At PSI, several projects are dedicated to important research questions concerning the Sars-CoV-2 coronavirus and the resulting diseases. We provide information on activities and projects, for example on investigations of lung tissue, on the production of proteins and antibodies or on ideas for new research on Covid-19.
Useful links
Airpocalypse explained
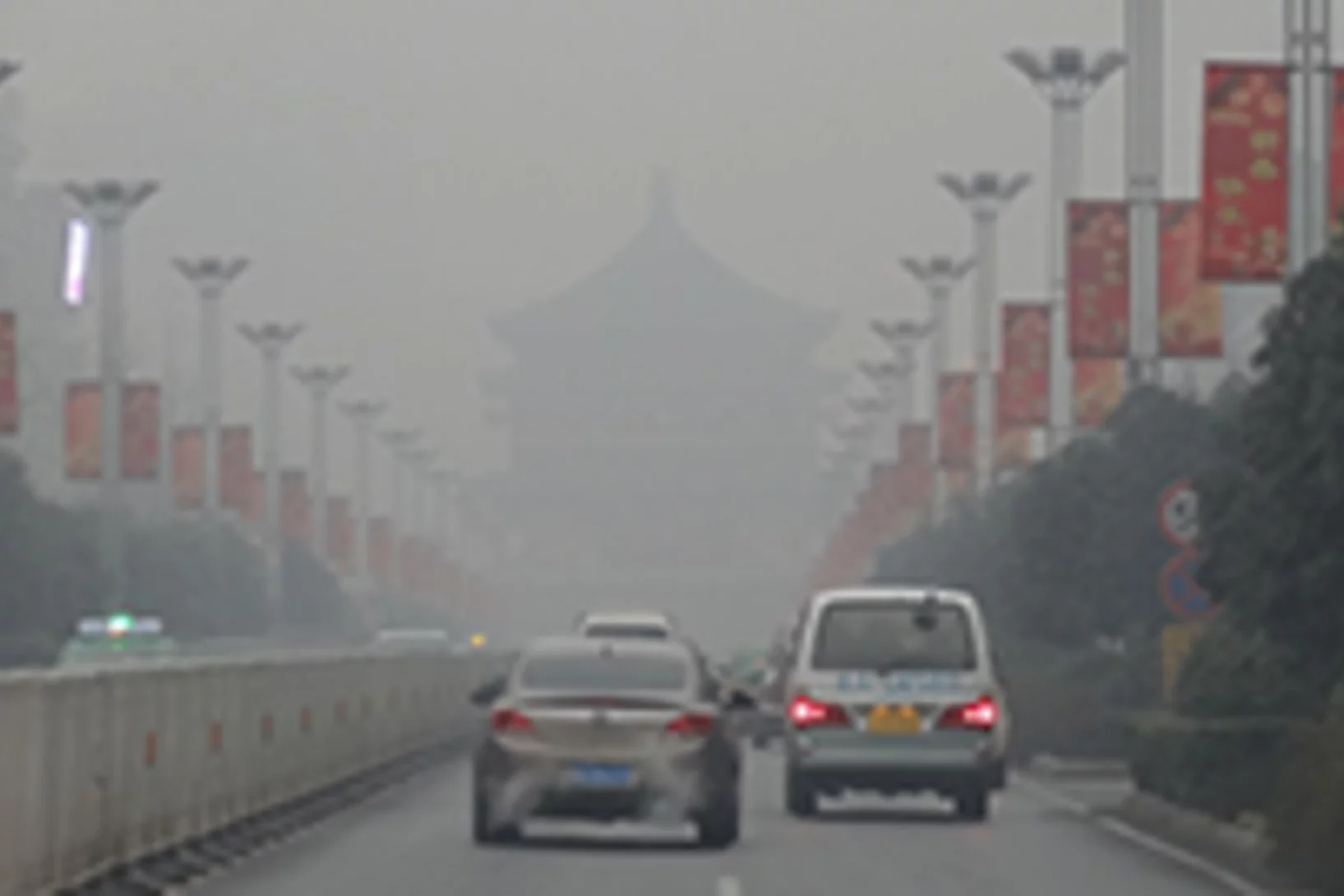
The causes of China's record level fine particulate pollution in winter 2013 At the beginning of 2013 a greyish-brown blanket of smog lay over large areas of China for several months. The fine particle pollution was higher by 1 to 2 orders of magnitude than the levels normally measured in Western Europe and the United States. An international team of researchers under the lead of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and the Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of the Sciences revealed the causes of the airpocalypse. The study published in the journal Nature also describes what steps are to be taken to prevent an environmental crisis of this kind in the future.
Energiewende in Reinkultur – in Wädenswil zu bestaunen
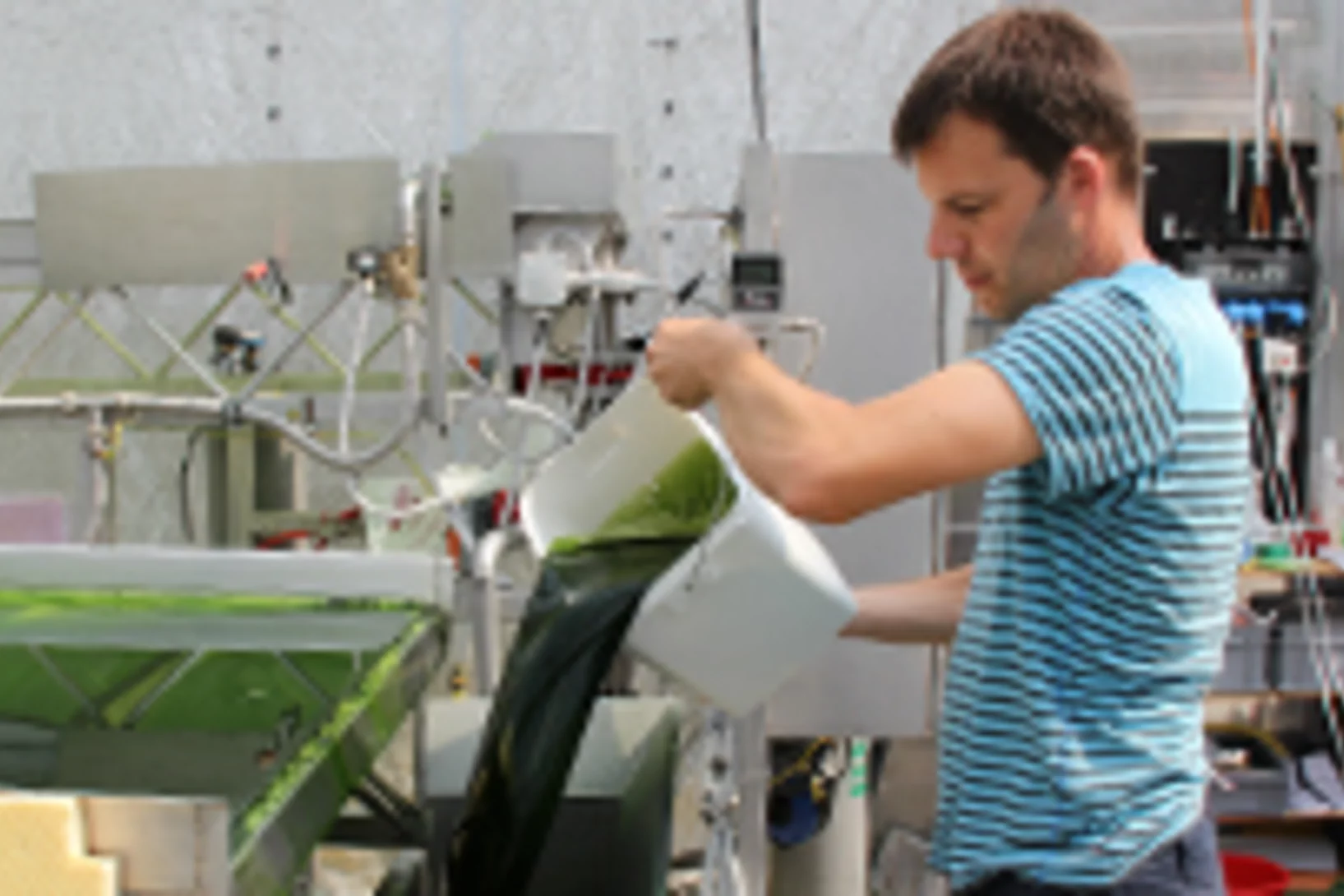
Der am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI entwickelte Prozess der hydrothermalen Methanierung von wässriger Biomasse erreicht einen wichtigen Meilenstein: Dank der Zusammenarbeit im neuen Kompetenzzentrum des Bundes für Bioenergie BIOSWEET konnten Forschende des PSI, der ZHAW, der ETH Lausanne, der Empa und der Hochschule für Technik Rapperswil die technische Machbarkeit der Methanherstellung aus Mikroalgen demonstrieren. Der dazu verwendete Algenbioreaktor sowie die Anlage zur Methanierung der Algen können am 24. September auf dem Campus Grüental der ZHAW in Wädenswil besichtigt werden. Für Medienschaffende gibt es von 14:00 bis 14:30 eine spezielle Führung.This news release is only available in German.
