Data storage using individual molecules
The research group of Prof. T.A. Jung at the University of Basel has reported on a new method that allows the physical state of just a few atoms or molecules within a network to be controlled.
2018 Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation
The Innovation Award on Synchrotron Radiation 2018 went to Dr. Christian David, also from the Paul Scherrer Institute, and to Prof. Alexei Erko, who recently moved from the HZB to the Institute for Applied Photonics (IAP) in Berlin-Adlershof.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consetetur sadipscing elitr
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consetetur sadipscing elitr, sed diam nonumy eirmod tempor invidunt ut labore et dolore magna aliquyam erat, sed diam voluptua.
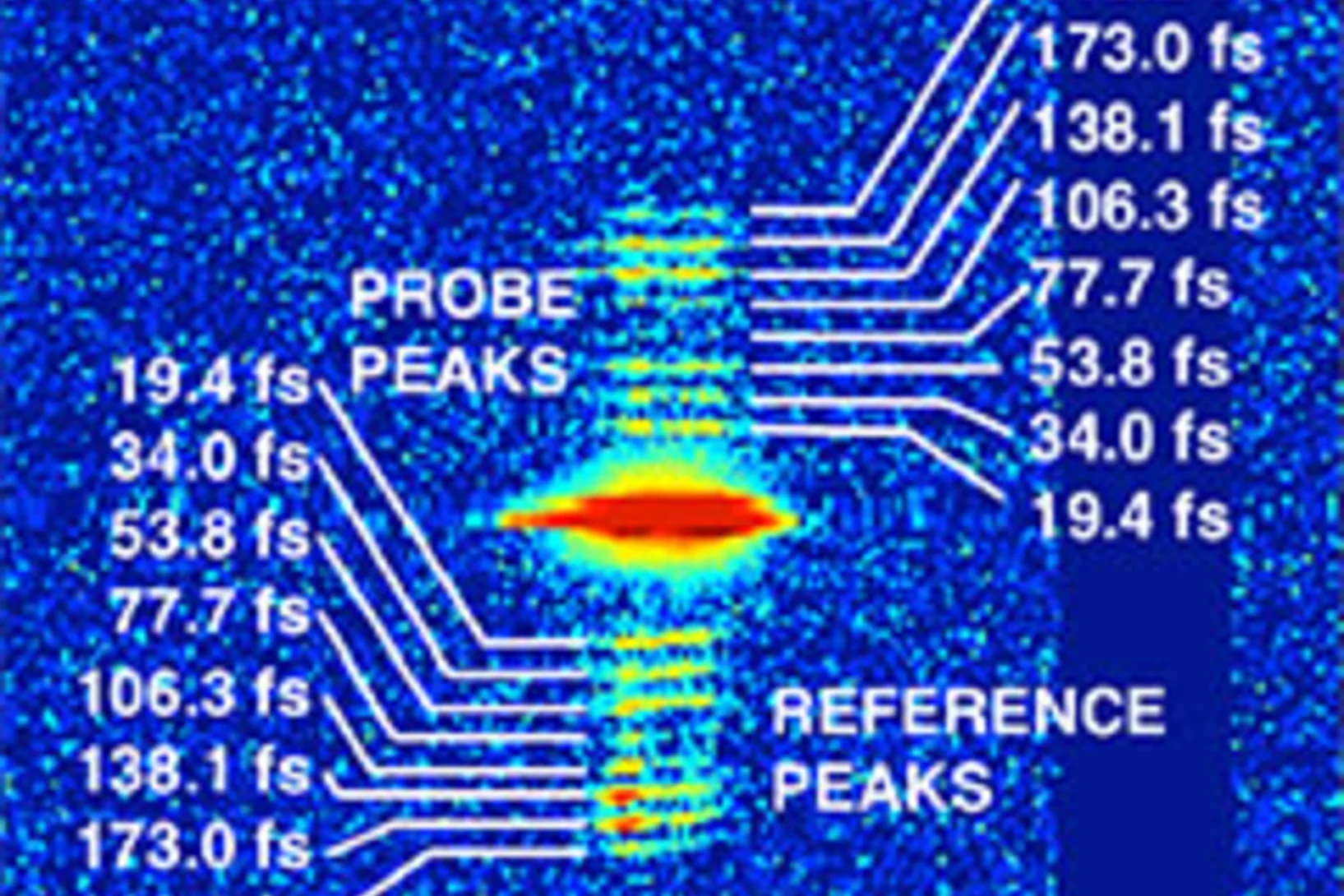
Demonstration of femtosecond X-ray pump X-ray probe diffraction on protein crystals
Our experiments, published in the September issue of Structural Dynamics, demonstrate the feasibility of time-resolved pump-multiprobe X-ray diffraction experiments on protein crystals using a split-and-delay setup which was temporarily installed at the LCLS X-ray Free Electron Laser.
SNI Honorary Membership for Jens Gobrecht
At this year's annual meeting of the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI) Jens Gobrecht, the former Head of LMN, received the SNI Honorary Membership.
Diamond: a gem for micro-optics
Our image of a diamond structure was published on the cover page of the September 2018 issue of the journal "Materials Today". The corresponding paper reports on the nano-frabrication of micro-optical elements in diamond.
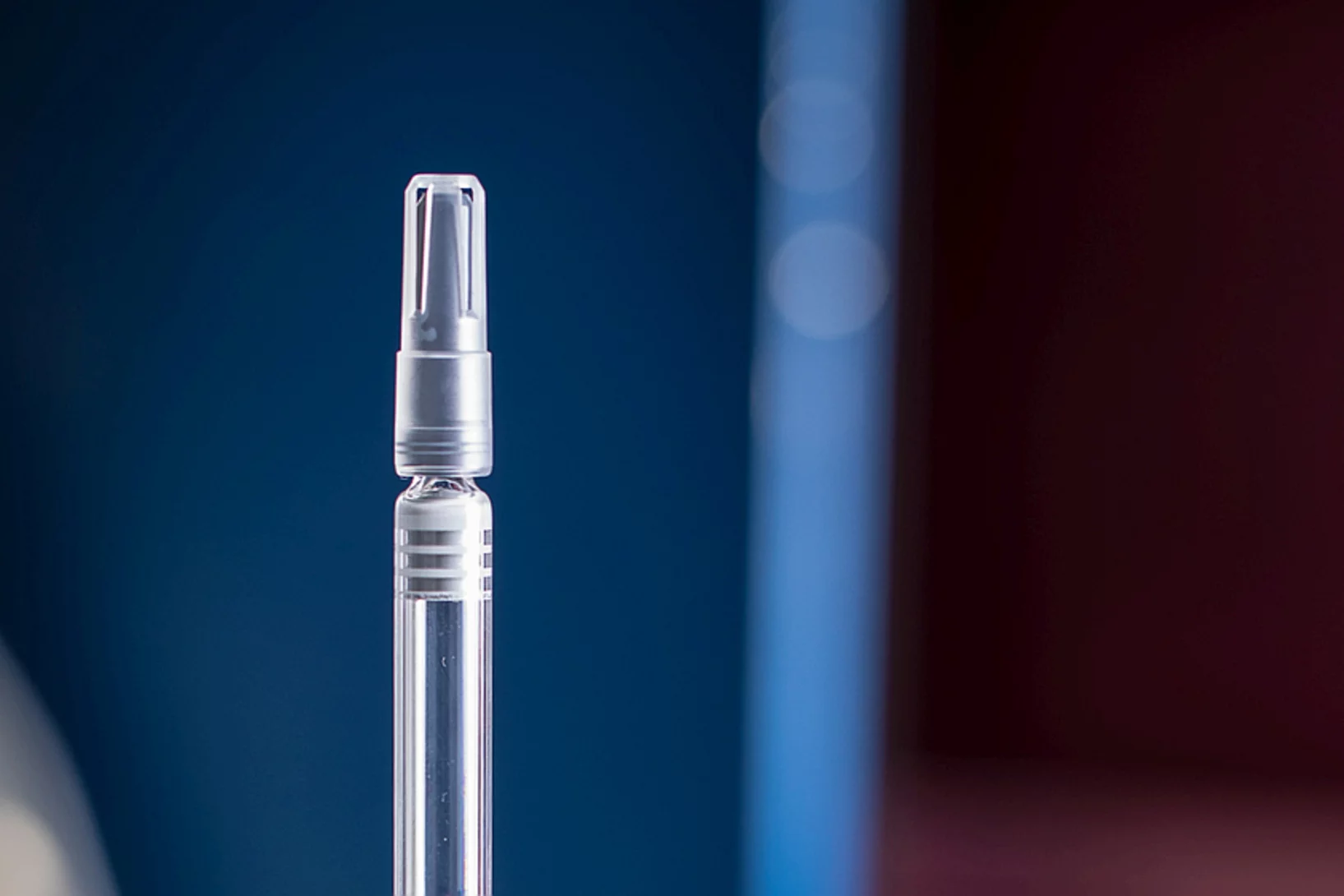
Imaging the inside of injection needles with neutrons
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, the University of Basel and Roche have used neutron imaging to investigate why cool storage is crucial for syringes pre-filled with a liquid medication.
