Abandon de l’énergie nucléaire, développement de l’énergie solaire et éolienne, production d’énergie à partir de la biomasse, réduction de la consommation d’énergie. D’ici 2050, la Suisse doit atteindre la neutralité climatique. Un objectif ambitieux, rendu plus urgent que jamais par une situation géopolitique de plus en plus difficile. Comment faire pour mettre en place ces prochaines années un approvisionnement énergétique durable et résistant pour la Suisse? Comment les énergies renouvelables peuvent-elles être utilisées de manière optimale? Quelles sont les nouvelles technologies les plus prometteuses? Au PSI, des chercheurs s’efforcent de trouver des réponses à ces questions décisives.
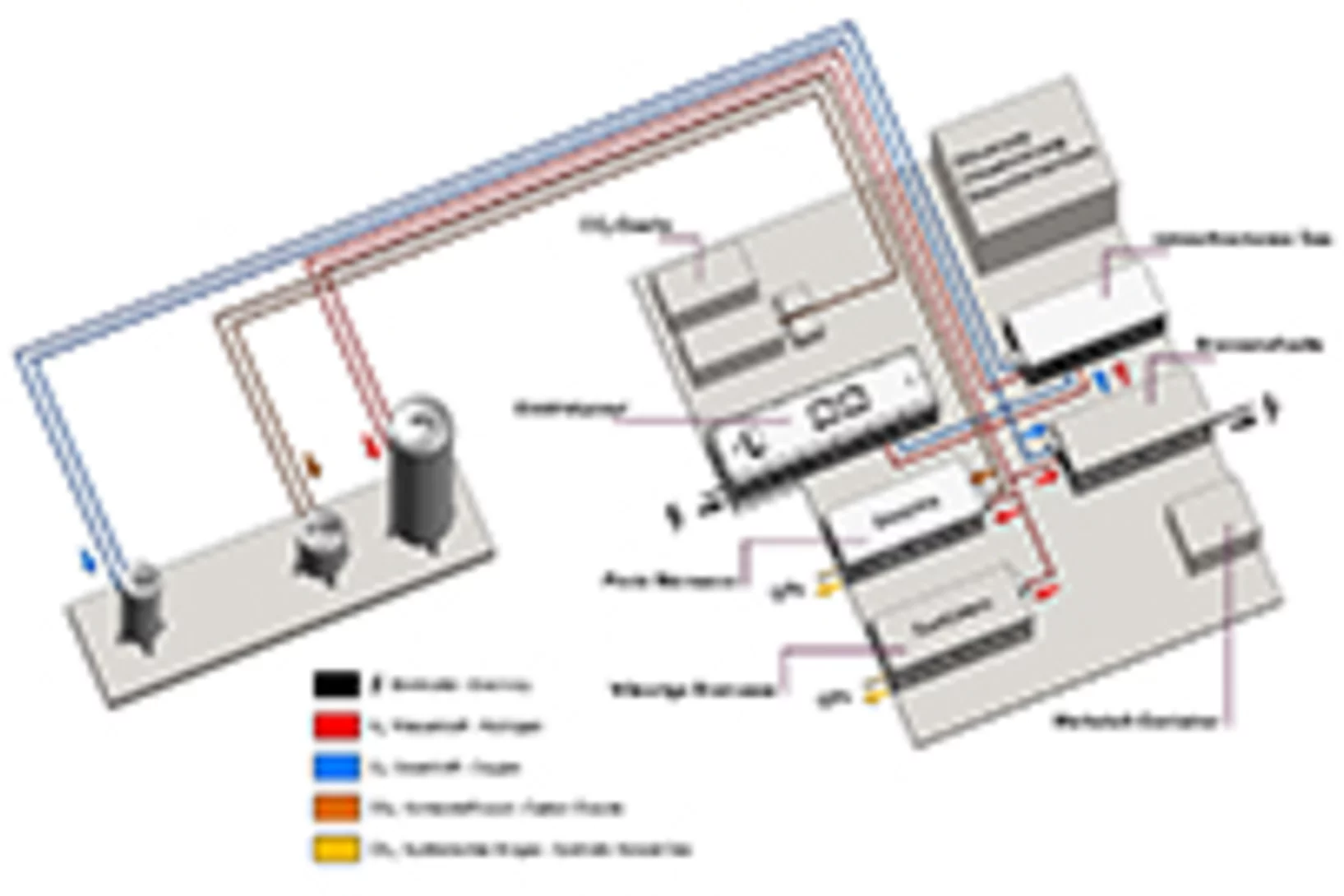
Les nouvelles énergies renouvelables sur la voie de l’intégration
La Stratégie énergétique 2050 de la Confédération prévoit un développement important des énergies renouvelables, comme l’énergie solaire et l’énergie éolienne. L’intégration de cette énergie décentralisée et produite avec des fluctuations temporelles représente un important défi pour les réseaux électriques. Une solution possible serait d’exploiter les excès de courant qui surchargent les réseaux pour produire des gaz à haut rendement, comme l’hydrogène ou le méthane. Ce concept, appelé « conversion d’électricité en gaz » (ou « power to gas »), est au centre de la nouvelle plate-forme Energy System Integration (ESI) au PSI.
Cérémonie : la pose de la première pierre de l’ESS souligne son importance scientifique
Aujourd’hui, plusieurs centaines de représentants du monde scientifique, venus de différents pays européens, se sont rassemblé sur le chantier de la source européenne de spallation (European Spallation Source ESS) à Lund, en Suède, pour la cérémonie de pose de la première pierre de l’ESS. Cet événement marque la pose des fondations de cette nouvelle installation, dont la construction a récemment démarré, mais aussi celle d’une nouvelle phase dans la recherche scientifique européenne.
La dernière pièce du puzzle
En tant que post-doctorante, Julia H. Smith travaille au développement de l'un des détecteurs destinés au laser à rayons X SwissFEL. Ces derniers sont en quelque sorte les yeux du futur grand instrument du PSI. La chercheuse a de bonnes chances d'accompagner son détecteur jusqu'à son utilisation dans la nouvelle installation pendant qu'elle sera encore au PSI. Mais ce qui compte pour moi, plus encore que de vivre les premières expériences, c'est d'assimiler le plus de connaissances possibles pendant mon post-doctorat, dit-elle. Car pour la suite, Julia Smith a bien l'intention de rester dans le domaine des détecteurs et du développement de technologies, que ce soit dans l'industrie ou dans un autre institut de recherche.
Direct Spectroscopic Observation of a Shallow Hydrogenlike Donor State in Insulating SrTiO3
We present a direct spectroscopic observation of a shallow hydrogenlike muonium state in SrTiO3 which confirms the theoretical prediction that interstitial hydrogen may act as a shallow donor in this material. The formation of this muonium state is temperature dependent and appears below ∼70 K. From the temperature dependence we estimate an activation energy of ∼50 meV in the bulk and ∼23 meV near the free surface. The field and directional dependence of the muonium precession frequencies further supports the shallow impurity state with a rare example of a fully anisotropic hyperfine tensor.
The μ → eγ decay in a systematic effective field
We implement a systematic effective field theory approach to the benchmark process μ → eγ, performing automated one-loop computations including dimension 6 operators and studying their anomalous dimensions. We obtain limits on Wilson coefficients of a relevant subset of lepton-flavour violating operators that contribute to the branching ratio μ → eγ at one-loop.
Des colosses pour commander de minuscules particules
Dans un accélérateur de particules, ce sont les aimants qui tirent les ficelles : si protons et électrons gardent le cap, c’est en effet grâce à eux. Ces aimants n’ont toutefois pas grand-chose en commun avec ceux qui garnissent la porte de notre réfrigérateur. Au PSI, ils sont nombreux à peser bien plus lourd que ledit réfrigérateur. Et malgré leur puissance, ce sont des chefs-d’uvre de précision.
Il date des années 1980, mais il est toujours aussi fiable
L’origine du faisceau de protons au PSI est un accélérateur linéaire au look rétro. Ce modèle charismatique est baptisé Cockcroft-Walton, du nom de l’inventeur du principe. Depuis 1984, il fournit la première étape d’accélération des protons, qui sont ensuite amenés dans l’accélérateur circulaire à une vitesse équivalant à 80% de la vitesse de la lumière. Depuis des décennies, c’est ici qu’est généré un faisceau de protons remarquable qui, grâce à des améliorations continues, détient même depuis 1994 le record du monde du faisceau le plus performant.
