IMPACT for Swiss society
World leader in muons and in production of medical radionuclides: The far-reaching significance of the planned upgrade.
New nuclear medicine therapy successfully tested
A promising radiopharmaceutical against metastatic neuroendocrine tumours – developed at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI – has been successfully tested.
„IMPACT is very important in terms of international competition“
Daniela Kiselev talks about the upgrade planned at PSI's proton accelerator facility.
Terbium-161: new radionuclide therapy hits the clinic
Highly targeted cancer treatment has the potential to eliminate ultra-small cancer lesions that cause disease recurrence.
Fighting tumours down to the last cancer cell
A project that promises to improve the chances of survival for prostate cancer patients has received 2 million Swiss francs in funding.
Radionuclides for personalised medicine
TATTOOS is part of the upgrade project IMPACT. Roger Schibli explains its importance for the future of cancer treatment.
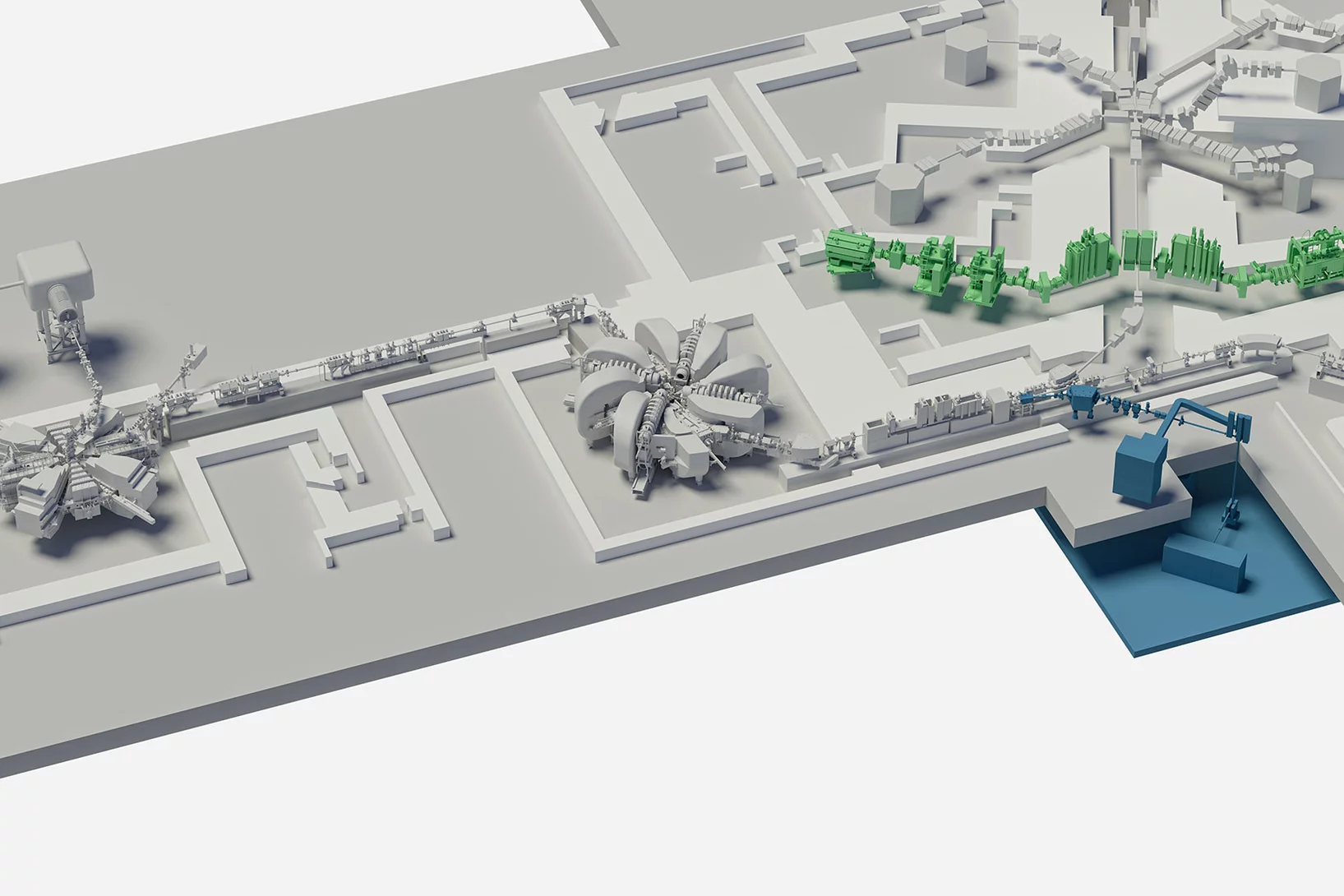
A two-part upgrade for the proton accelerator
A two-part upgrade is planned for HIPA starting in 2025. Preparations are already under way.
