Abandon de l’énergie nucléaire, développement de l’énergie solaire et éolienne, production d’énergie à partir de la biomasse, réduction de la consommation d’énergie. D’ici 2050, la Suisse doit atteindre la neutralité climatique. Un objectif ambitieux, rendu plus urgent que jamais par une situation géopolitique de plus en plus difficile. Comment faire pour mettre en place ces prochaines années un approvisionnement énergétique durable et résistant pour la Suisse? Comment les énergies renouvelables peuvent-elles être utilisées de manière optimale? Quelles sont les nouvelles technologies les plus prometteuses? Au PSI, des chercheurs s’efforcent de trouver des réponses à ces questions décisives.
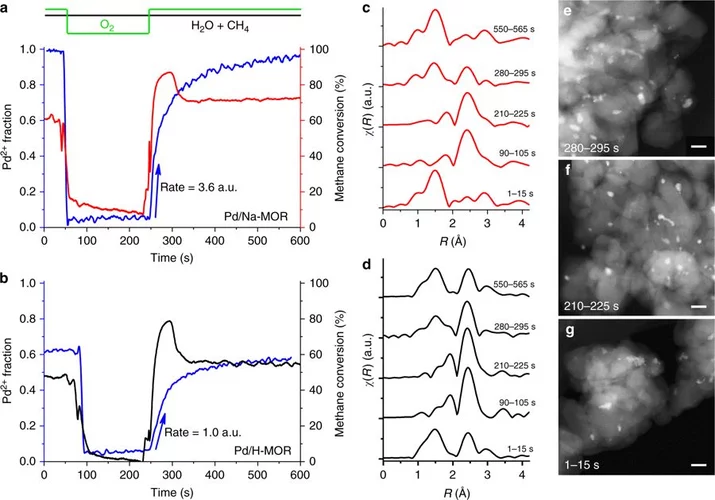
Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Using targeted synthesis and in situ characterization a palladium catalyst with improved stability against sintering during methane oxidation was prepared.
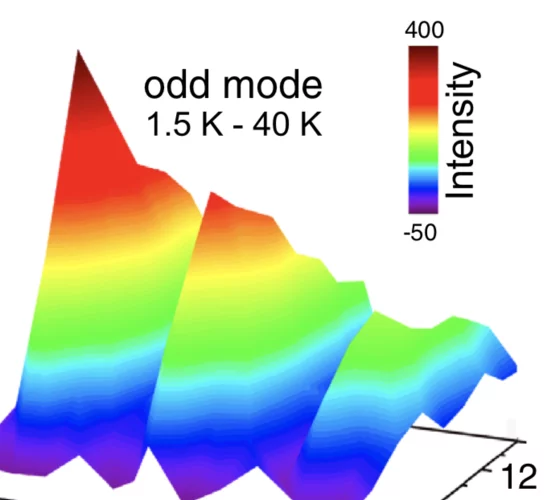
Odd and Even Modes of Neutron Spin Resonance in the Bilayer Iron-Based Superconductor CaKFe4As4
We report an inelastic neutron scattering study on the spin resonance in the bilayer iron-based superconductor CaKFe4As4. In contrast to its quasi-two-dimensional electron structure, three strongly L-dependent modes of spin resonance are found below Tc = 35 K.
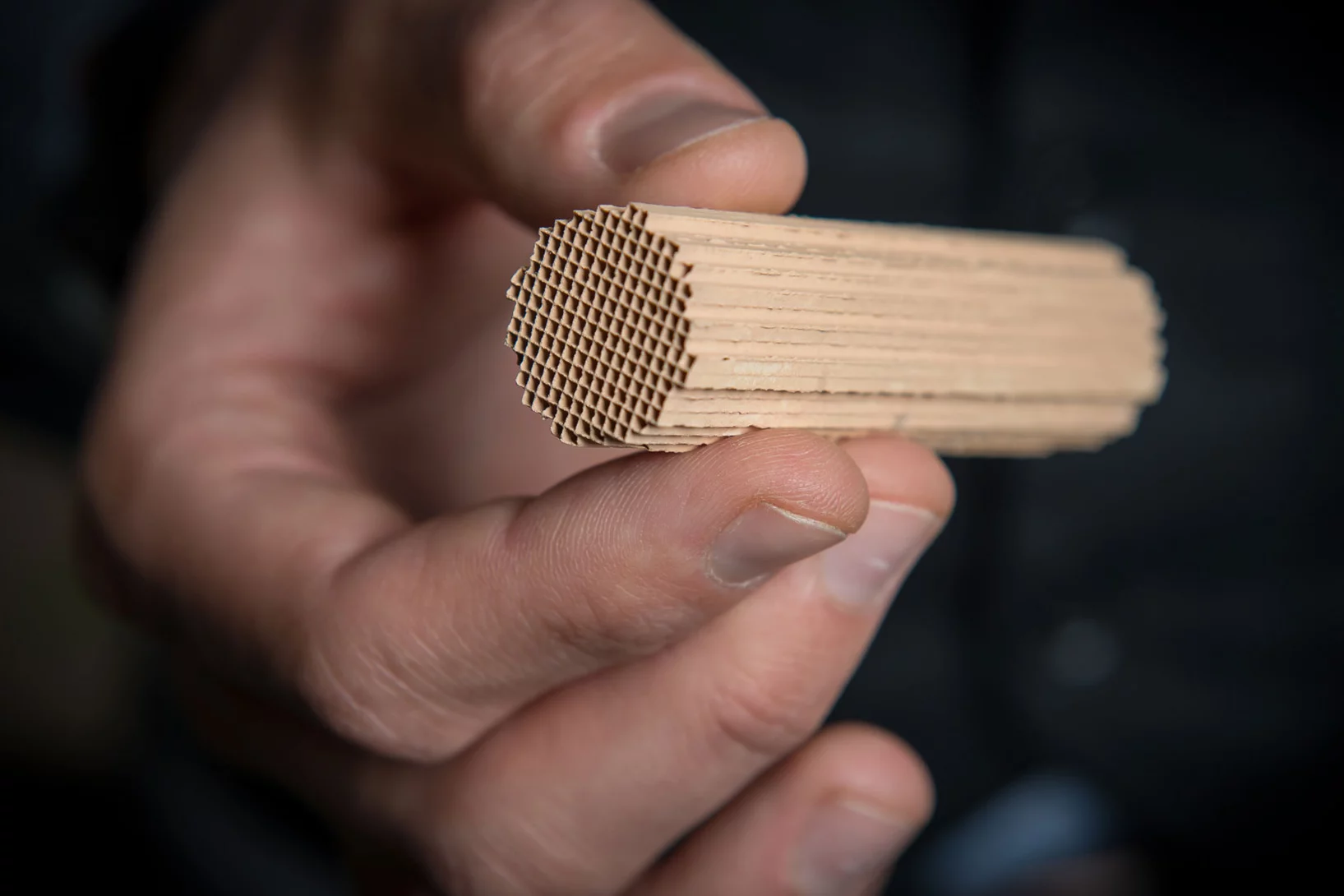
Gaz d'échappement purifiés grâce à une structure en éponge
Des chercheurs du PSI ont développé un nouveau catalyseur pour le traitement des gaz d'échappement des moteurs à gaz naturel. Il reste très actif même à basse température et pendant longtemps. La combustion du gaz naturel est ainsi plus propre et plus respectueuse du climat. Cela renforce l'attrait du gaz naturel et du biogaz comme alternative aux produits pétroliers, par exemple comme carburant pour les voitures.
Brennstoffzellen zum Durchbruch verhelfen
