At PSI, several projects are dedicated to important research questions concerning the Sars-CoV-2 coronavirus and the resulting diseases. We provide information on activities and projects, for example on investigations of lung tissue, on the production of proteins and antibodies or on ideas for new research on Covid-19.
Useful links
From synchrotron to CEO
Roger Herger wrote his diploma thesis and doctoral dissertation on X-ray diffraction of complex metal oxides at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) synchrotron. At the end of June 2020, he founded the high-tech startup maXerial, together with two business partners. Their goal: to combine industrial X-ray technology with artificial intelligence. We trace his path from research to entrepreneur and show how cutting-edge PSI know-how and laboratory-based X-ray technology ideally complement each other to solve the challenges of the Swiss high-tech industry by means of data-driven materials development.
Weissbuch Radiochemie Schweiz
In December 2020, the Swiss Academy of Sciences (SCNAT) published its white book on radiochemical education in Switzerland. The report was authored under the lead of Prof. Dr. Roger Alberto (University of Zurich), Dr. Mario Burgener (Spiez Laboratory), and Prof. em. Dr. Heinz W. Gäggeler (University of Bern/Paul Scherrer Institute) and comprises contributions from many experts on the topic from various institutions throughout Switzerland. The white book highlights the imminent loss of experts in the field of radiochemistry and provides solutions to counteract this development.