Paul Scherrer Institute and Apollo Health Ventures Launch Focal Biosciences
Newly established Focal Biosciences will focus on bringing together leading experts and scientific discoveries to harness cellular reprogramming in the fight against common age-related diseases.
Making tumour diagnosis kinder to kidneys
Improved method thanks to a molecular trick
Swissmedic grants operating licence for new radiopharmaceutical production facility
From research to production – the new pharmaceutical lab at PSI supplies neighbouring hospitals with novel cancer drugs.
Effective combination cancer treatment
Combining two chemotherapeutic drugs inhibits tumour growth.
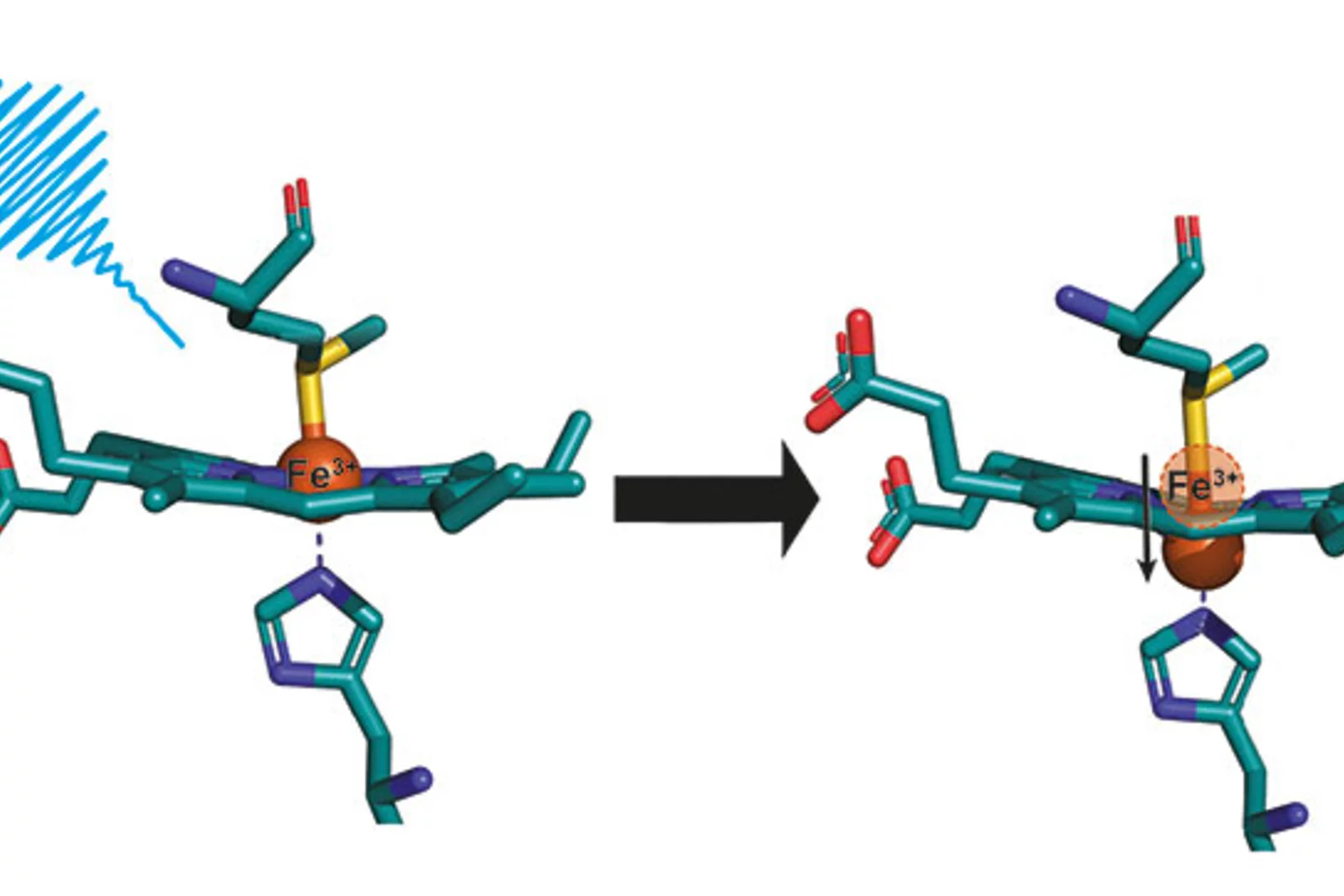
A protein's unexpected "doming"
Researchers have coaxed a secret out of the vital protein cytochrome c that it kept well-hidden up to now. Measurements at the X-ray free-electron laser SwissFEL reveal structural changes that science had previously ruled out for this kind of biomolecule.
