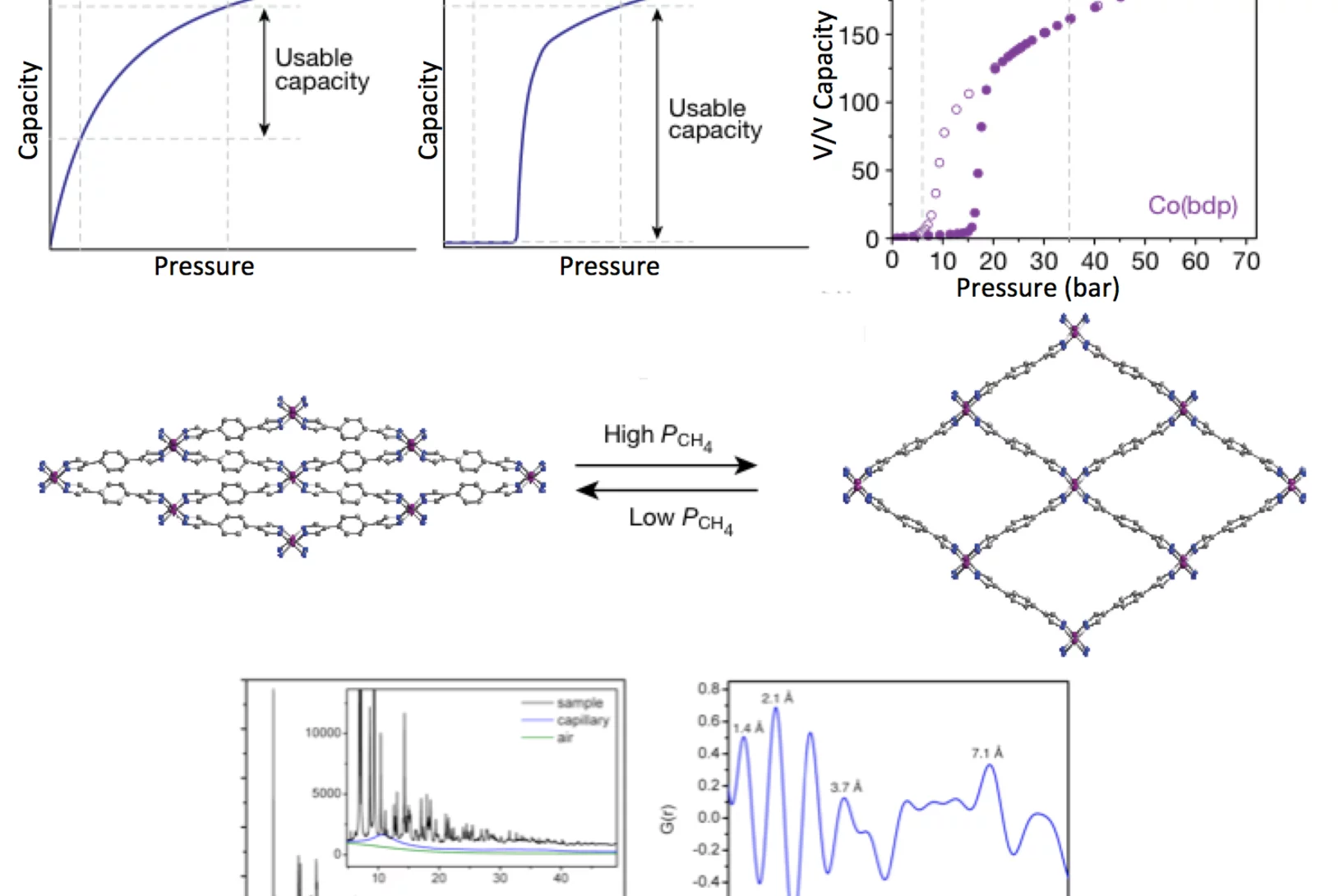
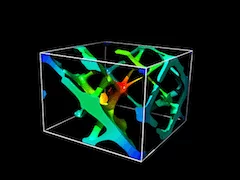
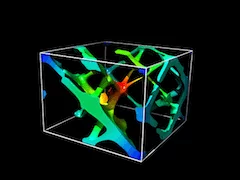
Methane storage in flexible metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic thermal management
As a cleaner, cheaper, and more globally evenly distributed fuel, natural gas has considerable environmental, economic, and political advantages over petroleum as a source of energy for the transportation sector. Despite these benefits, its low volumetric energy density at ambient temperature and moderate pressure presents substantial challenges, particularly for light-duty vehicles with little space available for on-board fuel storage.
La bonne mise en lumière
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont réussi à visualiser de la lumière térahertz grâce à une technologie de caméra disponible dans le commerce. Non seulement ils ouvrent ainsi la voie vers une alternative économique aux procédés en principe utilisés jusqu’ici. Mais ils ont aussi réussi à multiplier par vingt-cinq la résolution de l’image en comparaison. Grâce à ses propriétés particulières, la lumière térahertz est intéressante pour de nombreuses applications. Au PSI, elle sera utilisée dans le cadre des expériences au laser à électrons libres SwissFEL.
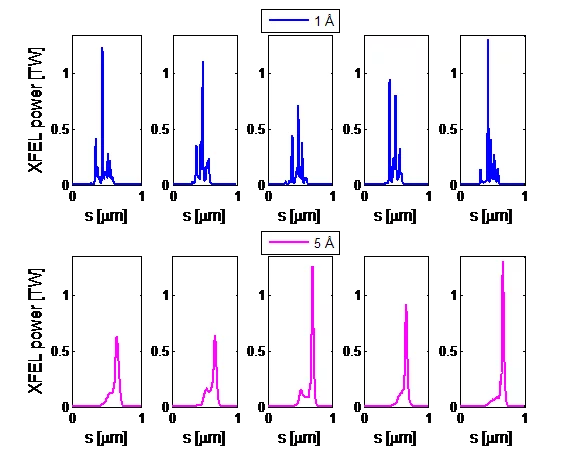
New methods to generate short and high-power X-ray Free-Electron-Laser pulses
State-of-the-art X-ray Free-Electron-Laser (XFEL) facilities like SwissFEL are able to provide radiation pulses with pulse powers of a few tens of gigawatts and pulse durations of several tens of femtoseconds and shorter. There is, however, a strong demand in research fields such as bioimaging and nonlinear optics to obtain higher radiation powers and shorter pulses than in standard facilities. In this context, we have developed two new methods able to generate terawatt-attosecond XFEL pulses. Both proposals are based on superradiance, a regime with quadratic growth of the radiation power and a shortening of the spike while it slips into unspoiled (good-beam) regions of the bunch.
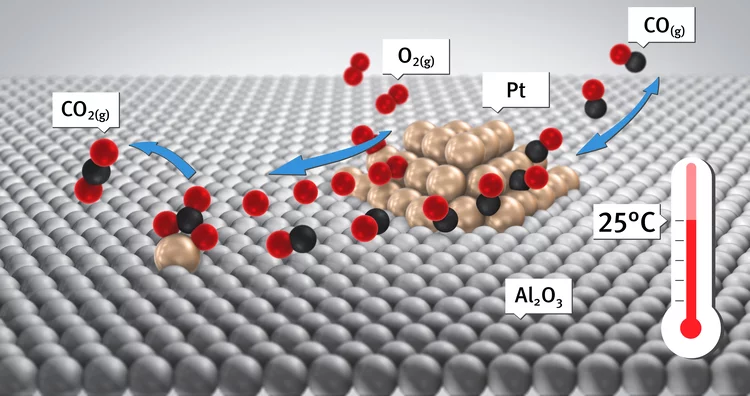
Room-temperature carbon monoxide oxidation by oxygen over Pt-Al2O3 mediated by reactive platinum carbonates
A new possibility for the attainment of low-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide is demonstrated. Here we report using time-resolved DRIFTS, XAS, and mass spectrometry a platinum carbonate-mediated mechanism for the room-temperature oxidation of carbon monoxide.
