A l’Institut Paul Scherrer, les scientifiques cherchent des réponses à la question essentielle des structures élémentaires de la matière et des principes fondamentaux de fonctionnement dans la nature. Ils étudient la structure et les propriétés des particules élémentaires – les plus petits composants de la matière – ou se penchent sur la question de savoir comment les molécules biologiques sont structurées et remplissent leur fonction. Les connaissances qu’ils acquièrent de la sorte ouvrent de nouvelles pistes de solution en sciences, en médecine ou dans le domaine des technologies.
Pour en savoir plus, reportez-vous à Aperçu Fondements de la nature
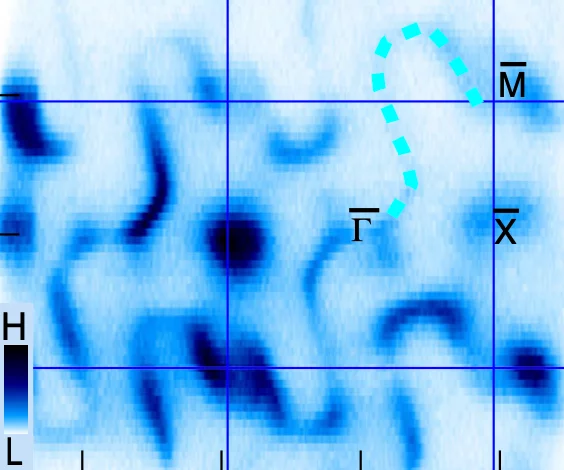
Visualizing Higher-Fold Topology in Chiral Crystals
Novel topological phases of matter are fruitful platforms for the discovery of unconventional electromagnetic phenomena. Higher-fold topology is one example, where the low-energy description goes beyond standard model analogs. Despite intensive experimental studies, conclusive evidence remains elusive for the multigap topological nature of higher-fold chiral fermions. In this Letter, we leverage a combination of fine-tuned chemical engineering and photoemission spectroscopy with photon energy contrast to discover the higher-fold topology of a chiral crystal.
Spectroscopy vs. Electrochemistry: Catalyst Layer Thickness Effects on Operando/In Situ Measurements
