A l’Institut Paul Scherrer, les scientifiques cherchent des réponses à la question essentielle des structures élémentaires de la matière et des principes fondamentaux de fonctionnement dans la nature. Ils étudient la structure et les propriétés des particules élémentaires – les plus petits composants de la matière – ou se penchent sur la question de savoir comment les molécules biologiques sont structurées et remplissent leur fonction. Les connaissances qu’ils acquièrent de la sorte ouvrent de nouvelles pistes de solution en sciences, en médecine ou dans le domaine des technologies.
Pour en savoir plus, reportez-vous à Aperçu Fondements de la nature
Nanoforscher untersuchen Karies
Forscher der Universität Basel und des Paul Scherrer Instituts konnten im Nanomassstab zeigen, wie sich Karies auf die menschlichen Zähne auswirkt. Ihre Studie eröffnet neue Perspektiven für die Behandlung von Zahnschäden, bei denen heute nur der Griff zum Bohrer bleibt. Die Forschungsergebnisse wurden in der Fachzeitschrift «Nanomedicine» veröffentlicht.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Nationaler Zukunftstag erstmals auch für Knaben
Der Nationale Zukunftstag, früher bekannt als Tochtertag, gehört zu den Traditionsanlässen am PSI. Seit diesem Jahr ist der Tag nicht mehr den Mädchen vorbehalten, auch die Jungs sind eingeladen. 40 Mädchen und 50 Knaben begleiteten am Donnerstag, 10. November 2011 ihre Eltern zur Arbeit in die Labors, Experimentierstationen, Werkstätten und Büros. Sie nutzten die Gelegenheit, Vater oder Mutter einmal bei der Arbeit über die Schulter zu schauen.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Bilayer manganites reveal polarons in the midst of a metallic breakdown
The origin of colossal magnetoresistance (CMR) in manganese oxides is among the most challenging problems in condensed- matter physics today. The true nature of the low-temperature electronic phase of these materials is heavily debated. By combining photoemission and tunnelling data, we show that in the archetypal bilayer system La2-2xSr1+2xMn2O7, polaronic degrees of freedom win out across the CMR region of the phase diagram.
«Facettenauge» liefert Strom
«swisselectric research award 2011»Kostengünstiger Strom aus Sonnenenergie: Der Maschinenbauingenieur Illias Hischier hat einen Sonnenstrahlempfänger entwickelt, der die aufgenommene Energie über eine Gasturbine für die hocheffiziente Stromerzeugung nutzt. Hischier hat den Empfänger als Doktorand an der ETH Zürich in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Labor für Solartechnik am Paul Scherrer Institut entwickelt. Er erhält dafür den «swisselectric research award 2011».Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
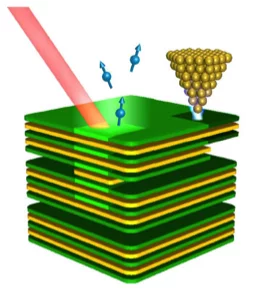
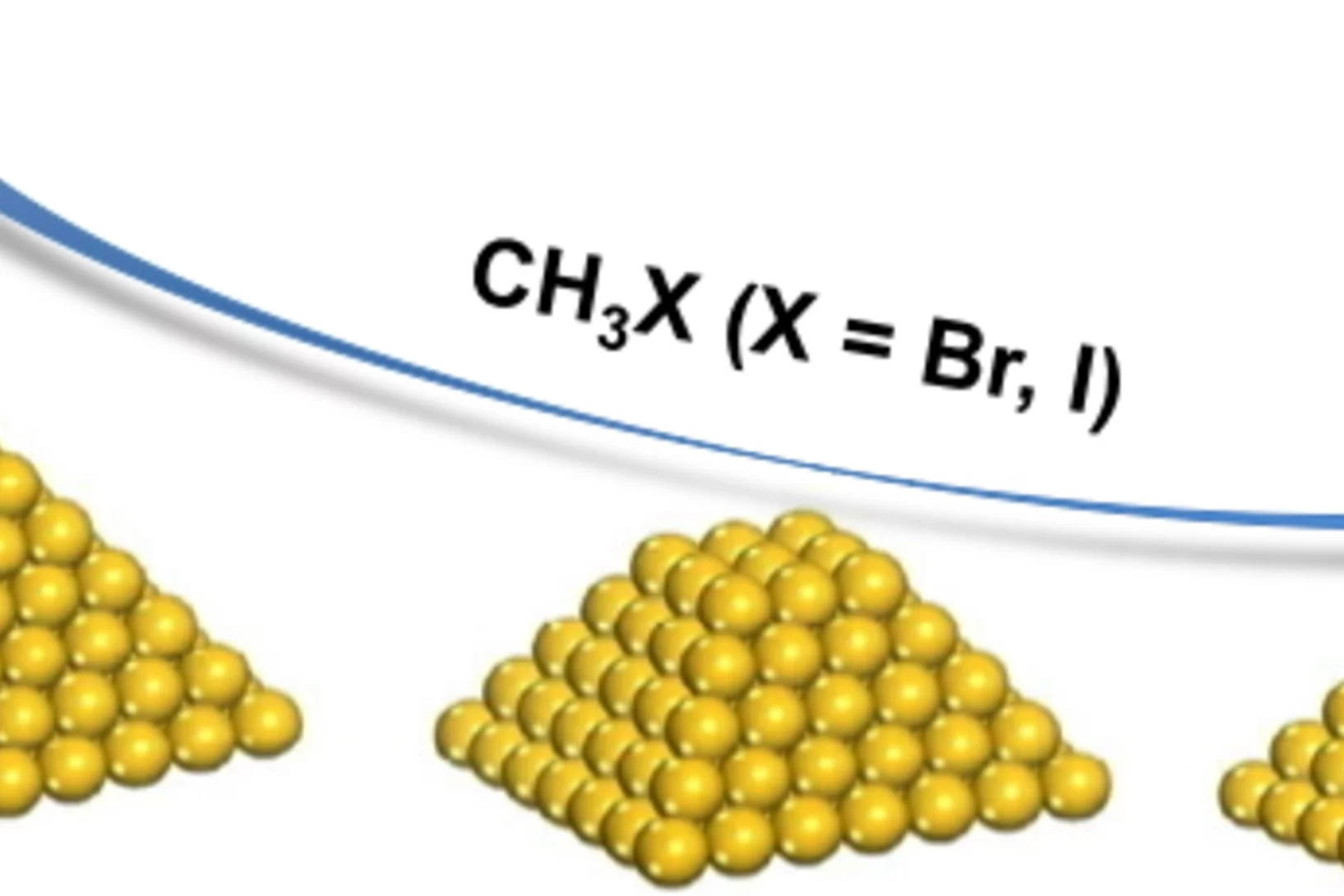
Influence of Methyl Halide Treatment on Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Activated Carbon
Gold particles supported on carbon when subjected to a flow of methyl iodide or bromide redisperse from large ensembles to single atoms and/or dimers of gold. Methyl halide oxidizes gold leading to gradual particle dissolution. The process could be carried out at temperatures as low as 50 °C. The excess of halide could be removed by a post-treatment of the material with 1%H2O/H2, which does not influence the metal dispersion. This remarkable transformation opens the possibility of re-activating gold catalysts that lost their performance due to metal particles sintering.
