PSI expertise boosts research for the energy transition
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) are involved in several projects under the new National Research Programme Energy Turnaround (NRP70) of the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF). The PSI experts tackle issues such as particle emissions from wood heating systems, the holistic evaluation of energy systems and the production of semiconductor components for novel transformers.
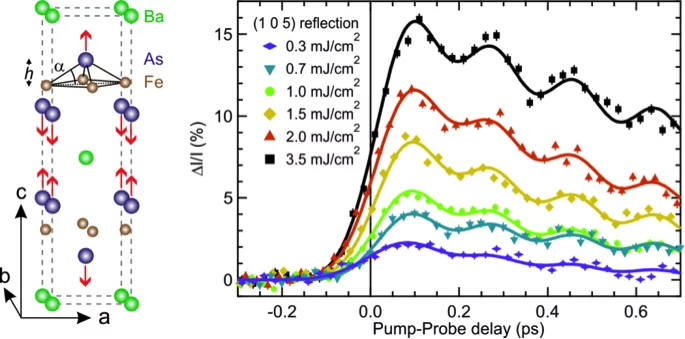
Ultrafast structural dynamics of the Fe-pnictide parent compound BaFe2As2
Understanding the interplay of the various degrees of freedom such as the electrons, spins and lattice is essential for many complex materials, including the high-temperature superconductors.
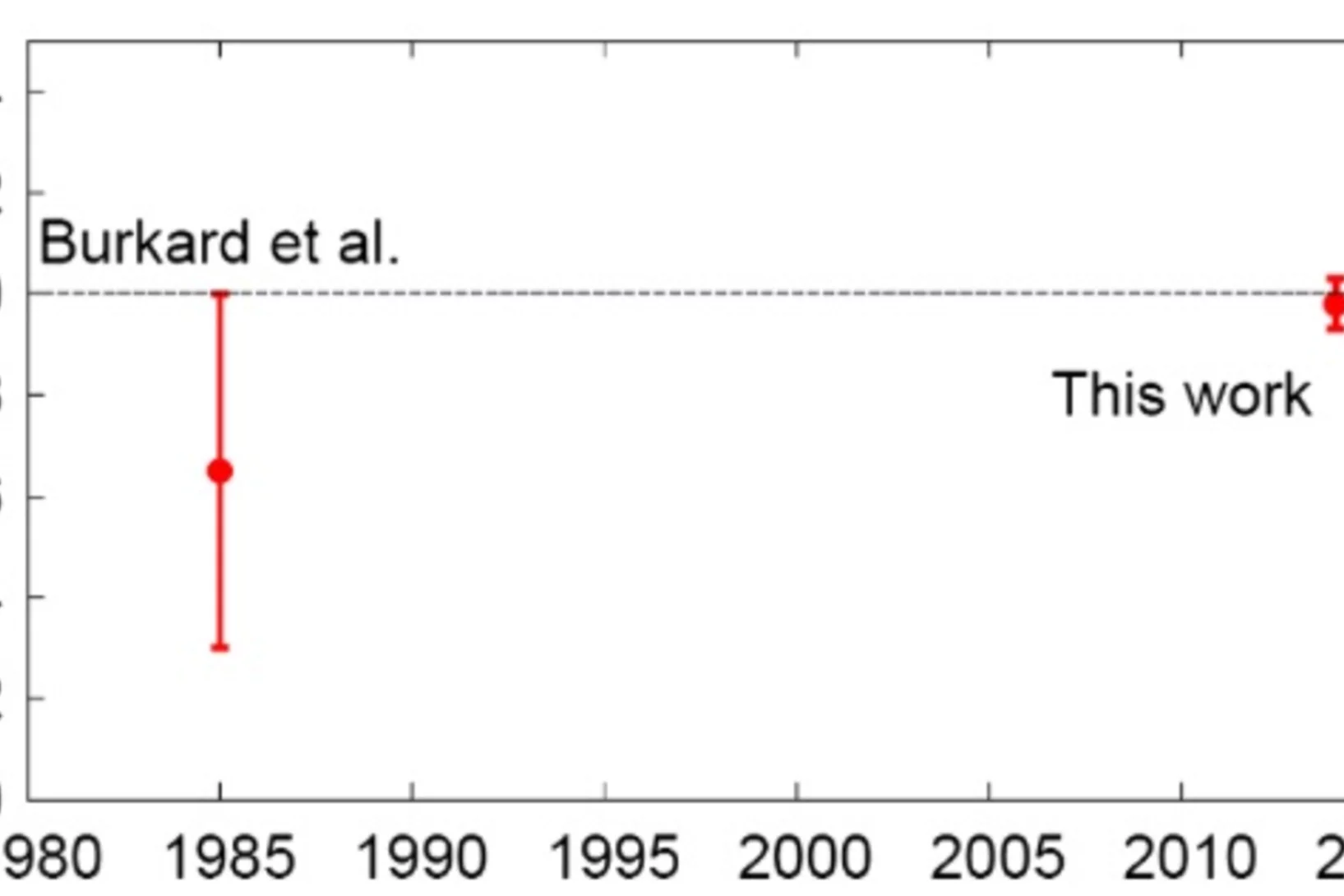
Pressure dependence of the magnetic order in CrAs
The suppression of magnetic order with pressure concomitant with the appearance of pressure-induced superconductivity was recently discovered in CrAs. Here we present a neutron diffraction study of the pressure evolution of the helimagnetic ground state towards and in the vicinity of the superconducting phase. Neutron diffraction on polycrystalline CrAs was employed from zero pressure to 0.65 GPa and at various temperatures.
Pressure dependence of the magnetic order in CrAs
L. Keller et al., Phys. Rev. B 91, 020409(R) (2015). The suppression of magnetic order with pressure concomitant with the appearance of pressure-induced superconductivity was recently discovered in CrAs. Here we present a neutron diffraction study of the pressure evolution of the helimagnetic ground state towards and in the vicinity of the superconducting phase. Neutron diffraction on polycrystalline CrAs was employed from zero pressure to 0.65 GPa and at various temperatures.