Operando/in situ spectro-electrochemical studies often require high loadings and thick catalyst layers (CLs) leading to large ion- and mass-transport limitations. In this study we investigate PdH-formation in two Pd-catalysts with similar surface areas but drastically different morphologies. Our results unveil that the CL-thickness largely determines the PdH formation trends calling for the minimization of the CL-thickness in such experiments.
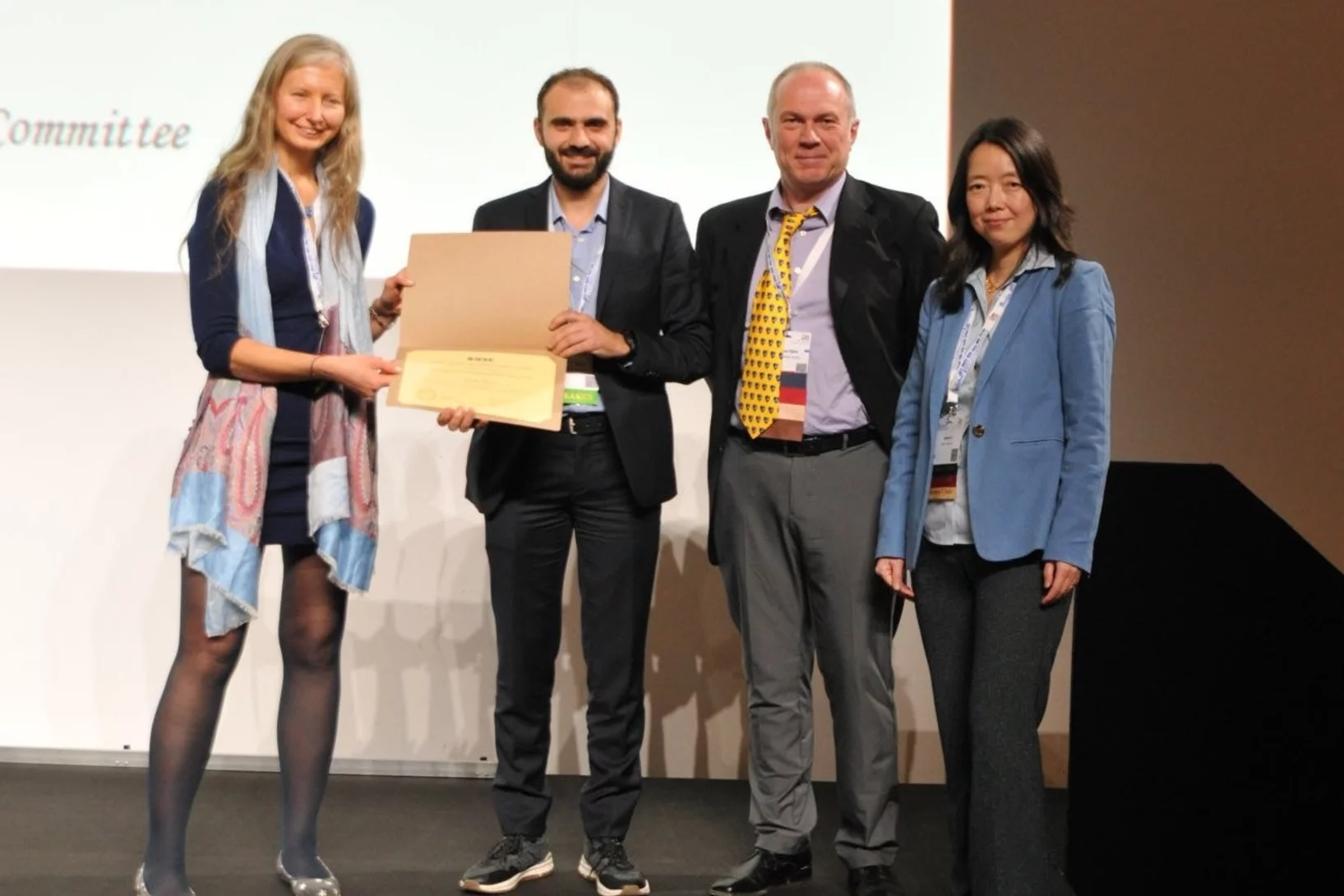
IEEE Early Career Award 2022
For contributions to the development of detectors for XFELs and specifically for their verification, characterization, and calibration
Commissioning of the novel Continuous Angle Multi-energy Analysis spectrometer at the Paul Scherrer Institut
We report on the commissioning results of the cold neutron multiplexing secondary spectrometer CAMEA (Continuous Angle Multi-Energy Analysis) at the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source at the Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland. CAMEA is optimized for ...
Welcome Vlad
Vladislav Zobnin is a new Phd student, who has recently joined the group of Isotope and Target Chemistry. He will work on the “PASCAL” project (EU), under the supervision of Dr. Jörg Neuhausen.
PSI Alumni Karrieren: Marco Taddei – vom Postdoc bei ENE zum assoziierten Professor an der Universität Pisa, Italien
