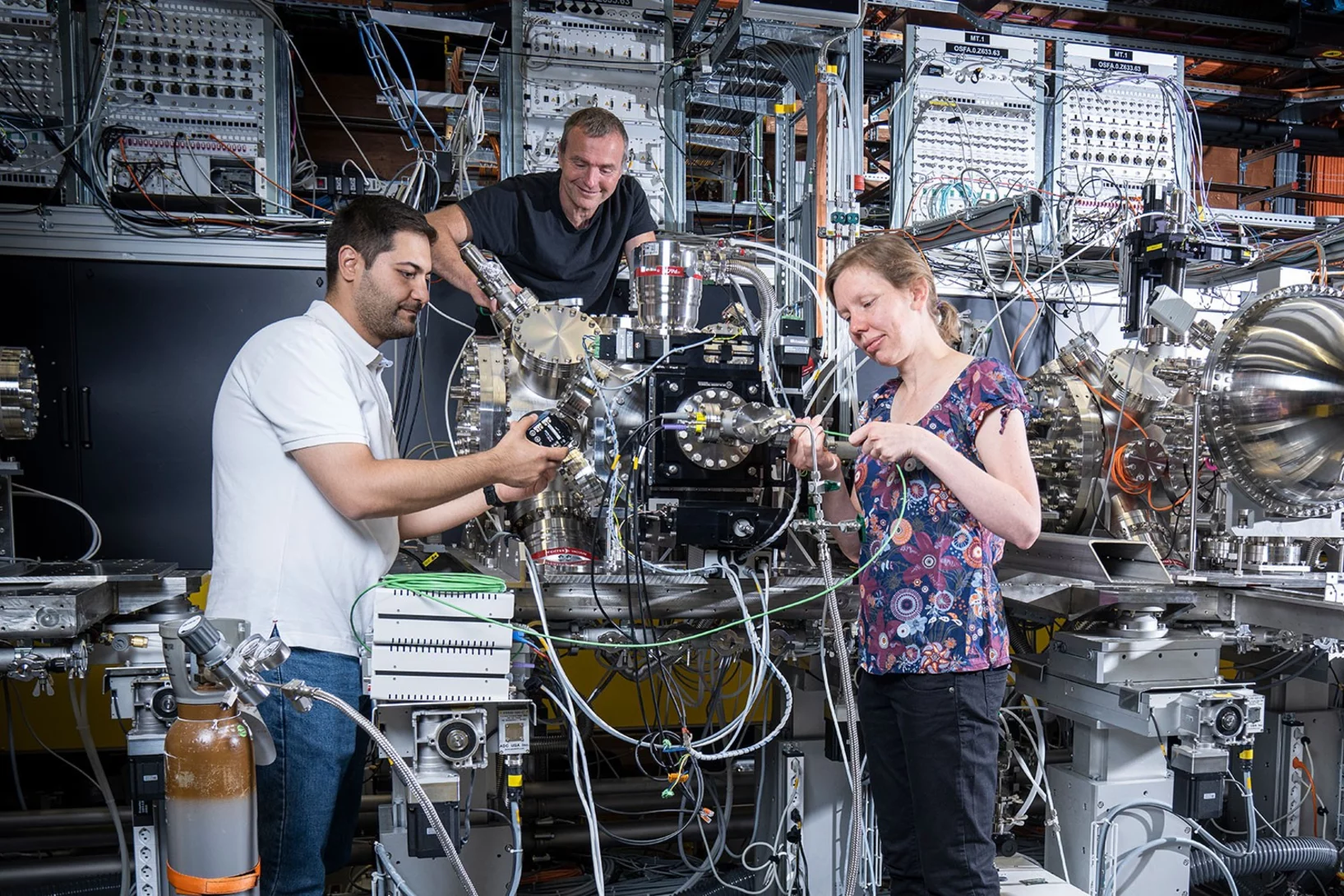
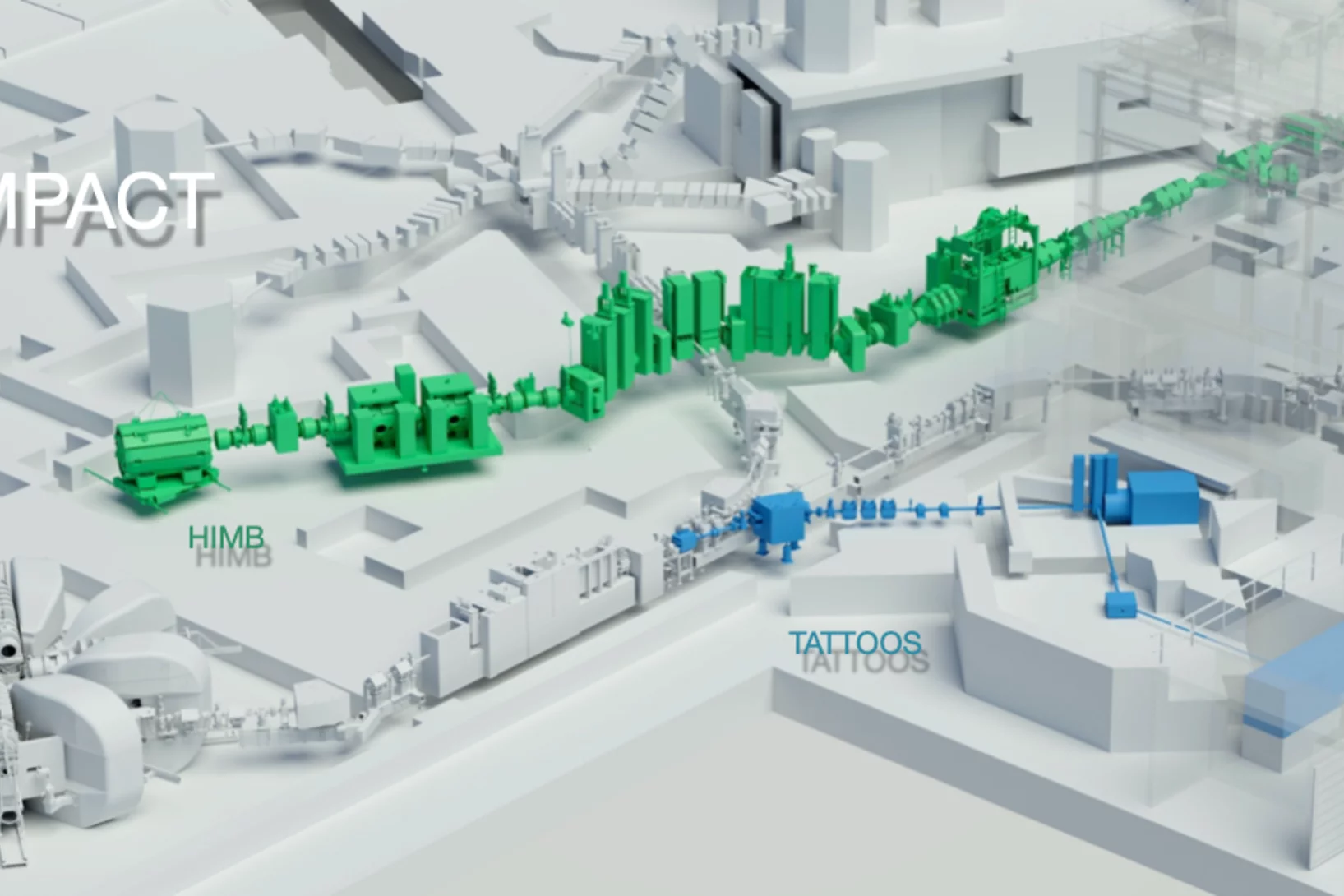
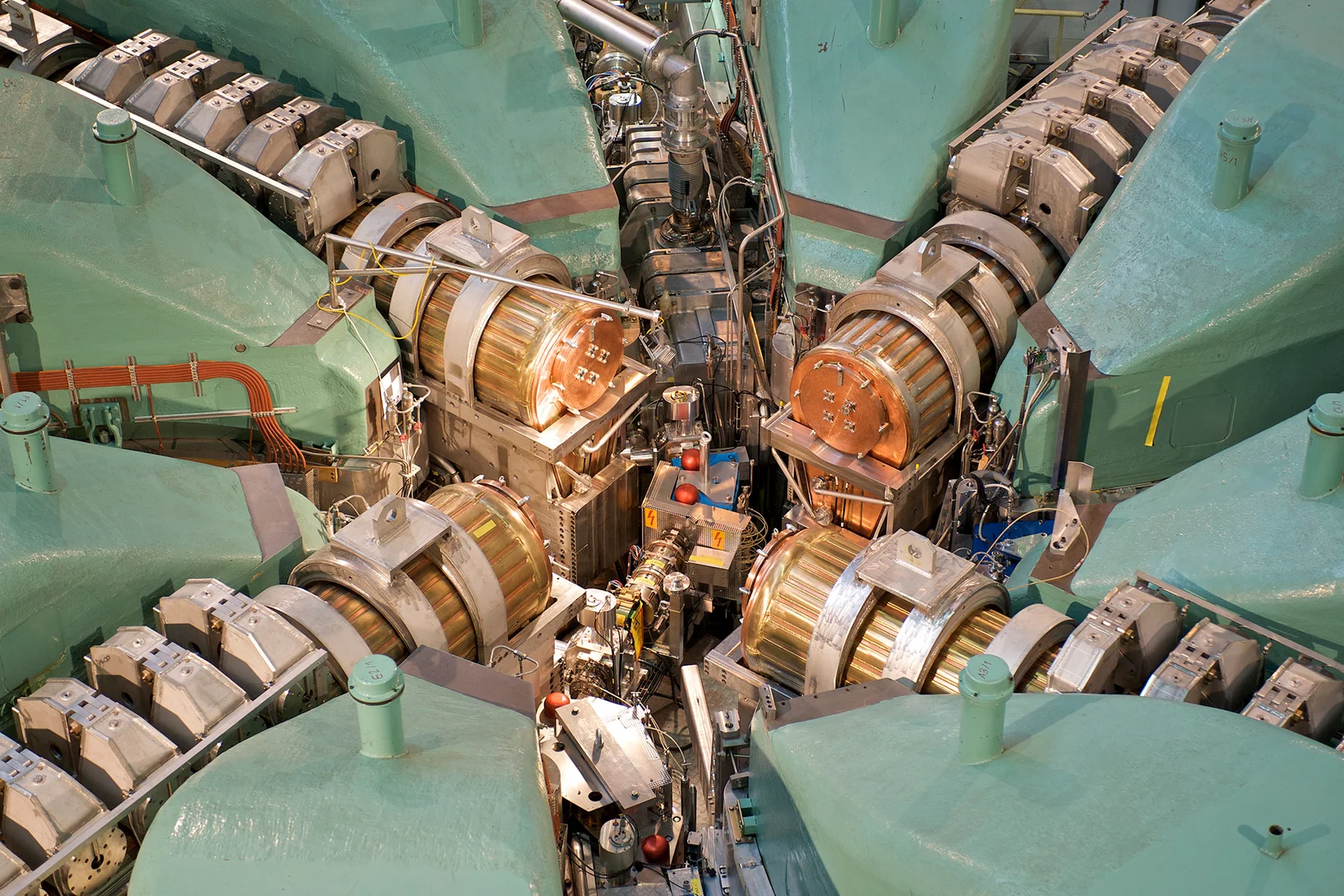
Das PSI bietet mit seiner weltweit einmaligen Forschungsinfrastruktur einzigartige Möglichkeiten für die nationale und internationale Spitzenforschung.
Die Forschungsschwerpunkte des PSI
Aktuelle Highlights aus unserer Forschung
Daten für einen besseren Vanadium-Flow
Forschende des PSI haben eine dynamische Datenbank zur globalen Vanadiumwirtschaft entwickelt. Sie soll den Einsatz spezieller Energiespeicher vorantreiben – und damit die Energiewende.
POLIZERO: PSI-Projekt zeigt Wege zur Klimaneutralität
Das Netto-Null-Ziel ist erreichbar – wenn die Schweiz jetzt die richtigen politischen Weichen stellt.
Merlin-7: Neues Modell für Höchstleistungsrechnen
