The below articles contain recent news related to the upgrade.
SLS 2.0: How to start up a particle accelerator
The electrons are back: after its upgrade, the Swiss Light Source SLS is starting up again, step by step.
Sample-position tracking using computer vision algorithms
In a collaboration between PSI and the Zurich University of Applied Sciences, a sample position tracking setup based on a computer vision algorithm was developed to automatically track the sample position. A factor of ten improvement on the overlap between consecutive x-ray absorption spectra was obtained when the automatic sample tracking was used.
Unlocking the secrets of proteins
This year’s Nobel Prize in Chemistry goes to three researchers who have made a decisive contribution to cracking the code of proteins – important building blocks of life. However, developing applications from this knowledge, for example in medicine, requires research institutes such as PSI.
New Monochromators for SLS 2.0
The brand-new monochromators that have been built by XDS Oxford for the hard X-ray beamlines at SLS 2.0 have now arrived. They were unpacked beginning of the week, and are currently being tested in our new lab space at Park Innovaare. These advanced instruments will play a crucial role in enhancing the beamline performance, ensuring superior precision and efficiency in the upcoming experiments.
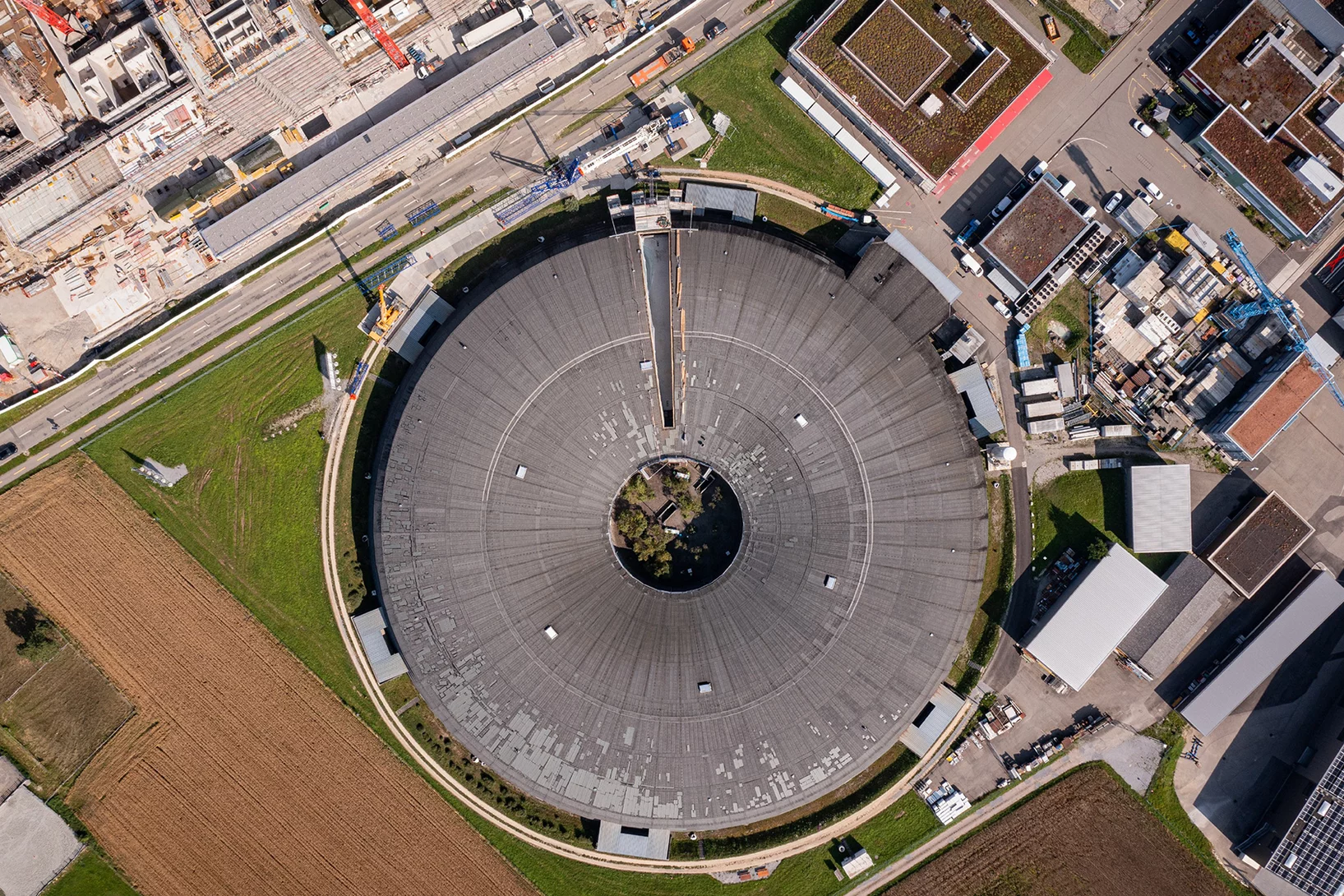
Installation of the first two front ends for the SLS2.0 completed
At the Swiss Light Source SLS of the Paul Scherrer Institute, another important step has been taken towards the completion of the SLS 2.0 upgrade project.
Fundamentally different
Artificial intelligence is helping to evaluate an unimaginably vast amounts of data efficiently and exploit the facilities’ full potential for research.