The phase diagram of electron-doped La2-xCexCuO4-δ
Superconductivity is a striking example of a quantum phenomenon in which electrons move coherently over macroscopic distances without scattering. The high-temperature superconducting oxides (cuprates) are the most studied class of superconductors, composed of two-dimensional CuO2 planes separated by other layers that control the electron concentration in the planes. A key unresolved issue in cuprates is the relationship between superconductivity and magnetism.
New laser for computer chips
Germanium-Zinn-Halbleiterlaser lässt sich direkt auf Siliziumchips aufbringenWinzige Laser, die in Computerchips aus Silizium eingebaut werden, sollen in Zukunft die Kommunikation innerhalb der Chips und zwischen verschiedenen Bauteilen eines Computers beschleunigen. Lange suchten Experten nach einem dafür geeigneten Lasermaterial, das sich mit dem Fertigungsprozess von Siliziumchips vereinbaren lässt. Wissenschaftler des Forschungszentrums Jülich und des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI haben hier nun einen wichtigen Fortschritt erzielt.This news release is only available in German.
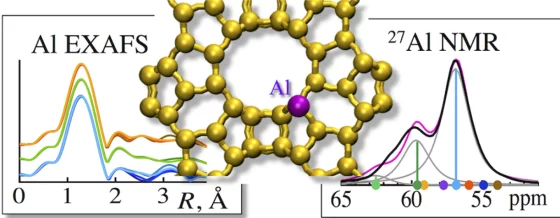
Quantitatively Probing the Al Distribution in Zeolites
The degree of substitution of Si4+ by Al3+ in the oxygen-terminated tetrahedra (Al T-sites) of zeolites determines the concentration of ion-exchange and Brønsted acid sites. Because the location of the tetrahedra and the associated subtle variations in bond angles influence the acid strength, quantitative information about Al T-sites in the framework is critical to rationalize catalytic properties and to design new catalysts.
Quantitatively Probing the Al Distribution in Zeolites
The degree of substitution of Si4+ by Al3+ in the oxygen-terminated tetrahedra (Al T-sites) of zeolites determines the concentration of ion-exchange and Brønsted acid sites. Because the location of the tetrahedra and the associated subtle variations in bond angles influence the acid strength, quantitative information about Al T-sites in the framework is critical to rationalize catalytic properties and to design new catalysts.
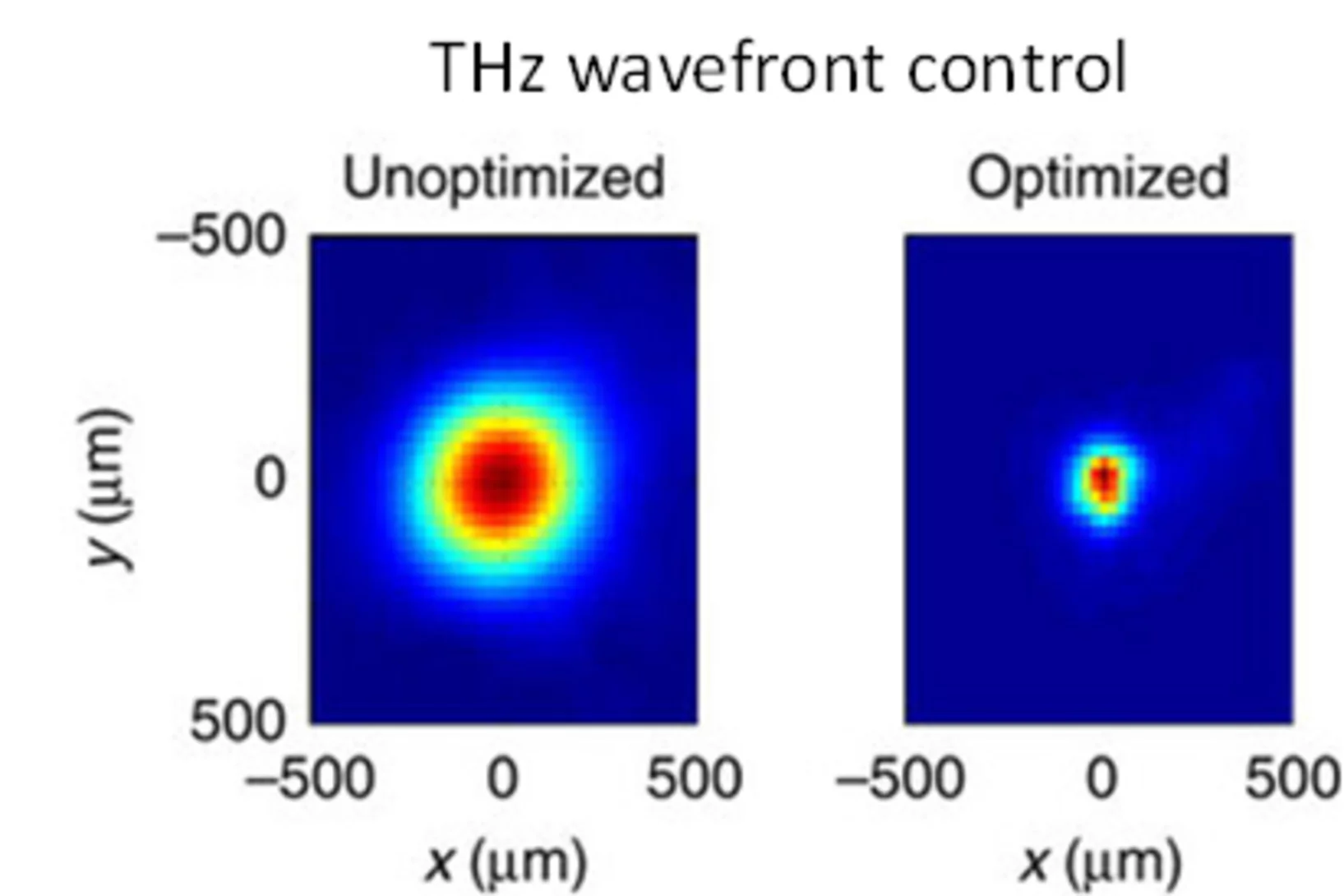
Terahertz wavefront control for extremely bright THz bullet
The brightness of a light source defines its applicability to nonlinear phenomena in science. The SwissFEL laser group has now overcome one of the two principal technological hurdles to produce bright pulses in the Terahertz range (0.1-5 THz).