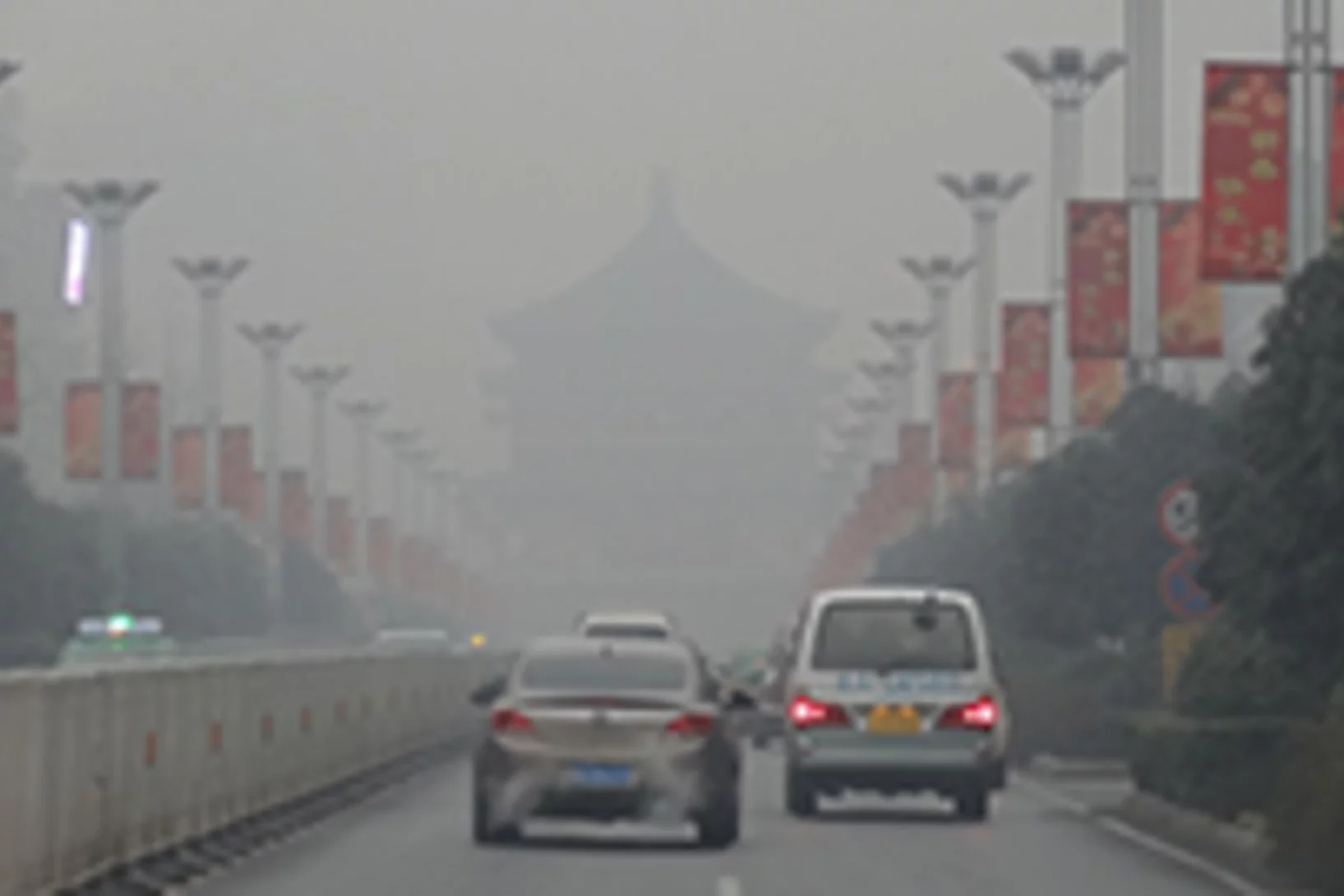
Les raisons de l'airpocalypse
Les origines de la pollution atmosphérique record qu’a connue la Chine à l’hiver 2013.Au début de l’année 2013, une cloche de brume gris-brun a recouvert durant plusieurs mois d’importantes portions du territoire chinois. La pollution due aux particules fines y était plusieurs fois plus importantes que les valeurs que l’on mesure d’habitude en Europe occidentale et aux Etats-Unis. Une équipe internationale de chercheurs, placée sous la conduite de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) et de l’Académie chinoise des sciences (Xi’an), révèle à présent les origines de cette airpocalypse. L’étude parue dans la revue « Nature » présente également des mesures qui permettraient de prévenir à l’avenir une nouvelle crise écologique de ce genre.
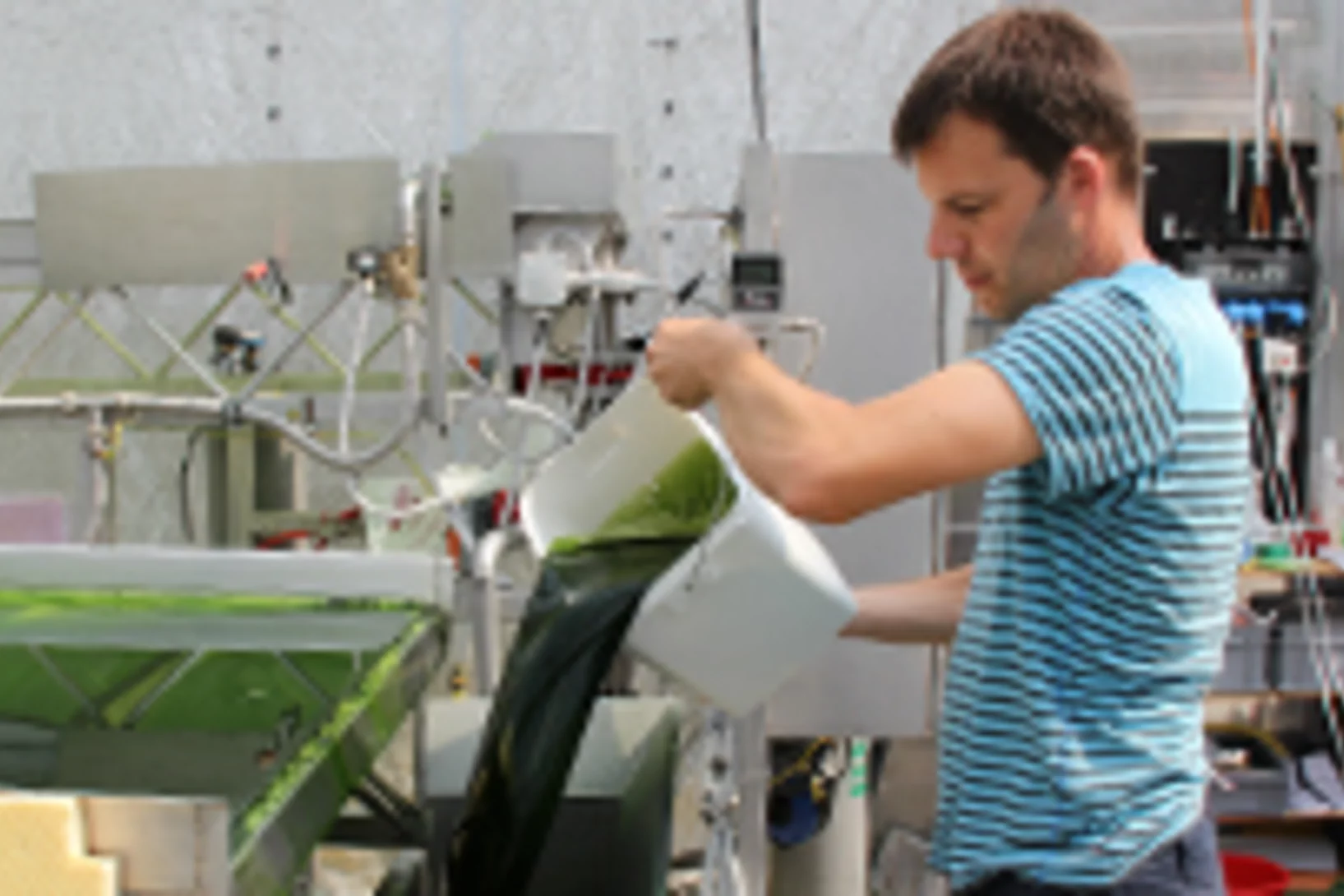
Energiewende in Reinkultur – in Wädenswil zu bestaunen
Der am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI entwickelte Prozess der hydrothermalen Methanierung von wässriger Biomasse erreicht einen wichtigen Meilenstein: Dank der Zusammenarbeit im neuen Kompetenzzentrum des Bundes für Bioenergie BIOSWEET konnten Forschende des PSI, der ZHAW, der ETH Lausanne, der Empa und der Hochschule für Technik Rapperswil die technische Machbarkeit der Methanherstellung aus Mikroalgen demonstrieren. Der dazu verwendete Algenbioreaktor sowie die Anlage zur Methanierung der Algen können am 24. September auf dem Campus Grüental der ZHAW in Wädenswil besichtigt werden. Für Medienschaffende gibt es von 14:00 bis 14:30 eine spezielle Führung.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