Schweiz beteiligt sich an Neutronenquelle der Zukunft
Mauro Dell’Ambrogio, Staatssekretär für Bildung und Forschung unterzeichnete heute die Absichtserklärung der Schweiz, sich an der neuen europäischen Neutronenquelle ESS (European Spallation Source) zu beteiligen. Darin bekennt sich die Schweiz zu dem Ziel, die ESS in Lund (Südschweden) zu bauen und verpflichtet sich, am Konzept mitzuarbeiten, in dem der endgültige Plan für die Anlage festgelegt wird. Kurz nach Fertigstellung des Konzepts im Frühjahr 2013 soll die Entscheidung für den Bau der ESS fallen. Die Schweizer Beiträge zur Entwicklung der Anlage werden durch das Paul Scherrer Institut, das langjährige Erfahrung in der Forschung mit Neutronen hat, sowie durch Schweizer Universitäten und die Schweizer Industrie erbracht.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
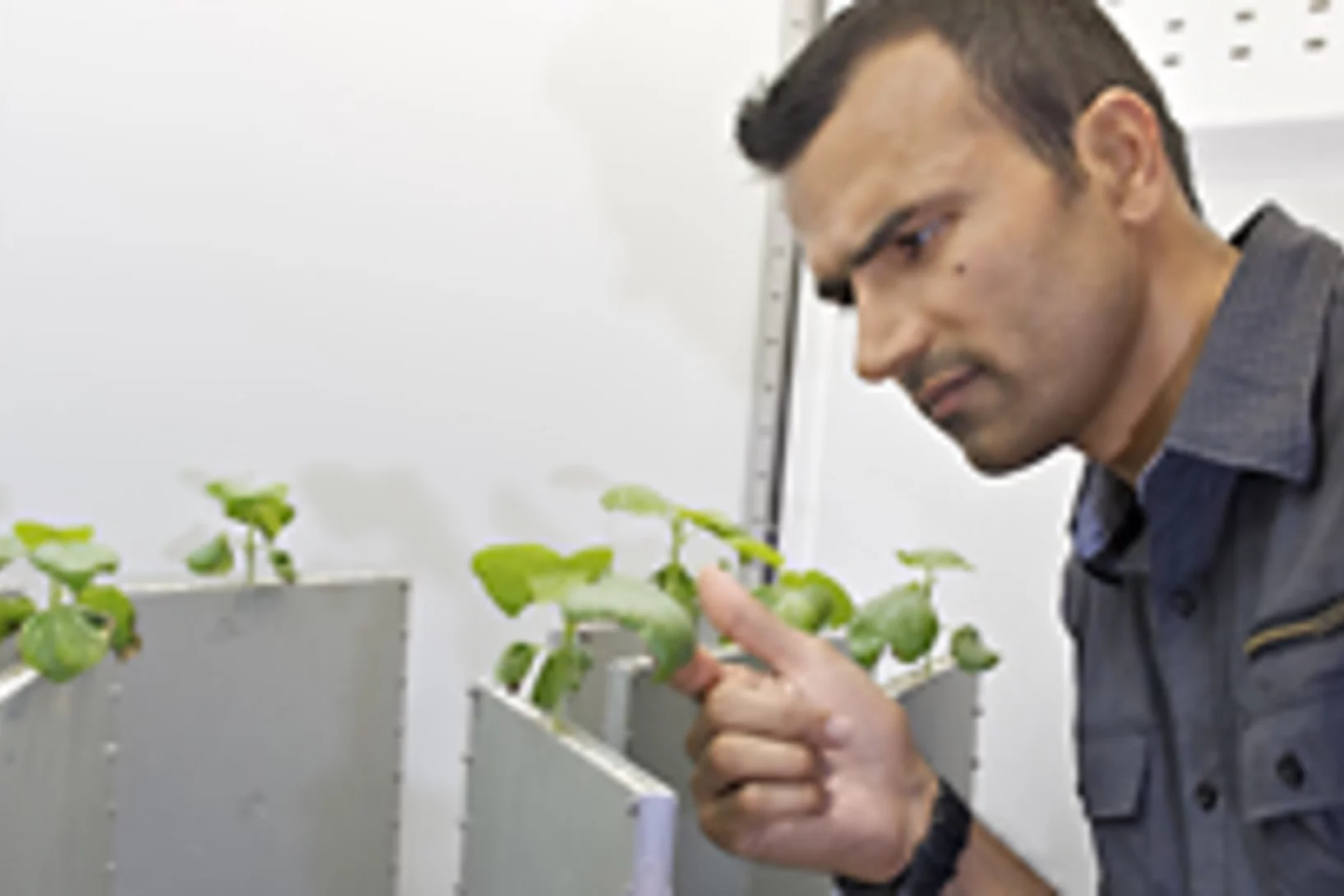
Les plantes se constituent une réserve d’eau dans le sol
Un groupe international de chercheurs a démontré, grâce a des expériences réalisées à l’institut Paul Scherrer, que le sol contient plus d’eau à proximité des racines qu’au-delà. Apparemment les plantes se constituent une petite réserve d’eau afin d’être capable de surmonter de courtes périodes de sécheresse. Ces résultats ont été obtenus grâce à l’imagerie neutronique.
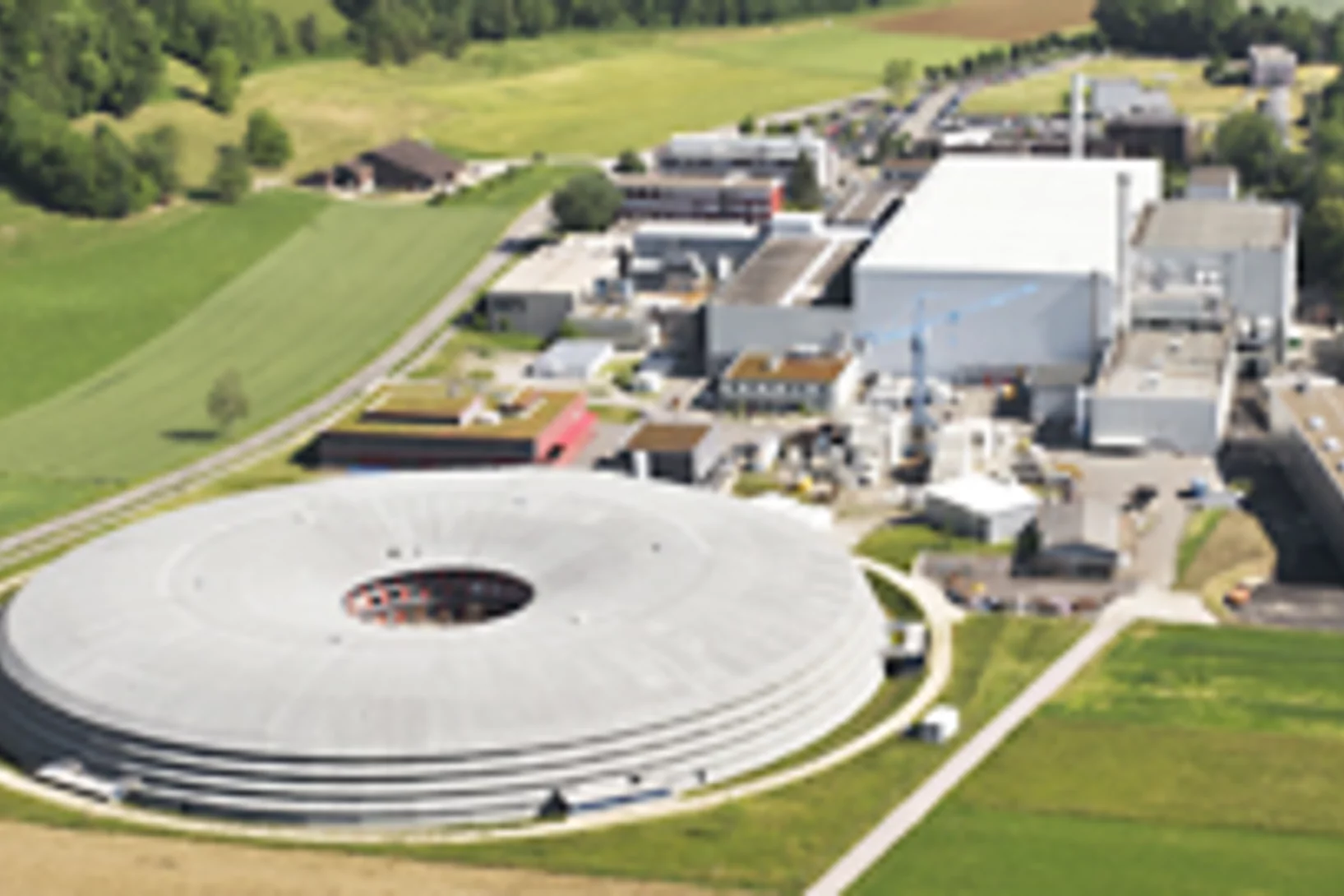
Zehn Jahre Forschung in der fliegenden Untertasse
Mit einem Festakt hat das Paul Scherrer Institut (PSI) in Villigen (AG) heute an das zehnjährige Bestehen ihrer bedeutendsten Grossforschungsanlage erinnert. Seit der Inbetriebnahme im Sommer 2001 haben Tausende von Forschern aus Hochschule und Industrie an der Synchroton Lichtquelle Schweiz (SLS) qualitativ hochwertige Experimente durchgeführt. Ihre Forschung mündete in über 2000 wissenschaftlichen Publikationen und brachte darüber hinaus einen Nobelpreis sowie eine Vielzahl industrieller Anwendungen hervor.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