Look Inside a Chemical Reactor
Operando X-ray spectrotomography allows scientists to look inside of functioning chemical reactors. A research team at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT), at Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in France have employed this method successfully.
Foundations for the energy system of tomorrow
On the way to a sustainable energy system, technologies that help to flexibly convert and efficiently store energy are becoming increasingly important. ReMaP, a novel research platform, aims to investigate these urgent issues under realistic conditions.
Radiochemistry at ETH Zurich
As of December 10, 2020, the ETH Zurich appointed PSI’s Prof. Dr. Patrick Steinegger as assistant professor of radiochemistry (tenure track). Thus, the ETH domain took first counter measures against the imminent loss of radiochemical expertise in Switzerland, emphasized in the “Weissbuch Radiochemie Schweiz” by the Swiss Academy of Sciences (SCNAT). Furthermore, the December issue of CHIMIA (Swiss Chemical Society) invited to present the diverse radiochemical activities throughout the country.
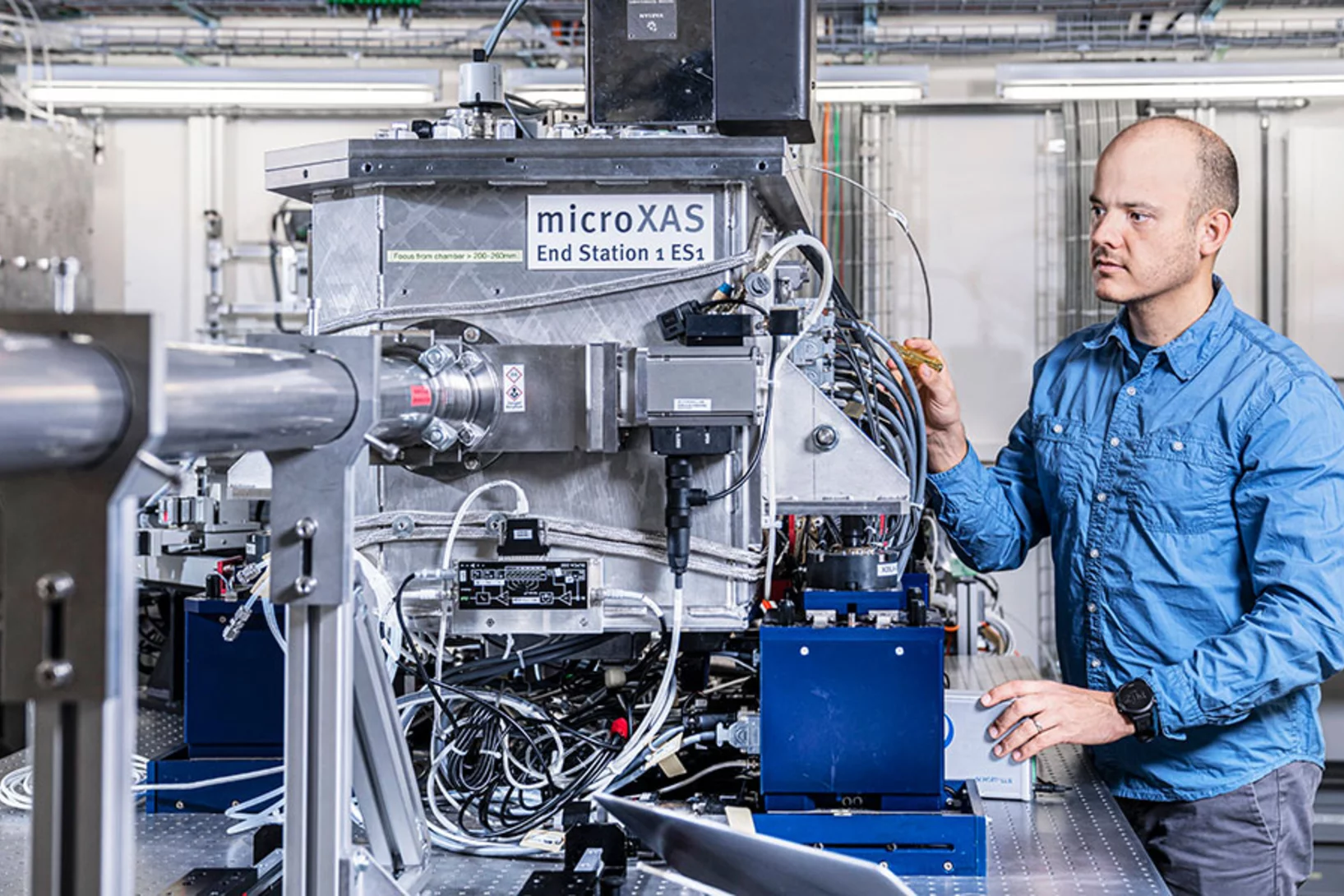
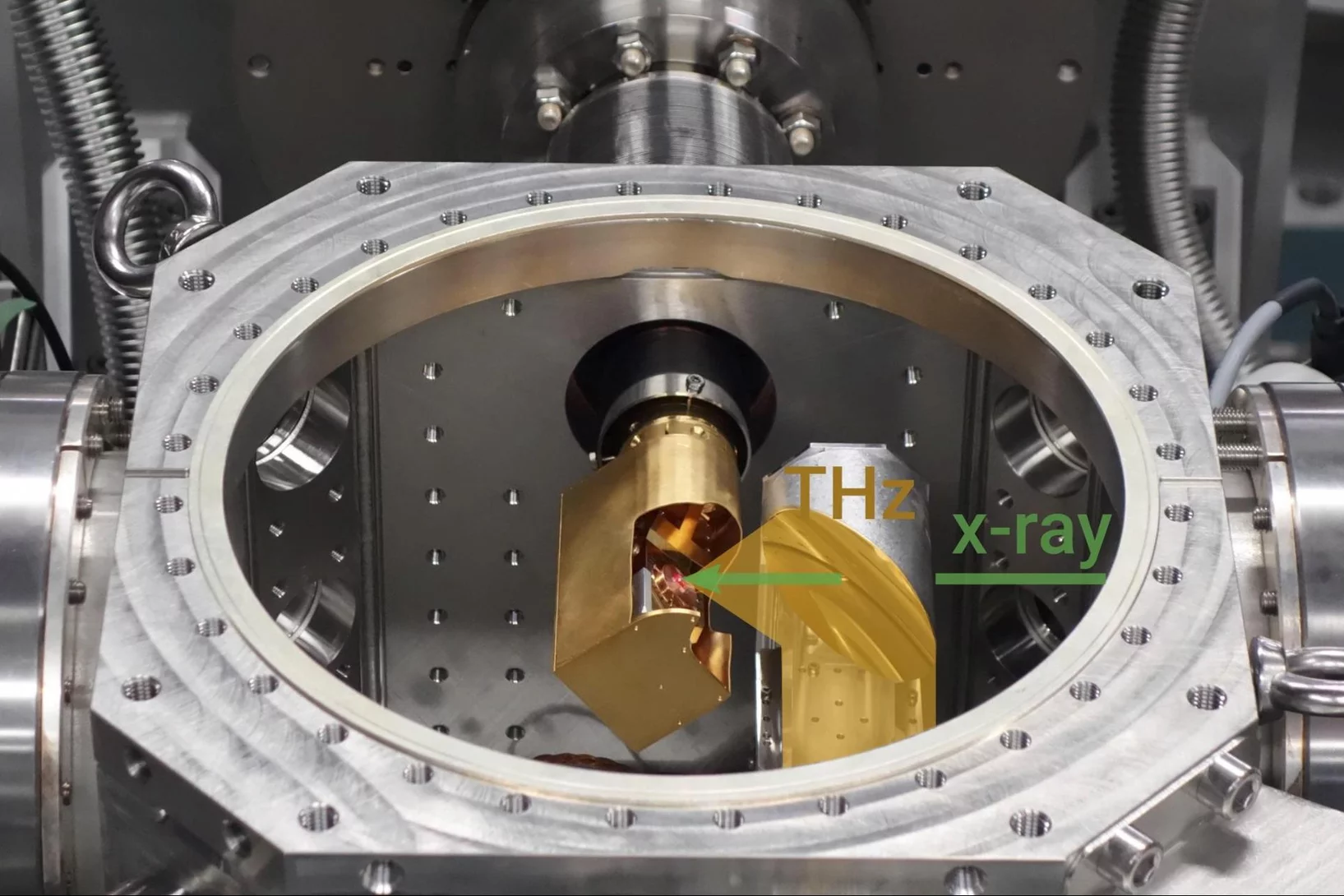
Long-range coherent dynamics of bound electrons in a solid
Ultrafast long-range coherent dynamics in electronic structure excited by THz pulses and studied using free electron laser based resonant X-ray diffraction.
