SLS
Puzzling new behaviour observed in high-temperature superconductors
New effect might be important for emergence of High-Temperature SuperconductivityAn international team of researchers has observed a new, unexpected kind of behaviour in copper-based high-temperature superconductors. Explaining the new phenomenon à an unexpected form of collective movement of the electrical charges in the material à poses a major challenge for the researchers. A success in explaining the phenomenon might be an important step toward understanding high-temperature superconductivity in general. The crucial experiments were conducted at the Paul Scherrer Institute.
Useful for spintronics: Big surprises in a thin surface region
The need for ever faster and more efficient electronic devices is growing rapidly, and thus the demand for new materials with new properties. Oxides, especially ones based on strontium titanate (SrTiO3), play an important role here. A collaborative project headed by scientists from the PSI has now revealed properties of strontium titanate that make it an important base material for applications in spintronics.
New material generated with light
PSI researchers garner experience for SwissFEL experimentsAided by short laser flashes, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have managed to temporarily change a material’s properties to such a degree that they have à to a certain extent àcreated a new material. This was done using the x-ray laser LCLS in California. Once the PSI x-ray laser SwissFEL is up and running, experiments of this kind will also be possible at PSI.
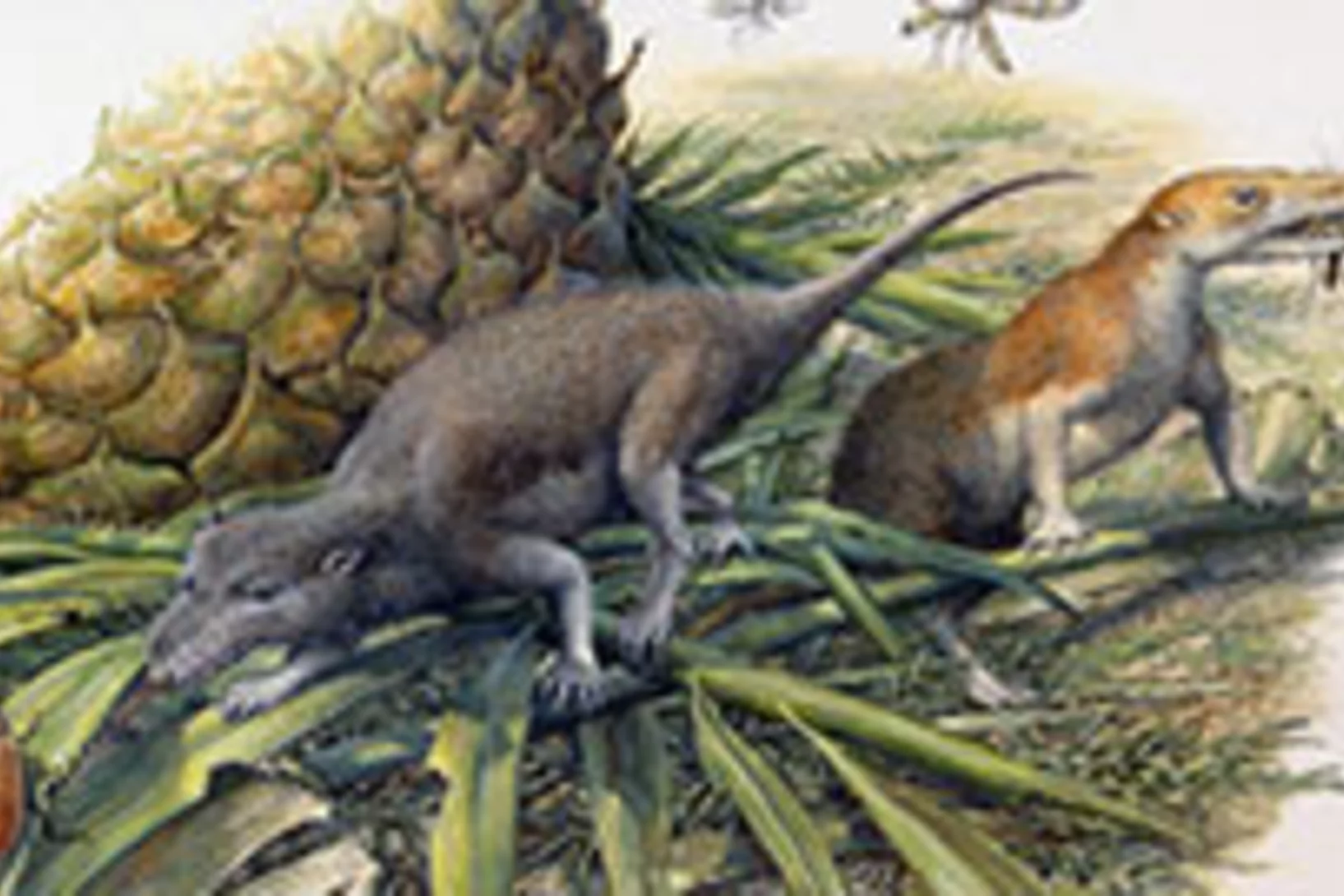
Jurassic Welsh mammals were picky eaters, study finds
New analyses of tiny fossil mammals from South Wales are shedding light on the function and diets of our earliest ancestors, a team led by researchers from the