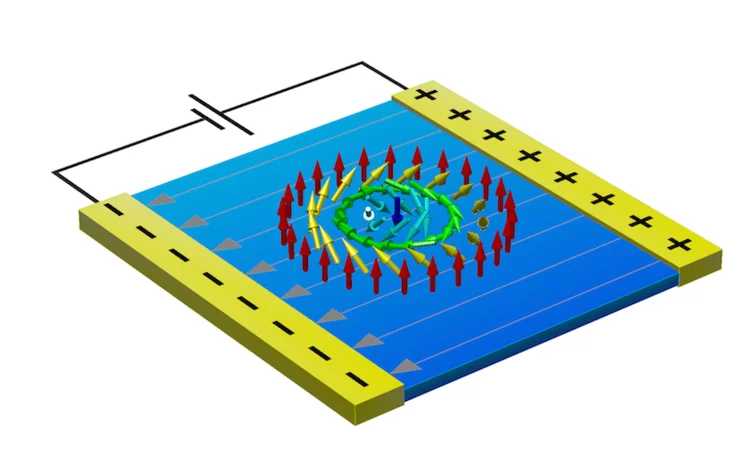
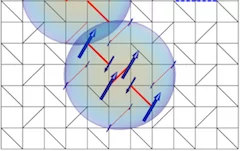
Electric-Field-Induced Skyrmion Distortion and Giant Lattice Rotation in the Magnetoelectric Insulator Cu2OSeO3
Discovering fundamentally new ways to manipulate magnetic spins is crucial for research into advanced technologies. Magnetic Skyrmions, which are topologically stable whirls of magnetic spins, are promising candidates for new device components since those found in metallic host materials can be manipulated using electric currents.
New material generated with light
PSI researchers garner experience for SwissFEL experimentsAided by short laser flashes, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have managed to temporarily change a material’s properties to such a degree that they have à to a certain extent àcreated a new material. This was done using the x-ray laser LCLS in California. Once the PSI x-ray laser SwissFEL is up and running, experiments of this kind will also be possible at PSI.
Controlling the near-surface superfluid density in under doped YBa2Cu3O6+x by photo-illumination
The interaction with light weakens the superconducting ground state in classical superconductors. The situation in cuprate superconductors is more complicated: illumination increases the charge carrier density, a photo-induced effect that persists below room temperature. Furthermore, systematic investigations in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6+x (YBCO) have shown an enhanced critical temperature Tc. Until now, studies of photo-persistent conductivity (PPC) have been limited to investigations of structural and transport properties, as well as the onset of superconductivity.
