A l’Institut Paul Scherrer, les scientifiques cherchent des réponses à la question essentielle des structures élémentaires de la matière et des principes fondamentaux de fonctionnement dans la nature. Ils étudient la structure et les propriétés des particules élémentaires – les plus petits composants de la matière – ou se penchent sur la question de savoir comment les molécules biologiques sont structurées et remplissent leur fonction. Les connaissances qu’ils acquièrent de la sorte ouvrent de nouvelles pistes de solution en sciences, en médecine ou dans le domaine des technologies.
Pour en savoir plus, reportez-vous à Aperçu Fondements de la nature
Collaboration meeting in Mainz and new collaborators
In a two day meeting in Mainz we had the pleasure of welcoming four new institutes, namely the universities of Liverpool, Oxford and Bristol as well as University College London to the collaboration. We also discussed progress on all subdetectors and a variety of integration issues.
L'atmosphère à la lumière des rayons X
Des chercheurs du PSI ont développé une chambre d’expérience où ils reconstituent certains processus qui se jouent dans l’atmosphère et peuvent étudier ces derniers avec une précision inégalée grâce à de la lumière de type rayons X issue de la SLS. Lors de leurs premières expériences, ils ont étudié la formation du brome, qui joue un rôle essentiel dans la dégradation de l’ozone dans les couches inférieures de l’atmosphère. A l’avenir, cette nouvelle chambre d’expérience sera également mise à disposition de chercheurs d’autres disciplines scientifiques.
Light from the particle accelerator helps to understand ozone decomposition
PSI researchers have developed an experimental chamber in which they can recreate atmospheric processes and probe them with unprecedented precision, using X-ray light from the Swiss Light Source SLS. In the initial experiments, they have studied the production of bromine, which plays an essential role in the decomposition of ozone in the lower layers of the atmosphere. In the future, the new experiment chamber will also be available for use by researchers from other scientific fields.
Dr. Konstantins Jefimovs wins the 2nd poster prize
Dr. Konstantins Jefimovs from the TOMCAT team at SLS was awarded with the 2nd poster prize at the 4th XNPIG Conference (X-ray and Neutron Phase Contrast Imaging with Gratings) held in Zürich, September 12th-15th. He presented latest achievements on gratings fabrication under the title: “Large area small pitch gratings for X-ray interferometry by Displacement Talbot Lithography”.
Dr. Matias Kagias receives the William H. F. Talbot Award 2017
Dr. Matias Kagias from the TOMCAT team at SLS is the recipient of the William H. F. Talbot Award 2017, as announced recently at the 4th XNPIG Conference (X-ray and Neutron Phase Contrast Imaging with Gratings) held in Zürich in September 12th-15th. The award is given to young PhD students for their outstanding contributions in the field of X-ray and Neutron Phase contrast imaging. This award has been introduced this year and Dr. Kagias is the first recipient ever.
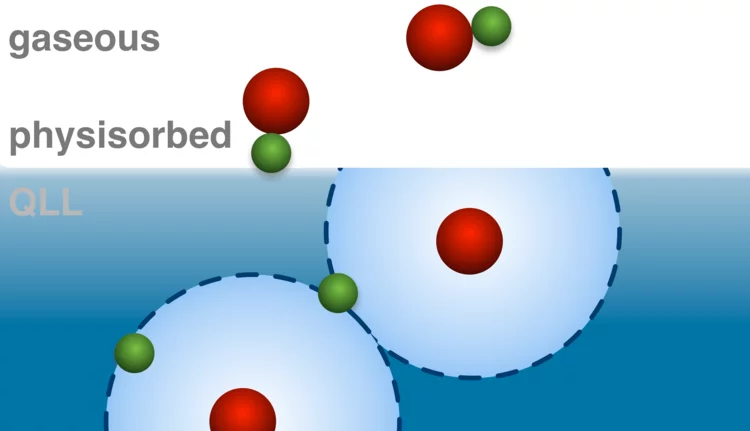
Coexistence of Physisorbed and Solvated HCl at Warm Ice Surfaces
The interfacial ionization of strong acids is an essential factor of multiphase and heterogeneous chemistry in environmental science, cryospheric science, catalysis research and material science. Using Near Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron (NAPP) spectroscopy, we directly detected a low surface coverage of adsorbed HCl at 253 K in both molecular and dissociated states and interpret the results as physisorbed molecular HCl at the outermost ice surface and dissociation occurring upon solvation deeper in the interfacial region. This study gives clear evidence for nonuniformity across the air−ice interface and questions the use of acid−base concepts in interfacial processes.