Universities of Bristol and Leicester report in the journal Nature. The team used CT scanning with synchrotron X-rays at PSI’s Swiss Light Source to reveal in unprecedented detail the internal anatomy of the mammals’ tiny jaws.
Insulator makes electrons move in an ordered way
Researchers at the PSI, the EPFL and the Chinese Academy of Science, have proven that the material SmB6 shows all the properties of a so called topological insulator à a material with electric currents flowing along its surface with all of them being polarized. Here, the property is very robust, i.e. the only current that can flow is spin polarized and is not easily destroyed by small irregularities in the structure or composition of the material. Spin polarized currents are necessary for spintronics, electronics using the electrons’ spin.
Sixteen nanometres in 3D
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI) have devised a method that opens up new scales of tomographic imaging and will thus allow in the future highly resolved measurements of biological and materials science specimens. With the aid of a special prototype instrument at the Swiss Light Source (SLS), they achieved a 3D resolution of sixteen nanometres in a large sample and thus set a new world record in X-ray tomography.
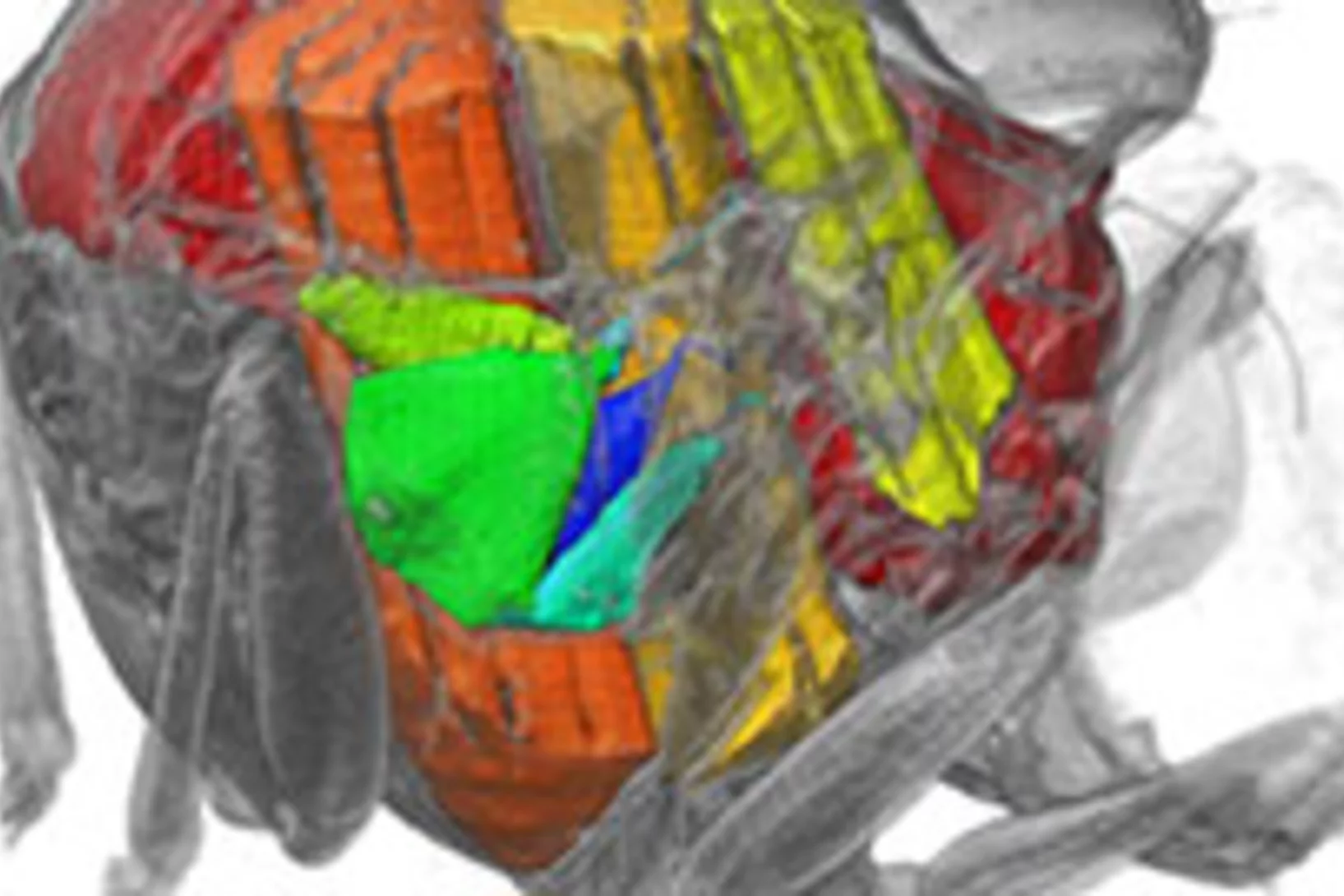
X-rays film inside live flying insects – in 3D
Scientists have used a particle accelerator to obtain high-speed 3D X-ray visualizations of the flight muscles of flies. The team from Oxford University, Imperial College, and the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) developed a groundbreaking new CT scanning technique at the PSI’s Swiss Light Source to allow them to film inside live flying insects. The movies offer a glimpse into the inner workings of one of nature’s most complex mechanisms, showing that structural deformations are the key to understanding how a fly controls its wingbeat.