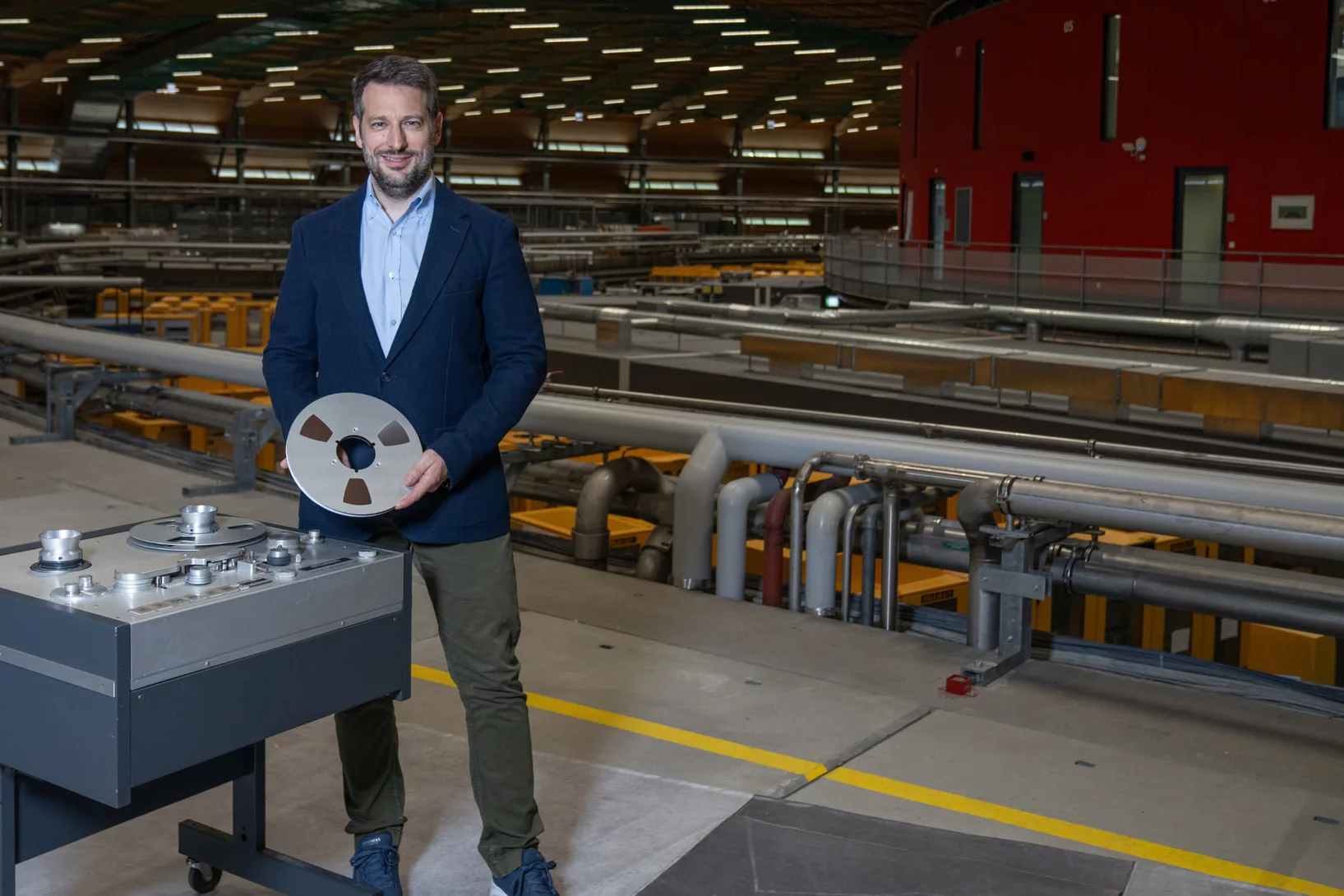
Rescuing music with X-rays
SLS plays the King of the Blues – B.B. King! In collaboration with the Montreux Jazz Digital Project, historic audio tapes are being digitised at PSI.
What will the SLS 2.0 upgrade mean for experiments?
Tighter beams, brighter light and extended photon energies open new experimental possibilities.
SLS 2.0: “Dark time” during the upgrade
The SLS is shutting down temporarily as it undergoes a major upgrade.
Thank You SLS
Our beamline scientists look back on 22 years of brilliant science made possible by the Swiss Light Source SLS.
A metal alloy like a sponge
Once the vacuum chambers for the SLS 2.0 upgrade are the right shape, they still need a special surface coating.
A six-metre high oven
The most complicated vacuum chambers for the SLS 2.0 upgrade are being built in the PSI workshop.
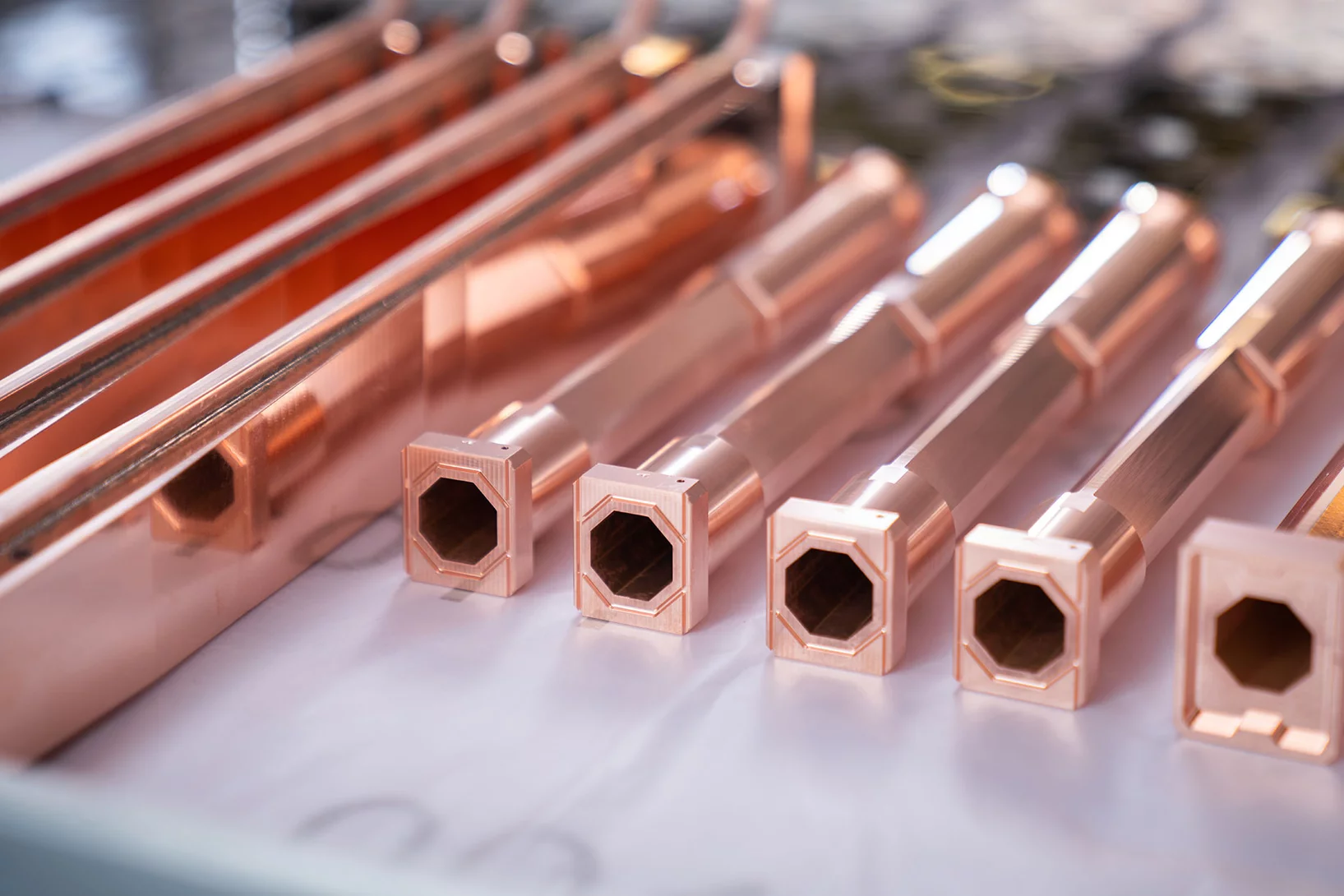
500 vacuum chambers for the new ring
Making the tube through which the electrons will race after the SLS 2.0 upgrade.