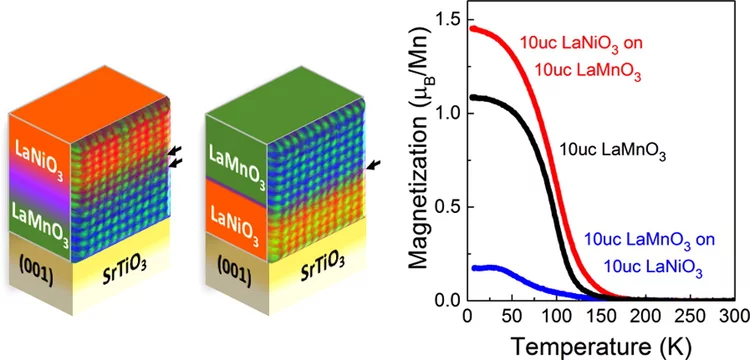
Interfacial Control of Magnetic Properties at LaMnO3/LaNiO3 heterostructures
Using a X-ray magnetic circular dichroism measured at the X-Treme beamline, SLS, in conjunction with X-ray reflectivity measured at the SEXTANTS beamline, SOLEIL, the authors show that the degree of intermixing at the monolayer scale allows interface-driven properties such as charge transfer and the induced magnetic moment in the nickelate layer to be controlled.
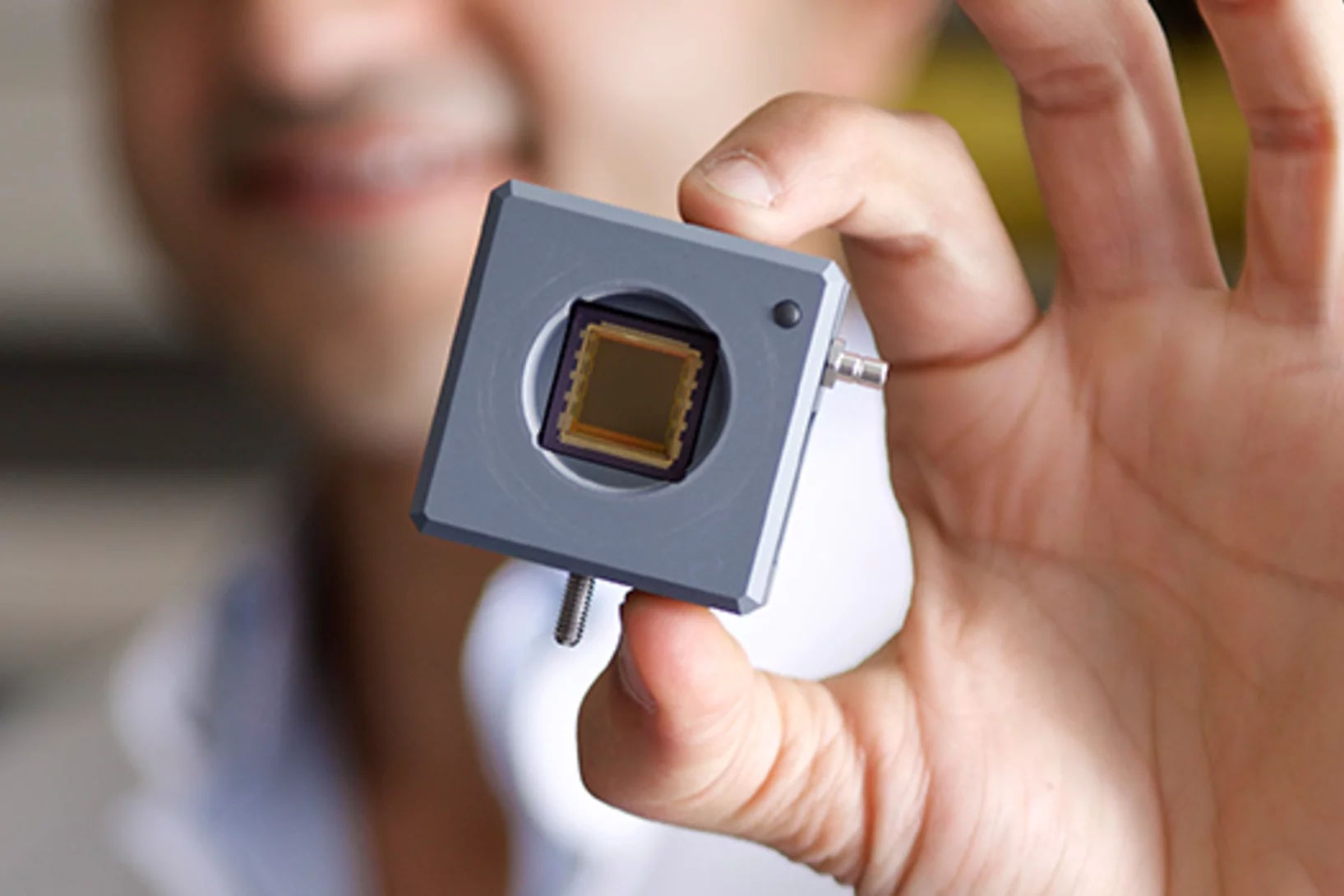
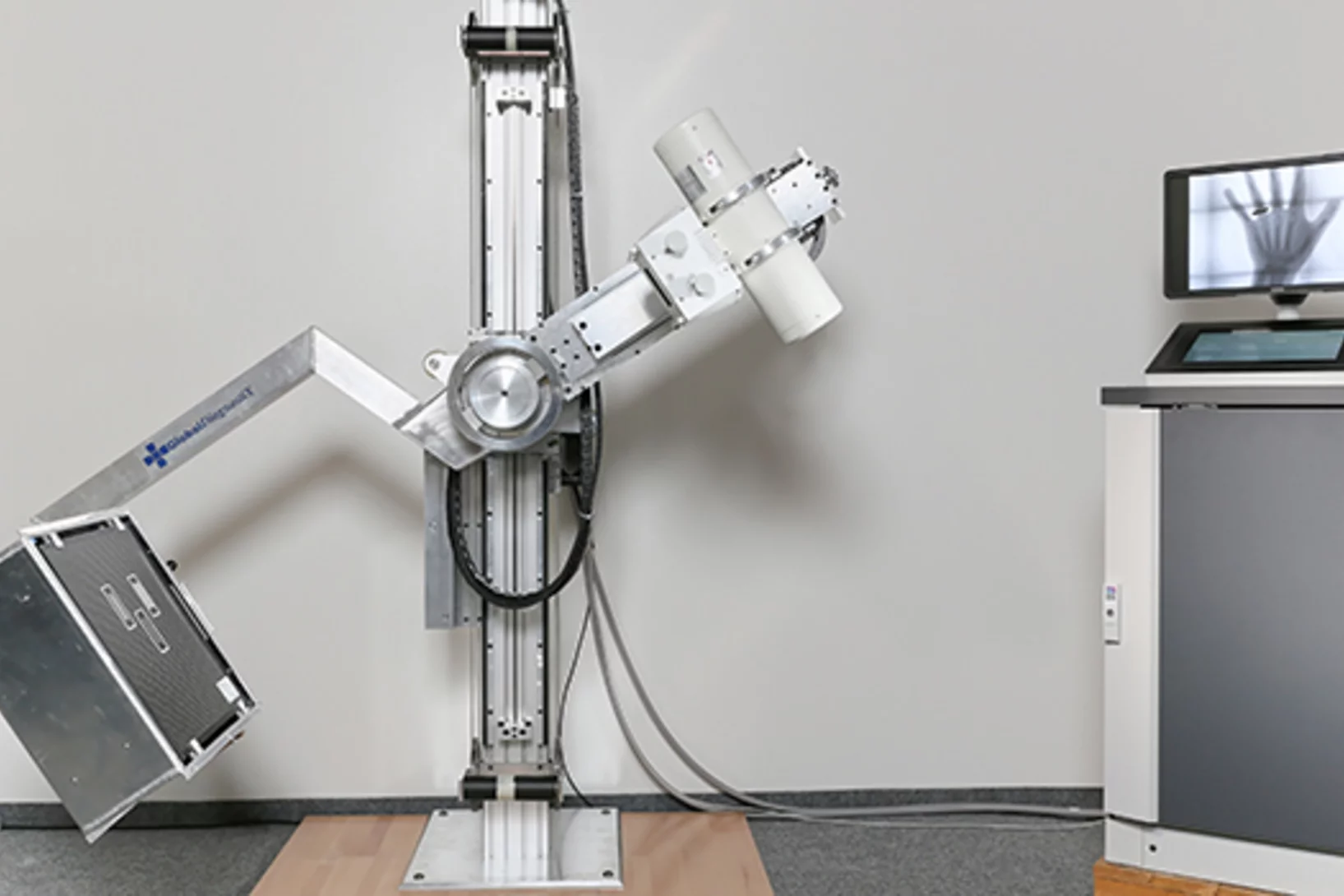
Un appareil de radiologie robuste pour les pays en développement
L’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI participe à un projet de plusieurs instituts de recherche (sous la direction de l’EPFL) afin de mettre au point un appareil de radiologie spécialement pour les pays en développement. L’appareil doit supporter le climat tropical, être bon