At PSI, several projects are dedicated to important research questions concerning the Sars-CoV-2 coronavirus and the resulting diseases. We provide information on activities and projects, for example on investigations of lung tissue, on the production of proteins and antibodies or on ideas for new research on Covid-19.
Useful links
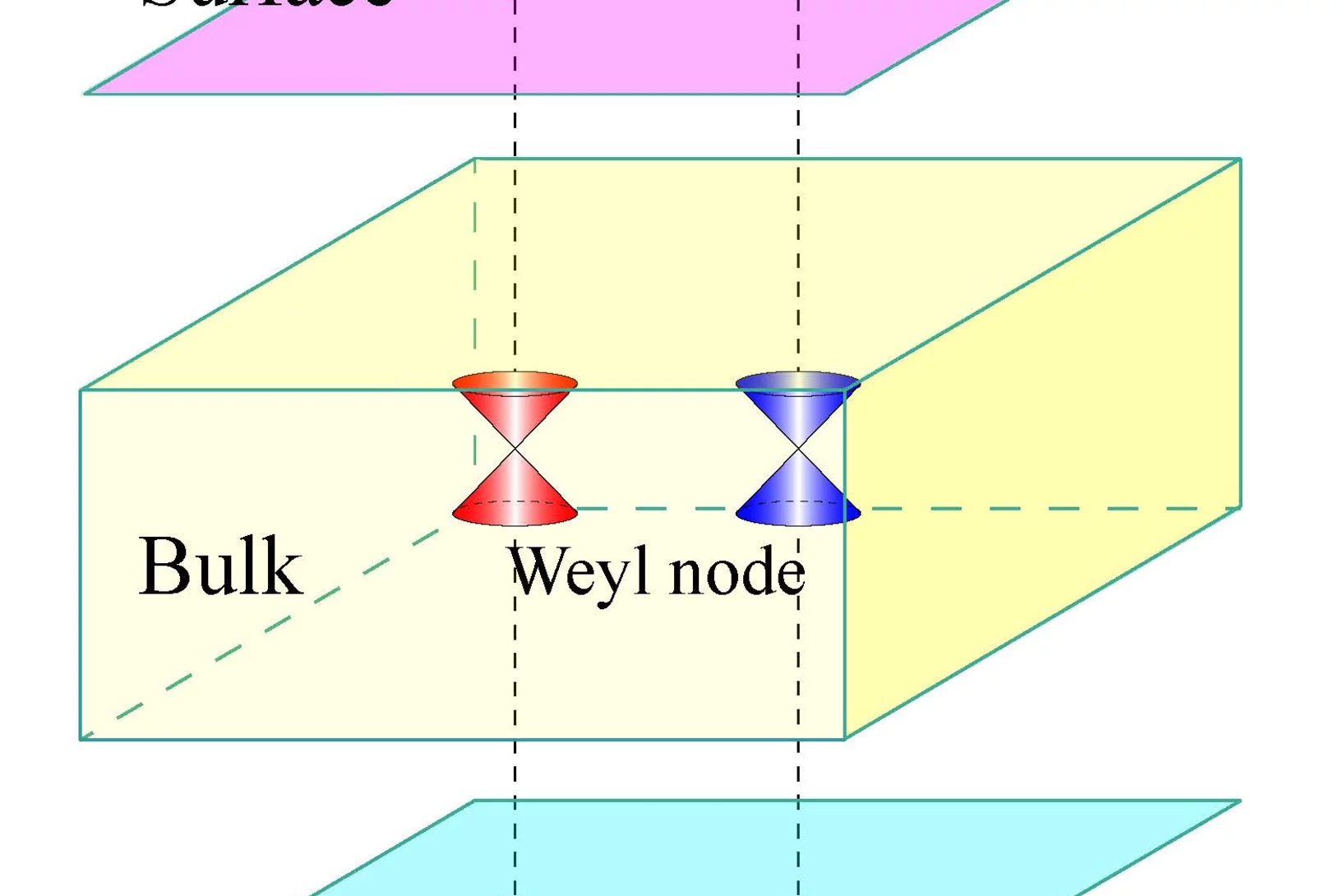
Observation of Fermi-Arc Spin Texture in TaAs
The study of nontrivial topological semimetals (TSM) is an emerging subject, providing a new frontier in topological aspects beyond insulators. Here, we have investigated the spin texture of surface Fermi arcs in the recently discovered Weyl semimetal TaAs using spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. The experimental results demonstrate that the Fermi arcs are spin polarized. The measured spin texture fulfills the requirement of mirror and time-reversal symmetries and is well reproduced by our first-principles calculations, which gives strong evidence for the topologically nontrivial Weyl semimetal state in TaAs. The consistency between the experimental and calculated results further confirms the distribution of chirality of the Weyl nodes determined by first principles calculations.
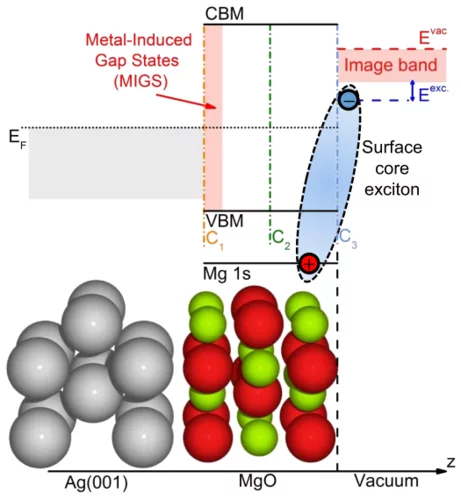
Excited states at interfaces of a metal-supported ultrathin oxide film
At the PEARL beamline, metal-supported ultrathin oxide films have been studied which are a class of materials of technological importance in various research fields such as catalysis, spintronics, or nanoelectronics.
Nationaler Zukunftstag 2015
Am Nationalen Zukunftstag 2015 durften wir 55 Mädchen und 56 Jungs am PSI begrüssen. Die 111 Kinder konnten aus den angebotenen 11 Stationen (Berech¬nungs-ingenieur, Chemieingenieure, Chemielaboranten, Elektroniker, Fachfrauen Betreuung, Metallographen, Physiker, Physiklaboranten, Strukturbiologen, Techn. Laborassistenten und iLab), jeweils zwei auswählen und diese beiden an einem halben Tag besichtigen.