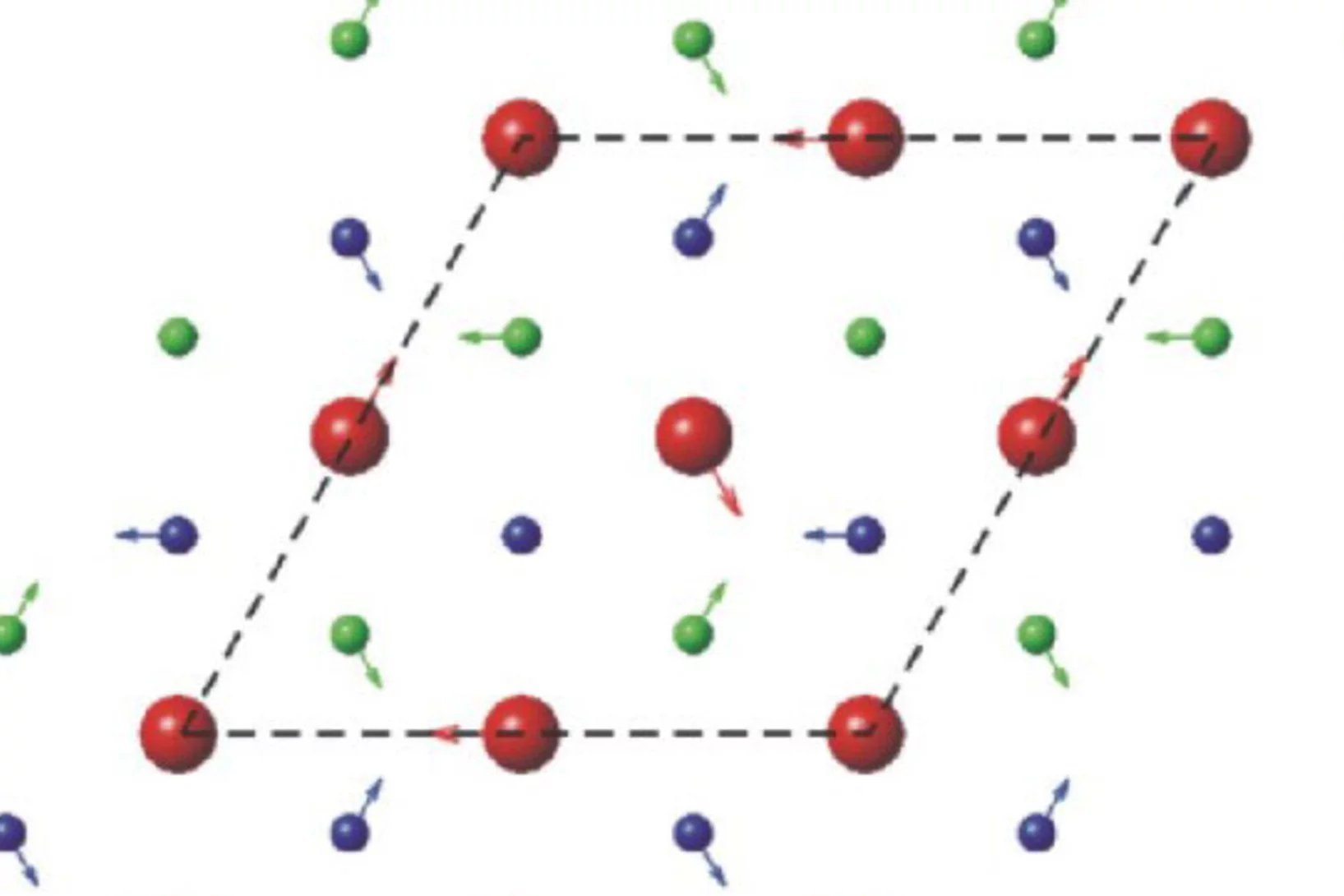
Direct Observation of Local Mn-Mn Distances in the Paramagnetic Compound CsMnxMg1-xBr3
We introduce a novel method for local structure determination with a spatial resolution of the order of 0.01 Å. It can be applied to materials containing clusters of exchange-coupled magnetic atoms. We use neutron spectroscopy to probe the energies of the cluster excitations which are determined by the interatomic coupling strength J.
Diamanten sind auch des Forschers bester Freund
Einem vom PSI geleiteten Forscherteam ist es gelungen, harte Röntgenlaserstrahlung 100'000-fach zu konzentrieren und so an einem Punkt Röntgenstrahlung zu erzeugen, die so intensiv war wie wohl nirgends zuvor. Als Linsen verwendeten die Forscher winzige Ringstrukturen aus Diamant à dem Material, das am besten dem Röntgenlaserlicht standhält. Diese Entwicklung schafft die Voraussetzung für einen Teil der Experimente am SwissFEL, dem geplanten Röntgenlaser des PSI.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
CCN formation mechanism in lower troposphere needs revision
Atmospheric aerosols exert an important influence on climate1 through their effects on stratiform cloud albedo and lifetime and the invigoration of convective storms. Model calculations suggest that almost half of the global cloud condensation nuclei in the atmospheric boundary layer may originate from the nucleation of aerosols from trace condensable vapours, although the sensitivity of the number of cloud condensation nuclei to changes of nucleation rate may be small. Despite extensive research, fundamental questions remain about the nucleation rate of sulphuric acid particles and the mechanisms responsible, including the roles of galactic cosmic rays and other chemical species such as ammonia. Here we present the first results from the CLOUD experiment at CERN.
