Shifting away from nuclear energy, expanding solar and wind power, generating energy from biomass, reducing energy consumption. Switzerland is committed to becoming climate-neutral by 2050. An ambitious goal, which has become more urgent than ever due to the increasingly challenging geopolitical situation. How can a sustainable and resilient energy supply for Switzerland be established over the coming years? What's the optimal way to use renewable energy sources? What new technologies are especially promising? At PSI, researchers are seeking answers to these crucial questions.
More robust thanks to imperfections
Microscopic deviations from the ideal structure render uranium dioxide, the fuel commonly used in nuclear power plants, more resistant to radiation damage.
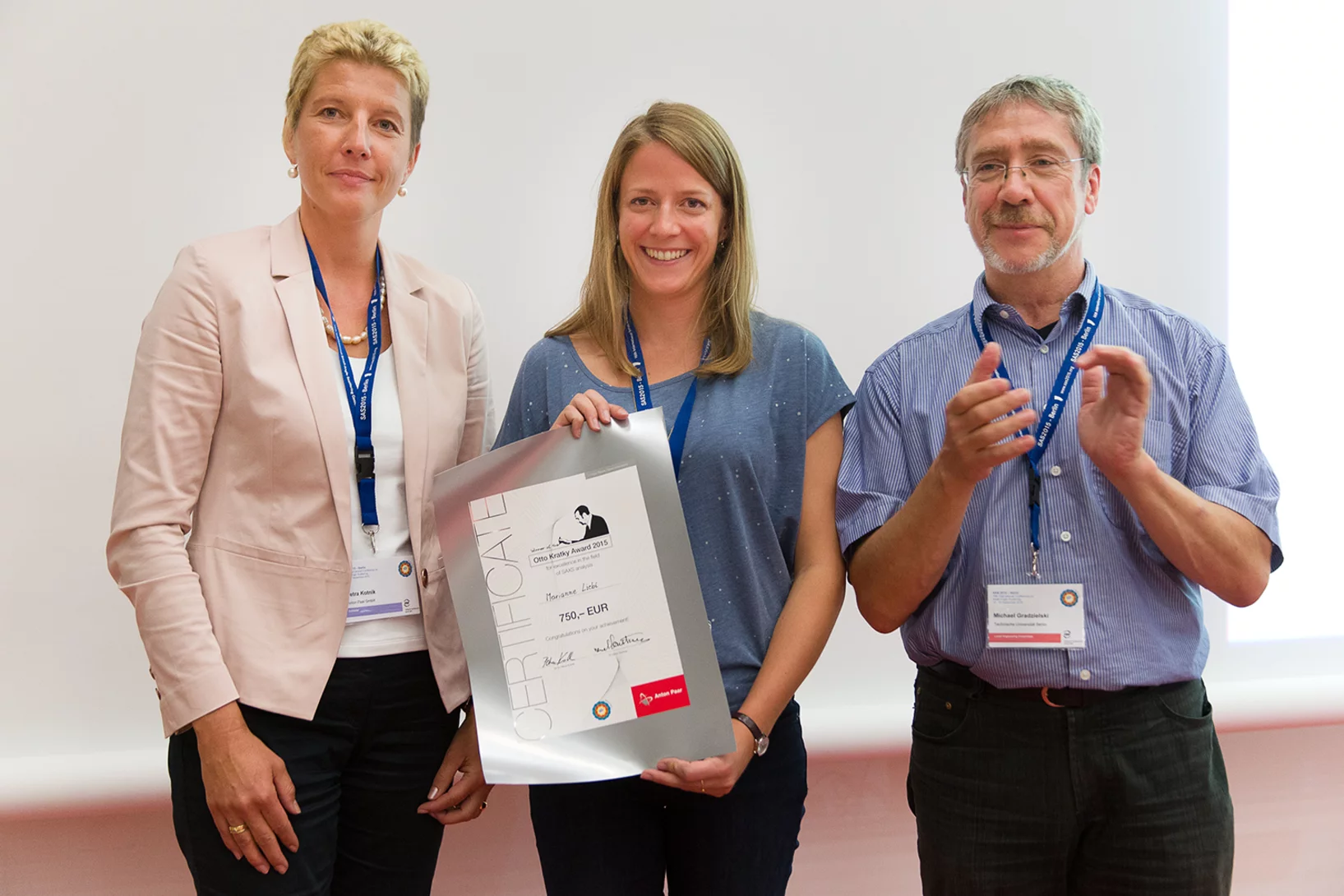
2015 Otto Kratky award
Marianne Liebi was awarded the 2015 Otto Kratky award by the Helmholtz-Centre Berlin for excellence in the field of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis. The award was bestowed in the last SAS2015 conference in Berlin. Marianne is a postdoctoral fellow in the coherent X-ray scattering group (CXS) in PSI, carrying out research in scanning SAXS measurement and analysis in 2D and 3D. Image credit ©HZB/Michael Setzpfandt
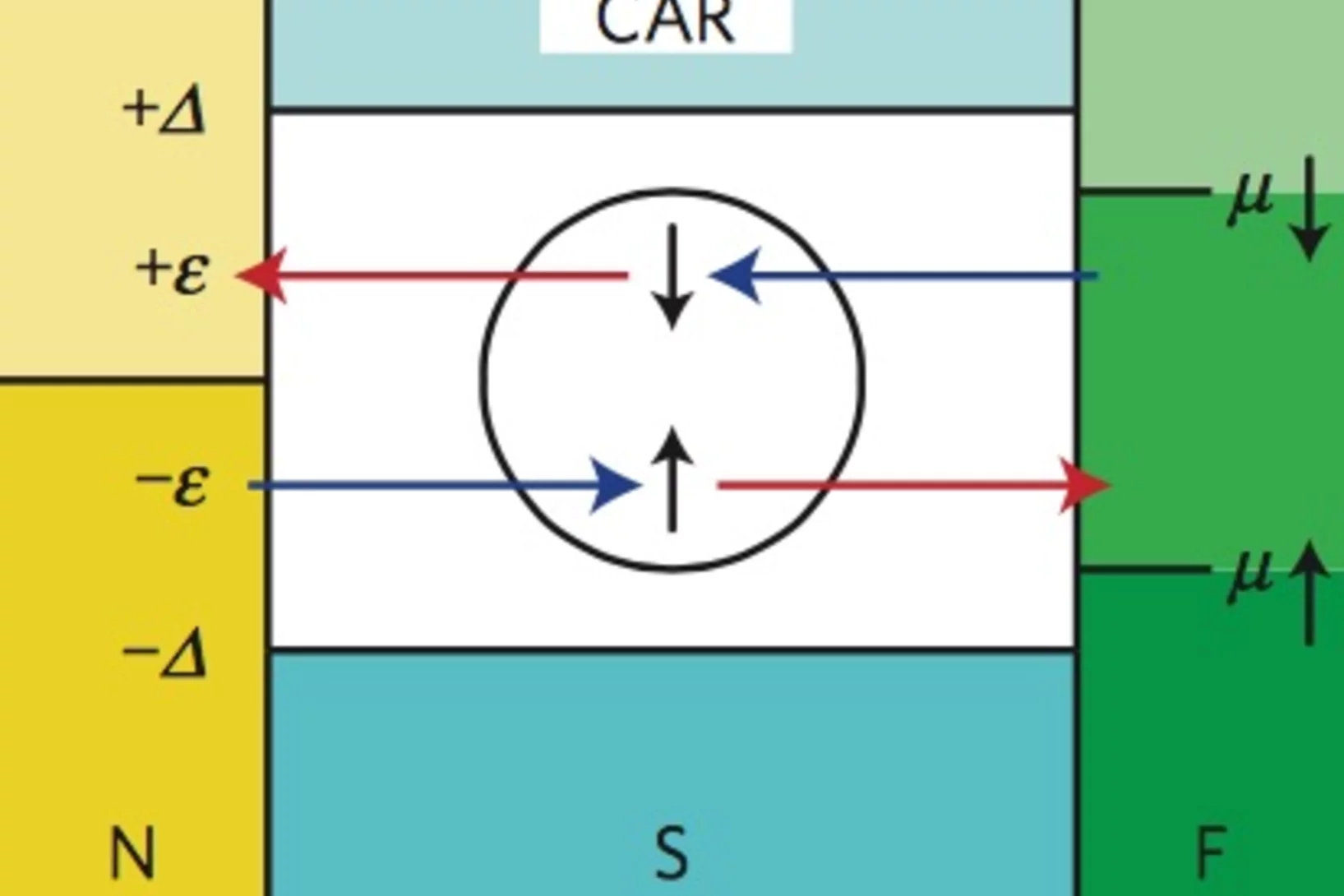
Remotely induced magnetism in a normal metal using a superconducting spin-valve
Superconducting spintronics has emerged in the past decade as a promising new field that seeks to open a new dimension for nanoelectronics by utilizing the internal spin structure of the superconducting Cooper pair as a new degree of freedom. Its basic building blocks are spin-triplet Cooper pairs with equally aligned spins, which are promoted by proximity of a conventional superconductor to a ferromagnetic material with inhomogeneous macroscopic magnetization.