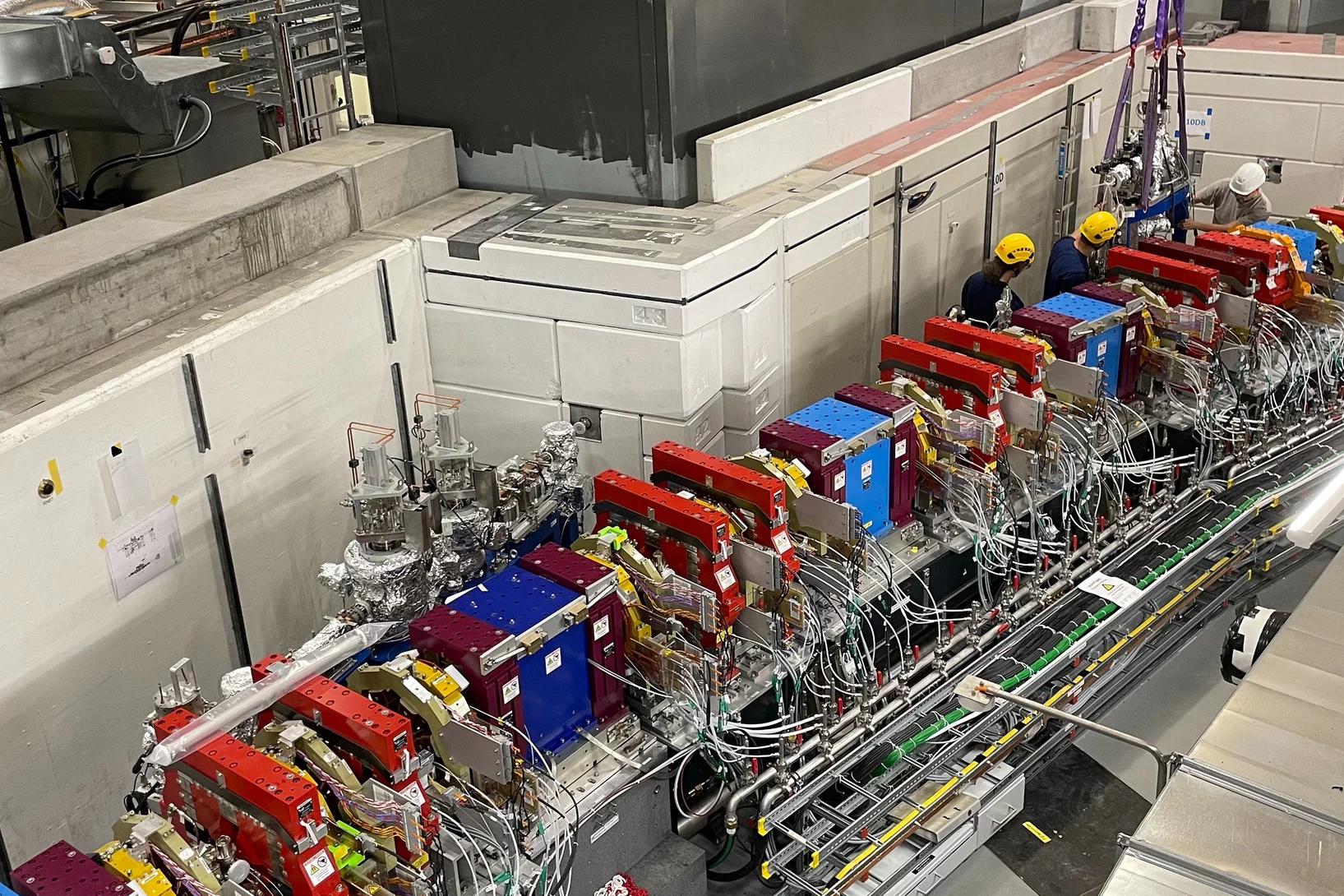
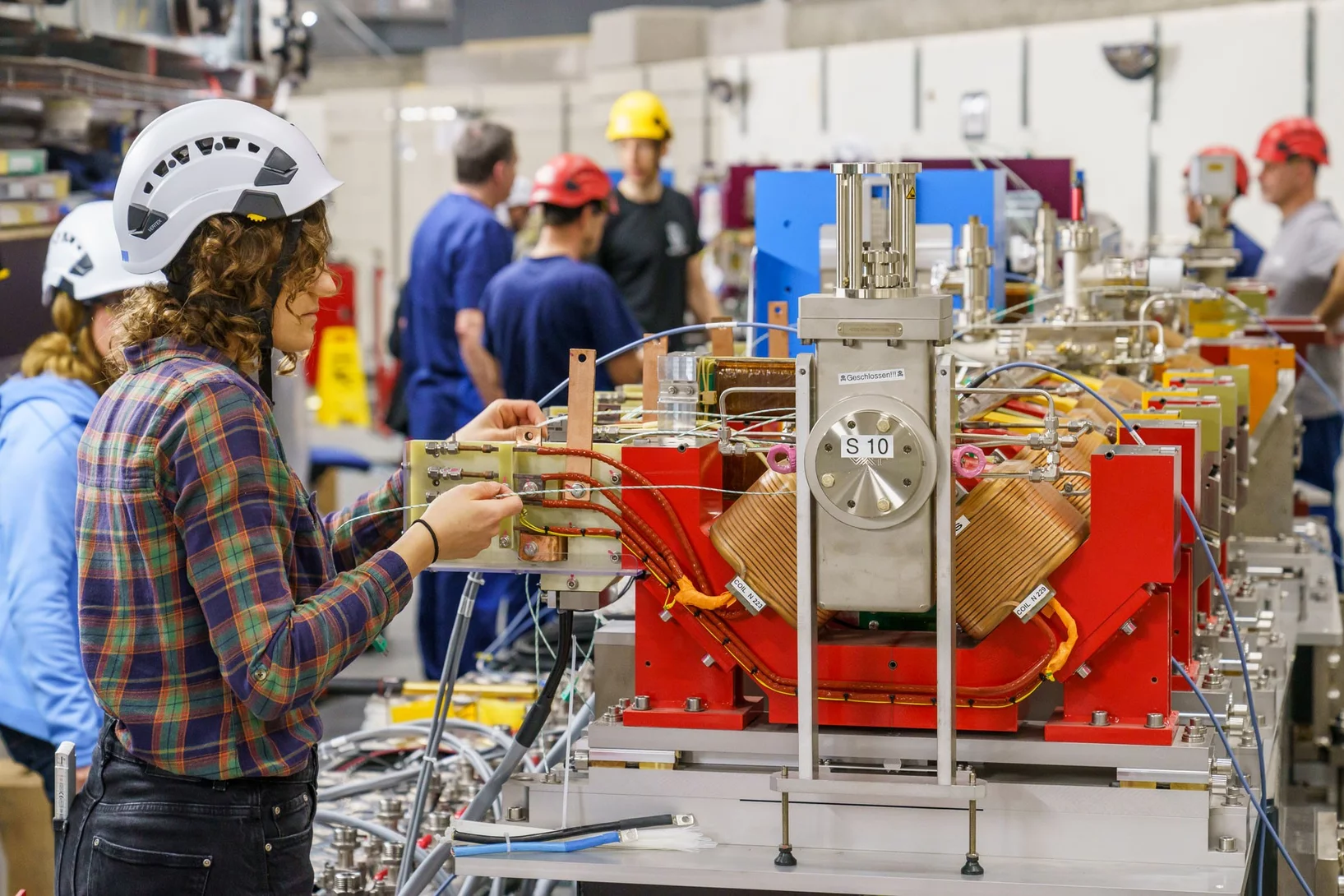
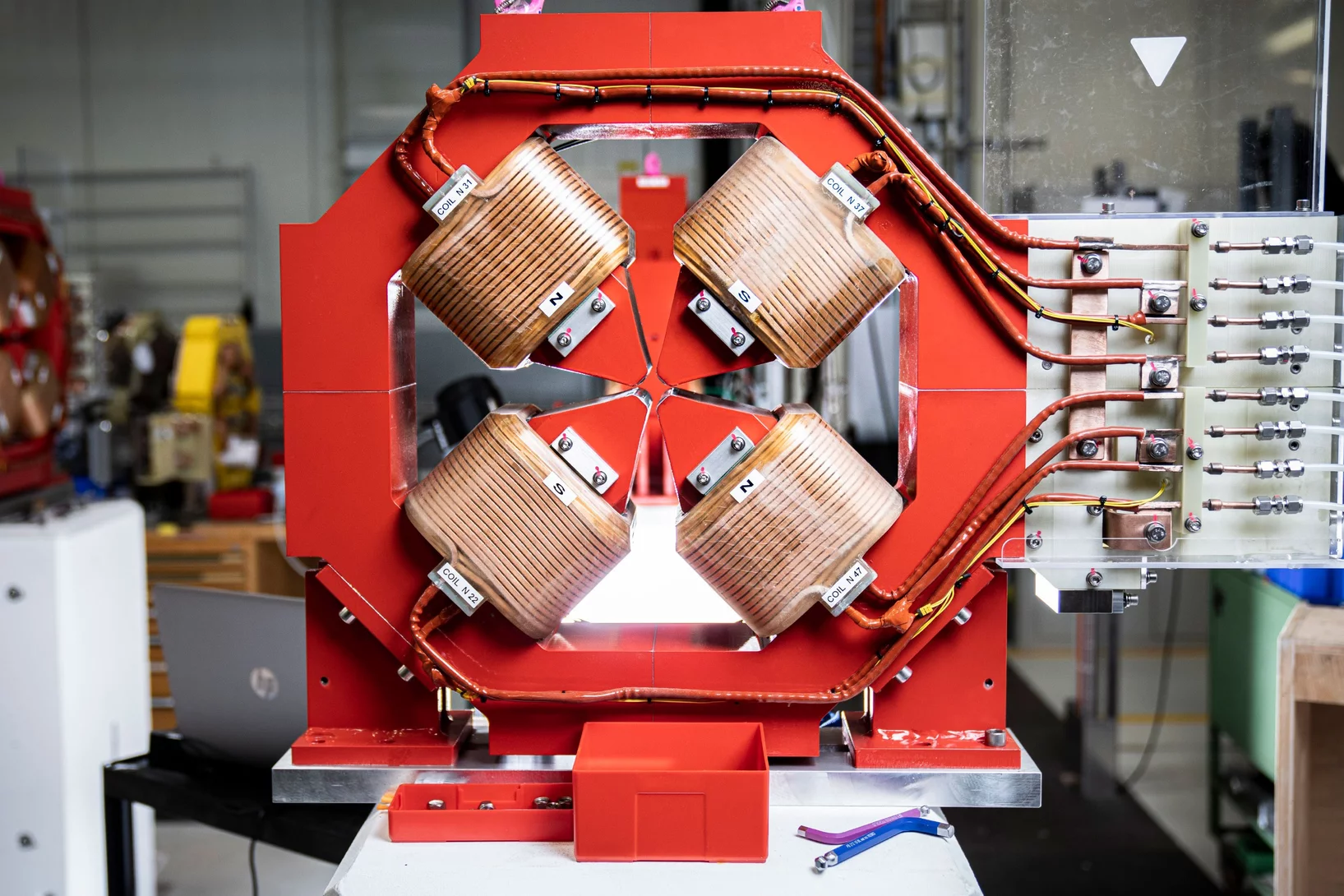
On-track for SLS2.0: First magnet series measured
Successful measurement of the first 112 magnets puts the PSI magnet section on-schedule to measure all of the 1000+ magnets needed for SLS2.0 by July 2024.
