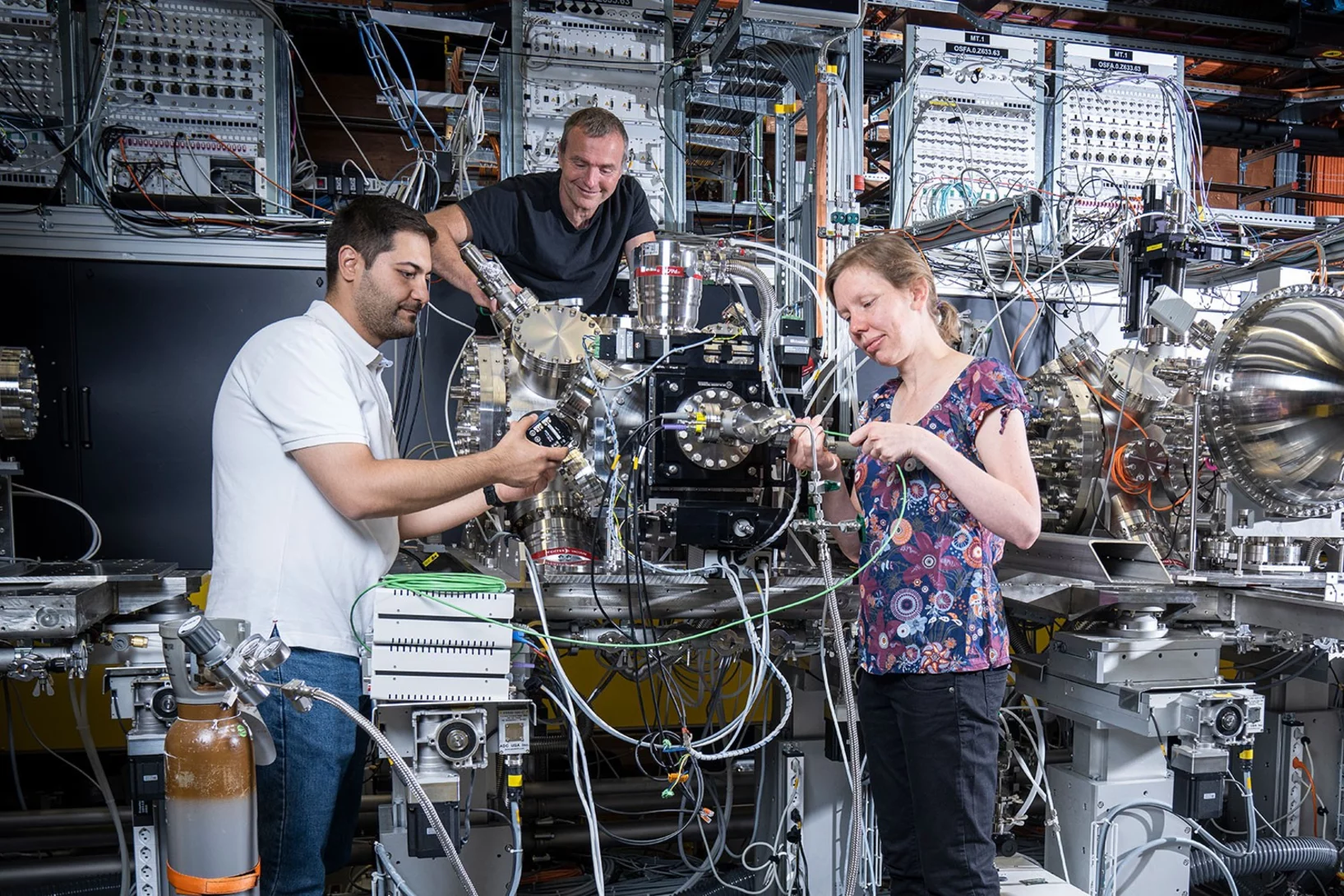
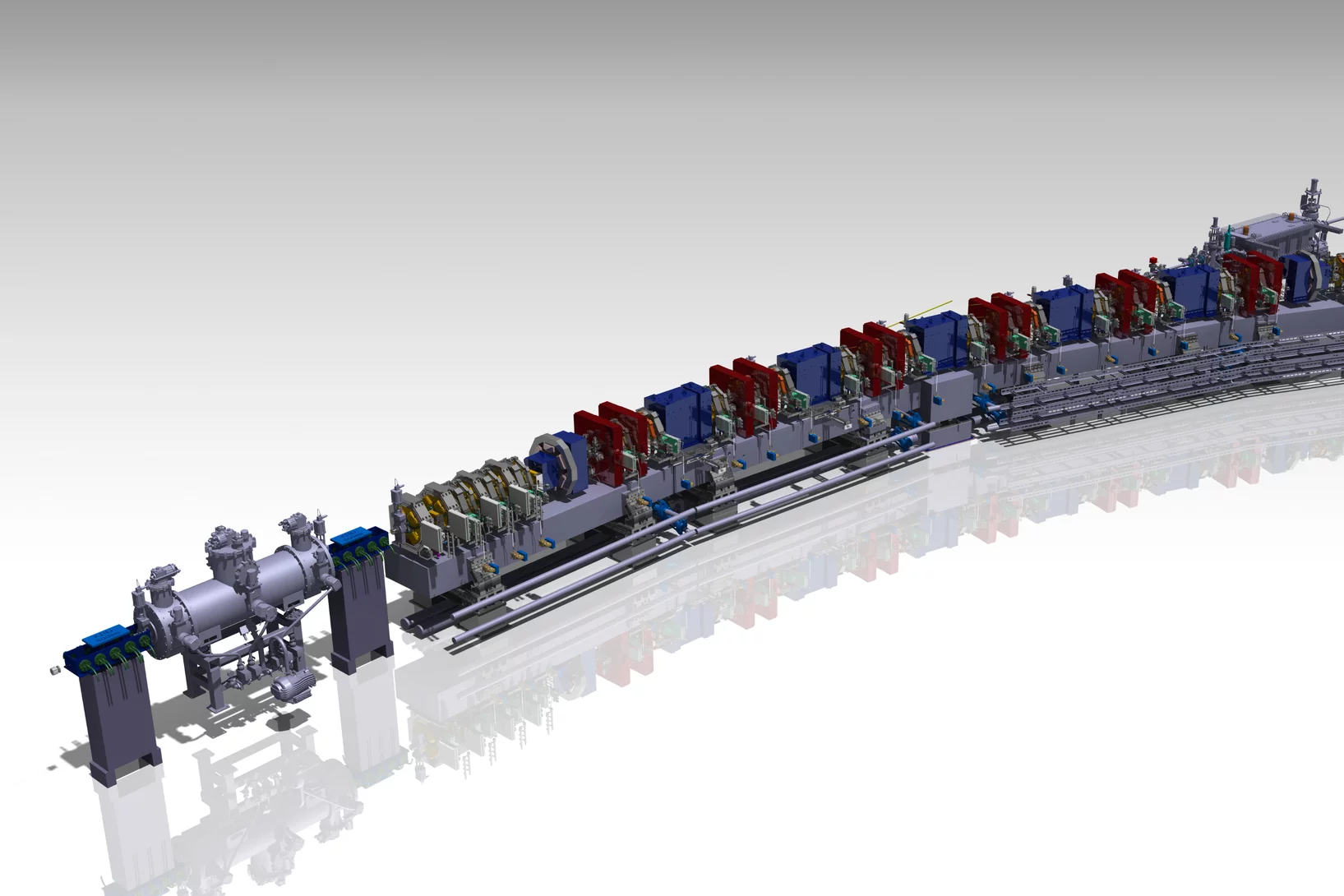
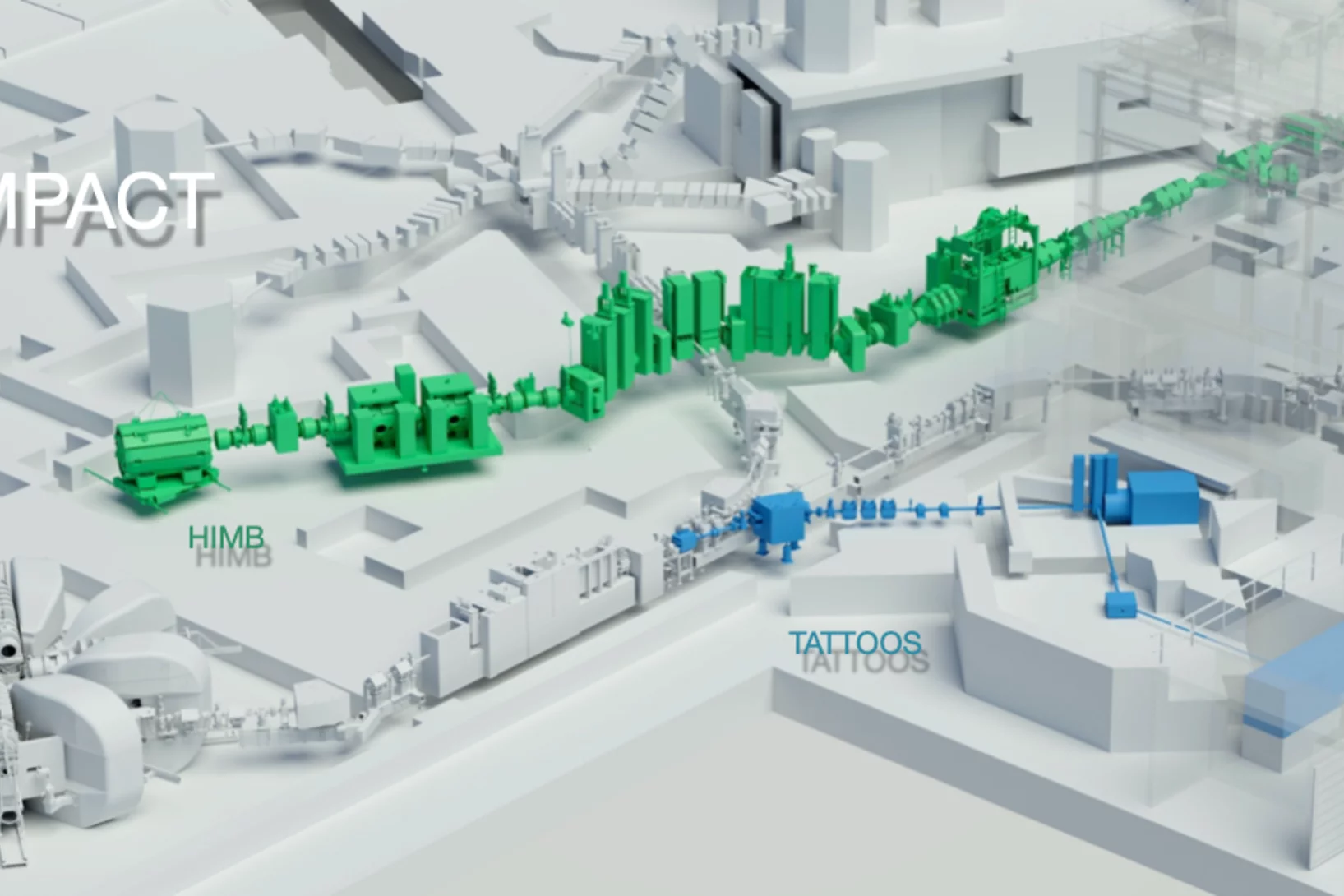
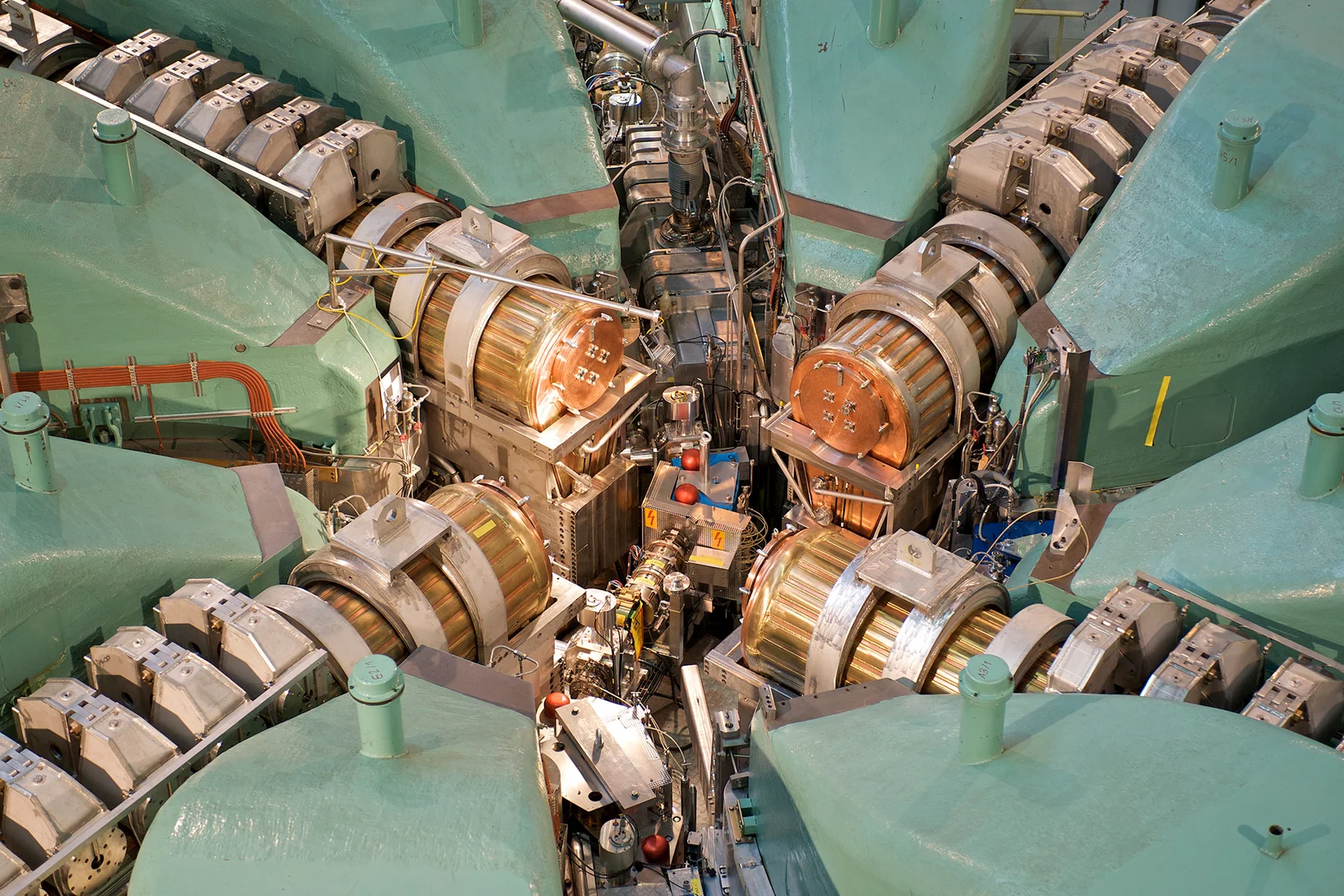
Avec son infrastructure de recherche unique au monde, le PSI offre des possibilités exceptionnelles pour la recherche de pointe nationale et internationale.
Explorez nos domaines de recherche
Scientific Highlights de nos centres
Les polluants ne se forment souvent que dans l'air
Dans le cadre de l’expérience CLOUD au CERN, des scientifiques du PSI ont mesuré avec une précision jamais atteinte à ce jour comment les polluants atmosphériques organiques se forment et se répartissent.
Un incroyable succès
Araris Biotech AG, spin-off du PSI, obtient une valorisation au niveau «licorne»
Comment le Botox pénètre dans nos cellules