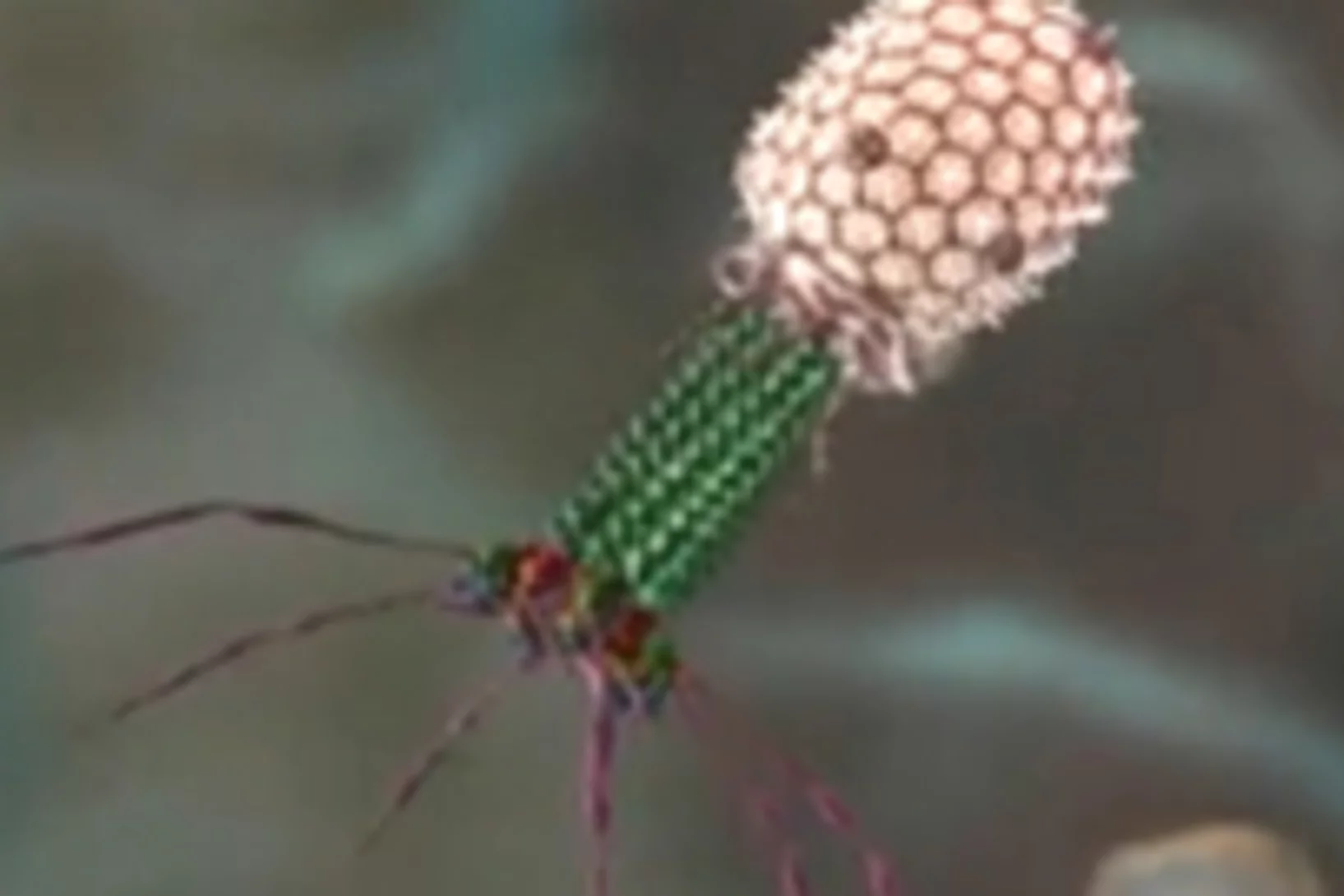
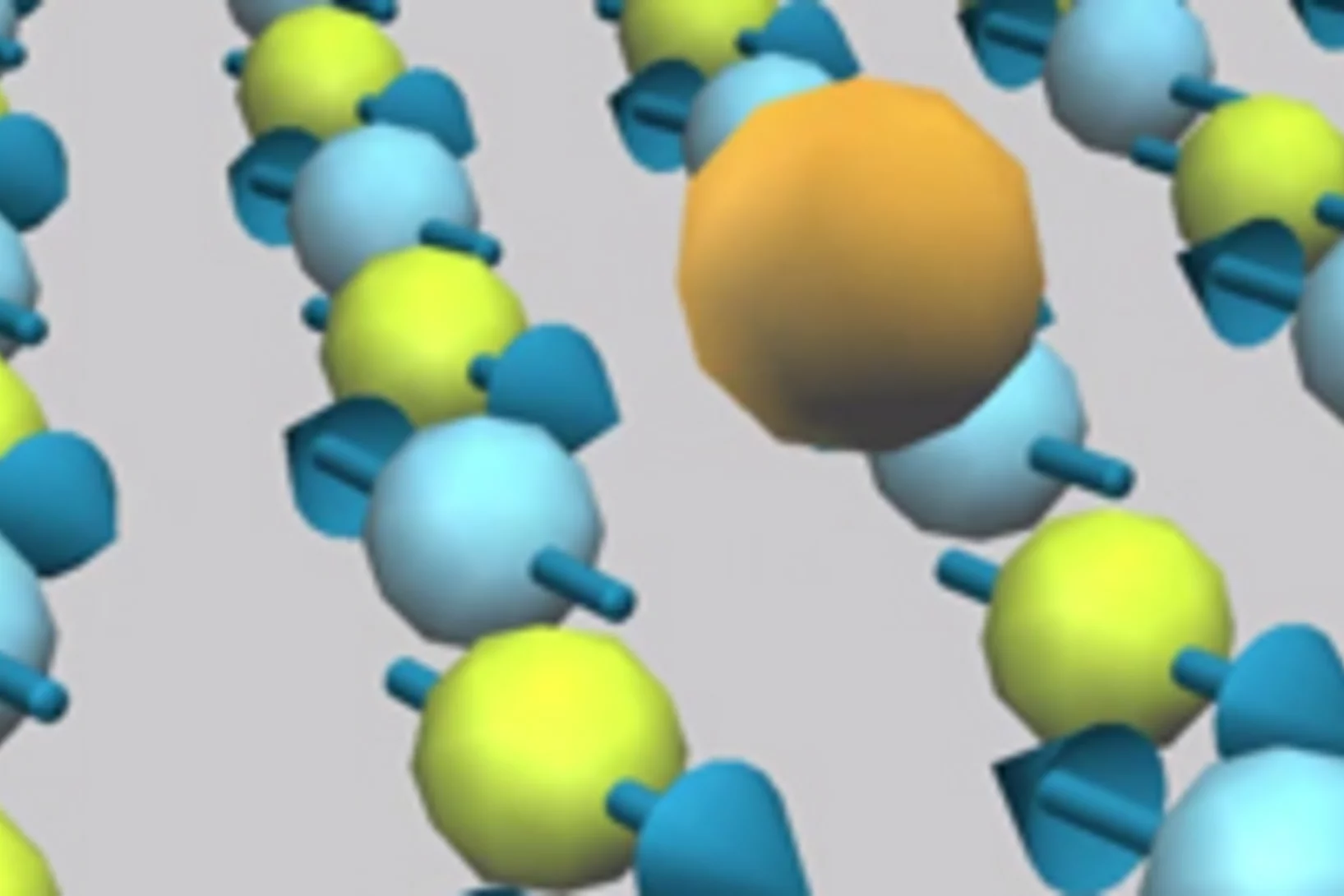
An infection tool with a metallic core
Thanks to the analysis of protein samples at the PSI, Lausanne researchers have managed to demonstrate which instrument bacteria use to transmit diseasesResearchers from ETH Lausanne EPFL have described how a particular strain of bacteria transmits diseases with unprecedented precision. The team of scientists headed by Petr Leiman, an assistant professor at the EPFL’s Laboratory of Structural Biology and Biophysics, demonstrated that the tip of a bacterial infection tool consists of a PAAR protein, which envelops a metal atom and tapers off to a sharp point. The findings are based on measurements carried out at the Swiss Light Source (SLS), one of the three large research facilities at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI).