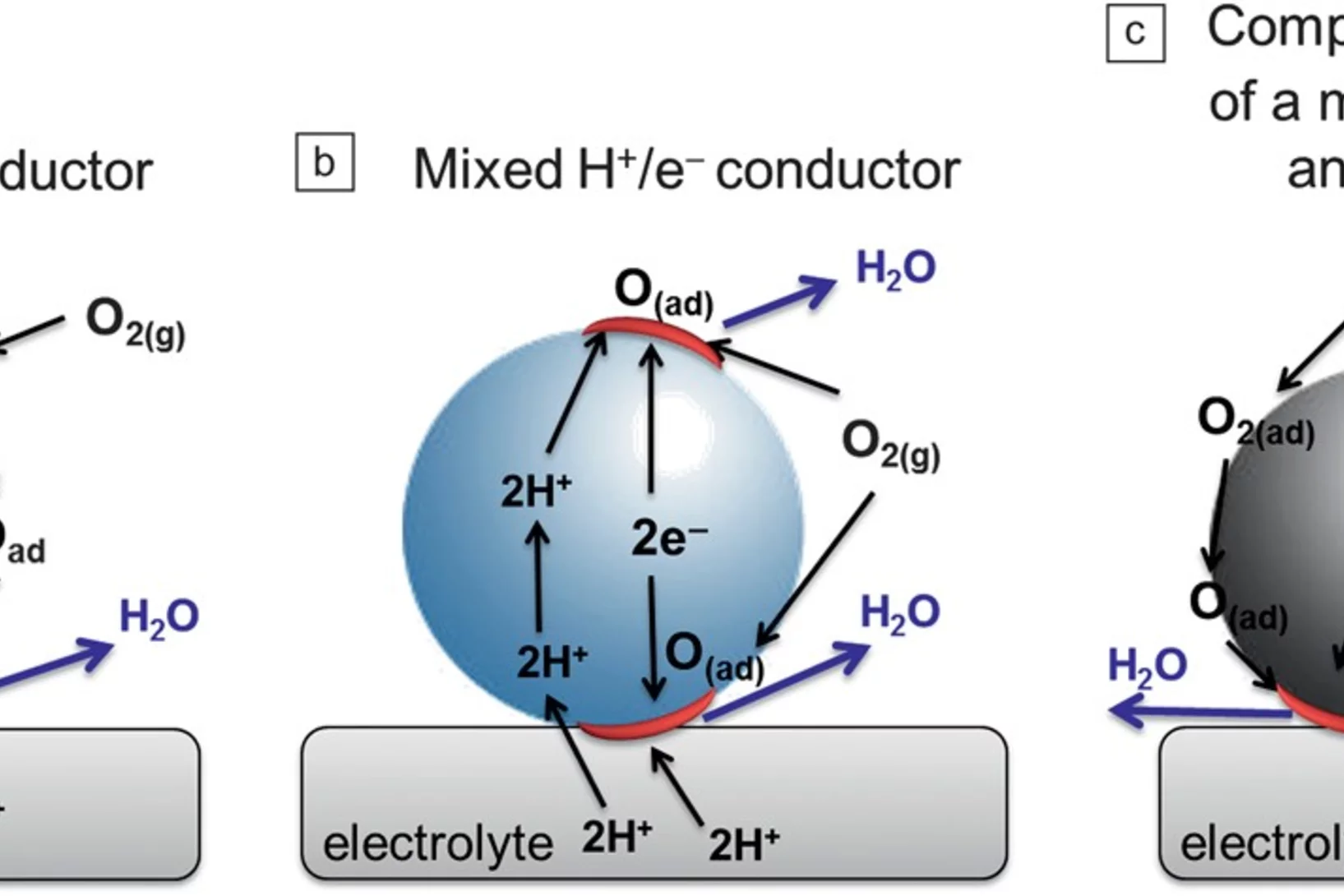
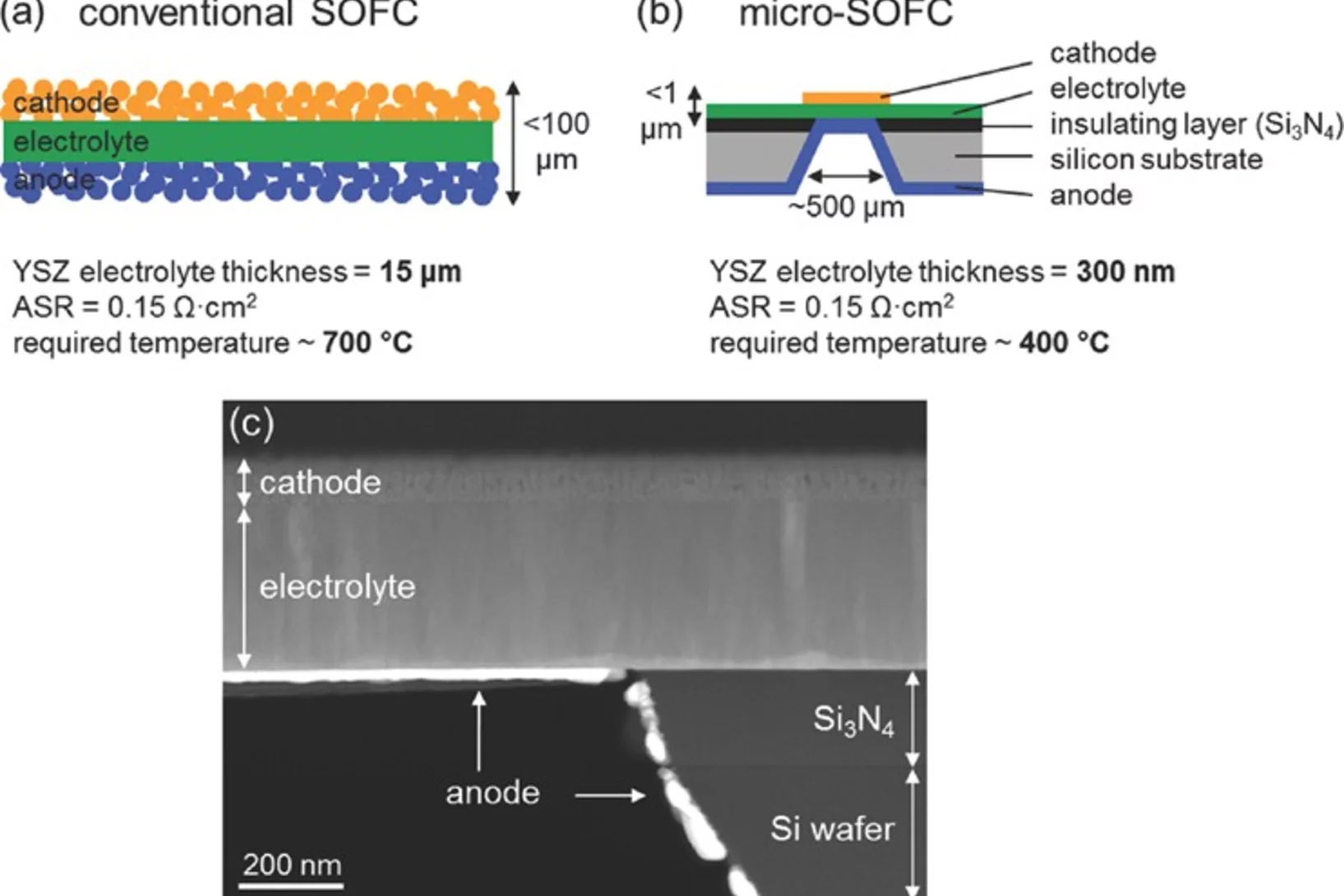
Low-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells based on proton-conducting electrolytes
The need for reducing the operating temperature of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) imposed by cost reduction has pushed significant progress in fundamental understanding of the individual components, as well as materials innovation and device engineering. Proton-conducting oxides have emerged as potential alternative electrolyte materials to oxygen-ion conducting oxides for operation at low and intermediate temperatures.
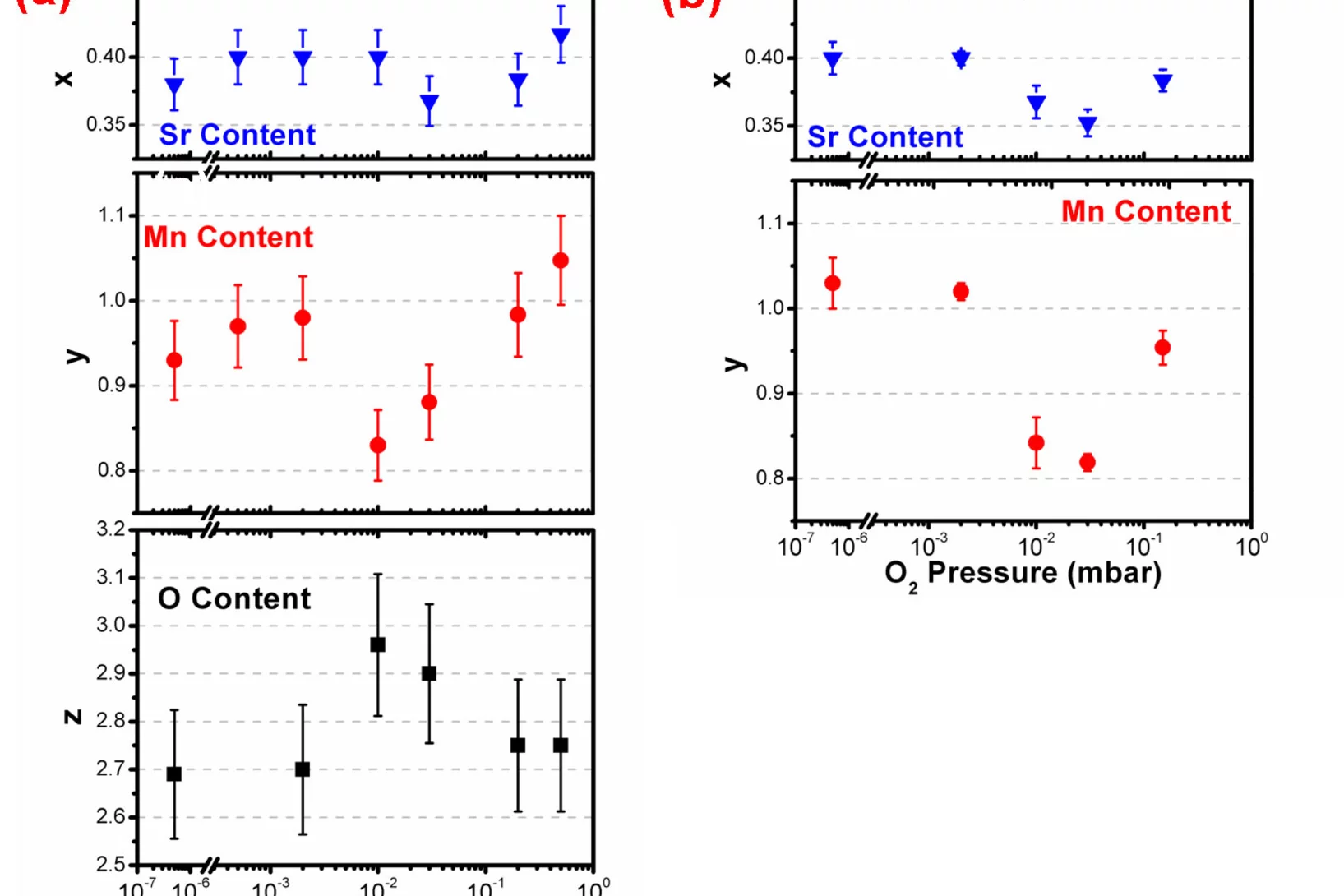
Plasma interactions determine the composition in pulsed laser deposited thin films
Plasma chemistry and scattering strongly affect the congruent, elemental transfer during pulsed laser deposition of target metal species in an oxygen atmosphere. Studying the plasma properties of La0.6Sr0.4MnO3, we demonstrate for as grown La0.6Sr0.4MnO3-δ films that a congruent transfer of metallic species is achieved in two pressure windows: ∼10−3 mbar and ∼2 × 10−1 mbar.
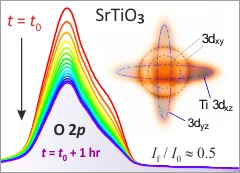
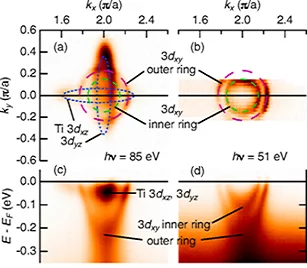
Mixed Dimensionality of Confined Conducting Electrons in the Surface Region of SrTiO3
Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, we show that the recently discovered surface state on SrTiO3 consists of nondegenerate t2g states with different dimensional characters.
