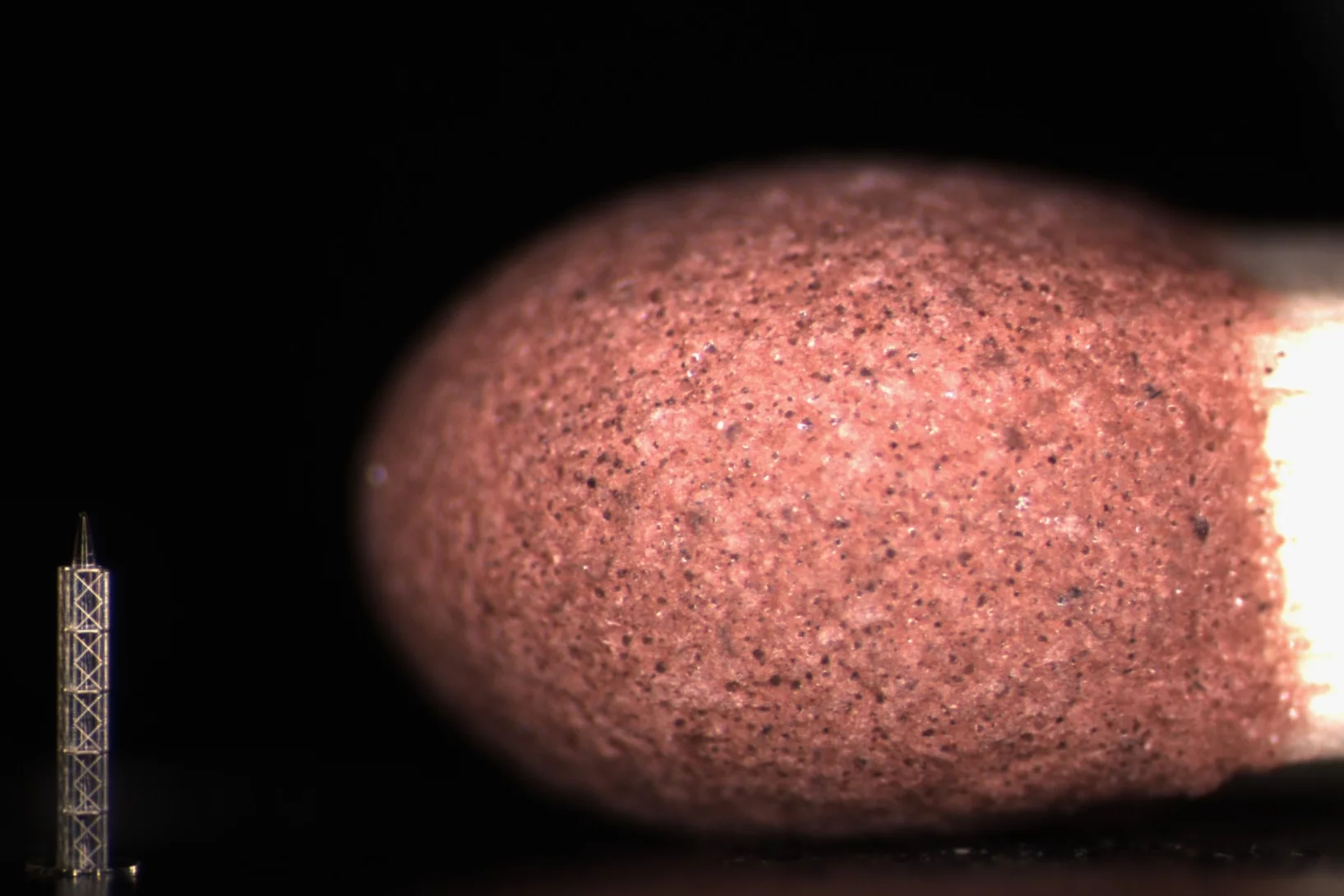
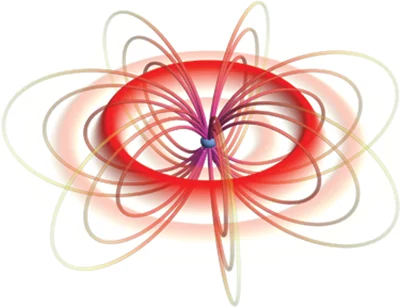
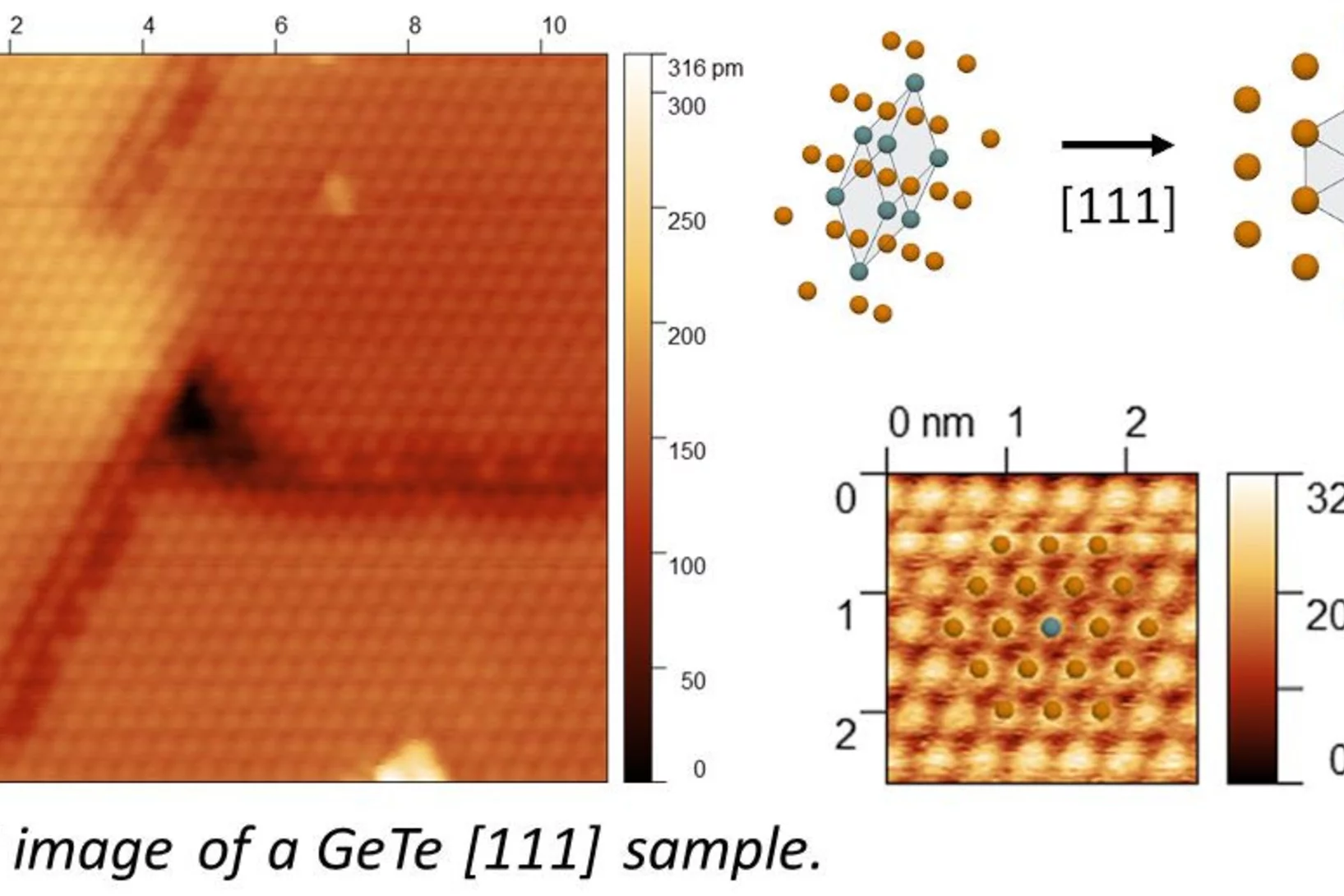
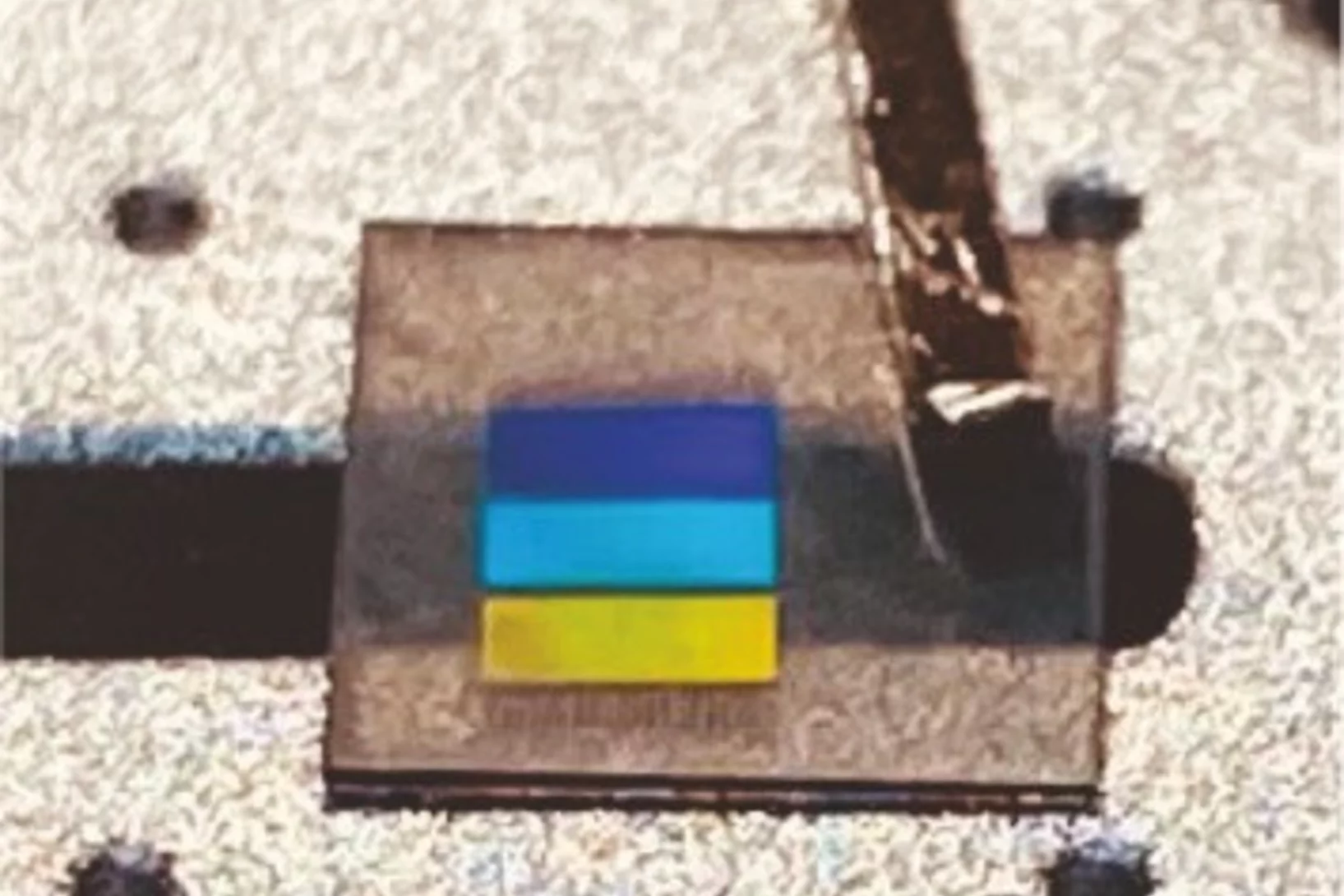
Recognition at MNE 2024 Micrograph Contest
The MNE conference is the flagship event of the International Society for Micro- and Nanotechnology (iMNEs). The research fields covered by the MNE conferences have consistently driven advancements in the development of smaller and smaller structures. To emphasize the significance of micrographs in this field, the conference features a micrograph contest, sponsored and hosted by Zyvex Labs. Entries are judged based on both their technological relevance and artistic merit.