A new small angle neutron scattering instrument arrives at SINQ from LLB
In 2018 an agreement between the Laboratoire Léon Brillouin (LLB) and Paul Scherrer Institut has been signed with the aim to jointly operate a new small angle neutron scattering (SANS) instrument at the Swiss spallation neutron source SINQ.
Marc Janoschek appointed Associate Professor ad personam at University of Zurich
Marc Janoschek, the head of the Laboratory for Neutron and Muon Instrumentation (LIN), was appointed as Associate Professor ad personam for experimental physics – correlated quantum materials at the University of Zurich starting February 1, 2021.
Seven years SCCER Mobility
Synthesis book reviews history, milestones and achievements of the center
The role of aerosols in the Coronavirus pandemic
It now seems certain that Covid-19 can be transmitted via airborne particles. But how are these particles produced? How quickly can transmission occur and how can we protect ourselves? PSI aerosol researcher Urs Baltensperger summarises the most important facts on this issue.
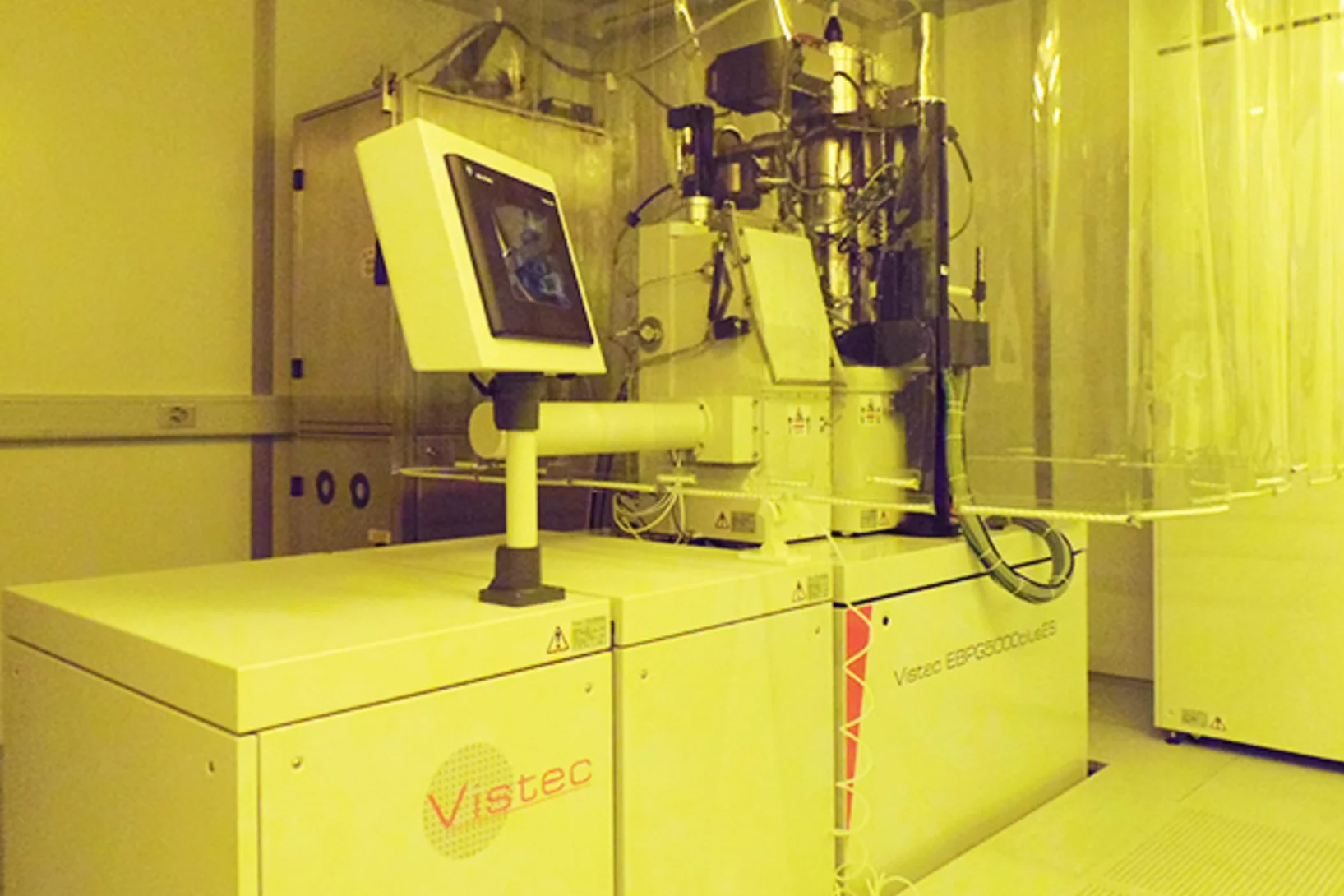
Installation of the new Pattern generator for Raith/Vistec EBPG5000Plus e-beam writer
