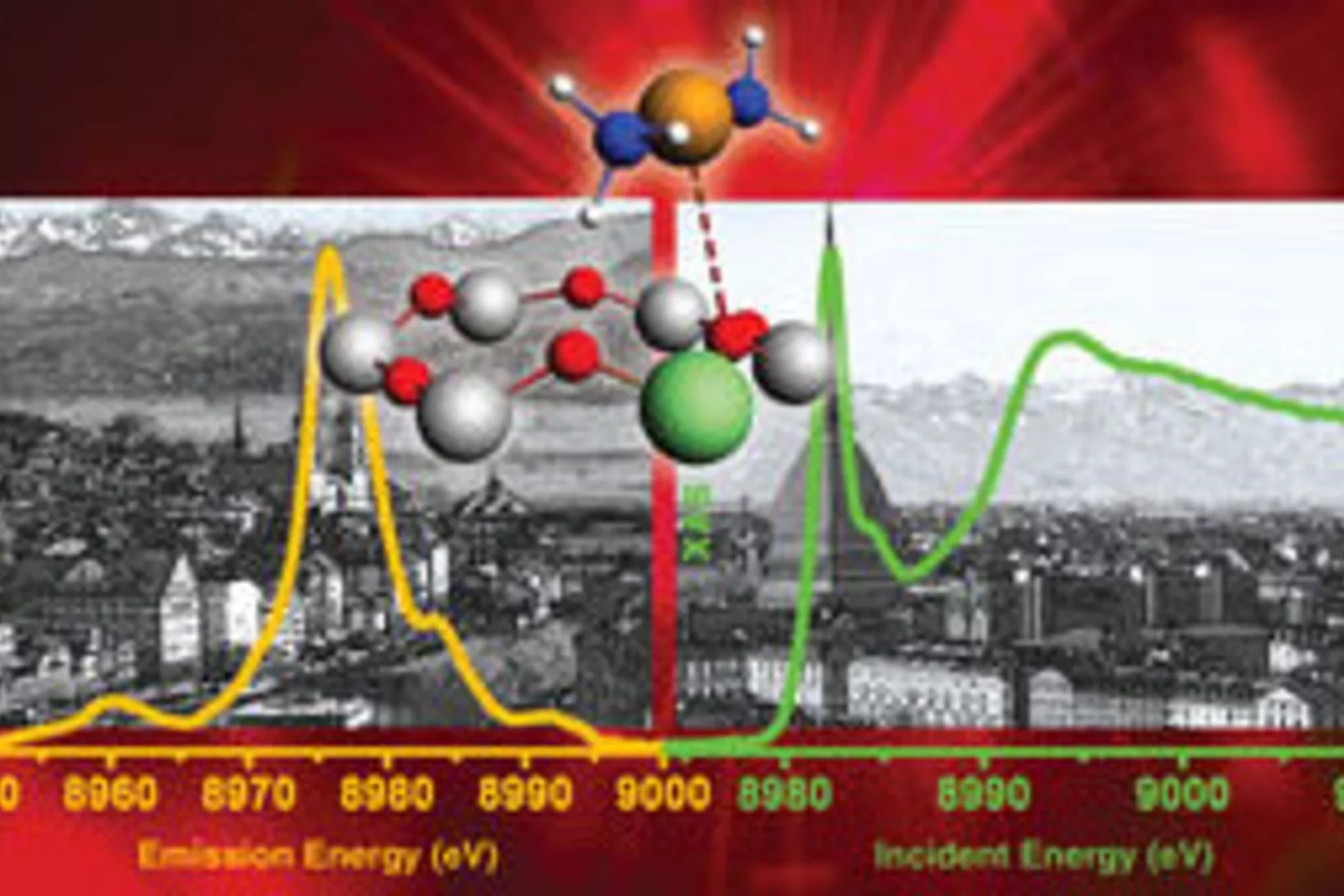
Textbook on XAS and XES
During the last two decades, remarkable and often spectacular progress has been made in the methodological and instrumental aspects of x–ray absorption and emission spectroscopy. This progress includes considerable technological improvements in the design and production of detectors especially with the development and expansion of large-scale synchrotron reactors All this has resulted in improved analytical performance and new applications, as well as in the perspective of a dramatic enhancement in the potential of x–ray based analysis techniques for the near future.
