Glycation of collagen: Quantifying rates
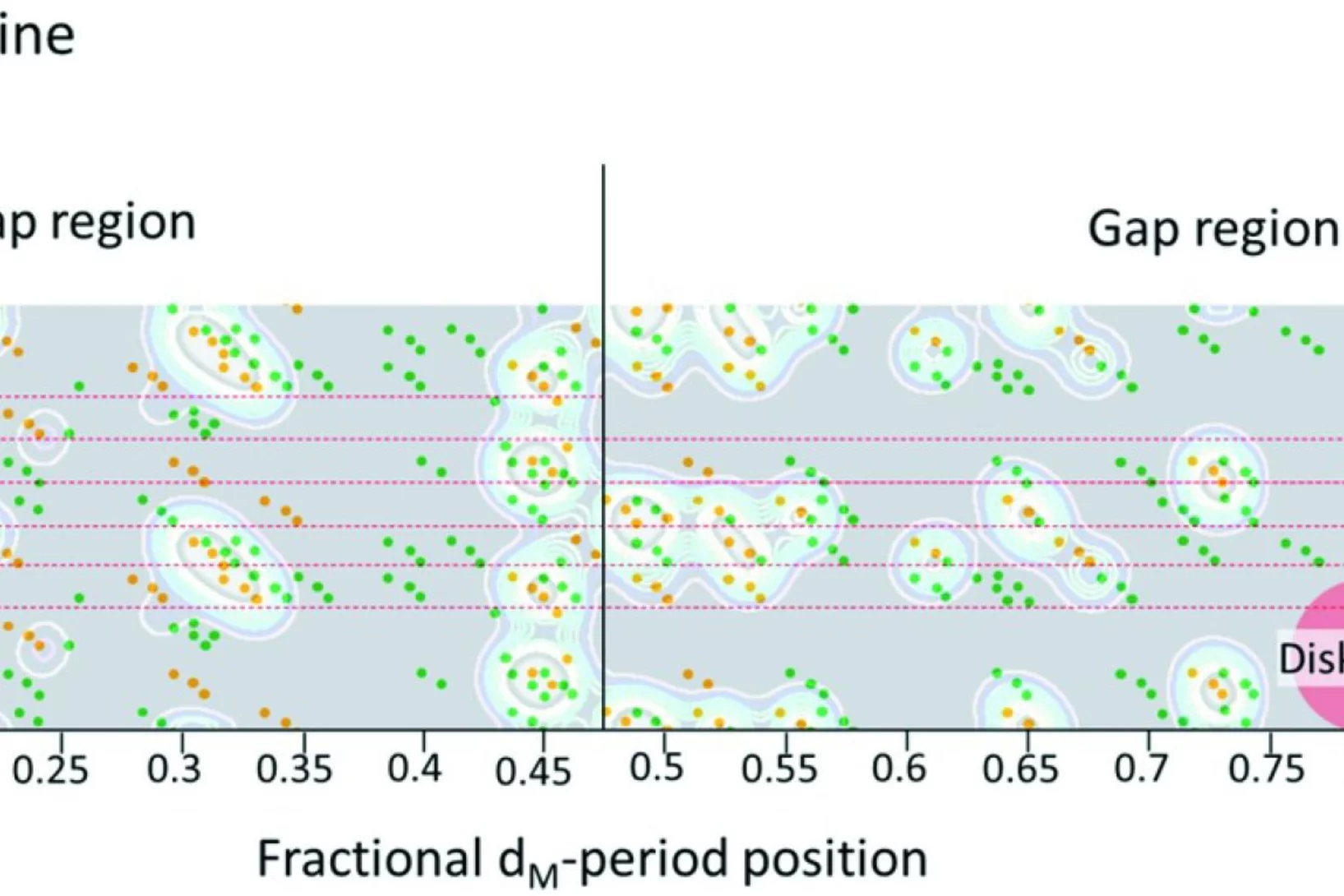
Collagen is abundant in the connective tissue of human beings, e.g. in tendons, ligament and cornea. Glycation of collagen distorts its structure, renders the extracellular matrix stiff and brittle and at the same time lowers the degradation susceptibility thereby preventing renewal. Based on models and with parameters determined from experimental data, we describe the glycation of type 1 collagen in bovine pericardium derived bio-tissues upon incubation in glucose and ribose. We hope that this contributes to a better quantitative understanding of the effects of diabetes on collagen.
Nouvel antiparasite
Des chercheurs du PSI identifient un principe actif potentiel contre plusieurs parasites unicellulaires, dont ceux à l’origine du paludisme et de la toxoplasmose.