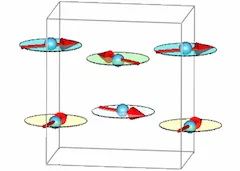
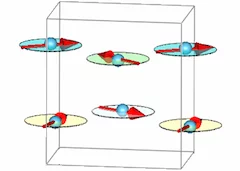
Competing superconducting and magnetic order parameters and field-induced magnetism in electron-doped Ba(Fe1-xCox)2As2
We have studied the magnetic and superconducting properties of Ba(Fe0.95Co0.05)2As2 as a function of temperature and external magnetic field using neutron scattering and muon spin rotation. Below the superconducting transition temperature the magnetic and superconducting order parameters coexist and compete. A magnetic field can significantly enhance the magnetic scattering in the superconducting state, roughly doubling the Bragg intensity at 13.5T.
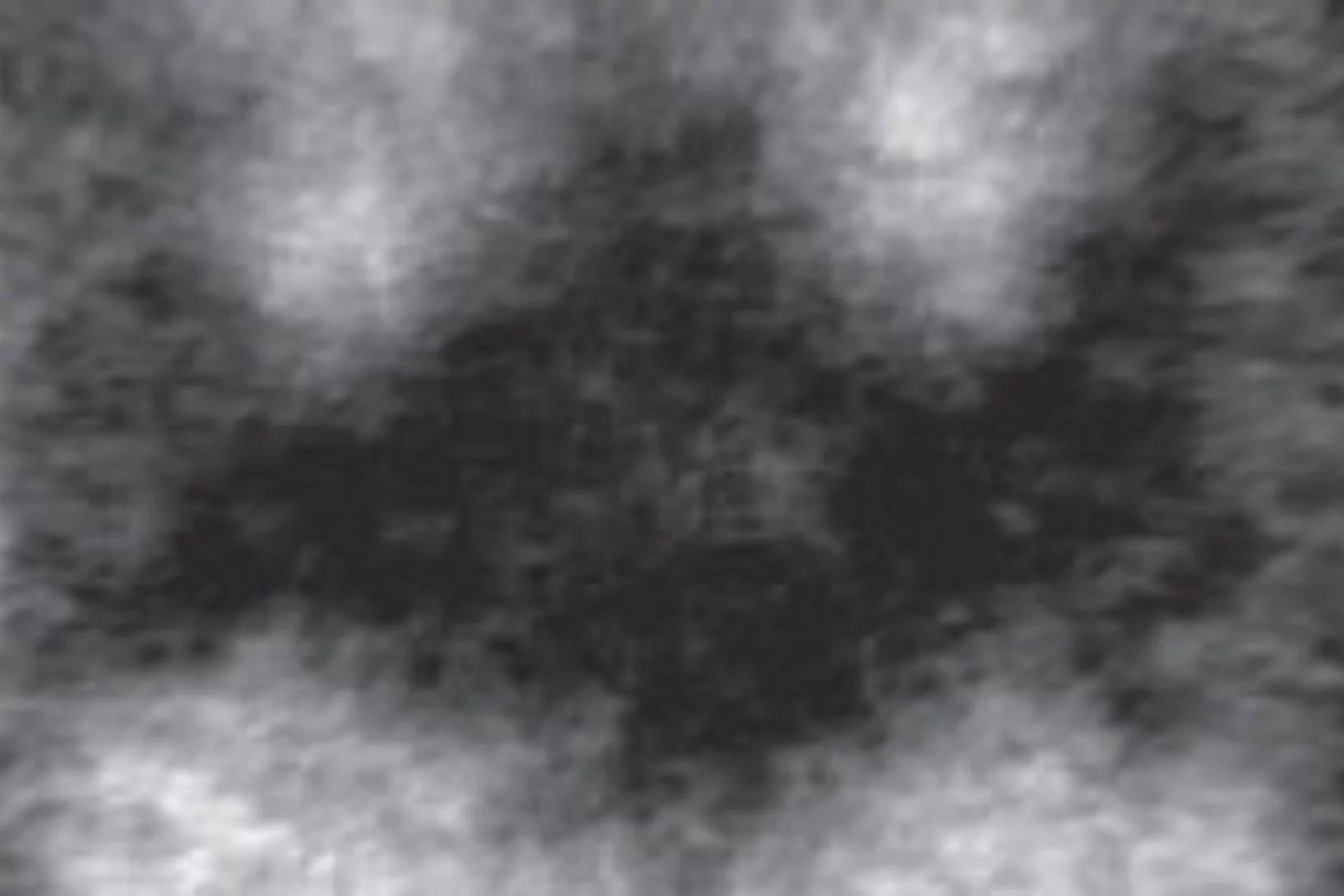
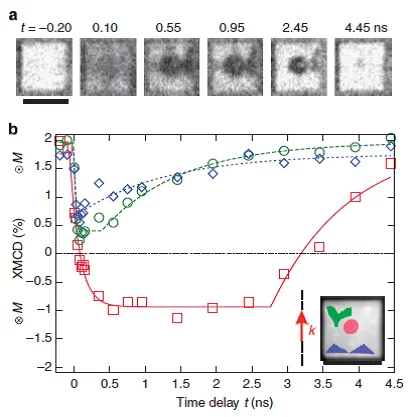
Batman lights the way to compact data storage
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have succeeded in switching tiny, magnetic structures using laser light and tracking the change over time. In the process, a nanometre-sized area bizarrely reminiscent of the Batman logo appeared. The research results could render data storage on hard drives faster, more compact and more efficient.