Faster and smarter
PSI is pooling its expertise regarding the evaluation of research data in the new research division Scientific Computing, Theory and Data.
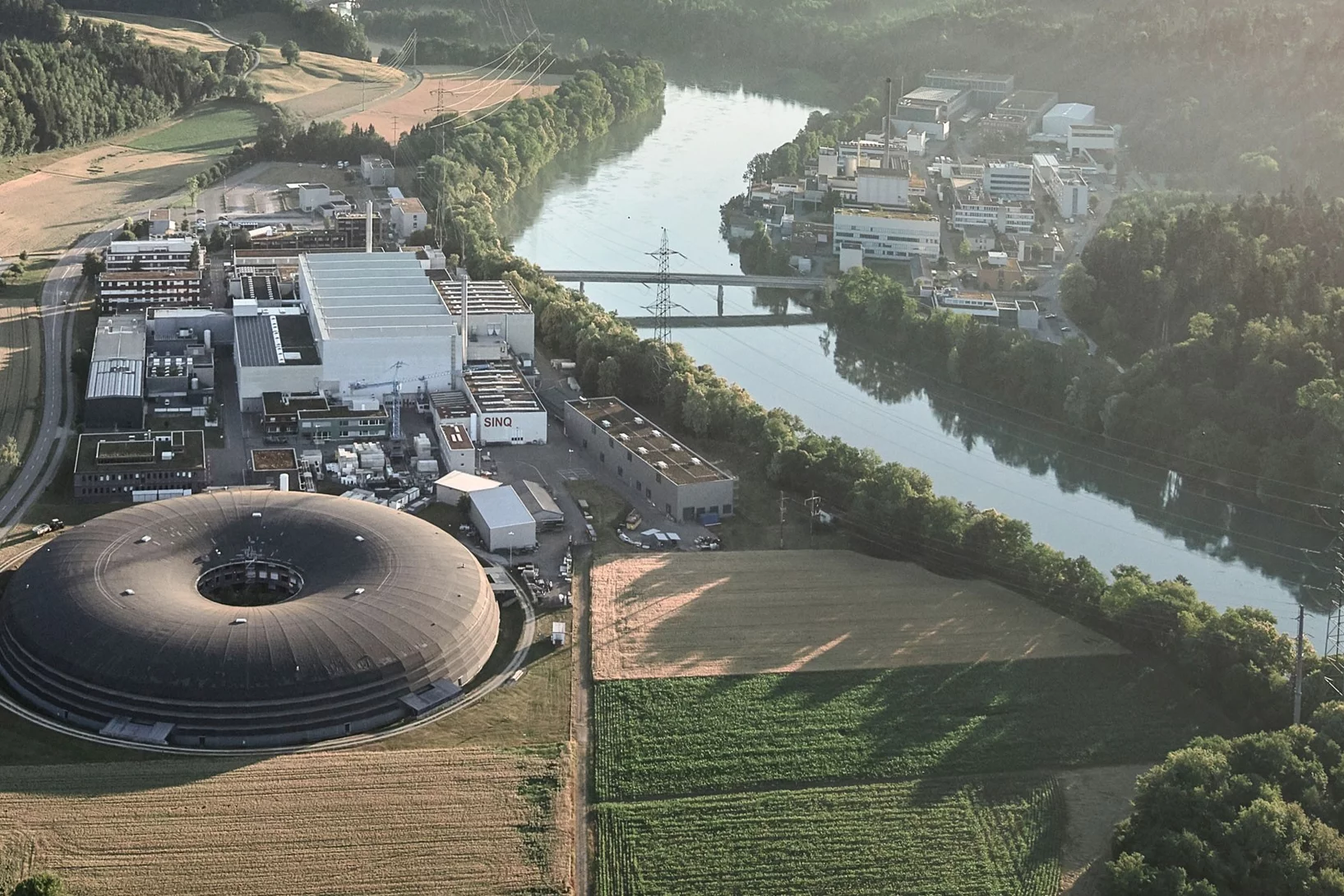
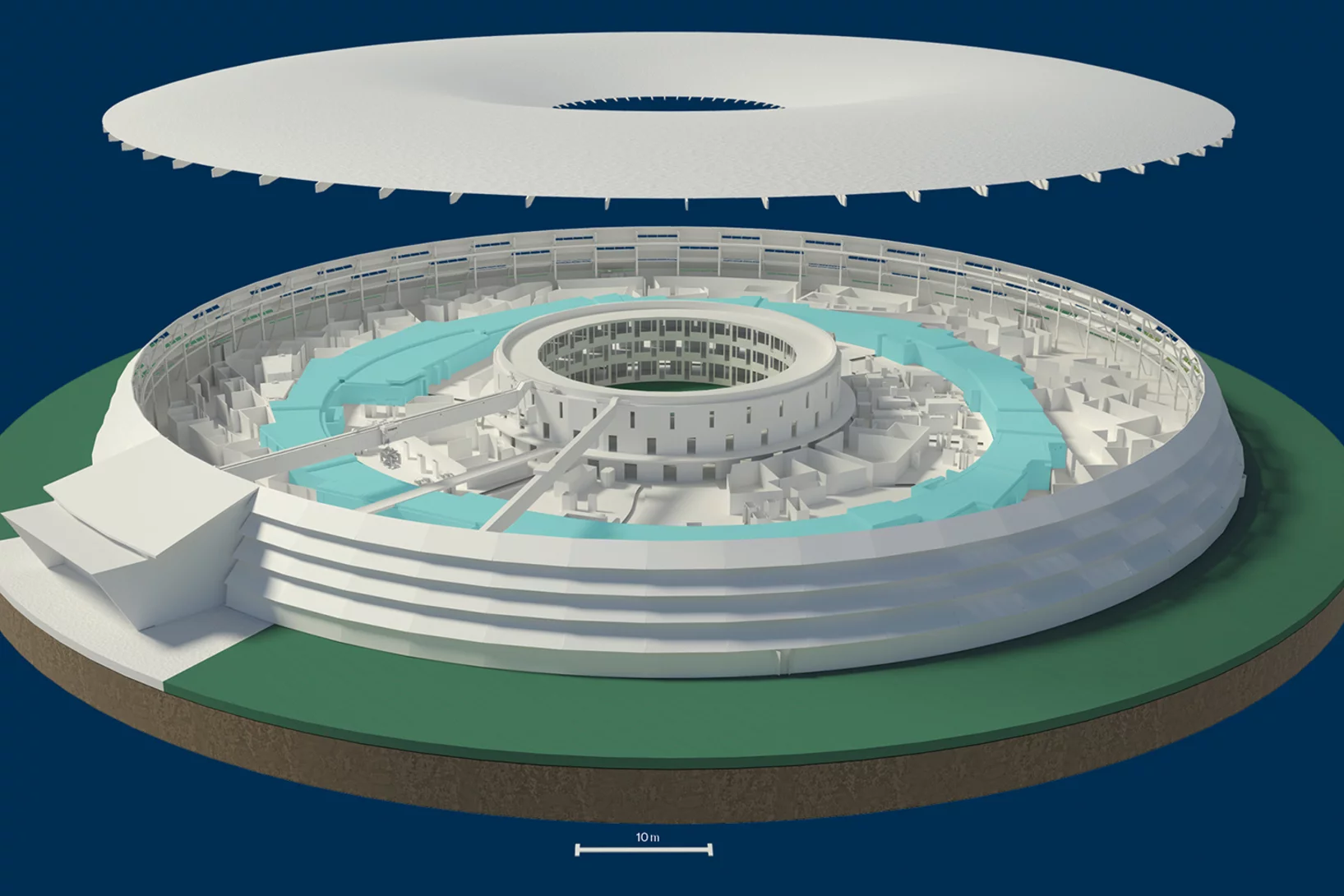
3D view: Swiss Light Source SLS
Linear accelerator, booster ring, storage ring: our 3D graphic of the Swiss Light Source shows the inside of the facility and how it serves research.