Award for the Best Poster at the 8th Annual World ADC
PSI Founder Fellow Philipp Spycher from the Group of Pharmacology at the Laboratory Center For Radiopharmaceutical Sciences (CRS) received the Award for the Best Poster at the 8th Annual World ADC (antibody-drug conjugate) conference San Diego (USA) from 20 to 22 September 2017. The poster on his latest work "Enzymatic (dual) site-specific conjugation of engineered and native antibodies" was highlighted as an exceptional poster with the highest impact in the field and Philipp was given the opportunity for a short-fire presentation in front of the whole plenum.
Radioscopie pour paléontologues et archéologues
Federica Marone radiographie les objets avec des rayons X de haute intensité, Eberhard Lehmann avec des neutrons. Ces deux chercheurs ont ouvert aux paléontologues et aux archéologues de nouvelles perspectives sur le passé.
Commissioning and first performance studies of the new CMS pixel detector
In the previous months the new CMS pixel detector was brought into operation. The detector was moved from PSI to CERN and installed in February, followed by an intensive period of commissioning and calibration. This process mostly involved the adjustment of many operational parameters which influence the detector performance, e.g.
Dr. Goran Lovric receives 2nd best abstract prize at the 34th SSAI Congress
Goran Lovric, a Postdoc at TOMCAT and CIBM, received the Best abstract 2nd Prize at the 34th congress of the Scandinavian Society of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care (SSAI) in Malmö (Sweden), 6-8th of September 2017. He presented the latest results of his work, entitled Spatial distribution of ventilator induced lung injury at the acinar level. An in-vivo synchrotron phase-contrast microscopy study in BALB/c mice.
ATHOS Conceptual Design Report (CDR)
The ATHOS Conceptual Design Report has recently been completed and describes the ATHOS project in detail. The CDR starts with a summary of the characteristics of the ATHOS undulator line. Especially the design parameters of the different ATHOS operation modes are explained and illustrated by simulation results. The core part of the report is a description of all key components, i.e. from the electron bunch extraction kicker down to the ATHOS experimental stations.
ATHOS Conceptual Design Report (CDR)
The ATHOS Conceptual Design Report has recently been completed and describes the ATHOS project in detail. The CDR starts with a summary of the characteristics of the ATHOS undulator line. Especially the design parameters of the different ATHOS operation modes are explained and illustrated by simulation results. The core part of the report is a description of all key components, i.e. from the electron bunch extraction kicker down to the ATHOS experimental stations.Download the full report Athos CDR .