Der PSI Career Blog stellt PSI Alumni und ihre Karrierewege vor, um die Vielseitigkeit der PSI-Gemeinschaft zu zeigen, und die nächste Generation zu inspirieren. Heute mit Marco Taddei, der uns von seiner Postdoc-Zeit am PSI und den Weg zum assoziierten Professor an der Universität Pisa in Italien erzählt.
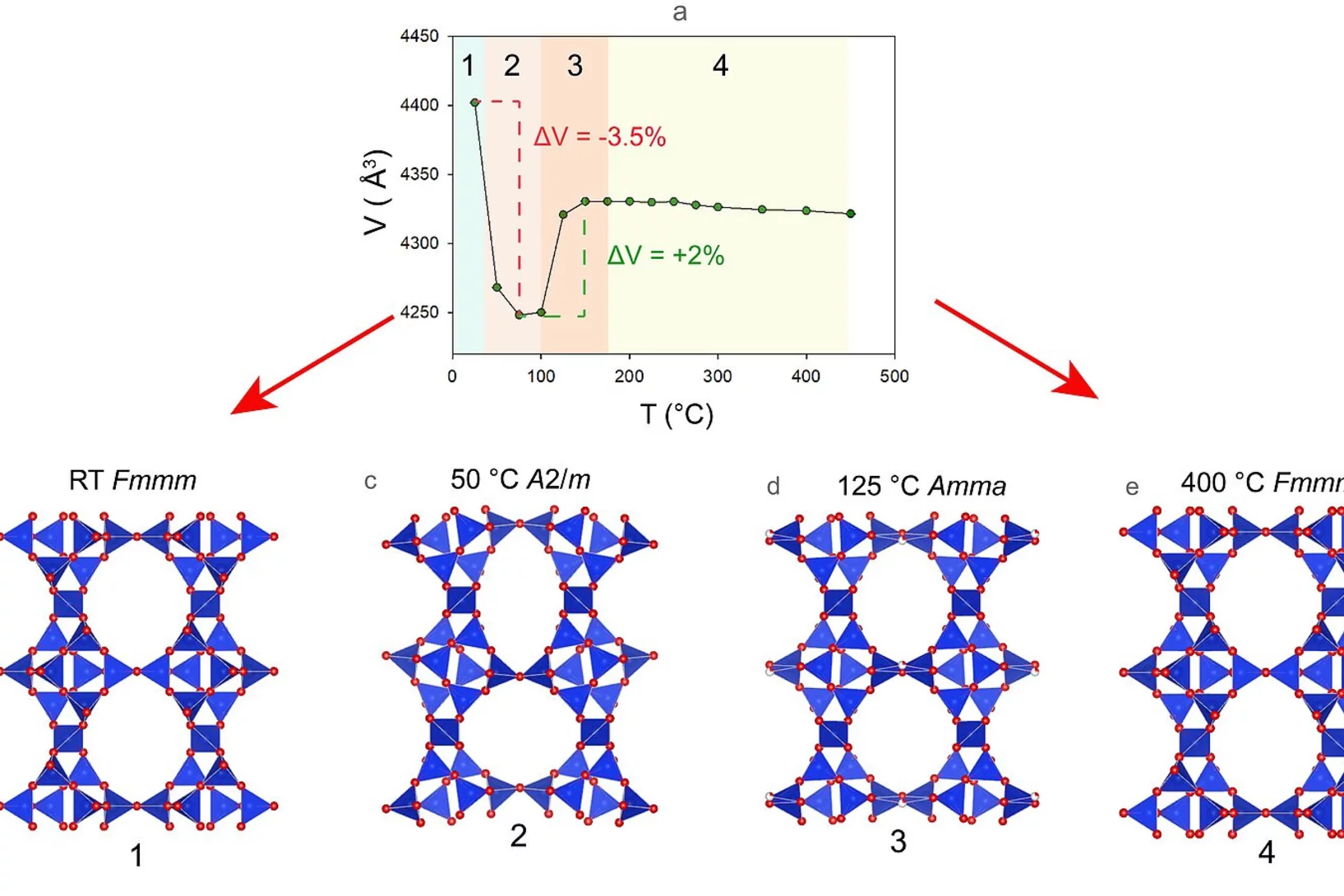
Simulations on "Piz Daint" explain surprising mineral behaviour
Zeolites are a class of shapely, colourful minerals with very special properties, making them omnipresent in our surroundings. They accelerate chemical reactions, absorb hazardous contaminants and water to a high degree, for example. Their only limitation is that they usually lose their peculiar crystalline structure at high temperatures. Now researchers at the University of Bern have found an unexpected exception.
6-wöchiges Praktikum in der Firma Heinz Baumgartner AG
Ich durfte ein spannendes 6-Wöchigespraktikum in der Firma Heinz Baumgartner AG in Tegerfelden machen. Das Praktikum war auf zwei Teile aufgeteilt. In den ersten 4 Wochen durfte ich die Serienfertigung an den CNC Maschinen kennenlernen. In den letzten 2 Wochen durfte ich noch ein wenig bei der Montage mithelfen.
Proposals with Russian participation
Due to the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, PSI cannot accept proposals for beam time and visits from scientists affiliated to organisations based in Russia or Belarus until further notice.