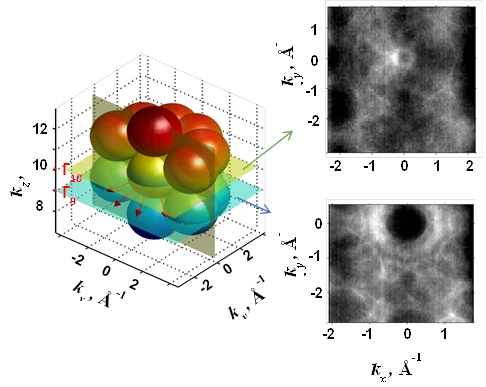
Electron’s cousin discovered after eighty-six-year search
In a series of experiments at the Swiss Light Source SLS, physicists from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have discovered a particle, the existence of which was predicted eighty-six years ago. It is a member of the particle family that also includes the electron, the carrier of electrical currents. The particle now discovered is massless and can exist only within a special class of materials known as Weyl semi-metals.
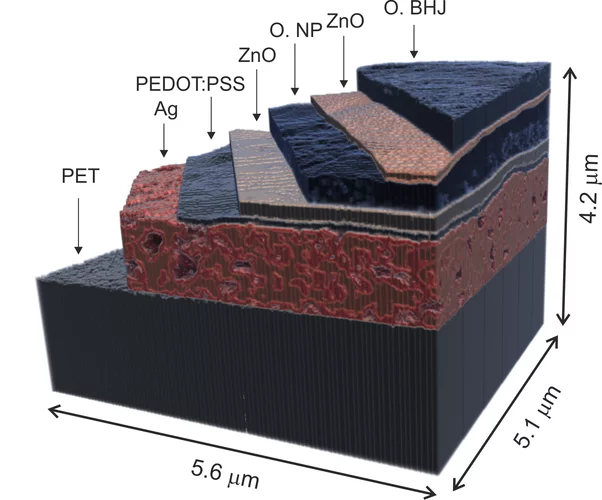
X-ray nanotomography aids the production of eco-friendly solar cells
Polymer solar cells are in the spotlight for sustainable energy production of the future. Characterization of these devices by X-ray nanotomography helps to improve their production using environmentally friendly materials.
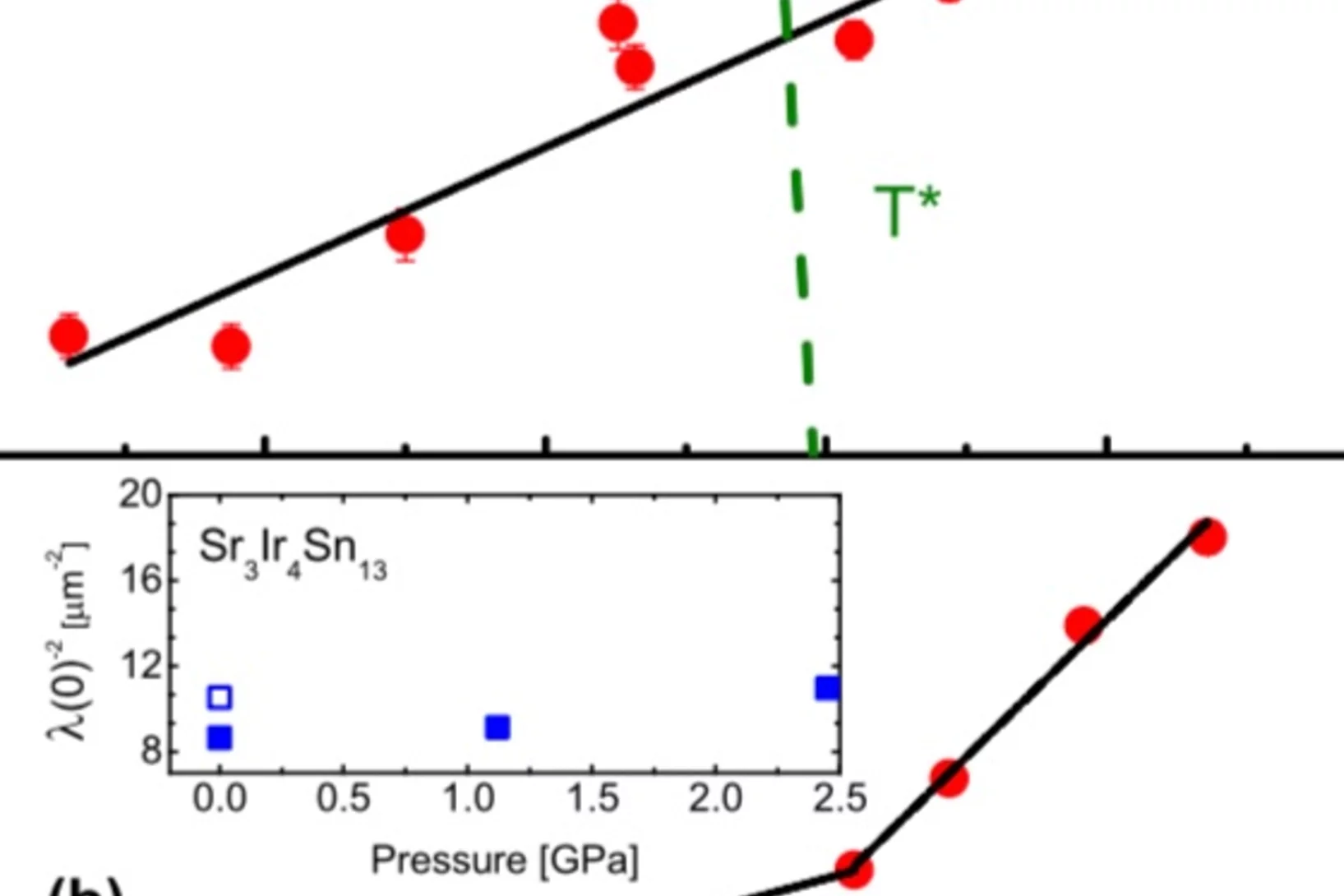
Strong enhancement of s-wave superconductivity near a quantum critical point of Ca3Ir4Sn13
We report microscopic studies by muon spin rotation/relaxation as a function of pressure of the Ca3Ir4Sn13 and Sr3Ir4Sn13 cubic compounds, which are members of the (Ca1−xSrx)3Ir4Sn13 system displaying superconductivity and a structural phase transition associated with the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
At the imaging Photoelectron Photoion Coincidence (iPEPICO) endstation of the VUV beamline evidence of H-atom tunneling was shown.