SLS: The new crane comes from above
The Swiss Light Source SLS is getting a second hall crane. But how can the 42-metre-long, 40-tonne monster get into the building? The only way is from above.
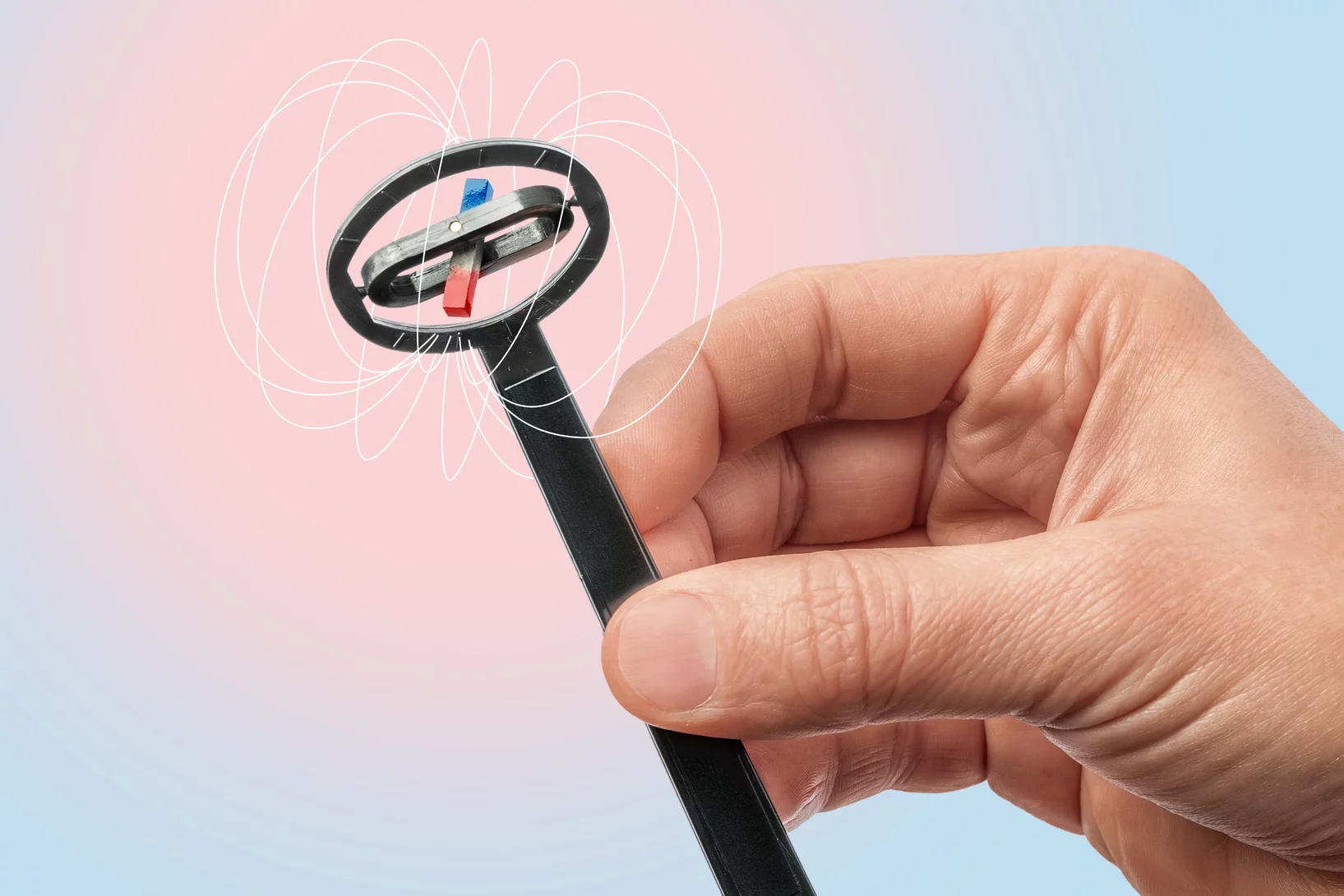
A "magical" power with major impact
Microrobots, materials with shape memory, and better particle accelerators are made possible through the exploration of magnetism at PSI.