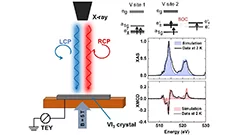
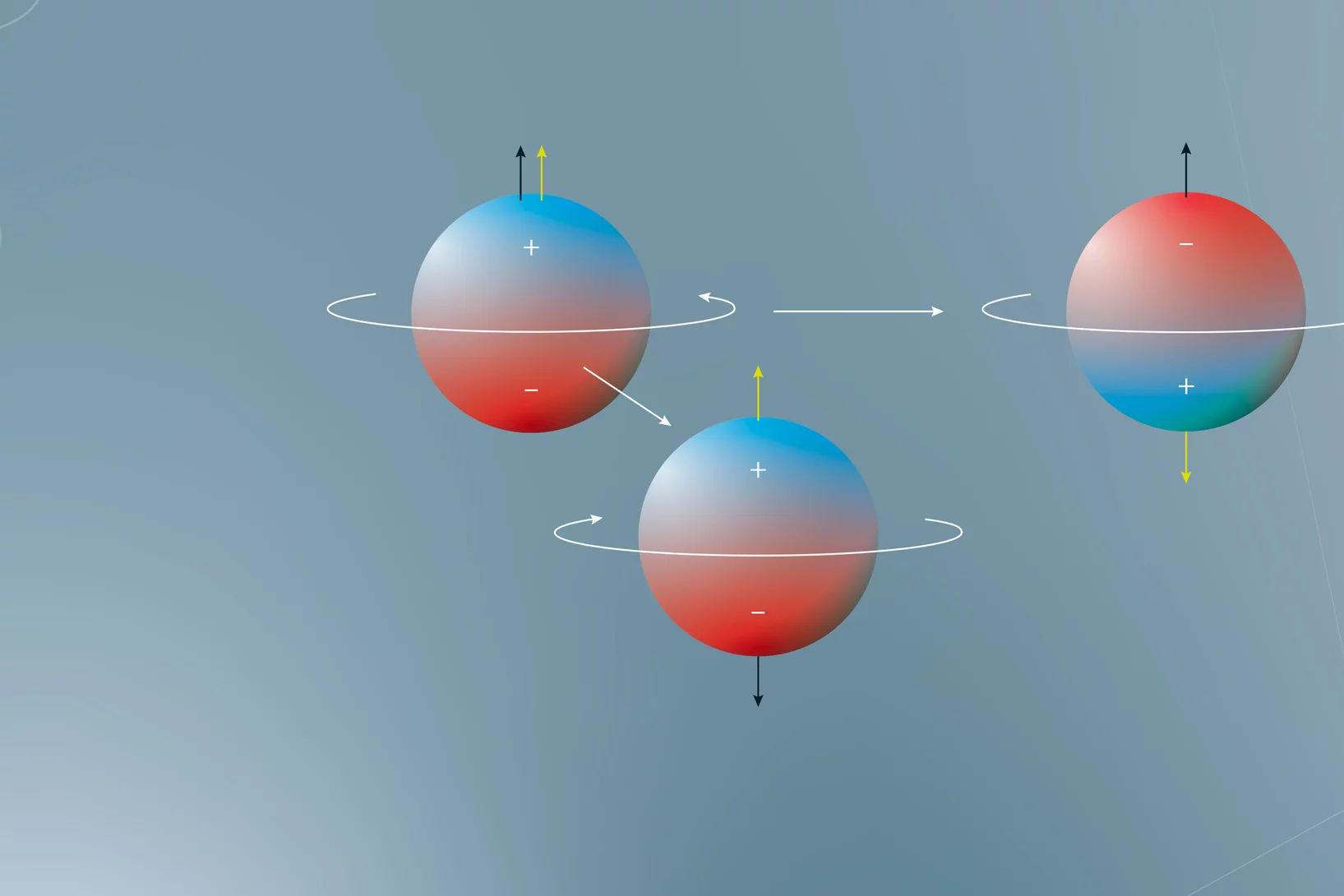
Discovery of a large unquenched orbital moment in a 2D van der Waals ferromagnet
3d transition metals often exhibit a quenched orbital moment when in a solid state system. Therefore, the proposition of a large unquenched orbital moment for V in VI3 caused some surprise and discussion in the scientific community. Experimental and theoretical works diverge on the fact of whether the orbital moment is quenched or not. In our work we have been able to give an answer this open issue, proposing also a model for the ground state of VI3.
Plus de lumière dans l’obscurité
Au PSI, les chercheurs veulent combler les dernières lacunes du modèle standard de la physique à l'aide des grandes installations de recherche.
Unconventional superconductivity found in kagome metal
Physicists using muon spin spectroscopy at PSI make the missing link between their recent breakthrough in Nature and unconventional superconductivity
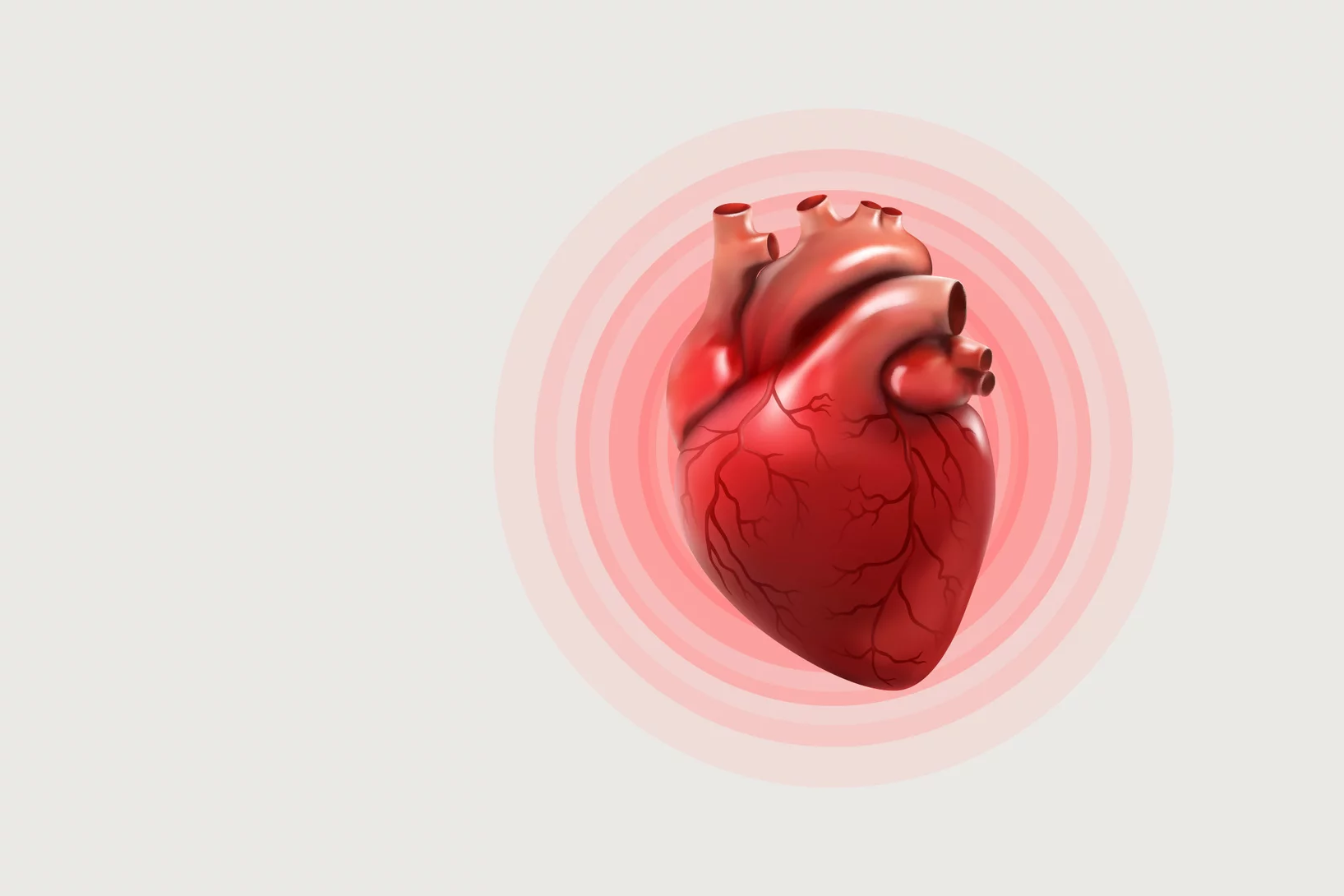
X-ray tomography helps understand how the heart beats
Researchers at the Swiss Light Source SLS use X-ray phase contrast imaging to study a heart in action as it beats.
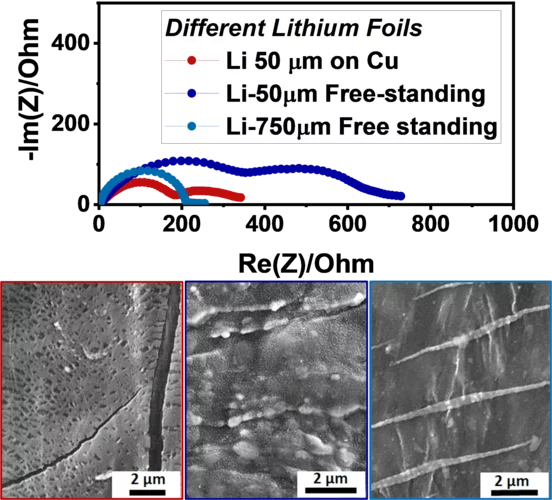
Updated electrochemical impedance model for understanding the interface of metallic lithium