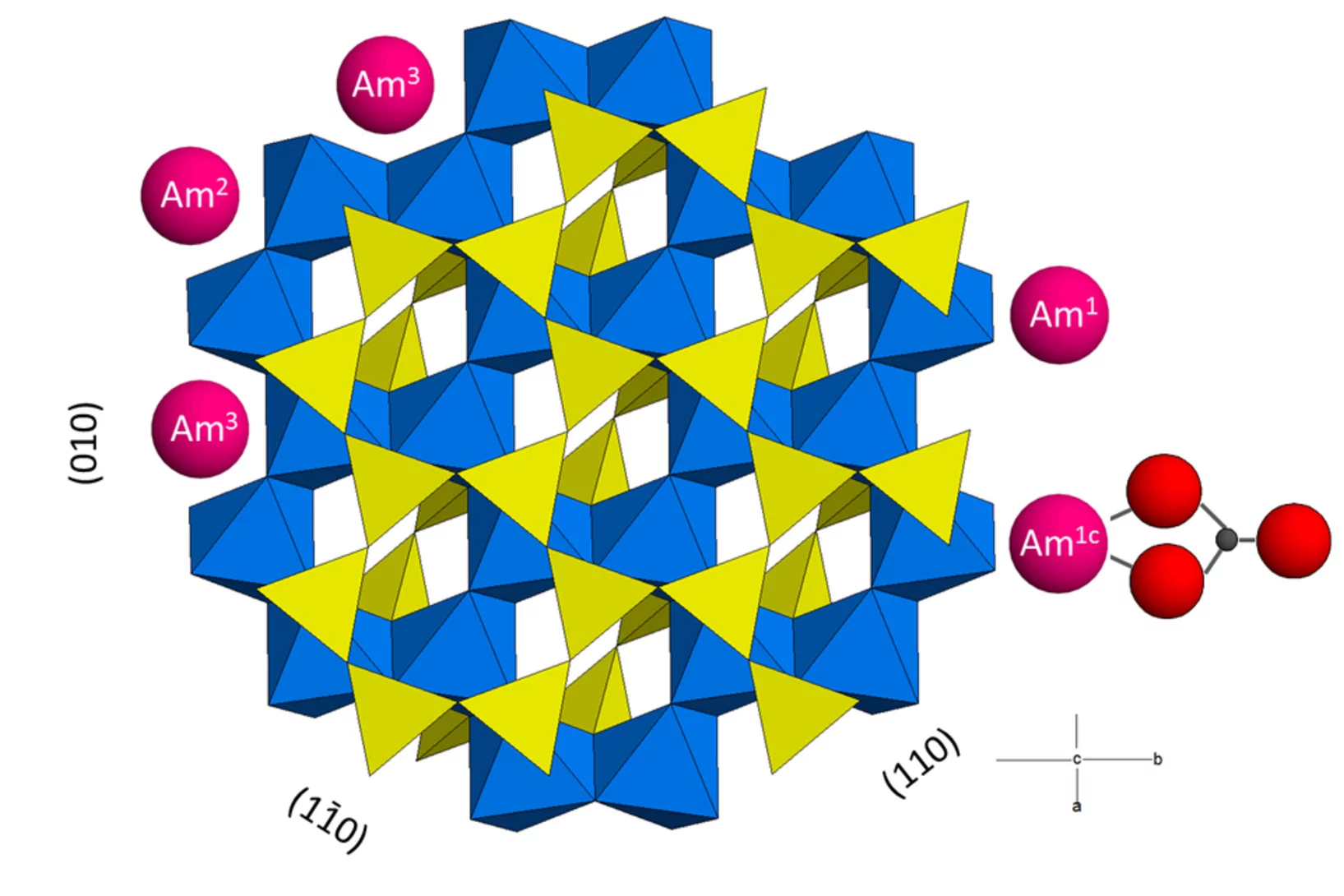
Sorption of trivalent lanthanides and actinides onto montmorillonite
The credibility of long-term safety assessments of radioactive waste repositories may be greatly enhanced by a molecular level understanding of the sorption processes onto individual minerals present in the near- and far-fields. A study conducted at LES in collaboration with the Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden Rossendorf used extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) and time-resolved laser fluorescence spectroscopies (TRLFS) to elucidate the uptake mechanism of trivalent lanthanides and actinides (Ln/AnIII) by the clay mineral montmorillonite.The excellent agreement between the thermodynamic model parameters obtained by fitting the macroscopic data, and the spectroscopically identified mechanisms, demonstrates the mature state of the 2SPNE SC/CE sorption model developed at LES for predicting and quantifying the retention of Ln/AnIII elements by montmorillonite-rich clay rocks.
Le travailleur de force du val Mesolcina
Aldo Antognini a la physique et la convivialité dans le sang. Aldo Antognini, chercheur au PSI, a reçu plus de 2 200 000 francs de l’UE pour sa nouvelle expérience. Son objectif: déterminer la répartition du magnétisme dans le proton. Pour y arriver, ce physicien des particules devra mettre ses talents scientifiques et techniques à contribution, mais aussi son entregent.