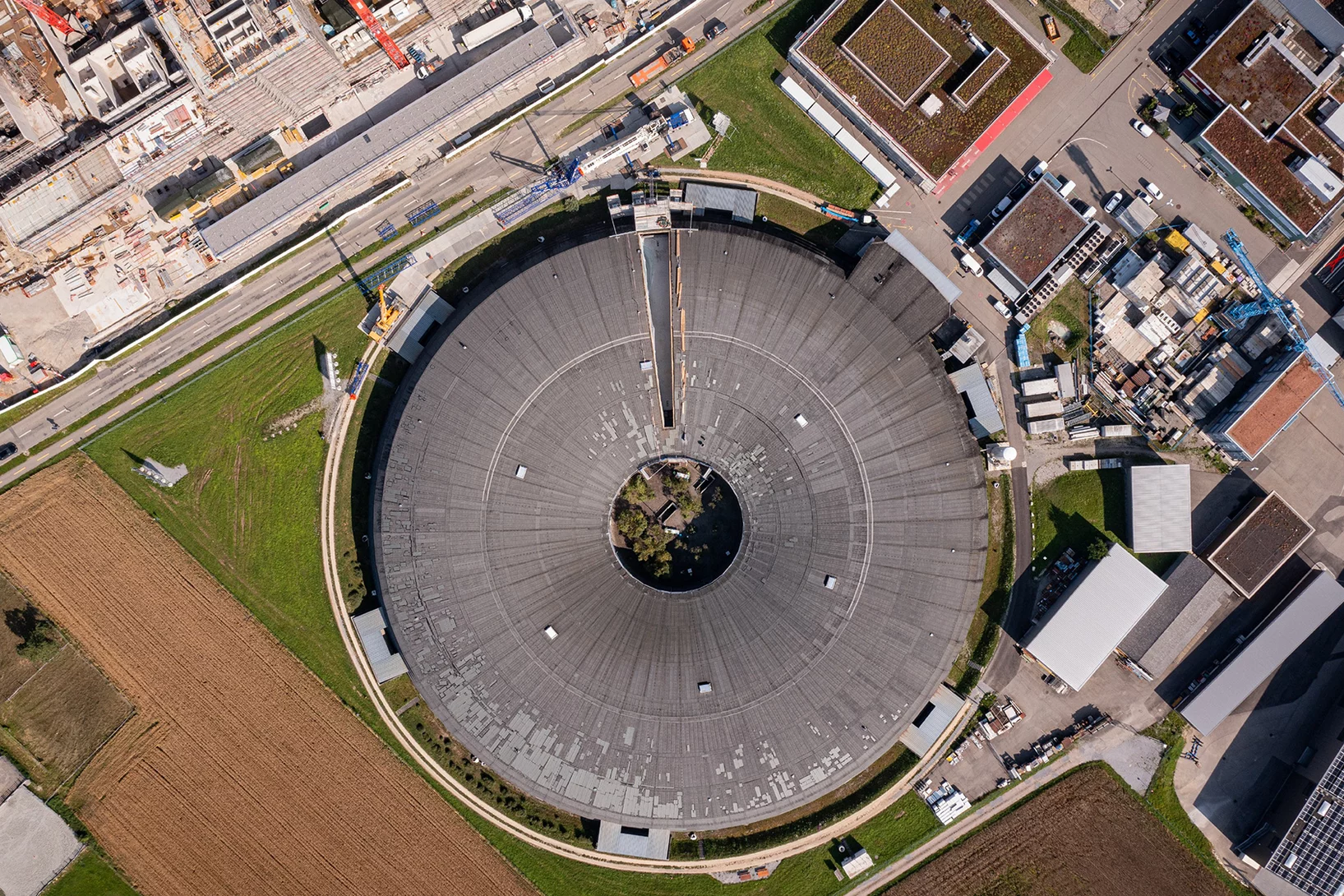
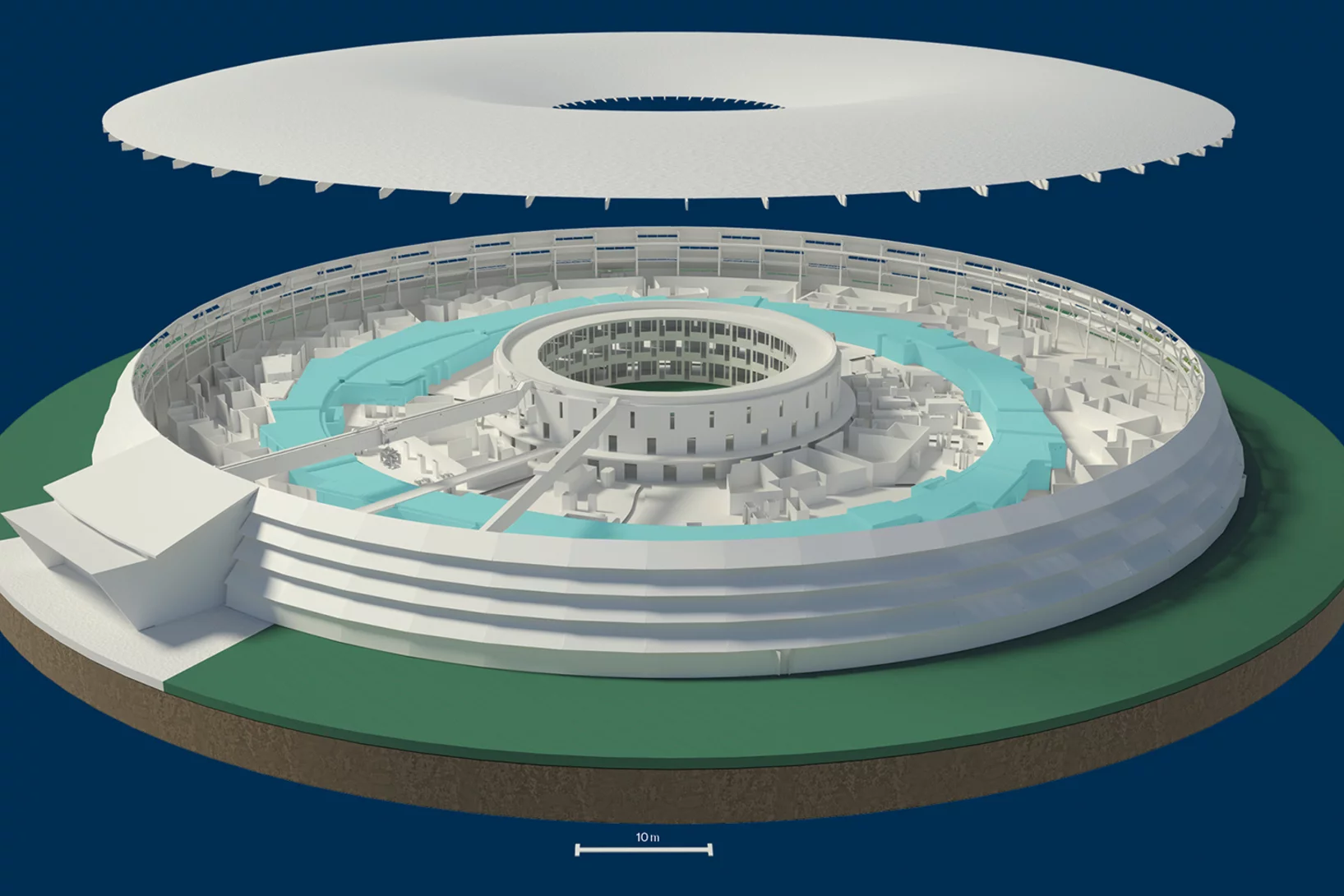
Perspective en 3D: La Source de Lumière Suisse SLS
Accélérateur linéaire, anneau d'accélération, anneau de stockage: notre graphique 3D de la Source de Lumière Suisse montre l'intérieur de l'installation et comment elle sert la recherche.
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos is awarded ICO prize
Dr. Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, beamline scientist at the cSAXS beamline, is the 2019 recipient of the International Commission for Optics (ICO) Prize. The distinction was awarded in the EOSAM conference in Rome.
Protéines maintenues à distance
Les chercheurs du PSI ont mis au point une nouvelle méthode pour fixer les protéines à la surface des particules de type viral.
Le pratique dans l’extraordinaire
Niels Schröter se voit décerner un prix de la Société Suisse de Physique (SSP).