Wasserstoff gilt als vielversprechende Alternative für eine Zukunft ohne fossile Energieträger. Um Brennstoffzellen weiterzuentwickeln und für einen Markteintritt vorzubereiten, verstärkt die Empa die Zusammenarbeit mit der H2 Energy Holding AG und dem Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI).
CMS Young Researcher Prize awarded to Lea Caminada
Lea Caminada, a researcher in the High-Energy Particle Physics group of the Laboratory for Particle Physics (LTP) in NUM, has received the annual CMS Young Researcher Prize. This Prize is given once a year to outstanding young physicists who made very significant and sustained contributions to the CMS experiment at the LHC facility at CERN. Dr. Caminada has been recognized for her contribution to the construction, installation and commissioning of the two pixel detectors which were build at PSI for the CMS experiment. Her work also included the measurement of the B-meson production cross section and the observation of the Higgs boson in association with top quarks.
Isotope effect on the spin dynamics of single-molecule magnets probed by muon spin spectroscopy
Muon spin relaxation (μSR) experiments on a single molecule magnet enriched in different Dy isotopes detect unambiguously a slowing down of the zero field spin dynamics for the non-magnetic isotope. This occurs in the low temperature regime dominated by quantum tunnelling, in agreement with previous ac susceptibility investigations. In contrast to the latter, however, μSR is sensitive to all fluctuation modes affecting the lifetime of the spin levels.
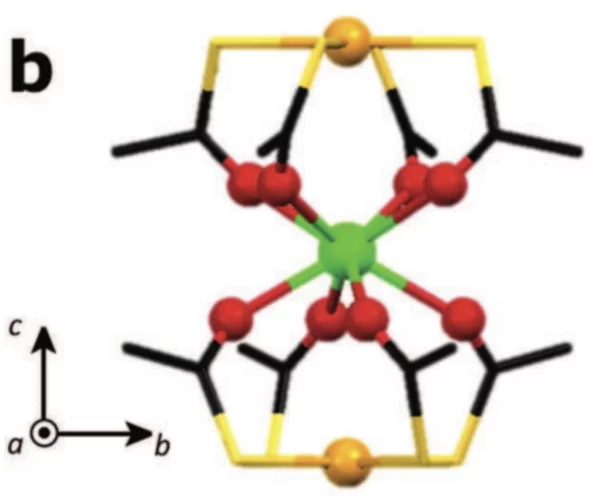
Magnetic Anisotropy Switch: Easy Axis to Easy Plane Conversion and Vice Versa
The rational design of the magnetic anisotropy of molecular materials constitutes a goal of primary importance in molecular magnetism. Indeed, the applications of molecular nanomagnets, such as single-molecule magnets and molecular magnetic refrigerants, depend on the full control over this property.