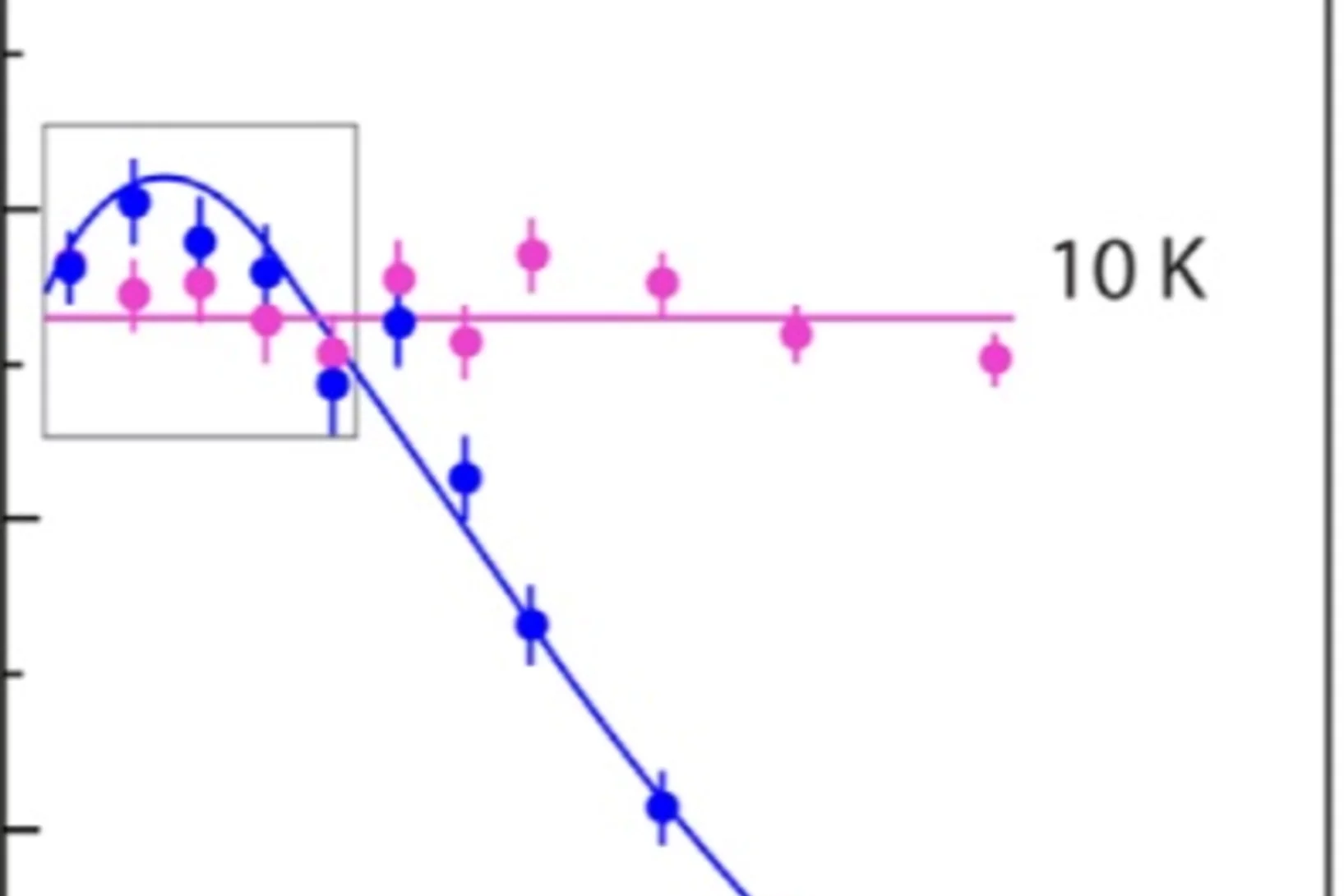
Direct evidence for a pressure-induced nodal superconducting gap in the Ba0.65Rb0.35Fe2As2 superconductor
The superconducting gap structure in iron-based high-temperature superconductors (Fe-HTSs) is non-universal. In contrast to other unconventional superconductors, in the Fe-HTSs both d-wave and extended s-wave pairing symmetries are close in energy. Probing the proximity between these very different superconducting states and identifying experi- mental parameters that can tune them is of central interest.
Intrinsic Paramagnetic Meissner Effect Due to s-Wave Odd-Frequency Superconductivity
In 1933, Meissner and Ochsenfeld reported the expulsion of magnetic flux - the diamagnetic Meissner effect - from the interior of superconducting lead. This discovery was crucial in formulating the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory of superconductivity. In exotic superconducting systems BCS theory does not strictly apply.