Supported by SNF R'Equip, a new 20bit low-noise pattern generator for our 100 keV direct write electron beam lithography system Raith/Vistec EBPG5000Plus has been successfully installed. This allows for faster exposures (up to 125MHz stepping frequency) with better placement accuracy within the writing field up to 1x1 mm². The so called Universal Pattern Generator (UPG) supports now a broad spectrum of primitiv shapes, which can dramatically improve the quality of exposed nanostructures by optimized fracturing of designs.
LEC Contribution to the SCCER Mobility Project
Two groups from the Electrochemistry Laboratory, together with a team from ZHAW and EPFL have developed a novel evaporative cooling concept for polymer electrolyte fuel cells from the material to the cell level.
The 5 min movie explains and summarizes the development.
The librarian of the petabytes
It is necessary to prepare now for the planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS. In order to do justice to future research, Alun Ashton is estimating the amount of data that future experiments will produce.
Der ICT-Campus Lenzburg ist eröffnet
Seit 2020 ist das PSI Mitglied beim «ICT-Campus», dem vielversprechendsten Informatik und MINT Nachwuchs Förderungsprojekt der Schweiz. Am 21.10.2020 wurde der neue Standort in Lenzburg mit prominenter Beteiligung eröffnet. Dabei wurden, wegen der Pandemie, die modernsten Mittel eingesetzt.
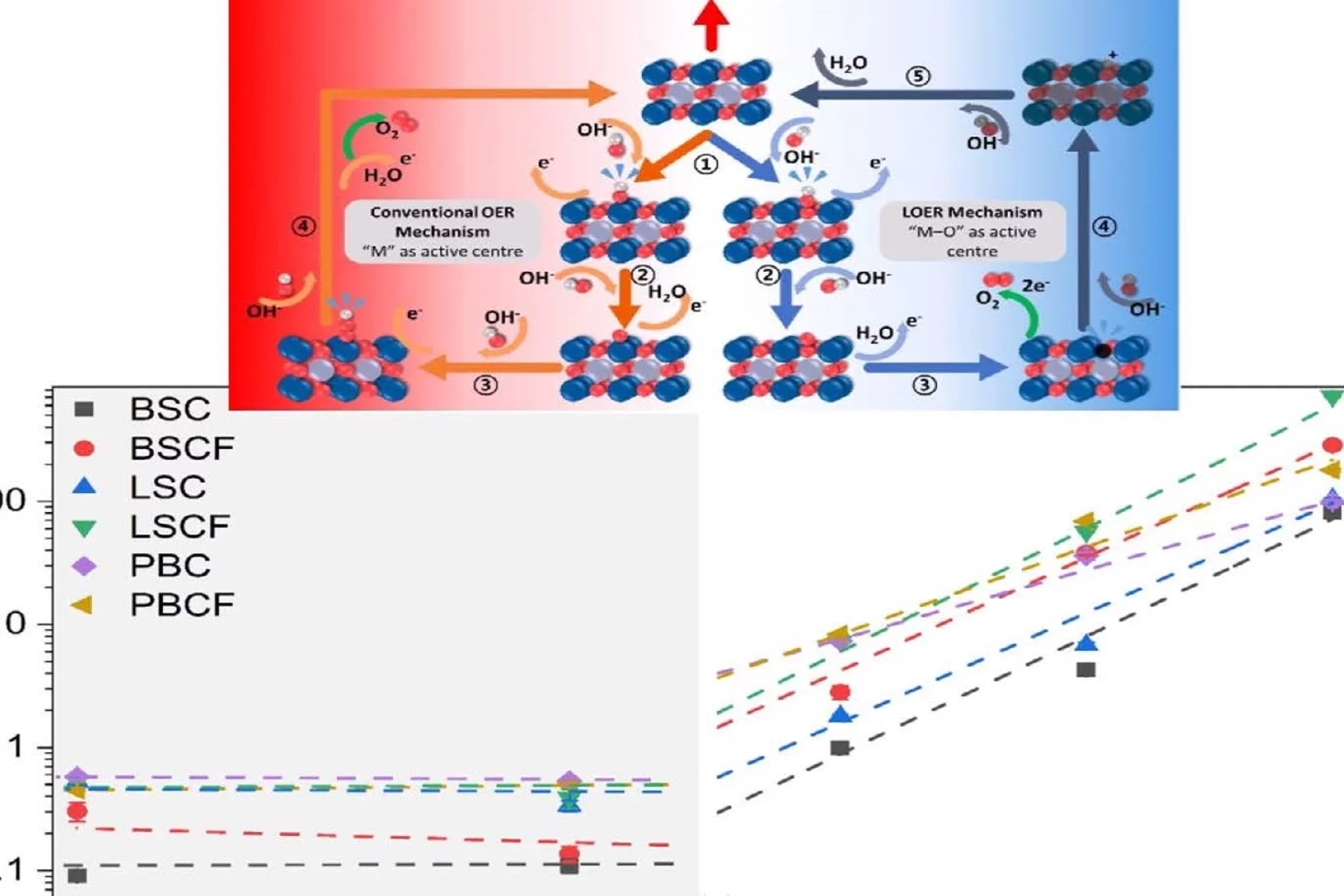
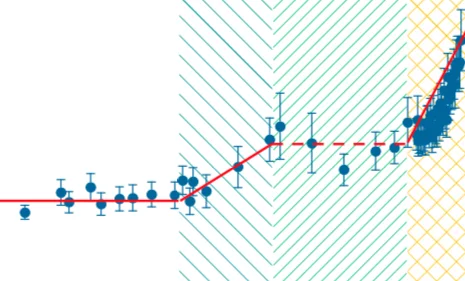