marché et facile à réparer. Les chercheurs du PSI se consacrent à la production d’un capteur bon marché, nécessaire à la réalisation des clichés. Comparable à la puce d’un appareil de photo numérique, ce détecteur capte la lumière de type rayons X.
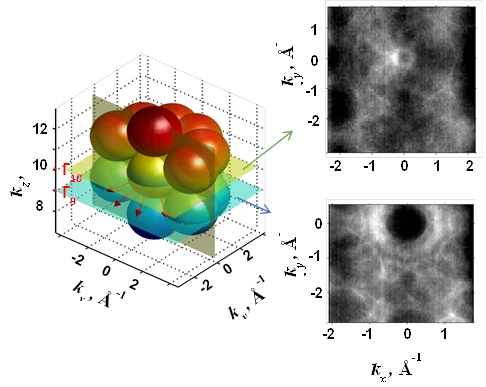
Fermi states and anisotropy of Brillouin zone scattering in the decagonal Al–Ni–Co quasicrystal
Quasicrystals (QCs) are intermetallic alloys where excellent long-range order coexists with lack of translational symmetry in one or more dimensions. These materials have a high potential in application as a material for a solar cells, hydrogen storage applications, heat insulating layers, and others.
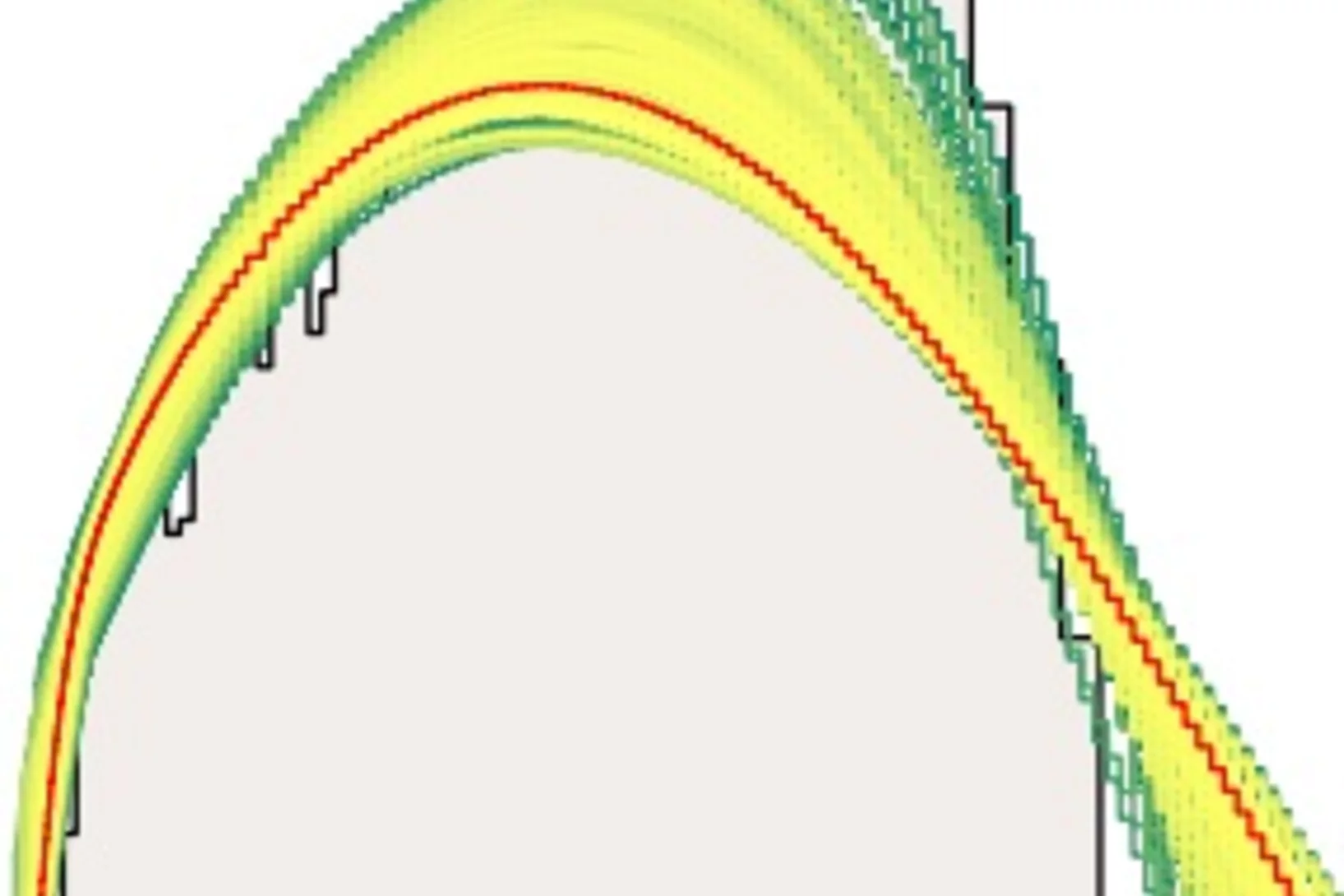
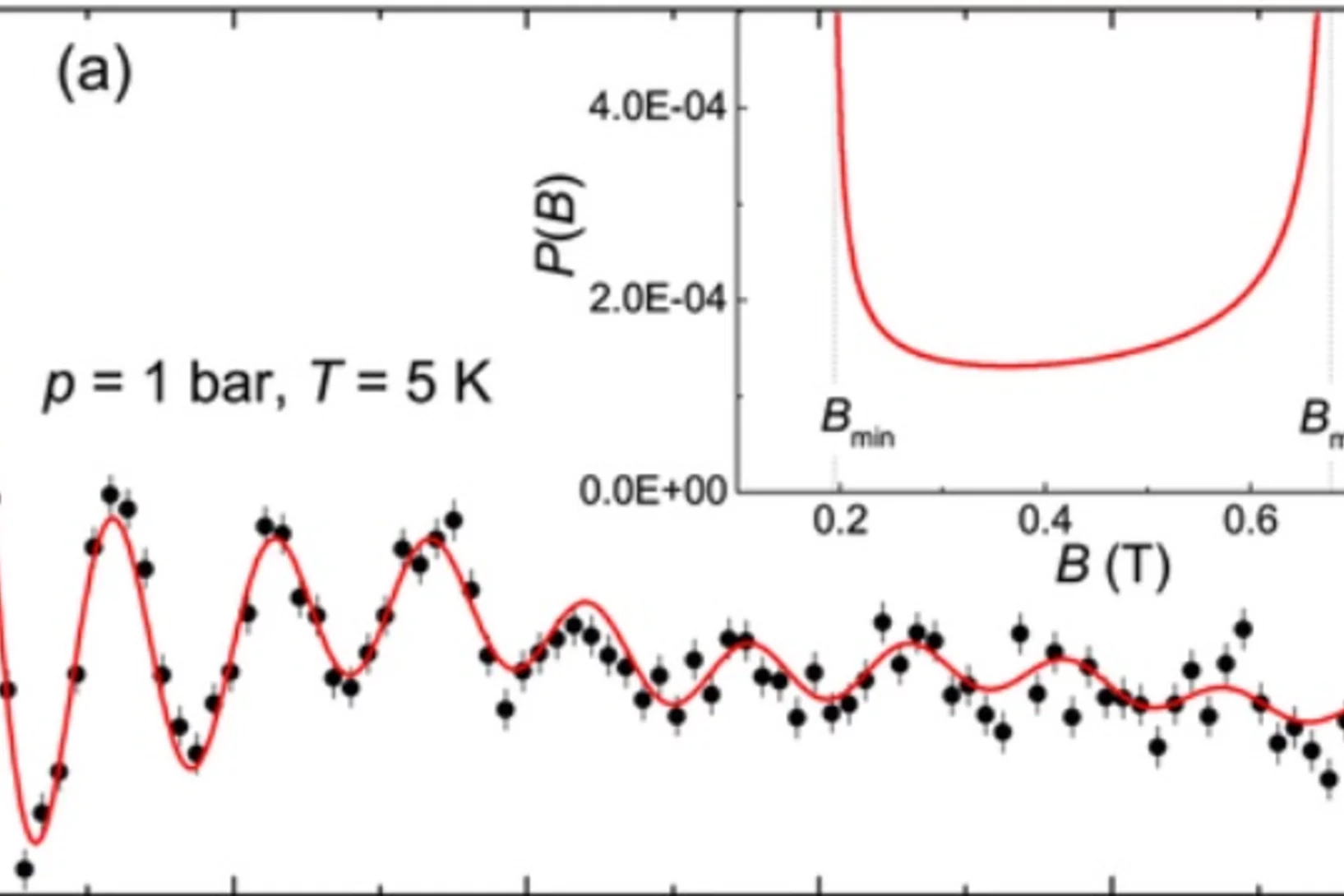
Observation of Gravitationally Induced Vertical Striation of Polarized Ultracold Neutrons by Spin-Echo Spectroscopy