Nanoscale sub-100 picosecond all-optical magnetization switching in GdFeCo microstructure
Ultrafast magnetization reversal driven by femtosecond laser pulses has been shown to be a promising way to write information. Seeking to improve the recording density has raised intriguing fundamental questions about the feasibility of combining ultrafast temporal resolution with sub-wavelength spatial resolution for magnetic recording. Here we report on the experimental demonstration of nanoscale sub-100 ps all-optical magnetization switching, providing a path to sub-wavelength magnetic recording.
Keeping geothermal energy on the table
A study by the Centre for Technology Assessment TA-Swiss, coordinated by the Paul Scherrer Institute, recommends further pursuing deep geothermal energy in Switzerland. The energy resources underground are vast, environmentally friendly to extract and available around the clock, the authors conclude. The earthquake risk and the cost of electricity production, which are still too high, however, remain challenges that society needs to weigh up against the advantages of deep geothermal energy.
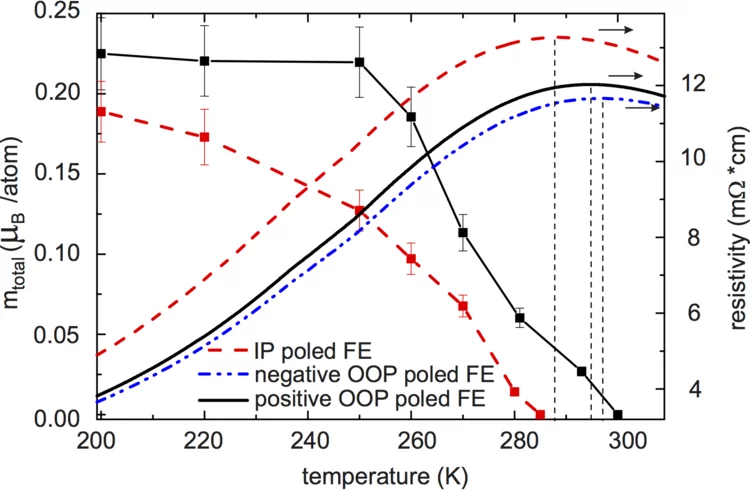
Control of Tc in La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 via piezostrain
X-ray magnetic circular dichroism measurements evidence a 10K shift of the magnetic Curie temperature for La0.7Sr0.3MnO3 deposited on the piezoelectric substrate [Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3]0.68−[PbTiO3]0.32 (011) for two different remanent piezostrain states.
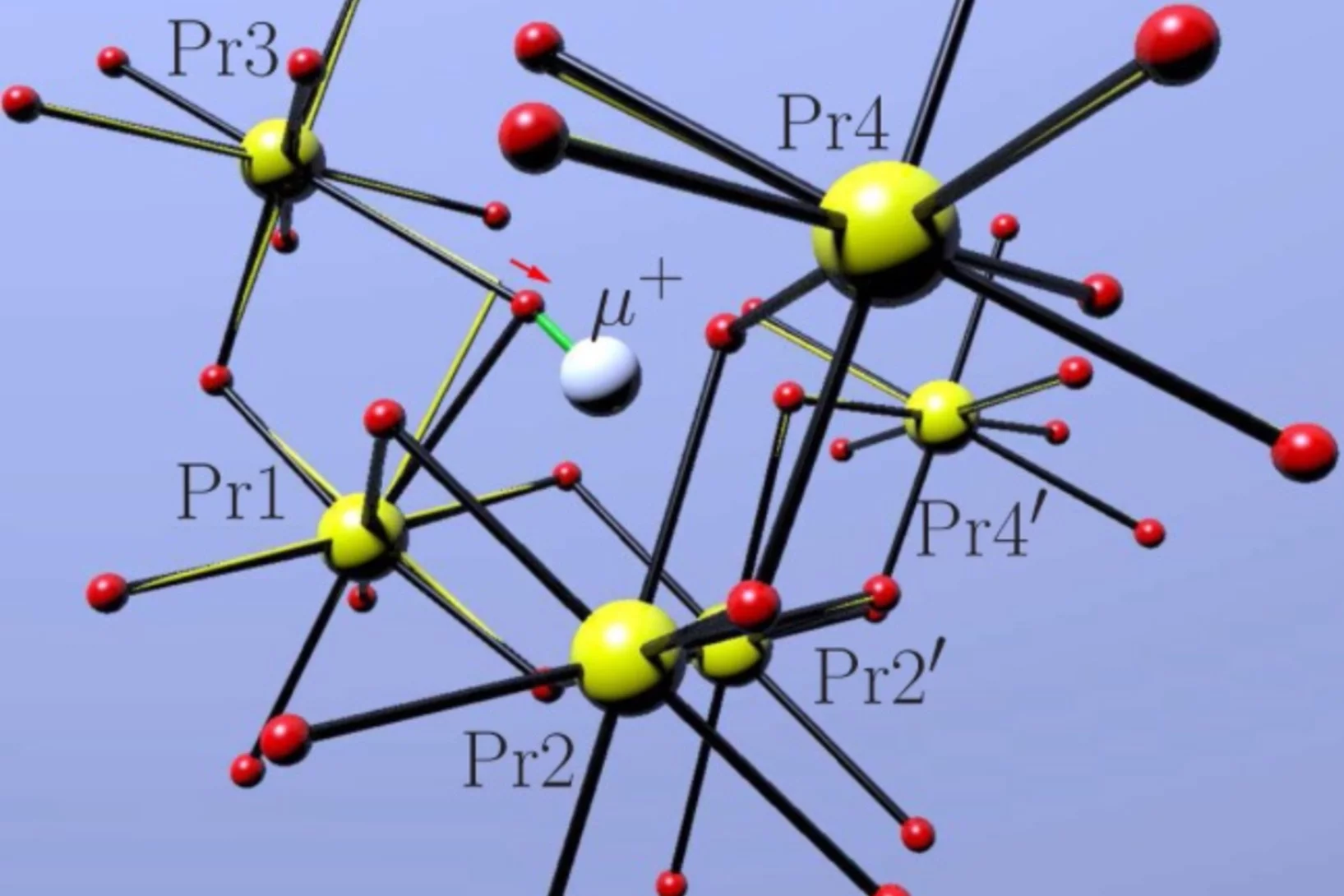
Anisotropic Local Modification of Crystal Field Levels in Pr-Based Pyrochlores: A Muon-Induced Effect Modeled Using Density Functional Theory
Although muon spin relaxation is commonly used to probe local magnetic order, spin freezing, and spin dynamics, we identify an experimental situation in which the measured response is dominated by an effect resulting from the muon-induced local distortion rather than the intrinsic behavior of the host compound.