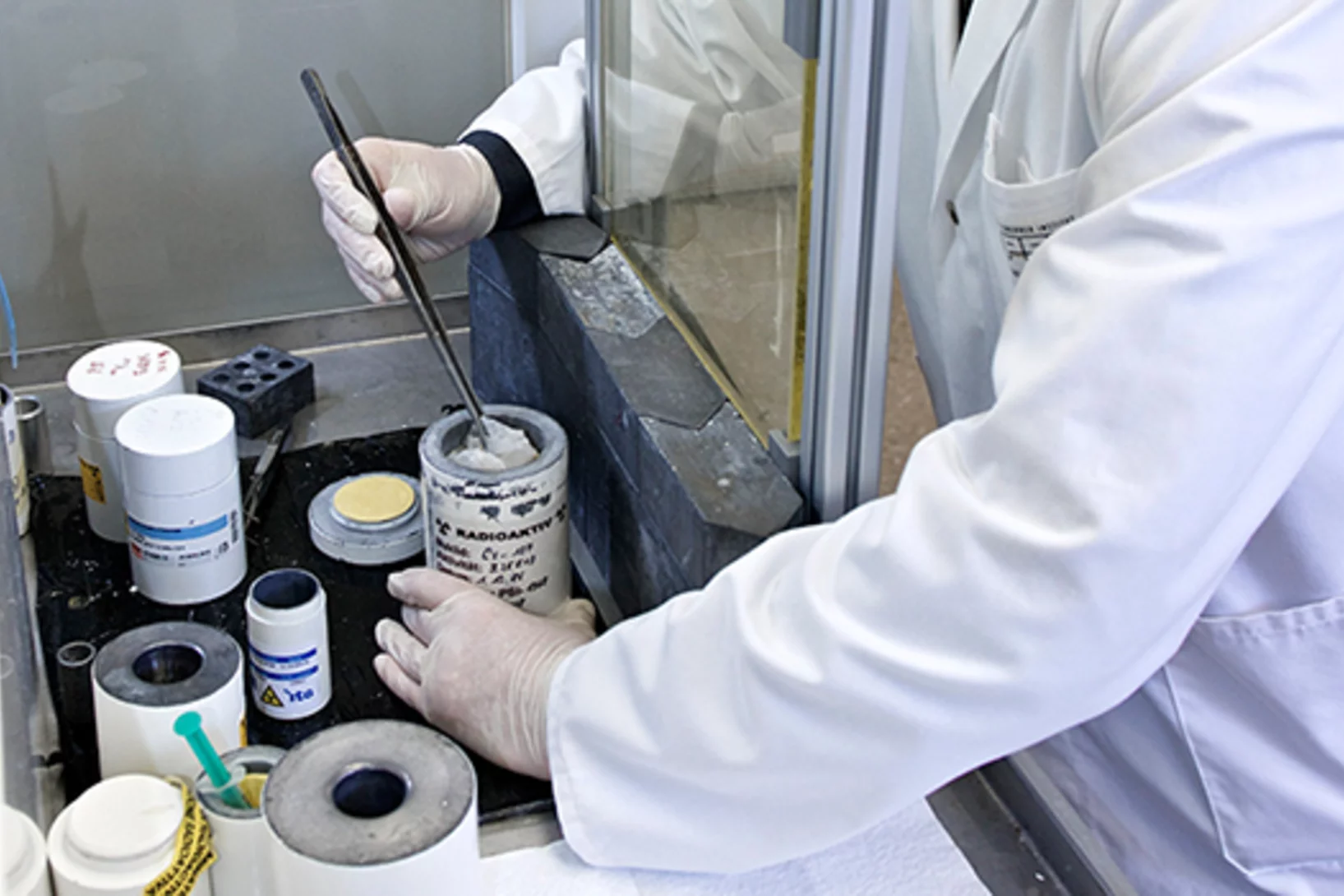
Transport aux Etats-Unis du stock de plutonium liquidé par la Confédération
De janvier à février 2016, quelque 20 kg de plutonium détenus par la Confédération ont été transportés aux Etats-Unis dans le respect de stricts dispositifs de sécurité. Il s’agit de matériel qui était stocké depuis les années 1960 sur le site de l’actuel Institut Paul Scherrer (IPS). Le plutonium provenait de barres de combustibles retraitées du réacteur de recherche Diorit, exploité de 1960 à 1977. En 2014, dans le cadre du Sommet sur la sécurité nucléaire, le Conseil fédéral a décidé de liquider le stock de plutonium afin de contribuer aux efforts en vue de sécuriser le matériel nucléaire à l’échelle internationale.