We describe a spin-echo method for ultracold neutrons (UCNs) confined in a precession chamber and exposed to a |B0| = 1μT magnetic field. We have demonstrated that the analysis of UCN spin-echo resonance signals in combination with knowledge of the ambient magnetic field provides an excellent method by which to reconstruct the energy spectrum of a confined ensemble of neutrons.
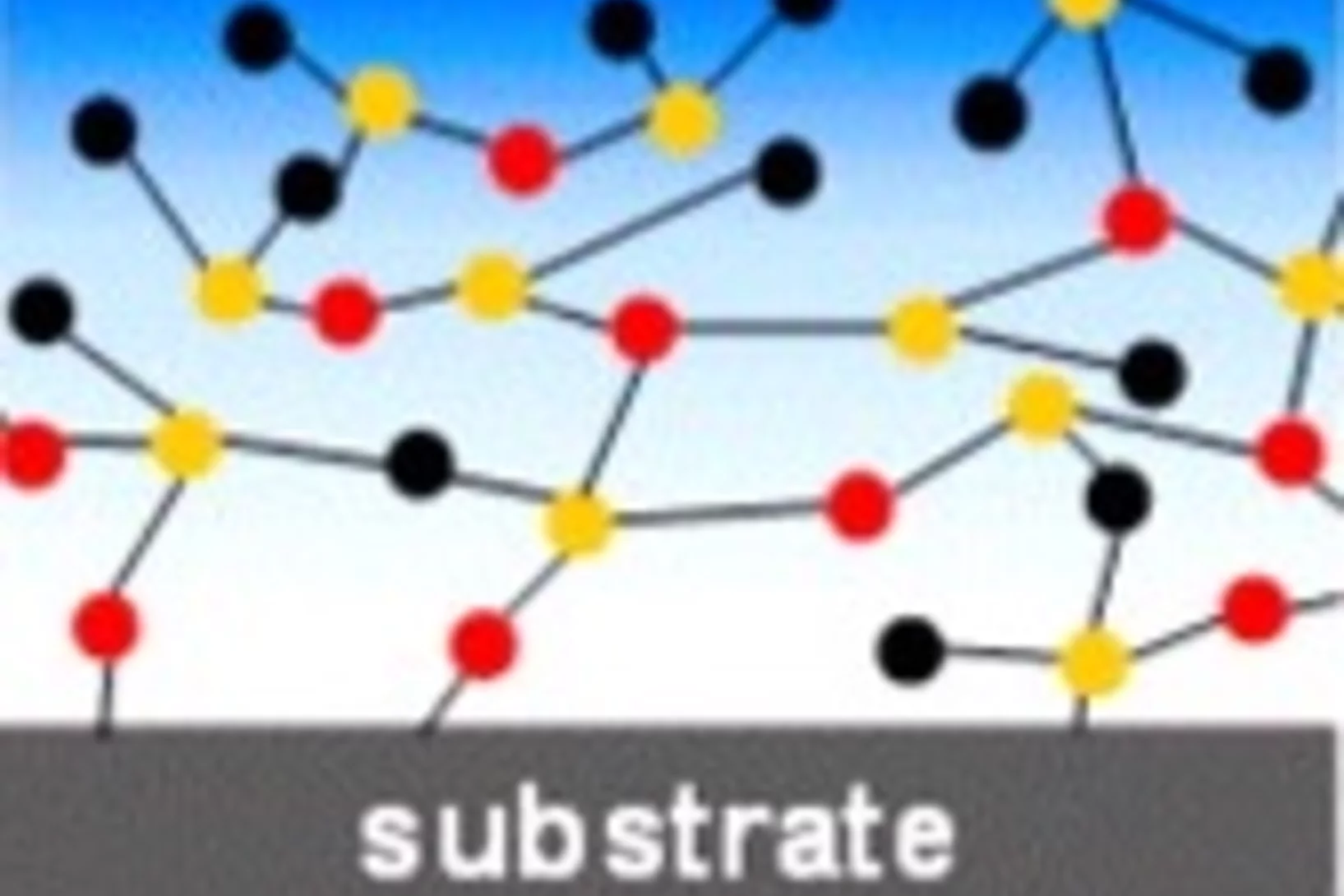
Response of Plasma-Polymerized Hexamethyldisiloxane Films to Aqueous Environments
Thin plasma polymer films were deposited in hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) and HMDSO/O2 low-pressure discharges and their chemical structures analyzed using infrared (IR) spectroscopy and neutron reflectometry (NR). The (plasma-polymerized) ppHMDSO film exhibits hydrophobic, poly(dimethylsiloxane)-like properties, while the retention of carbon groups is reduced by O2 addition, yielding a more inorganic, hydrophilic ppSiOx film.