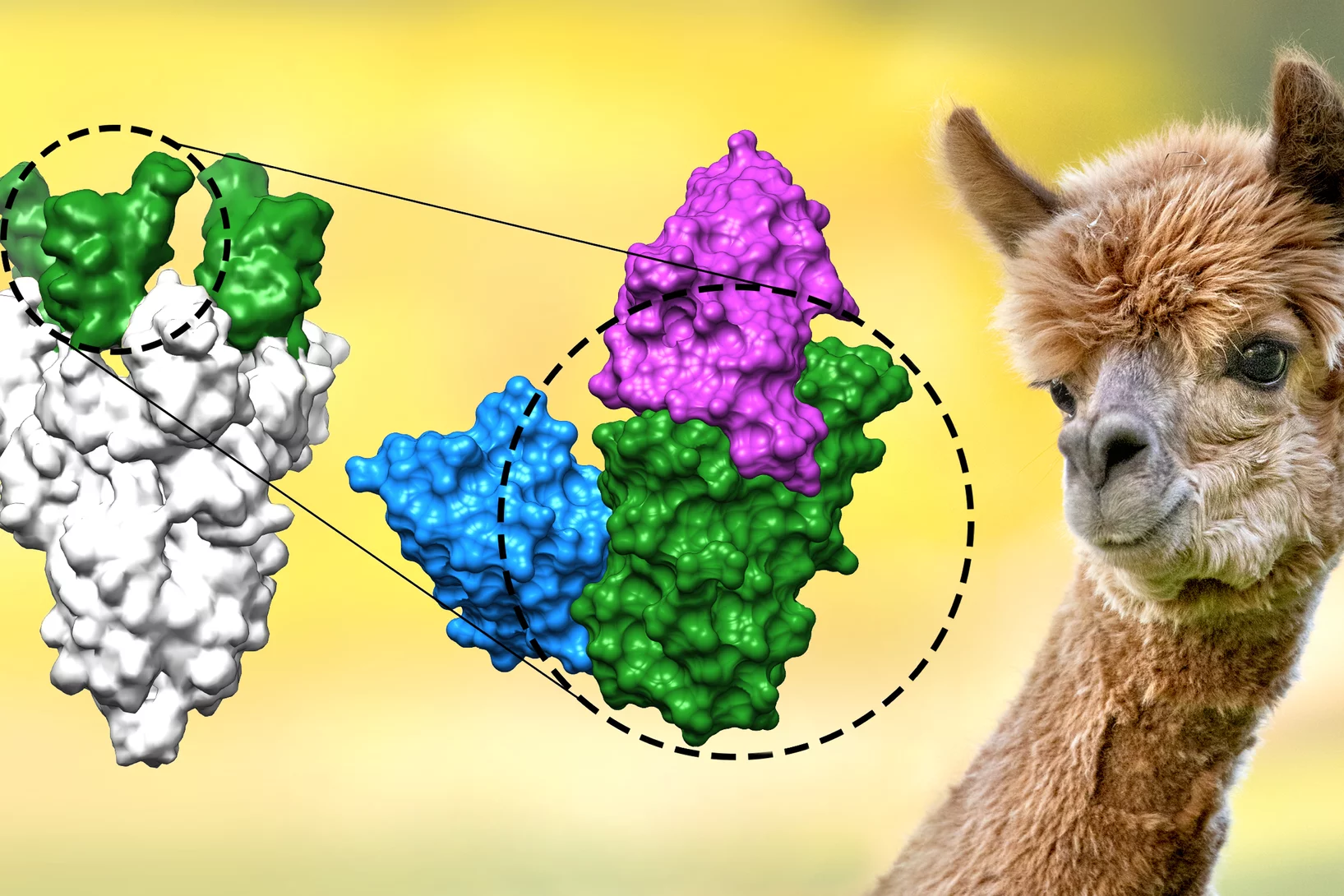
Nanobodies against SARS-CoV-2
In a study published in EMBO Journal, researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany, developed nanobodies that efficiently block the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. The high resolution structural characterization was performed at the X10SA crystallography beamline at the Swiss Light Source.
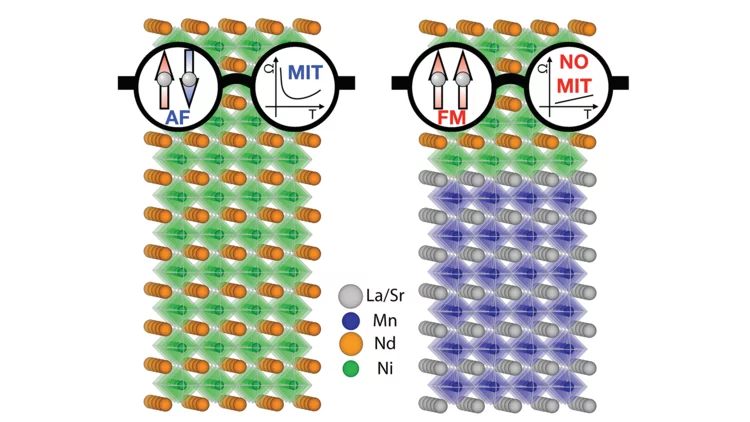
Creating novel quantum phases via the heterostructure engineering
Within this synergetic collaboration, PSI scientists have investigated the correlation between magnetic and electronic ordering in NdNiO3 by tuning its properties through proximity to a ferromagnetic manganite layer. The main outcome is that the stray magnetic field from the manganite layer causes a novel ferromagnetic-metallic (FM-M) phase in NNO. This work demonstrates the utilization of heterostructure engineering for creating novel quantum phases.
SLS: le nouveau pont roulant vient du ciel
La Source de Lumière Suisse SLS se voit dotée d’un deuxième pont roulant. Mais comment entre-t-il dans le bâtiment? Le seul moyen est de passer par le toit.