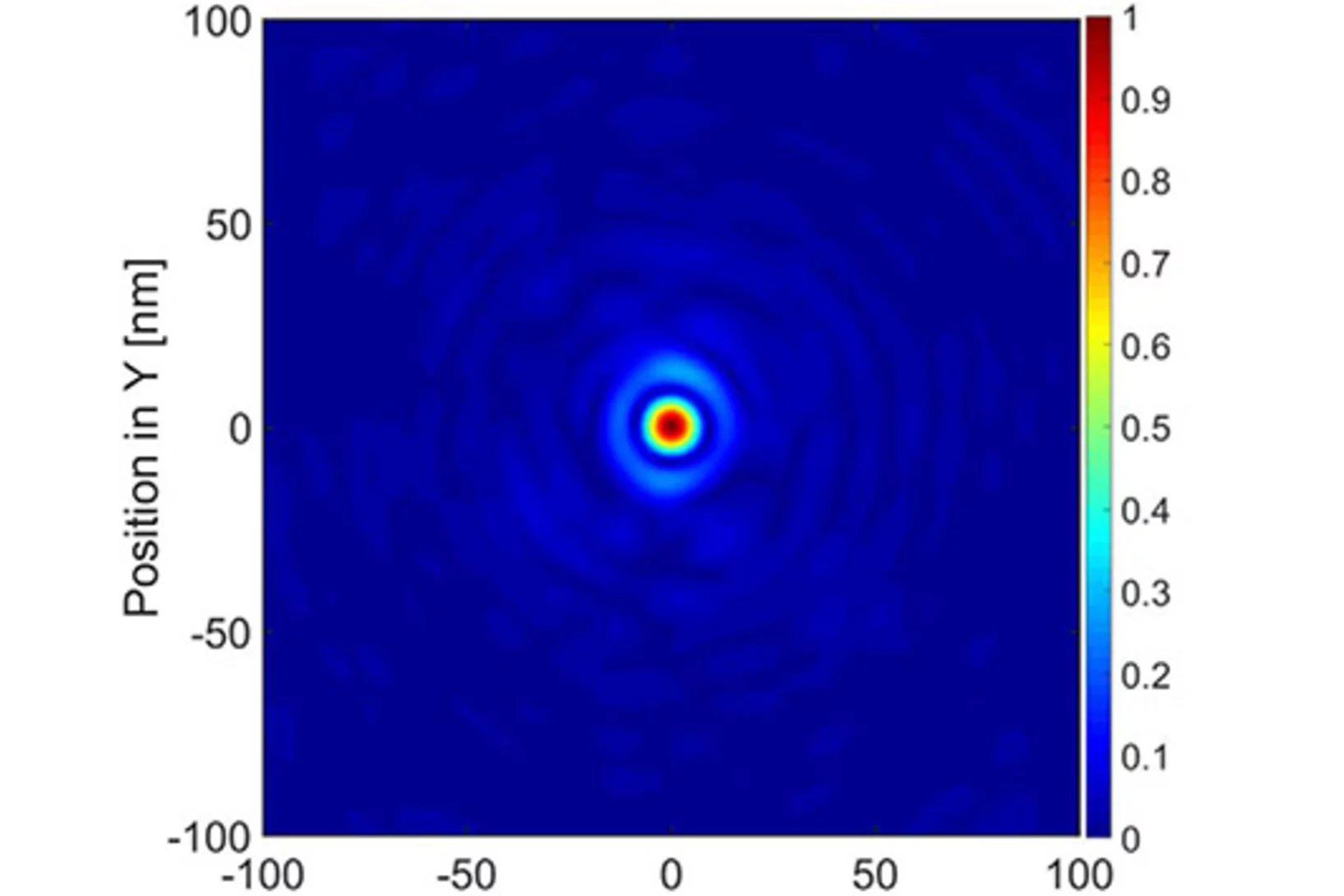
Fresnel Zone Plates with Zone Widths below 10 nm
The spot size of a Fresnel Zone Plate lens is mainly determined by the zone widths of its outermost zone. It is therefore essential to fabricate zone plates with structures as small as possible for high-resolution X-ray microscopy. Researchers at the Laboratory for Micro- and Nanotechnology at the PSI have now developed Fresnel zone plates with zone widths well below 10 nm, down to 6.4 nm. These lenses are capable of pushing resolution in X-ray microscopy to the single-digit regime.
A first glance at the SwissFEL x-rays wave-front
X-ray Free Electron Lasers (XFELs) combine the properties of synchrotron radiation (short wavelengths) and laser radiation (high lateral coherence, ultrashort pulse durations). These outstanding machines allow to study ultra-fast phenomena at an atomic level with unprecedented temporal resolution for answering the most intriguing open questions in biology, chemistry and physics.
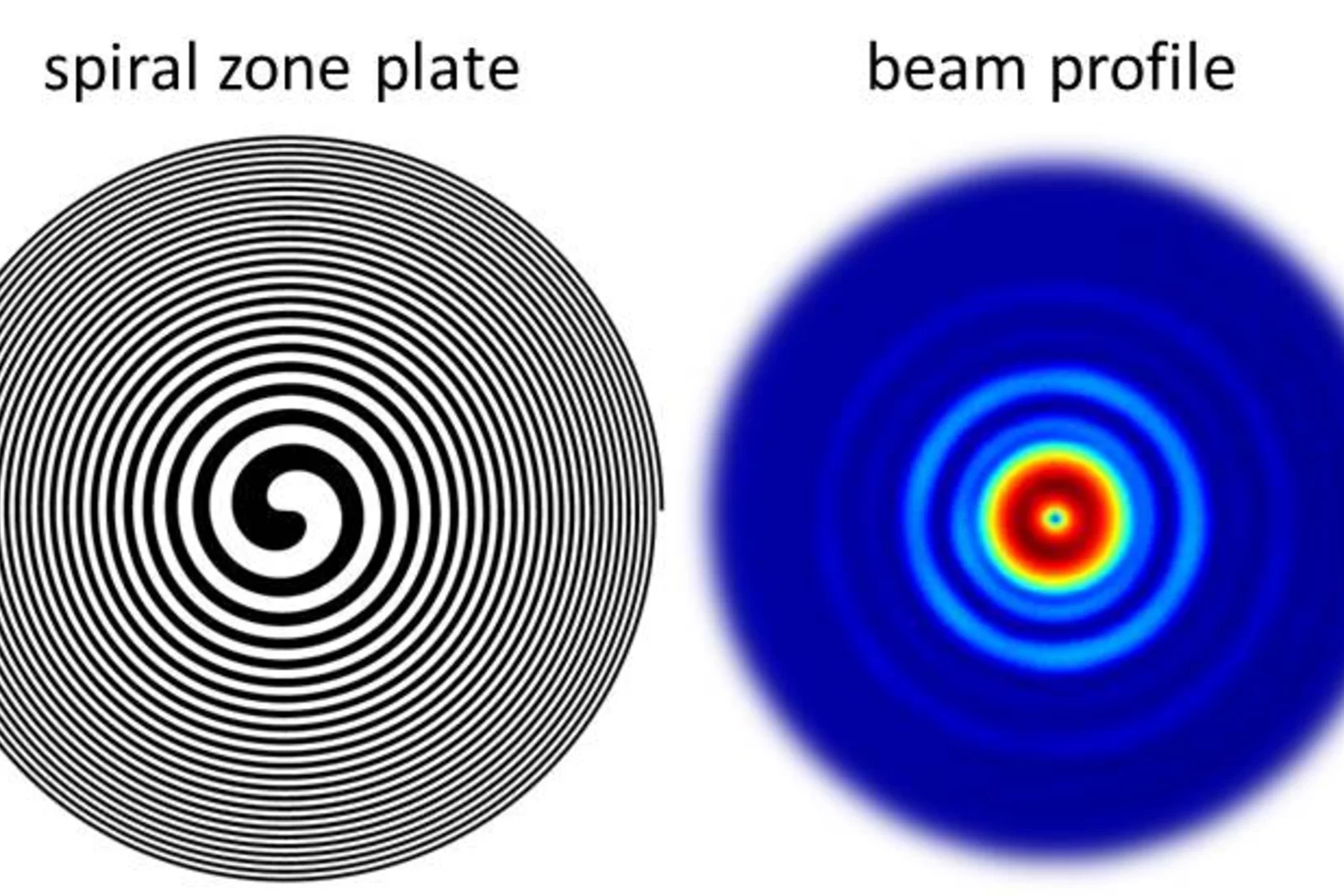
Extreme Ultraviolet Vortices at Free Electron Lasers
PSI scientists have developed tailored diffractive X-ray optics for a free electron laser that induces an optical vortex in extreme ultraviolet radiation. The experiment facilitates the first demonstration of orbital angular momentum in radiation created by a free electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet regime, with an extraordinary clean and defined wavefront. In a collaborative effort with researchers from the FERMI free electron laser in Trieste, Italy and from the University of Nova Gorica in Slovenia, the wavefront of the intense beams carrying an orbtial angular momentum was characterized. Furthermore, a method to characterize the footprint of a focused beam from a free electron laser was refined based on ablation imprints in polymers and subsequent treatment with organic solvents. In this way, the sensitivity of the imprint method could be enhanced to a dynamic range of three orders of magnitude in a single shot.