Oxygen Evolution Reaction Activity and Underlying Mechanism of Perovskite Electrocatalysts at Different pH
PSI researchers have studied the how the electrolyte pH values influence the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity and stability of different promising perovskite oxide catalysts for application as anodic electrodes in alkaline water electrolyzers. The OER activity and stability decreased decreasing the electrolyte pH values. By combining electrochemical studies and operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements, it has been suggested that different reaction mechanisms dominate in alkaline and near-neutral electrolyte pH region.
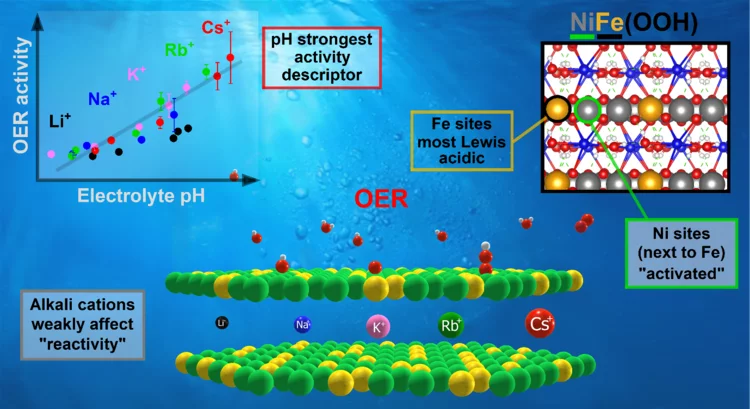
Key activity descriptors of nickel-iron oxygen evolution electrocatalysts in the presence of alkali metal cations
Ni-Fe oxyhydroxide is among the most active oxygen evolution electrocatalysts. Electrolyte alkali metal cations modify the activity and reaction intermediates, however, the exact mechanism is at question due to unexplained deviations from the cation size trend. Our X-ray absorption spectroelectrochemical results show that the OER activity follows the variations in .electrolyte pH rather than a specific cation. Our DFT-based reactivity descriptors confirm the conclusions of an indirect pH effect.