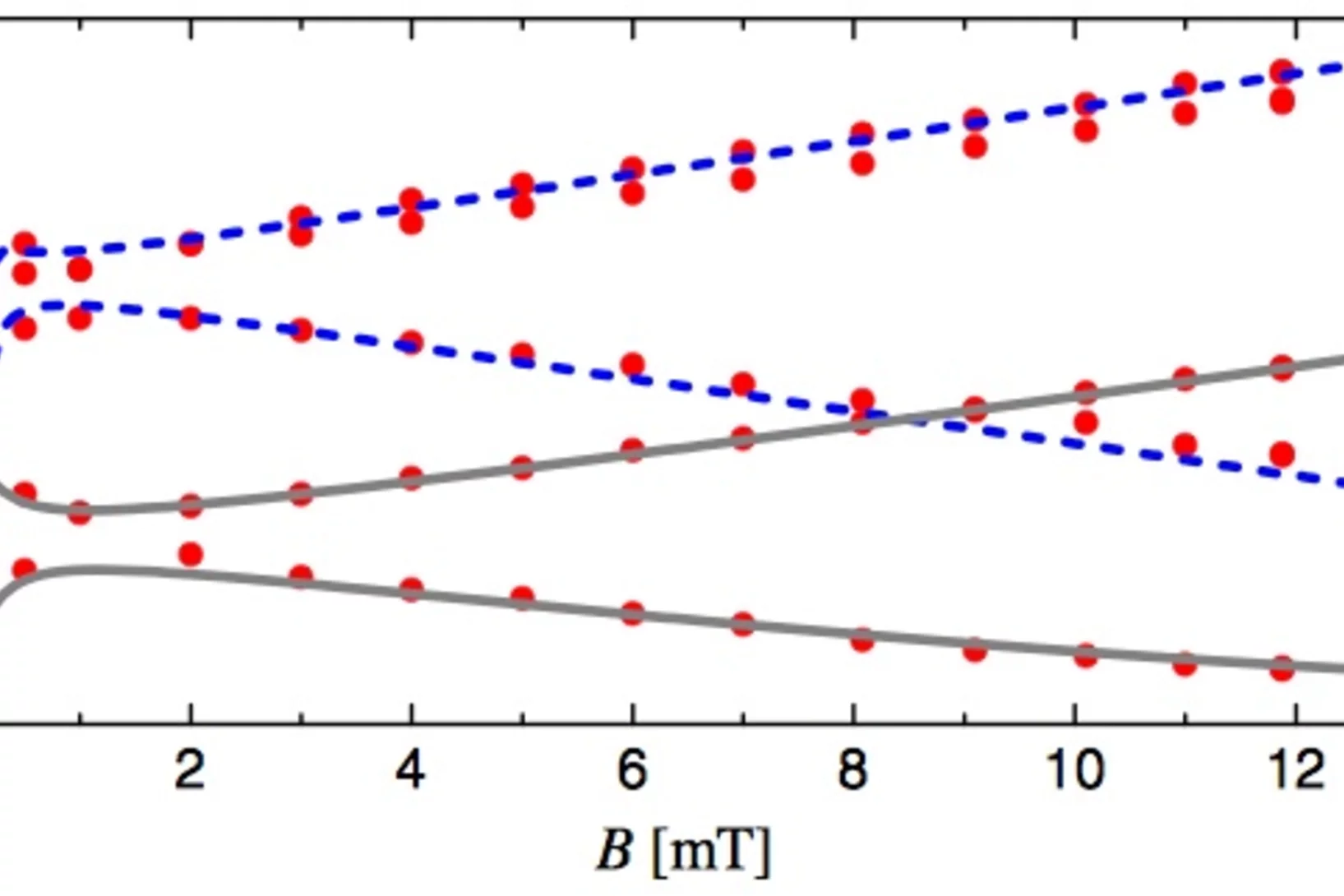
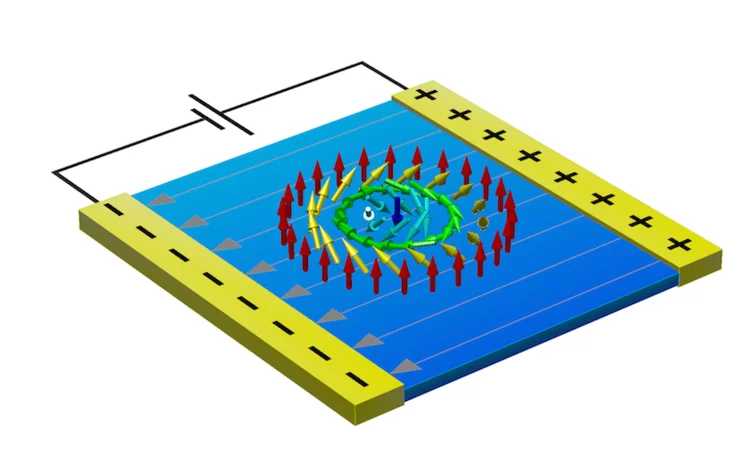
Electric-Field-Induced Skyrmion Distortion and Giant Lattice Rotation in the Magnetoelectric Insulator Cu2OSeO3
Discovering fundamentally new ways to manipulate magnetic spins is crucial for research into advanced technologies. Magnetic Skyrmions, which are topologically stable whirls of magnetic spins, are promising candidates for new device components since those found in metallic host materials can be manipulated using electric currents.
Mit Licht neues Material erzeugt
Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts haben mithilfe kurzer Lichtblitze aus einem Laser die Eigenschaften eines Materials kurzzeitig so deutlich verändert, dass gewissermassen ein neues Material entstanden ist und die Veränderungen am Röntgenlaser LCLS in Kalifornien untersucht. Nach der Inbetriebnahme des PSI-Röntgenlasers SwissFEL werden solche Experimente auch am PSI möglich sein.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Controlling the near-surface superfluid density in under doped YBa2Cu3O6+x by photo-illumination
The interaction with light weakens the superconducting ground state in classical superconductors. The situation in cuprate superconductors is more complicated: illumination increases the charge carrier density, a photo-induced effect that persists below room temperature. Furthermore, systematic investigations in underdoped YBa2Cu3O6+x (YBCO) have shown an enhanced critical temperature Tc. Until now, studies of photo-persistent conductivity (PPC) have been limited to investigations of structural and transport properties, as well as the onset of superconductivity.