A new RIXS analyzer scheme based on transmission zone plates
PSI scientists have developed a new type of X-ray optics that allows for analyzing the emission in resonant inelastic x-ray scattering (RIXS) experiments. The new approach combines the energy dispersion with imaging capabilities. In a collaborative effort with research groups from Göttingen and Hamburg, two new classes of RIXS experiments, energy mapping and RIXS imaging, have been demonstrated.
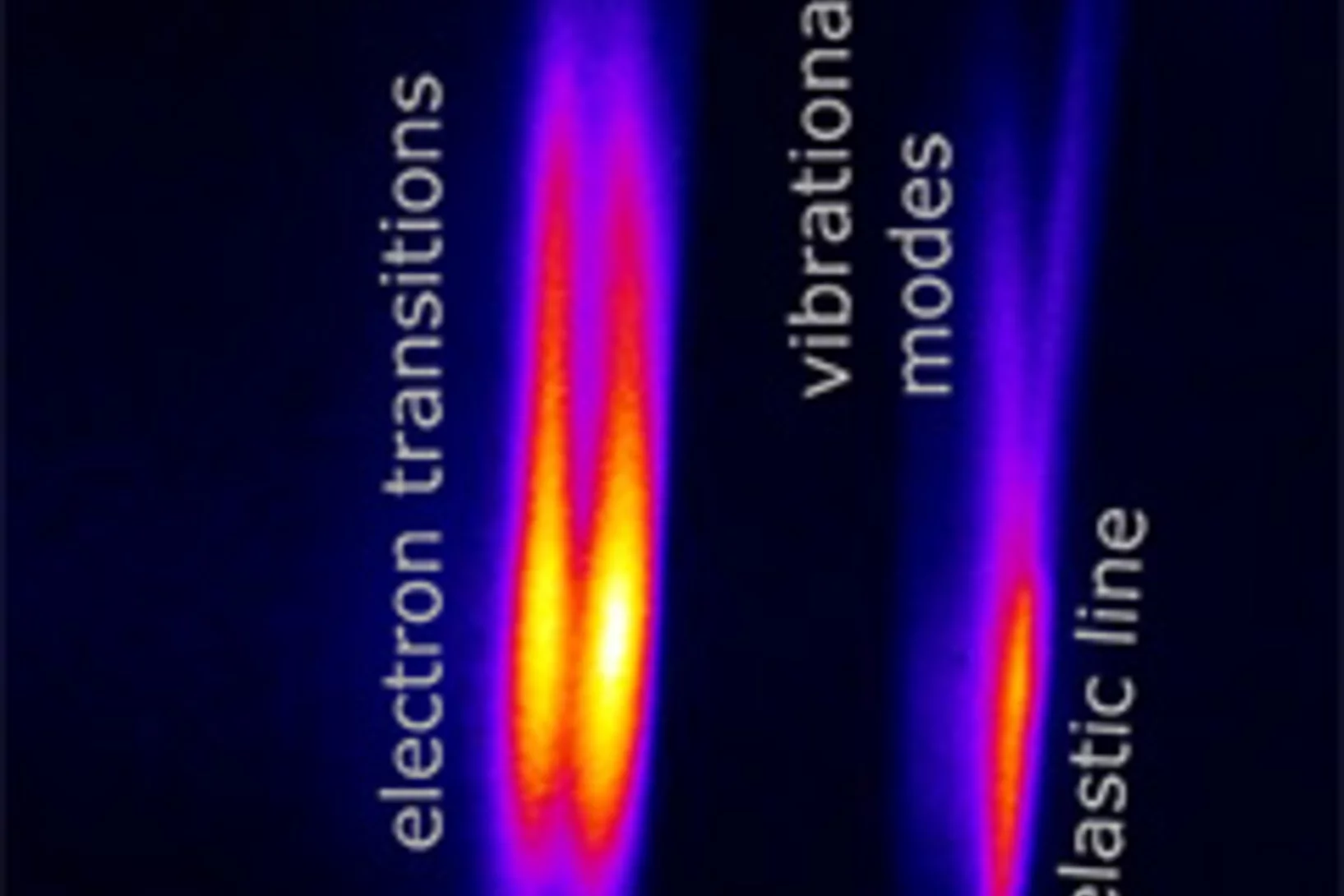
Scientists get first direct look at how electrons ‘dance’ with vibrating atoms
Research experience from California's X-ray free-electron laser benefits SwissFEL. It's the camera that allows researchers to make extremely rapid processes visible: the X-ray free-electron laser. Currently, however, only three sites worldwide—in the US, Japan and South Korea—have facilities capable of carrying out such measurements. Two current articles in Science and Nature Communications co-authored by researchers now at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI exemplify the kind of outstanding scientific work that can be carried out at such facilities, enabling new insights into the mechanisms of superconductors and magnetic switching in molecules. The measurements were conducted at the Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS) free-electron laser in California. Press release PSI / Press release SLAC