Structure of concrete disease
solved
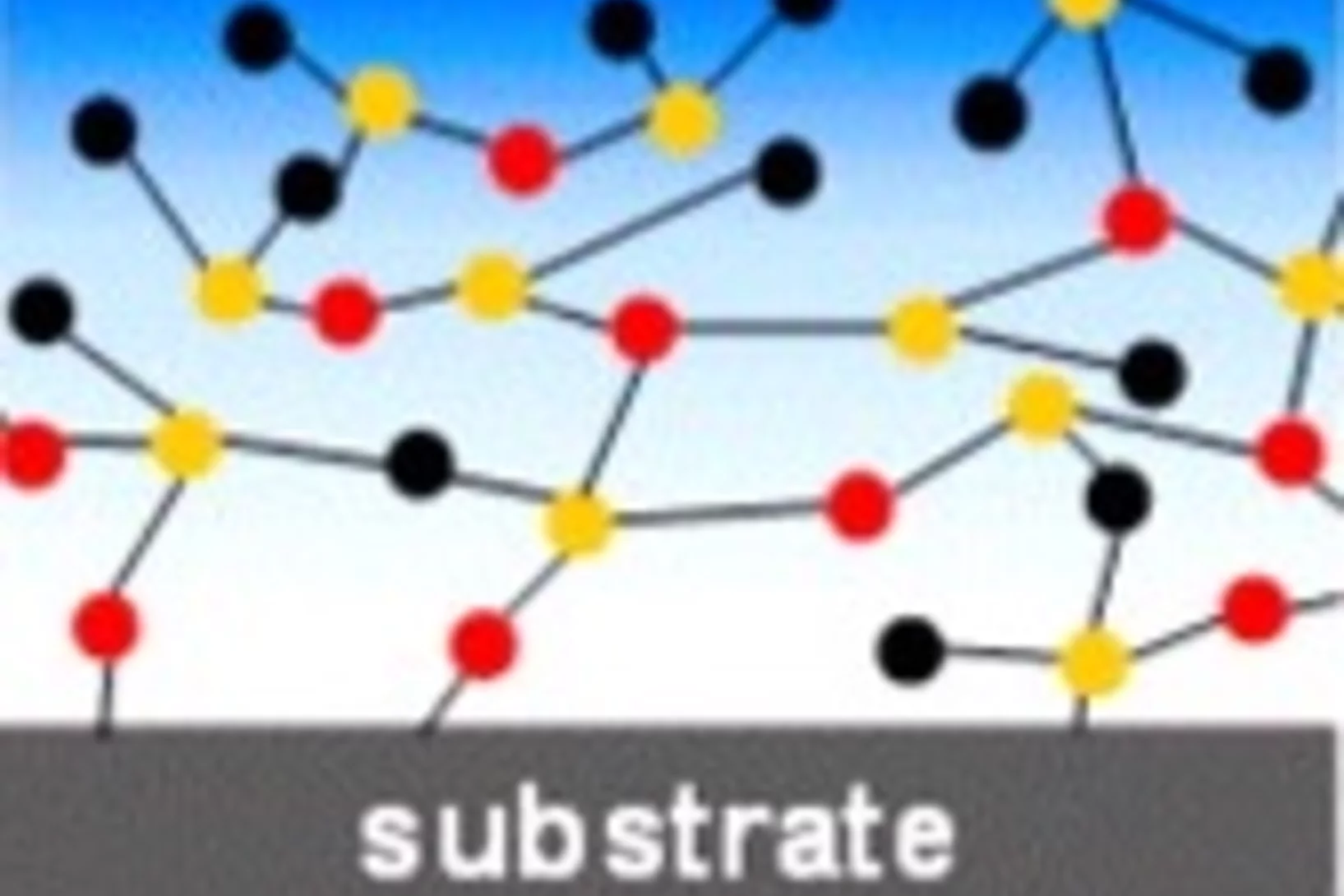
When bridges, dam walls and other structures made of concrete are streaked with dark cracks after a few decades, the culprit is the so-called the concrete disease. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and Empa have now solved the structure of the material produced in these cracks at atomic level - and have thereby discovered a previously unknown crystalline arrangement of the atoms.
New EU project: Guiding light for the world's brightest light sources
EUCALL will build bridges between major laser and X-ray research centres: For the past half-century, two special kinds of light have changed the landscape of research. Advanced visible-spectrum optical lasers have propelled studies into ultrafast processes, new materials, telecommunications, and many other fields, while intense X-rays produced at synchrotrons have helped image tiny structures and otherwise invisible parts of matter, enabling huge leaps in biochemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. New developments have enhanced the generation of X-rays at optical-laser and accelerator facilities, resulting in the creation of large international research centres. The European Union is now funding a 7 million-euro effort to bring these research centres together through the European Cluster of Advanced Laser Light Sources (EUCALL) project.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
X-ray research in the UFO
At first glance, the Swiss Light Source SLS stands out as a striking building. The inside reveals a setting of cutting-edge research. A journey through a world where electrons race a slalom course and X-rays help decode proteins.
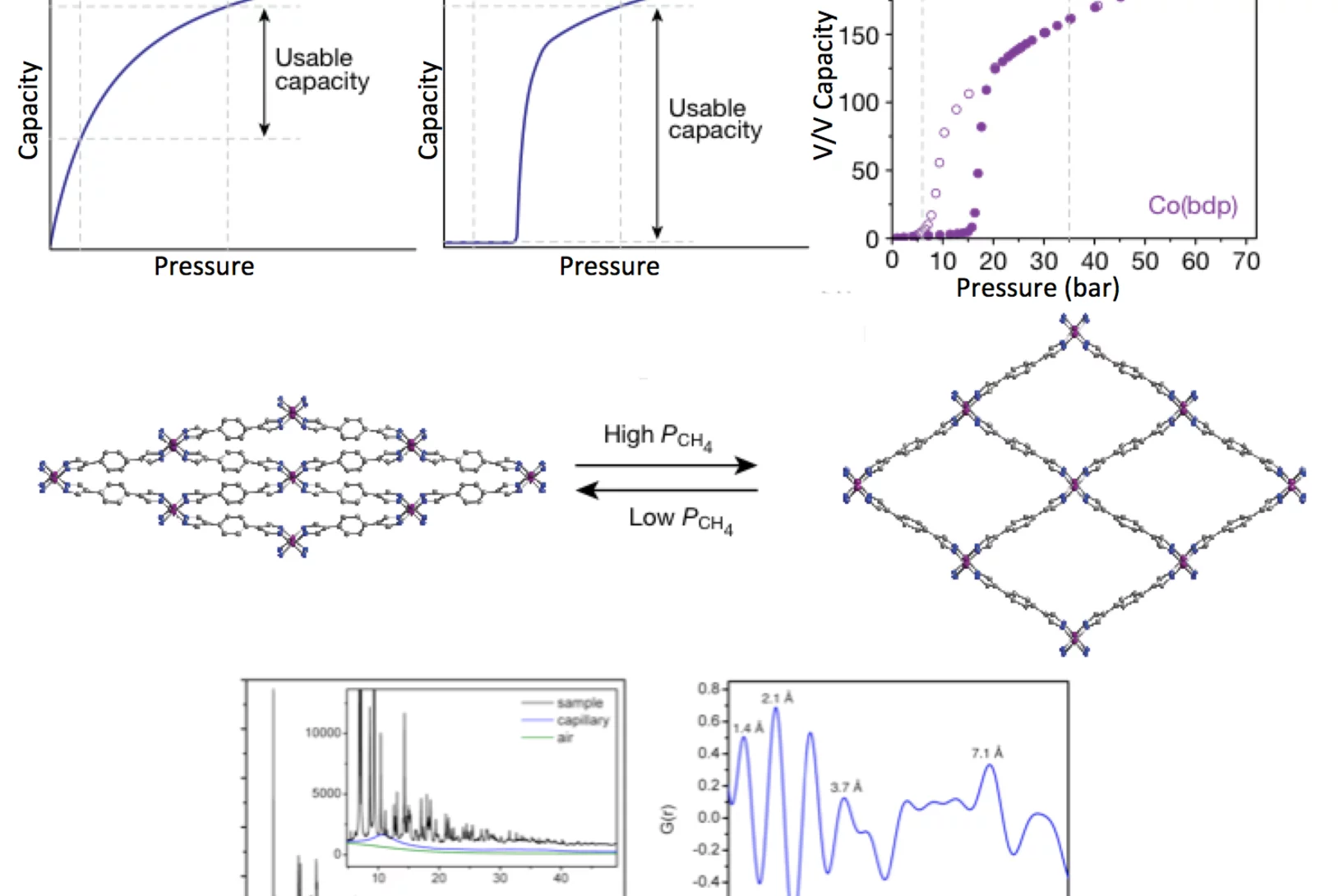
Methane storage in flexible metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic thermal management
As a cleaner, cheaper, and more globally evenly distributed fuel, natural gas has considerable environmental, economic, and political advantages over petroleum as a source of energy for the transportation sector. Despite these benefits, its low volumetric energy density at ambient temperature and moderate pressure presents substantial challenges, particularly for light-duty vehicles with little space available for on-board fuel storage.