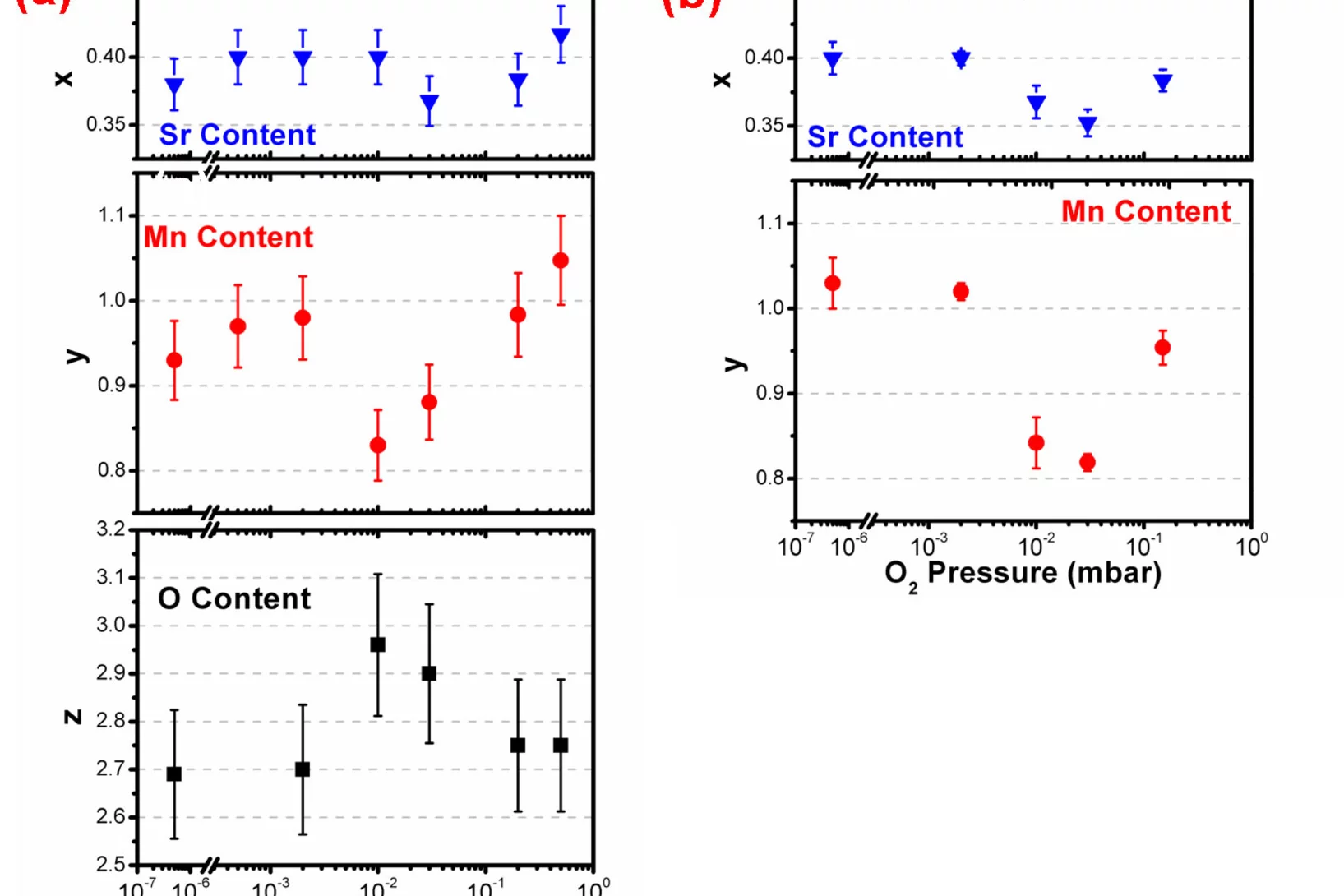
Plasma interactions determine the composition in pulsed laser deposited thin films
Plasma chemistry and scattering strongly affect the congruent, elemental transfer during pulsed laser deposition of target metal species in an oxygen atmosphere. Studying the plasma properties of La0.6Sr0.4MnO3, we demonstrate for as grown La0.6Sr0.4MnO3-δ films that a congruent transfer of metallic species is achieved in two pressure windows: ∼10−3 mbar and ∼2 × 10−1 mbar.
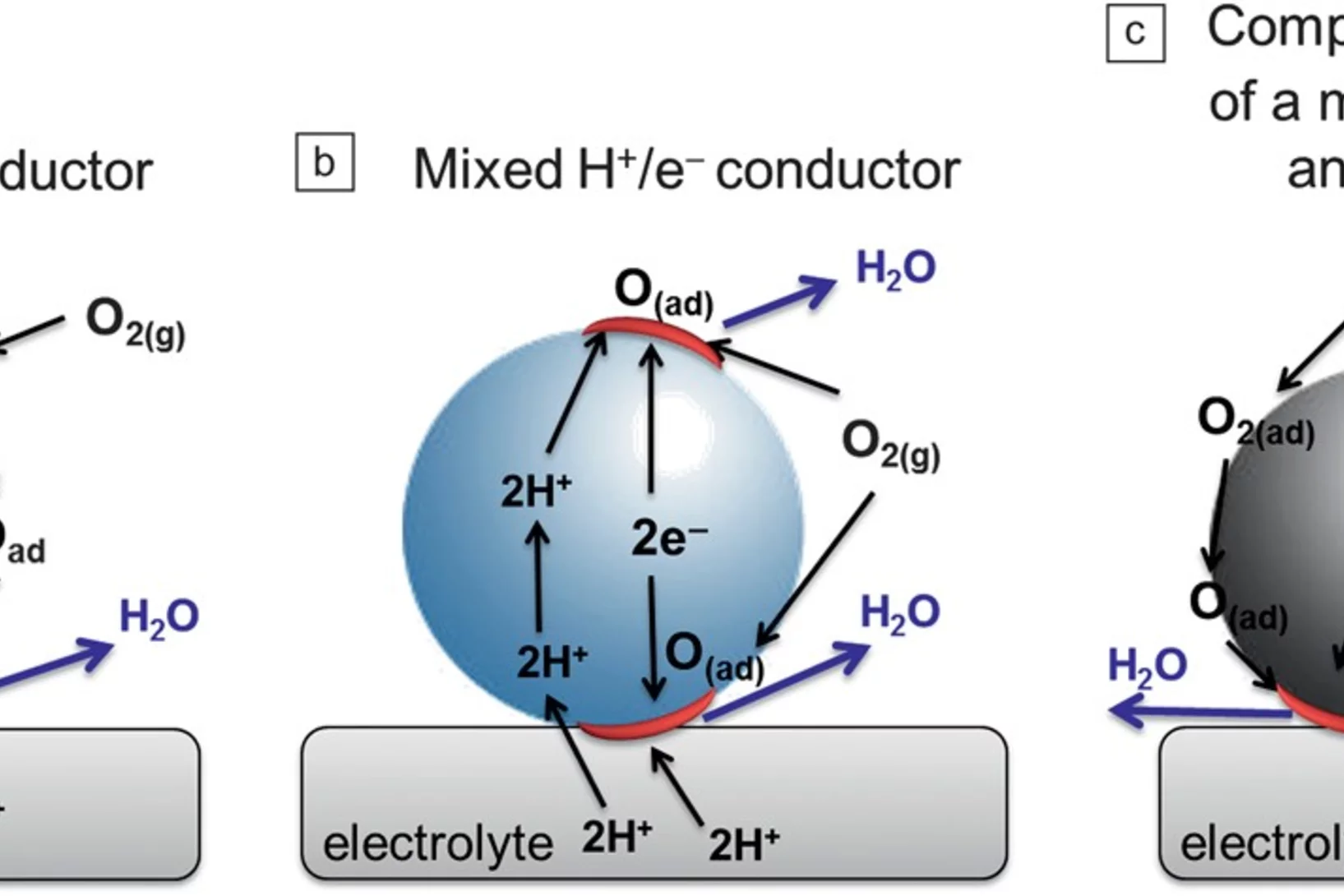
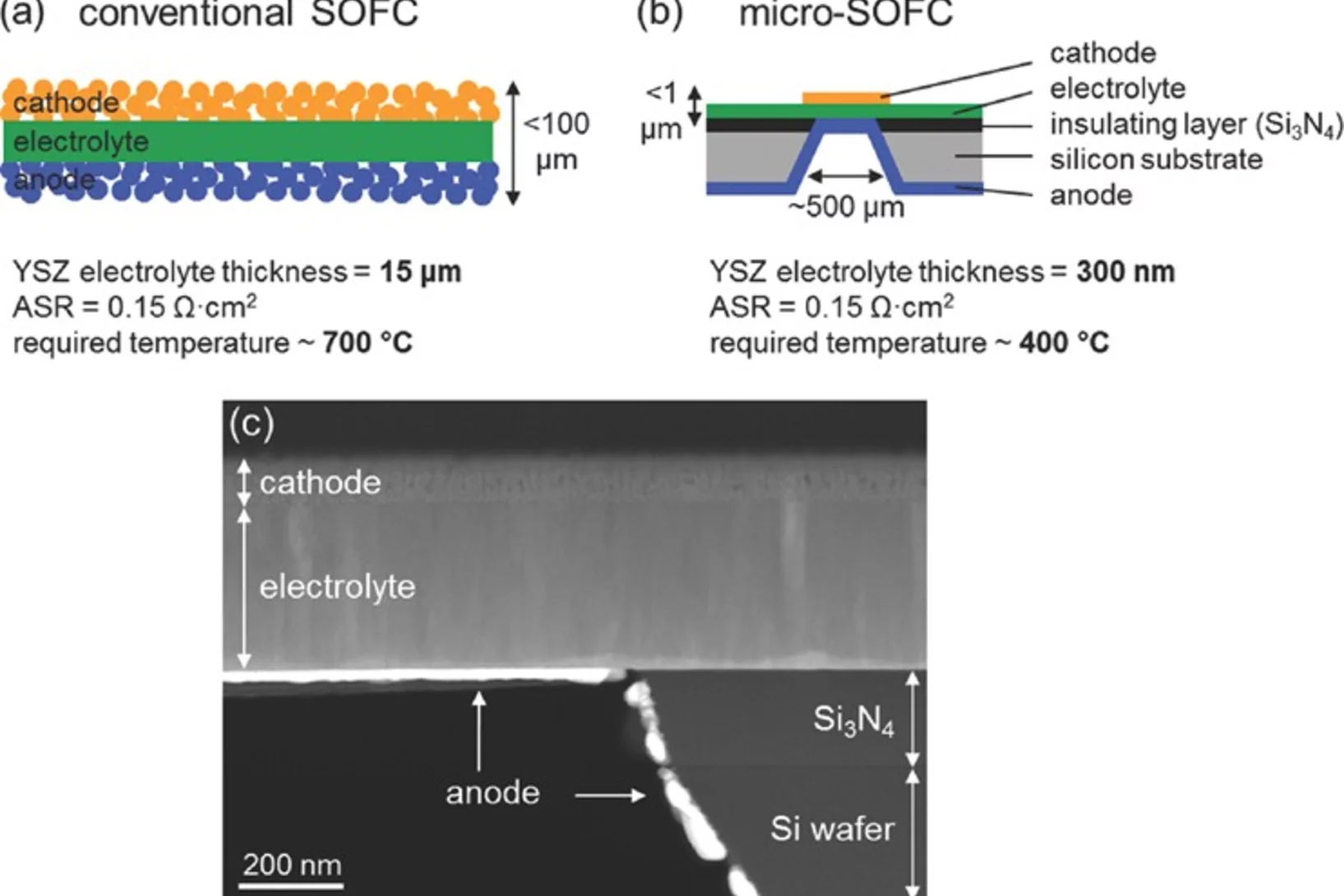
Low-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells based on proton-conducting electrolytes
The need for reducing the operating temperature of solid-oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) imposed by cost reduction has pushed significant progress in fundamental understanding of the individual components, as well as materials innovation and device engineering. Proton-conducting oxides have emerged as potential alternative electrolyte materials to oxygen-ion conducting oxides for operation at low and intermediate temperatures.