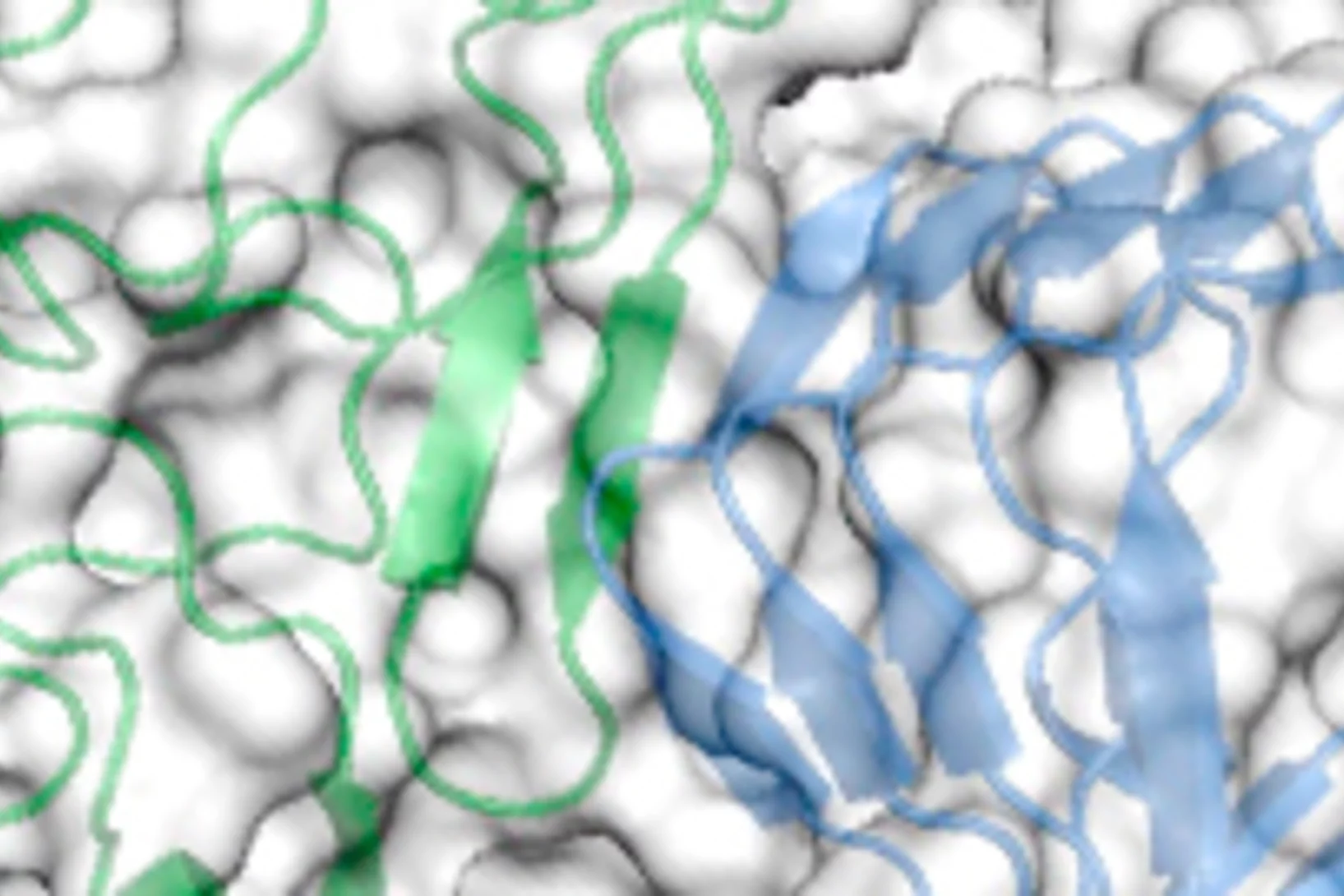
How botox binds to neurons
Botox is a highly dangerous toxin that causes paralysis. In cosmetic applications it is used to temporarily eliminate wrinkles and in medicine as a treatment for migraine or to correct strabismus. An international research team has now established how the toxin molecule binds to the neuron whose activity is then blocked by the poison. The findings may be useful for the development of improved drugs with a lower risk of overdosage.
Electrons with a "split personality"
Above the transition temperature, some electrons in the superconducting material La1.77Sr0.23CuO4 behave as if they were in a conventional metal, others as in an unconventional one à depending on the direction of their motion. This is the result of experiments performed at the SLS. The discovery of this anisotropy makes an important contribution towards understanding high-temperature superconductors. The effect will also have to be taken into account in future experiments and theories of high-temperature superconductors.