Put in perspective
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded in using commercially available camera technology to visualise terahertz light. In doing so, they are enabling a low-cost alternative to the procedure available to date, whilst simultaneously increasing the comparative image resolution by a factor of 25. The special properties of terahertz light make it potentially advantageous for many applications. At PSI, it will be used for the experiments on the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL.
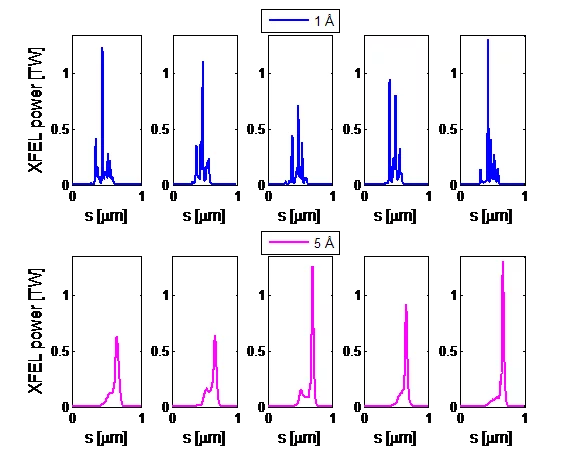
New methods to generate short and high-power X-ray Free-Electron-Laser pulses
State-of-the-art X-ray Free-Electron-Laser (XFEL) facilities like SwissFEL are able to provide radiation pulses with pulse powers of a few tens of gigawatts and pulse durations of several tens of femtoseconds and shorter. There is, however, a strong demand in research fields such as bioimaging and nonlinear optics to obtain higher radiation powers and shorter pulses than in standard facilities. In this context, we have developed two new methods able to generate terawatt-attosecond XFEL pulses. Both proposals are based on superradiance, a regime with quadratic growth of the radiation power and a shortening of the spike while it slips into unspoiled (good-beam) regions of the bunch.
Put in perspective
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded in using commercially available camera technology to visualise terahertz light. In doing so, they are enabling a low-cost alternative to the procedure available to date, whilst simultaneously increasing the comparative image resolution by a factor of 25. The special properties of terahertz light make it potentially advantageous for many applications, from safety technology to medical diagnostics.
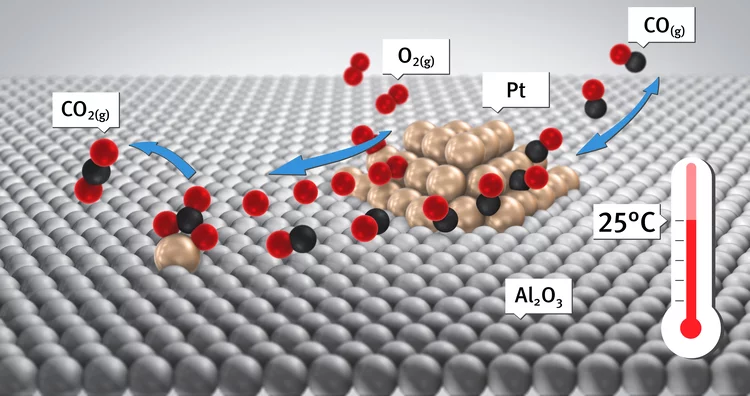
Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt-Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
A new possibility for the attainment of low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide is demonstrated. Here we report using time-resolved DRIFTS, XAS, and mass spectrometry a platinum carbonate-mediated mechanism for the room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide.
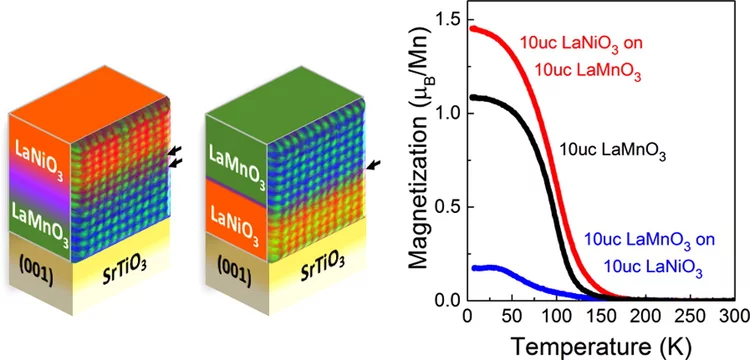
Interfacial Control of Magnetic Properties at LaMnO3/LaNiO3 heterostructures
Using a X-ray magnetic circular dichroism measured at the X-Treme beamline, SLS, in conjunction with X-ray reflectivity measured at the SEXTANTS beamline, SOLEIL, the authors show that the degree of intermixing at the monolayer scale allows interface-driven properties such as charge transfer and the induced magnetic moment in the nickelate layer to be controlled.