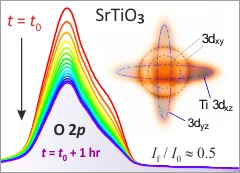
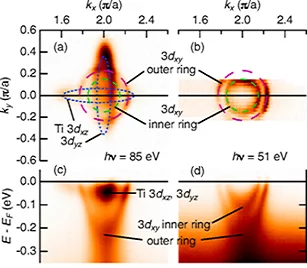
Mixed Dimensionality of Confined Conducting Electrons in the Surface Region of SrTiO3
Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, we show that the recently discovered surface state on SrTiO3 consists of nondegenerate t2g states with different dimensional characters.
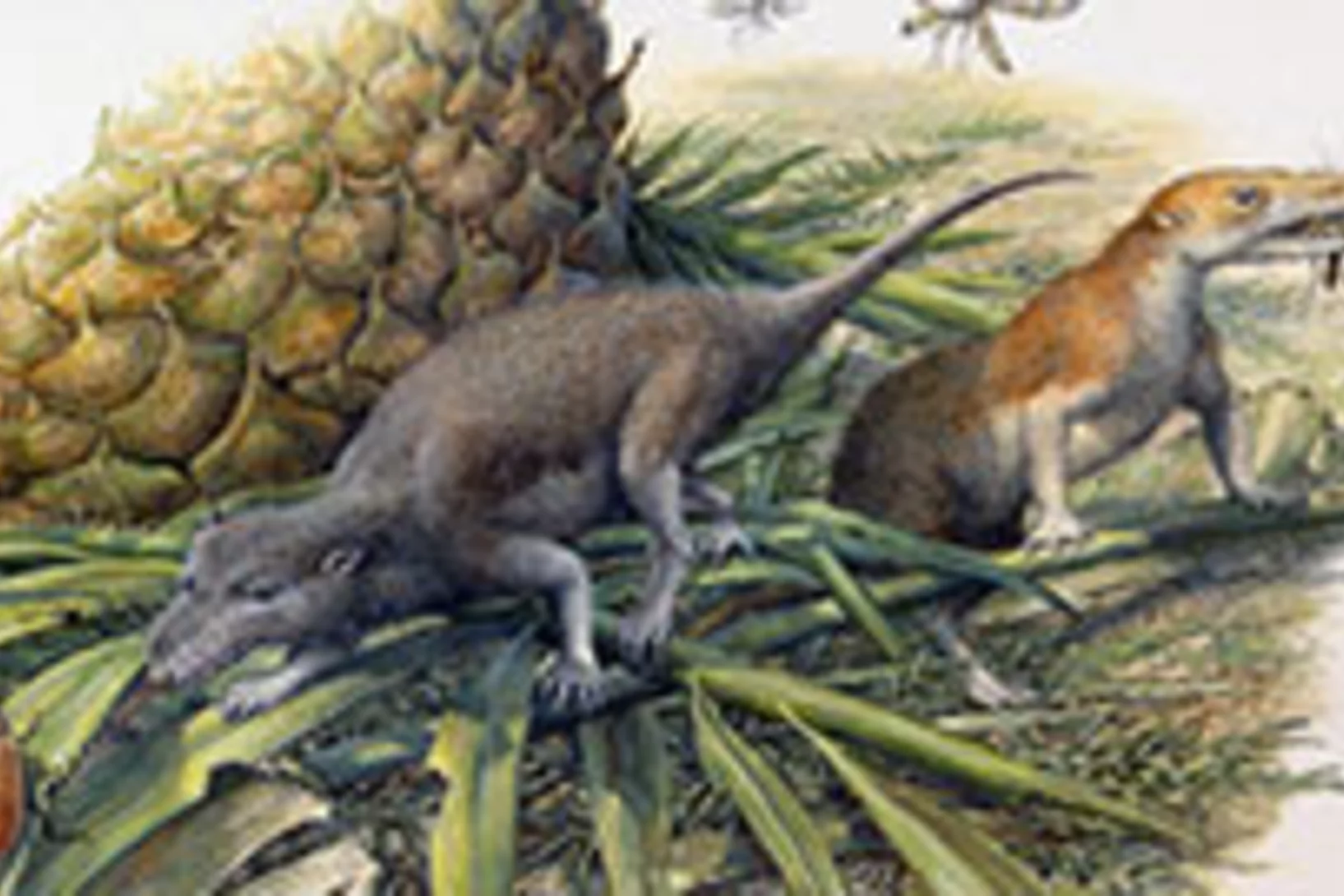
Côté menu, les premiers mammifères avaient déjà leurs préférences
De toutes nouvelles analyses de petits mammifères fossiles livrent de nouveaux éléments sur la connaissance du menu de nos plus lointains ancêtres. Les résultats permettent de comprendre comment sont apparues certaines caractéristiques typiques des mammifères actuels. Ces conclusions reposent sur des analyses, qui ont été réalisées à la Source de Lumière Suisse (SLS) de l’Institut Paul Scherrer, au moyen de la tomographie par rayons X.