Sustainability Assessment of Potential Areas for Deep Geothermal Energy Systems in Switzerland
In this study, scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) assessed the suitability of potential areas for Deep Geothermal Energy (DGE) systems in Switzerland with regard to their sustainability.
Milestone for the second beamline of SwissFEL
At the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the second beamline is currently being put into operation. With Athos, researchers want to understand how catalysts work or how biomolecules cause hereditary diseases.
CHIMIA: Radiochemistry in Switzerland
The December issue of CHIMIA of the Swiss Chemical Society (SCS) focused on the radiochemical activities throughout Switzerland. Scientists of the Laboratory of Radiochemistry contributed with a number of articles ranging from topics of fundamental sciences to applied research, thereby reflecting on the diverse projects carried out in our laboratory.
From research at PSI to the Aargauer SME Medicoat AG
Even as a doctoral student at PSI, Agnese Carino wanted to put the findings of her research into practice and did not hesitate to present her business idea to the CEO of Medicoat AG, Philipp Gruner. She wanted to develop a novel coating for small implants, which accelerates the recovery of the patient, into a product. Supported by the Hightech Zentrum Aargau this was the starting point of the joint SNI project NanoCoat. Carino was awarded the Founder Fellowship by PSI for her business idea. This program supports the transition from promising research findings to marketable products. We are pleased that Dr. Carino is now working with Medicoat to advance the commercialization of this technology.
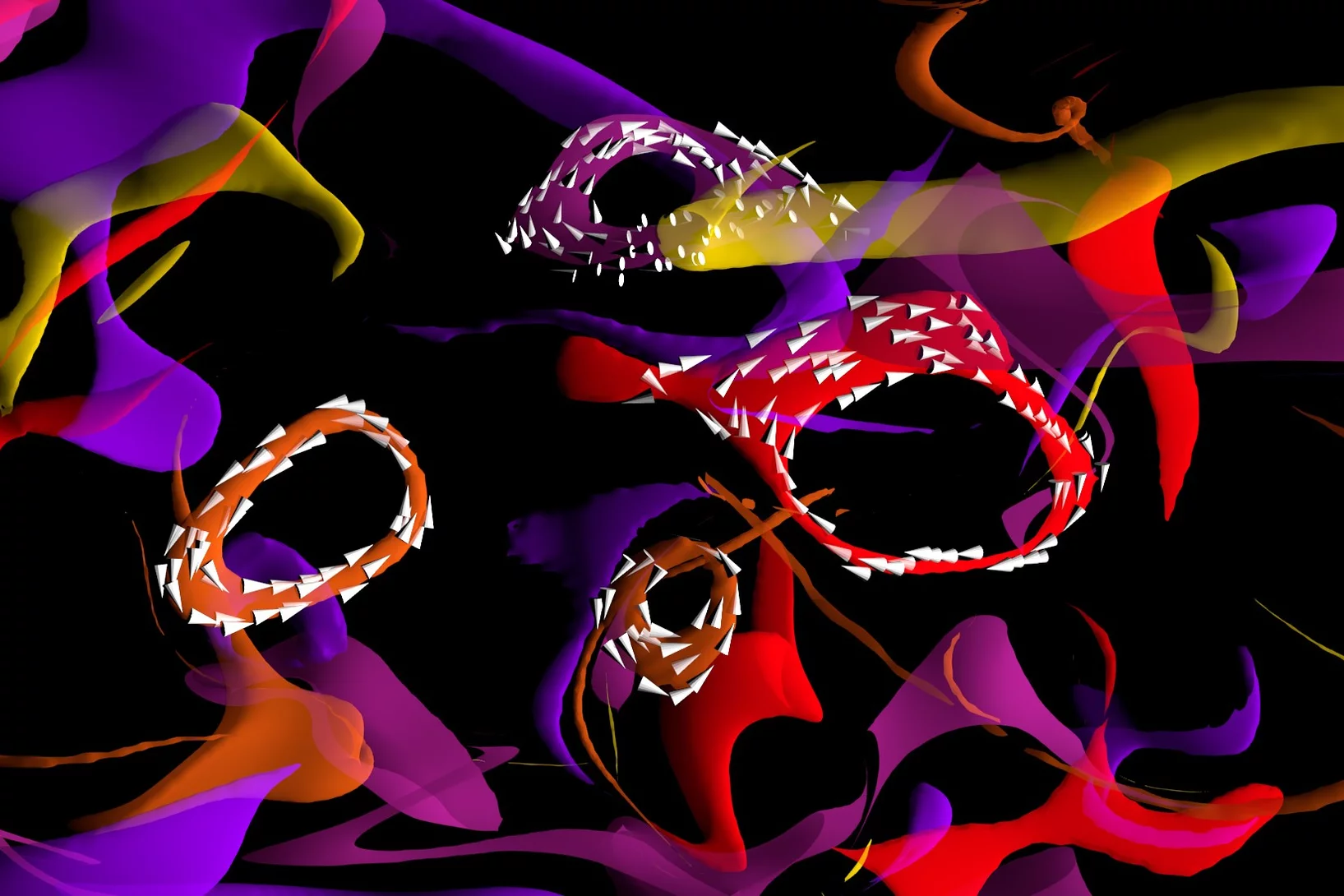
Magnetic vortices come full circle