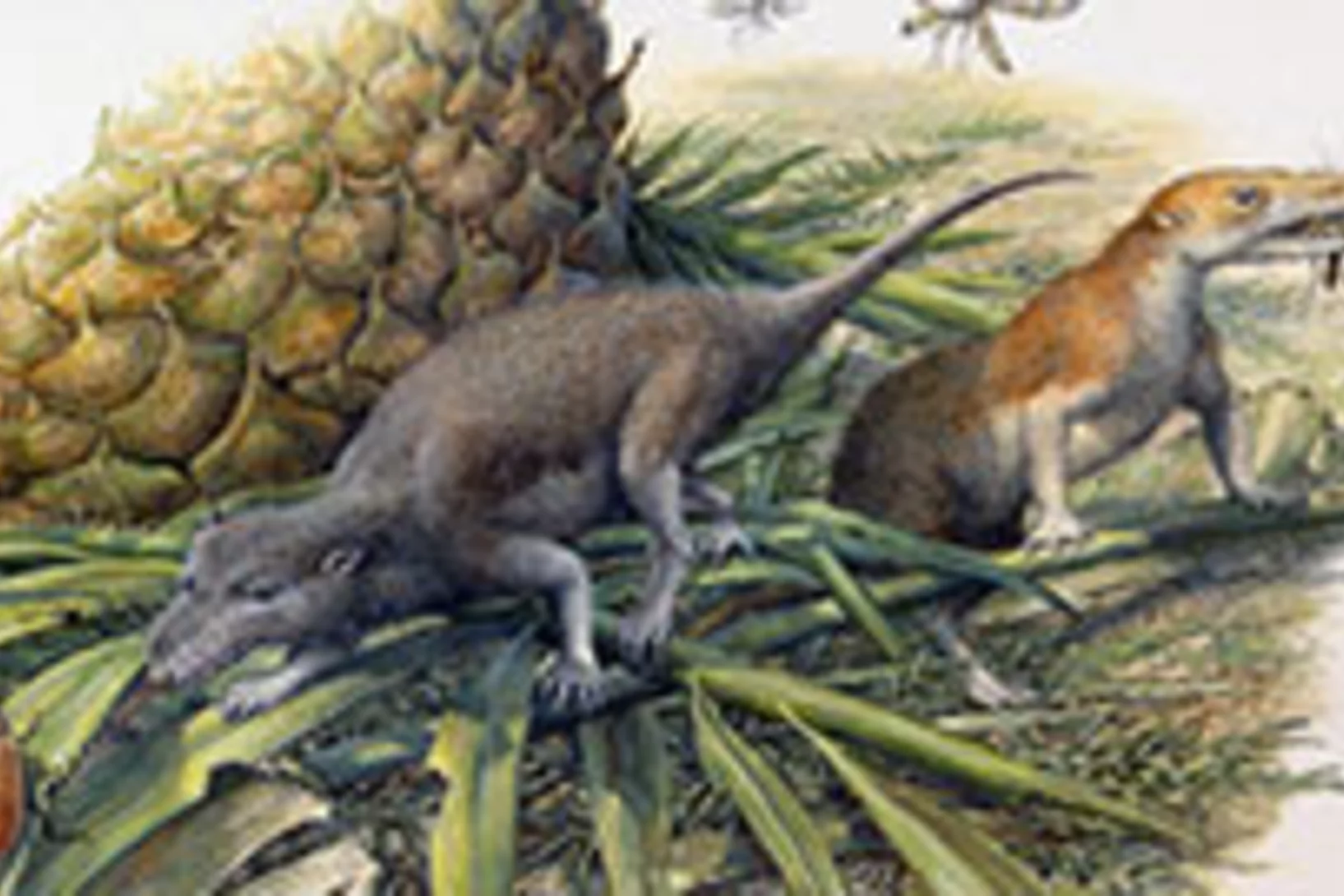
Jurassic Welsh mammals were picky eaters, study finds
New analyses of tiny fossil mammals from South Wales are shedding light on the function and diets of our earliest ancestors, a team led by researchers from the Universities of Bristol and Leicester report in the journal Nature. The team used CT scanning with synchrotron X-rays at PSI’s Swiss Light Source to reveal in unprecedented detail the internal anatomy of the mammals’ tiny jaws.
A revealing mixture: The surface of an oxide insulator can host two distinct types of conducting electrons
Strontium titanate, SrTiO3, is an important material for the realization of next-generation electronic devices. A famous example is the interface of LaAlO3 grown on SrTiO3, which is metallic and magnetic at its interface, even though the individual compounds are insulating and nonmagnetic in bulk form. The physics behind how novel interface states form on SrTiO3 - and how they become endowed with such surprising properties - is not well understood.
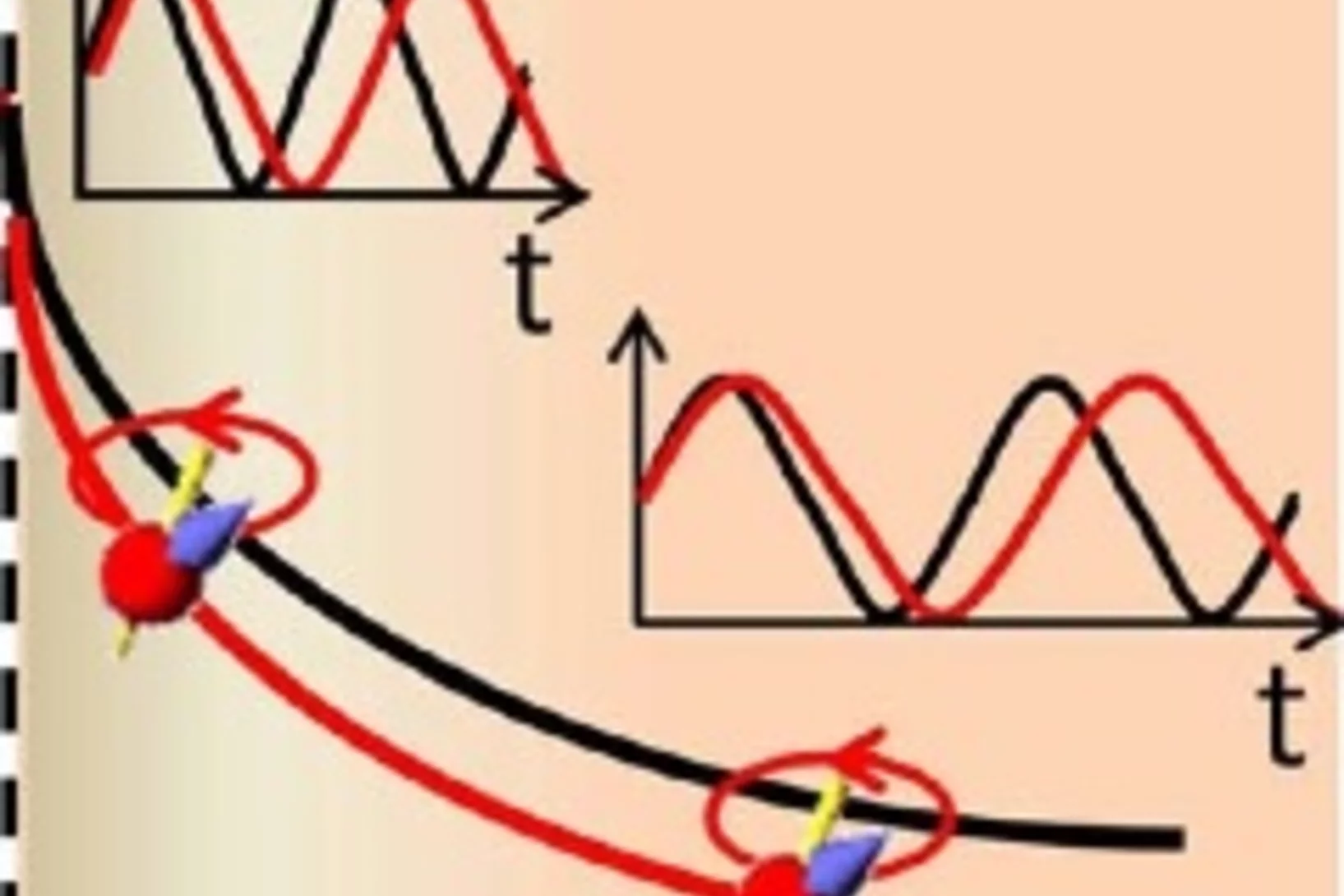
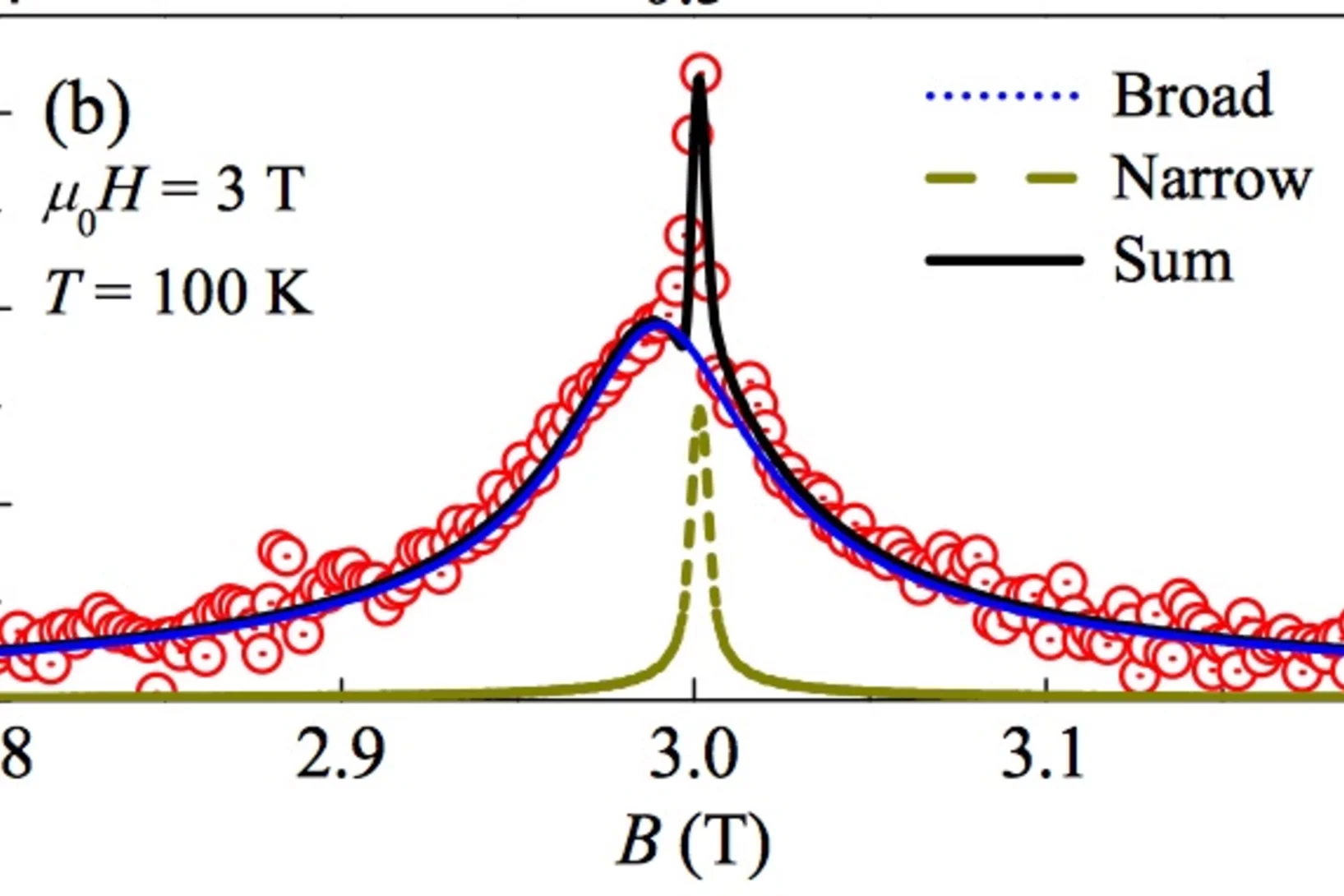
Spin-lattice coupling induced weak dynamical magnetism in EuTiO3 at high temperatures
EuTiO3, which is a G-type antiferromagnet below TN = 5.5 K, has some fascinating properties at high temperatures, suggesting that macroscopically hidden dynamically fluctuating weak magnetism exists at high temperatures. This conjecture is substantiated by magnetic field dependent magnetization measurements, which exhibit pronounced anomalies below 200 K becoming more distinctive with increasing magnetic field strength. Additional results from muon spin rotation experiments provide evidence for weak fluctuating bulk magnetism induced by spin-lattice coupling which is strongly supported in increasing magnetic field.
Low-Temperature Micro-Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Partially Amorphous La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ Cathodes
Partially amorphous La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ (LSC) thin-film cathodes are fabricated using pulsed laser deposition and are integrated in free-standing micro-solid oxide fuel cells (micro-SOFC) with a 3YSZ electrolyte and a Pt anode. A low degree of crystallinity of the LSC layers is achieved by taking advantage of the miniaturization of the cells, which permits low-temperature operation (300–450 °C).