Ein innovativer Rechencluster läutet am PSI eine neue Ära der computergestützten Forschung ein.
Möchten Sie unsere Anlagen für Ihre Forschung nutzen?
Erfahren Sie mehr über unsere Grossforschungsanlagen und weiteren Forschungseinrichtungen.
PSI Center & Labs
Unsere Forschungs- und Servicezentren betreiben international anerkannte Spitzenforschung in den Natur- und Ingenieurwissenschaften und stellen der Wissenschaft wie auch der Industrie hochkomplexe Grossforschungsanlagen für eigene Forschungsvorhaben zur Verfügung.
Scientific Highlights aus unseren Centren
Generating structured foam via flowing through a wire array
Efficient manufacturing methods could unlock foams with tailored, anisotropic properties. Conventional foam production methods rely on the self-arrangement of bubbles, typically leading to isotropic materials, or involve intricate additive layering processes. This study presents a simple, passive technique to modify the foam structure. A set of thin parallel wires ...
HPCP Summer School FHNW/PSI
The institute for Data Science of the FHNW in Brugg - Windisch and AWI department of PSI held a joint course on high performance computing. The course addressed computer science students of FHNW and interested individuals at PSI. Two full days at the FHNW (with Apero) were followed by two full days at PSI using Merlin6 (with tour).
Carbocation, diradical, and superelectrophile in one molecule?
The pentafluorophenyl cation (C₆F₅⁺) breaks these rules with a borderline “crazy” reactivity.