Klimaforschung am Teilchenbeschleuniger: Beschreibung der Aerosolneubildung muss revidiert werden
Vom Menschen verursachte Aerosole wirken in der Atmosphäre kühlend: Klimaforscher nehmen an, dass sie einen Grossteil des anthropogenen Treibhauseffekts kompensieren. Allerdings müssen sich die Partikel zum Teil in der Atmosphäre erst neu bilden. Diesen bisher kaum untersuchten Prozess nimmt das CLOUD-Experiment am CERN, an dem auch Forscher des Paul Scherrer Instituts beteiligt sind, unter die Lupe. Dabei wurde erstmals ein Teilchenbeschleuniger für die Untersuchung von Vorgängen in der Atmosphäre eingesetzt. Die Ergebnisse zeigen: die Beschreibungen der Aerosolbildung in Klimamodellen muss revidiert werden.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Décision prise pour le site du SwissFEL
L’Institut Paul Scherrer a franchi une nouvelle étape importante vers la réalisation de sa nouvelle grande installation de recherche.Aujourd’hui, le Grand Conseil du canton d’Argovie a donné son accord pour l’adaptation du plan directeur pour le secteur d’agglomérations de Würenlingen, ainsi que pour l’adaptation du plan d’occupation relatif à la zone de protection des eaux souterraines qui s’y trouve. L’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI se réjouit de cette importante décision sur la voie de la réalisation de sa nouvelle grande installation de recherche SwissFEL (laser à rayons X suisse à électrons libres).
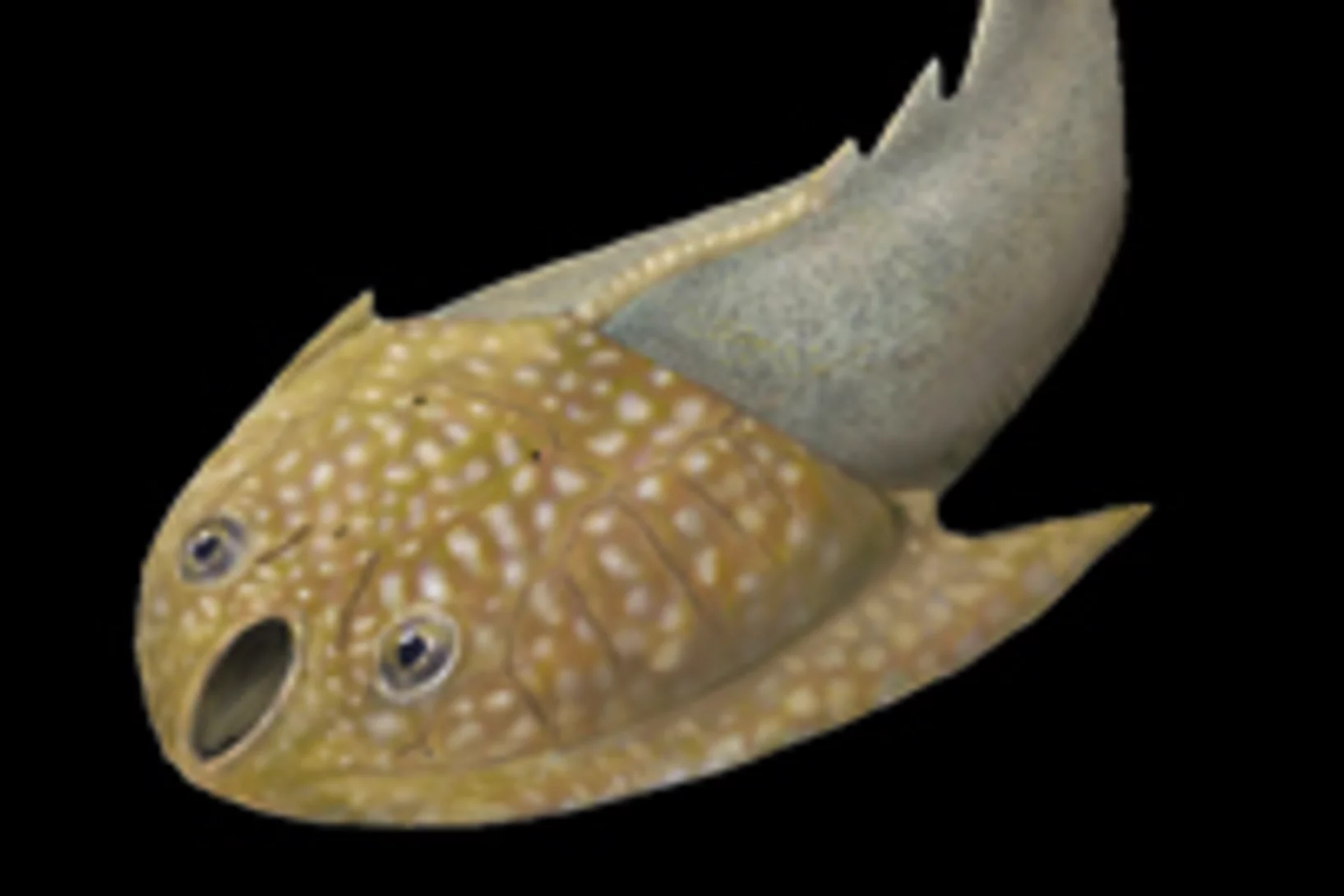
Unseren frühen Vorfahren in den Kopf (und in die Nase) geschaut
Der Umbau des Gehirns und der Sinnesorgane dürfte den Erfolg der Wirbeltiere, eines der grossen Rätsel der Evolutionsbiologie, erklären à so die Aussage einer Arbeit, die heute im Wissenschaftsjournal Nature erschienen ist. Die Forschenden konnten das Rätsel durch Untersuchungen des Gehirns eines 400 Millionen Jahre alten versteinerten Fisches à eines evolutionären Bindeglieds zwischen den heute lebenden kiefertragenden Wirbeltieren und den Kieferlosen.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.