The first experimental observation of three-dimensional magnetic ‘vortex rings’ provides fundamental insight into intricate nanoscale structures inside bulk magnets, and offers fresh perspectives for magnetic devices.
KIWI-Ausbildungssitzung - XL vom 24.11.20
14 Frauen und ein Mann trafen sich zur späten Stunde
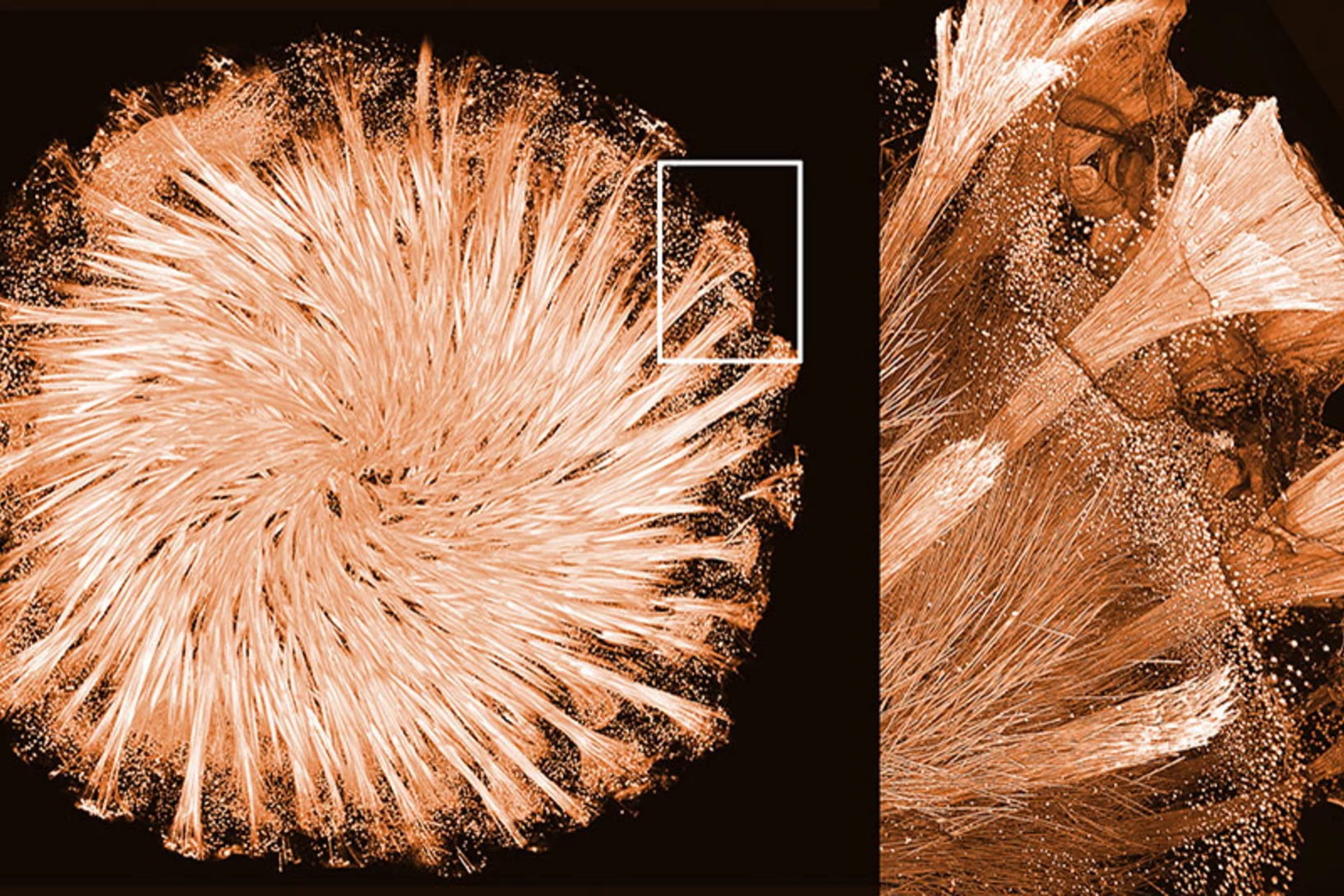
Scientists determine the structure of glass-shaping protein in sponges
Measurements at the Swiss Light Source SLS have helped to understand how the only known natural protein-mineral crystal is formed. It is part of the fascinating glass skeleton of sponges.
Extraordinary times at PSI
In view of the coronavirus pandemic, the Paul Scherrer Institute changed to the extraordinary situation in spring 2020. By then, only a maximum of 20 percent of all PSI employees work at PSI. Five pictures show how research and operations at PSI nevertheless continued.
Ruzicka Prize
The Ružička Prize 2020 goes to Dr. Patrick Hemberger (PSI) for his research on understanding the mechanisms of catalytic fast pyrolysis by unveiling reactive intermediates in heterogeneous catalysts.
BEATS beamline scientist from SESAME synchrotron trains at TOMCAT
TOMCAT welcomes Gianluca Iori, beamline scientist from BEATS - the new beamline for tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan, to a 3-month training on beamline operations. Gianluca’s visit is part of the Staff Training (BEATS Work Package 2) organized for BEATS scientific staff and SESAME control engineers. BEATS is a European project, funded under the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and coordinated by the ESRF.
BEATS beamline scientist from SESAME synchrotron trains at TOMCAT