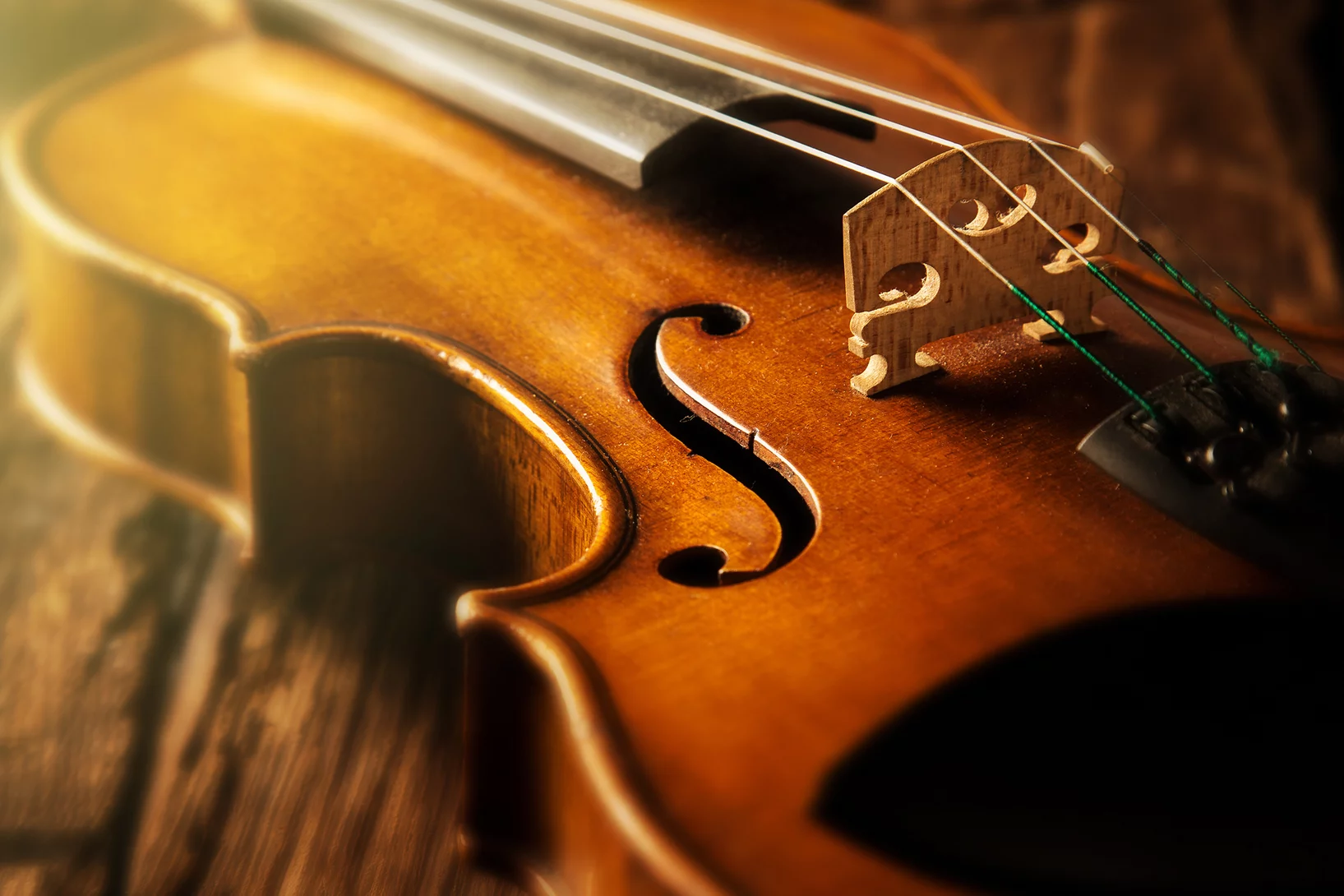
Le secret des Stradivarius dévoilé
Comme l’a découvert une équipe internationale de chercheurs, les anciens maîtres luthiers Stradivari et Guarneri utilisaient des adjuvants chimiques inattendus pour leurs violons.
Comprendre la physique à l’œuvre dans certains matériaux innovants
Une équipe internationale réunissant des chercheurs du PSI et leurs collègues pourrait avoir réussi à rendre utilisables certains matériaux fortement corrélés pour une application dans les domaines de la supraconductivité, du traitement des données ou encore des calculateurs quantiques.
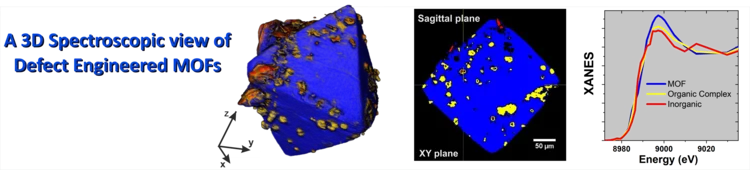
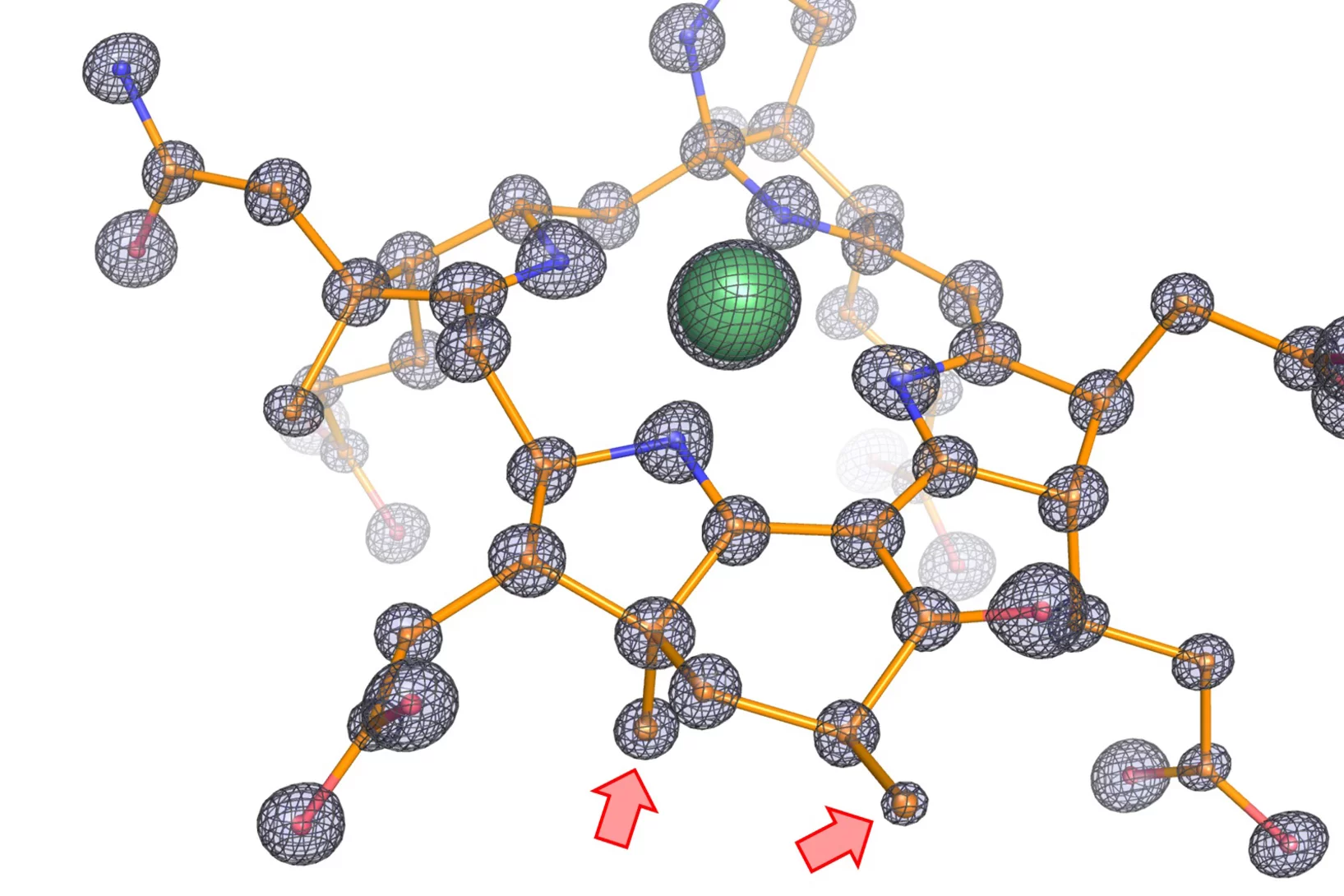
Full-field X-ray absorption tomography reveals the chemical structure of defects in metal-organic frameworks
Cryo-full-field XANES computed tomography was used to visualize the presence and distribution of a second coordination polymer of reduced copper coordination within defect-engineered HKUST-1 MOF crystals. Observations encourage a revisitation of the structure-property relationships of defect-engineered MOFs.