Poster Prize for Marcin Gorzny at the Swiss Nanoconvention 2017
Dr. Marcin Gorzny, Post-Doc at LMN in the PSI career return program recieved a poster prize at the Swiss Nanoconvention 2017 for his contribution entitled: "Silicon chip as lipid membrane holder for serial crystallography experiments".
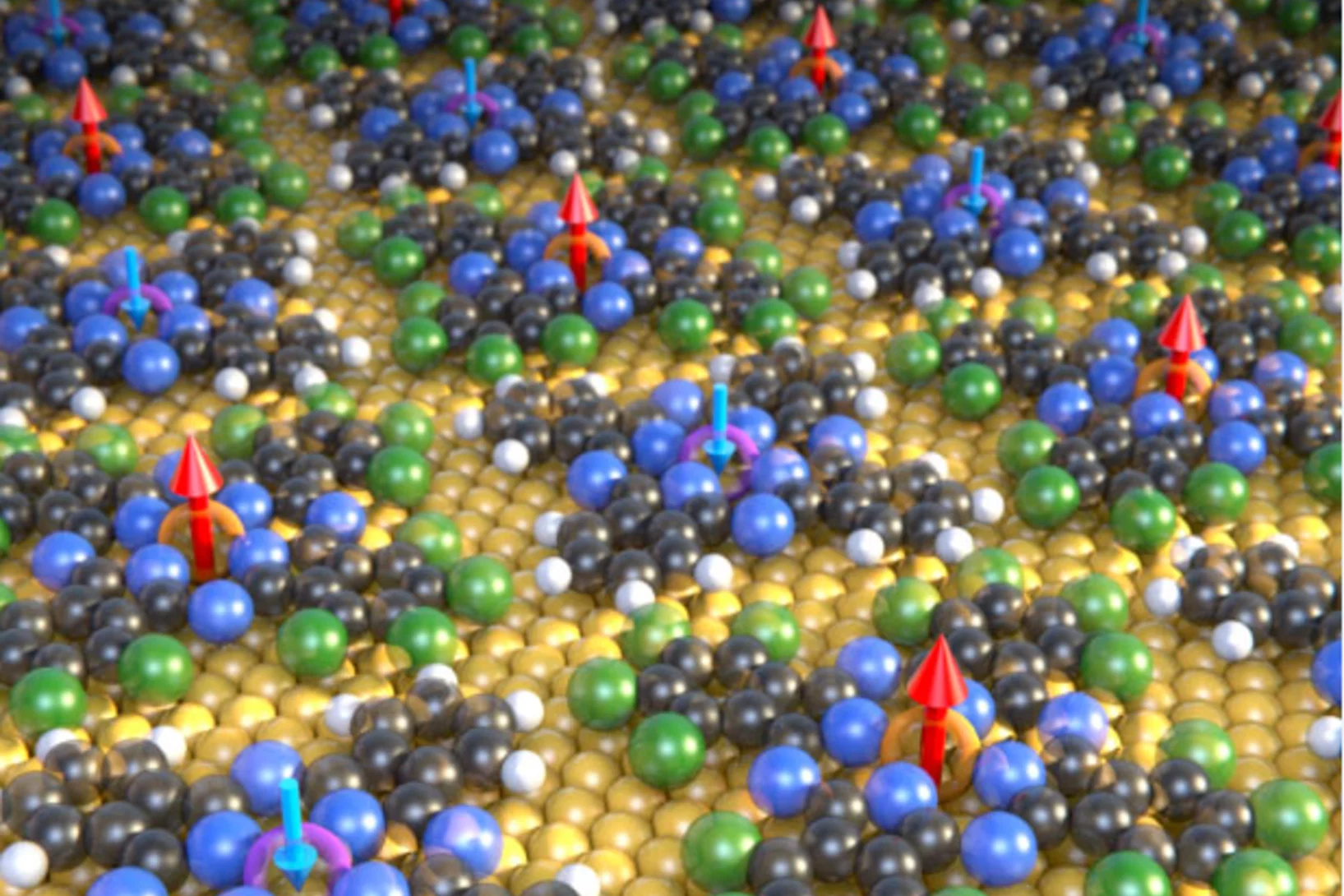
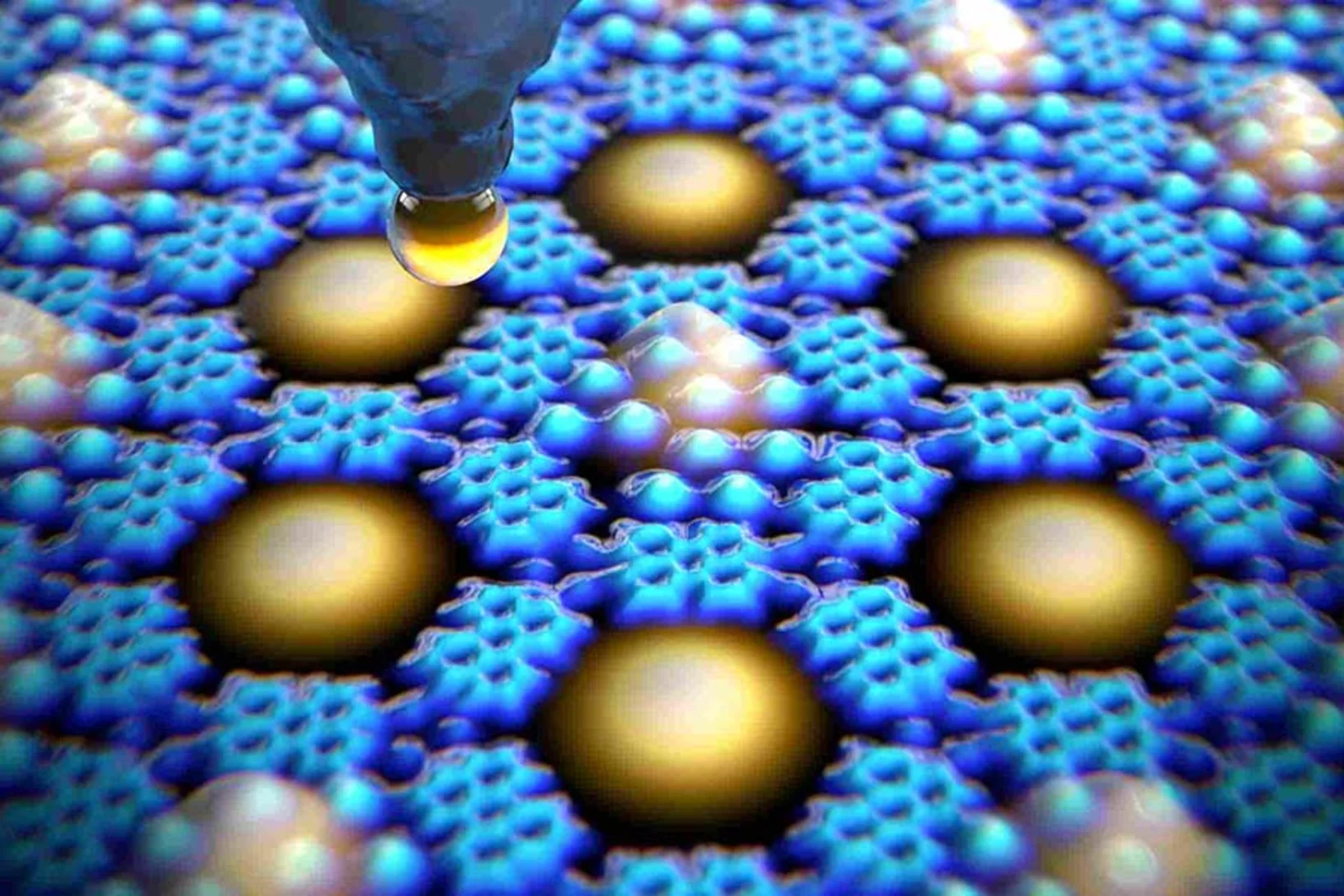
Wafer-thin Magnetic Materials Developed for Future Quantum Technologies
For the first time, researchers have produced a wafer-thin ferrimagnet, in which molecules with different magnetic centers arrange themselves on a gold surface to form a checkerboard pattern. Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute, in collaboration with their research partners, published the findings in the journal Nature Communications.
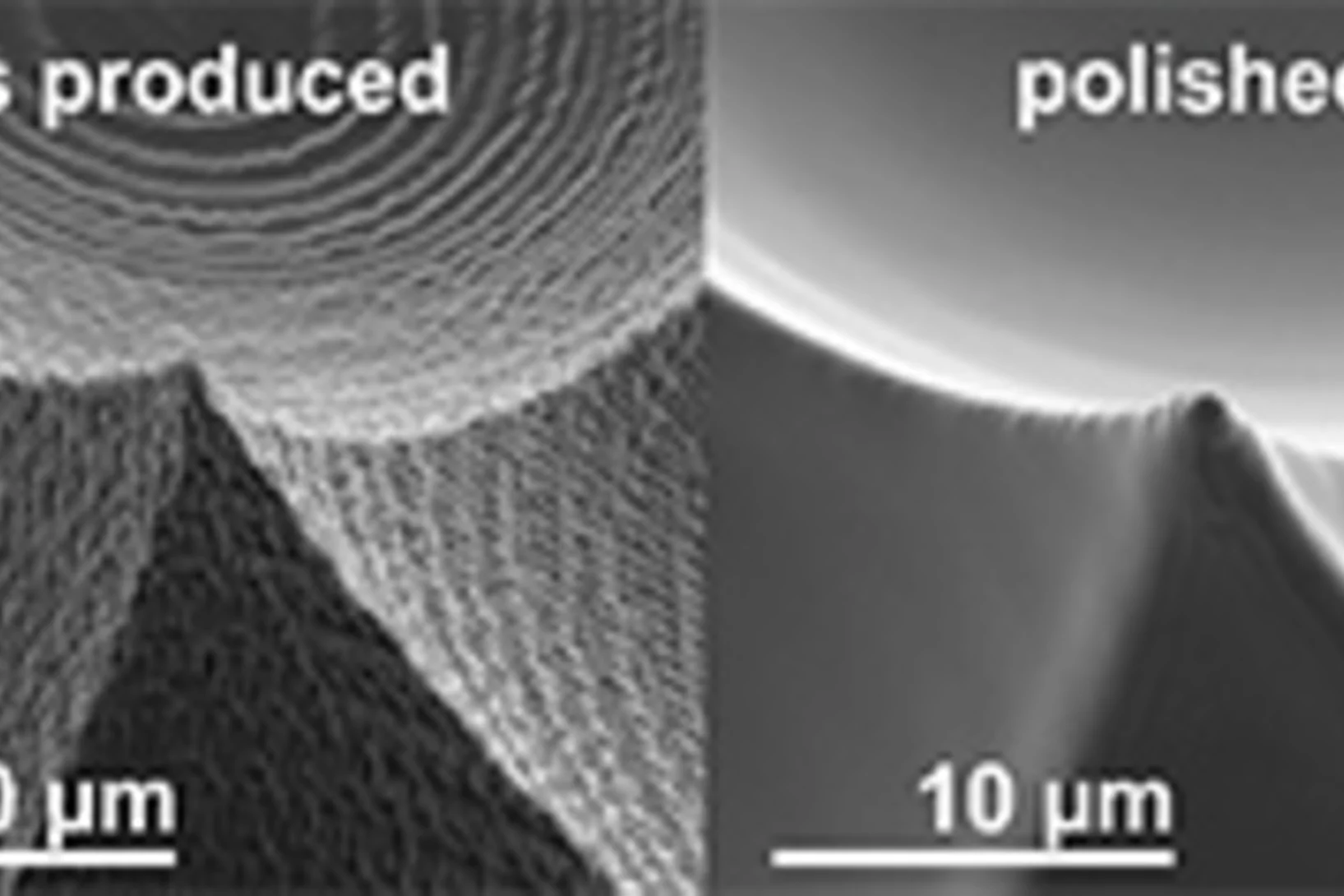
Contact-less micro-polishing
A new method of material modification using 172 nm UV photons enables to fabricate ultra-smooth and self-optimized polymer surfaces. The method, published in Advanced Materials Technologies, was used in the production of high quality micro-optics to remove typical process flaws after a 2-photon-lithography process.