More effective treatment of thyroid cancer
PSI researchers have found a more effective treatment for a form of thyroid cancer – and with fewer side effects – by increasing the uptake of the cancer drug in tumour cells. The results have been published in the medical journal Theranostics.
Brilliant medicines
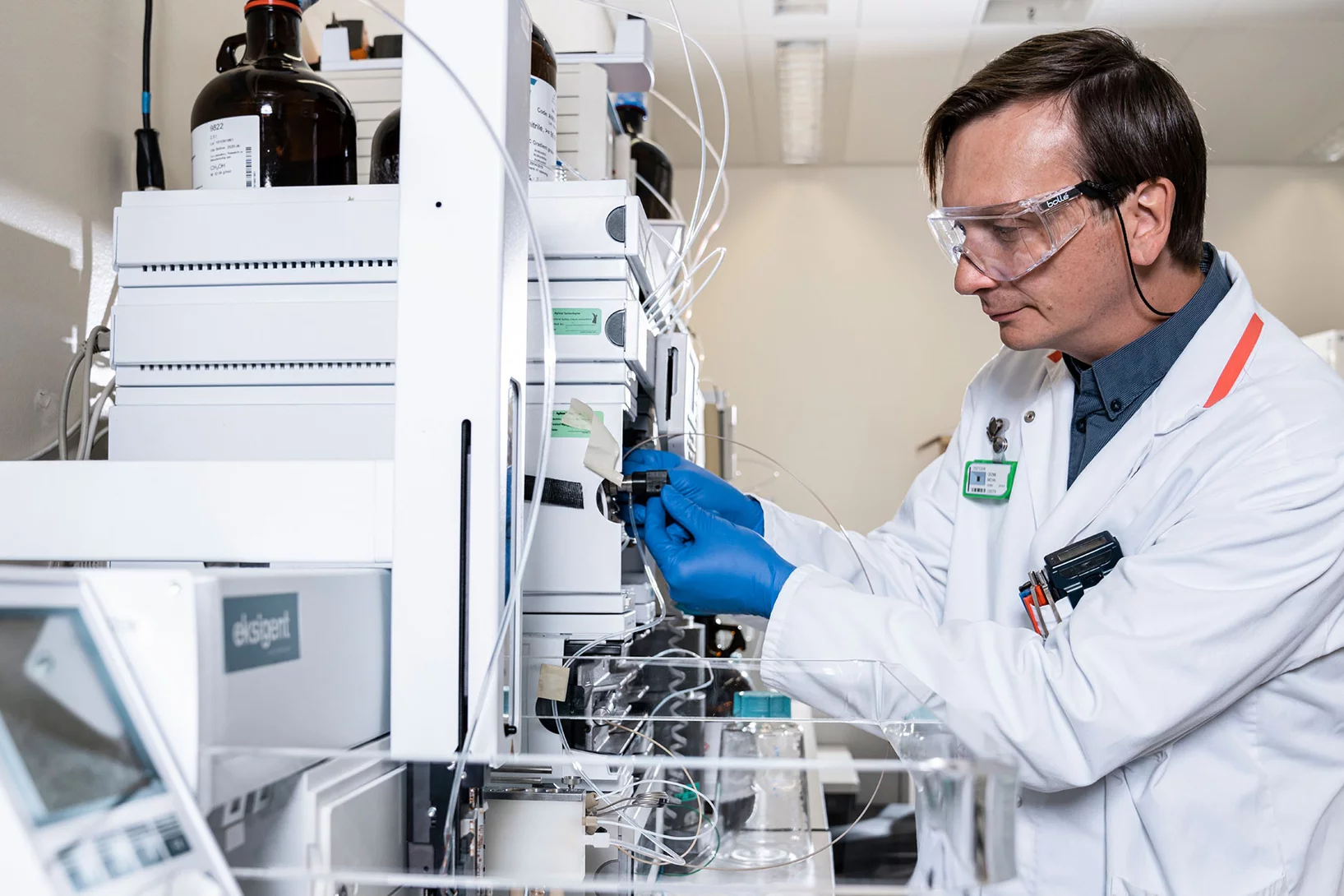
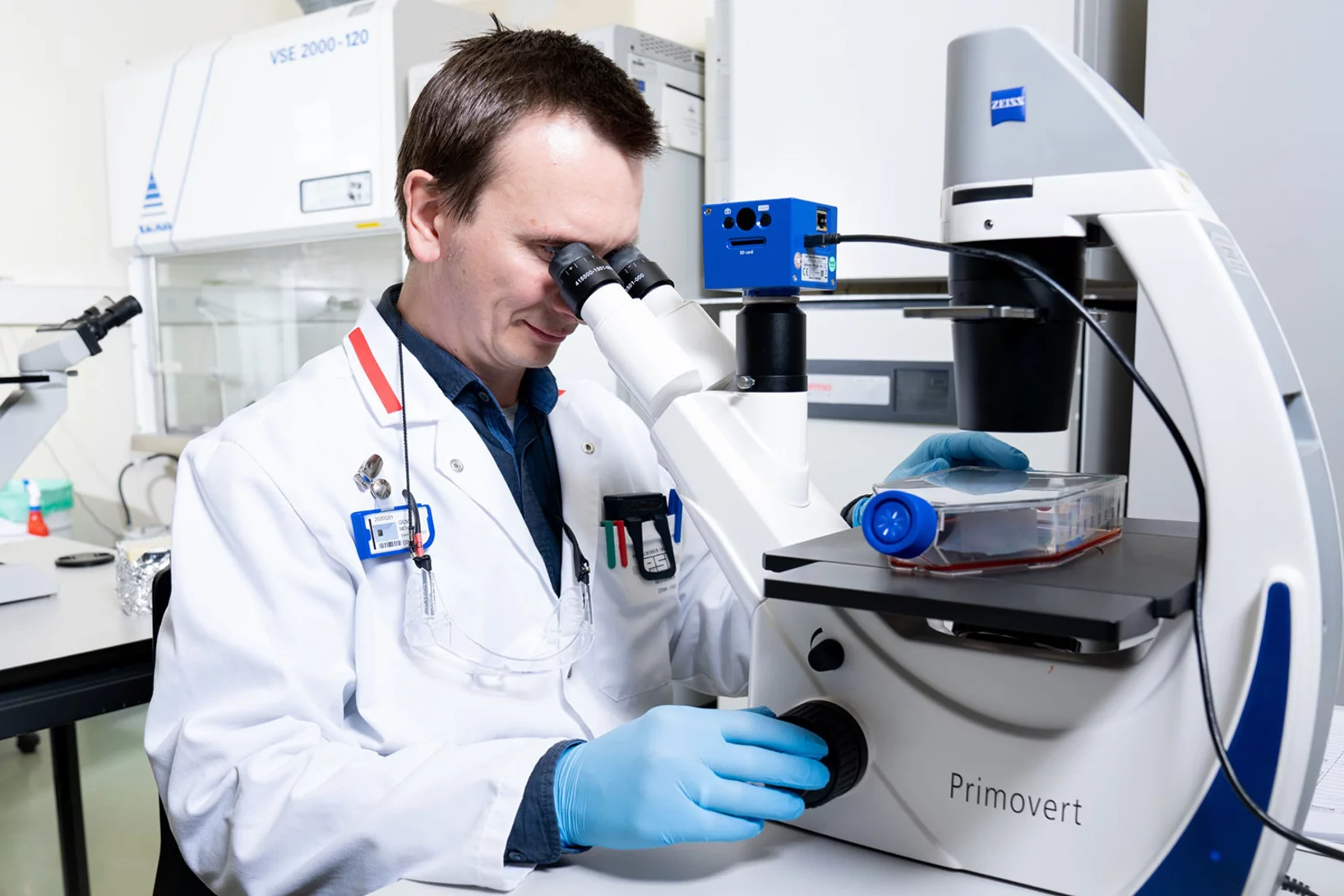
In the service of health, scientists at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI work with radionuclides and develop agents to treat cancer and to detect tumours. Their research provides support to hospitals and is of great interest to Swiss industry.
Licence agreement with Swiss pharma firm for development of a cancer drug
A radioactive agent, developed at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI to fight an especially malignant form of thyroid cancer, has the potential to become a blockbuster drug. Due to its structure, it might also be able to dock onto cells of other tumours and destroy them with its radiation. The Lausanne-based biopharmaceutical company Debiopharm wants to further develop the PSI agent to the point where it is approved as a drug. Debiopharm and PSI have now created the contractual basis for this.