Une plus grande robustesse grâce aux imperfections
Le dioxyde d’uranium, combustible des centrales nucléaires, résiste mieux aux dégâts causés par les radiations quand sa structure présente des écarts microscopiques par rapport à un agencement idéal.
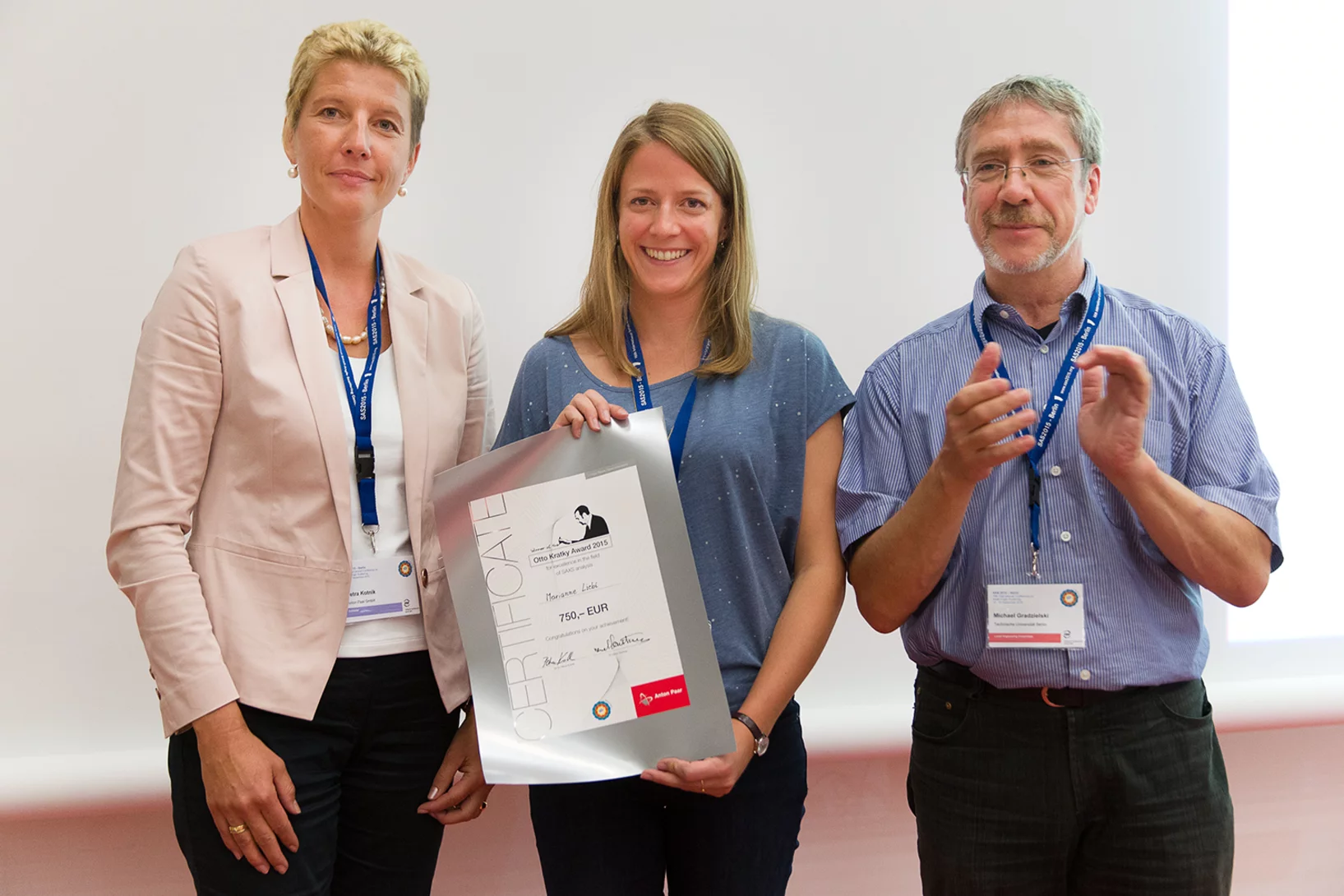
2015 Otto Kratky award
Marianne Liebi was awarded the 2015 Otto Kratky award by the Helmholtz-Centre Berlin for excellence in the field of small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) analysis. The award was bestowed in the last SAS2015 conference in Berlin. Marianne is a postdoctoral fellow in the coherent X-ray scattering group (CXS) in PSI, carrying out research in scanning SAXS measurement and analysis in 2D and 3D. Image credit ©HZB/Michael Setzpfandt
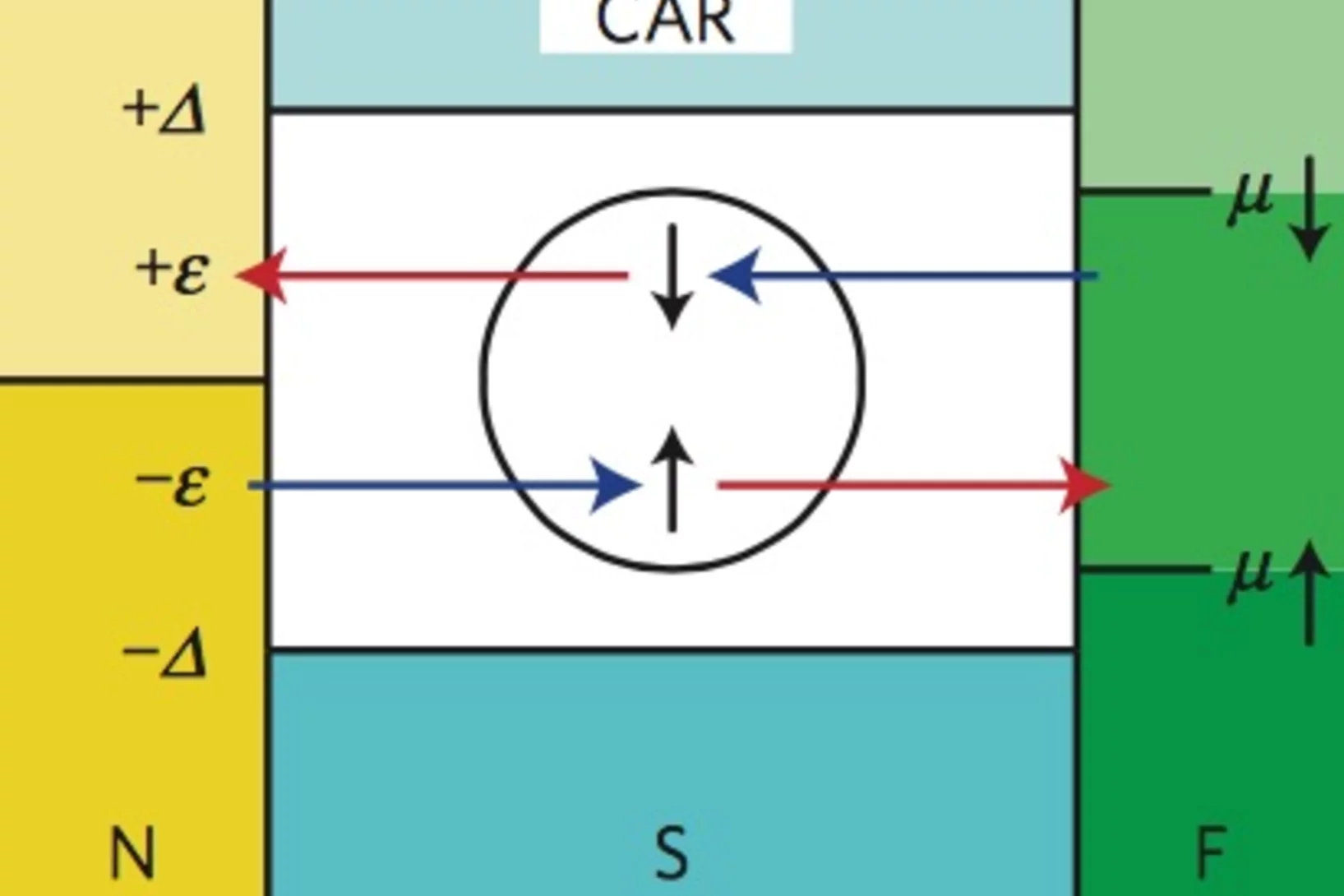
Remotely induced magnetism in a normal metal using a superconducting spin-valve
Superconducting spintronics has emerged in the past decade as a promising new field that seeks to open a new dimension for nanoelectronics by utilizing the internal spin structure of the superconducting Cooper pair as a new degree of freedom. Its basic building blocks are spin-triplet Cooper pairs with equally aligned spins, which are promoted by proximity of a conventional superconductor to a ferromagnetic material with inhomogeneous macroscopic magnetization.
Une nouvelle méthode va permettre de mesurer les neutrons avec une précision inédite
Notre univers est composé de nettement plus de matière que ce que les théories actuelles permettent d’expliquer. Ce fait représente l’une des grandes énigmes de la science moderne. Une manière de clarifier cette dissension passe par ce qu’on appelle le moment dipolaire électrique du neutron. Dans le cadre d’une coopération internationale, des chercheurs du PSI ont développé une nouvelle méthode pour aider à déterminer plus précisément ce moment dipolaire.