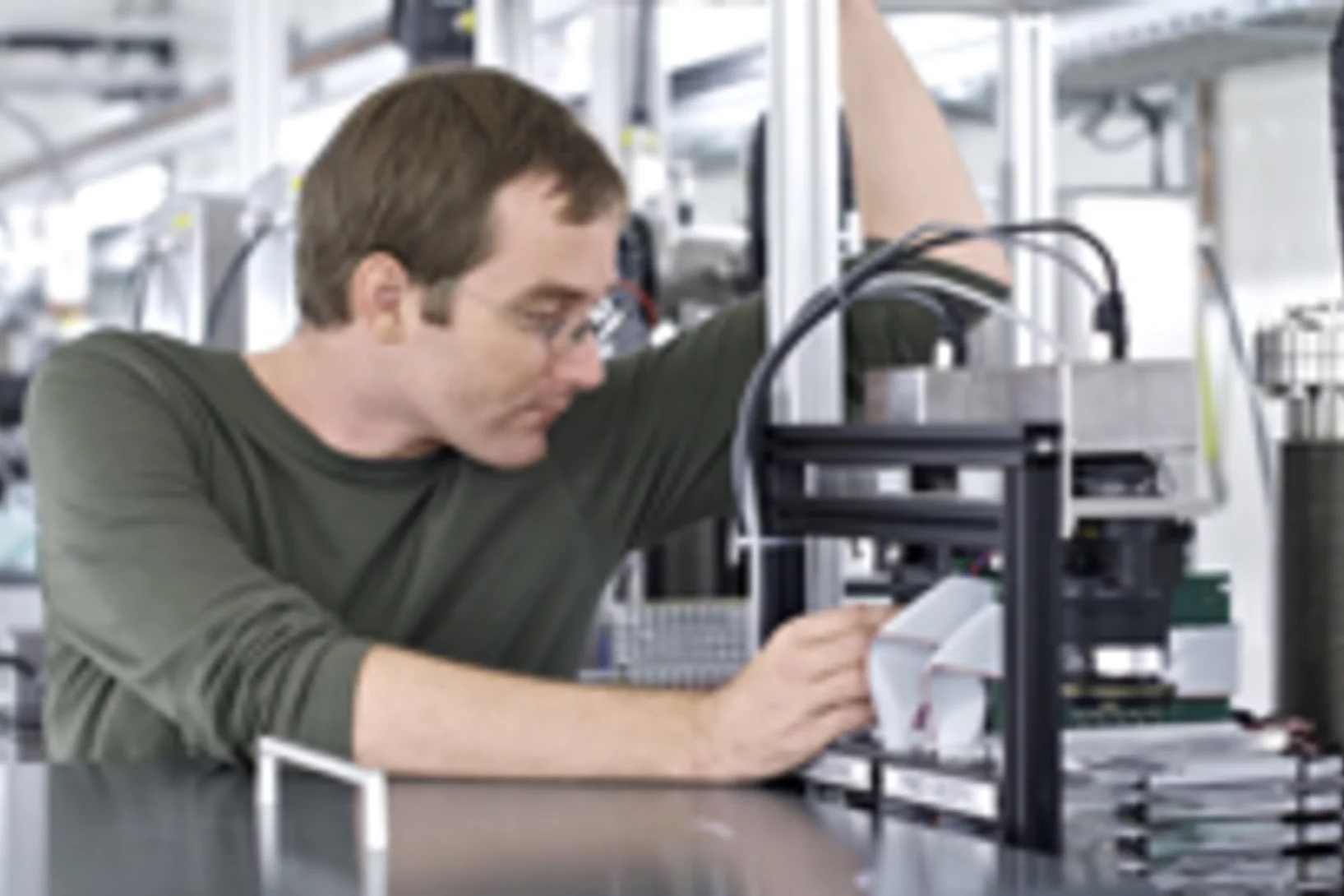
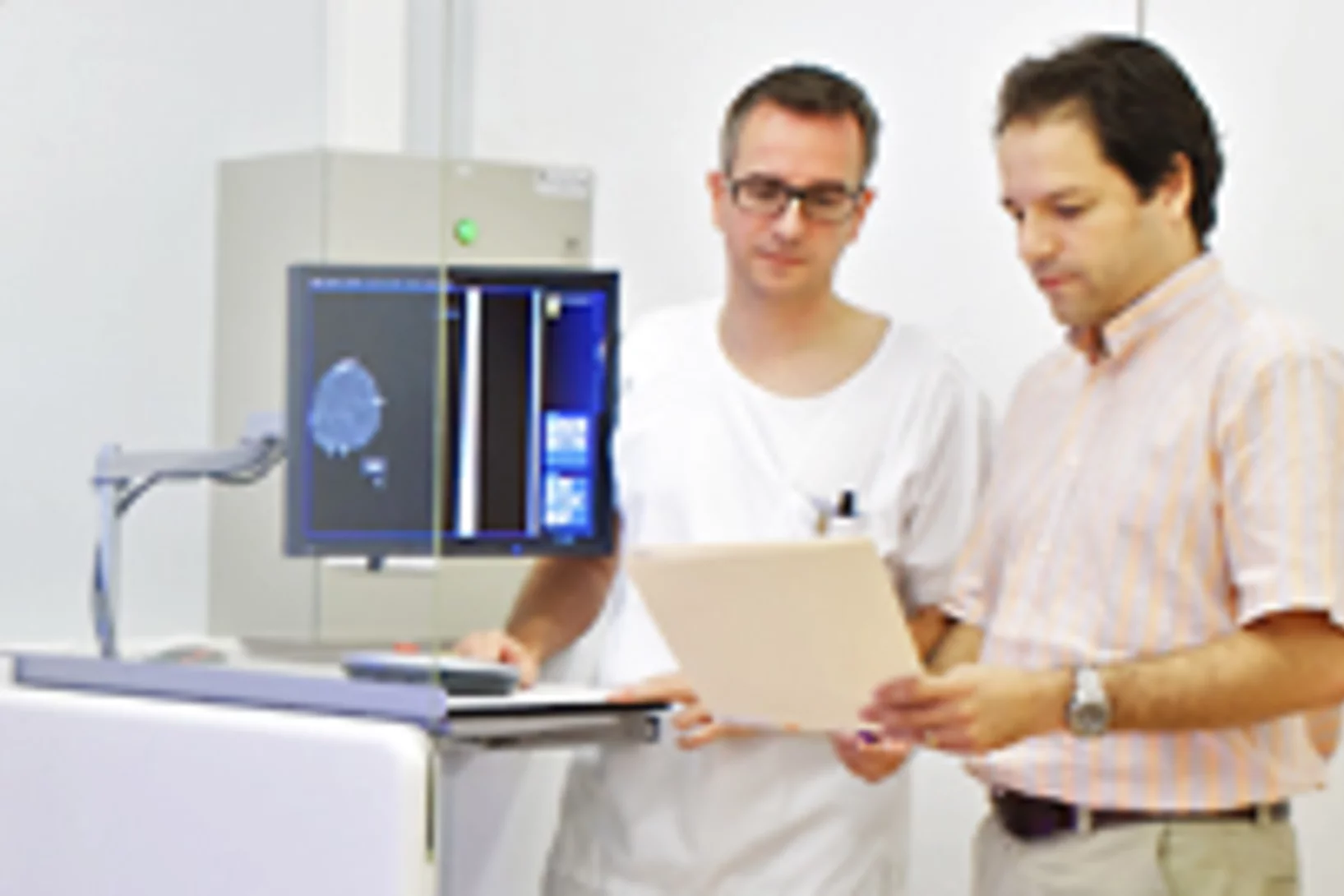
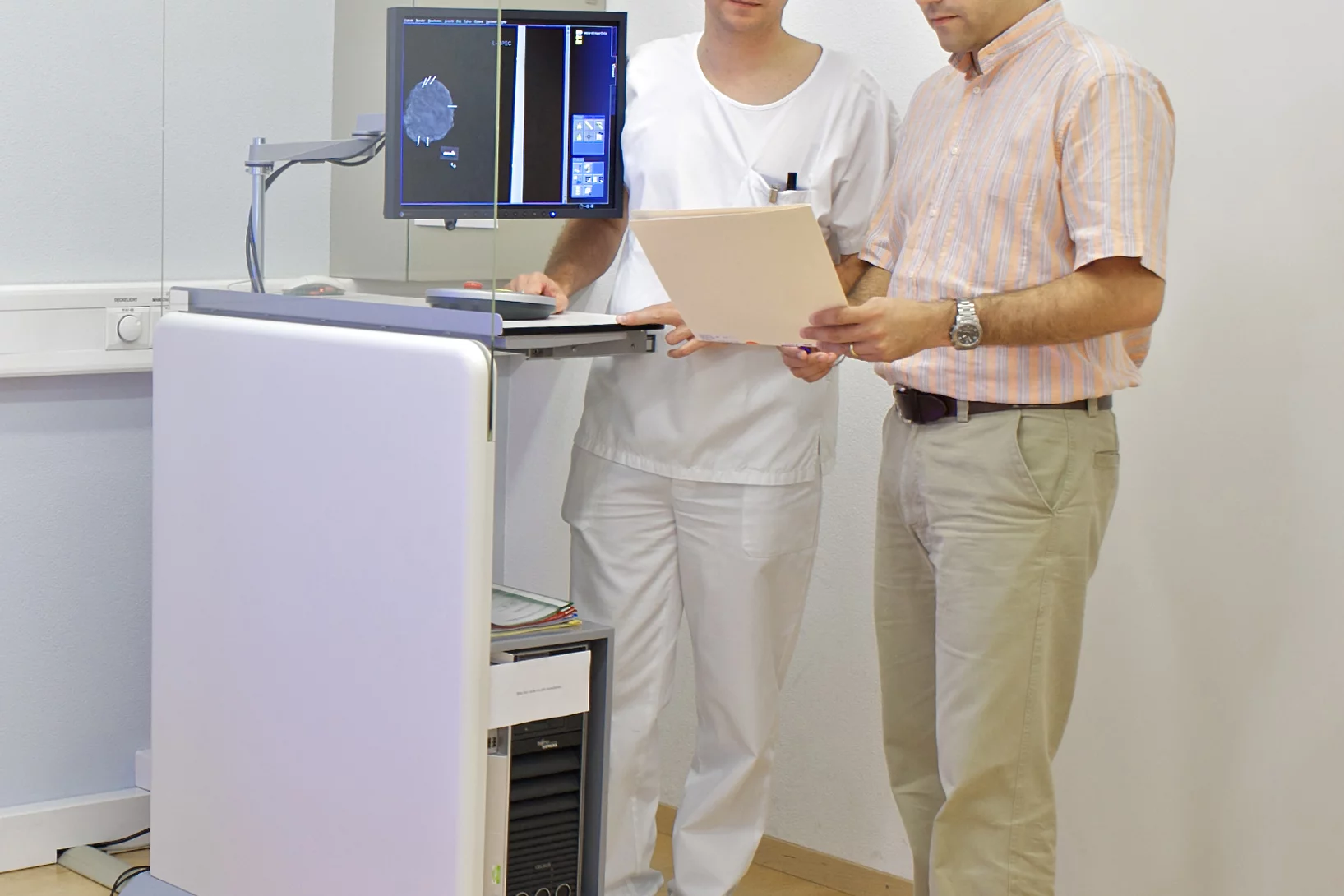
Expérimentation d’une nouvelle méthode pour le dépistage du cancer dans les tissus mammaires
L’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI a développé une nouvelle méthode pour le diagnostic du cancer du sein et a réalisé pour la première fois, en collaboration avec l’hôpital cantonal de Baden AG, des tests sur des tissus humains non conservés. Cette nouvelle méthode permet de révéler des structures invisibles par les techniques de mammographie traditionnelle. Les scientifiques du département de recherche de l’entreprise Philips étudient actuellement l’utilisation de ce procédé dans la pratique médicale.
Investigation of a new method for the diagnosis of cancer in breast tissue
Collaboration between research, hospital and industry aimed at transferring innovative procedure into daily practice.
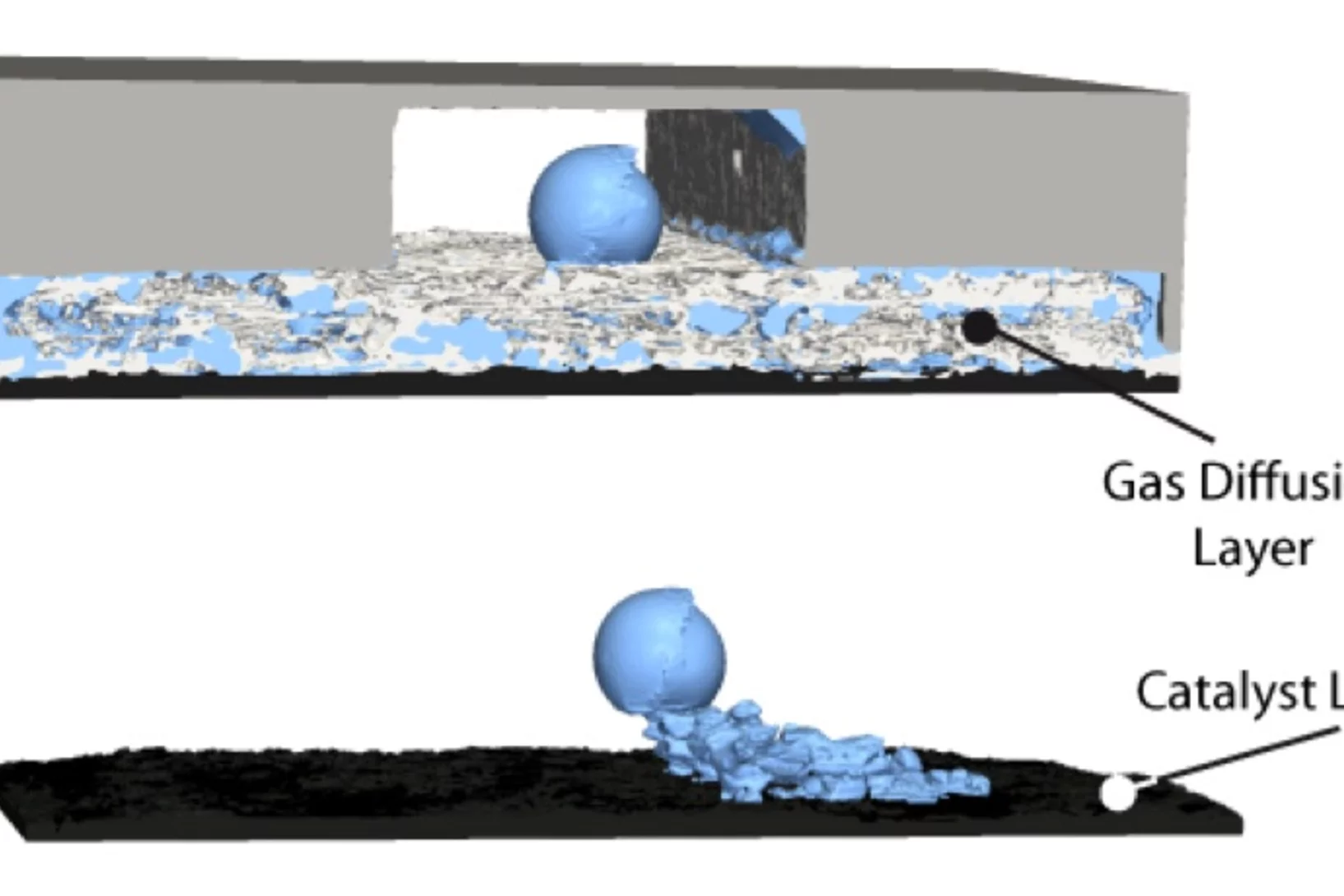
X-Ray Tomography of Water in Operating Fuel Cell
Polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFC) convert the chemical energy of hydrogen with a high efficiency (40-70 %) directly into electricity. The product of the overall reaction is water, produced at the cathode of the cell. The interaction of liquid water with the porous structures of the cell is one of the mechanisms in the PEFC that are commonly believed to be key for further optimization with regard to performance, durability and cost.
Non-thermal melting of a charge density wave
We use time-resolved optical reflectivity and x-ray diffraction with femtosecond resolution to study the dynamics of the structural order parameter of the charge density wave phase in TiSe2. We find that the energy density required to melt the charge density wave nonthermally is substantially lower than that required for thermal suppression and is comparable to the charge density wave condensation energy.