PSI summer school 2015
The PSI summer school 2015 on Condensed Matter Research will be organized at the Lyceum Alpinum in Zuoz, Switzerland from August 15-21, 2015. International experts and PSI staff members will introduce and deepen your knowledge not only on methods but also on those phenomena, which are presently at the forefront of modern solid state physics and chemistry. The school will be followed by hands-on practical training at the PSI large user facilities SINQ, SμS and SLS. Online registration and detailed information is available from the school's webpage.
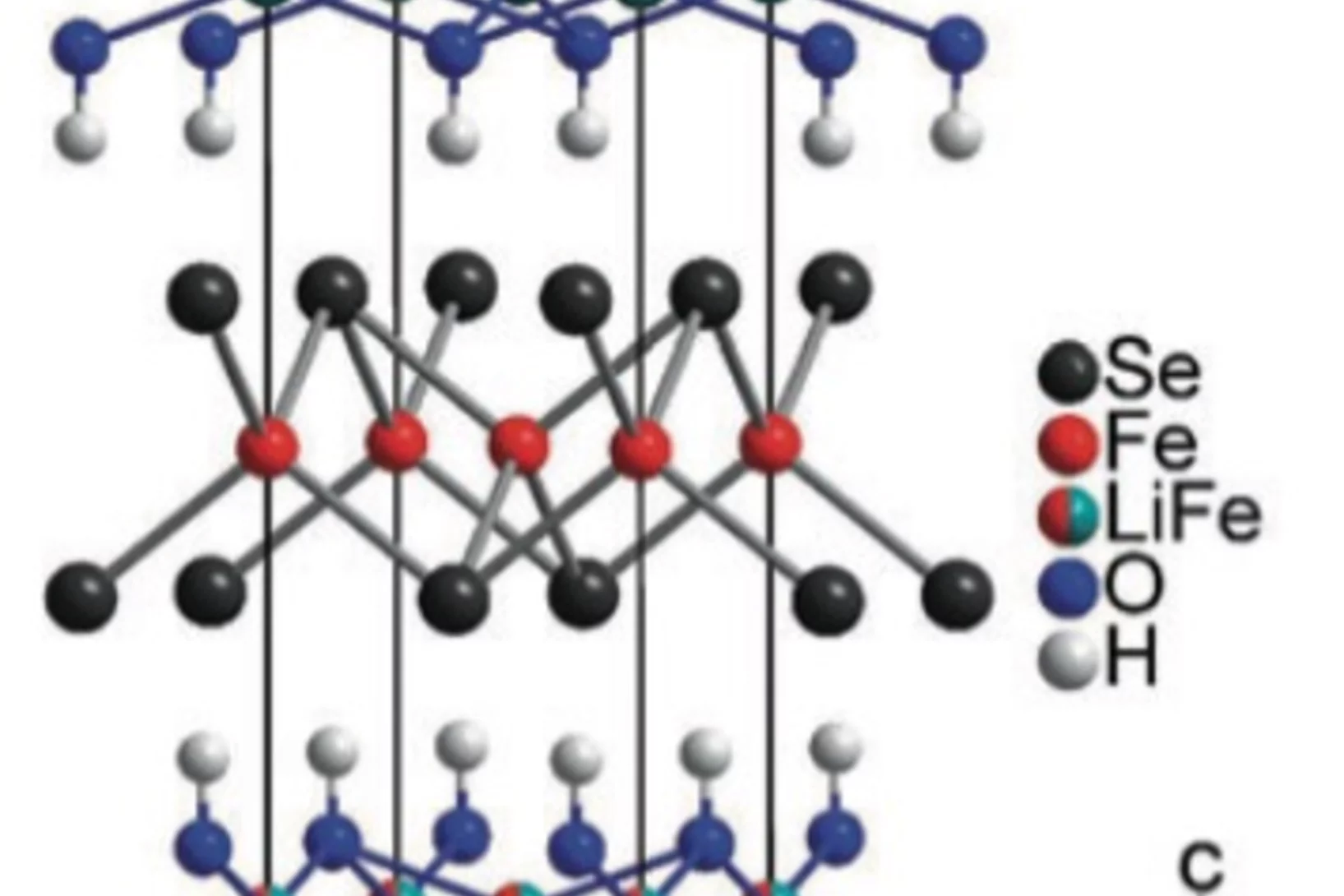
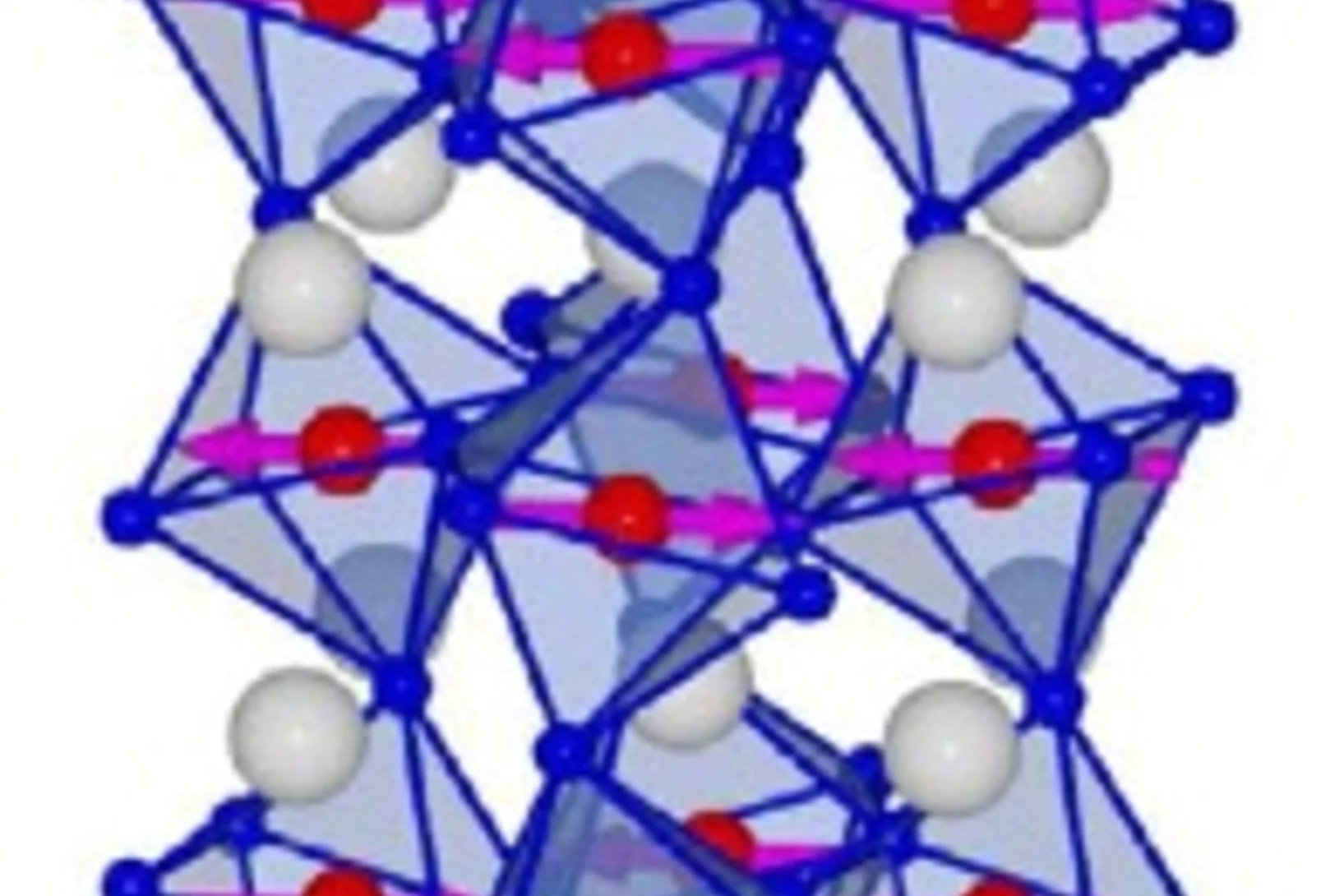
Coexistence of 3d-Ferromagnetism and Superconductivity in [(Li1-Fex)OH](Fe1-yLiy)Se
Superconducting [(Li1-xFex)OH](Fe1-yLiy)Se (x≈0.2, y≈0.08) was synthesized by hydrothermal methods and characterized by single-crystal and powder X-ray diffrac- tion. The structure contains alternating layers of anti-PbO type (Fe1-yLiy)Se and (Li1-xFex)OH. Electrical resistivity and magnetic susceptibility measurements reveal superconductivity at 43K.
Fractional excitations in the square-lattice quantum antiferromagnet
Quantum magnets have occupied the fertile ground between many-body theory and low-temperature experiments on real materials since the early days of quantum mechanics. However, our understanding of even deceptively simple systems of interacting spin-1/2 particles is far from complete. The quantum square-lattice Heisenberg antiferromagnet, for example, exhibits a striking anomaly of hitherto unknown origin in its magnetic excitation spectrum.
Shortcut to protein portraits
All living organisms, from bacteria to humans, rely on proteins to perform their vital functions. How these proteins accomplish their tasks depends on their structure. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute have now devised a novel method to determine the crystal structure of proteins using X-ray light, which could also hasten the development of new drugs in future. The study will be published in the journal Nature Methods on 15 December.
Biomasse als Stütze der Energiewende
Mit 80 Teilnehmerinnen und Teilnehmern fand am 2. Dezember am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI die erste Jahreskonferenz des Kompetenzzentrums des Bundes für Bioenergie (SCCER BIOSWEET) statt. Das im Rahmen des Aktionsplans Energieforschung Schweiz gegründete Kompetenzzentrum definierte in der Tagung die Ziele, Strategien und Positionierung der Bioenergie-Forschung vor dem Hintergrund der neuen schweizerischen Energiepolitik.This news release is only available in German.
A measurement of the neutron to 199Hg magnetic moment ratio
The neutron gyromagnetic ratio has been measured relative to that of the 199Hg atom with an uncertainty of 0.8 ppm. We employed an apparatus where ultracold neutrons and mercury atoms are stored in the same volume and report the result γn/γHg = 3.8424574(30).