A biotechnological revolution
Gebhard Schertler is head of the research division Biology and Chemistry at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI and professor for Structural Biology at ETH Zurich. In this interview he talks about biological research at PSI and the future of drug development.
A new bio-robot
With a new method for modifying antibodies, Philipp Spycher, winner of a Founder Fellowship at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, wants to develop drugs that are more stable and, thus, have fewer side-effects.
In the focus of the protons
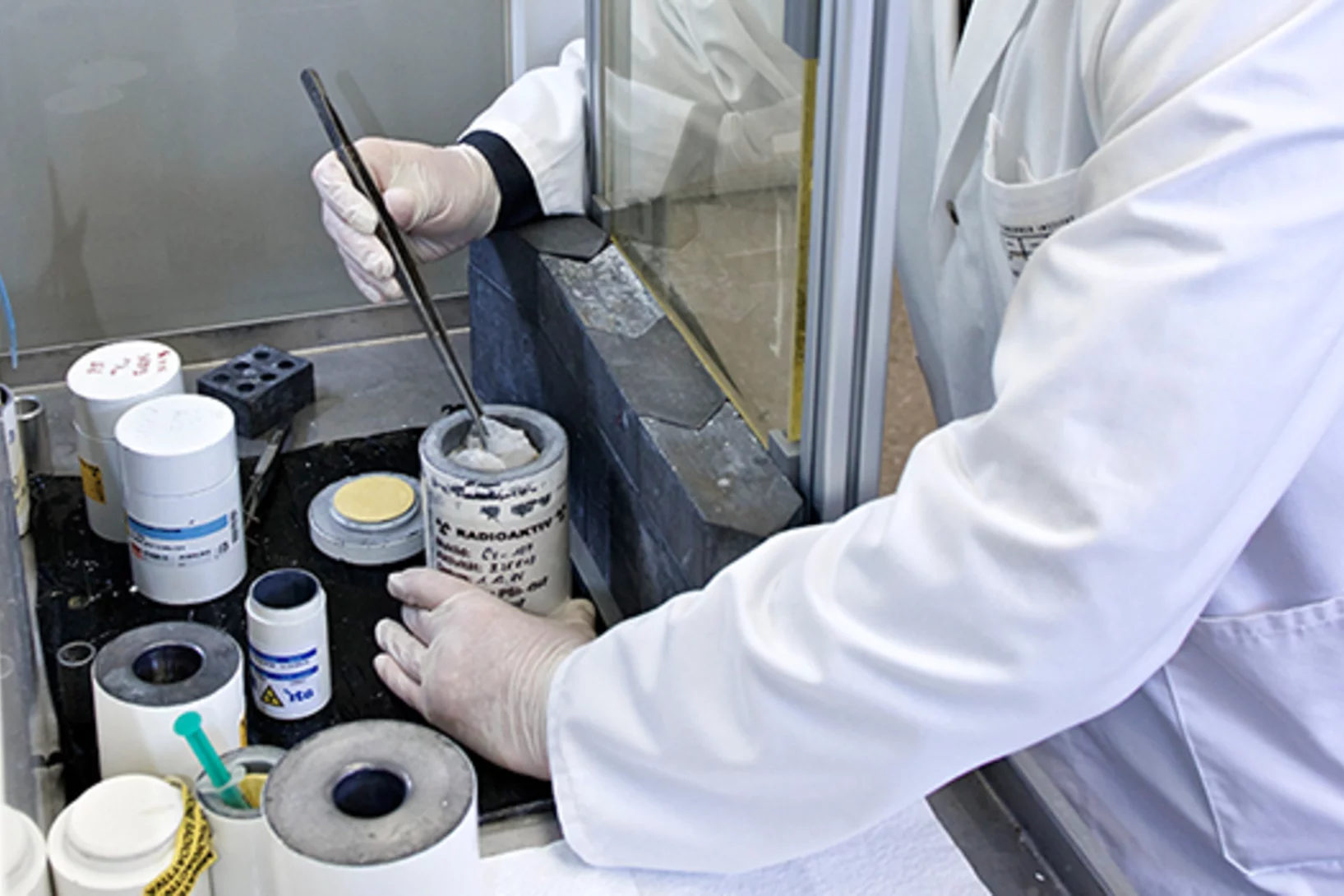
At the PSI, researchers work with radioactivity every day in order to develop advanced treatment methods for patients. Naturally, they take special safety precautions working with a material that decays. It's a race against time. To make sure everything functions smoothly, a dedicated work group takes care of the infrastructure.