New method will enable most accurate neutron measurement yet
Our universe consists of significantly more matter than existing theories are able to explain. This is one of the great puzzles of modern science. One way to clarify this discrepancy is via the neutron’s so-called electric dipole moment. In an international collaboration, researchers at PSI have now devised a new method which will help determine this dipole moment more accurately than ever before.
Perfect beamlines go unnoticed
Interview with Luc PattheyLuc Patthey is in charge of designing and implementing the beamlines for the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL. In this Interview, he explains the requirements the beamlines need to meet for the X-ray light pulses generated by SwissFEL to reach the experiments in an optimal form and what role collaborations play in the development of beamlines.
Water pathways make fuel cells more efficient
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have developed a coating technique in the laboratory conditions that could raise the efficiency of fuel cells. The PSI scientists have already applied to patent the technique, which is suitable for mass production.
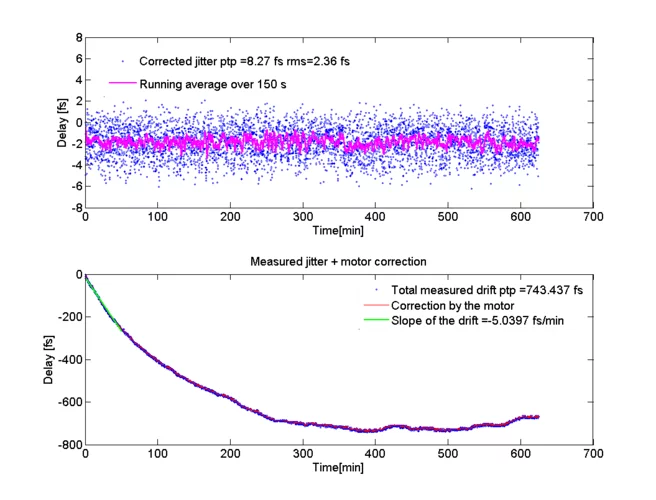
Laser arrival time measurement and correction for the SwissFEL lasers
To probe ultrafast processes at SwissFEL it is crucial that the pump laser, used at the end stations, arrives in time with the generated X-ray pulses. For fs resolution pump probe experiments a path-length change of few-hundred nanometers already affects the measurement quality. The length of SwissFEL and the total propagation path of the pump laser light to the experiment is in the scale of several hundred meters, which makes this task challenging.