Lithium metal negative electrodes are often used as counter electrodes while testing other electrochemically active materials, and are considered to be equivalent, independently of their thickness, supplier and production processes used. Here, we clearly demonstrate, using Electrochemical Impedance spectroscopy (EIS) that it is not the case, as well as the often-used symmetric cells are actually not so symmetric, when EIS spectra are disentangled using Thee-electrode cells.
Neues Technologietransferzentrum für die Photonik-Industrie
Das Technologietransferzentrum Swiss PIC wurde Anfang Januar 2023 gegründet. Es wird bei der Integration optischer Systeme auf elektronischen Komponenten Innovation schaffen und der Industrie zugänglich machen. Das Swiss PIC wird am Park Innovaare angesiedelt sein und damit in unmittelbarer Nachbarschaft zum Paul Scherrer Institut PSI, das neben weiteren Beteiligten aus Industrie und Forschung einer der Gründungspartner ist.
Swiss PIC soutient l’industrie suisse de la photonique
Le centre de transfert de technologie Swiss PIC sera sis au Park Innovaare.
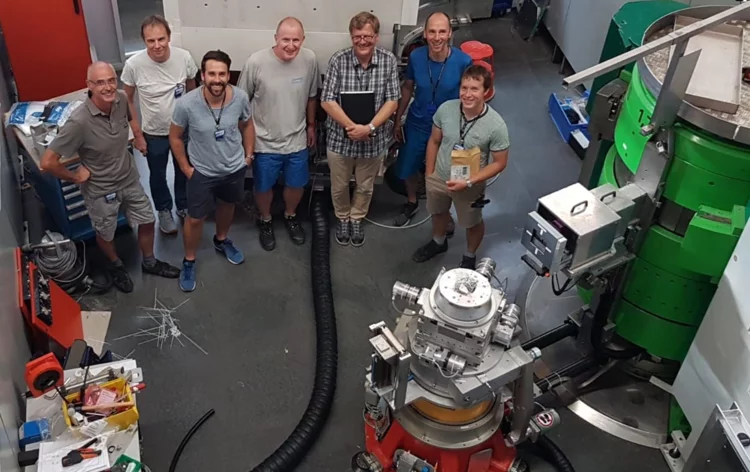
CHART MagDev CCT Dipole achieves record field
As one of the first CHART projects, the MagDev activity at PSI designed and built a canted-cosine theta (CCT) demonstrator magnet, wound from Nb3Sn conductor.