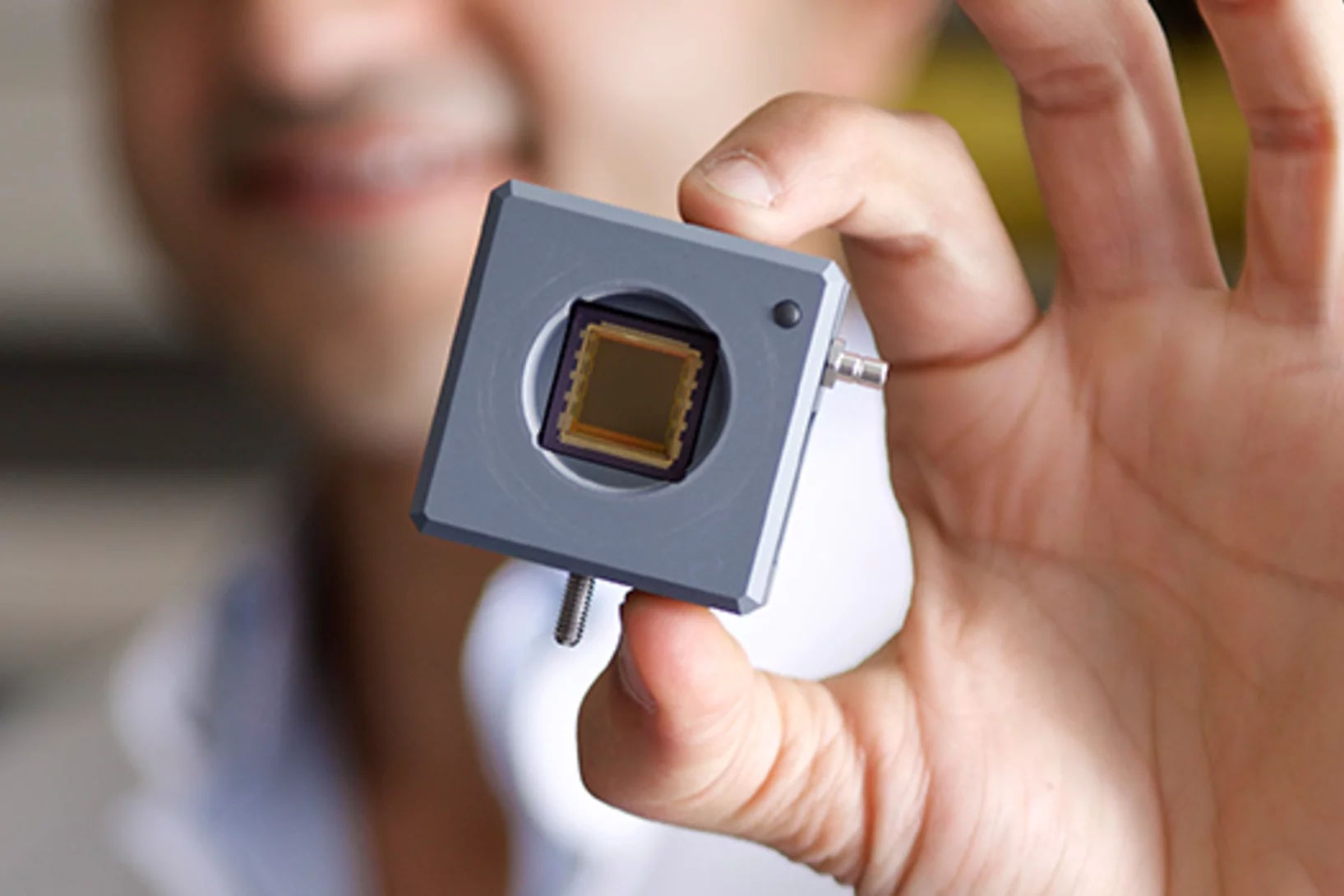
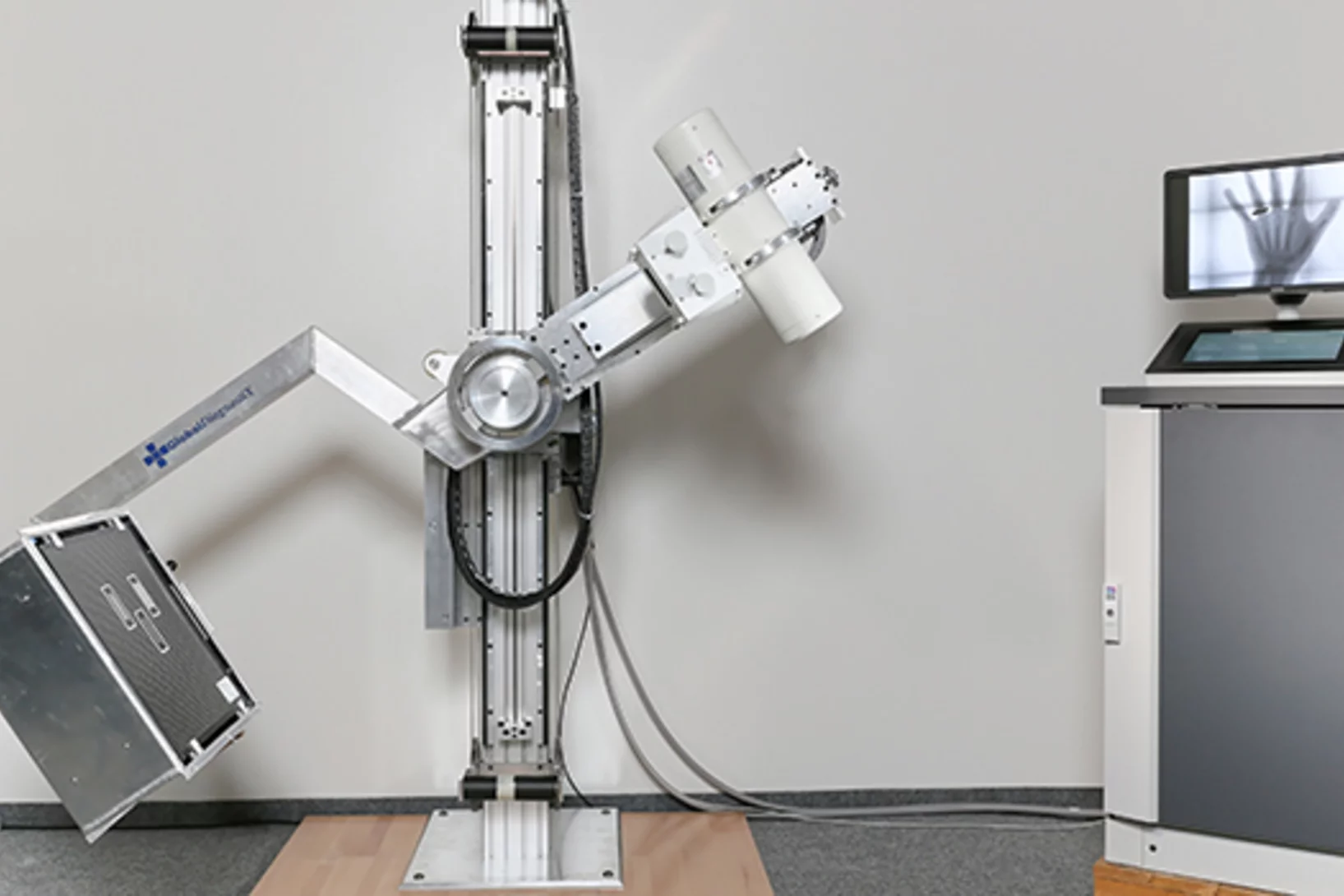
Robust X-ray machine for developing countries
The Paul Scherrer Institute PSI is involved in a project conducted by several research institutes (spearheaded by EPFL) to devise an X-ray machine especially for developing countries. The device should be able to cope with tropical climes and be easy and cheap to repair. PSI researchers are focusing on producing a cost-effective detector that is necessary for the imaging. The detector registers the X-ray light much like a chip in a digital camera.