A revealing mixture: The surface of an oxide insulator can host two distinct types of conducting electrons
Strontium titanate, SrTiO3, is an important material for the realization of next-generation electronic devices. A famous example is the interface of LaAlO3 grown on SrTiO3, which is metallic and magnetic at its interface, even though the individual compounds are insulating and nonmagnetic in bulk form. The physics behind how novel interface states form on SrTiO3 - and how they become endowed with such surprising properties - is not well understood.
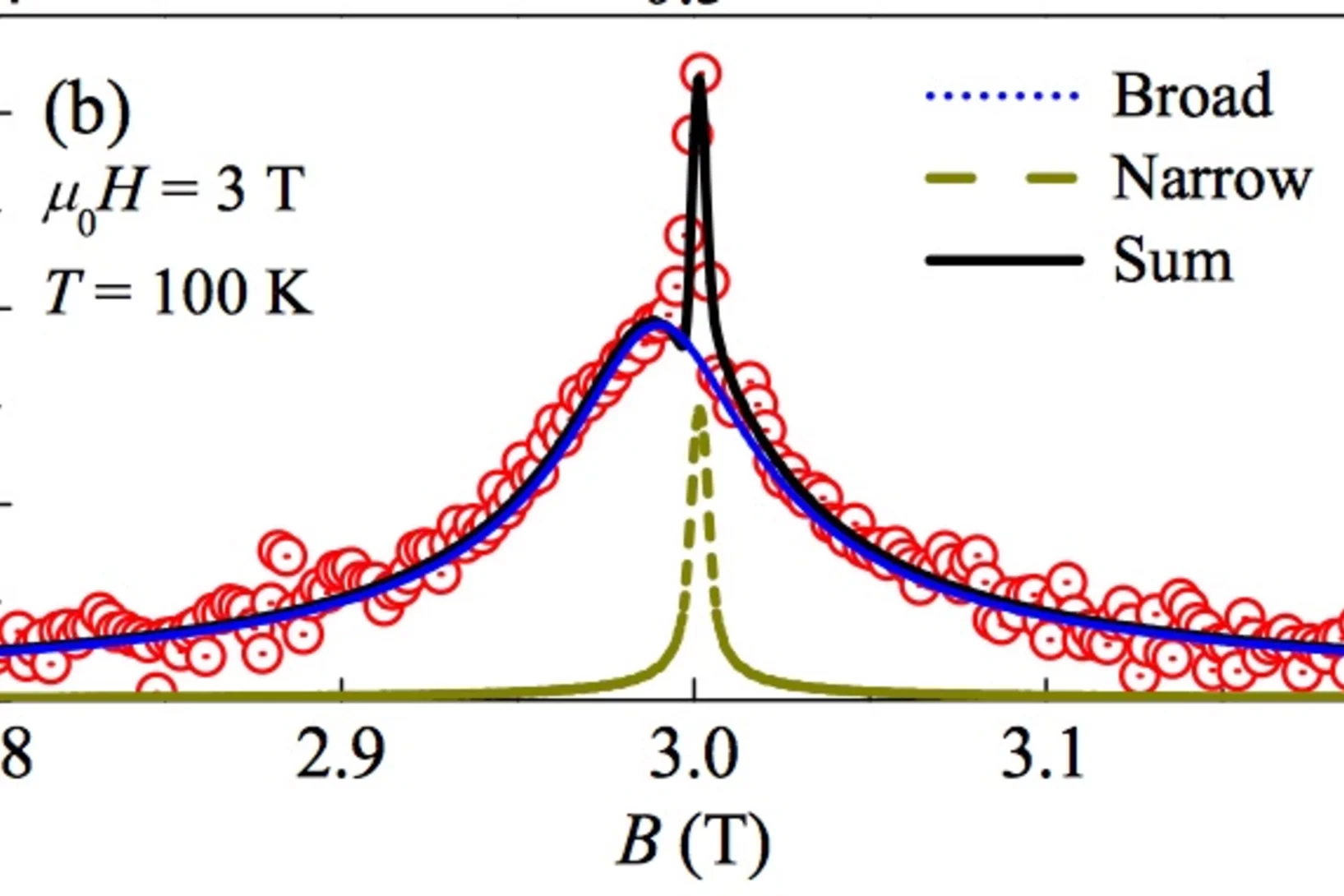
Spin-lattice coupling induced weak dynamical magnetism in EuTiO3 at high temperatures
EuTiO3, which is a G-type antiferromagnet below TN = 5.5 K, has some fascinating properties at high temperatures, suggesting that macroscopically hidden dynamically fluctuating weak magnetism exists at high temperatures. This conjecture is substantiated by magnetic field dependent magnetization measurements, which exhibit pronounced anomalies below 200 K becoming more distinctive with increasing magnetic field strength. Additional results from muon spin rotation experiments provide evidence for weak fluctuating bulk magnetism induced by spin-lattice coupling which is strongly supported in increasing magnetic field.
Low-Temperature Micro-Solid Oxide Fuel Cells with Partially Amorphous La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ Cathodes
Partially amorphous La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ (LSC) thin-film cathodes are fabricated using pulsed laser deposition and are integrated in free-standing micro-solid oxide fuel cells (micro-SOFC) with a 3YSZ electrolyte and a Pt anode. A low degree of crystallinity of the LSC layers is achieved by taking advantage of the miniaturization of the cells, which permits low-temperature operation (300–450 °C).
Attaques d’oléoducs et épidémies : des points communs
A quel point l’infrastructure énergétique globale est-elle vulnérable aux attaques d’acteurs non gouvernementaux ? Le nombre d’attentats a-t-il vraiment augmenté récemment ? Quelles sont les régions du monde particulièrement vulnérables ? Et quelles sont les tactiques utilisées par les assaillants ? Autant de questions auxquelles les scientifiques entendent trouver des réponses, à l’aide d’une base de données développée par les chercheurs de l’ETH Zurich en collaboration avec l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI).
Correlated Decay of Triplet Excitations in the Shastry-Sutherland Compound SrCu2(BO3)2
The temperature dependence of the gapped triplet excitations (triplons) in the 2D Shastry-Sutherland quantum magnet SrCu2(BO3)2 is studied by means of inelastic neutron scattering. The excitation amplitude rapidly decreases as a function of temperature, while the integrated spectral weight can be explained by an isolated dimer model up to 10 K.
Fast scanning coherent X-ray imaging using Eiger
The smaller pixel size, high frame rate, and high dynamic range of next-generation photon counting pixel detectors expedites measurements based on coherent diffractive imaging (CDI). The latter comprises methods that exploit the coherence of X-ray synchrotron sources to replace imaging optics by reconstruction algorithms. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institut have recently demonstrated fast CDI image acquisition above 25,000 resolution elements per second using an in-house developed Eiger detector. This rate is state of the art for diffractive imaging and even on a par with the fastest scanning X-ray transmission instruments. High image throughput is of crucial importance for both materials and biological sciences for studies with representative population sampling.