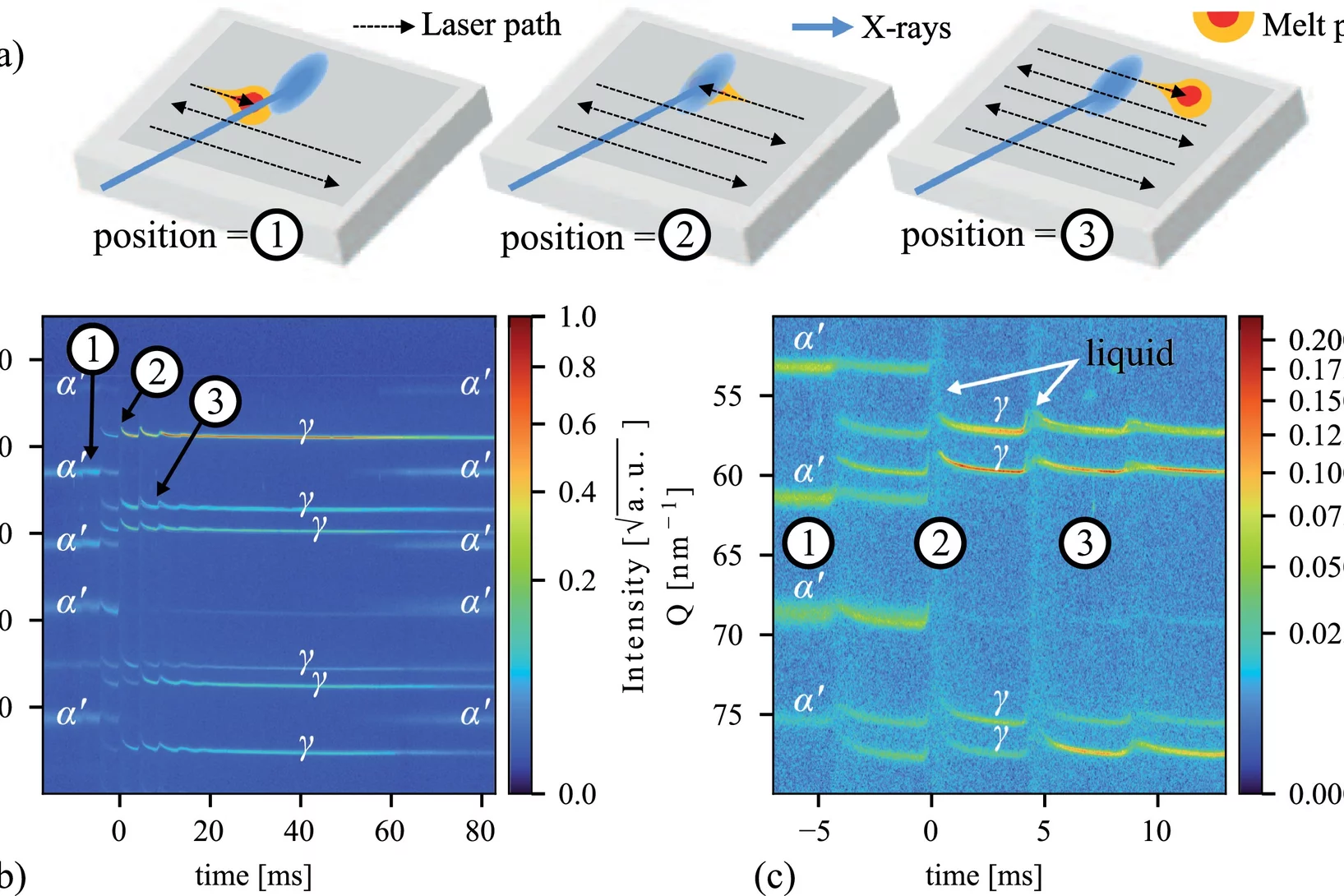
Solidification modes during additive manufacturing
The thermal conditions during laser-based additive manufacturing are inferred from high-speed X-ray diffraction data and can be linked to a model for rapid solidification.
Elektroniker-Sitzung vom 23.12.2022
In jedem Quartal führen alle Elektroniker-Lernenden mit den Berufsbildnern eine Sitzung, wo alle synchronisieren. Hier berichten wir über die letzte Sitzung 2022.
PSI am diesjährigen KMU Swiss Symposium!
Am 23. März 2023 findet das diesjährige KMU Swiss Symposium in Baden statt – wir freuen uns, dass wir auch in diesem Jahr wieder vor Ort dabei sind!