Imaging strain with high resolution
Imaging strain in crystalline materials with high resolution can be a challenging task. Researchers demonstrate an original use of X-ray ptychography for this purpose: ptychographic topography.
How ethane-consuming archaea pick up their favorite dish
Scientists decode the structure of the enzyme responsible for the ethane fixation by – beside others – using the SLS.
Comment les catalyseurs vieillissent
La structure du matériau utilisé dans les catalyseurs en industrie chimique se modifie au fil des ans. Des chercheurs du PSI ont étudié ce phénomène au moyen d’une nouvelle méthode.
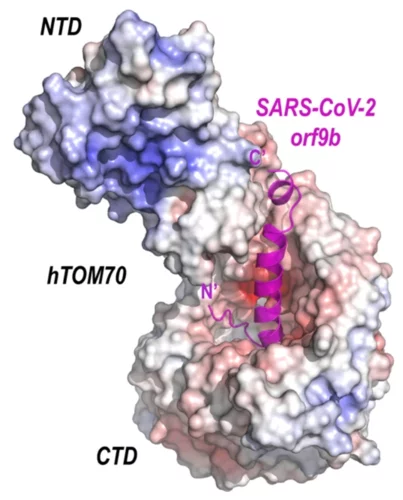
Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b in complex with human TOM70 suggests unusual virus-host interactions
In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers at the NHC Key Laboratory of Systems Biology of Pathogens in Beijing, China, in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institut characterize the interactions of SARS-CoV-2 orf9b and human TOM70 biochemically, and they determine the 2.2 Å crystal structure of the TOM70 cytosolic domain with a bound SARS-CoV-2 orf9b peptide.
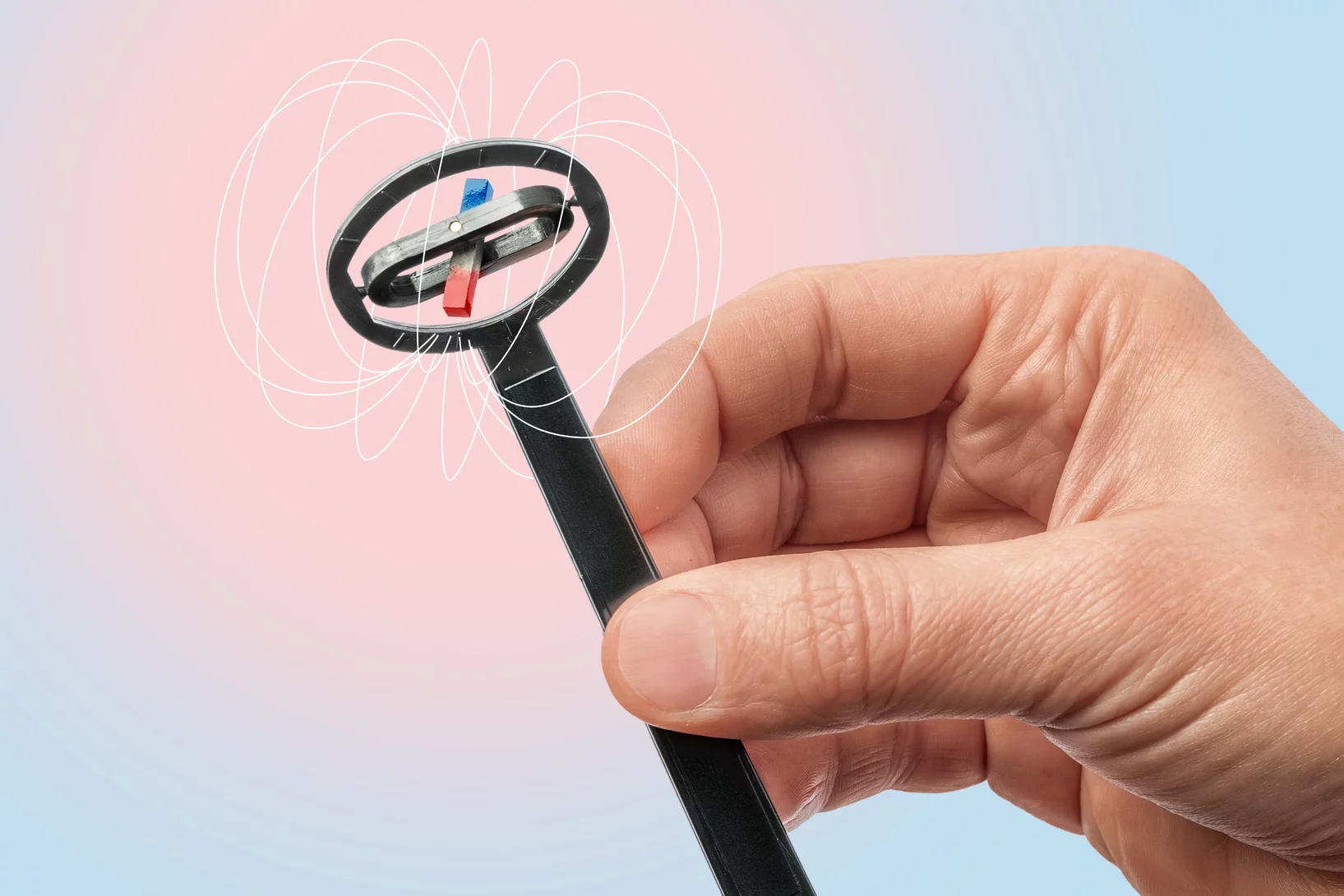
Une force magique qui fait grand effet
Des microrobots ou de meilleurs accélérateurs de particules deviennent possibles par la recherche sur le magnétisme au PSI.