Metteurs en scène avec missions additionnelles
Par rapport aux modèles actuels, les mémoires informatiques fabriquées à partir de certains matériaux novateurs devraient permettre d'enregistrer les informations beaucoup plus rapidement et dans un espace plus restreint, en consommant nettement moins d'énergie. Les séquences filmées au moyen du laser à rayons X montrent ce qui se passe au cœur de ces mémoires informatiques potentielles et comment optimiser les processus au cours desquels le matériau commute entre deux états.
MOOCs – a paradigm shift in education
In March 2018, the nine-week MOOC “Introduction to synchrotrons and x-ray free-electron lasers” (abbreviated to “SYNCHROTRONx”) came online via the edX provider of the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), created by Phil Willmott of the Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institute. “MOOC” is an acronym for “massive open online course”, a teaching platform started in the first decade of this century, which has become increasingly popular in the last five to six years. MOOCs have no limits to participation and are free. Some of the most popular MOOCs can attract many tens of thousands of participants. Even the most specialized subjects may have an initial enrollment of over a thousand, more than an order of magnitude larger than that typically found in traditional higher education. There were over 70 million MOOC enrollments covering nearly 10’000 subjects offered by the top five providers in 2017 alone!
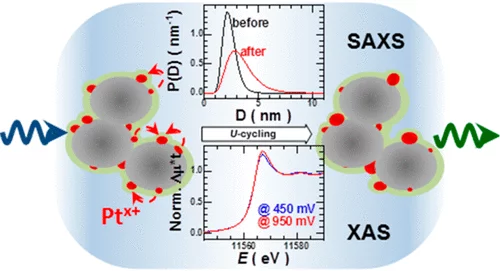
Combining SAXS and XAS To Study the Operando Degradation of Carbon-Supported Pt-Nanoparticle Fuel Cell Catalysts
In the last two decades, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) have evolved into two well-established techniques capable of providing complementary and operando information about a sample’s morphology and composition, respectively. Considering that operation conditions can often lead to simultaneous and related changes in a catalyst’s speciation and shape, herein we introduce a setup that combines SAXS and XAS in a configuration that allows optimum acquisition and corresponding data quality for both techniques.
Dr. Anne Bonnin gives an invited talk at SRI 2018
The 13th International Conference on Synchrotron Radiation Instrumentation (SRI 2018) was hosted by the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center (NSRRC) from June 10 to 15, 2018. The 5-day conference was gathering scientists and engineers around the world involved in development of new concepts, techniques, and instruments related to synchrotron radiation and free electron laser research.
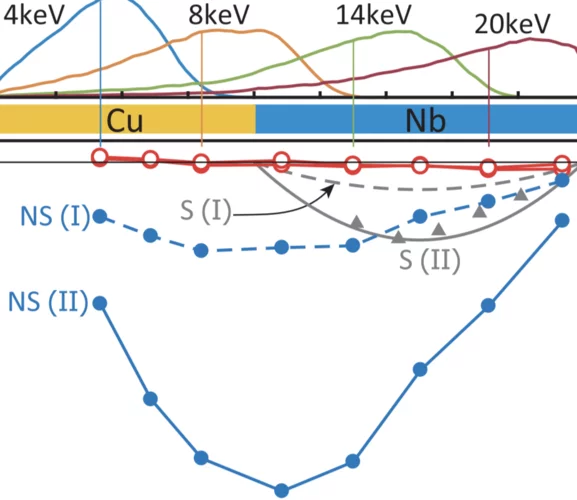
Observation of Anomalous Meissner Screening in Cu/Nb and Cu/Nb/Co Thin Films
We have observed the spatial distribution of magnetic flux in Nb, Cu/Nb, and Cu/Nb/Co thin films using muon-spin rotation. In an isolated 50-nm-thick Nb film, we find a weak flux expulsion (Meissner effect) which becomes significantly enhanced when adding an adjacent 40 nm layer of Cu. The added Cu layer exhibits a Meissner effect (due to induced superconducting pairs) and is at least as effective as the Nb to expel flux.
Capteur biologique de lumière filmé en pleine action
Une équipe de chercheurs de l'Institut Paul Scherrer PSI a enregistré, à l'aide d'un laser à rayons X, l'un des processus les plus rapides en biologie. Le film moléculaire ainsi réalisé révèle la manière dont le capteur de lumière rétinal est activé dans une molécule de protéine. Des réactions de ce type interviennent dans de nombreux organismes. Ce film montre pour la première fois comment une protéine pilote de manière efficace la réaction du capteur de lumière intégré en son sein.
Revisiting the magnetic structure of La1/3Sr2/3FeO3 by neutron powder diffraction and Mössbauer spectroscopy
La1/3Sr2/3FeO3 is reported to show a 2Fe4+ → Fe3+ + Fe5+ charge disproportionation (CD) accompanied by Fe3+/Fe5+ charge ordering (CO) and a metal-insulator (MI) transition at 200 K [1]. The MI transition was ascribed to CD and CO. Based on the CO, the magnetic structure was reported to be P-3m1 or P1 from the neutron diffraction studies performed at 50 K and 15 K, respectively [2]. The former seems not to be a correct solution since the presence of rotoinversion -3 is incompatible with the claimed collinear magnetic structure, with the collinear moments in the ab-plane in R-3c metric; and the latter might be a correct solution, but without any symmetry restrictions in space group P1.