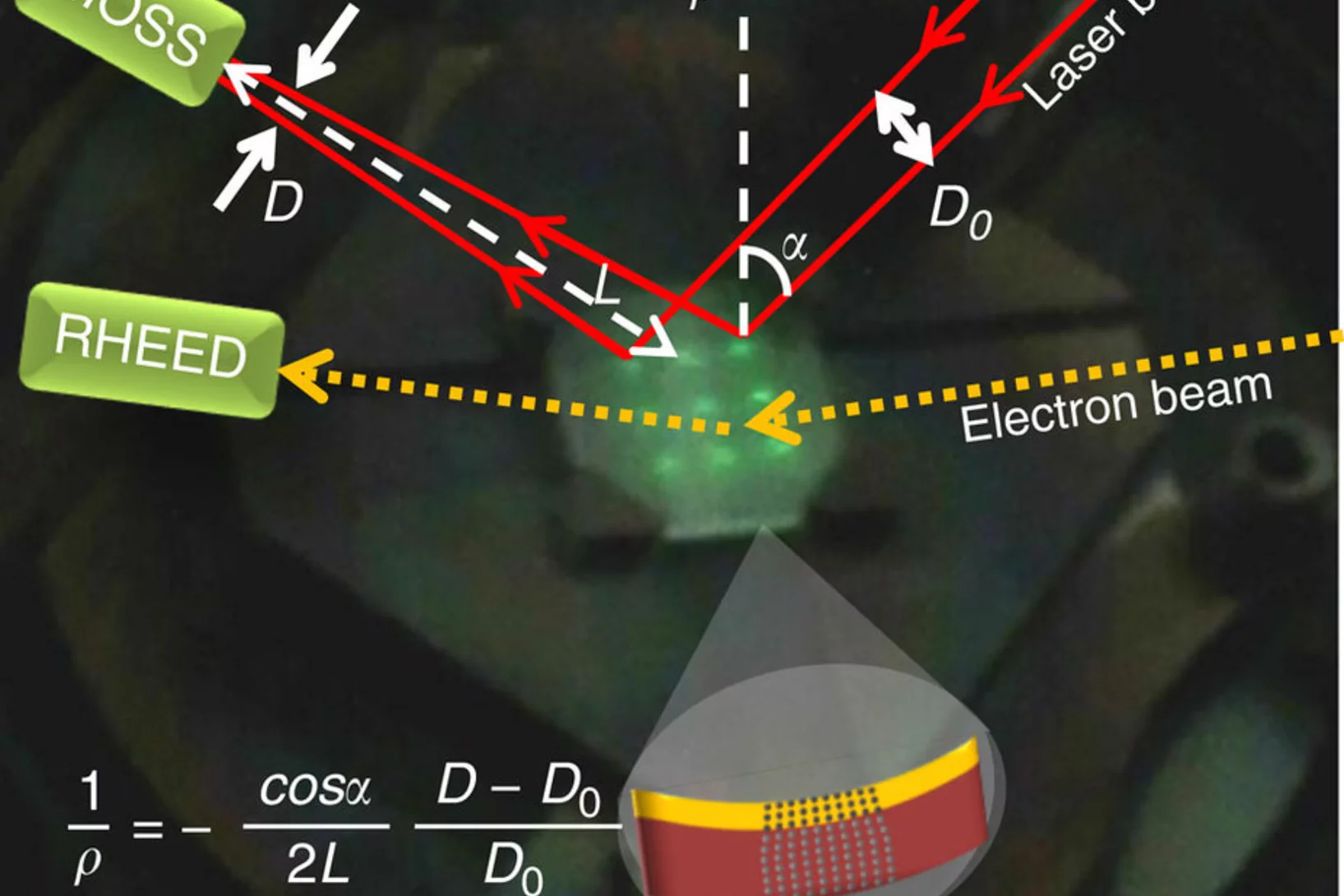
In situ stress observation in oxide films and how tensile stress influences oxygen ion conduction
Many properties of materials can be changed by varying the interatomic distances in the crystal lattice by applying stress. Ideal model systems for investigations are heteroepitaxial thin films where lattice distortions can be induced by the crystallographic mismatch with the substrate. Here we describe an in situ simultaneous diagnostic of growth mode and stress during pulsed laser deposition of oxide thin films.
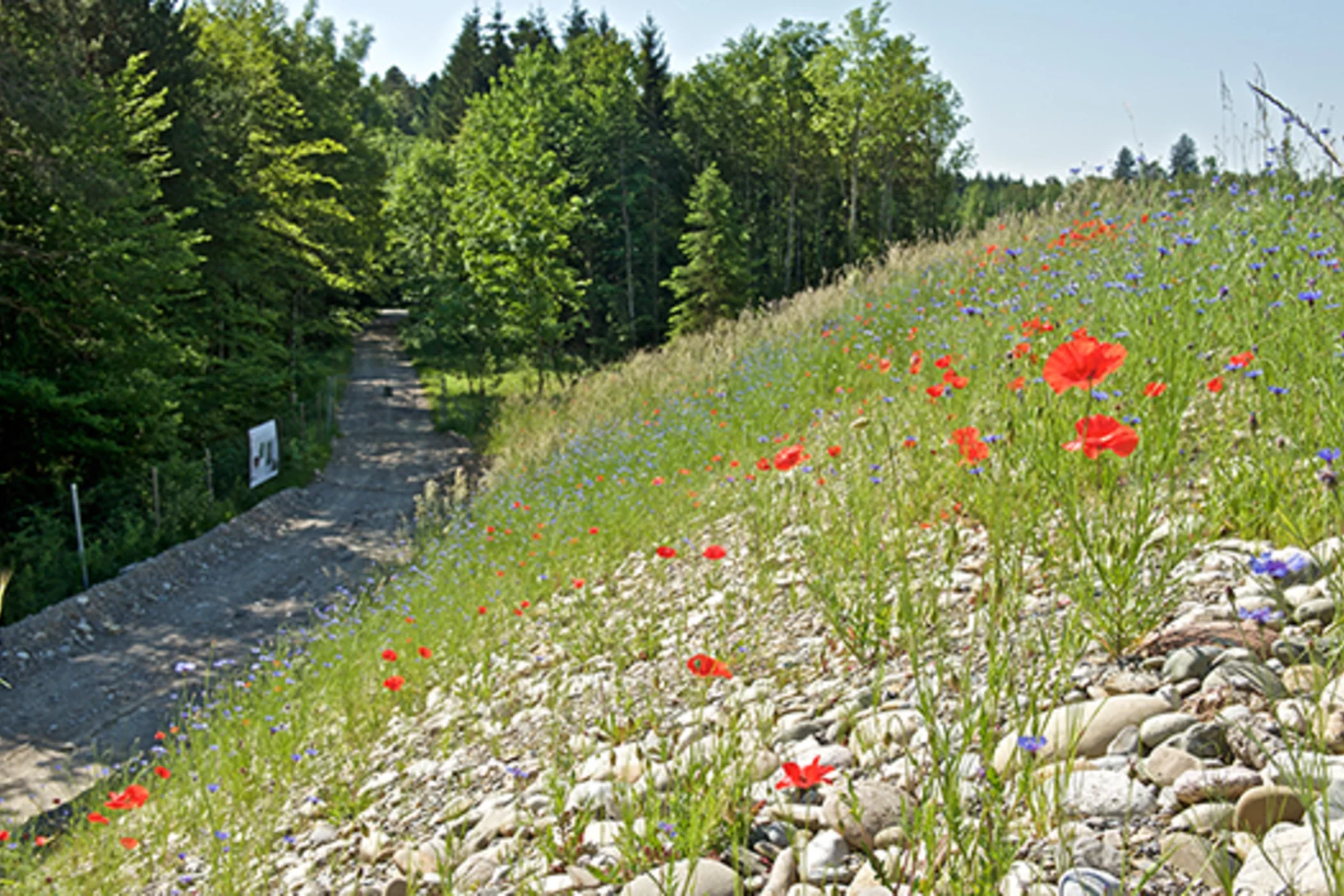
Coopération avec la nature
Avec le SwissFEL, un nouveau paysage émergeA peine construit, le bâtiment du laser à rayons X à électrons libres SwissFEL a déjà disparu sous une levée de terre. Depuis, l’heure est aux plantations et aux