What attacks on oil pipelines have in common with epidemics
How susceptible is the global energy infrastructure to attacks by non-state actors? Has the number of attacks on this infrastructure actually increased of late? Which regions of the world are especially vulnerable? And which tactics do the attackers use? Scientists are looking to find the answers to these and other related questions with the aid of a database developed by researchers from the Center of Security Studies at ETH Zurich in collaboration with the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI.
Fast scanning coherent X-ray imaging using Eiger
The smaller pixel size, high frame rate, and high dynamic range of next-generation photon counting pixel detectors expedites measurements based on coherent diffractive imaging (CDI). The latter comprises methods that exploit the coherence of X-ray synchrotron sources to replace imaging optics by reconstruction algorithms. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institut have recently demonstrated fast CDI image acquisition above 25,000 resolution elements per second using an in-house developed Eiger detector. This rate is state of the art for diffractive imaging and even on a par with the fastest scanning X-ray transmission instruments. High image throughput is of crucial importance for both materials and biological sciences for studies with representative population sampling.
Correlated Decay of Triplet Excitations in the Shastry-Sutherland Compound SrCu2(BO3)2
The temperature dependence of the gapped triplet excitations (triplons) in the 2D Shastry-Sutherland quantum magnet SrCu2(BO3)2 is studied by means of inelastic neutron scattering. The excitation amplitude rapidly decreases as a function of temperature, while the integrated spectral weight can be explained by an isolated dimer model up to 10 K.
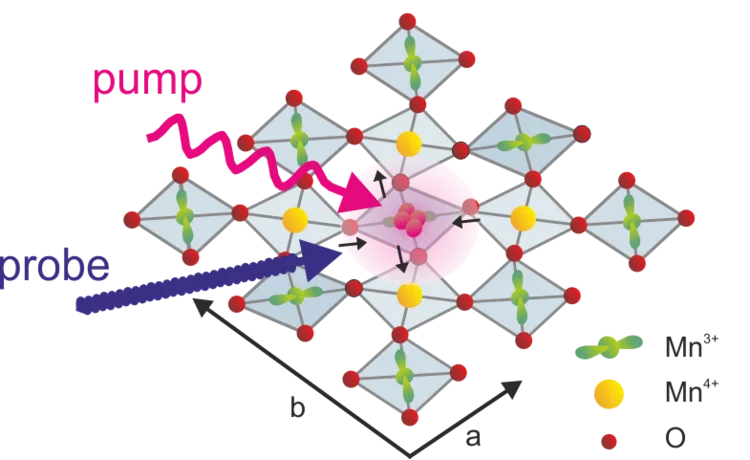
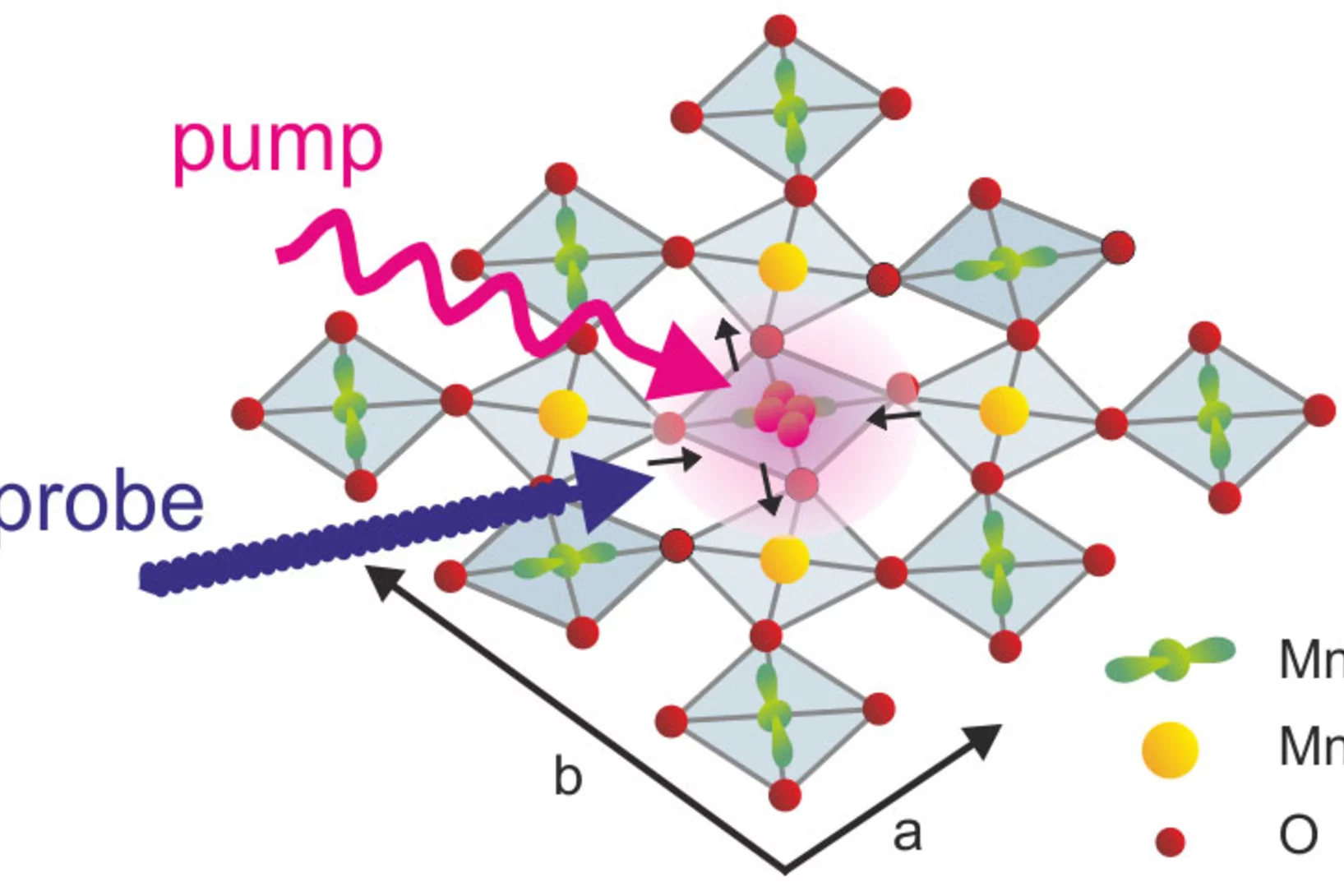
Square dance of the atoms: Shedding light on ultrafast phase transitions
The exploration of the interaction of structural and electronic degrees of freedom in strongly correlated electron systems on the femtosecond time scale is an emerging area of research. One goal of these studies is to advance our understanding of the underlying correlations, another to find ways to control the exciting properties of these materials on an ultrafast time scale.