Les lignes de faisceaux parfaites passent inaperçues
Entretien avec Luc PattheyLuc Patthey est responsable de la conception et de la réalisation des lignes de faisceaux pour le laser à rayons X à électrons libres SwissFEL. Dans cet entretien, il explique quelles sont les exigences auxquelles les lignes de faisceaux doivent satisfaire, si l'on veut que les impulsions de rayons X produites par le SwissFEL atteignent les expériences sous une forme optimale. Il évoque aussi le rôle joué par les coopérations dans le développement des lignes de faisceaux.
Des chemins hydrophiles pour améliorer l’efficacité des piles à combustible
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) ont développé un procédé de revêtement qui pourrait améliorer l’efficacité des piles à combustible. Les scientifiques du PSI ont déjà déposé un brevet pour ce procédé qui se prête à la fabrication en série.
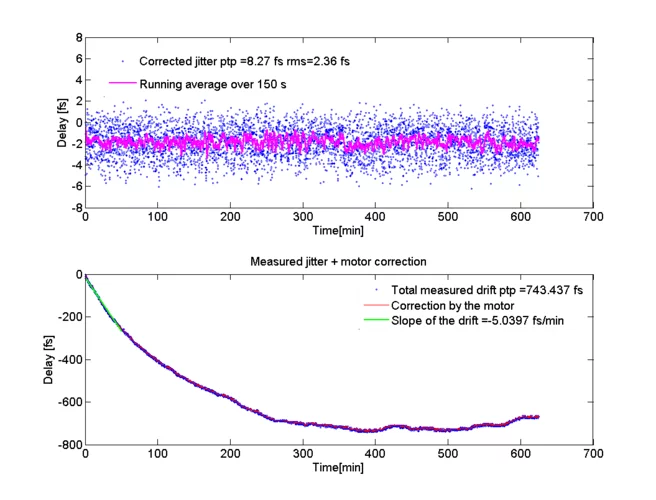
Laser arrival time measurement and correction for the SwissFEL lasers
To probe ultrafast processes at SwissFEL it is crucial that the pump laser, used at the end stations, arrives in time with the generated X-ray pulses. For fs resolution pump probe experiments a path-length change of few-hundred nanometers already affects the measurement quality. The length of SwissFEL and the total propagation path of the pump laser light to the experiment is in the scale of several hundred meters, which makes this task challenging.