Des scientifiques du PSI ont identifié des modifications structurelles moléculaires de la neurotoxine bactérienne Botox qui sont importantes pour son absorption par les cellules nerveuses. Cela pourrait permettre à l'avenir des utilisations plus ciblées du Botox en médecine.
Vous souhaitez utiliser nos installations pour votre recherche?
Découvrez nos grands installations de recherche et autres infrastructures de recherche.
Les centres du PSI en un coup d'œil
Nos centres de recherche et de services mènent de la recherche de pointe reconnue au niveau international dans les sciences naturelles et les science de l’ingénierie et mettent à la disposition de la science ainsi que de l'industrie de grandes installations de recherche très complexes pour leurs propres projets de recherche.
Scientific Highlights de nos centres
Anomalous Hall Effect due to Magnetic Fluctuations in a Ferromagnetic Weyl Semimetal
The anomalous Hall effect (AHE) has emerged as a key indicator of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB) and topological features in electronic band structures. Absent of a magnetic field, the AHE requires spontaneous TRSB but has proven hard to probe due to averaging over domains. The anomalous component of the Hall effect is thus frequently derived from extrapolating the magnetic field dependence of the Hall response. We show ....
Rhodium recovery from acidic wastewater using radiografted chelating adsorbents
Platinum group metals (PGMs), particularly rhodium (Rh), are rare and vital for industrial applications, with Rh being scarcer (≈ 20 t/y) than platinum (Pt) and palladium (Pd). Its high cost and limited supply emphasize the need for efficient recovery from industrial waste. New radiografted chelating adsorbents, created through irradiation, offer a sustainable, cost-effective alternative to existing extraction methods. They exhibit high efficiency, selectivity, and reusability, making them ideal for recovering and recycling Rh from industrial wastewater.
Two Characteristic Contributions to the Superconducting State of 2H-NbSe2
Multiband superconductivity arises when multiple electronic bands contribute to the formation of the superconducting state, allowing distinct pairing interactions and gap structures. Here, we present field- and temperature-dependent data ...