Interlaced zone plates push the resolution limit in x-ray microscopy
A novel type of diffractive lenses based on interlaced structures enable x-ray imaging at resolutions below 10 nm. The fabrication method and the test results of these novel x-ray lenses have been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
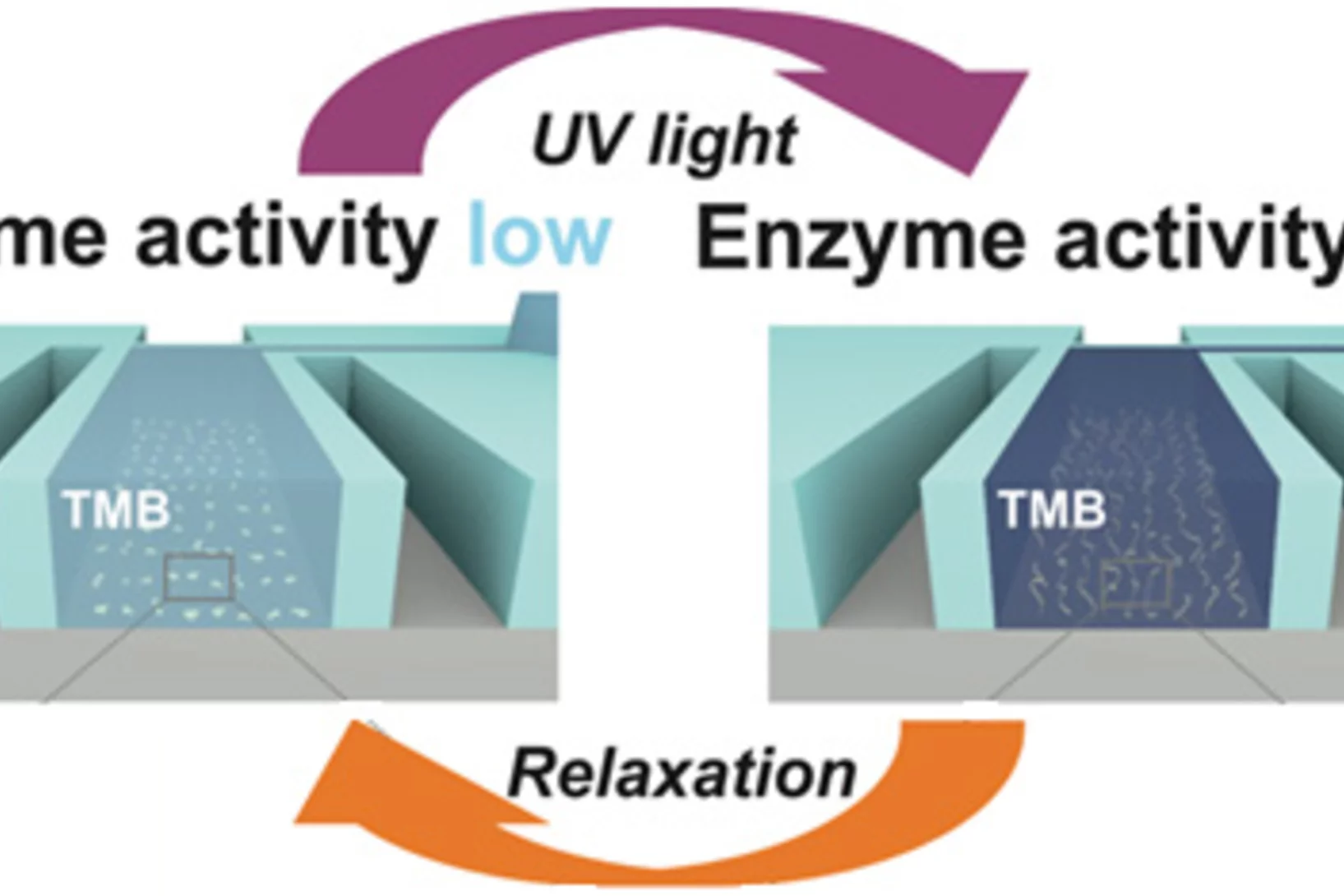
Light-switching of enzymatic activity on orthognonally functionalized polymer brushes
UV- and visible light-induced switching of enzymatic activity has been demonstrated using surface-grafted polymer brushes functionalized with microperoxidase MP-11 and spiropyran mojeties. Integration into an optofluidic device allowed reversible switching of the enzymatic activity under flow.
Nanotechnology enables new insights into chemical reactions
Eighty percent of all products of the chemical industry are manufactured with catalytic processes. Catalysis is also indispensable in energy conversion and treatment of exhaust gases. Industry is always testing new substances and arrangements that could lead to new and better catalytic processes. Researchers of the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI in Villigen and ETH Zurich have now developed a method for improving the precision of such experiments, which may speed up the search for optimal solutions.
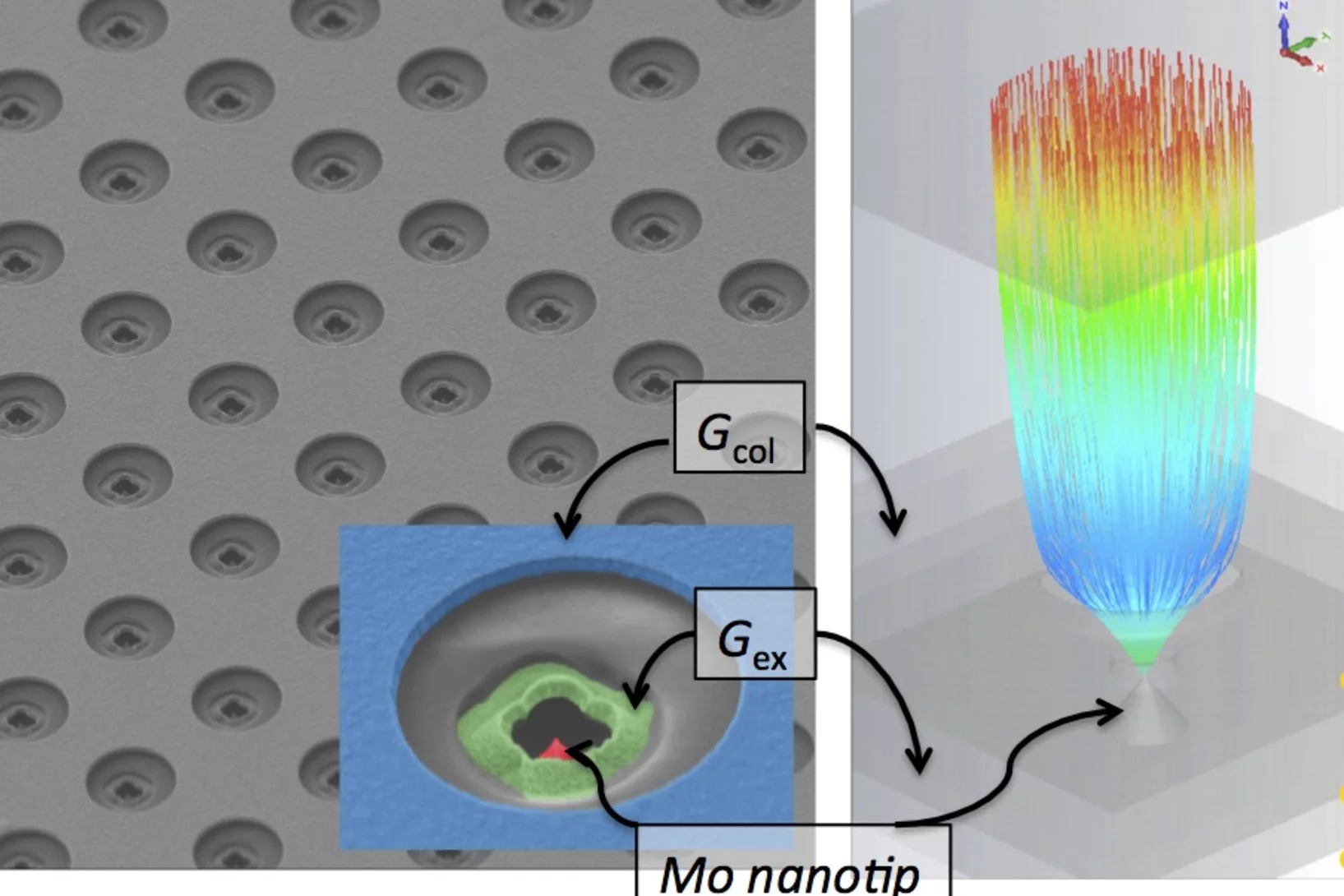
Can a metal nanotip array device be a low-emittance and coherent cathode?
A nanofabricated low emittance field emitter array cathode was demonstrated for the first time, and successfully applied to observe the low-energy electron diffraction from suspended monolayer graphene. The work has an impact on the future development of compact X-ray free electron lasers, THz/RF vacuum electronic sources, and ultrafast electron imaging and diffraction experiments.
Technology award for microneedle-optofluidic sensor system
Sahan Ranamukhaarachchi, PhD student from UBC in Vancouver, won the 2016 "Brian L. Barge Award for Excellence in Microsystems Integration" for his work on a biosensing platform with integrated hollow microneedles carried out at PSI in 2015 in collaboration with Dr. Victor Cadarso and Dr. Celestino Padeste.
Therapeutic drug monitoring in sub-nanoliter volumes
A promising system for painless and minimally-invasive therapeutic drug monitoring has been demonstrated. The proposed device combines biofunctionalized hollow microneedles with an optofluidic system to measure drug concentrations in volumes as small as 0.6 nL.