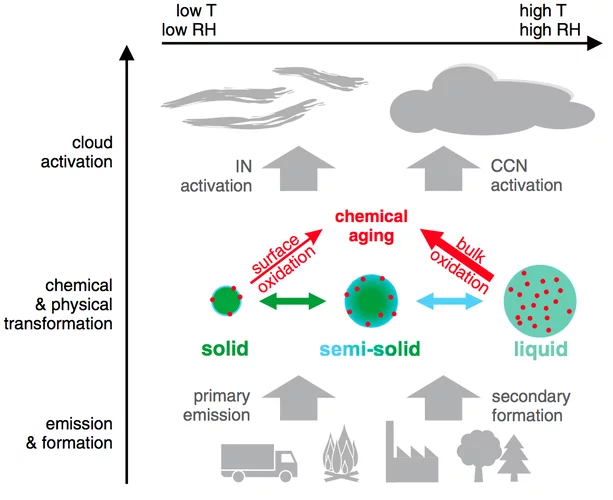
Auch Feinstaub altert
Ob fest, gelartig oder flüssig ist entscheidendFeinstaubpartikel tragen wesentlich zur Luftverschmutzung bei. Durch Reaktionen mit anderen Luftschadstoffen verändern sich diese Partikel mit der Zeit, sie altern. Der Alterungsprozess hängt wesentlich von der Luftfeuchte ab, und damit auch die Auswirkungen von Feinstaubpartikeln auf unsere Gesundheit und unser Klima. Dies zeigen gemeinsame Versuche von Wissenschaftlern des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI und des Max-Planck-Instituts für Chemie sowie der Universität Bielefeld in Deutschland.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
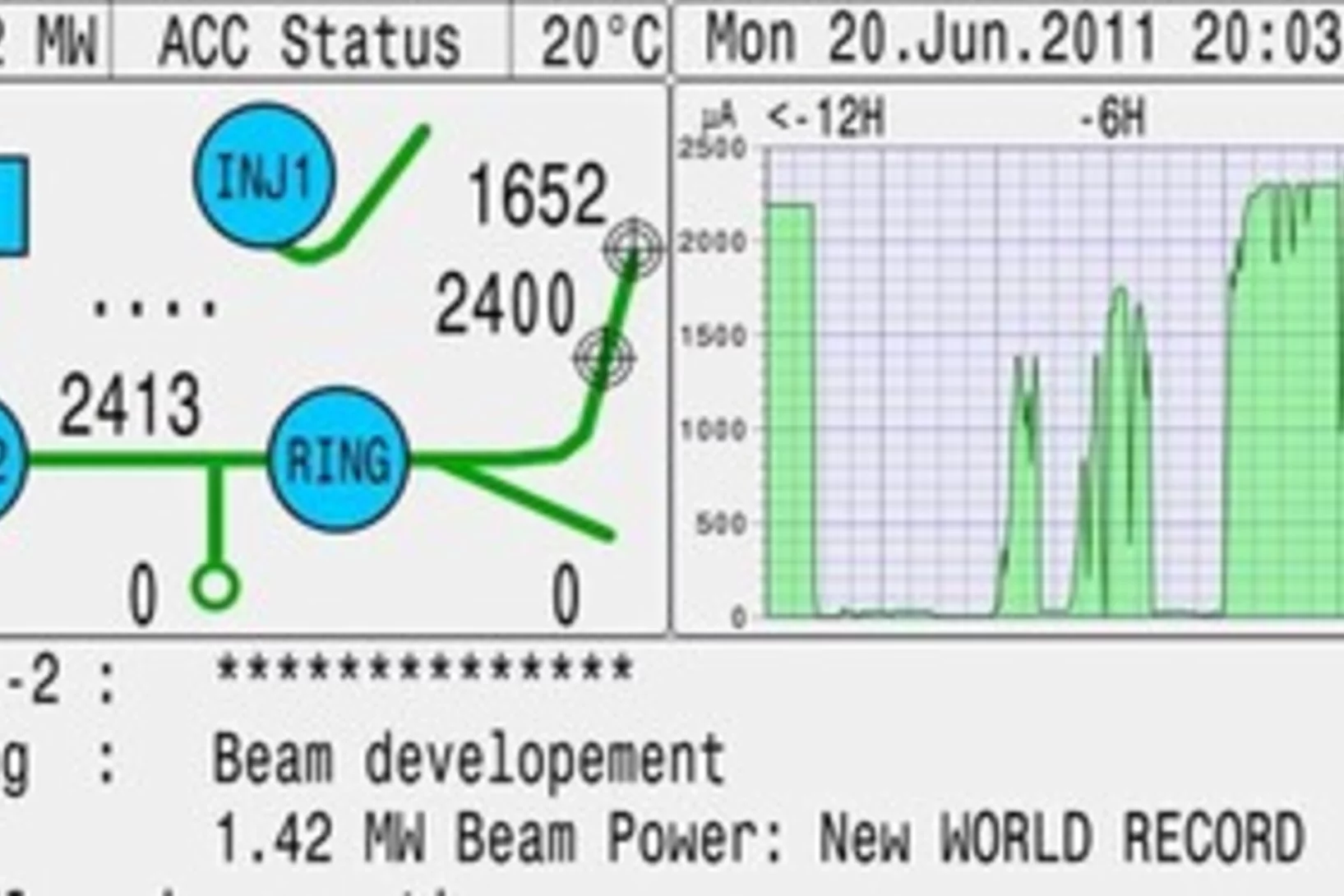
PSI sets world record with 1.4 MW proton beam
The highest average power proton beam in the world was produced on 20th of June in the 590 MeV cyclotron at Paul Scherrer Institut. Extremely low beam losses achieved in this 35 years old veteran cyclotron allowed PSI team of accelerator scientists and engineers to put 1.4 MW beam of protons onto the muon and neutron spallation targets. This beam is used to produce the brightest beam of muons in the world, as well as supply neutrons for the spallation source SINQ.
Gas uptake and chemical aging of semisolid organic aerosol particles
Organic substances can adopt an amorphous solid or semisolid state, influencing the rate of heterogeneous reactions and multiphase processes in atmospheric aerosols. Here we demonstrate how molecular diffusion in the condensed phase affects the gas uptake and chemical transformation of semisolid organic particles. Flow tube experiments show that the ozone uptake and oxidative aging of amorphous protein is kinetically limited by bulk diffusion.