Breakdown of Magnetic Order in the Pressurized Kitaev Iridate β-Li2IrO3
Temperature-pressure phase diagram of the Kitaev hyperhoneycomb iridate β-Li2IrO3 is explored using magnetization, thermal expansion, magnetostriction, and muon spin rotation measurements, as well as single-crystal x-ray diffraction under pressure and ab initio calculations.
Huangshan Chen successfully defends his thesis on the development of the MuTRiG ASIC for the Mu3e timing detecors
Huangshan Chen was instrumental in the development of the MuTRiG ASIC, which performs the time-to-digital conversion for the Mu3e fibre and tile timing detectors. He has now successfully defended his thesis at Heidelberg University.
Rhine-Knee Regiomeeting 2018
Since it was first established in 1987, the annual Regio-Meeting has been instrumental in facilitating interactions in the structural biology community in southwestern Germany, the eastern region of France and an expanding area of Switzerland. It is set as an informal event to foster young scientists to discuss their research results in an international context. The 2018 edition will take place in the heart of Switzerland in Emmetten from September 26 to 28, 2018. Registration and abstract submission deadline: September 7, 2018.
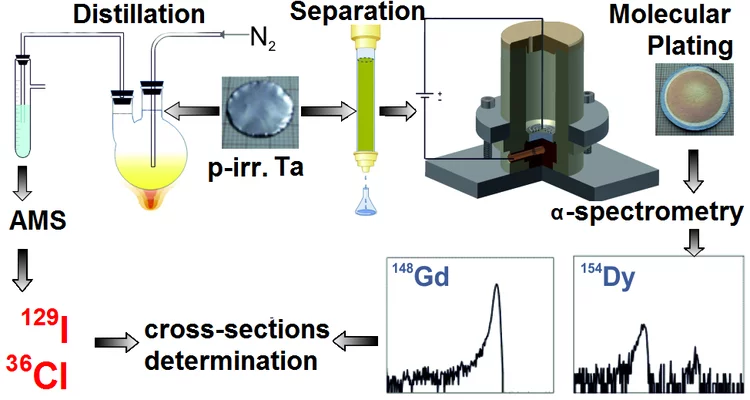
Nuclear data for nuclear installations: Radiochemistry improves the precision of the cross-section data of long-lived radionuclides
Knowledge about the cross sections data of the target materials used for spallation neutron facilities (SNF) and accelerator driven systems (ADS) is essential for the licensing, safe operation and decommissioning of these facilities. In addition, these data are important to evaluate and improve the existing computer simulation codes. Especially the α-emitter 148Gd has a large contribution to radio-toxicity of spallation target facilities with its 74.6 years of half-life.
Observation of ttH Production
The observation of Higgs boson production in association with a top quark-antiquark pair is reported, based on a combined analysis of proton-proton collision data at center-of-mass energies of √s = 7,8, and 13 TeV, corresponding to integrated luminosities of up to 5.1, 19.7, and 35.9 fb-1, respectively. The data were collected with the CMS detector at the CERN LHC.