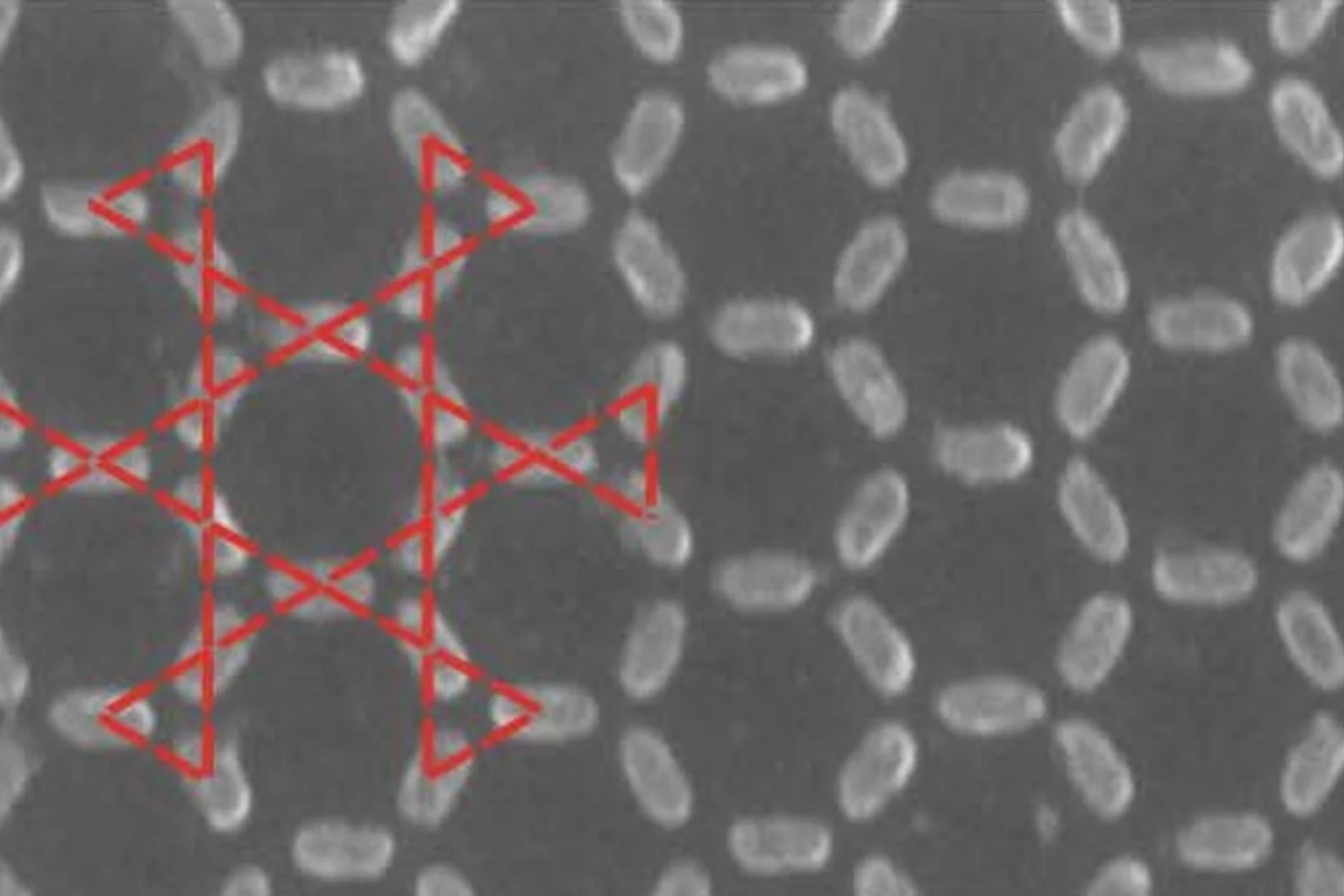
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Materials with interacting magnetic degrees of freedom display a rich variety of magnetic behaviour that can lead to novel collective equilibrium and out-of-equilibrium phenomena. In equilibrium, thermodynamic phases appear with the associated phase transitions providing a characteristic signature of the underlying collective behaviour.
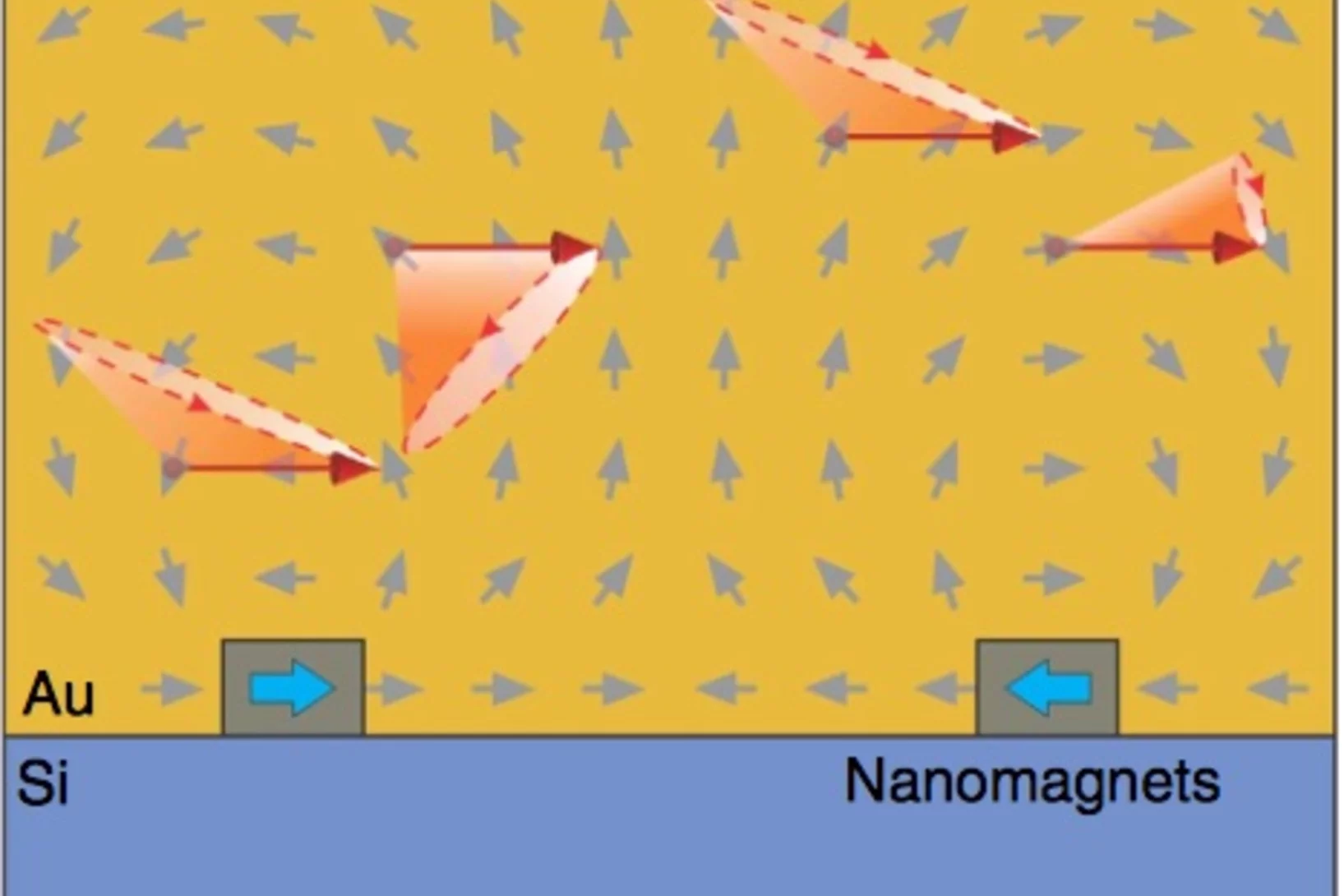
Tiny magnets mimic steam, water and ice
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) created a synthetic material out of 1 billion tiny magnets. Astonishingly, it now appears that the magnetic properties of this so-called metamaterial change with the temperature, so that it can take on different states; just like water has a gaseous, liquid and a solid state.