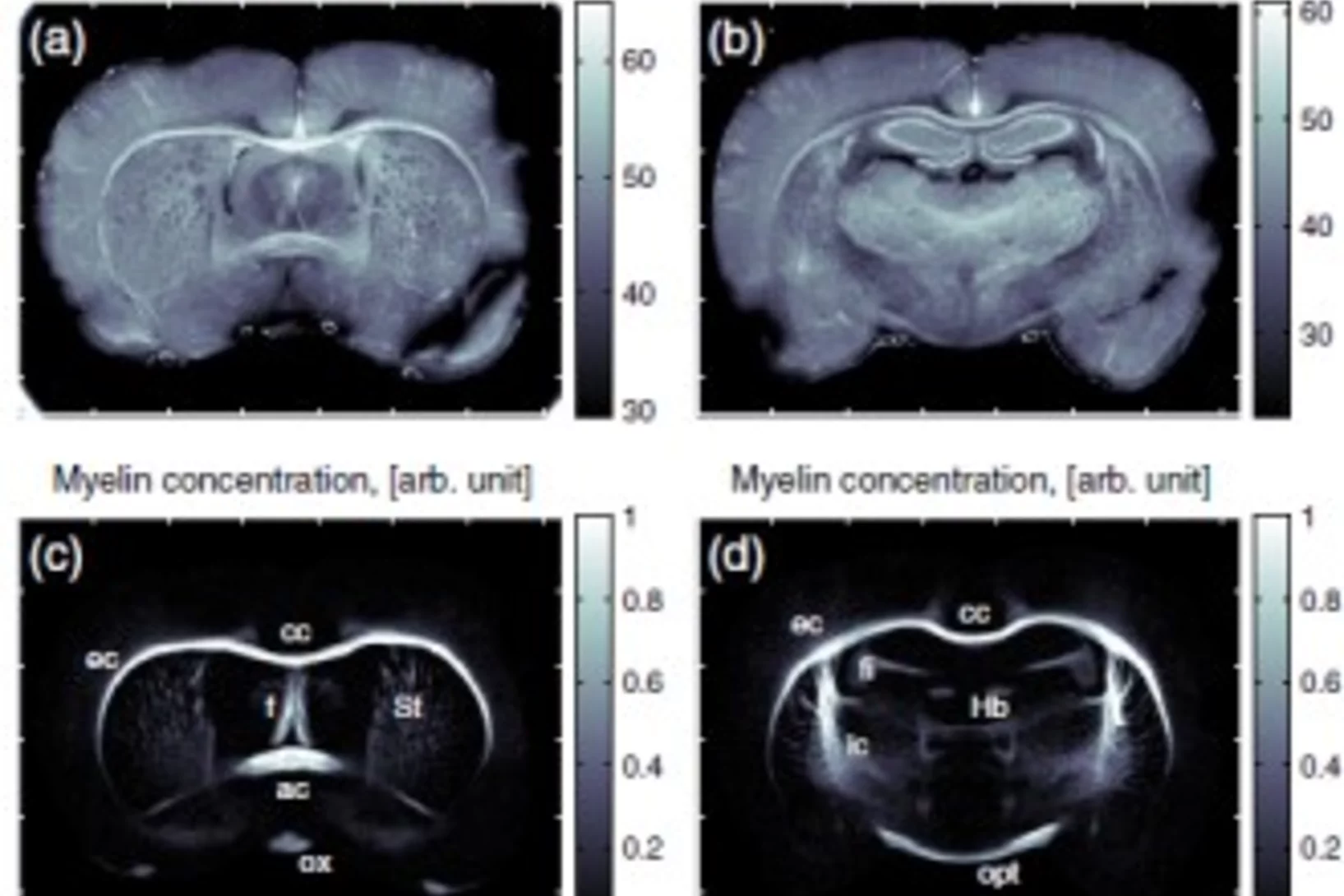
Röntgen-Methode hilft Hirnerkrankungen besser zu verstehen
Ein internationales Forschungsteam hat eine neue Methode entwickelt, mit der man detaillierte Röntgenbilder von Hirngewebe erstellen kann. Die Methode wurde verwendet, um die Myelinscheide der Nervenfasern sichtbar zu machen. Schäden an der Myelinscheide führen zu verschiedenen Erkrankungen wie etwa Multiple Sklerose. Die Anlage, an der diese Aufnahmen erstellt werden können, wird an der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS des Schweizer Paul Scherrer Instituts betrieben.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en anglais et allemand.
La différence entre le fin et l’extra-fin
La différence entre le fin et l’extra-finDe nombreux matériaux ont une structure cristalline spéciale - leurs atomes sont disposés en couches superposées. Un groupe de chercheurs allemands et suisses a observé pour la première fois de manière précise comment les propriétés physiques d’une substance dépendent du nombre de ces couches. Le fait de pouvoir contrôler maintenant également de cette façon les charactéristiques physiques ouvre de nouvelles possibilités d’identifier des matériaux dont les puces informatiques de l’avenir pourraient êtres faites.
Physiklaboranten bremsen Raser aus
Fachhochschule und PSI freuen sich über die gemeinsame ArbeitDie Physiklaborantenlernenden Severin Jörg und Mathias Graf vom Paul Scherrer Institut PSI und ihr Berufskollege Thomas Rastija von der NTB Interstaatliche Hochschule für Technik in Buchs (SG) haben eine kleine Box entwickelt, die Geschwindigkeitsexzesse mit dem Auto verhindert. Das mittlerweile patentierte und von Schweizer Jugend forscht mit hervorragend ausgezeichnete Projekt heisst Setomat und ist das Resultat der Berufsmaturitätsarbeit des aufgeweckten Trios.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Observation of Orbital Currents in CuO
Although high-temperature (Tc) superconductivity was discovered in the cuprates 25 years ago, there is still no consensus on its microscopic origin.
X-ray methods help to understand brain disorders better
An international team of researchers from Denmark, Germany, Switzerland and France has developed a new method for making detailed X-ray images of brain tissue, which has been used to make the myelin sheaths of nerve fibres visible. Damage to these protective sheaths can lead to various disorders, such as multiple sclerosis. The facility for creating these images of the protective sheaths of nerve cells is being operated at the Swiss Light Source (SLS), at the Paul Scherrer Institute.
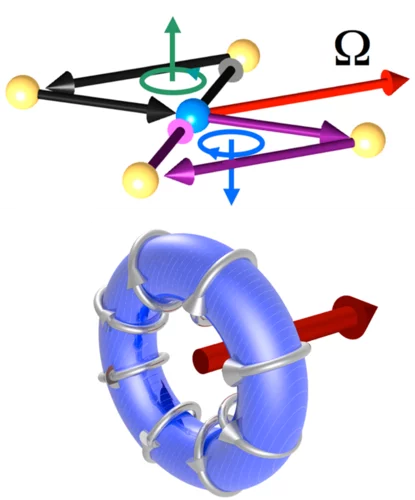
The electron torus can help us to understand high-temperature superconductors
Paul Scherrer Institute researchers prove, for the first time, the existence of toroidal currents in solids
Golden Idea Award der IDEE-SUISSE an Aldo Steinfeld
Für seine Arbeiten zur Erzeugung von Syngas aus Kohlendioxid und Wasser mithilfe konzentrierter Sonnenenergie erhält Aldo Steinfeld, Leiter des Labors für Solartechnik am Paul Scherrer Institut und Professor für Erneuerbare Energieträger an der ETH Zürich, den Golden Idea Award der IDEE-SUISSE, der Schweizerischen Gesellschaft für Ideen- und Innovationsmanagement. Syngas ist eine Vorstufe verschiedener flüssiger Treibstoffe.Cette actualité n'existe qu'en allemand.
Des chercheurs ont décrypté les structures fondamentales de la vision
L’interaction entre la lumière et la protéine rhodopsine se situe au début du processus de la vision. Cette protéine contient le véritable capteur de lumière, qui est stimulé de manière à changer de forme et à activer ainsi le reste du processus. Des chercheurs ont déterminé la structure de la molécule de rhodopsine dans cet état d’excitation de courte durée et ont ainsi fourni un tableau précis de la première étape du processus de la vision.
PSI-Feriencamp 2011
Suchen Sie für Ihr Kind ein spannendes Angebot während den Sommerferien? Möchten Sie in ihm die Neugier und Begeisterung für naturwissenschaftlich-technische Themen wecken? Die Berufsbildung und das Komitee für Chancengleichheit führt dieses Jahr zum achten Mal das PSI-Feriencamp durch!