Rosaria Pileci was one out of four scientific speakers at EYE2018
Rosaria Pileci, a PhD student at the LAC, presented aerosol research at the European Parliament's European Youth Event (EYE2018).
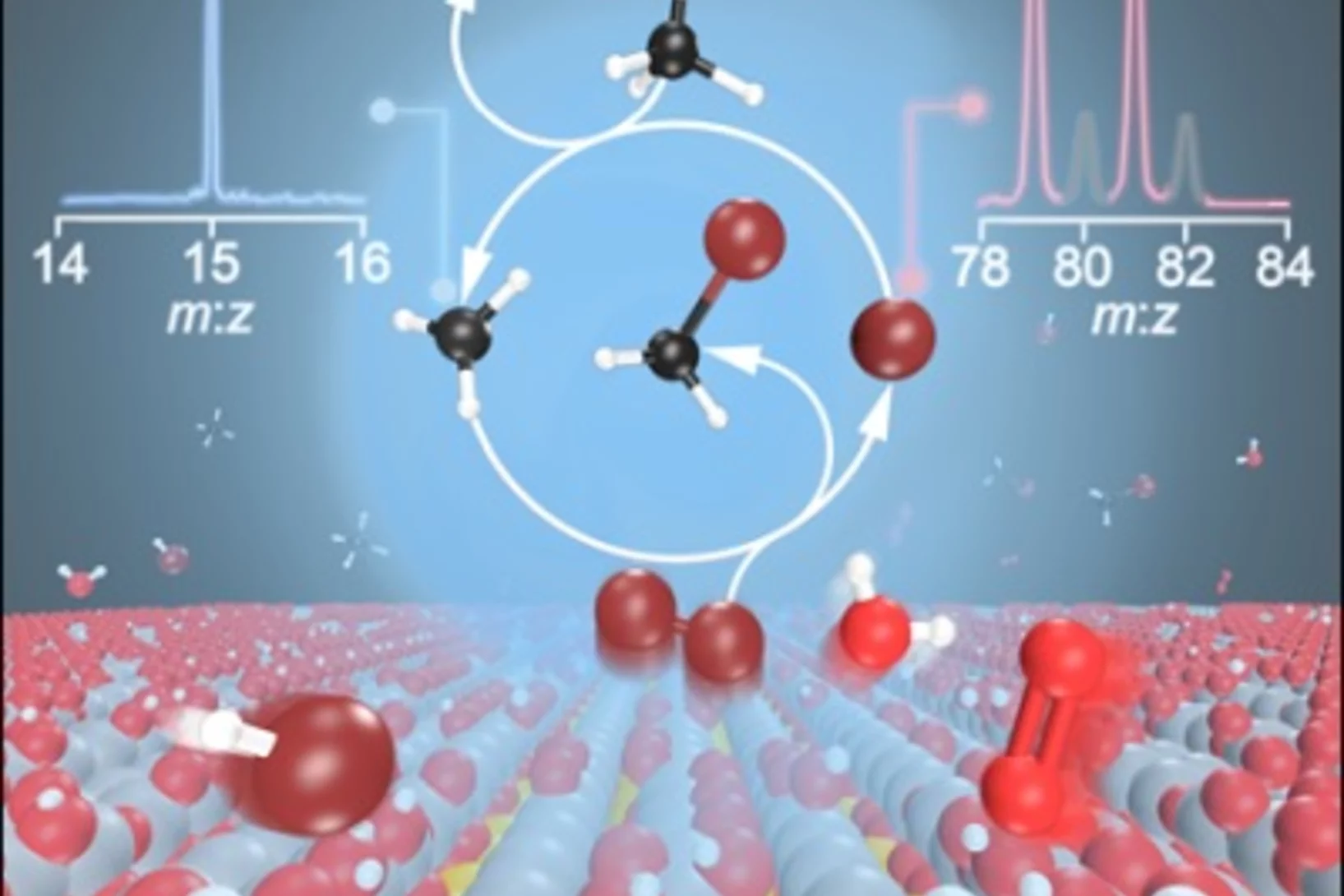
Tracking down radicals in methane oxybromination
Catalytic oxybromination may turn the cheap and abundant feedstock methane into the platform compounds bromomethane and dibromomethane. Yet researchers have been puzzled by the catalysis mechanism, which was speculated to involve free radical intermediates. Operando photoelectron photoion coincidence helped distinguish surface and gas-phase reaction steps and elucidated the crucial halogen-mediated C–H bond activation step, which is driven by elusive bromine and methyl radicals.
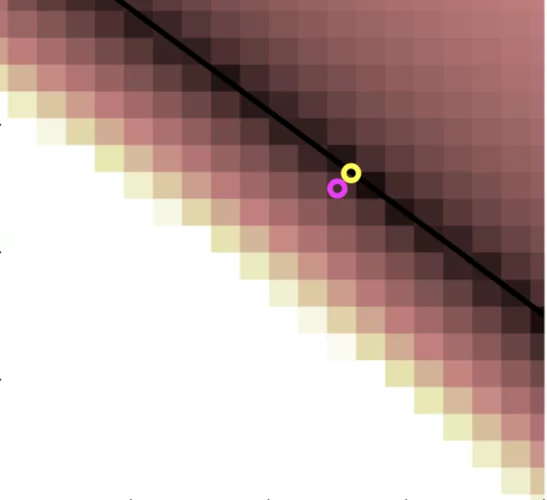
Clogging in staked-in needle pre-filled syringes (SIN-PFS): Influence of water vapor transmission through the needle shield
Staked-in needle pre-fillable syringes (SIN-PFS) are a convenient delivery system widely established in the growing pharmaceutical market. Under specific storage conditions, the needle of PFS containing high concentration drug product (DP) solution is prone to clogging, which prevents administration of the liquid.
Hollywood en forêt de Würenlingen
Les chercheurs du PSI veulent utiliser le laser à rayons X SwissFEL pour réaliser des films qui présenteront des biomolécules en action. Ces productions montreront comment fonctionne notre œil ou quel est le mode d’action de nouveaux médicaments.
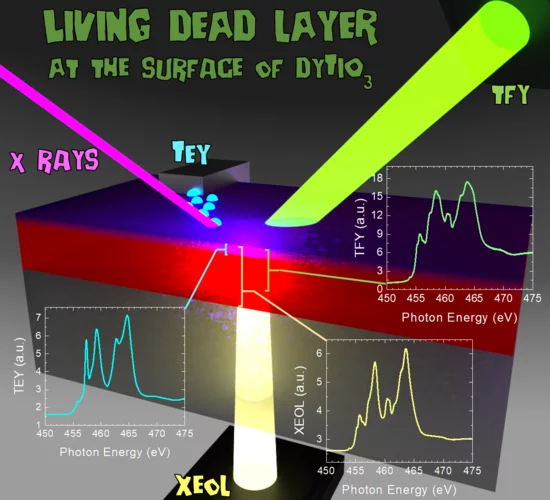
Revealing a Living-Dead Magnetic Layer
A peculiar magnetic “dead layer” is detected at the surface of thin films of DyTiO3, a ferrimagnetic Mott insulator. Depth dependent X-ray absorption measurements performed at the X-Treme beamline in the Swiss Light Source indicate that this layer is associated with a deviation of the Ti valence from 3+ toward 4+ at the film surface, suppressing the magnetic coupling between Ti ions and unleashing a strong paramagnetic response from uncoupled Dy ions.