Square dance of the atoms: Shedding light on ultrafast phase transitions
The exploration of the interaction of structural and electronic degrees of freedom in strongly correlated electron systems on the femtosecond time scale is an emerging area of research. One goal of these studies is to advance our understanding of the underlying correlations, another to find ways to control the exciting properties of these materials on an ultrafast time scale. So far a general model is lacking that provides a quantitiative description of the correlations between the structural and electronic degrees of freedom.
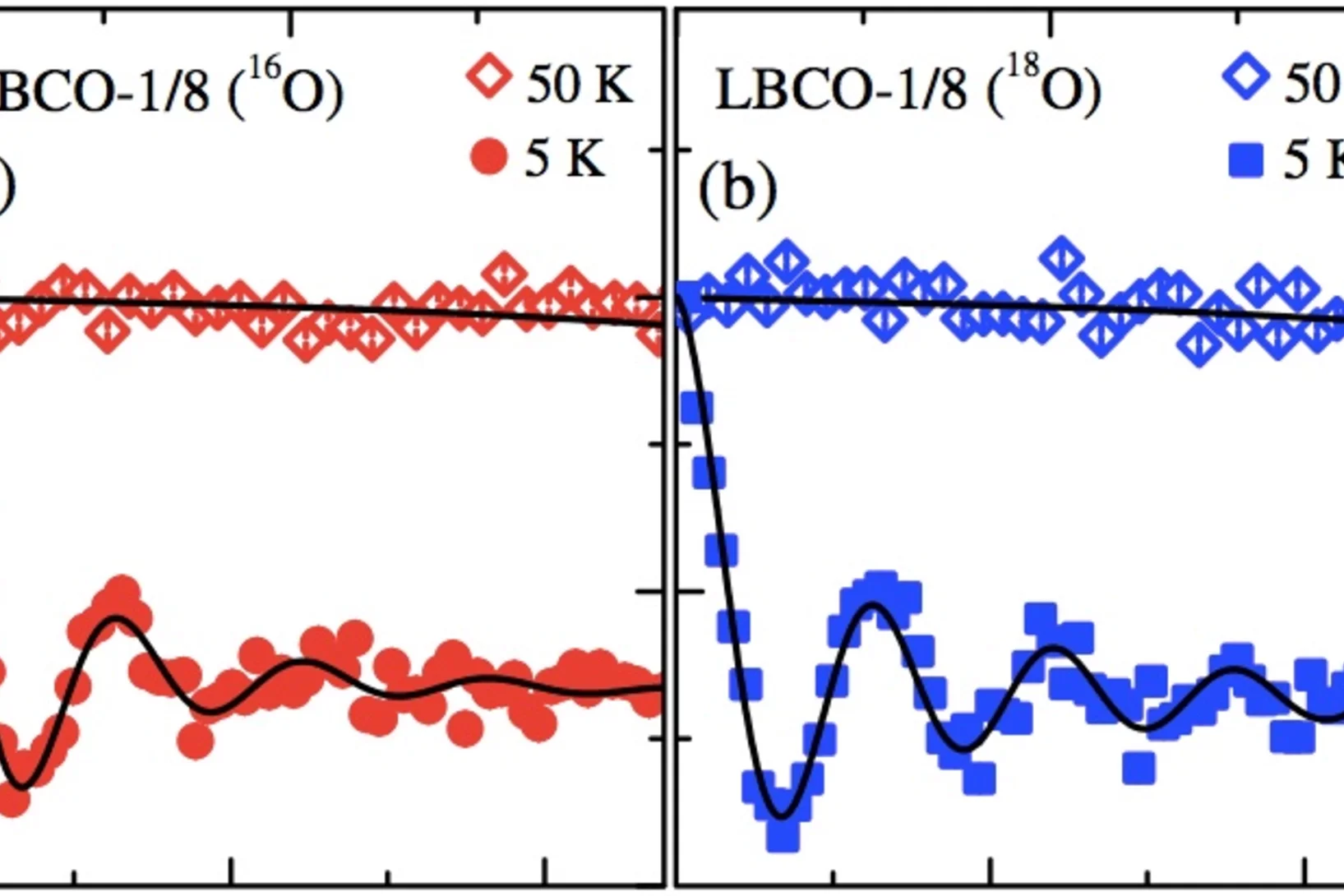
Negative Oxygen Isotope Effect on the Static Spin Stripe Order in Superconducting La2−xBaxCuO4(x=1/8) Observed by Muon-Spin Rot
Large negative oxygen-isotope (16O and 18O) effects (OIEs) on the static spin-stripe-ordering temperature Tso and the magnetic volume fraction Vm were observed in La2−xBaxCuO4(x=1/8) by means of muon-spin-rotation experiments. The corresponding OIE exponents were found to be αTso=-0.57(6) and αVm=-0.71(9), which are sign reversed to αTC=0.46(6) measured for the superconducting transition temperature Tc. This indicates that the electron-lattice interaction is involved in the stripe formation and plays an important role in the competition between bulk superconductivity and static stripe order in the cuprates.