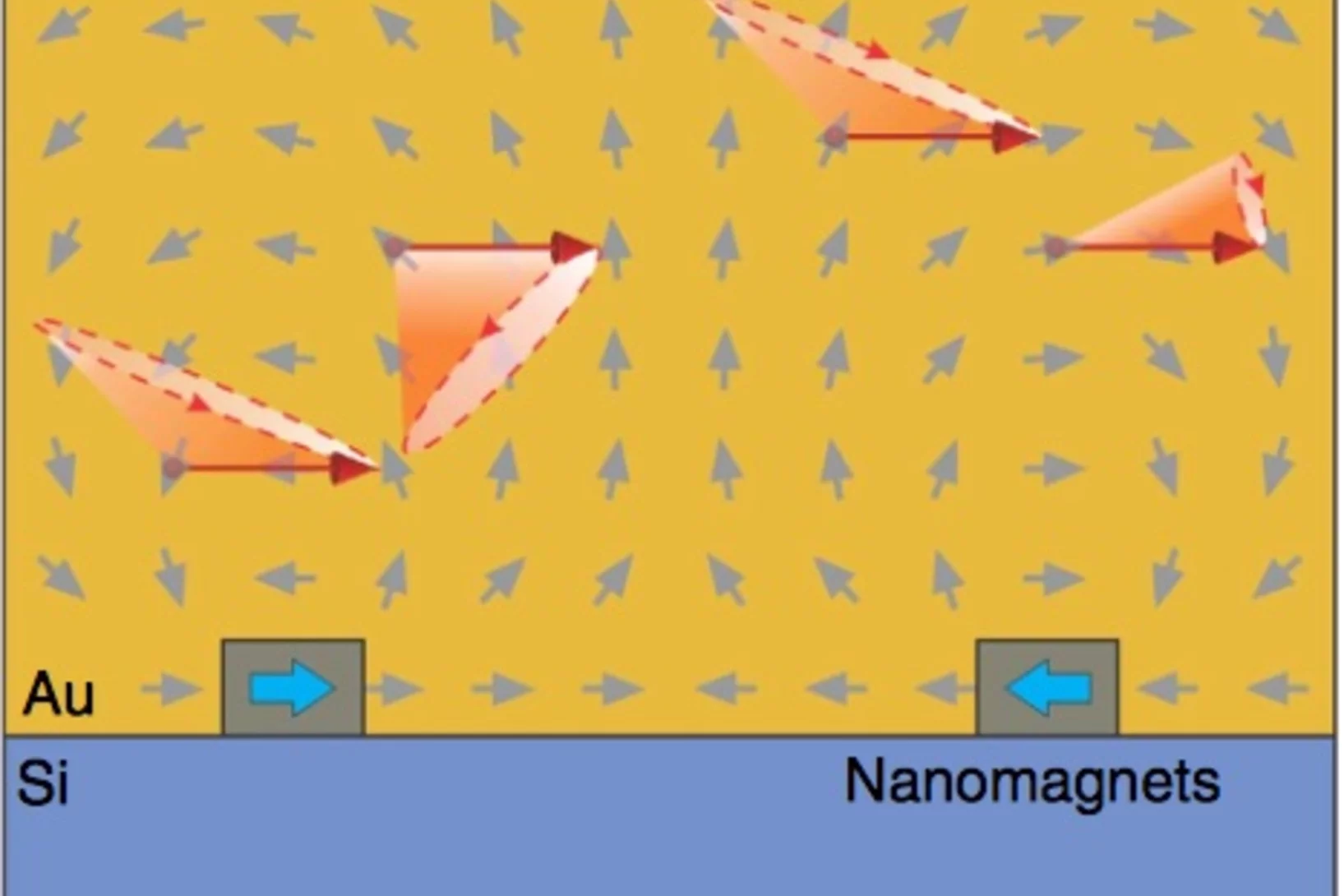
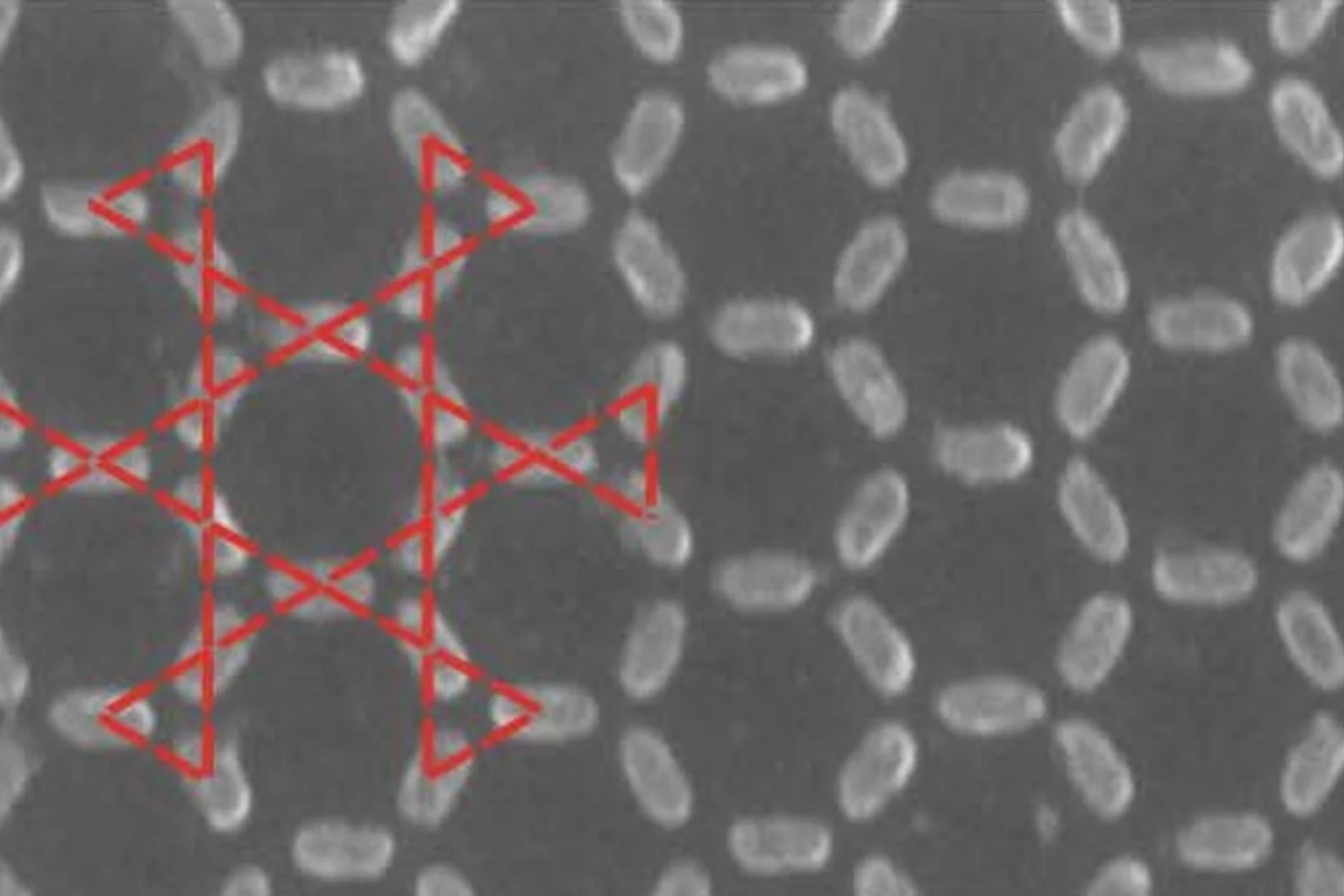
Thermodynamic phase transitions in a frustrated magnetic metamaterial
Materials with interacting magnetic degrees of freedom display a rich variety of magnetic behaviour that can lead to novel collective equilibrium and out-of-equilibrium phenomena. In equilibrium, thermodynamic phases appear with the associated phase transitions providing a characteristic signature of the underlying collective behaviour.
De minuscules aimants imitent la vapeur, l’eau et la glace
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer (PSI) ont créé un matériau artificiel à partir d’un milliard de minuscules aimants. Fait étonnant : il s’avère à présent que les propriétés magnétiques de ce métamatériau changent avec la température de sorte qu’il peut prendre des états différents, semblable à l’eau qui a un état gazeux, un état liquide et un état solide.
La clé pour recharger plus vite une batterie lithium-ion
Les batteries Li-ion utilisant le phosphate de fer lithié comme électrode positive (cathode) ont une longue durée de vie et peuvent être rechargées relativement vite. Des chercheurs de l'Institut Paul Scherrer PSI et du constructeur automobile japonais Toyota expliquent dans une nouvelle étude pourquoi cela est possible. Ce phénomène a pu être mis en évidence grâce à des mesures réalisées à l'aide d'une nouvelle technique développée au sein du laboratoire électrochimique de PSI et du synchrotron Swiss Light Sources (SLS) au PSI.
Pressure-induced electronic phase separation of magnetism and superconductivity in CrAs
The recent discovery of pressure (p) induced superconductivity in the binary helimagnet CrAs has raised questions on how superconductivity emerges from the magnetic state and on the mechanism of the superconducting pairing. In the present work the suppression of magnetism and the occurrence of superconductivity in CrAs were studied by means of muon spin rotation.