This year, Peng Qi from the X-ray Nano Optics group, LXN, CPS, earned third place and an honorable mention for his two submitted images.
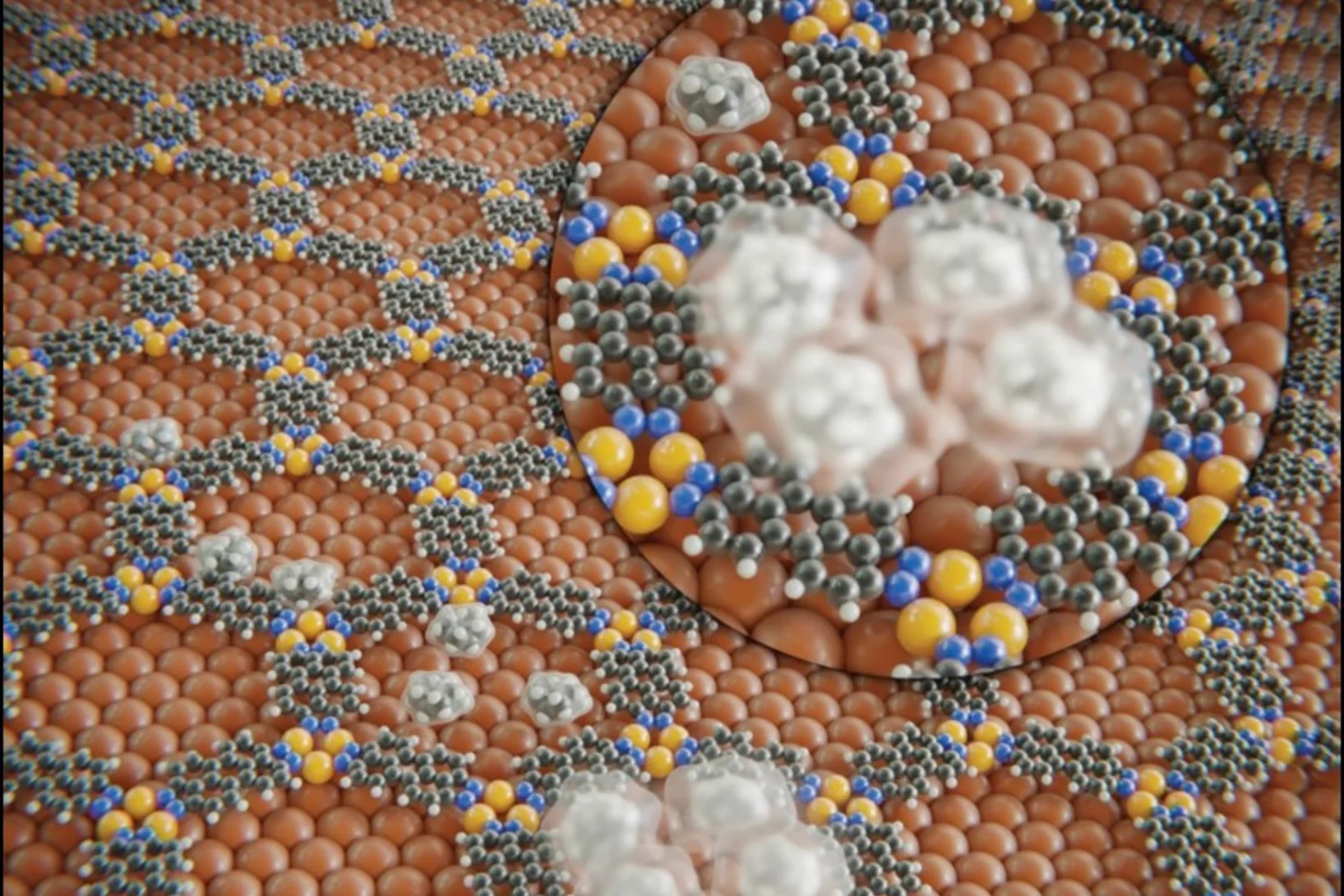
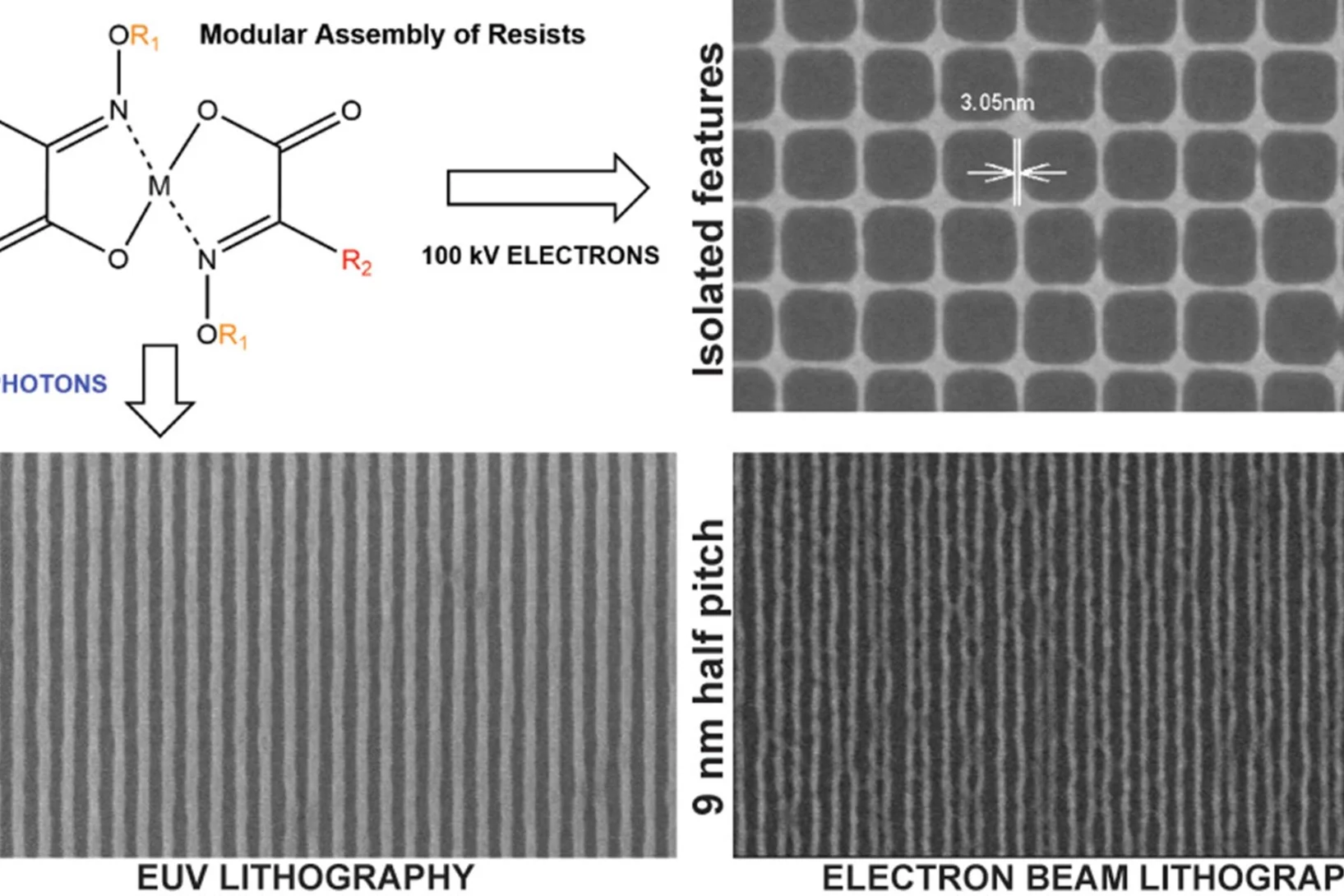
Novel Photoresist Chemistry Enables Lithography Approaching Angstrom-Scale Resolution
Photoresist materials are crucial in the manufacturing of computer chips, where the circuits are initially printed in the photoresist using photolithography. As the demand for smaller and more precise circuitry in computer chips grows, photoresists must resolve features with smaller sizes and higher density. One of the factors determining the ultimate resolution in lithography is the molecular size/mass of the photoresists.
Researchers show that computer chips have the potential to become even smaller
Researchers at PSI reach unprecedented 5 nanometres half pitch resolution with EUV lithography.
New process for the production of semiconductors
The Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and the Finnish company PiBond to collaborate in the commercialization of advanced EUV semiconductor lithography products.