The key to charging a lithium-ion battery rapidly
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are very durable and can be charged relatively quickly. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), ETH Zurich and Japanese car manufacturer Toyota reveal the reasons for these properties in a new study. The findings were made possible thanks to measurements using a new method at the Swiss Light Source (SLS) at PSI.
Pressure-induced electronic phase separation of magnetism and superconductivity in CrAs
The recent discovery of pressure (p) induced superconductivity in the binary helimagnet CrAs has raised questions on how superconductivity emerges from the magnetic state and on the mechanism of the superconducting pairing. In the present work the suppression of magnetism and the occurrence of superconductivity in CrAs were studied by means of muon spin rotation.
Néel-type skyrmion lattice with confined orientation in the polar magnetic semiconductor GaV4S8
Following the early prediction of the skyrmion lattice (SkL) - a periodic array of spin vortices - it has been observed recently in various magnetic crystals mostly with chiral structure. Although non-chiral but polar crystals with Cnv symmetry were identified as ideal SkL hosts in pioneering theoretical studies, this archetype of SkL has remained experimentally unexplored.
In search of the smallest bit
For increasingly compact storage media, magnetic areas – the memory bits – also need to become smaller and smaller. But just how small can a magnet be? Frithjof Nolting and his colleagues at the Paul Scherrer Institute investigate the surprising phenomena in the field of nanomagnetism.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass. The article was selected to illustrate the cover page of Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 27, Nr. 30.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
B. Wehinger et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 305401 (2015). This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass.
Candidate Quantum Spin Liquid in the Ce3+ Pyrochlore Stannate Ce2Sn2O7
We report the low-temperature magnetic properties of Ce2Sn2O7, a rare-earth pyrochlore. Our suscep- tibility and magnetization measurements show that due to the thermal isolation of a Kramers doublet ground state, Ce2Sn2O7 has Ising-like magnetic moments of ∼1.18 μB. The magnetic moments are confined to the local trigonal axes, as in a spin ice, but the exchange interactions are antiferromagnetic.
Umbrella MoU Signed by 14 Parties
The Memorandum of Understanding of the Umbrella Collaboration was signed by 14 parties: ALBA, DESY, Diamond Light Source Ltd, Elettra, EMBL Heidelberg, ESRF, European XFEL, HZB, ILL, Instruct Academic Services Ltd, KIT, PSI, STFC and SOLEIL.
In Situ Serial Crystallography Workshop at the SLS
The Macromolecular Crystallography group at SLS is organizing a three days workshop on in situ serial crystallography (http://indico.psi.ch/event/issx) between November 17 and 19, 2015. It will be dedicated in the presentation of a novel method facilitating the structure determination of membrane proteins, which are highly important pharmaceutical targets but are difficult to handle using 'classical' crystallographic tools. Designed for 20 Ph.D. students, postdocs and young scientists from both academia and industry, the workshop will consist of introductory lectures, followed by hands-on practicals on in meso or lipidic cubic phase (LCP) crystallization, on in situ serial crystallography data collection using a micro-sized beam and on data processing.
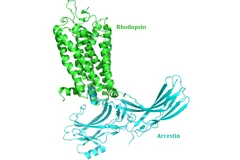
New insight into receptor signalling
A team of 72 investigators across 25 institutions including researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institut obtained the X-ray structure of a rhodopsinàarrestin complex, which represents a major milestone in the area of G-protein-coupled-receptor (GPCR), a protein family recognized in the award of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Terahertz laser light focused to the extreme
There are limits to how short a flash of light can be – in both time and space. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have now succeeded in reaching these physical limits and producing the smallest possible flash. To do so, they used terahertz light, which is physically related to visible light or radio waves, but differs in its wavelength.
Terahertz laser light focused to the extreme
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute have managed to focus the light pulse terahertz laser at the limit of what is permitted by the classical laws of physics. This opens up new possibilities for studying the properties of materials.
New details of the transmission of stimuli in living organisms unveiled
Researchers unveil new details of how cells in a living organism process stimuli. So-called G-proteins, which help conduct external stimuli that reach a cell into its interior, play a central role here. For the first time, the study shows which parts of the G-proteins are vital for their function. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, ETH Zurich, the pharmaceutical company Roche and the British MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology report their results in the journals Nature and Nature Structural and Molecular Biology.