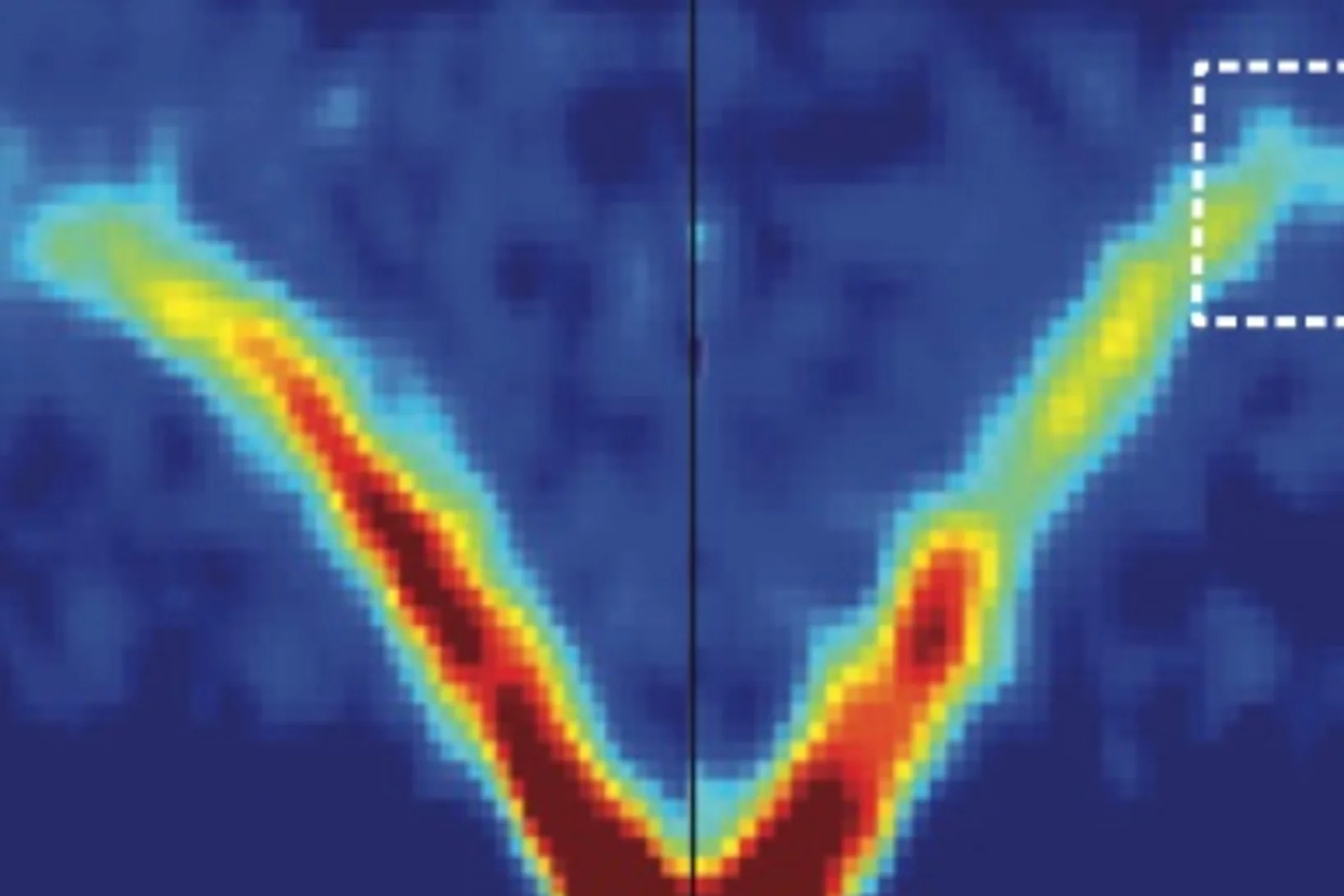
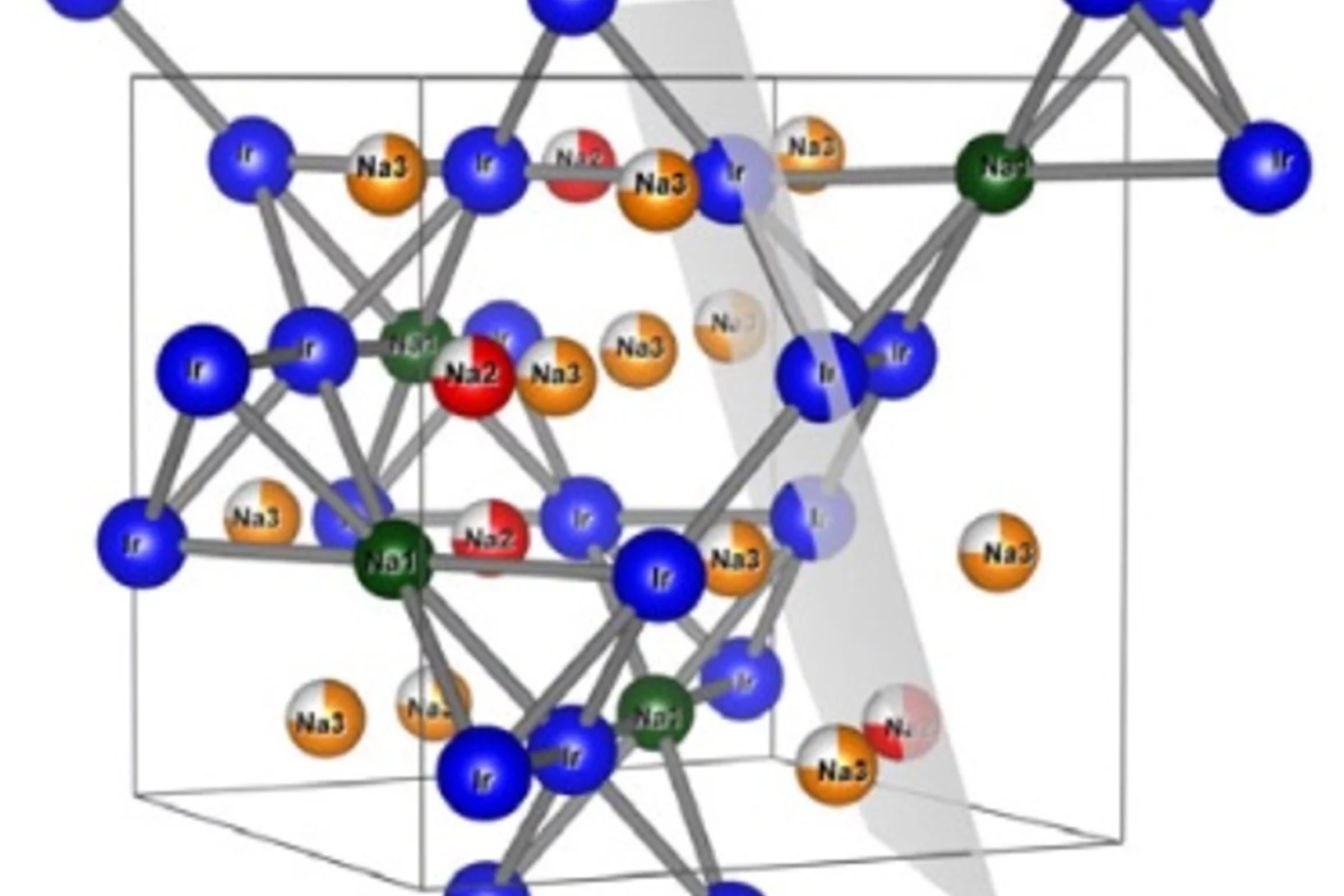
Short-Range Correlations in the Magnetic Ground State of Na4Ir3O8
The magnetic ground state of the Jeff = 1/2 hyperkagome lattice in Na4Ir3O8 is explored via combined bulk magnetization, muon spin relaxation, and neutron scattering measurements. A short-range, frozen state comprised of quasistatic moments develops below a characteristic temperature of TF = 6K, revealing an inhomogeneous distribution of spins occupying the entirety of the sample volume. Quasistatic, short- range spin correlations persist until at least 20 mK and differ substantially from the nominally dynamic response of a quantum spin liquid. Our data demonstrate that an inhomogeneous magnetic ground state arises in Na4Ir3O8 driven either by disorder inherent to the creation of the hyperkagome lattice itself or stabilized via quantum fluctuations.
Measurement of the parameter ξ″ in polarized muon decay and implications on exotic couplings of the leptonic weak interaction
The muon decay parameter ξ″ has been determined in a measurement of the longitudinal polarization of positrons emitted from polarized and depolarized muons. The result, ξ″ = 0.981 ± 0.045stat ± 0.003syst, is consistent with the Standard Model prediction of unity, and provides an order of magnitude improvement in the relative precision of this parameter. This value sets new constraints on exotic couplings beyond the dominant V-A description of the leptonic weak interaction.
Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2014 for high-resolution 3D hard X-ray microscopy
The 2014 Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation was bestowed to researchers Ana Diaz, Manuel Guizar-Sicairos, Mirko Holler, and Jörg Raabe from the Paul Scherrer Institut, Switzerland, for their contributions to method and instrumentation development, which have set new standards in high-resolution 3D hard X-ray microscopy.
k=0 Magnetic Structure and Absence of Ferroelectricity in SmFeO3
SmFeO3 has attracted considerable attention very recently due to its reported multiferroic properties above room temperature. We have performed powder and single crystal neutron diffraction as well as complementary polarization dependent soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy measurements on floating-zone grown SmFeO3 single crystals in order to determine its magnetic structure. We found a k=0 G-type collinear antiferromagnetic structure that is not compatible with inverse Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction driven ferroelectricity. While the structural data reveal a clear sign for magneto-elastic coupling at the Néel-temperature of ∼675 K, the dielectric measurements remain silent as far as ferroelectricity is concerned.