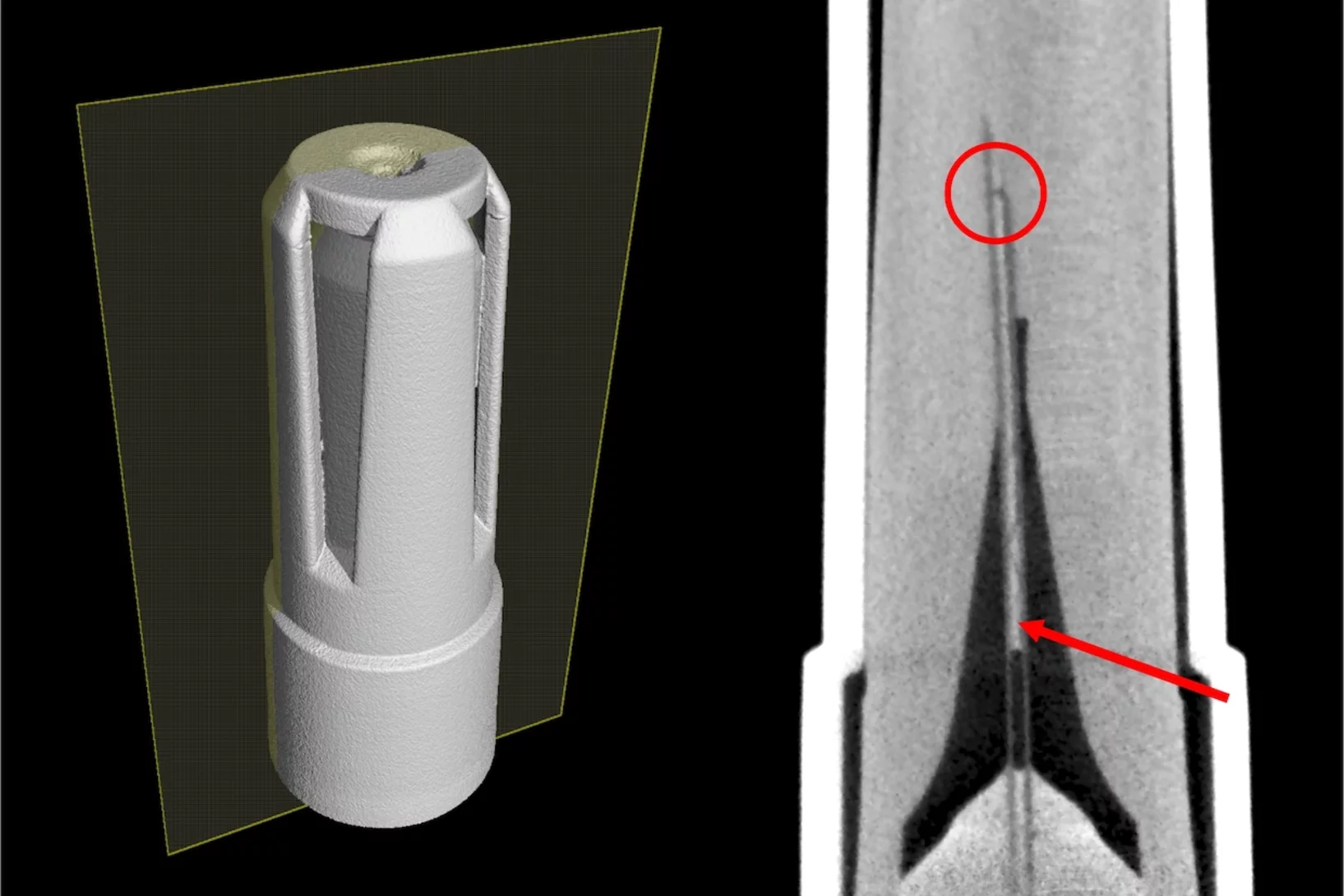
Radiographie neutronique d'aiguilles hypodermiques
Des chercheurs de l'Institut Paul Scherrer PSI, de l'Université de Bâle et de la société F. Hoffmann-La Roche ont recouru à un procédé d'imagerie neutronique afin d'analyser le rôle décisif que joue l'entreposage frigorifique des seringues médicales préremplies.
ETH Medal for outstanding MSc thesis
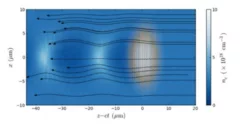
The characteristics of low energy electrons accelerated by a laser wakefield (Laser Wakefield Acceleration LWFA) has been studied. The work included understanding the acceleration process, setting up the experiment and measuring properties like charge, divergence and energy of the accelerated electrons. The experiment included diagnostics for the laser and the electrons. In order to make high-resolution energy distribution measurements with relative errors ∆E/E of below 10%, a tunable electron spectrometer has been designed, built and characterized. A tunable permanent magnet quadrupole triplet has been designed for stigmatic focusing in a range of 5 keV to 5 MeV.