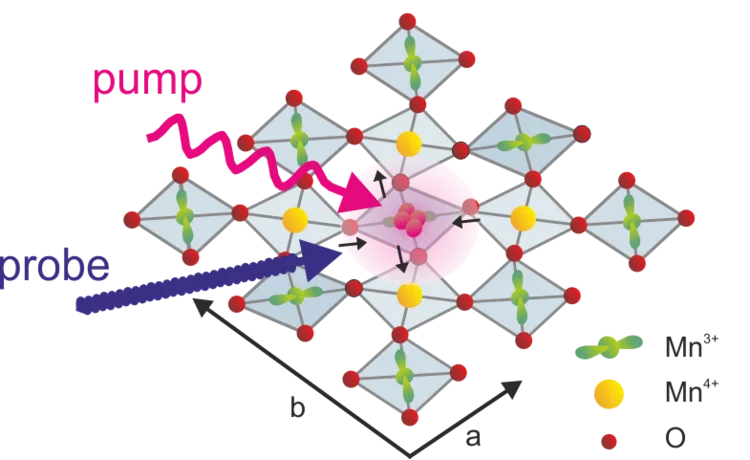
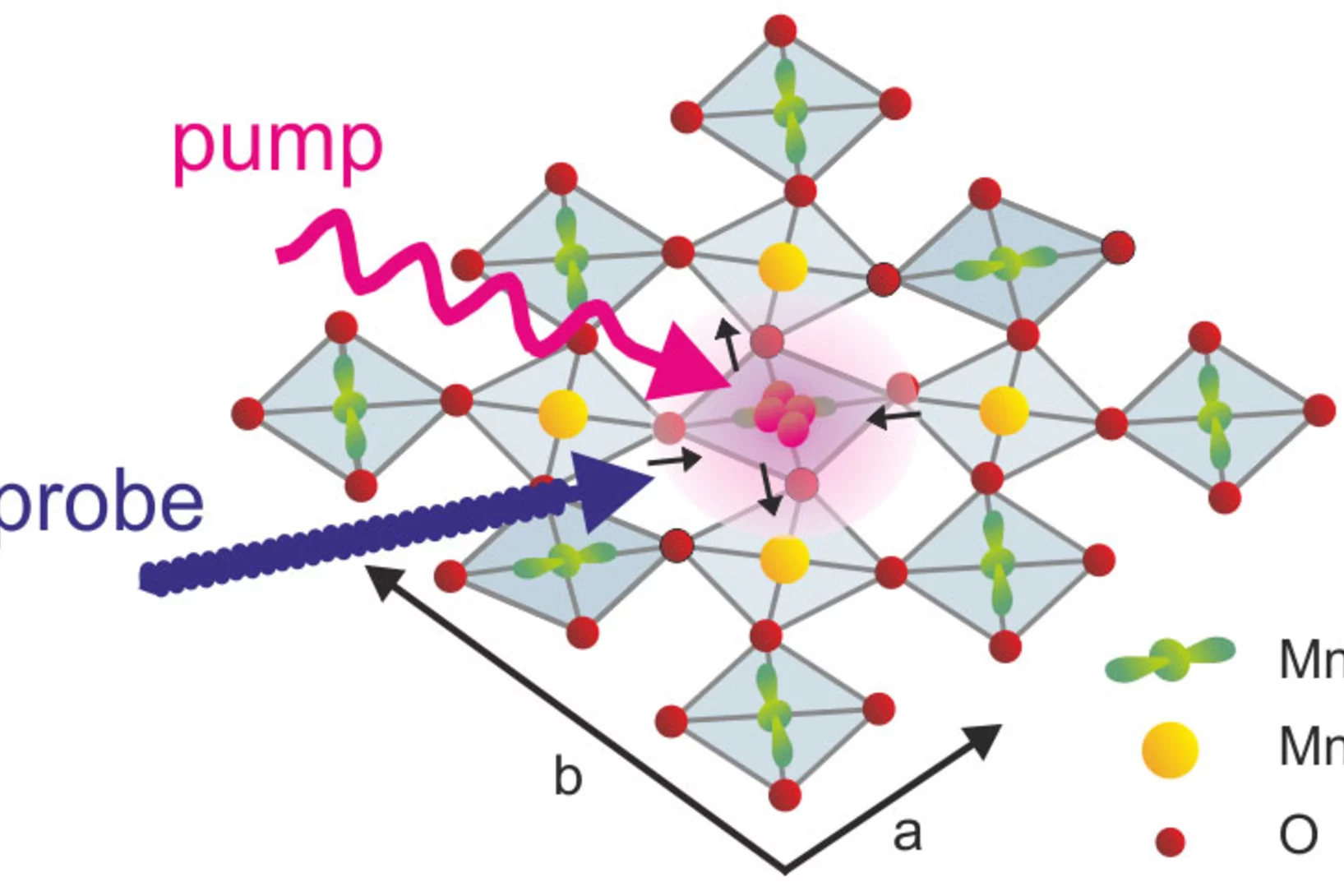
Square dance of the atoms: Shedding light on ultrafast phase transitions
The exploration of the interaction of structural and electronic degrees of freedom in strongly correlated electron systems on the femtosecond time scale is an emerging area of research. One goal of these studies is to advance our understanding of the underlying correlations, another to find ways to control the exciting properties of these materials on an ultrafast time scale.
Square dance of the atoms: Shedding light on ultrafast phase transitions
The exploration of the interaction of structural and electronic degrees of freedom in strongly correlated electron systems on the femtosecond time scale is an emerging area of research. One goal of these studies is to advance our understanding of the underlying correlations, another to find ways to control the exciting properties of these materials on an ultrafast time scale. So far a general model is lacking that provides a quantitiative description of the correlations between the structural and electronic degrees of freedom.
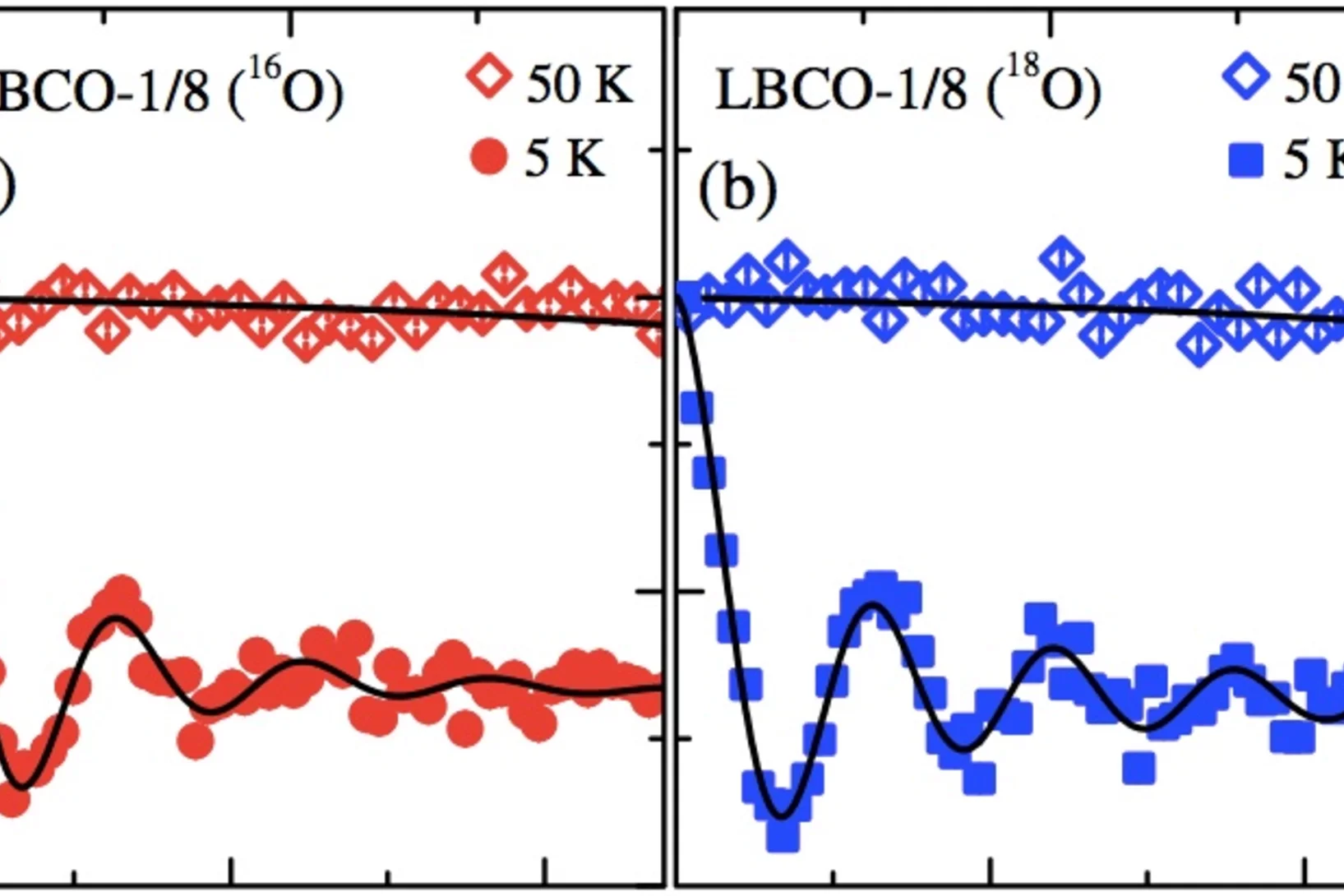
Negative Oxygen Isotope Effect on the Static Spin Stripe Order in Superconducting La2−xBaxCuO4(x=1/8) Observed by Muon-Spin Rot
Large negative oxygen-isotope (16O and 18O) effects (OIEs) on the static spin-stripe-ordering temperature Tso and the magnetic volume fraction Vm were observed in La2−xBaxCuO4(x=1/8) by means of muon-spin-rotation experiments. The corresponding OIE exponents were found to be αTso=-0.57(6) and αVm=-0.71(9), which are sign reversed to αTC=0.46(6) measured for the superconducting transition temperature Tc. This indicates that the electron-lattice interaction is involved in the stripe formation and plays an important role in the competition between bulk superconductivity and static stripe order in the cuprates.