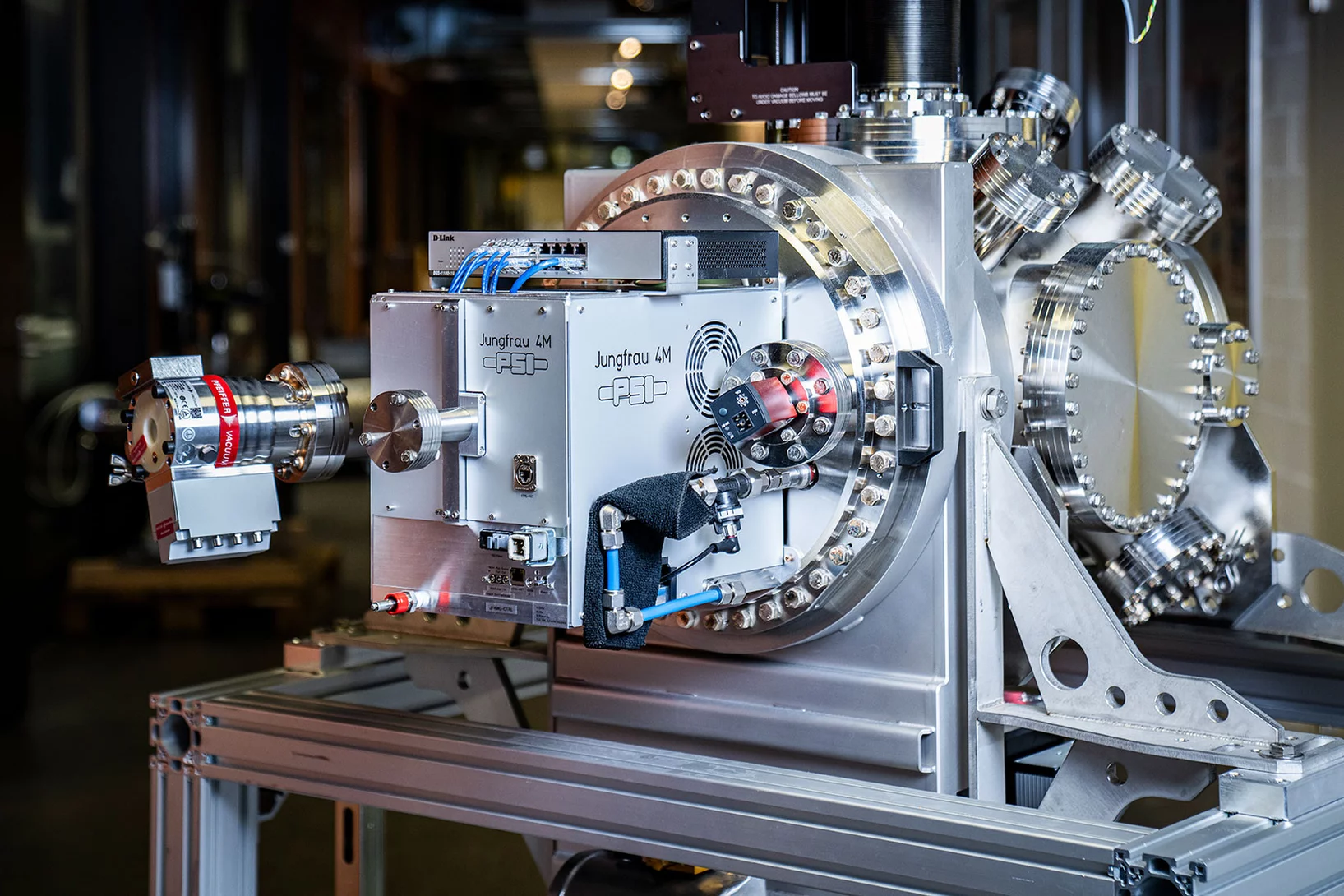
Developing detectors to transform science with light (part 2)
Part II: Why detecting soft X-rays is hard, and how a new breakthrough is set to transform low energy X-ray science.
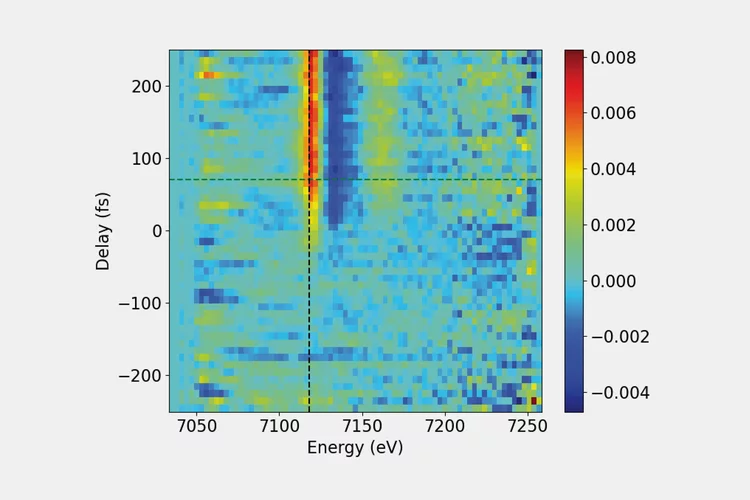
Efficient transient X-ray absorption spectroscopy
By combining the unique large bandwidth emission mode of SwissFEL’s ARAMIS undulator and diffractive X-ray optics made of diamond, we have demonstrated a new method for time-resolved X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy that enables faster data acquisition and requires smaller sample quantities for high-quality data.