Fermi states and anisotropy of Brillouin zone scattering in the decagonal Al–Ni–Co quasicrystal
Quasicrystals (QCs) are intermetallic alloys where excellent long-range order coexists with lack of translational symmetry in one or more dimensions. These materials have a high potential in application as a material for a solar cells, hydrogen storage applications, heat insulating layers, and others.
Observation of Gravitationally Induced Vertical Striation of Polarized Ultracold Neutrons by Spin-Echo Spectroscopy
We describe a spin-echo method for ultracold neutrons (UCNs) confined in a precession chamber and exposed to a |B0| = 1μT magnetic field. We have demonstrated that the analysis of UCN spin-echo resonance signals in combination with knowledge of the ambient magnetic field provides an excellent method by which to reconstruct the energy spectrum of a confined ensemble of neutrons.
Response of Plasma-Polymerized Hexamethyldisiloxane Films to Aqueous Environments
Thin plasma polymer films were deposited in hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) and HMDSO/O2 low-pressure discharges and their chemical structures analyzed using infrared (IR) spectroscopy and neutron reflectometry (NR). The (plasma-polymerized) ppHMDSO film exhibits hydrophobic, poly(dimethylsiloxane)-like properties, while the retention of carbon groups is reduced by O2 addition, yielding a more inorganic, hydrophilic ppSiOx film.
More robust thanks to imperfections
Microscopic deviations from the ideal structure render uranium dioxide, the fuel commonly used in nuclear power plants, more resistant to radiation damage.
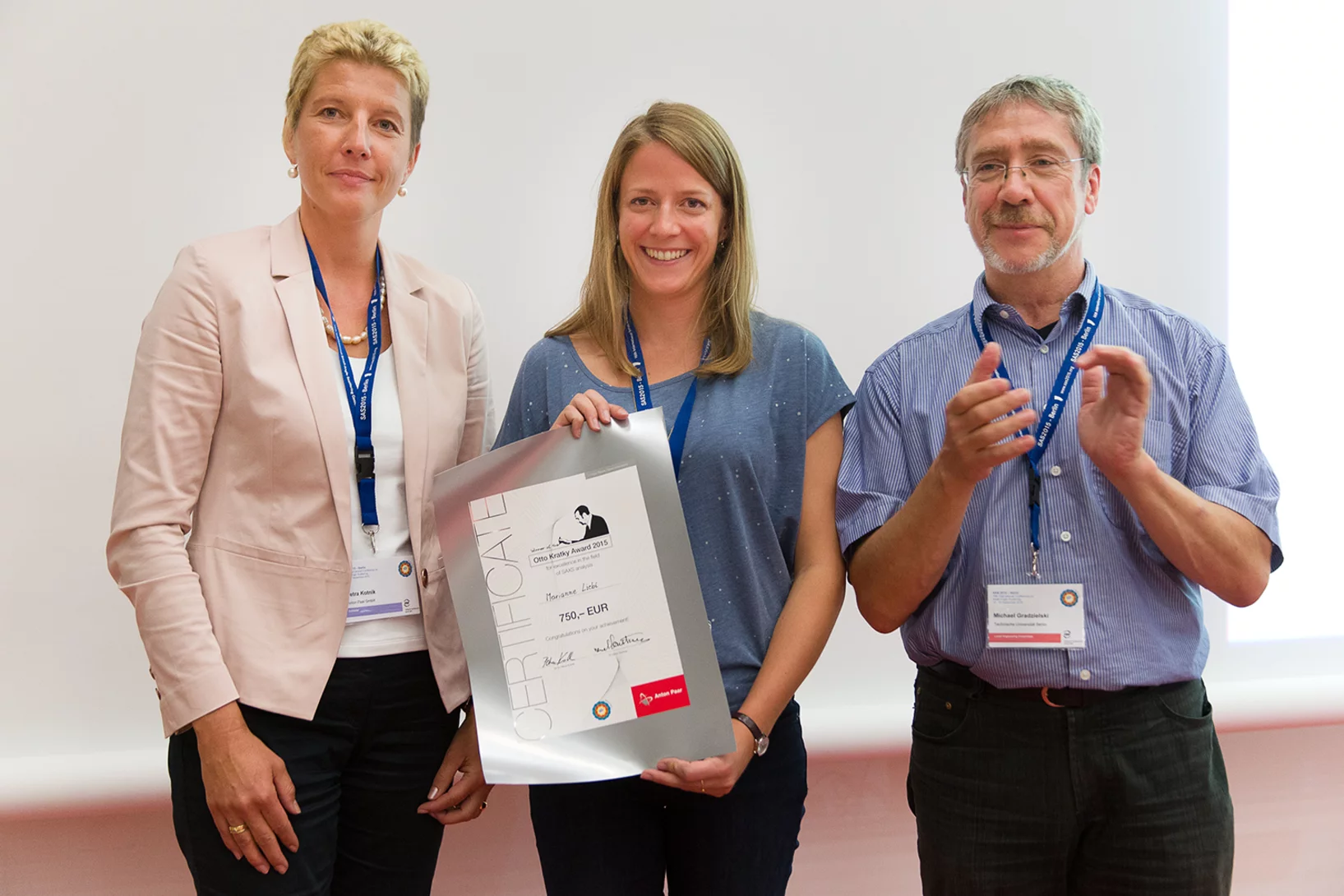
2015 Otto Kratky award
Marianne Liebi was awarded the 2015 Otto Kratky award by the Helmholtz-Centre Berlin for excellence in the field of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis. The award was bestowed in the last SAS2015 conference in Berlin. Marianne is a postdoctoral fellow in the coherent X-ray scattering group (CXS) in PSI, carrying out research in scanning SAXS measurement and analysis in 2D and 3D. Image credit ©HZB/Michael Setzpfandt