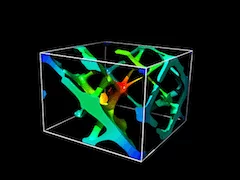
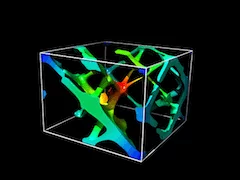
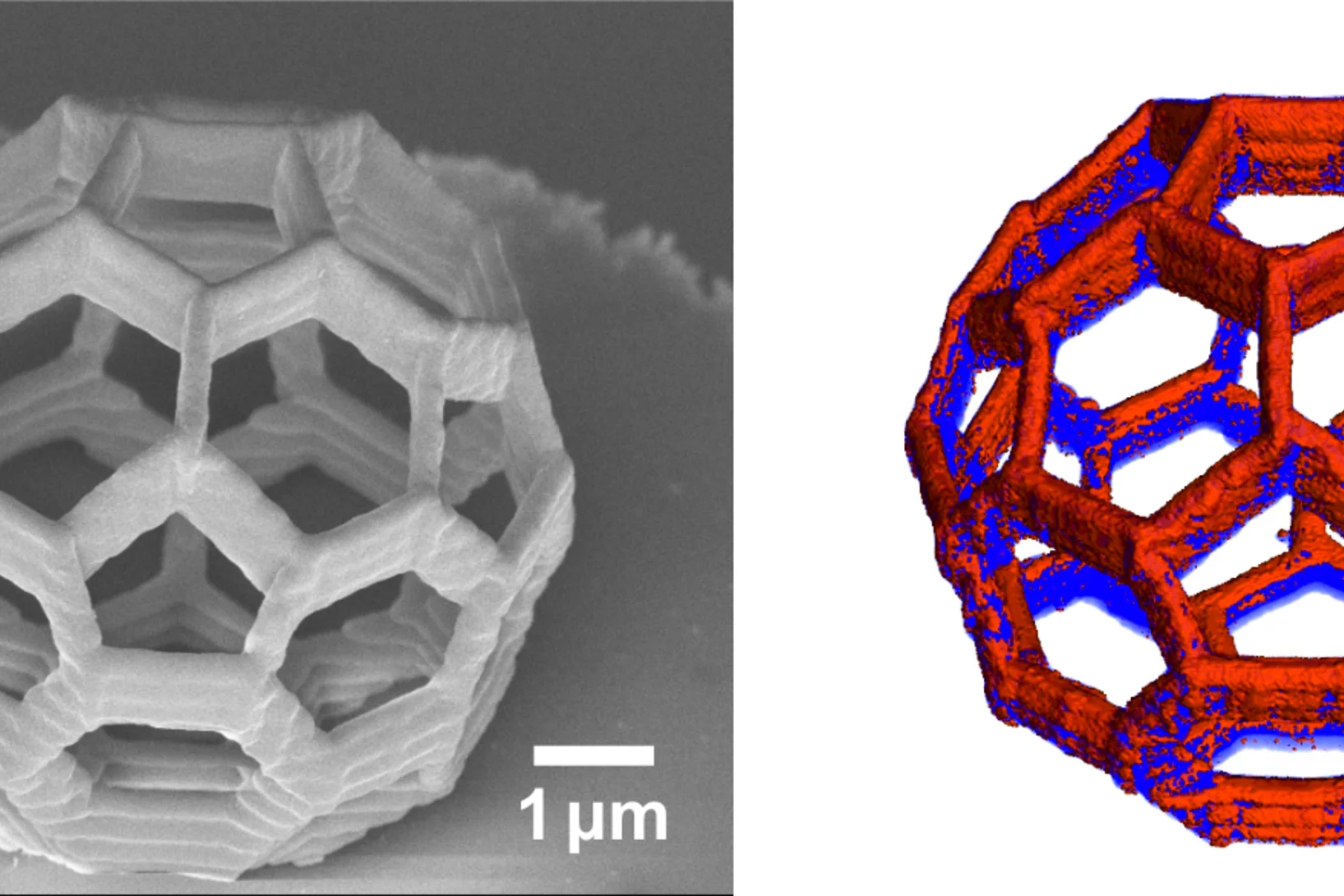
Element-Specific X-Ray Phase Tomography of 3D Structures at the Nanoscale
Recent advances in fabrication techniques to create mesoscopic 3D structures have led to significant developments in a variety of fields including biology, photonics, and magnetism. Further progress in these areas benefits from their full quantitative and structural characterization.
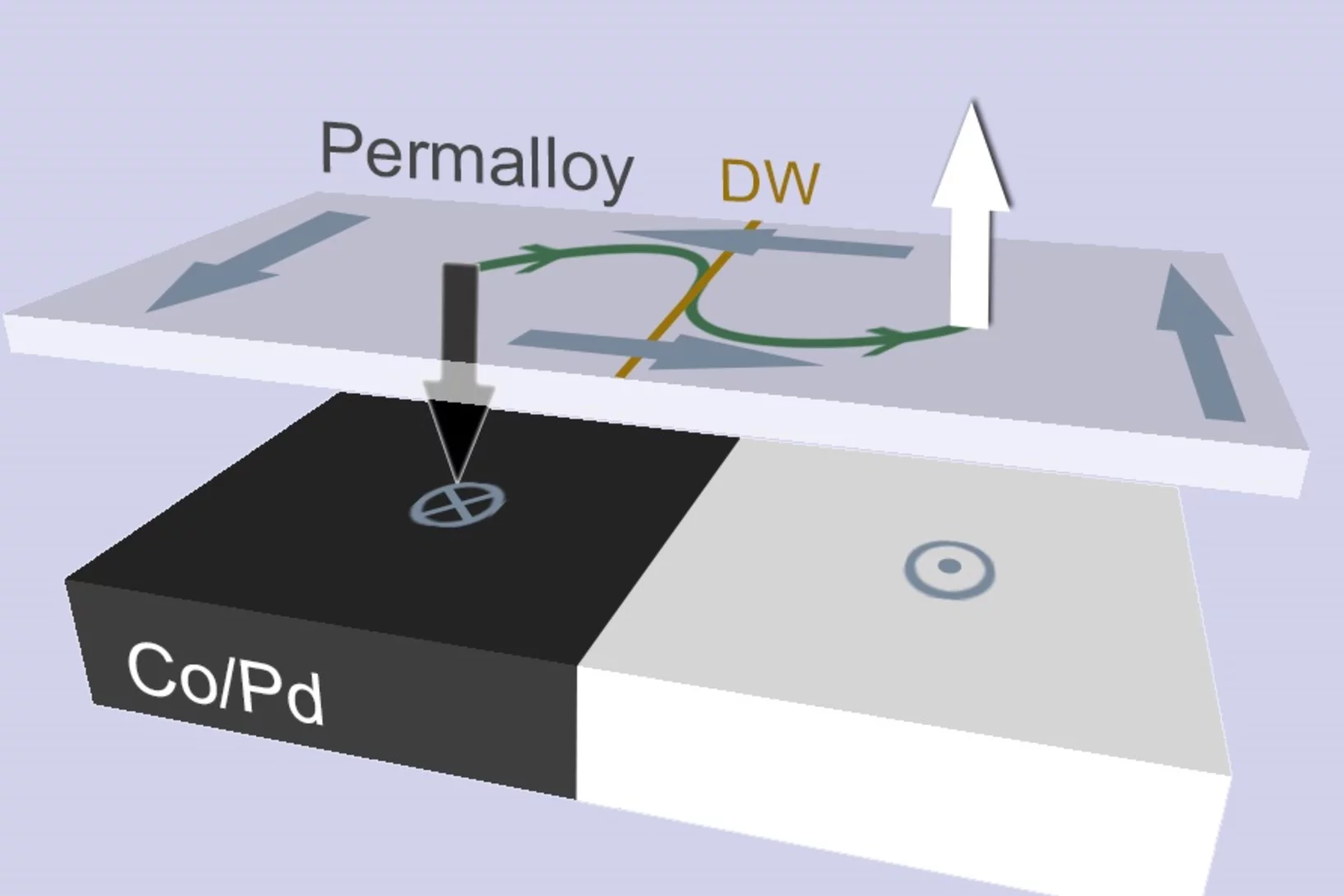
Nanoscale switch for vortex polarization mediated by Bloch core formation in magnetic hybrid systems
Vortices are fundamental magnetic topological structures characterized by a curling magnetization around a highly stable nanometric core.