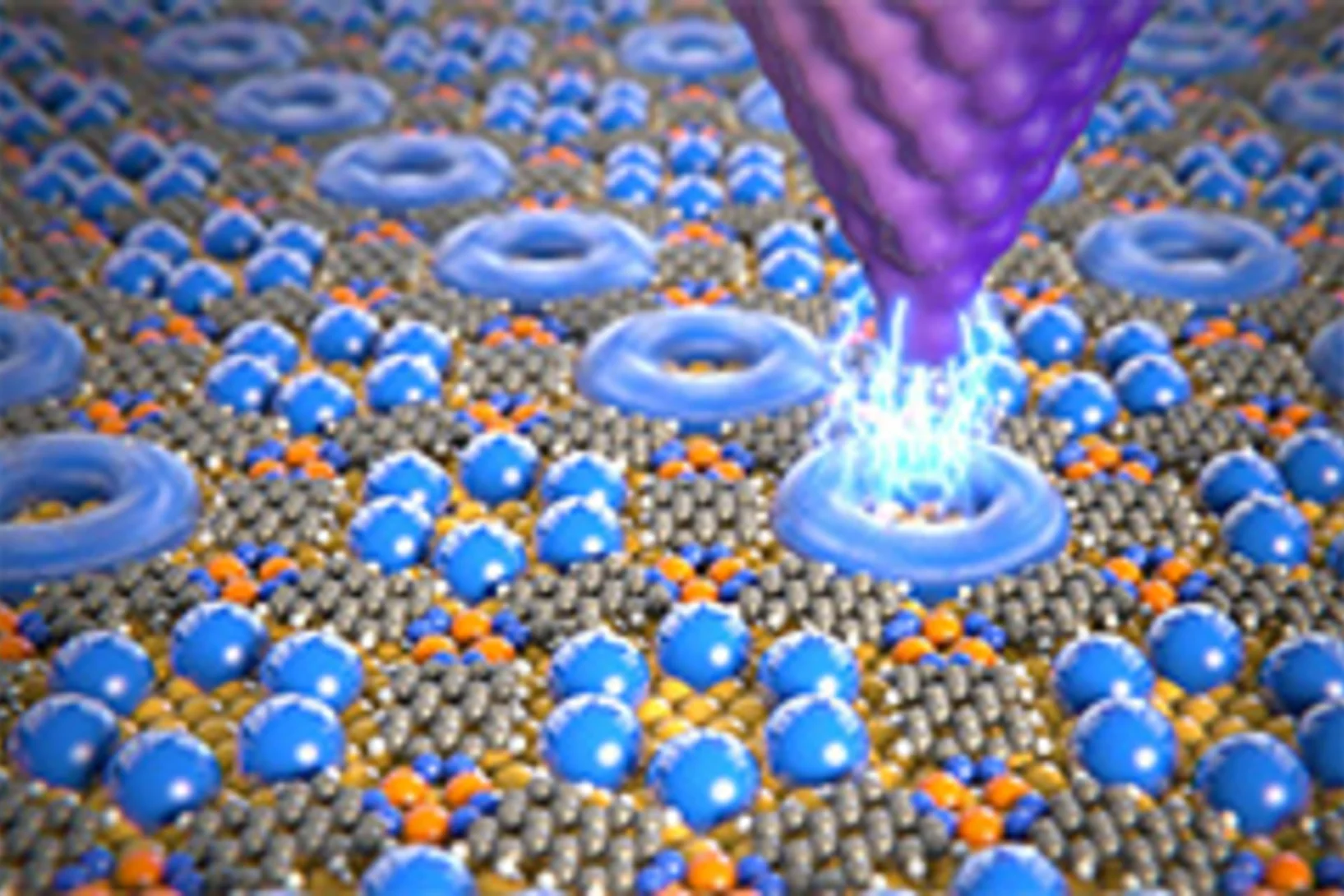
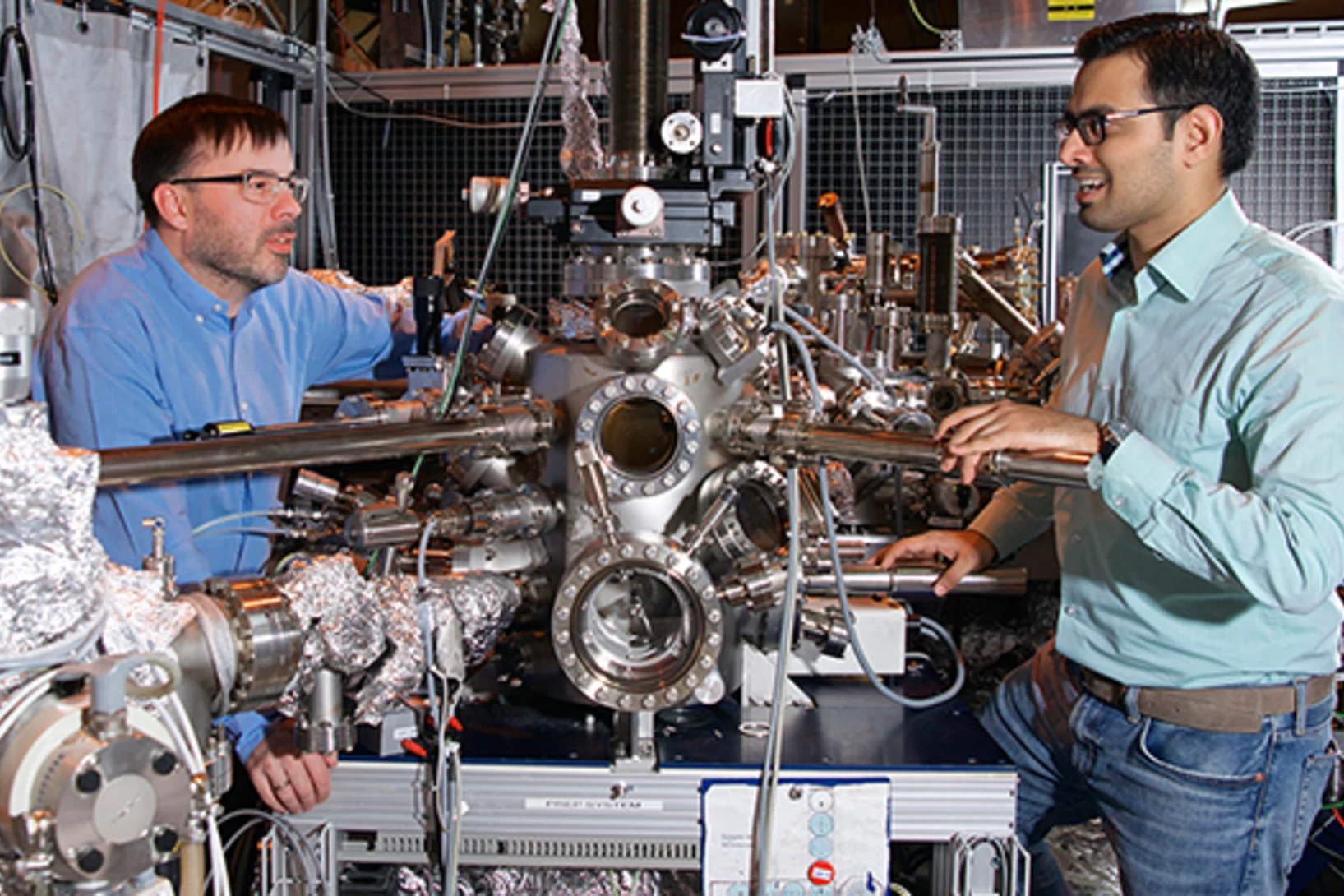
Controlling Quantum States Atom by Atom
A method to precisely alter the quantum mechanical states of electrons within an array of quantum boxes has been developped by an international consortium also including PSI. The method can be used to investigate the interactions between various types of atoms and electrons, which is essential for future quantum technologies.