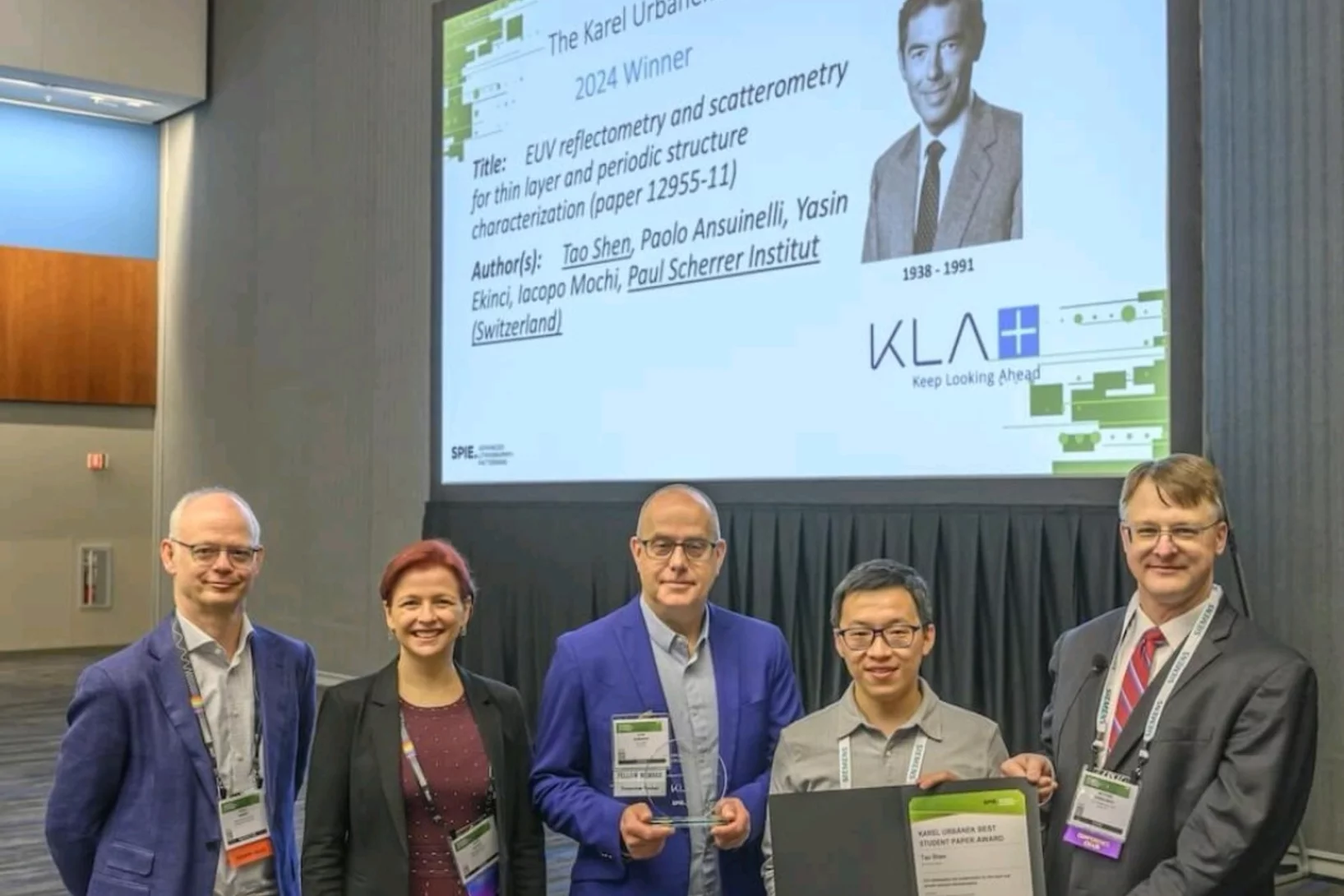
2024 SPIE Advanced Lithography + Patterning, San Jose, California
2024 SPIE Advanced Lithography + Patterning symposium hosted leading researchers who are solving challenges in optical and EUV lithography, patterning technologies, metrology, and process integration for semiconductor manufacturing and adjacent applications. The symposium features six conference topics.
Charge fractionalisation observed spectroscopically
Quantum mechanics tells us that the fundamental unit of charge is unbreakable – but exceptions exist.
Developing detectors to transform science with light (part 1)
Part I: How the Jungfrau detector went from inception to perfection to ubiquity.
Solid-state qubits: Forget about being clean, embrace mess
So says new recipe for dense arrays of qubits with long lifetimes.
Using quantum computers already today
Analogue quantum computers make ultrafast chemical reactions observable.
LXN post-doctoral researcher Dr. Prajith Karadan wins Best Poster Award at MNE conference 2023, Berlin
The MNE (Micro and Nano Engineering) conference is a prestigious annual event that serves as a global platform for experts, researchers, and innovators in the field of micro and nanotechnology. This conference brings together leading minds from academia and industry to share cutting-edge research, exchange ideas, and explore emerging trends and breakthroughs in the world of micro and nanoengineering.
“Molecular chains could be useful for the electronics of the future”
Christian Wäckerlin talks about fundamental research into novel nanowires and their potential applications.
PSI researchers use extreme UV light to produce tiny structures for information technology.
Synchrotron light can be used in follow-up after a heart transplant to determine whether the body may be rejecting the new organ.
Dr Christian Wäckerlin is appointed as assistant professor at EPFL
Dr Christian Wäckerlin (*1983), currently Research and Teaching Associate at EPFL and Project Leader at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), as Assistant Professor of Physics in the School of Basic Sciences. Christian Wäckerlin’s research focuses on nanoscience and quantum engineering.
Apochromatic X-ray focusing
A team of scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institut, the University of Basel and DESY have demonstrated the first-ever realization of apochromatic X-ray focusing using a tailored combination of a refractive lens and a Fresnel zone plate. This innovative approach enables the correction of the chromatic aberration suffered by both refractive and diffractive lenses over a wide range of X-ray energies. This groundbreaking development in X-ray optics have been just published in the scientific journal Light: Science & Applications.