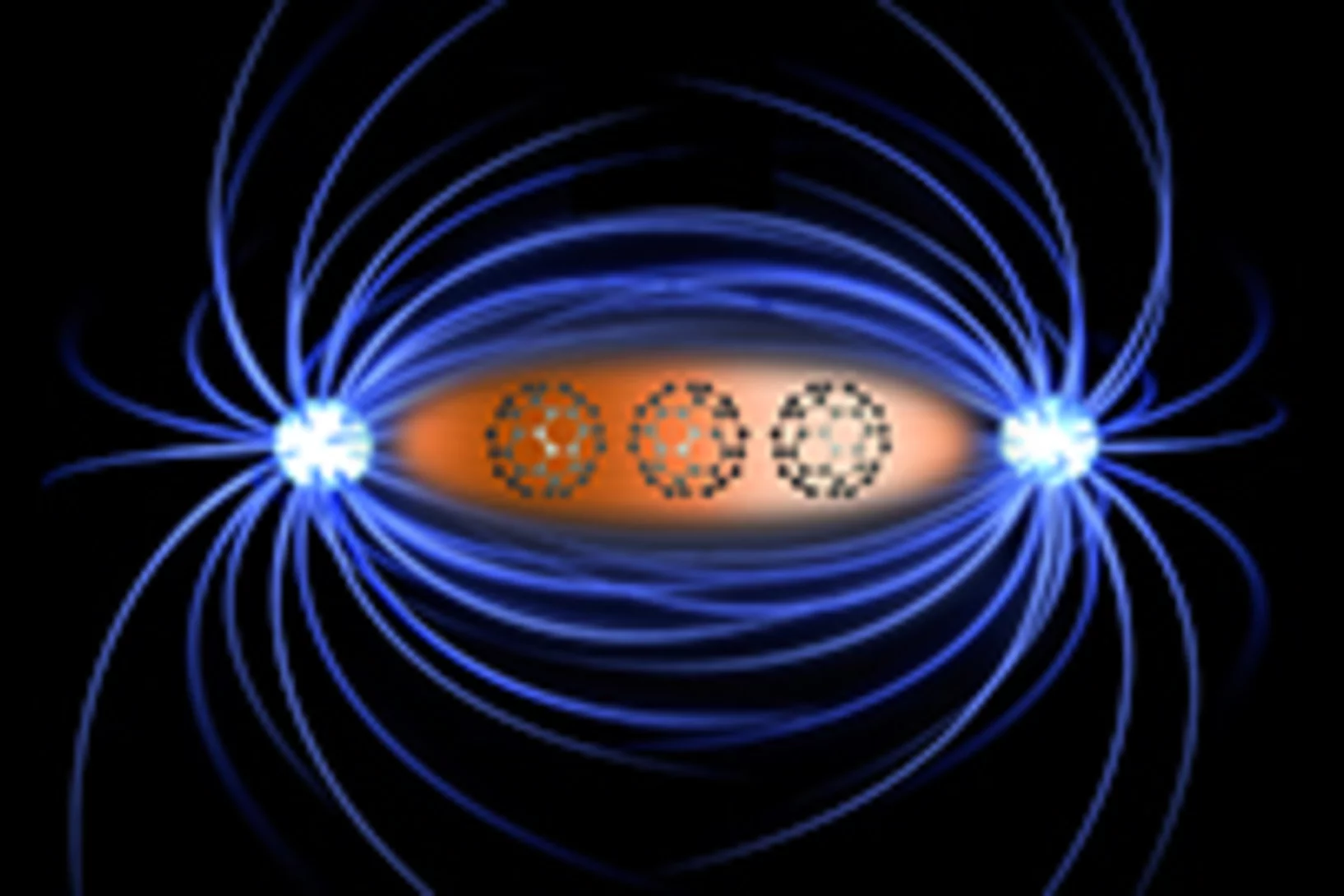
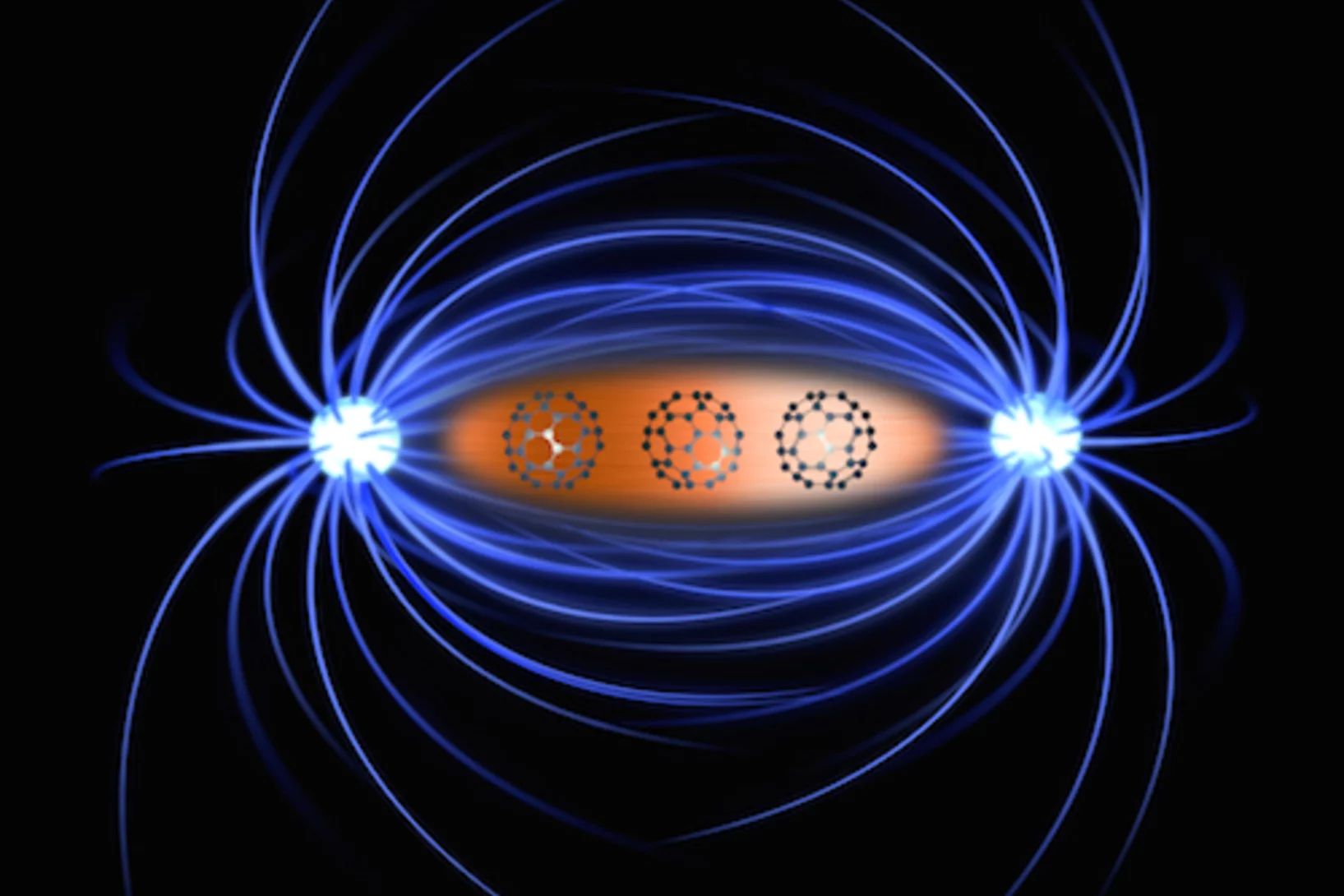
Magnets made of non-magnetic metals
For the first time, an international research team has demonstrated how to generate magnetism in metals that aren’t naturally magnetic, such as copper. The discovery could help develop novel magnets for a wide range of technical applications. Crucial measurements to understand this phenomenon were carried out at PSI à the only place where magnetic processes inside materials can be studied in sufficient detail.
Beating the Stoner criterion using molecular interfaces
Only three elements are ferromagnetic at room temperature: the transition metals iron, cobalt and nickel. The Stoner criterion explains why iron is ferromagnetic but manganese, for example, is not, even though both elements have an unfilled 3d shell and