Ann-Kathrin Perrevoort successfully defends her PhD thesis on the sensitivity of the Mu3e experiment for new physics and pixel frontend firmware.
Ann-Kathrin Perrevoort studied the sensitivity of the Mu3e experiment for the main search channel using an effective field theory approach and also simulated the performance for searches for two-body decays of the muon and electron-positron resonances. In addition she contributed a core piece of the pixel front-end firmware, namely the real-time time sorting of hits.
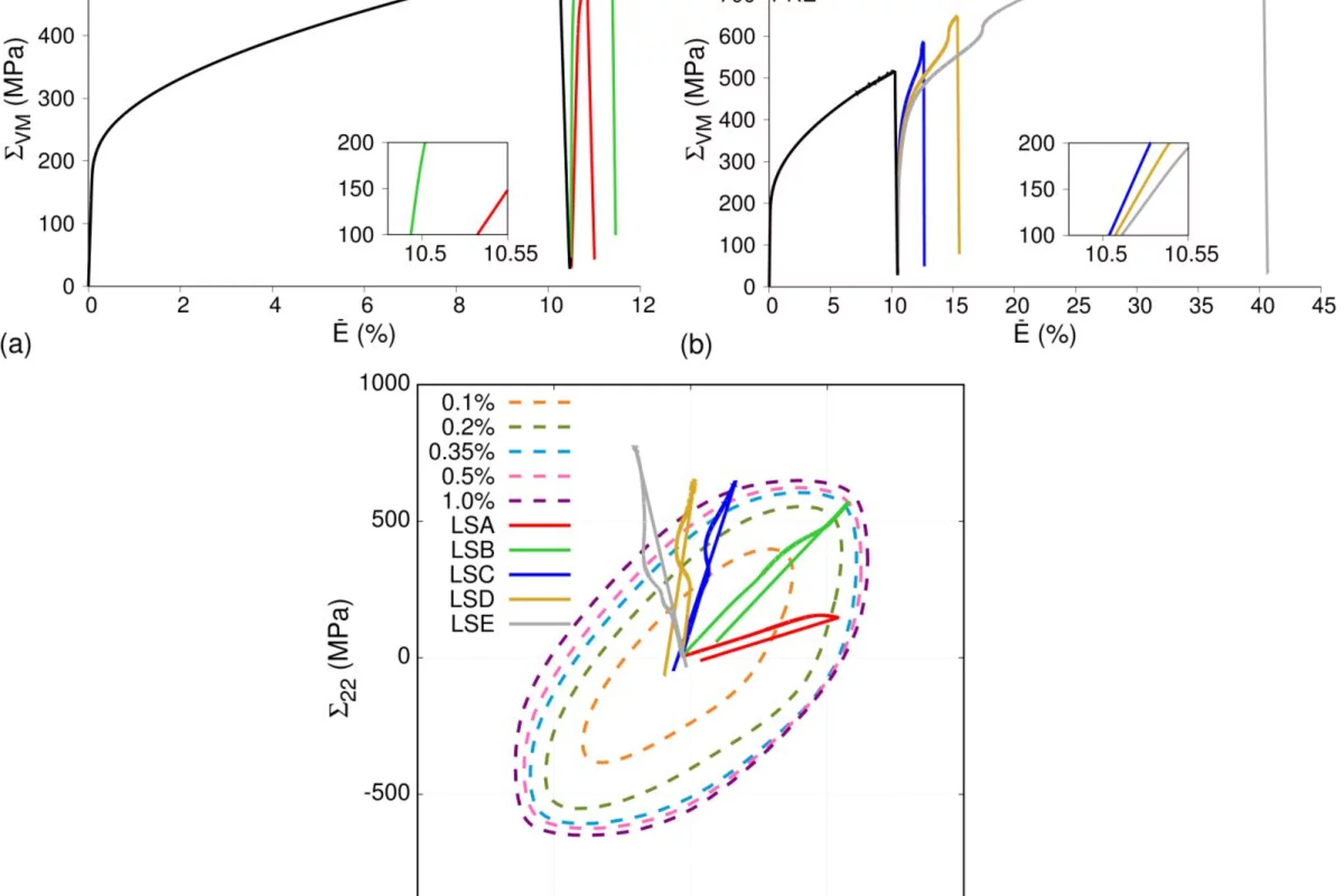
Mechanical response of stainless steel subjected to biaxial load path changes: cruciform experiments and multi-scale modeling
In this work, we have enhanced our originally proposed experiment-modeling synergy in Upadhyay et al. Acta Mat. 2016, to capture the stress evolution in the complex cruciform geometry during arbitrary multi-axial load path changes. We perform cruciform simulations using the implementation of the visco-plastic self-consistent (VPSC) model as a user material (UMAT) into the ABAQUS finite element (FE) solver. We also use the Elasto-viscoplastic fast Fourier transform (EVP-FFT) approach to compute yield surfaces. This experiment-modeling synergy is exploited to understand the mechanical response (including the elastic response, Bauschinger effect and hardening) of 316L stainless steel following biaxial load path changes.