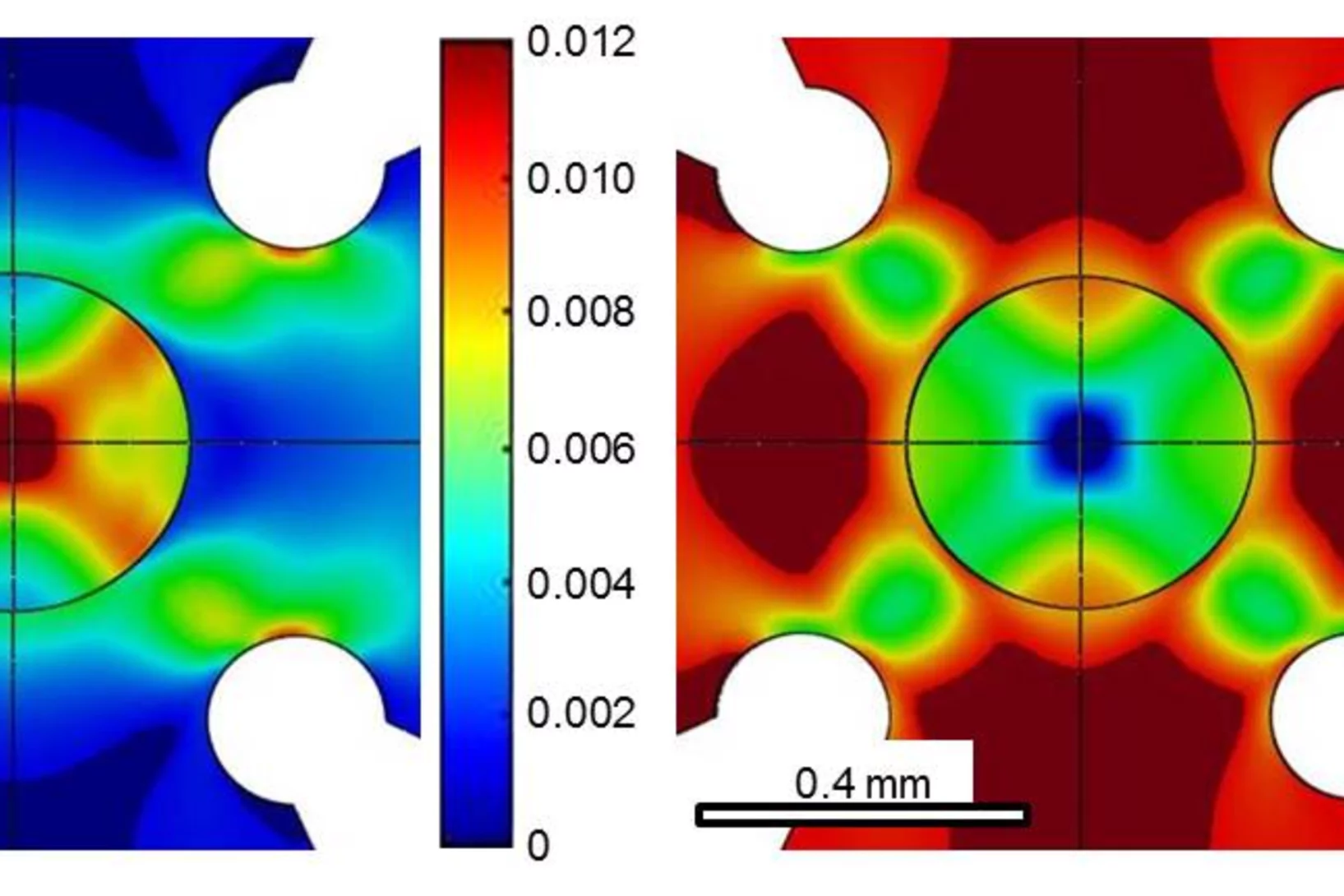
Composite laminated cruciform design for multiaxial testing of metals
Multiaxial mechanical testing of sheet metals is far from trivial, which is mainly related to issues with sample design and fabrication. PSI scientists have developed a new methodology to produce cruciform shaped samples from thin sheet metals based on a novel bottom-up approach. A proof-of-principle experiment based on polymer lamination of an aluminum thin sheet demonstrates the effectiveness of this new approach.