Designer nuclide for medical applications
Researchers at the PSI have for the first time used a cyclotron to produce the radionuclide scandium-44 in a quantity and concentration as needed for medical treatment. With that, they have achieved the first precondition for scandium-44 to be used one day for medical tests in hospitals.
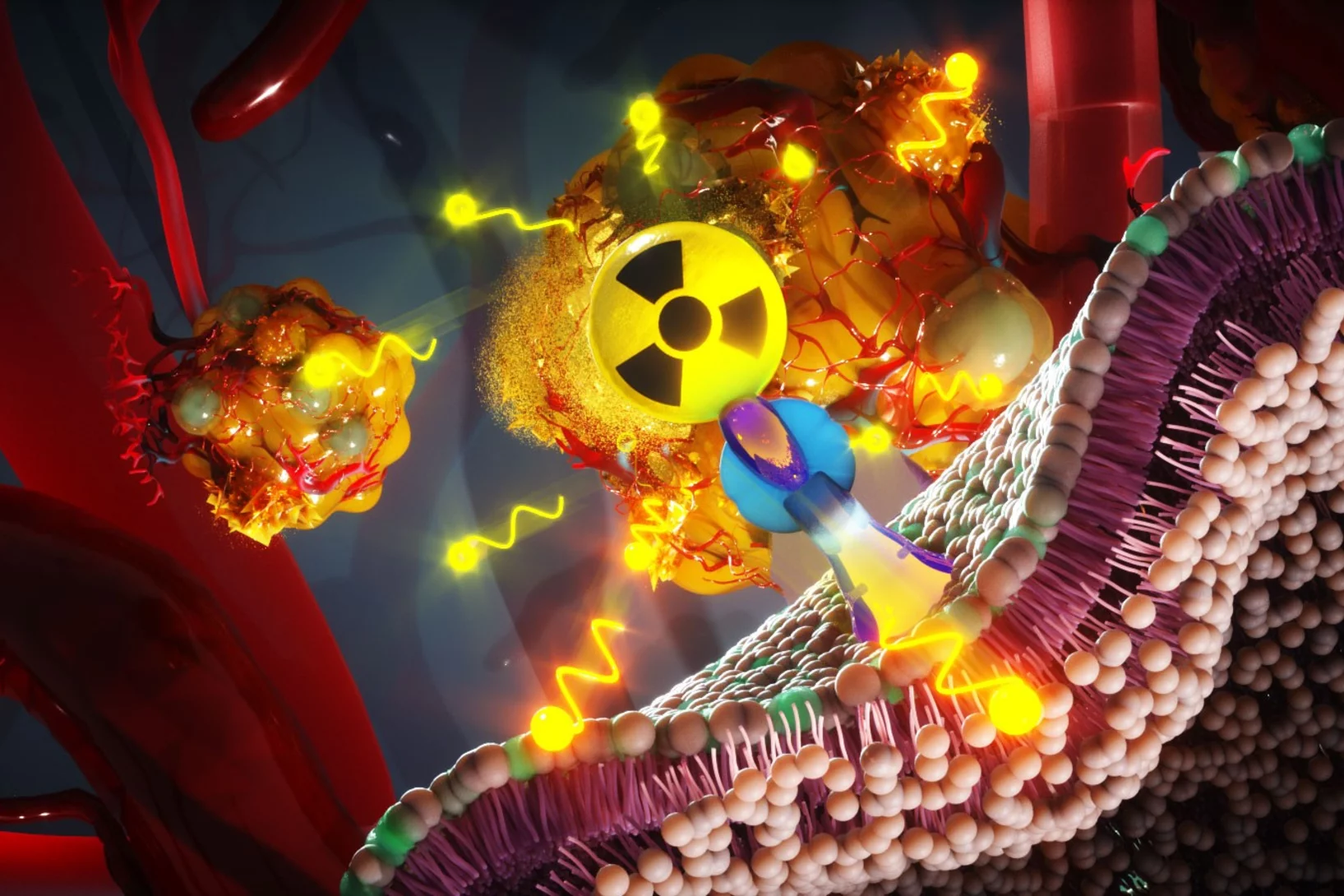
Hitting cancer from the inside
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI are now investigating a new method to channel radioactive substances directly into the nucleus of a cancer cell. Through this approach, the radiation source remains inside the cell and works in a more targeted way, because it gets closer to the cell's genetic information.