are adjacent in the periodic table: according to this criterion, the product of the density of states and the exchange integral must be greater than unity for spontaneous spin ordering to emerge.
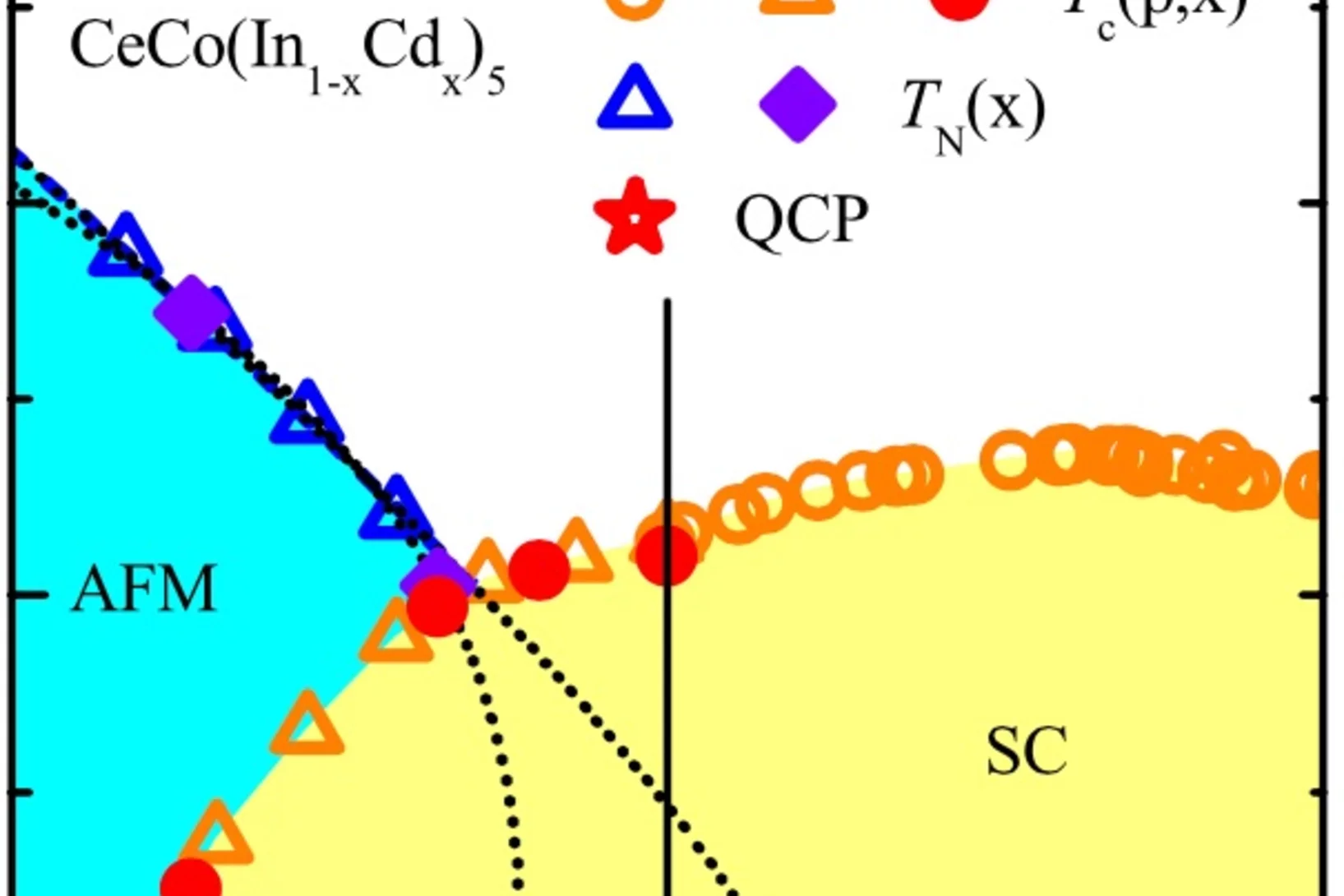
Evidence for Coexistence of Bulk Superconductivity and Itinerant Antiferromagnetism in the Heavy Fermion System CeCo(In1−xCdx)5
In the generic phase diagram of heavy fermion systems, tuning an external parameter such as hydrostatic or chemical pressure modifies the superconducting transition temperature. The superconducting phase forms a dome in the temperature-tuning parameter phase diagram, which is associated with a maximum of the superconducting pairing interaction. Proximity to antiferromagnetism suggests a relation between the disappearance of antiferromagnetic order and superconductivity.