TOMCAT welcomes Gianluca Iori, beamline scientist from BEATS - the new beamline for tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan, to a 3-month training on beamline operations. Gianluca’s visit is part of the Staff Training (BEATS Work Package 2) organized for BEATS scientific staff and SESAME control engineers. BEATS is a European project, funded under the EU’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and coordinated by the ESRF.
Quantum spin-liquid states in an organic magnetic layer and molecular rotor hybrid
A better understanding of quantum spin liquids (QSLs), where spin dimer configurations are fluctuating even at the low- est temperatures, could be of use in quantum information, in superconducting or other technologies. This macroscopic collective state typically arises from geometrical frustration or low dimensionality. In the layered EDT-BCO, we report a QSL state, which is generated, on different bases, with the intrinsic disorder.
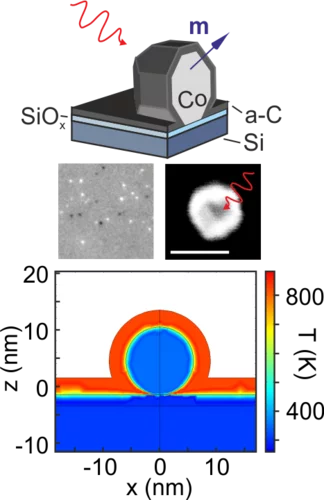
Single femtosecond laser pulse excitation of individual cobalt nanoparticles
The interaction of light and magnetism at the nanoscale is a topic of fundamental interest and with potential impact to future spintronics applications. in this work we address theoretically and experimentally the effect of femtosecond laser pulse excitation on the magnetic, structural, and chemical stability of individual magnetic cobalt nanoparticles including the role of the substrate or matrix. Eventually, we discuss possible pathways to achieve laser-induced magnetic switching in individual nanostructures.
This work has been highlighted as "Editors' Suggestion" in Physical Review B.
Arbeitseinsatz im Naherholungsgebiet der Aare entlang
Da wir dieses Jahr kein Lehrlingslager durchführen konnten, waren unsere Lernenden in der Umgebung des PSIs im Einsatz.