegg est le nouveau directeur de l’Institut Paul Scherrer
Le nouveau directeur de l'Institut Paul Scherrer entre en fonction aujourd'hui: Christian Rüegg veut continuer à développer la position de leader des grandes installations de recherche du PSI et ainsi renforcer la Suisse en tant que site de recherche.
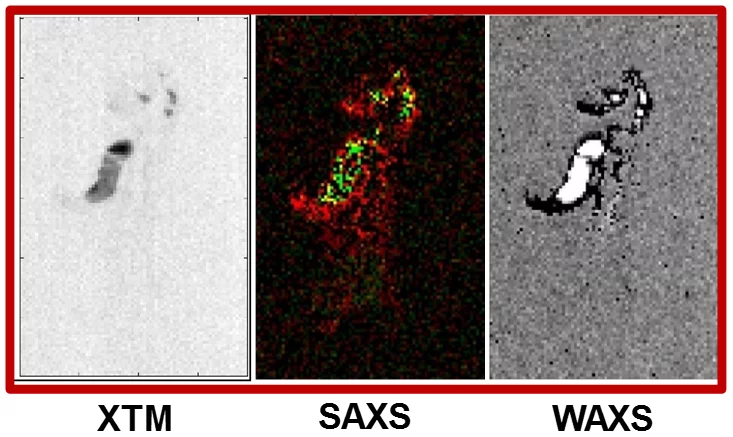
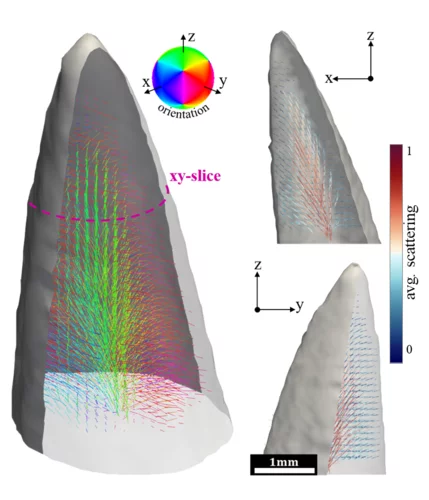
Rapid 3D directional small-angle scattering imaging achieved at TOMCAT
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline have developed a small-angle scattering tensor tomography method to visualize microscopic features within a macroscopic field of view with unprecedented data acquisition speed. The results of the study were published in Applied Physics Letters on April 1, 2020.
Rapid 3D directional small-angle scattering imaging achieved at TOMCAT
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline have developed a small-angle scattering tensor tomography method to visualize microscopic features within a macroscopic field of view with unprecedented data acquisition speed. The results of the study were published in Applied Physics Letters on April 1, 2020.
SLS MX beamtime update
Update of the SLS MX beamline operation during the COVID-19 period
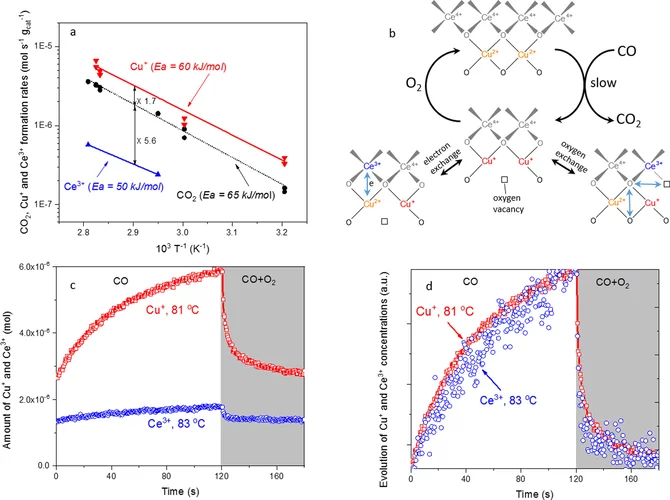
Elucidating the Oxygen Activation Mechanism on Ceria-Supported Copper-Oxo Species Using Time-Resolved X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
We monitored the dynamic structure of the active sites in a catalyst containing highly dispersed copper-oxo species on ceria during low-temperature CO oxidation using time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. We quantitatively demonstrate that the CO oxidation mechanism below 90 °C involves an oxygen intermediate strongly bound to the active sites as well as the redox activity of Cu2+/Cu+ and Ce4+/Ce3+ couples.
SNF funds dynamic X-ray imaging of the human auditory system in motion
In collaboration with clinicians from the Inselspital and engineers of the University Hospital of Bern, the X-Ray Tomography Group will be part of a new SNF project entitled “The Human Auditory System in Motion: Direct Observation of the Microfunction of Sound Transmission using Dynamic Phase-contrast X-ray Imaging”.