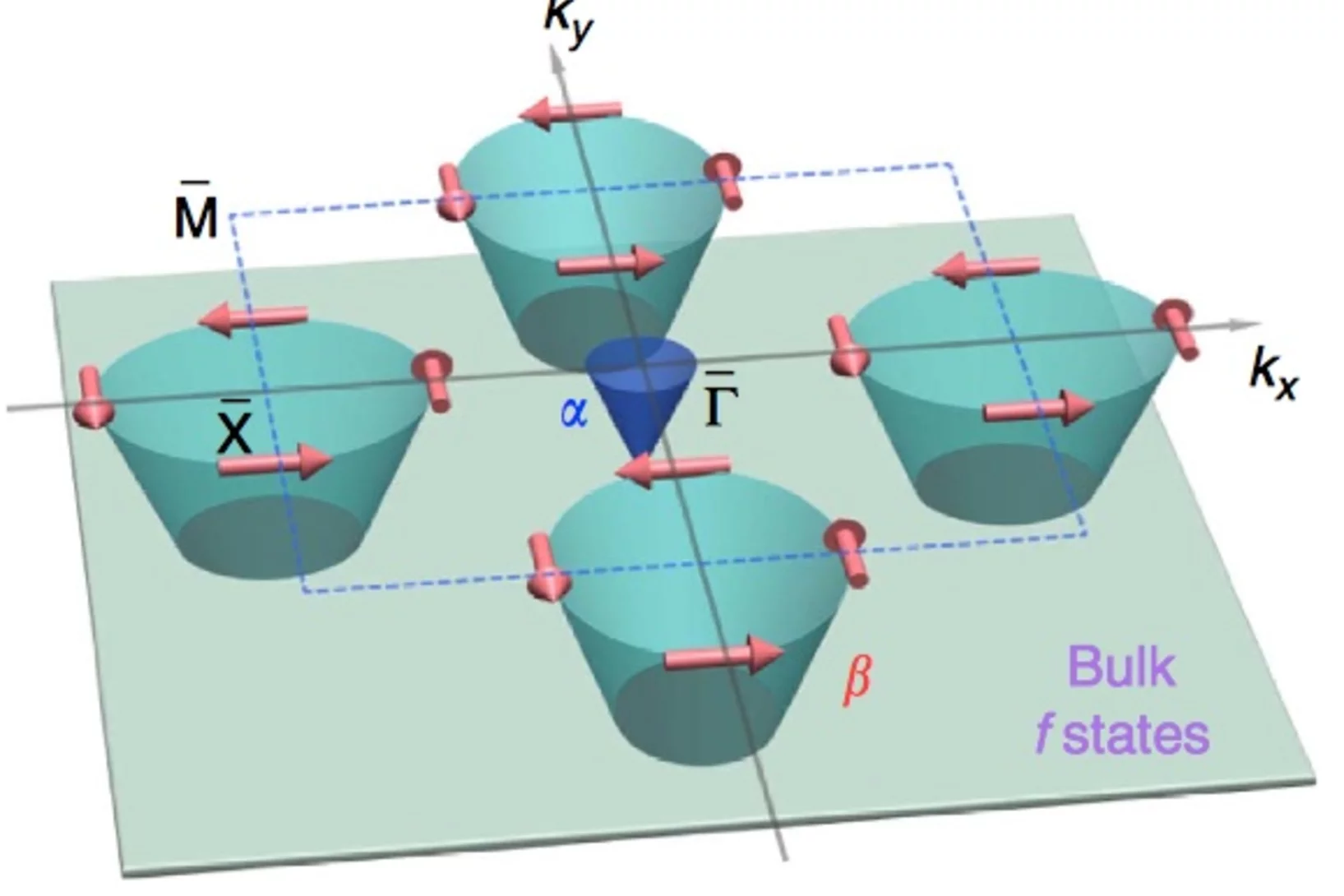
Direct observation of the spin texture in SmB6 as evidence of the topological Kondo insulator
Topological Kondo insulators have been proposed as a new class of topological insulators in which non-trivial surface states reside in the bulk Kondo band gap at low temperature due to strong spin–orbit coupling. In contrast to other three-dimensional topological insulators, a topological Kondo insulator is truly bulk insulating. Furthermore, strong electron correlations are present in the system, which may interact with the novel topological phase. By applying spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, here we show that the surface states of SmB6 are spin polarized. The spin is locked to the crystal momentum, fulfilling time reversal and crystal symmetries.
Insulator makes electrons move in an ordered way
Researchers at the PSI, the EPFL and the Chinese Academy of Science, have proven that the material SmB6 shows all the properties of a so called topological insulator à a material with electric currents flowing along its surface with all of them being polarized. Here, the property is very robust, i.e. the only current that can flow is spin polarized and is not easily destroyed by small irregularities in the structure or composition of the material. Spin polarized currents are necessary for spintronics, electronics using the electrons’ spin.
Small-angle neutron scattering study of the mixed state of Yb3Rh4Sn13
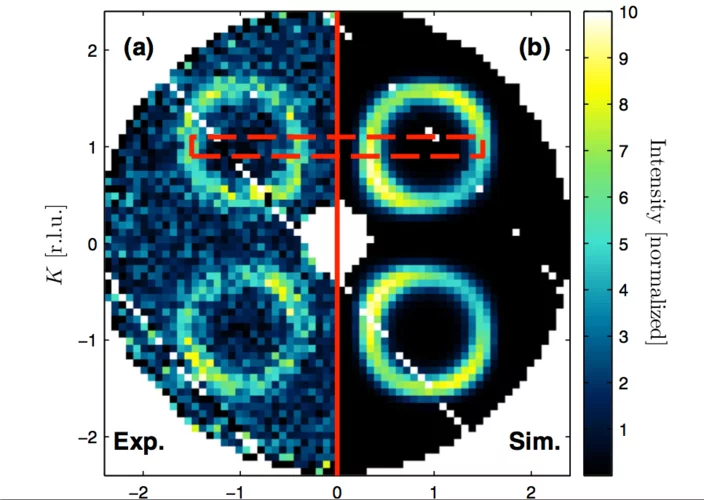
Using the small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique we investigated the vortex lattice (VL) in the mixed state of the stannide superconductor Yb3Rh4Sn13. We find a single domain VL of slightly distorted hexagonal geometry for field strengths between 350 and 18 500 G and temperatures between T=0.05 and 6.5 K. We observe a clear in-plane rotation of the VL for different magnetic field directions relative to the crystallographic axes.
Spin-Wave Spectrum of the Quantum Ferromagnet on the Pyrochlore Lattice Lu2V2O7
Neutron inelastic scattering has been used to probe the spin dynamics of the quantum (S=1/2) ferromagnet on the pyrochlore lattice Lu2V2O7. Well-defined spin waves are observed at all energies and wave vectors, allowing us to determine the parameters of the Hamiltonian of the system.
Hydrogen: a Trojan horse in fuel-rod cladding tubes
In nuclear reactors, water is dissociated at the surface of the hot fuel elements, thereby producing hydrogen. This hydrogen can penetrate the fuel cladding surrounding the actual fuel and weaken it mechanically. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have been using neutrons and synchrotron radiation to study how the hydrogen gets into the cladding tube and what impact it can have once inside.
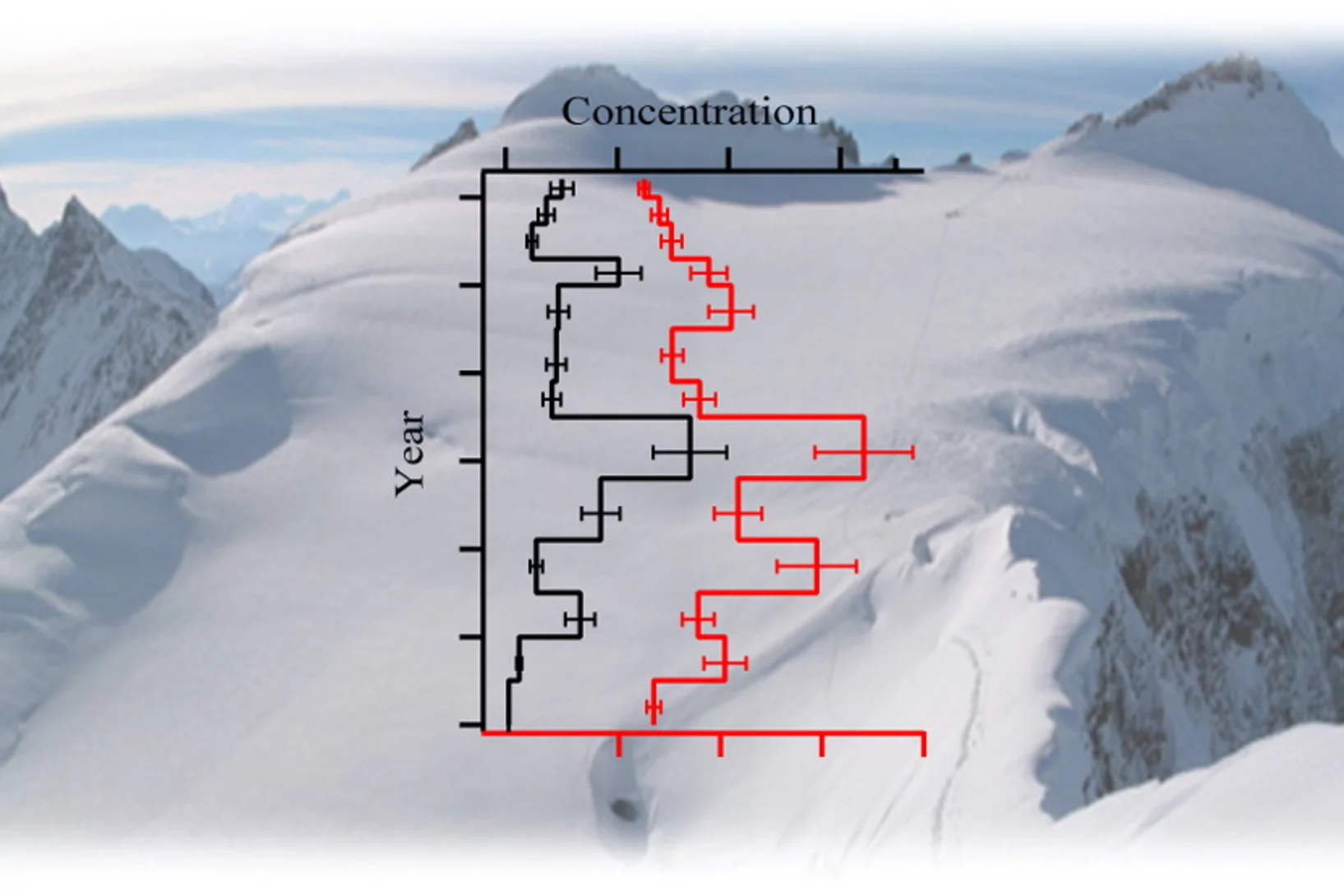
Polychlorinated biphenyls in glaciers
We present a highly time-resolved historical record of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) from an Alpine ice core (Fiescherhorn glacier, Switzerland). Introduced in the 1940s, PCBs were widely used industrial chemicals. Because of their persistence they are still found in the environment, long after their production phase-out. The Fiescherhorn ice core record covers the entire time period of industrial use of PCBs, that is, 1940?2002. The total concentration of six PCBs varies from 0.5 to 5 ng/L and reveals a temporal trend, with an 8-fold increase from the early 1940s to the peak value in the 1970s.