New Sample and Task Management Software
The AHL accounts, according to internal as well as external regulations, nuclear materials and moderators. For the detection and control of nuclear fuel samples and monitoring with respect to criticality safety, AHL developed a new sample and task management software (IPV).
Hector Dejea presented a talk at the conference Functional Imaging and Modelling of the Heart (FIMH2017) in Toronto
Hector Dejea (PhD student at ETH and TOMCAT) just attended the biennial FIMH conference in Toronto (Canada), which aims to integrate the state-of-the-art scientific advances in the fields cardiovascular imaging, image analysis and heart modelling fields.
MuPix8, our first large sensor, has arrived
We have just received first samples of the MuPix8 chip from the foundry. This is our first large (20mm x 10mm) pixel sensor prototype and a big step on the way to building the Mu3e tracking detector. The prototype will now be thoroughly tested in the labs in Karlsruhe and Heidelberg and will also soon see first beam at DESY in Hamburg, PSI and MAMI in Mainz.
Dr. Nan Xu awarded SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics
The SPS 2017 Prize in Condensed Matter Physics, sponsored by IBM, has been awarded to Dr. Nan Xu for his excellent work on topological quantum states. Dr. Nan Xu is a joint postdoc of Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL).
First beam in optics hutch
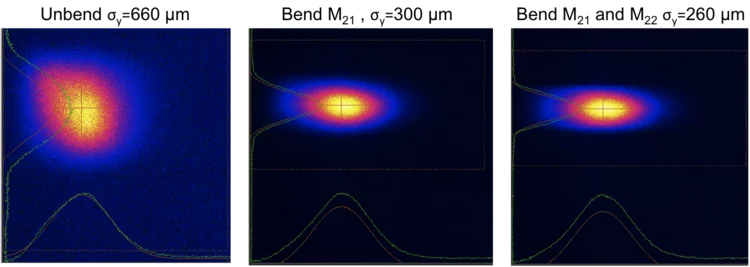
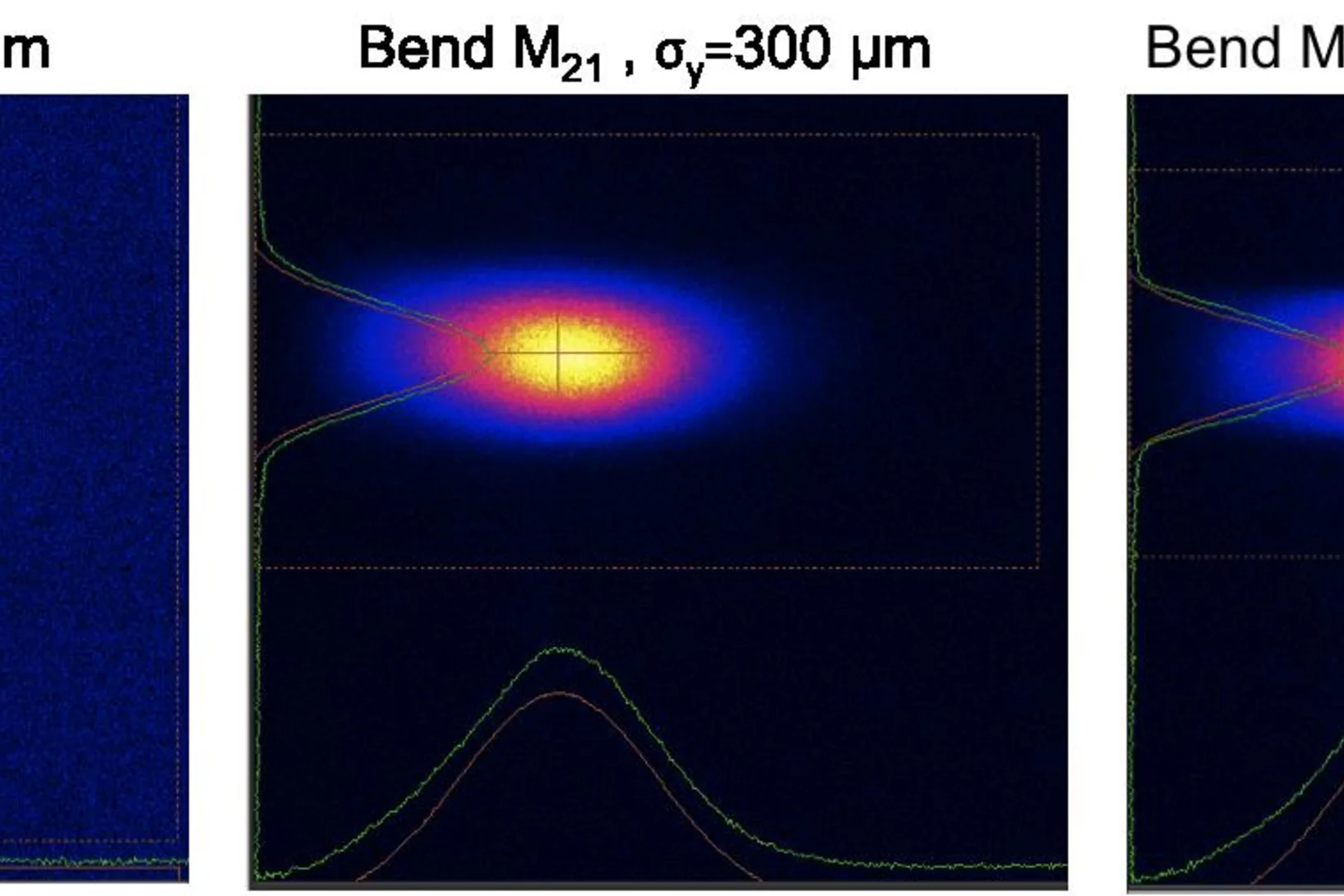