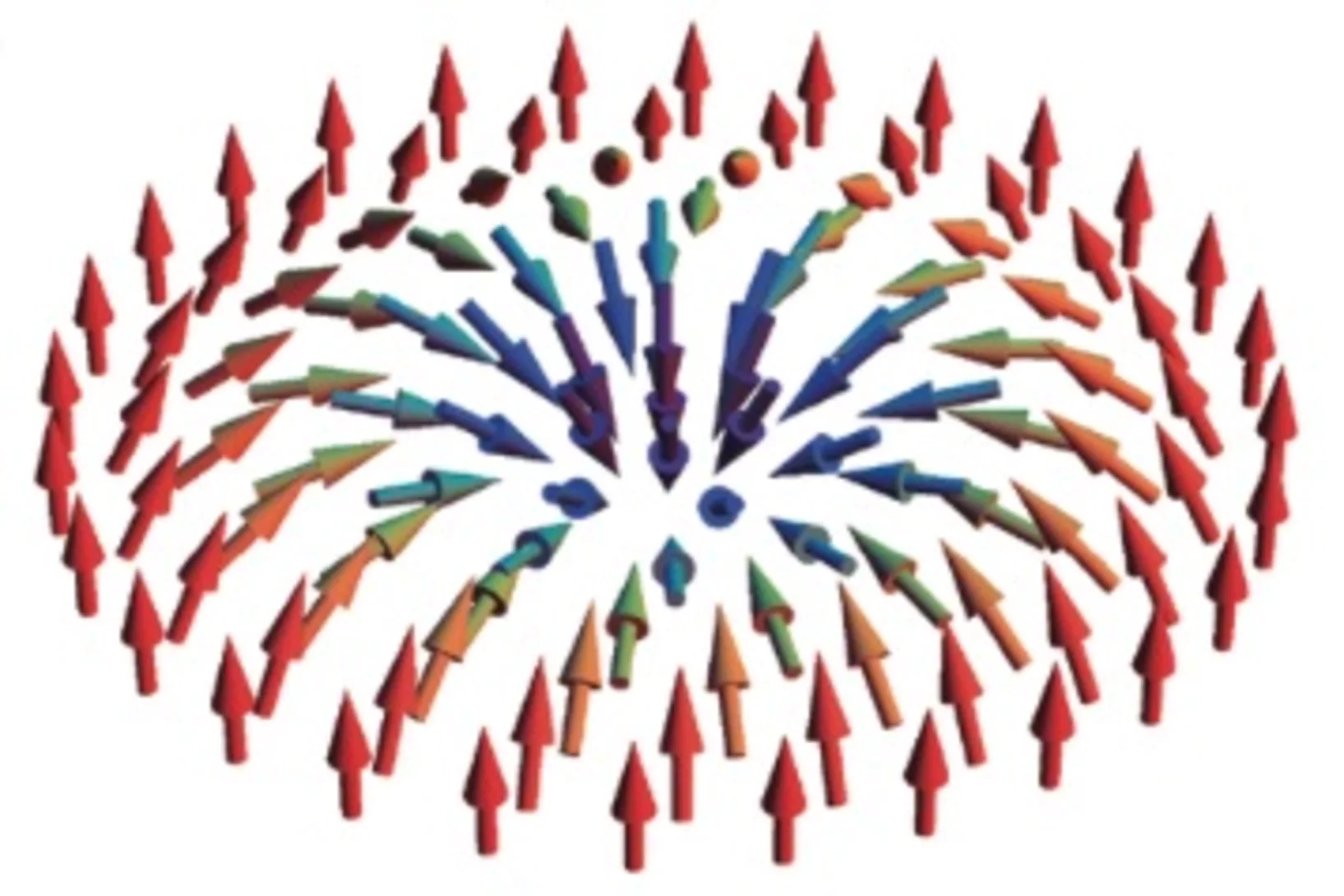
Néel-type skyrmion lattice with confined orientation in the polar magnetic semiconductor GaV4S8
Following the early prediction of the skyrmion lattice (SkL) - a periodic array of spin vortices - it has been observed recently in various magnetic crystals mostly with chiral structure. Although non-chiral but polar crystals with Cnv symmetry were identified as ideal SkL hosts in pioneering theoretical studies, this archetype of SkL has remained experimentally unexplored.
A la recherche du plus petit bit
Si l’on veut produire à l’avenir des supports de stockage pour média toujours plus compacts, il faut que les domaines magnétiques à les bits de stockage à soient de plus en plus petits. Mais quelle est la taille minimale d’un tel aimant ? Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI étudient les phénomènes surprenants du nanomagnétisme.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass. The article was selected to illustrate the cover page of Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, Vol. 27, Nr. 30.
Lattice dynamics of α-cristobalite and the Boson peak in silica glass
B. Wehinger et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 27, 305401 (2015). This work marks a decisive step in the solution of the longstanding problem understanding the origin of the Boson peak in silica glass. The investigation by means of diffuse and inelastic x-ray scattering and lattice dynamics calculations from first principles allow for a direct comparison of the atomic motion in crystalline silica polymorphs and silica glass.
Candidate Quantum Spin Liquid in the Ce3+ Pyrochlore Stannate Ce2Sn2O7
We report the low-temperature magnetic properties of Ce2Sn2O7, a rare-earth pyrochlore. Our suscep- tibility and magnetization measurements show that due to the thermal isolation of a Kramers doublet ground state, Ce2Sn2O7 has Ising-like magnetic moments of ∼1.18 μB. The magnetic moments are confined to the local trigonal axes, as in a spin ice, but the exchange interactions are antiferromagnetic.
Umbrella MoU Signed by 14 Parties
The Memorandum of Understanding of the Umbrella Collaboration was signed by 14 parties: ALBA, DESY, Diamond Light Source Ltd, Elettra, EMBL Heidelberg, ESRF, European XFEL, HZB, ILL, Instruct Academic Services Ltd, KIT, PSI, STFC and SOLEIL.
In Situ Serial Crystallography Workshop at the SLS
The Macromolecular Crystallography group at SLS is organizing a three days workshop on in situ serial crystallography (http://indico.psi.ch/event/issx) between November 17 and 19, 2015. It will be dedicated in the presentation of a novel method facilitating the structure determination of membrane proteins, which are highly important pharmaceutical targets but are difficult to handle using 'classical' crystallographic tools. Designed for 20 Ph.D. students, postdocs and young scientists from both academia and industry, the workshop will consist of introductory lectures, followed by hands-on practicals on in meso or lipidic cubic phase (LCP) crystallization, on in situ serial crystallography data collection using a micro-sized beam and on data processing.
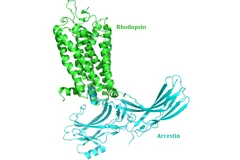
New insight into receptor signalling
A team of 72 investigators across 25 institutions including researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institut obtained the X-ray structure of a rhodopsinàarrestin complex, which represents a major milestone in the area of G-protein-coupled-receptor (GPCR), a protein family recognized in the award of the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Terahertz laser light focused to the extreme
There are limits to how short a flash of light can be – in both time and space. Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) have now succeeded in reaching these physical limits and producing the smallest possible flash. To do so, they used terahertz light, which is physically related to visible light or radio waves, but differs in its wavelength.
La lumière laser térahertz concentrée à l’extrême
Des chercheurs de l'Institut Paul Scherrer ont réussi à concentrer l'impulsion lumineuse d'un laser térahertz à la limite de ce qu'autorisent les lois de la physique. Cela ouvre une nouvelle voie pour examiner les propriétés des matériaux.