Quality control of future transistors: Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
Tackling the challenge of looking at atoms buried in silicon without moving them
IEEE Early Career Award 2022
For contributions to the development of detectors for XFELs and specifically for their verification, characterization, and calibration
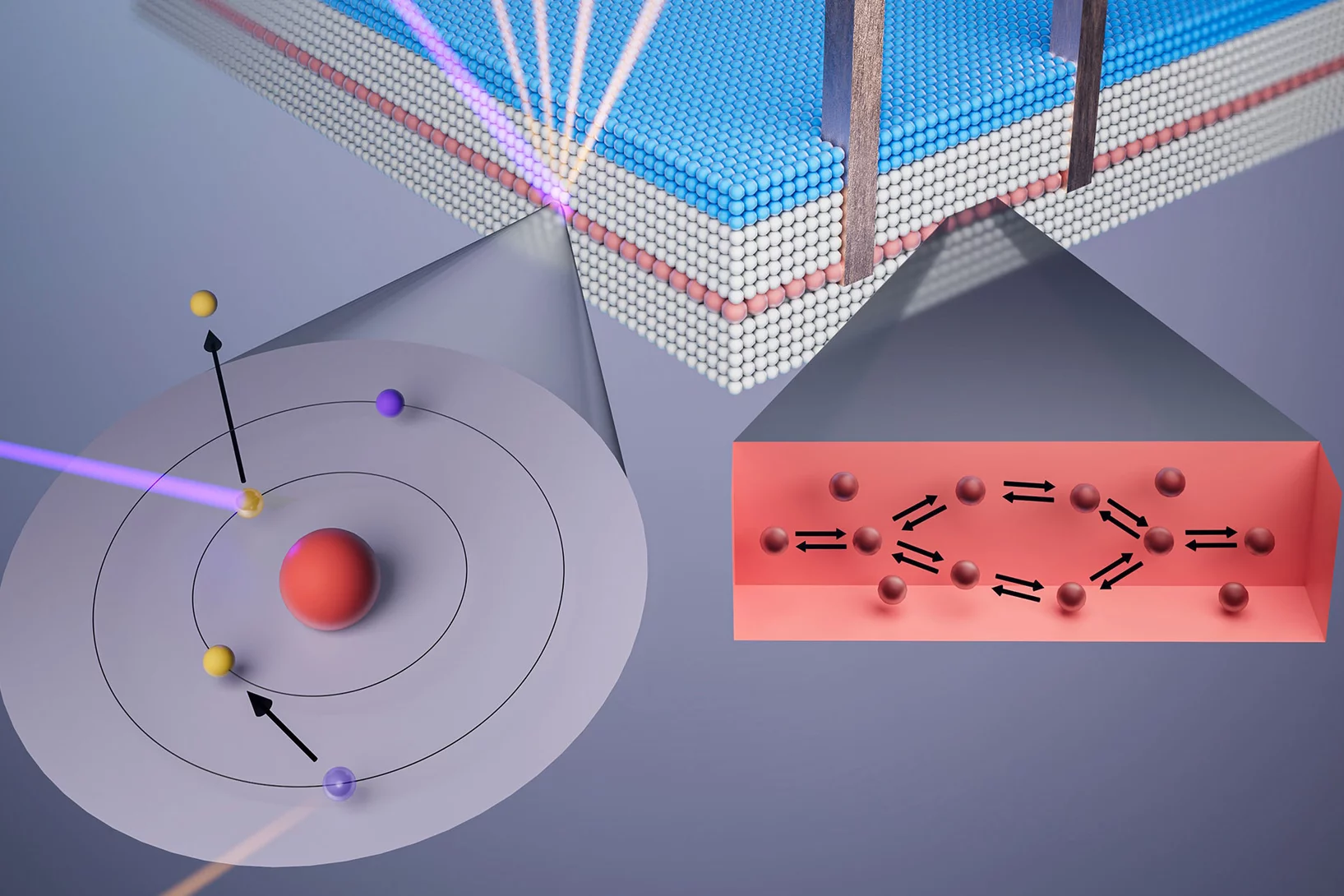
Dancing molecules
When cycloalkanes are enclosed in a nanometer-sized pore, they adapt their shape - similar to the induced fit concept described in #biochemistry. The molecules do not all behave in the same way and surprisingly start to move when there is a lack of space at 5K.
Thomas Mortelmans receives the Swiss Nanotechnology PhD award
Thomas Mortelmans has been a PhD at the Laboratory for X-ray Nanosciences and Technologies for the last four years. He recently defended his PhD-thesis at the University of Basel entitled: "The development of a nanofluidic particle size sorter and its biomedical sciences" and was awarded the grade of summa cum laude.