On August 31st, 2017, SwissFEL reached the next milestone by sending the first X-rays into the Optics Hutch. The Aramis undulators of SwissFEL produced SASE-radiation with 1.2 nm wavelength. The beam entered the Aramis-beamline along the pink beam path of Bernina via two vertical offset mirrors and was detected on the diagnostic photon screen at the end of the Optics Hutch. A stable and well shaped beam with a diameter of 1.5 mm was observed. With the bendable offset mirrors we were able to manipulate the profile to enlarge and reduce the vertical its size from 660 µm (rms) down to 260 µm (rms) without introducing distortions. The gas based intensity and position monitor in the frontend could be calibrated and determined a pulse energy of approximately 5 µJ. We are now looking forward to the next commissioning time in October to commission the monochromatic beam path of Bernina and the second branchline Alvra.
First beam in optics hutch
On August 31st, 2017, SwissFEL reached the next milestone by sending the first X-rays into the Optics Hutch. The Aramis undulators of SwissFEL produced SASE-radiation with 1.2 nm wavelength.
Swiss Neutron Scattering Prize
Viviane Lutz-Bueno was awarded the Swiss Neutron Scattering Prize of the Swiss Neutron Scattering Society, at the Joint Annual Meeting of the Swiss and Austrian Physical Society, for her PhD thesis Effects of formulation and flow on the structure of micellar aggregates carried out at ETH Zürich. Viviane is currently a postdoctoral fellow at the CXS group at PSI, developing scanning SAXS analysis methods.
Développer de manière ciblée de meilleurs métaux
Helena Van Swygenhoven-Moens étudie la vie intérieure des métaux au sein des grands instruments de recherche du PSI. Car l’industrie horlogère réclame de ressorts miniatures robustes et les ingénieurs de grandes aubes de turbine sans tensions au niveau des matériaux.