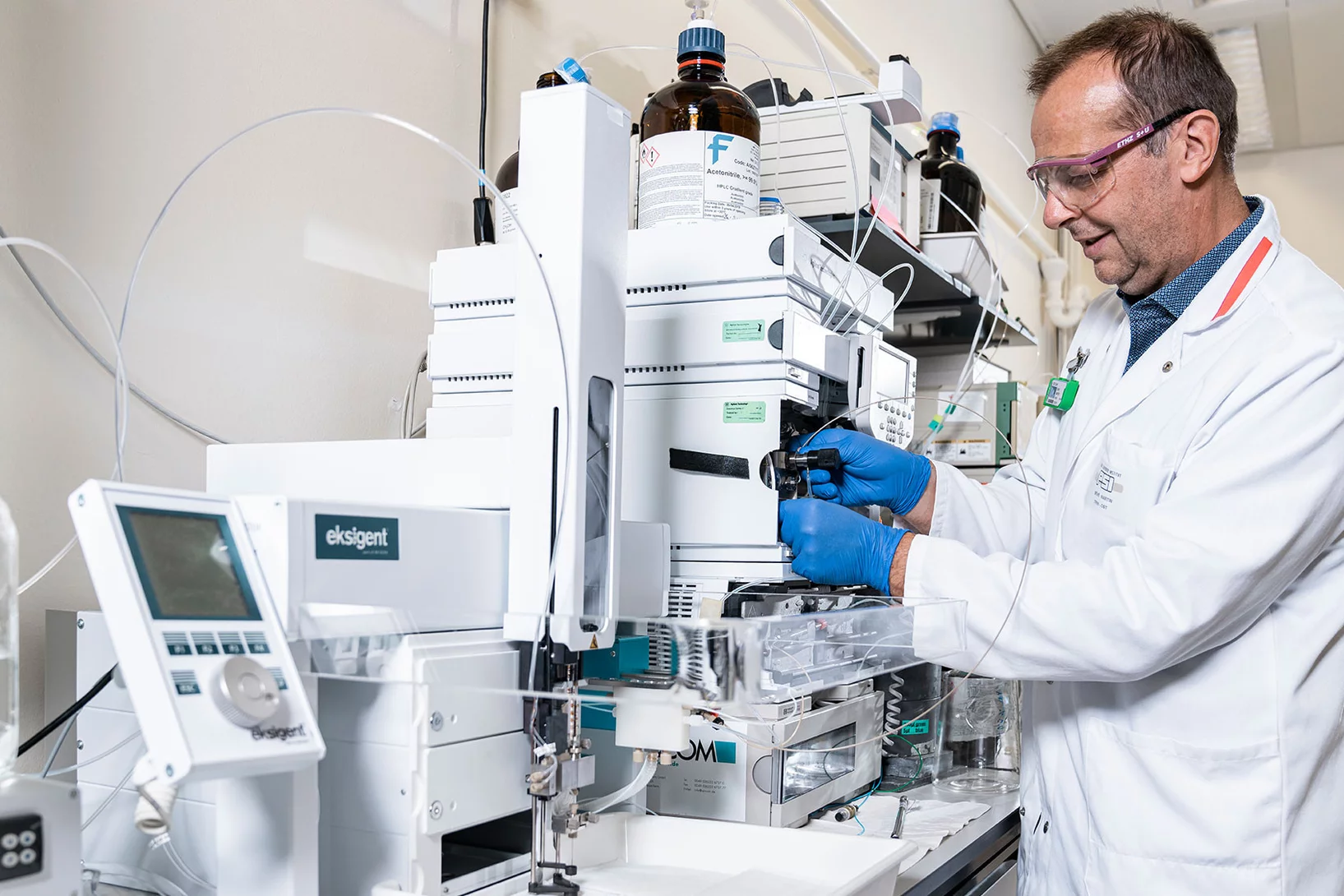
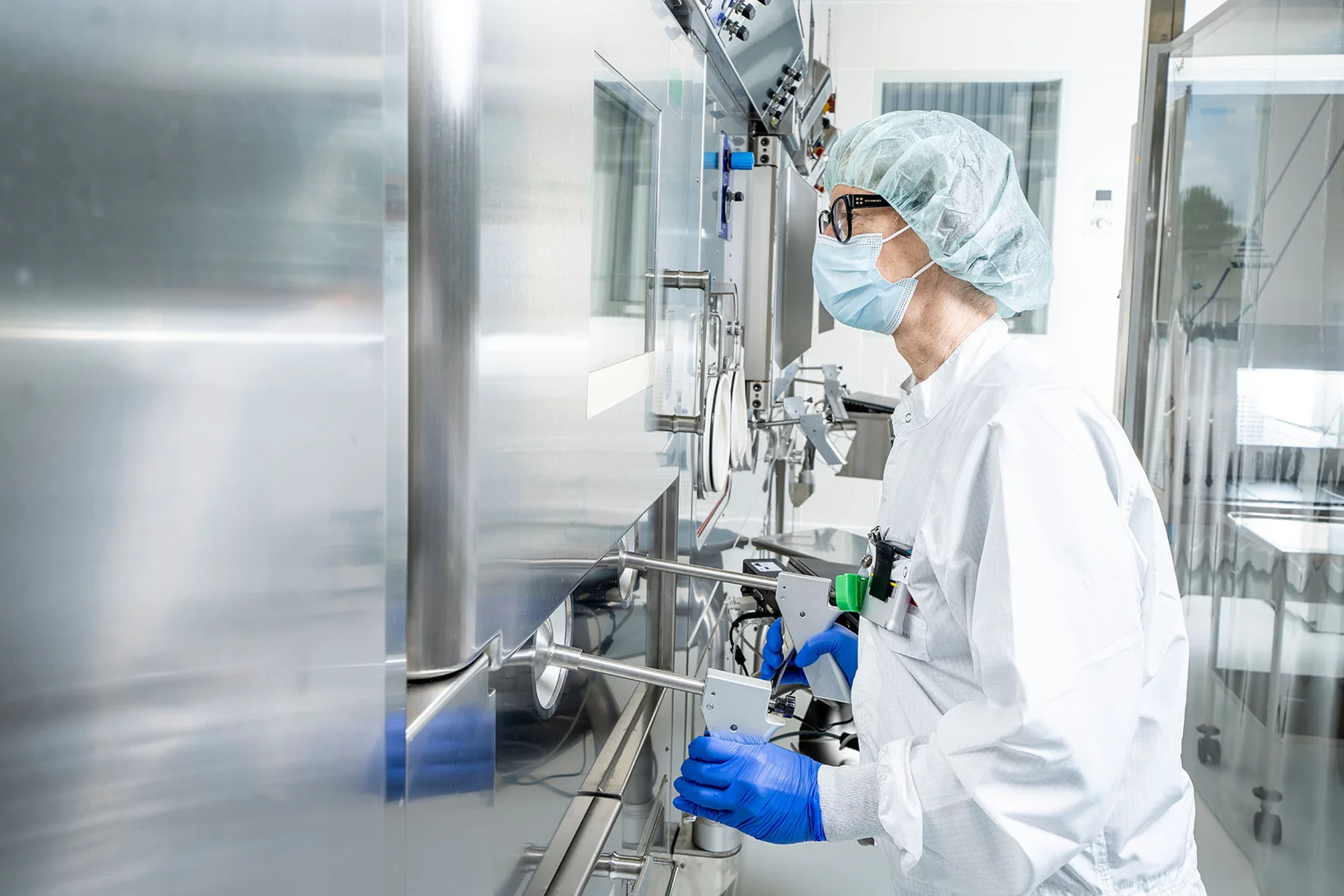
Medicines made to order with pinpoint precision
At PSI, scientists are developing new medicines against cancer. These contain radioactive substances that can be injected into the patients and thus make their way to the tumour. There, in direct contact, their radiation should destroy the cancer cells. Before such a radioactive medicine can be tested on patients in the first clinical trials, however, its safety must be guaranteed to ensure that the patient will not be harmed. Therefore every agent is produced at the PSI under sterile conditions and tested – separately for each patient, and only on the doctor's order.
Developing a new drug against thyroid cancer
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have developed a drug to trace and treat a particularly malignant strain of thyroid cancer more effectively. One advantage of the new drug is that it can be used to treat a strain of thyroid cancer where the established treatment is ineffective. The researchers at PSI have developed the new drug to such an extent that an initial study conducted on cancer patients at the University Hospital Basel can now get underway.
Targeting cancer
There are tumours where nothing seems to help: not chemotherapy, not external radiation therapy, not an operation. Often, they have already metastasised and can no longer be destroyed using conventional methods. The only option left here is internal radiotherapy with targeted radioactive drugs that strike directly at the heart of the disease. In order to make this possible, twenty specialists have been conducting research at the Centre for Radiopharmaceutical Sciences at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI, a joint facility of PSI, ETH Zurich and the University Hospital Zurich.