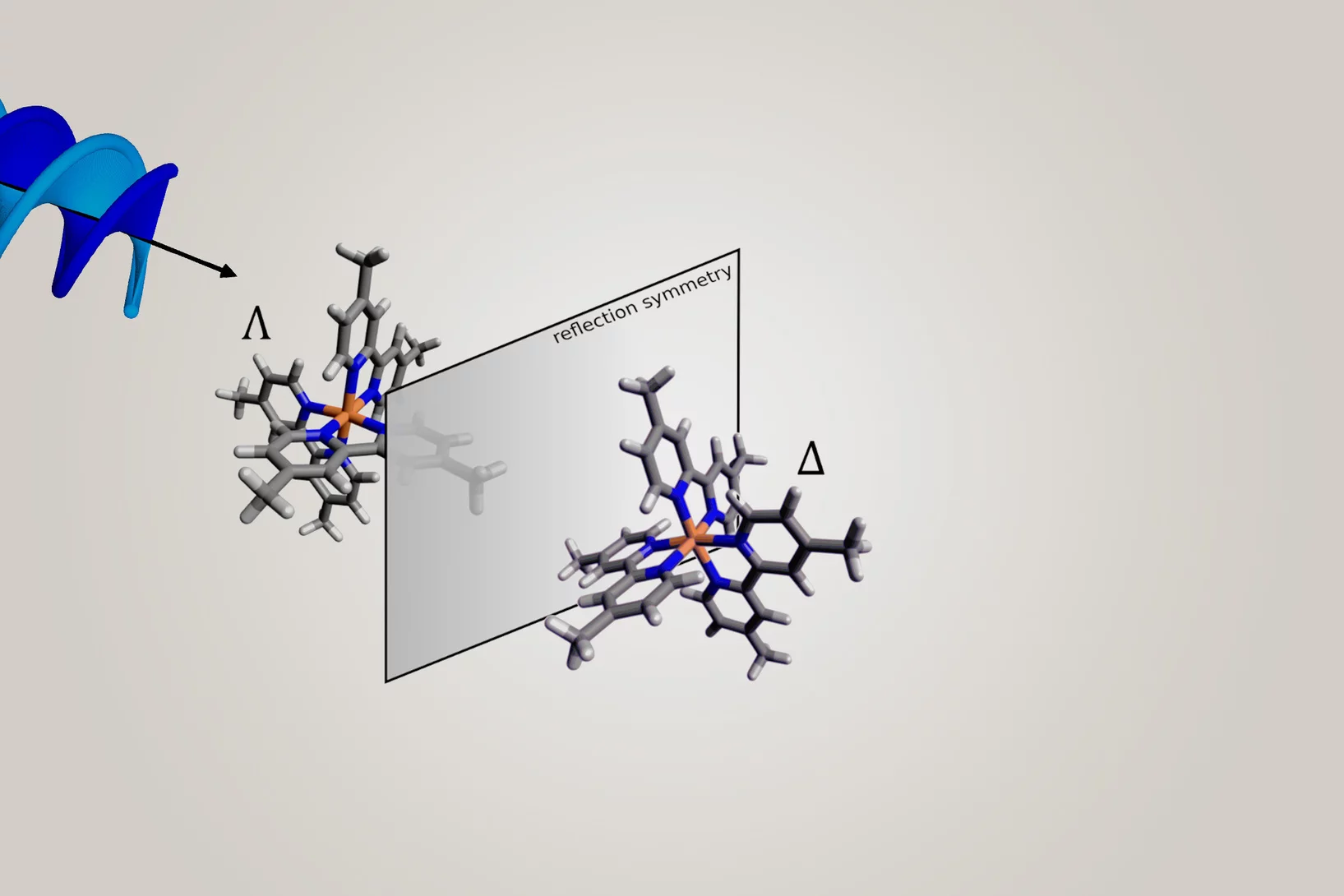
Making it easier to differentiate mirror-image molecules
Researchers have shown that mirror-image substances – so-called enantiomers – can be better distinguished using helical X-ray light.
Light-Induced Magnetization at the Nanoscale
Targeted manipulations of an atom's magnetic moment are tricky, as the charge currents used for this process are extremely difficult to control . Now, a consortium of collaborators in Germany, Switzerland, Slovenia and Italy reports on a solution to this problem in the cover page article of Physic Review Letters 128, Vol. 15. As it appears, the magnetization of an atomic gas can be altered by high-power lasers using a patterned wave front. The method is promising for studying and manipulating the magnetic properties of matter at the nanoscale.
Hercules School 2022
PSI hosted again the Hercules School in March 2022. We had the pleasure to welcome 20 international PhD students, PostDocs and scientists to demonstrate our state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies at our large scale facilities, the Swiss Light Source (SLS), the Swiss Spallation Neutron Source (SINQ) and our free electron laser SwissFEL.
Novel X-ray lens facilitates glimpse into the nanoworld
PSI develops a revolutionary achromatic lens for X-rays.
Opening the door to X-ray quantum optics
The 'perfect' X-ray beam-splitter: Researchers at SwissFEL have an ingenious solution to produce coherent copies of pulses, facilitating a realm of new X-ray techniques.
New, better coronavirus rapid test
The test identifies different virus variants and improves disease prognosis.
Millions in funding for brain and quantum research
The European Research Council approves PSI projects for the development of a quantum computer and brain research worth about 5 million euros.
LMN PhD student Martin Heinrich wins poster award
PhD student Martin Heinrich of the Molecular Nanoscience group won the best poster award at the Nano-BW 2021 symposium at Bad Herrenalb (Germany), October 6-7. The symposium is held annually within the research network “Functional Nanostructures” of Baden-Württemberg.
Martin introduced his project in the form of a poster titled “Local Manipulation of Spin Domains in a Multiferroic Rashba Semiconductor”. His project started in July 2021 and is funded by the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI) Basel. The poster award was selected by the vote of all attendees.
Diamond gratings for XFEL amplitude-splitting delay line
A split-and-delay line for XFEL pulses has been built and successfully tested by a team of researchers at the Linac Coherent Light Source. Key X-ray optical elements are two diamond diffraction gratings made at the Paul Scherrer Institut that are used to split and later recombine the intense ultrashort X-ray laser pulses for time-resolved measurements.
Ultrafast control of quantum materials
Using light to fundamentally change the properties of solids