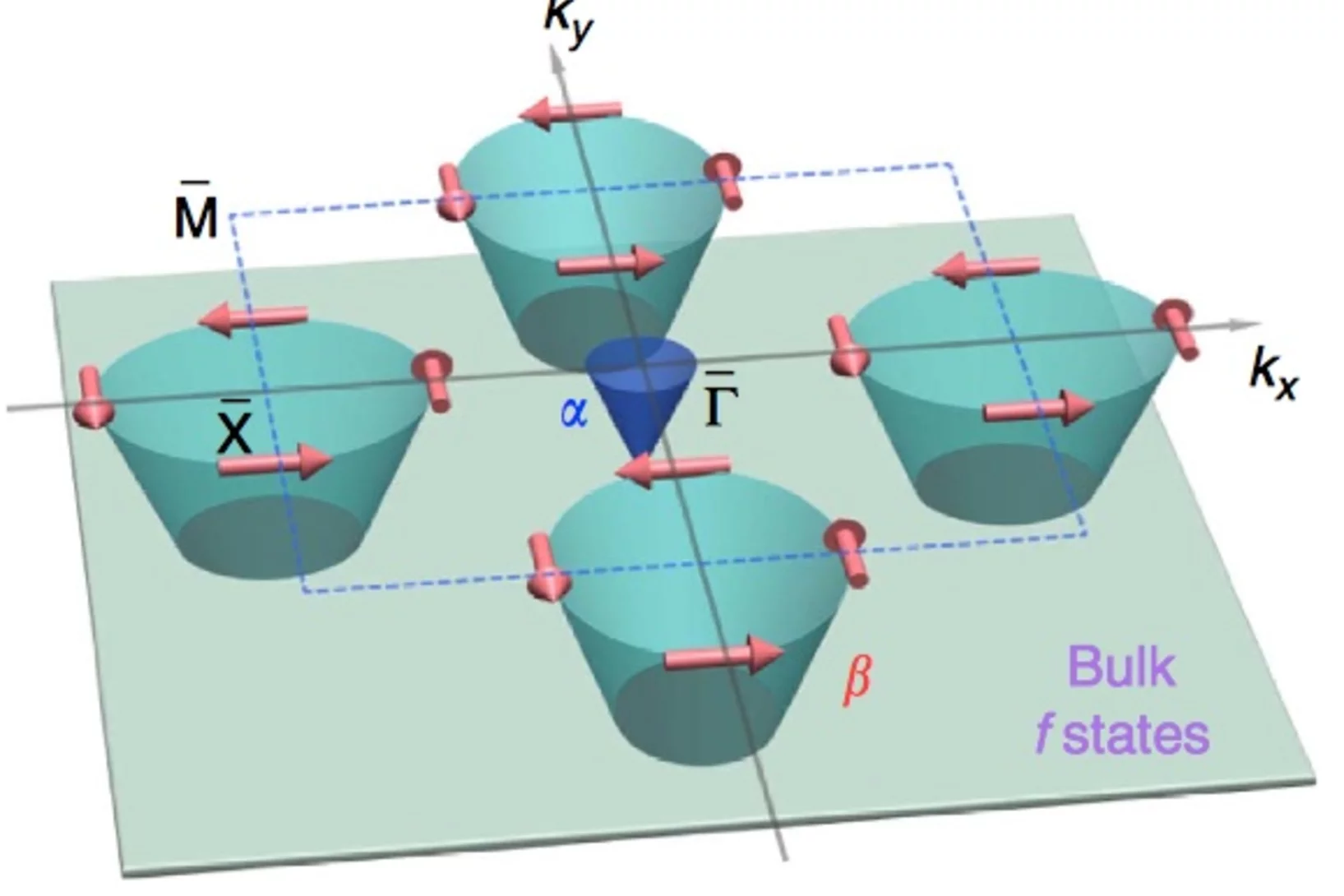
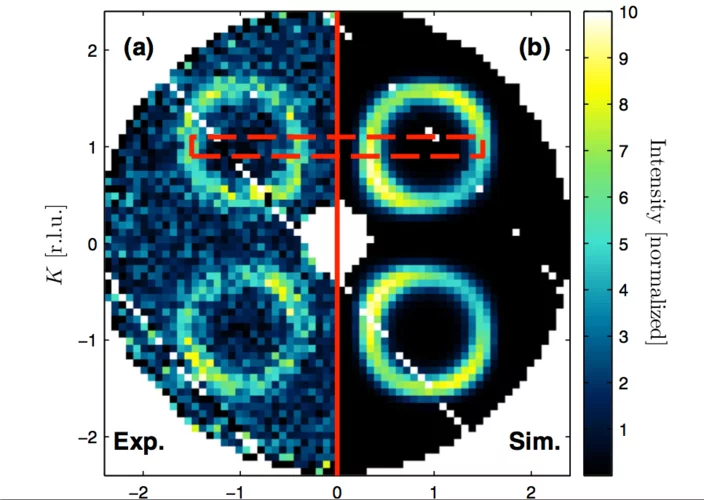
Direct observation of the spin texture in SmB6 as evidence of the topological Kondo insulator
Topological Kondo insulators have been proposed as a new class of topological insulators in which non-trivial surface states reside in the bulk Kondo band gap at low temperature due to strong spin–orbit coupling. In contrast to other three-dimensional topological insulators, a topological Kondo insulator is truly bulk insulating. Furthermore, strong electron correlations are present in the system, which may interact with the novel topological phase. By applying spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, here we show that the surface states of SmB6 are spin polarized. The spin is locked to the crystal momentum, fulfilling time reversal and crystal symmetries.
Geordneter Elektronenfluss im Isolator
Forschende des PSI, der EPFL und der Chinesischen Akademie der Wissenschaften haben gezeigt, dass das Material SmB6 alle Eigenschaften eines topologischen Isolators zeigt, also eines Materials, an dessen Oberfläche polarisierte Ströme fliessen können. Das Besondere an diesem Material ist, dass die Eigenschaft sehr robust ist à an der Materialoberfläche fliessen nur polarisierte Ströme und die Eigenschaft bleibt auch bei kleinen Unregelmässigkeiten in der Struktur oder Zusammensetzung des Materials erhalten. Polarisierte Ströme sind für die Spintronik à Elektronik, die den Elektronenspin nutzt à wichtig.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Small-angle neutron scattering study of the mixed state of Yb3Rh4Sn13
Using the small angle neutron scattering (SANS) technique we investigated the vortex lattice (VL) in the mixed state of the stannide superconductor Yb3Rh4Sn13. We find a single domain VL of slightly distorted hexagonal geometry for field strengths between 350 and 18 500 G and temperatures between T=0.05 and 6.5 K. We observe a clear in-plane rotation of the VL for different magnetic field directions relative to the crystallographic axes.
Spin-Wave Spectrum of the Quantum Ferromagnet on the Pyrochlore Lattice Lu2V2O7
Neutron inelastic scattering has been used to probe the spin dynamics of the quantum (S=1/2) ferromagnet on the pyrochlore lattice Lu2V2O7. Well-defined spin waves are observed at all energies and wave vectors, allowing us to determine the parameters of the Hamiltonian of the system.
L’hydrogène: un cheval de Troie dans la gaine du crayon combustible
Dans un réacteur nucléaire, l’eau se sépare en oxygène et en hydrogène au contact de la gaine contenant les pastilles de combustible, alors à haute température. Cet hydrogène peut pénétrer dans la gaine qui enrobe le combustible proprement dit, et la fragiliser mécaniquement. A l’aide de neutrons et de rayonnement synchrotron, des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) étudient le mécanisme de pénétration de l’hydrogène dans la gaine et l’effet qu’il peut y déployer.