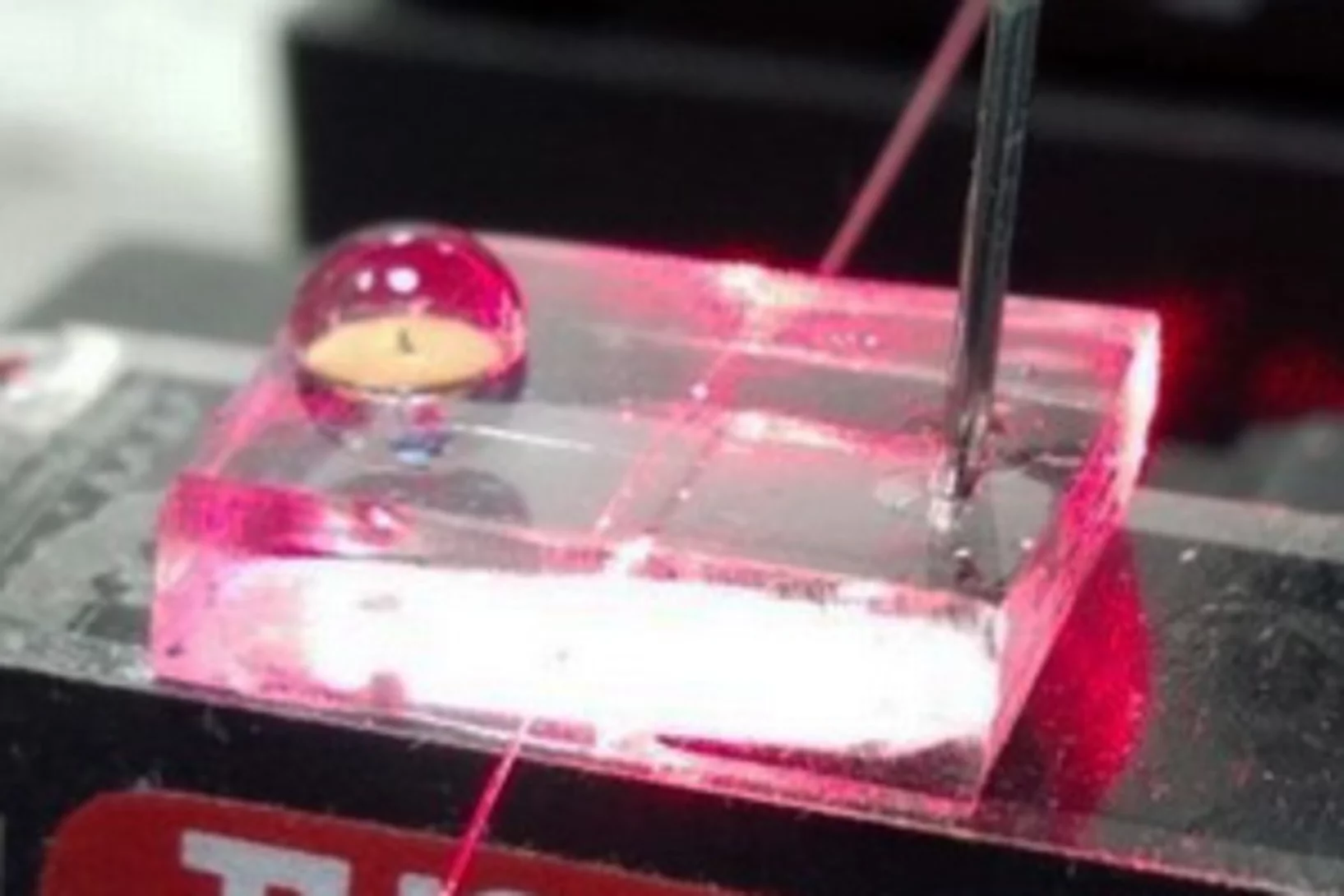
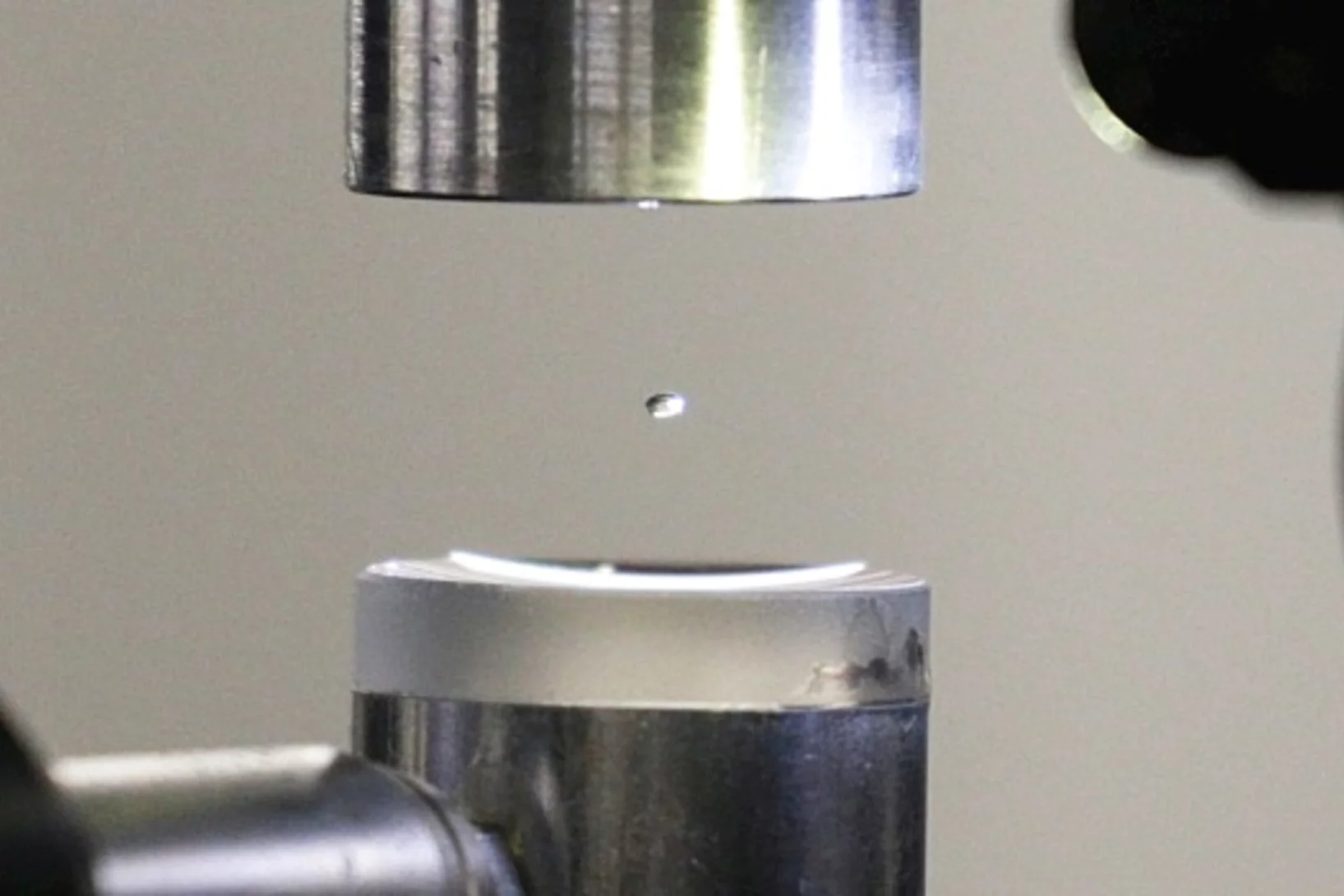
Experiment in a hovering droplet
At the PSI, the exact structure of proteins is deciphered in the standard way, with X-rays. Now two PSI researchers have used a clever trick to advance this method further: Instead of pinning down the proteins, they are studying them within a levitating drop of liquid.
A micrometer-sized model of the Matterhorn
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute have produced large numbers of detailed models of the Matterhorn, each one less than a tenth of a millimetre in size. With this, they demonstrated how 3-D objects so delicate could be mass-produced. Materials whose surface is covered with a pattern of such tiny 3-D structures often have special properties, which could for example help to reduce the wear and tear of machine parts.
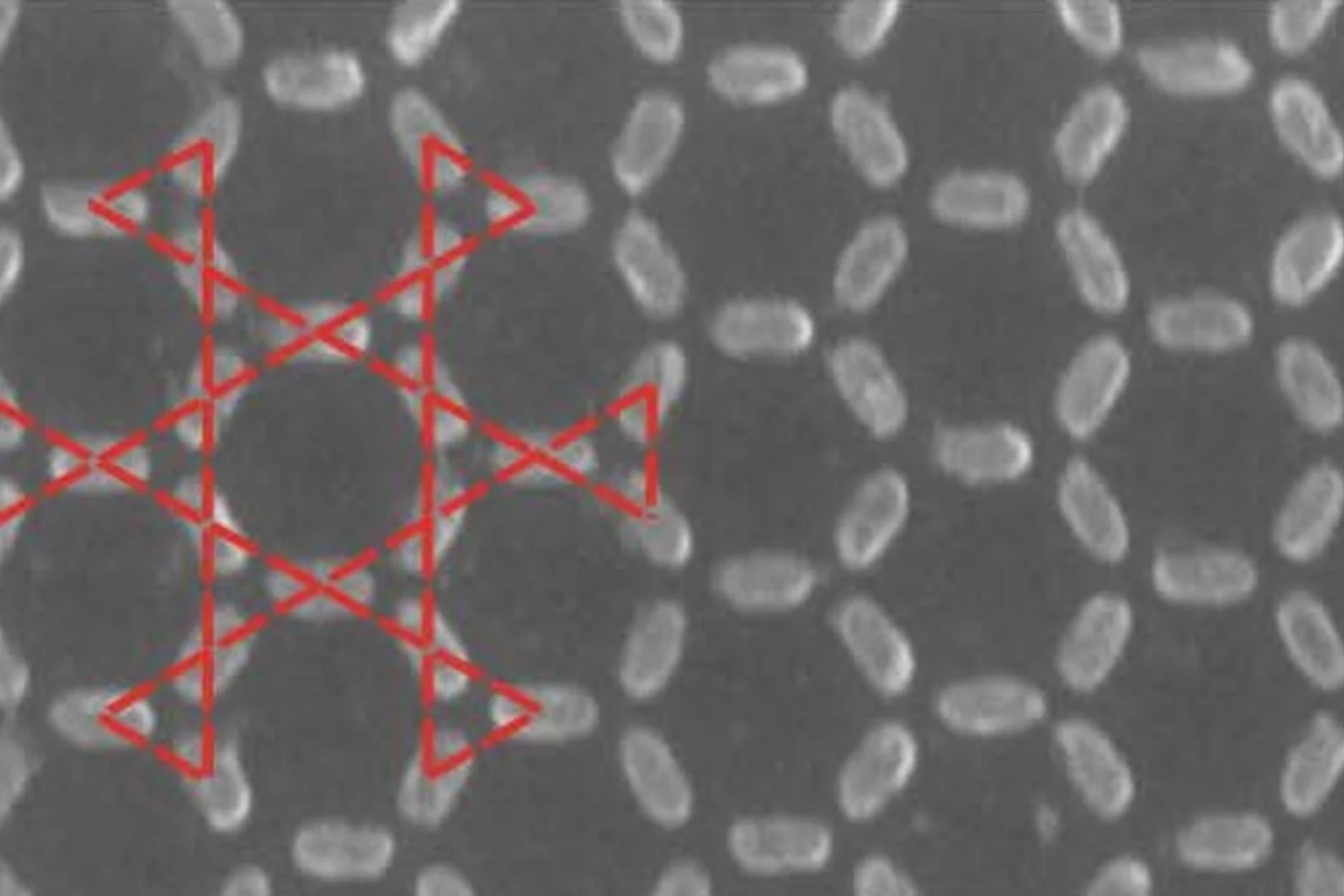
Tiny magnets mimic steam, water and ice
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) created a synthetic material out of 1 billion tiny magnets. Astonishingly, it now appears that the magnetic properties of this so-called metamaterial change with the temperature, so that it can take on different states; just like water has a gaseous, liquid and a solid state.