aménagements au-dessus du grand instrument de recherche du PSI et aux alentours. Car sa situation particulière dans la forêt nécessite une intégration qui tienne compte de cet environnement. Le SwissFEL est ainsi pratiquement invisible de l’extérieur. Un nouveau biotope destiné à une faune et une flore rares émerge.
Désaffectation du réacteur de recherche Proteus
Début de l’enquête publique relative à la désaffectation de l’installation nucléaire Proteus à l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSIL’installation nucléaire Proteus est ce qu’on appelle un réacteur de puissance nulle. La puissance thermique du réacteur était limitée en fonctionnement à 1 kW maximum. Ceci signifie qu’il s’agit d’un réacteur d’essai qui était exploité à une puissance tellement faible qu’un liquide de refroidissement n'était pas nécessaire. Proteus a été mis en service en 1968. Le PSI souhaite désaffecter l’installation. Le projet de désaffectation est dès aujourd’hui communiqué au public dans les organes de publication officiels prévus par la loi.
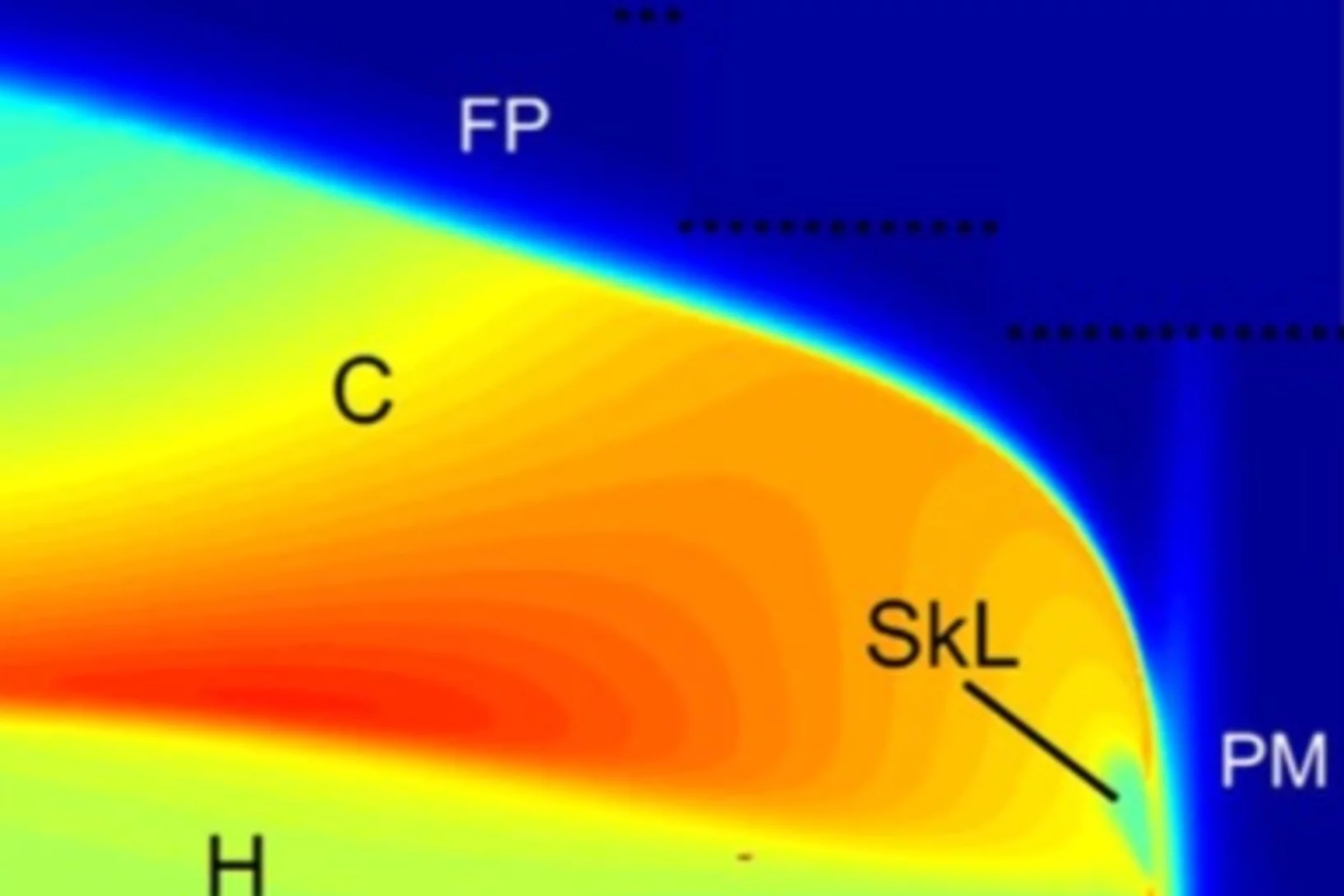
Dramatic pressure-driven enhancement of bulk skyrmion stability
The recent discovery of magnetic skyrmion lattices initiated a surge of interest in the scientic community. Several novel phenomena have been shown to emerge from the interaction of conducting electrons with the skyrmion lattice, such as a topological Hall-effect and a spin-transfer torque at ultra-low current densities.
Développement d'un nouveau médicament contre le cancer de la thyroïde
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI ont développé une substance active qui permet de cibler et traiter une forme particulièrement maligne du cancer de la thyroïde. Le nouveau médicament a un avantage: il permet de traiter une certaine forme de cancer de la thyroïde où le traitement actuel est inefficace. Les chercheurs du PSI ont développé le radiotraceur à un stade suffisamment avancé pour qu’une première étude puisse être menée sur des patients à l’Hôpital universitaire de Bâle.
Cervin miniature
Des chercheurs de l’Institut Paul Scherrer ont produit un grand nombre de maquettes détaillées du Cervin. Chacune d’elles mesure moins d’un dixième de millimètre. Ils démontrent ainsi comment fabriquer en série des objets 3D aussi délicats. Les matériaux qui portent à leur surface de minuscules structures 3D de ce genre présentent souvent des propriétés susceptibles de réduire l’usure de composants mécaniques, par exemple.