Das KMU Swiss Symposium bietet eine Plattform für Austausch und Inspiration – dies wird ermöglicht durch spannende Referate, diverse Messestände mit innovativen Projekten und Networking.
Hören Sie spannende Referate zum Thema «Macht des Vertrauens – Manipulation versus Vertrauen» von u.a. vom Schweizer Armeechef Thomas Süssli oder von Ivano Somaini, Security Analyst der Compass Security Schweiz AG.
Das PSI ist mit dabei – besuchen Sie uns an unserem gemeinsamen Stand mit dem Hightech Zentrum Aargau und erfahren Sie mehr darüber, wie wir Industrie und KMU bei Ihren technischen Herausforderungen und Innovationsprozessen unterstützen können.
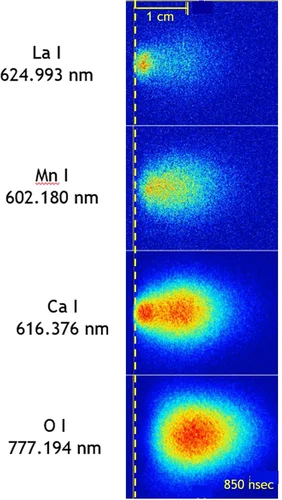
PLD plasma plume analysis, a summary of the PSI contribution
We report on the properties of laser-induced plasma plumes generated by ns pulsed excimer lasers as used for pulsed laser deposition to prepare thin oxide films. A focus is on the time and spatial evolution of chemical species in the plasma plume as well as the mechanisms related to the plume expansion. The overall dynamics of such a plume is governed by the species composition in particular if three or more elements are involved. We studied the temporal evolution of the plume, the composition of the chemical species in the plasma, as well as their electric charge. In particular, ionized species can have an important influence on film growth. Likewise, the different oxygen sources contributing to the overall oxygen content of an oxide film are presented and discussed. Important for the growth of oxide thin films is the compositional transfer of light element such as oxygen or Li. We will show and discuss how to monitor these light elements using plasma spectroscopy and plasma imaging and outline some consequences of our experimental results.
Das alljährliche Weihnachtsessen der Automatiker
Wir Automatiker Lernenden vom PSI pflegen jährlich untereinander einen gemeinsamen Abschluss des Jahres, den wir euch gerne näherbringen wollen.
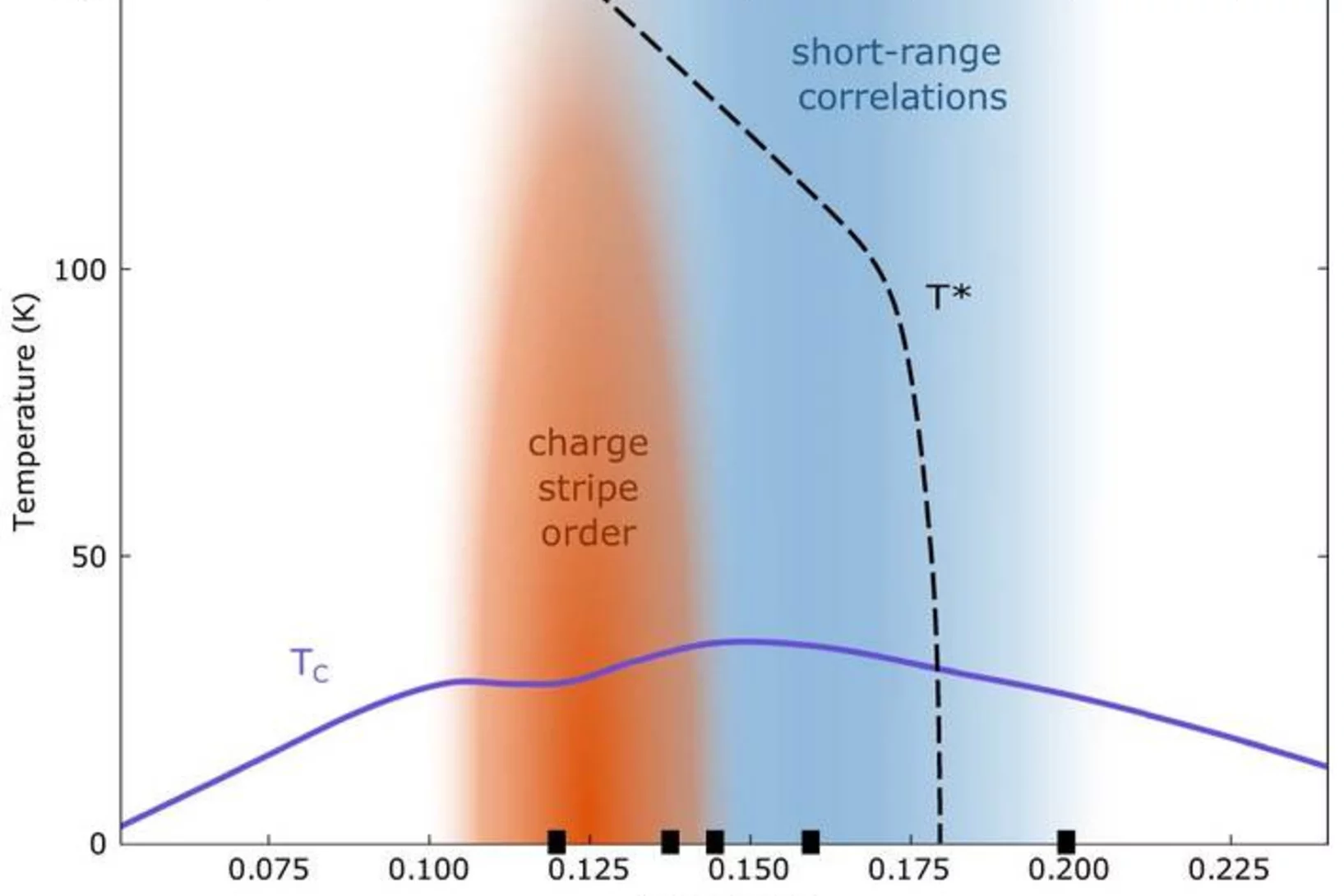
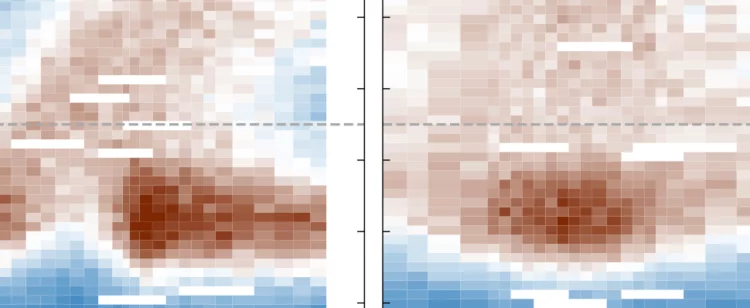
Fate of charge order in overdoped La-based cuprates