Growth in the data sciences
Another site for the Swiss Data Science Center will be established at PSI. This expansion is expected to give a further boost to the data sciences in Switzerland.
SLS 2.0 approved - TOMCAT 2.0 cleared for takeoff!
In December 2020 the Swiss parliament approved the Swiss Dispatch on Promotion of Education, Research and Innovation (ERI) for 2021 to 2024 which includes funding for the planned SLS 2.0 upgrade. The new machine will lead to significantly increased brightness, thus providing a firm basis for keeping the SLS and its beamlines state-of-the-art for the decades to come. The TOMCAT crew is very excited that the TOMCAT 2.0 plans (deployment of the S- and I-TOMCAT branches, see SLS 2.0 CDR, p. 353ff) have been included in the Phase-I beamline upgrade portfolio. These beamlines will receive first light right after the commissioning of the SLS 2.0 machine around mid 2025. A first milestone towards this goal has just been achieved, with the successful installation of the S-TOMCAT optics hutch during W1 of 2021. The TOMCAT scientific and technical staff would like to thank Mr. Nolte and his Innospec crew for delivering perfectly on schedule.
PSI equips the Swiss Light Source SLS for the future
Green light for SLS 2.0: The planned upgrade of the Swiss Light Source SLS can proceed; the funding is provided for within the framework of the ERI Dispatch for 2021-2024, which has been approved.
«We're making SLS fit for the future»
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to get an upgrade to make excellent research possible in the coming decades as well. Hans Braun, SLS 2.0 project leader, talks about this undertaking in an interview.
More magnets, smoother curves: The SLS upgrade