Radioactive waste caught in a cement trap
In a deep geological repository, low and intermediate level radioactive waste from nuclear applications is solidified by cementitious materials for several thousand years. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology have now demonstrated how cement limits the mobility of those radioactive substances. The new findings improve our understanding of the processes involved in this early phase of deep geological disposal.
Fighting tumours with protons
Interview with Damien Charles WeberDamien Charles Weber has been the head and chief physician of the Centre for Proton Therapy, the only centre of its kind in Switzerland, since 2013. In this interview, he talks about the successes of proton therapy in cancer treatment and the objectives for the next few years in this field.
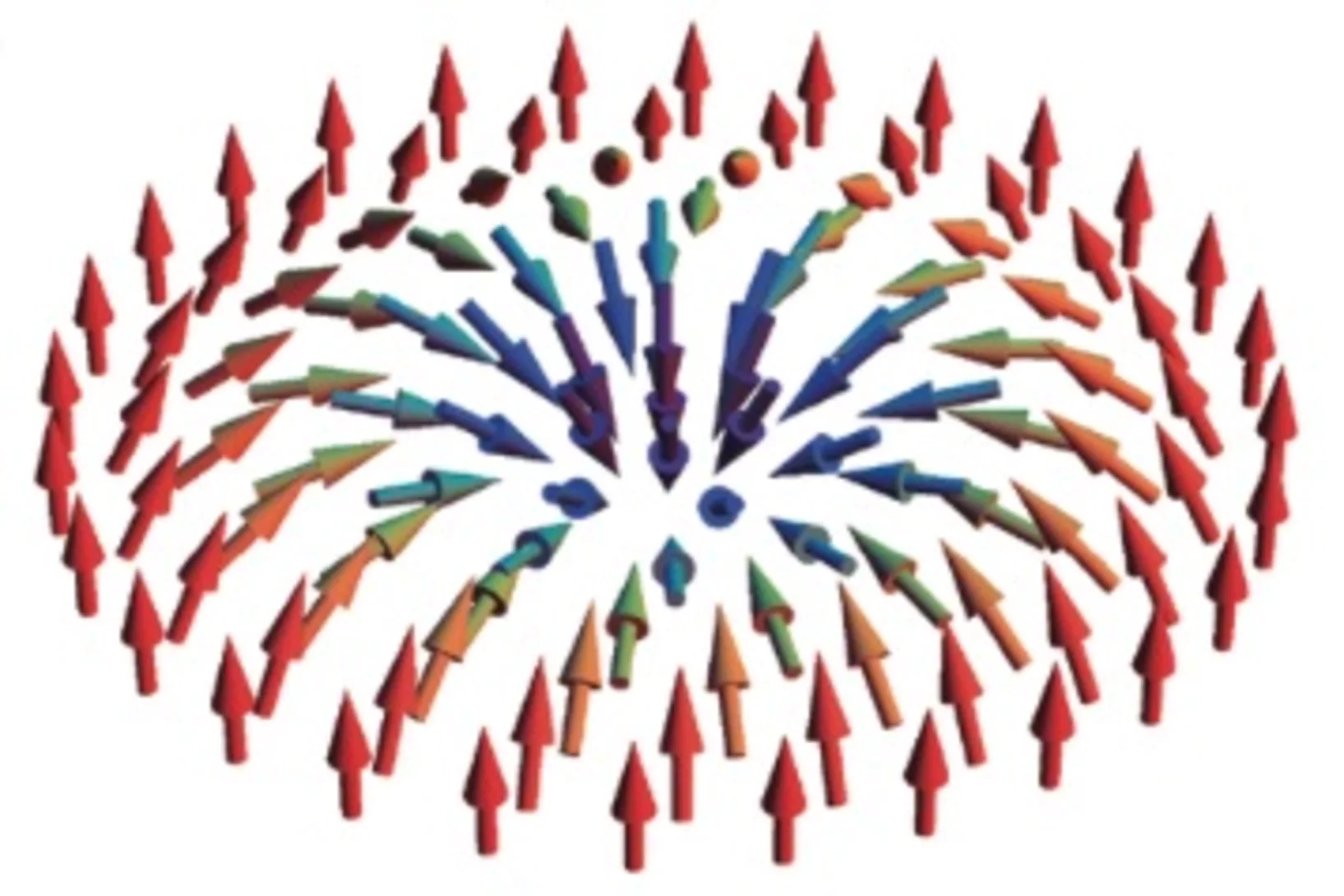
A new class of chiral materials hosting magnetic skyrmions beyond room temperature
Magnetic skyrmions are tiny, magnetic-spin vortices that can emerge in magnetic materials. Due to their nanometric size, skyrmions could be used to build extremely high density memory spintronics devices. However, stable skyrmions are not easy to find and control, and are usually only observed well below room temperature.