Coherent structural dynamics of a prototypical Charge-Density-Wave-to-Metal transition
In so called charge-density-wave compounds, the peculiar shape of the Fermi surface as well as electron-phonon coupling lead to a low-temperature broken symmetry ground state. This state is characterized by a modulation of the charge density (hence the name) and, via electron-phonon coupling, a distortion of the equilibrium lattice positions.
Origin of Anomalous Slip in Tungsten
Low-temperature deformation of body-centered cubic metals shows a significant amount of plastic slip on planes with low shear stresses, a phenomenon called anomalous slip. Despite progress in atomistic modeling of the consequences of complex stress states on dislocation mobility, the phenomenon of anomalous slip remained elusive. Using in situ Laue microdiffraction and discrete dislocation dynamics in micrometer sized tungsten single crystals, we demonstrate the occurrence of significant anomalous slip. It occurs as a consequence of cross kinks, topological configurations generated by prior dislocation interactions.
A dark state sheds light
The molecule dicarbon (C2) is present in all flames where a carbon-containing fuel is combusted. C2 burns visibly, is behind the blue colour inside a candle flame and could also play a key role in the formation of soot. Now, for the first time, scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institute have rendered a previously invisible C2 energy state, a so-called dark state, visible. Not only is its discovery interesting for combustion researchers; it also solves a century-old puzzle in the spectrum of this omnipresent molecule.
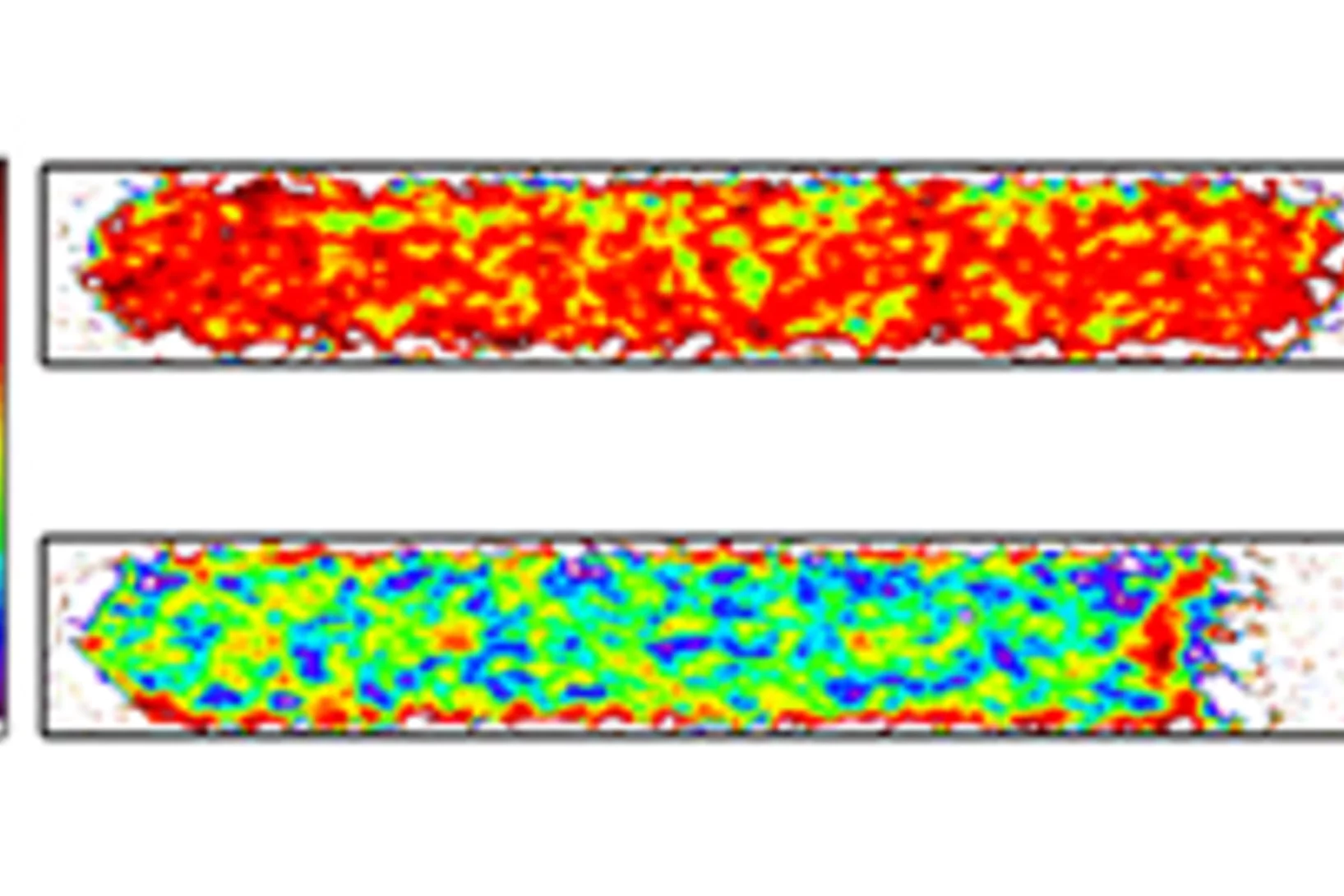
Identification of transitions between liquid water and ice with dual spectrum neutron imaging
The ability to start up at sub-zero Celsius temperatures is a prerequisite for the use of fuel cells in automotive applications, but specific measures need to be taken to prevent the product water to freeze and block the gas supply pathways. In this context, a method for imaging the distribution of liquid water and ice from neutron imaging experiments was developed.
Tag der offenen SwissFEL-Baustelle
Vergangenen Sonntag luden das Paul Scherrer Institut PSI und die Arbeitsgemeinschaft EquiFEL Suisse die Einwohnerinnen und Einwohner der Umgebung zum Tag der offenen SwissFEL-Baustelle ein. Rund 600 Interessierte informierten sich an mehreren Stationen über den aktuellen Bau- und Projektstand.This news release is only available in German.
Ice in fuel cells imaged directly for the first time
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have succeeded in imaging the distribution of frozen and liquid water in a hydrogen fuel cell directly for the first time. They applied a new imaging technique that uses successively two beams with different neutron energies to distinguish between areas with liquid water and those with ice extremely reliably. The method therefore opens up the prospect of studying one of the main problems of using fuel cells to power vehicles: ice can clog the pores in the fuel cells and affect their performance. The PSI scientists’ results will be published in the journal Physical Review Letters on 16 June 2014.