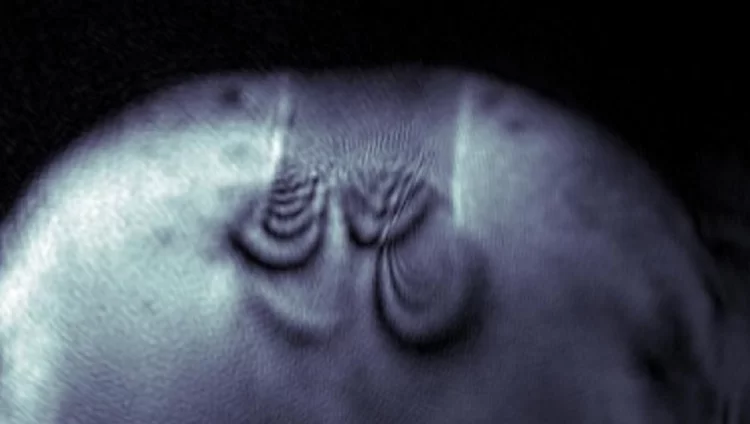
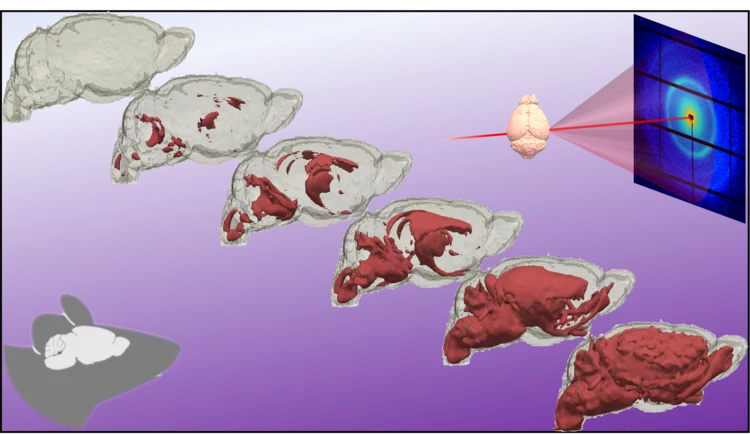
Quantifying oriented myelin in mouse and human brain
Myelin 'insulates' our neurons enabling fast signal transduction in our brain. Myelin levels, integrity, and neuron orientations are important determinants of brain development and disease. Small-angle X-ray scattering tensor tomography (SAXS-TT) is a promising technique for non-destructive, stain-free imaging of brain samples, enabling quantitative studies of myelination and neuron orientations, i.e. of nano-scale properties imaged over centimeter-sized samples.
Mode d’action du remdesivir contre le coronavirus
En coopération avec le PSI, des chercheurs de l’Université Goethe de Francfort ont probablement découvert un nouveau mécanisme d’action inconnu du remdesivir.
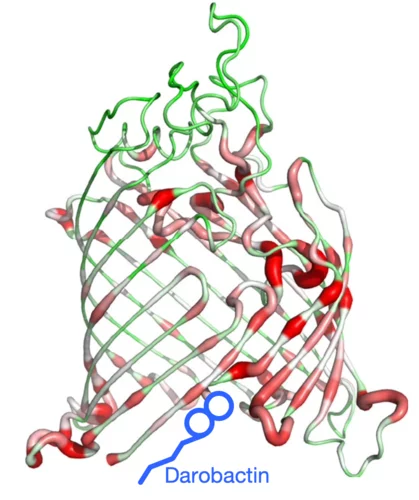
Combating antimicrobial resistance
In a study addressing the global health threat of drug resistance, researchers at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, have revealed how a new antibiotic, Darobactin, binds to the external membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