The Swiss Light Source SLS is set to undergo an upgrade in the coming years: SLS 2.0. The renovation is made possible by the latest technologies and will create a large research facility that will meet the needs of researchers for decades to come.
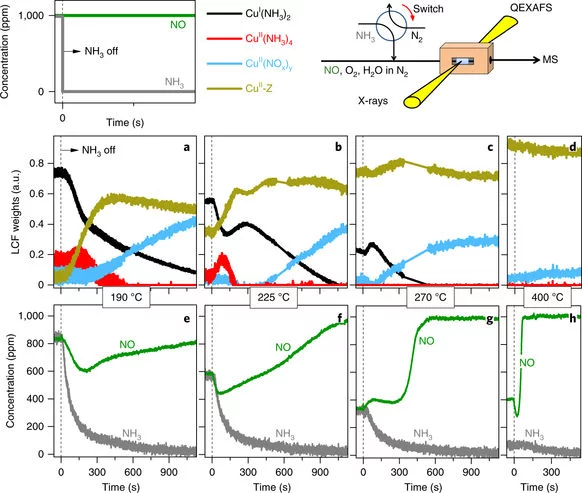
Time-resolved copper speciation during selective catalytic reduction of NO on Cu-SSZ-13
Through the combination of time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy and transient experimentation, we were able to capture an ammonia inhibition effect on the rate-limiting copper re-oxidation at low temperature.
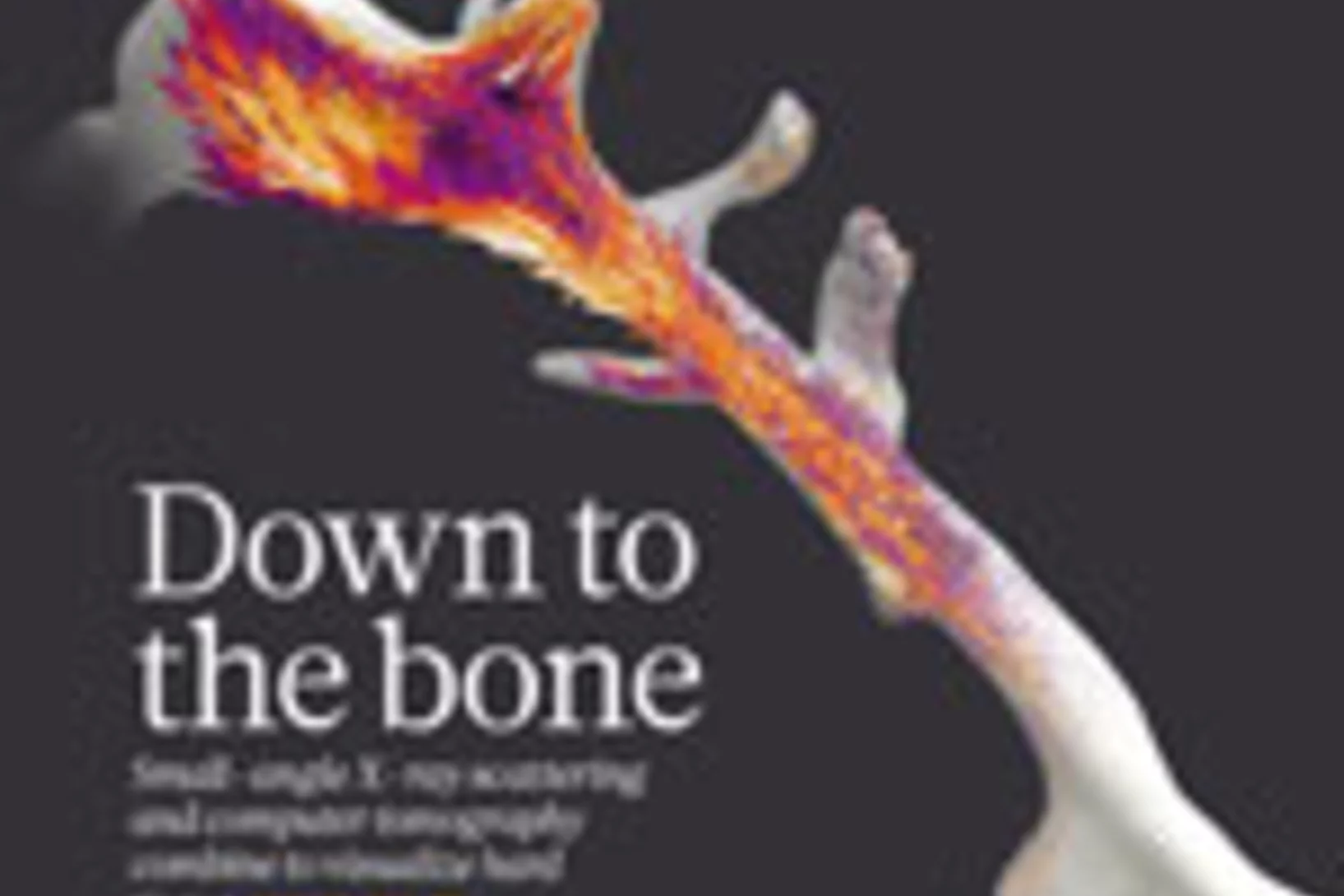
Nanostructure surveys of macroscopic specimens by small-angle scattering tensor tomography
The mechanical properties of many materials are based on the macroscopic arrangement and orientation of their nanostructure. This nanostructure can be ordered over a range of length scales. In biology, the principle of hierarchical ordering is often used to maximize functionality, such as strength and robustness of the material, while minimizing weight and energy cost.
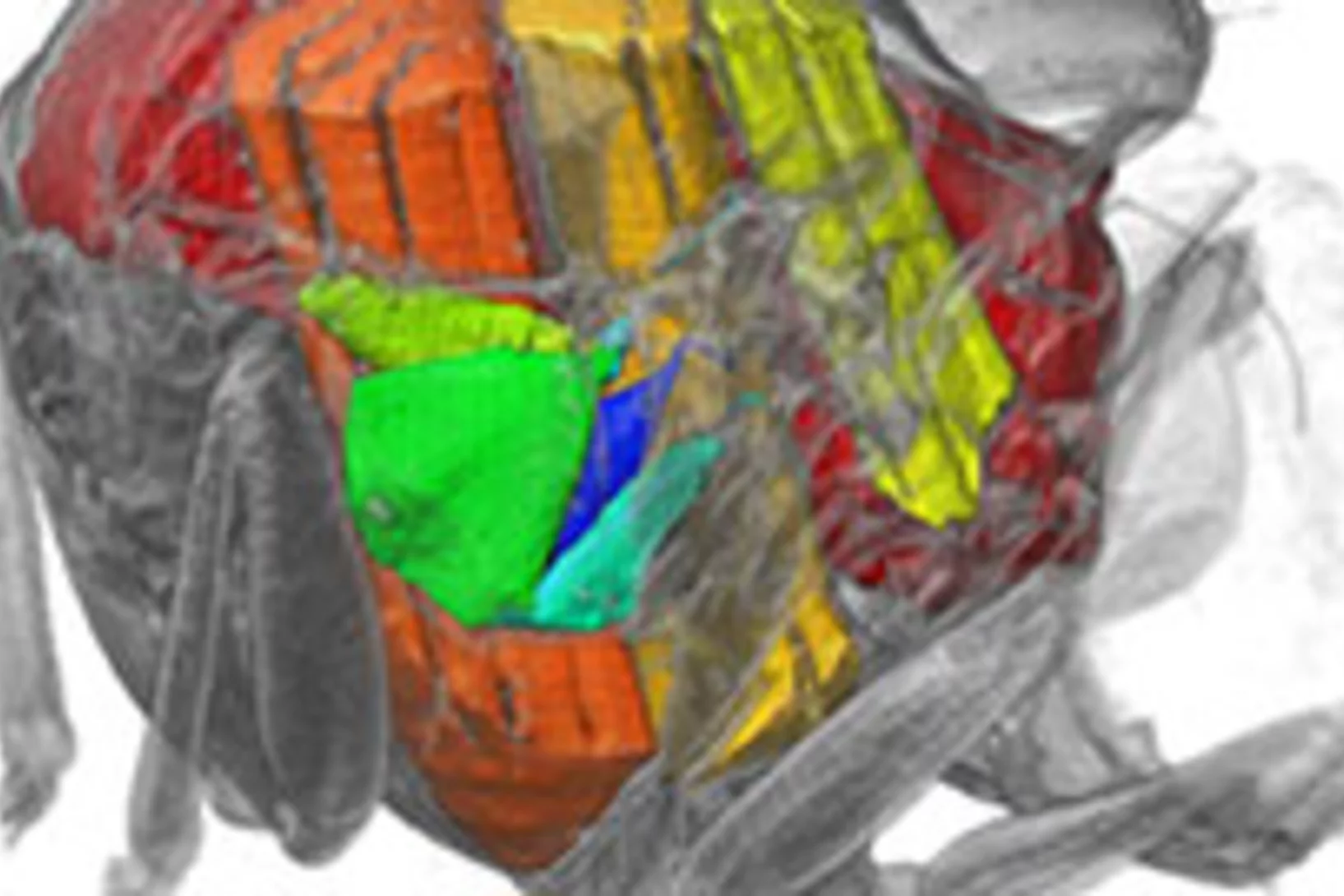
X-rays film inside live flying insects – in 3D
Scientists have used a particle accelerator to obtain high-speed 3D X-ray visualizations of the flight muscles of flies. The team from Oxford University, Imperial College, and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) developed a groundbreaking new CT scanning technique at the PSI’s Swiss Light Source to allow them to film inside live flying insects. The movies offer a glimpse into the inner workings of one of nature’s most complex mechanisms, showing that structural deformations are the key to understanding how a fly controls its wingbeat.