Complementary Response of Static Spin-Stripe Order and Superconductivity to Nonmagnetic Impurities in Cuprates
We report muon-spin rotation and neutron-scattering experiments on nonmagnetic Zn impurity effects on the static spin-stripe order and superconductivity of the La214 cuprates. Remarkably, it was found that, for samples with hole doping x ≈ 1/8, the spin-stripe ordering temperature Tso decreases linearly with Zn doping y and disappears at y ≈ 4%, demonstrating a high sensitivity of static spin-stripe order to impurities within a CuO2 plane.
A new RIXS analyzer scheme based on transmission zone plates
PSI scientists have developed a new type of X-ray optics that allows for analyzing the emission in resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) experiments. The new approach combines the energy dispersion with imaging capabilities. In a collaborative effort with research groups from Göttingen and Hamburg, two new classes of RIXS experiments, energy mapping and RIXS imaging, have been demonstrated.
L'avenir dans le marc de café
En raison de son important teneur en azote, le marc de café est un engrais que l’on utilise volontiers dans son jardin. Eliminé de cette manière, il contribue aujourd’hui déjà, à petite échelle, à une gestion écologique des déchets. Mais son potentiel est loin d’être épuisé: une méthode développée au PSI permet de produire du méthane, un gaz combustible, à partir de marc de café. Des chercheurs du PSI ont réussi à en faire la démonstration dans le cadre d’un essai pilote mené en collaboration avec le groupe alimentaire Nestlé, dont la production de café soluble génère du marc de café et qui souhaiterait voir ce dernier réutilisé de manière utile.
Felix Berg successfully defends his Ph.D. thesis on the Compact Muon Beam Line (CMBL) for Mu3e
Felix Berg has developed a full simulation of the high intensity, compact muon beam line for Mu3e. Beam tests he performed in the piE5 area have validated his simulations and established the beam setup for phase I of Mu3e. He has successfully defended his thesis at ETH Zürich.
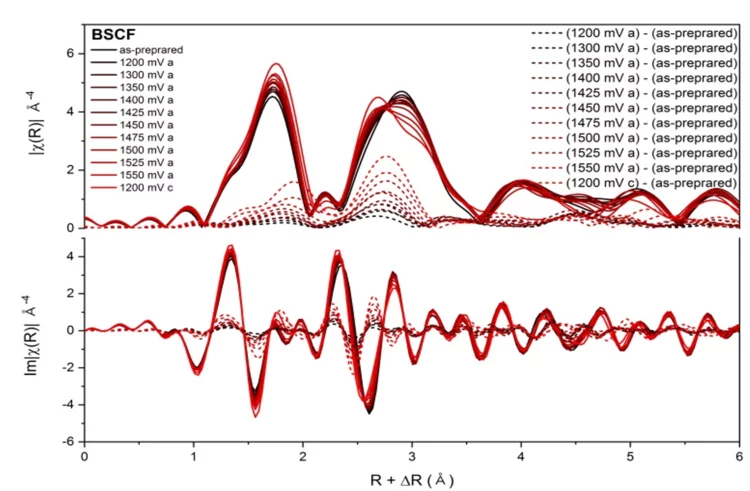
Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER)
Perovskite oxides
Time-resolved XAS is exploited to capture the dynamic local electronic and geometric structure of perovskite oxides under operando conditions.