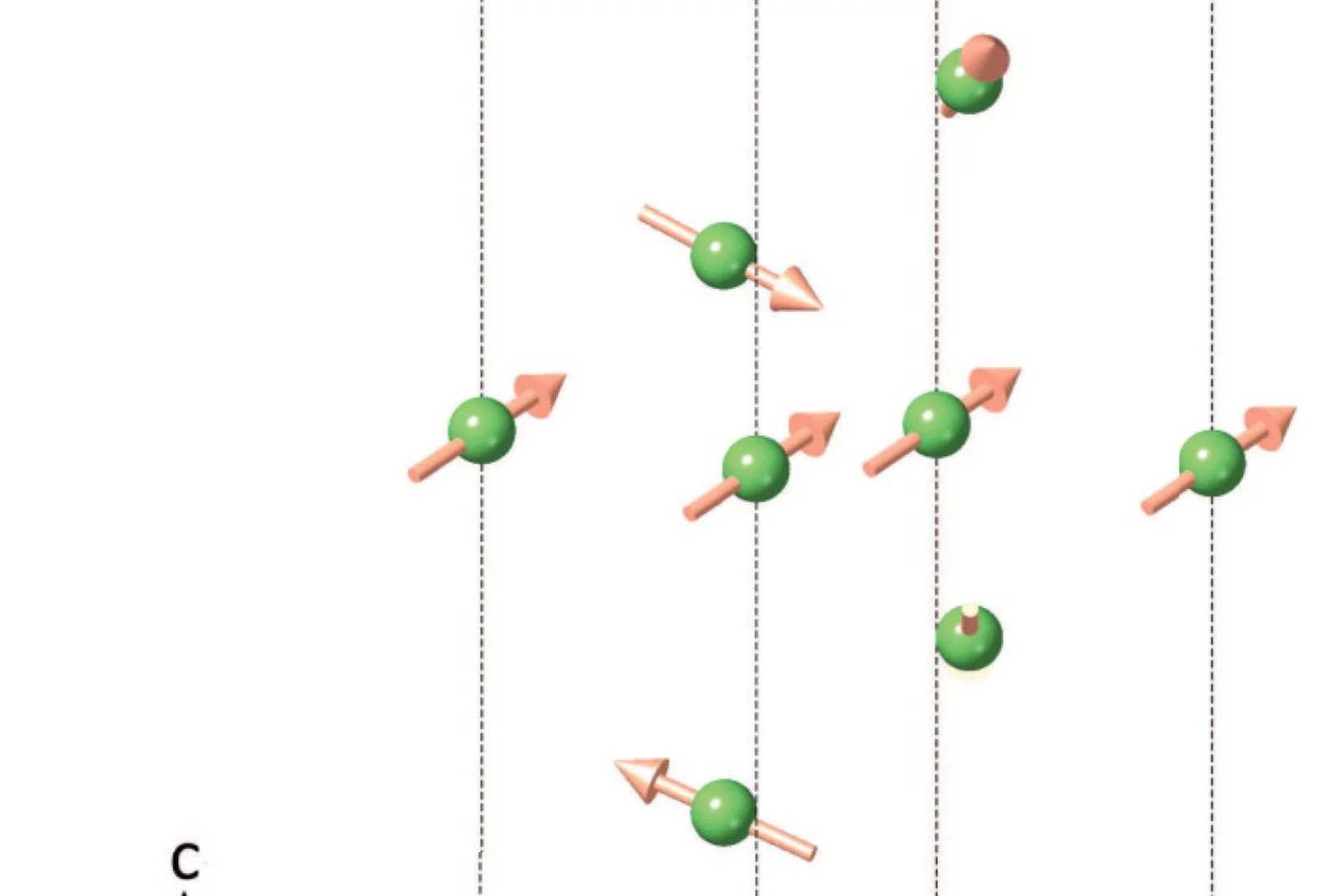
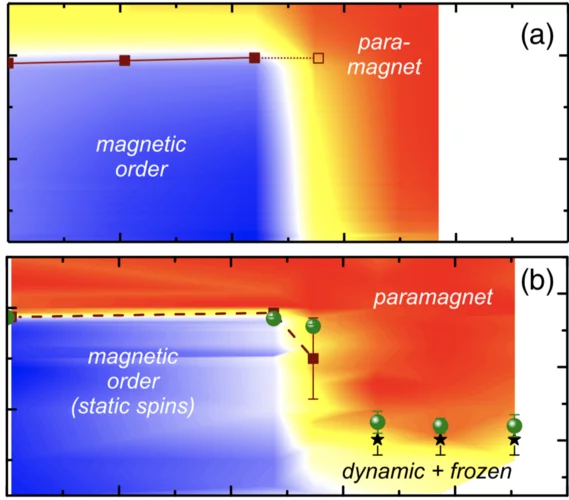
Special temperatures in frustrated ferromagnets
The description and detection of unconventional magnetic states, such as spin liquids, is a recurring topic in condensed matter physics. While much of the efforts have traditionally been directed at geometrically frustrated antiferromagnets, recent studies reveal that systems featuring competing antiferromagnetic and ferromagnetic interactions are also promising candidate materials.
Une journée dans la peau d'un jeune chercheur
La physique n'est pas la discipline préférée de tout le monde. A l'iLab du PSI, les élèves découvrent cette matière autrement: en effectuant des expériences plutôt qu'en apprenant des formules par cœur.