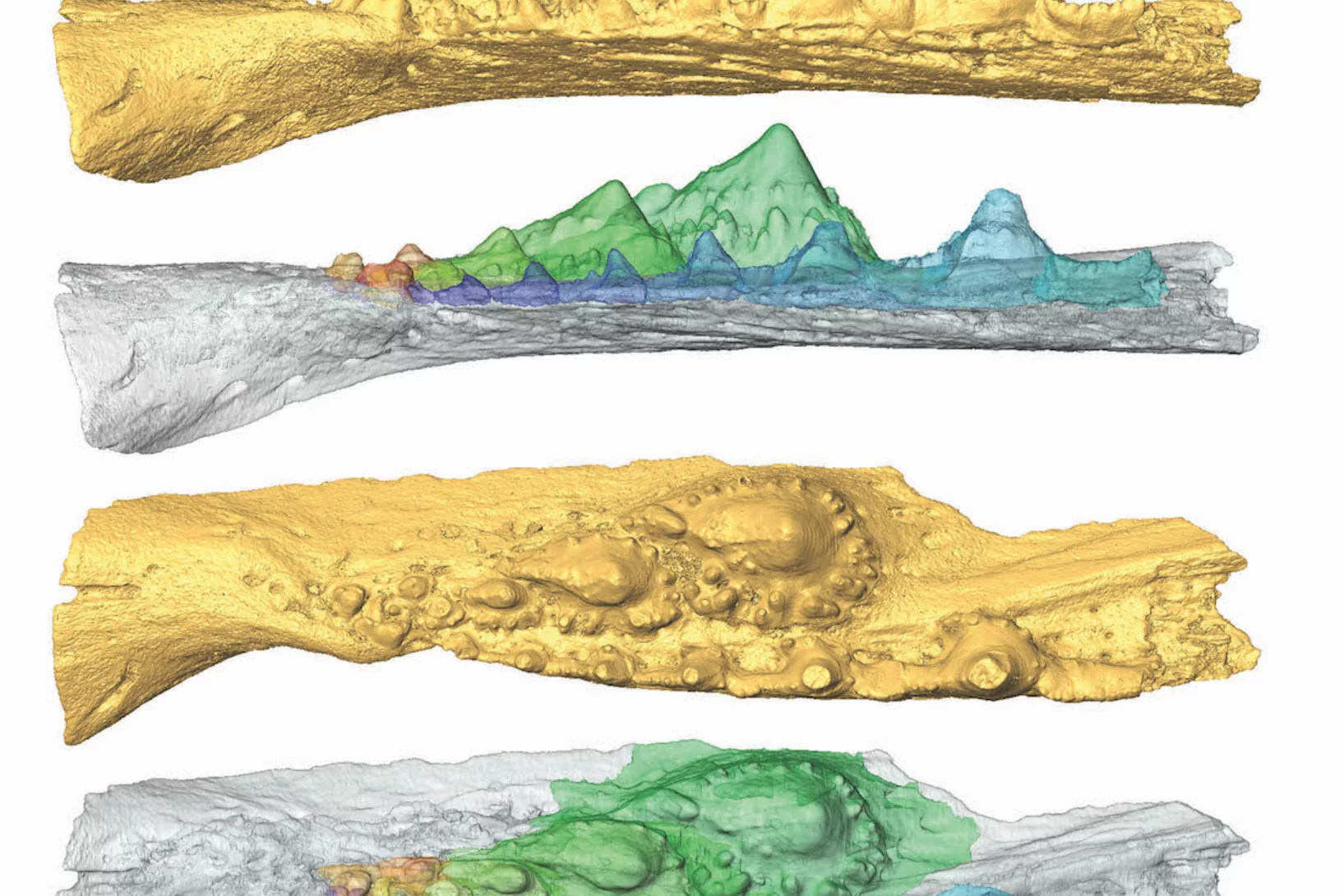
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
Un nouveau site pour les sciences des données
Un nouveau site du Swiss Data Science Center va voir le jour au PSI. Cette expansion devrait donner un nouvel élan à la science des données en Suisse.
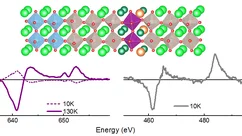
Hindering the magnetic dead layer in manganites
The authors demonstrate the stability of ferromagnetic order of one unit cell thick optimally doped manganite (La0.7Ba0.3MnO3, LBMO) epitaxially grown between two layers of SrRuO3 (SRO). LBMO shows ferromagnetism even above SRO Tc. Density Functional Theory calculations help understand the reasons behind this interesting result.
HERCULES SCHOOL 2021 AT PSI
During the week of March 15 – 19, we had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and assistant professors at PSI, taking part in the first virtual HERCULES SCHOOL on Neutrons & Synchrotron Radiation.
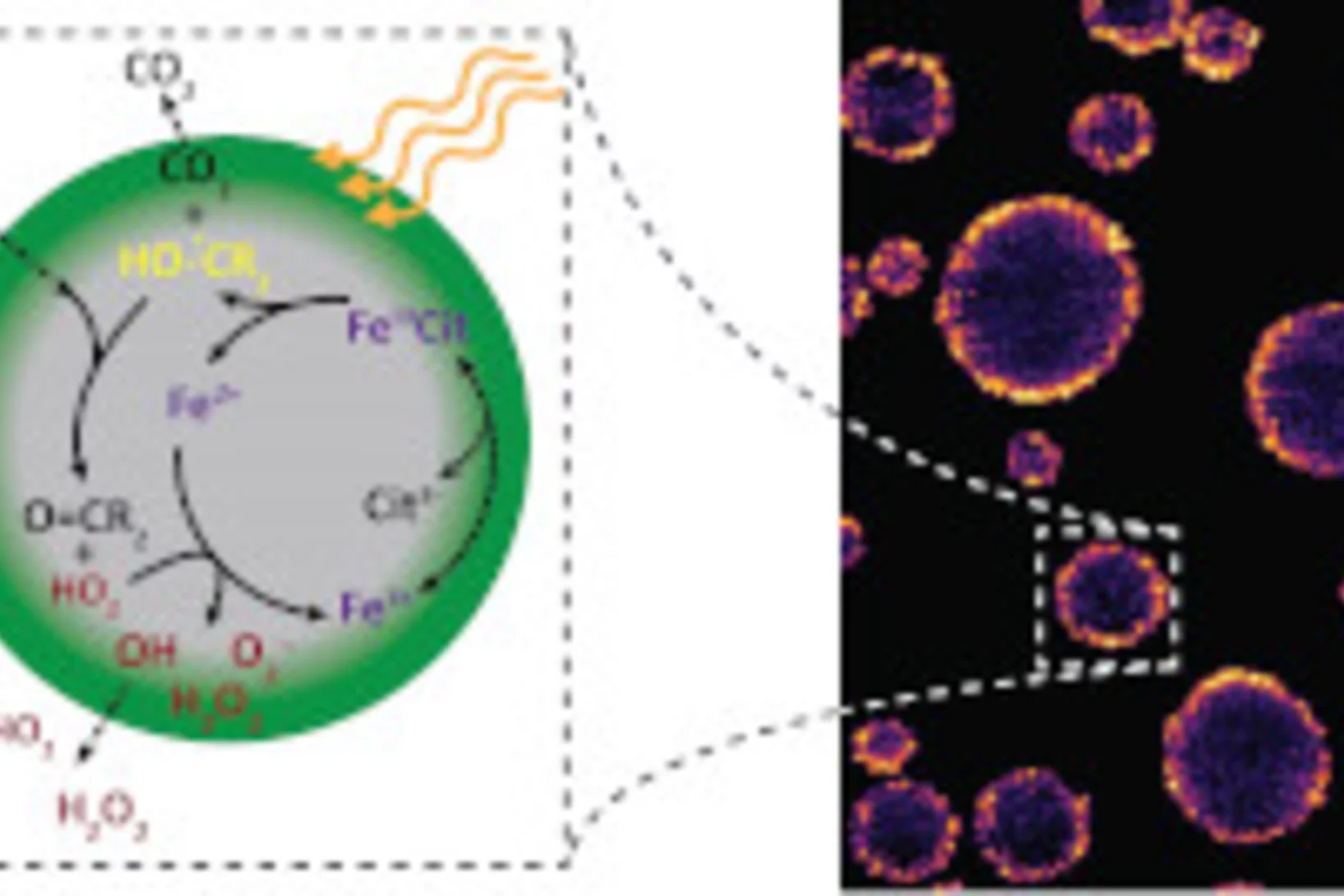
Looking inside airborne particles for the chemistry responsible for their adverse health effects.