In high-temperature cuprate superconductors, stripe order refers broadly to a coupled spin and charge modulation with a commensuration of eight and four lattice units, respectively. How this stripe order evolves across optimal doping remains a controversial question. Here we present a systematic resonant inelastic x-ray scattering study of weak charge correlations in La2−xSrxCuO4 and La1.8−xEu0.2SrxCuO4. Ultra high energy resolution experiments demonstrate the importance of the separation of inelastic and elastic scattering processes. Long-range temperature-dependent stripe order is only found below optimal doping. At higher doping, short-range temperature-independent correlations are present up to the highest doping measured. This transformation is distinct from and preempts the pseudogap critical doping. We argue that the doping and temperature-independent short-range correlations originate from unresolved electron–phonon coupling that broadly peaks at the stripe ordering vector. In La2−xSrxCuO4, long-range static stripe order vanishes around optimal doping and we discuss both quantum critical and crossover scenarios.
Fate of charge order in overdoped La-based cuprates
In high-temperature cuprate superconductors, stripe order refers broadly to a coupled spin and charge modulation with a commensuration of eight and four lattice units, respectively. How this stripe order evolves across optimal doping remains a controversial question. Here we present a systematic resonant inelastic x-ray scattering study of weak charge correlations in La2−xSrxCuO4 and La1.8−xEu0.2SrxCuO4. Ultra high energy resolution experiments demonstrate the importance of the separation of inelastic and elastic scattering processes.
Jisoo Kim receives PSI Thesis Medal 2023
Jisoo Kim receives the PSI Thesis Medal 2023. With this award, PSI recognises outstanding PhD theses, achieving a high degree of innovation and potentially leading to scientific breakthroughs. Jisoo holds a Master of Science from the Korean Advanced Institute of Science &Technology and defended his thesis entitled “Towards time-resolved X-ray scattering tensor tomography” at ETH Zürich.
Making the most of our data
New initiatives will develop open data practices in key strategic areas including electron microscopy and materials science at Paul Scherrer Institute PSI.
Le meilleur des deux mondes
Annalisa Manera travaille come chercheuse en physique nucléaire au PSI et comme professeure à l’ETH Zurich. Un portrait.
Welcome to LXN Paolo Ansuinelli
Herzlich Willkommen Paolo Ansuinelli in LXN!
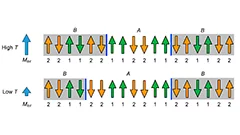
Unusual ferrimagnetism in CaFe2O4
Rare ferrimagnet states in a phase competing antiferromagnet.
Efficacité énergétique en période de pénurie potentielle d’électricité
Le PSI améliore sans cesse son efficacité énergétique et celle de ses grandes installations de recherche.