SwissFEL ready for assembly
Researchers from PSI have spent the last four years developing key technologies for the X-ray laser SwissFEL and subjecting them to the acid test in the injector test facility. Now that the development programme has drawn to a close, the installation of the new large research facility is due to get underway in early 2015.
Ist dies der richtige Zeitpunkt für ein waghalsiges Experiment?
PSI-Direktor Joël Mesot hat sich heute in der Aargauer Zeitung mit einem Gastkommentar zur Debatte um die Ecopop-Initiative geäussert. Lesen Sie hier seinen vollständigen Text.This news release is only available in German.
Das Kompetenzzentrum Speicherung zieht nach einem Jahr Bilanz
Am vergangenen 4. November fand am Paul Scherrer Institut das erste Jahressymposium des Kompetenzzentrum des Bundes für Forschung zu Strom- und Wärmespeicherung (SCCER Heat and Electricity Storage) statt. Vertreter aus den beteiligten Forschungsgruppen sowie aus Industrieunternehmen mit einem Bezug zum Thema Speicherung berichteten in ihren Vorträgen über die jüngsten Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Wärme- und Stromspeicherung in der Schweiz. Die Tagung zeigte die Intensität der Transformationen, die von der Energiestrategie 2050 in Gang gesetzt worden sind.This news release is only available in German.
When thawing glaciers release pollutants
As glaciers increasingly melt in the wake of climate change, it is not only the landscape that is affected. Thawing glaciers also release many industrial pollutants stored in the ice into the environment. Now, within the scope of a Swiss National Science Foundation project, researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Empa, ETH Zurich and the University of Berne have measured the concentrations of a class of these pollutants à polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB) à in the ice of an Alpine glacier accurately for the first time.
A high-pressure hydrogen time projection chamber for the MuCap experiment
The MuCap experiment at the Paul Scherrer Institute performed a high-precision measurement of the rate of the basic electroweak process of nuclear muon capture by the proton, μ- + p → n + νμ. The experimental approach was based on the use of a time projection chamber (TPC) that operated in pure hydrogen gas at a pressure of 10 bar and functioned as an active muon stopping target. The TPC detected the tracks of individual muon arrivals in three dimensions, while the trajectories of outgoing decay (Michel) electrons were measured by two surrounding wire chambers and a plastic scintillation hodoscope.