Seven nanometres for the electronics of the future
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute have succeeded in creating regular patterns in a semiconductor material that are sixteen times smaller than in today’s computer chips. As a result, they have taken an important step closer towards even smaller computer components. Industry envisages structures on this scale as the standard for the year 2028.
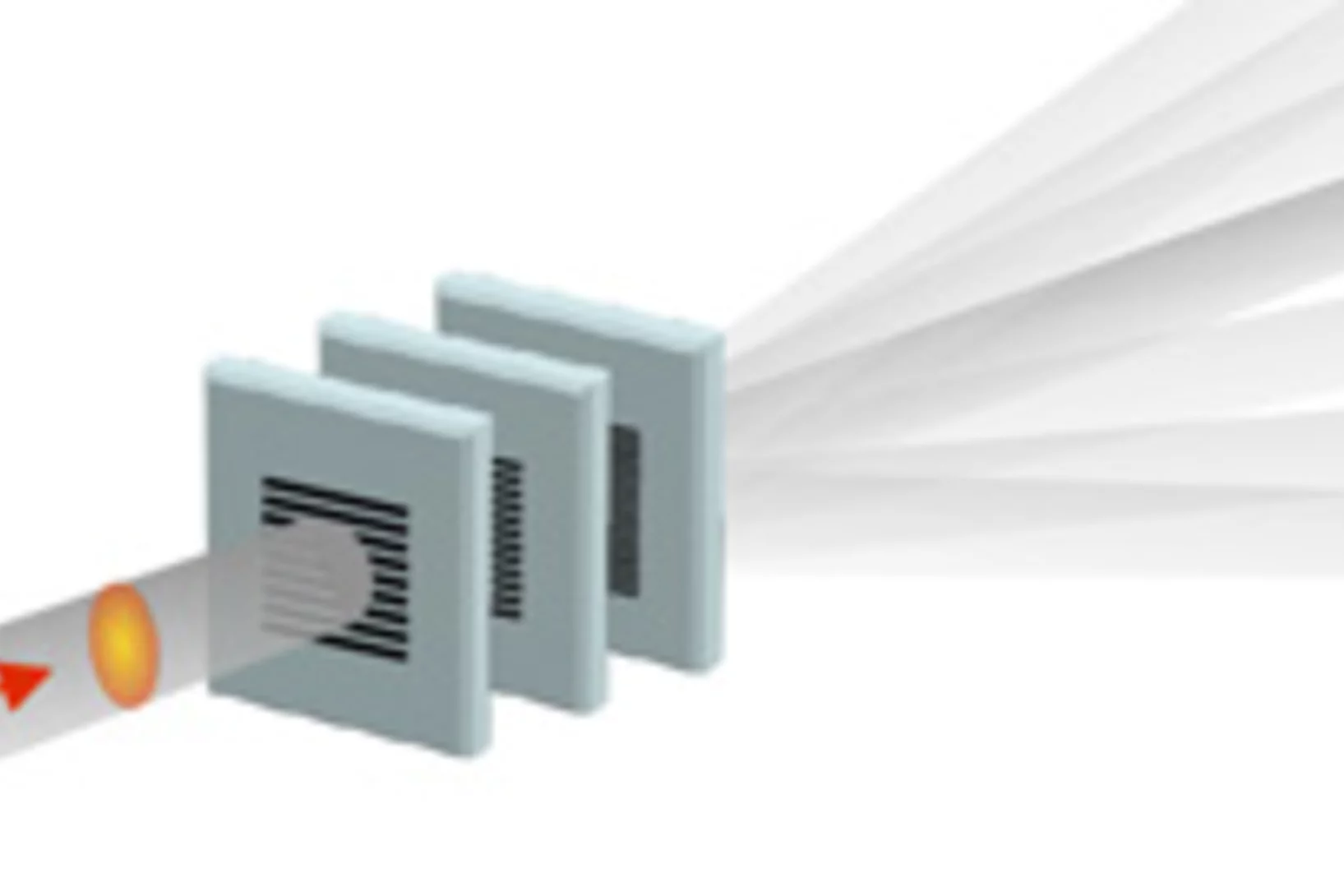
Split x-ray flash shows rapid processes
SwissFEL, PSI’s x-ray laser, is to render the individual steps of very rapid processes visible. A new method will facilitate especially precise experiments: the individual x-ray flashes are split into several parts that arrive at the object under examination one by one. The principle of the method harks back to the ideas of the earliest high-speed photography.
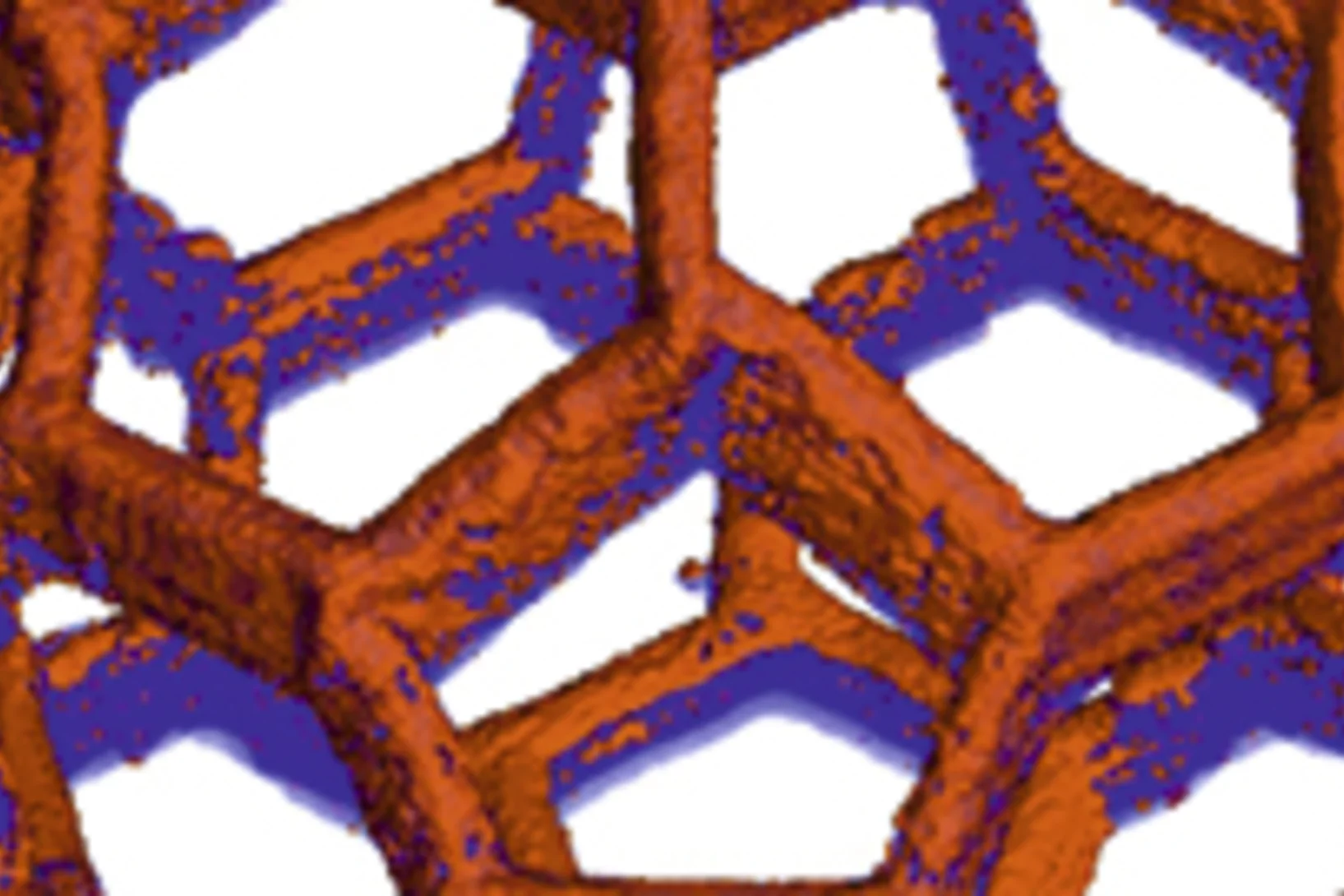
Nanometres in 3D
Scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute and ETH Zurich have created 3D images of tiny objects showing details down to 25 nanometres. In addition to the shape, the scientists determined how particular chemical elements were distributed in their sample and whether these elements were in a chemical compound or in their pure state.