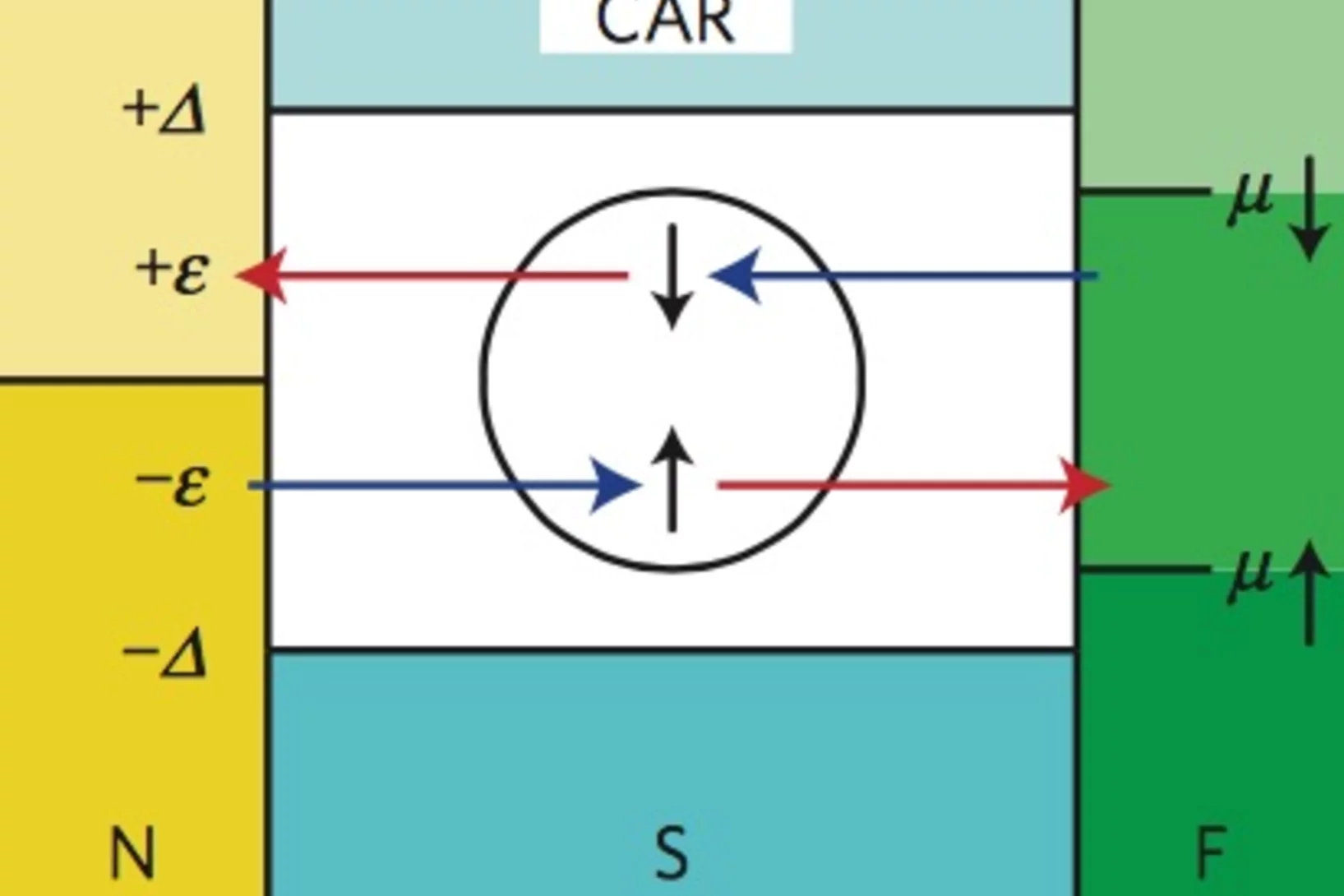
Remotely induced magnetism in a normal metal using a superconducting spin-valve
Superconducting spintronics has emerged in the past decade as a promising new field that seeks to open a new dimension for nanoelectronics by utilizing the internal spin structure of the superconducting Cooper pair as a new degree of freedom. Its basic building blocks are spin-triplet Cooper pairs with equally aligned spins, which are promoted by proximity of a conventional superconductor to a ferromagnetic material with inhomogeneous macroscopic magnetization.
New method will enable most accurate neutron measurement yet
Our universe consists of significantly more matter than existing theories are able to explain. This is one of the great puzzles of modern science. One way to clarify this discrepancy is via the neutron’s so-called electric dipole moment. In an international collaboration, researchers at PSI have now devised a new method which will help determine this dipole moment more accurately than ever before.
Perfect beamlines go unnoticed
Interview with Luc PattheyLuc Patthey is in charge of designing and implementing the beamlines for the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL. In this Interview, he explains the requirements the beamlines need to meet for the X-ray light pulses generated by SwissFEL to reach the experiments in an optimal form and what role collaborations play in the development of beamlines.
Water pathways make fuel cells more efficient
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have developed a coating technique in the laboratory conditions that could raise the efficiency of fuel cells. The PSI scientists have already applied to patent the technique, which is suitable for mass production.