Chemical changes inside of breathable airborne particles can cause reactive oxygen species (ROS) and carbon centered radicals (CCRs) to form, which are harmful to our bodies and induce oxidative stress in lungs. Using X-ray spectromicroscopy at the PolLux beamline and mimicking the environmental and sunlit conditions aerosol particles experience in the atmosphere near the Earth Surface, it was recently found that highly viscous organic particles with low water content can attain high concentrations of ROS and CCRs that persist over long times. Natural particles like these will occur in ambient humidity below 60% and effectively trap ROS and CCRs inside that react when exposed to light.
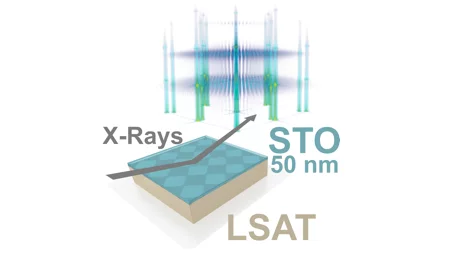
Buried moiré supercells through SrTiO3 nanolayer relaxation
The authors find that an annealing process can create a highly ordered network of two-dimensional line defects at the buried interface between a relaxed film and its substrate. The low dimensional network spacing is directly related to the lattice mismatch and can correspondingly be tuned by the choice of substrate.
Forschung zu Covid-19 am Paul Scherrer Institut
Während viele Bereiche des Lebens eingeschränkt sind, bleiben wichtige Forschungsanlagen am PSI in Betrieb.
Le PSI équipe la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS pour l’avenir
Feu vert pour la SLS 2.0: l’upgrade de la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS peut avoir lieu. Le financement est assuré dans le cadre du message FRI 2021-2024 approuvé à la mi-décembre.
Vue en trois dimensions de l’intérieur de catalyseurs actifs
La spectroscopie de rayons X in operando permet de jeter un coup d’œil à l’intérieur de réacteurs chimiques en fonction. Des chercheurs de l’Institut de technologie de Karlsruhe (KIT), à l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI et à l’European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) en France, appliquent avec succès cette méthode.
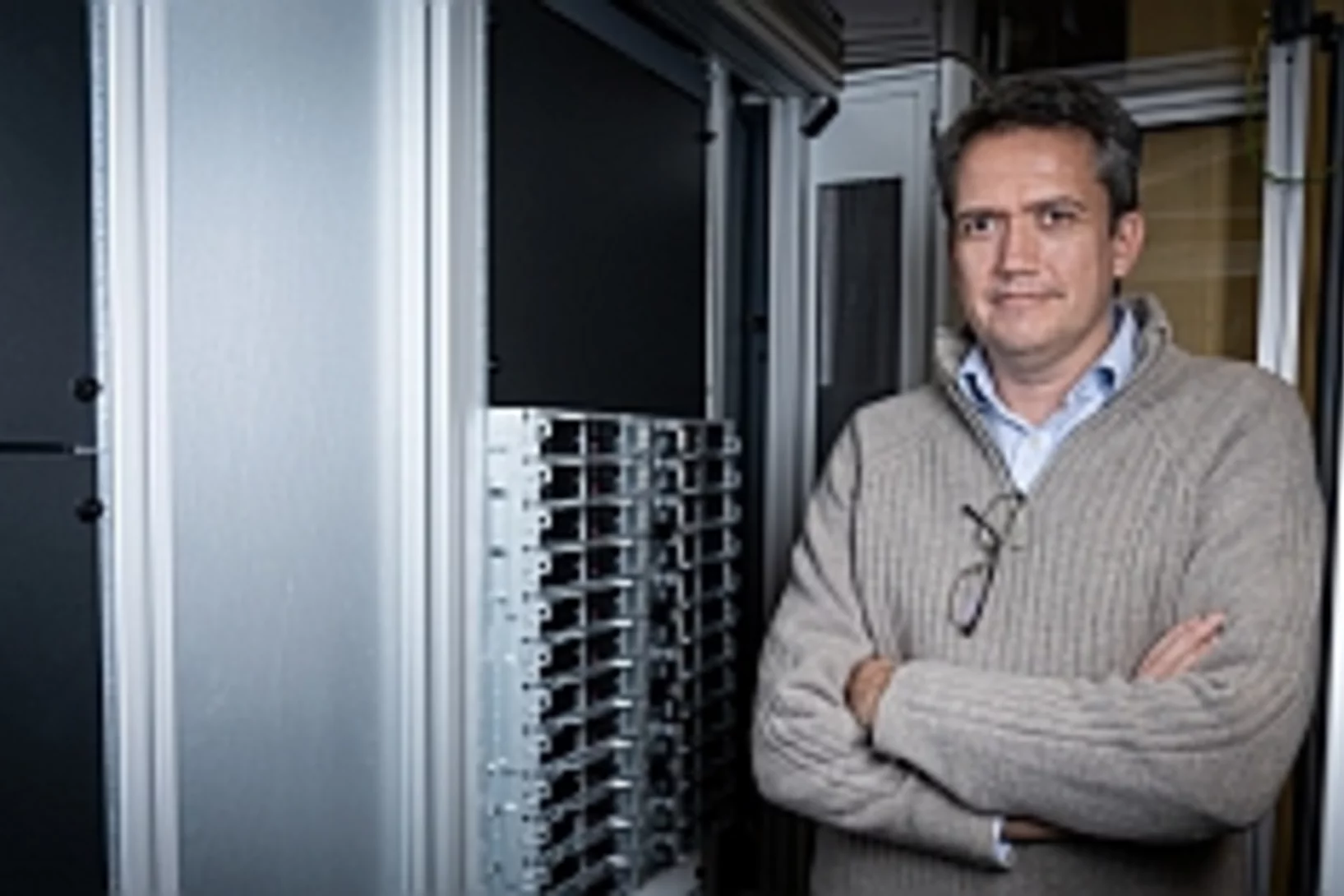
Le bibliothécaire des pétaoctets
L’upgrade prévu de la Source de Lumière Suisse SLS doit être préparé dès maintenant. Pour relever les défis de la recherche de l’avenir, Alun Ashton estime la quantité de données que les futures expériences produiront.