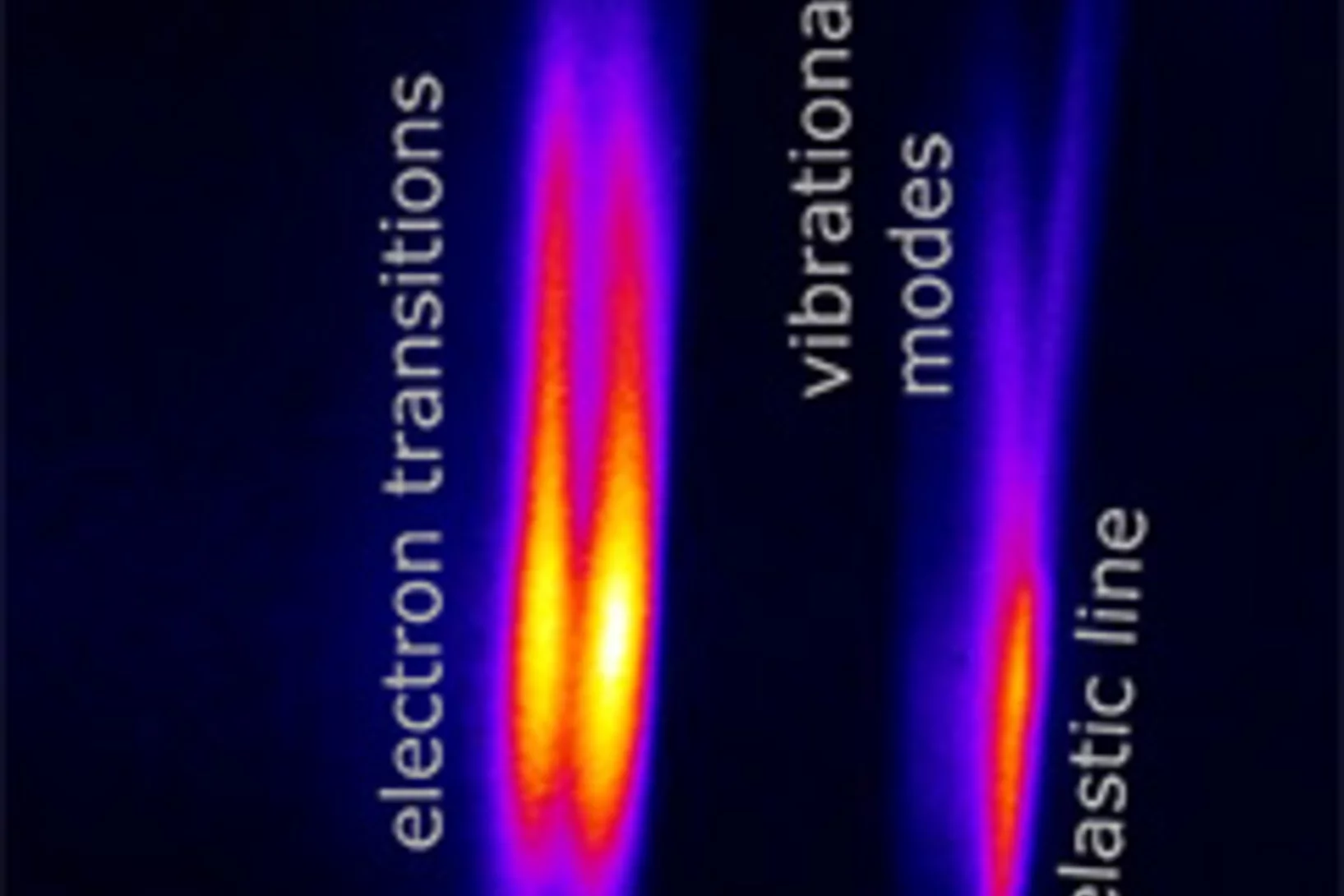
Single-shot Monitoring of Ultrafast Processes via X-ray Streaking at a Free Electron Laser
The advent of x-ray free electron lasers has extended the unique capabilities of resonant x-ray spectroscopy techniques to ultrafast time scales. Here, in collaboration between researchers from PSI, Sorbonne Universités, HASYLAB/DESY, Synchrotron SOLEIL, CNRS, and Uppsala University, we report on a novel experimental method that allows retrieving with a single x-ray pulse the time evolution of an ultrafast process, not only at a few discrete time delays, but continuously over an extended time window.
In Situ Serial Crystallography 2 Workshop at the SLS
A workshop dedicated to the presentation of the in meso in situ serial crystallography (IMISX) method (Huang et al. 2015, 2016 ActaD) for the X-ray structure determination of membrane proteins is organised at the Swiss Light Source at PSI for the second time. It will be held between November 27 and 29, 2017.