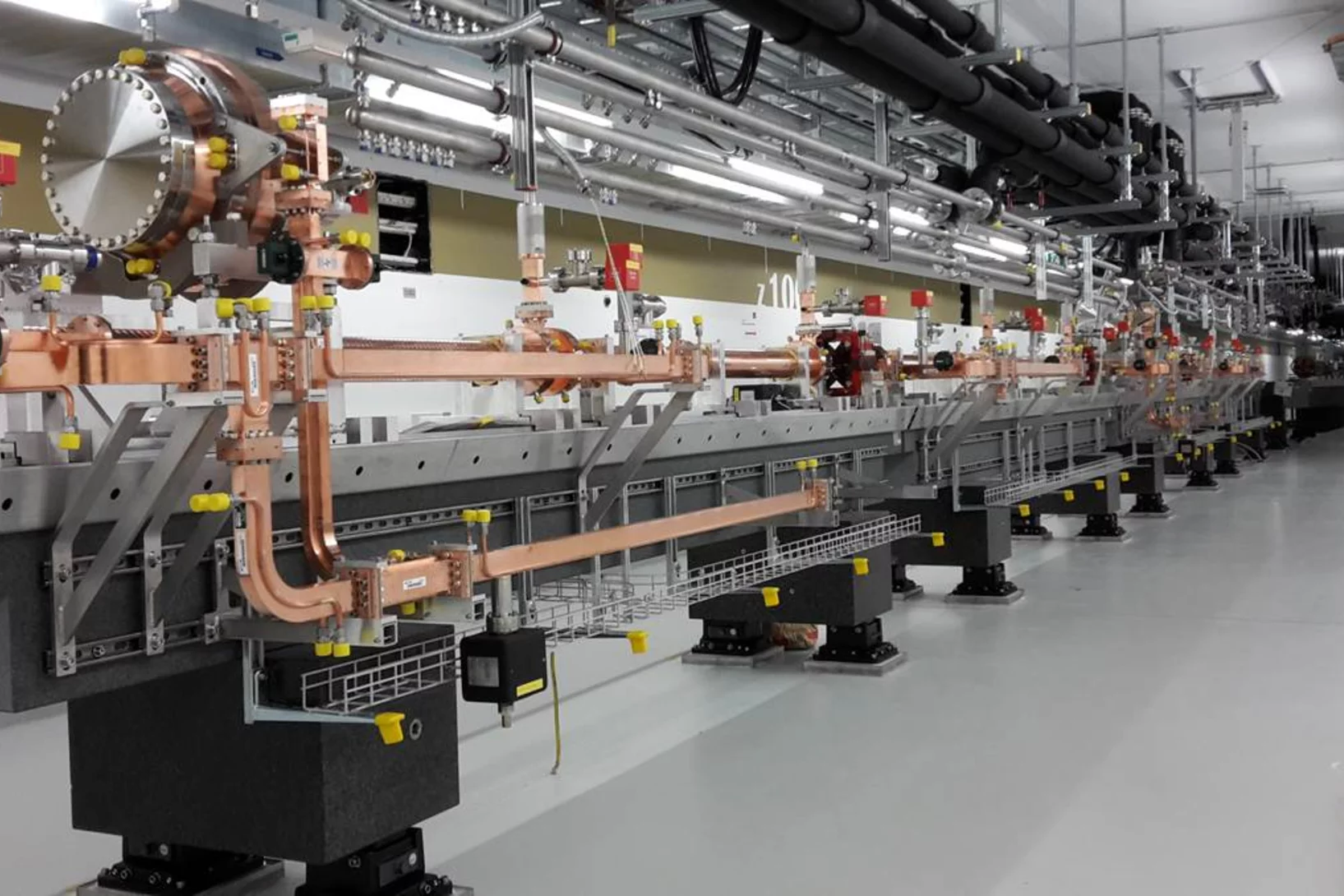
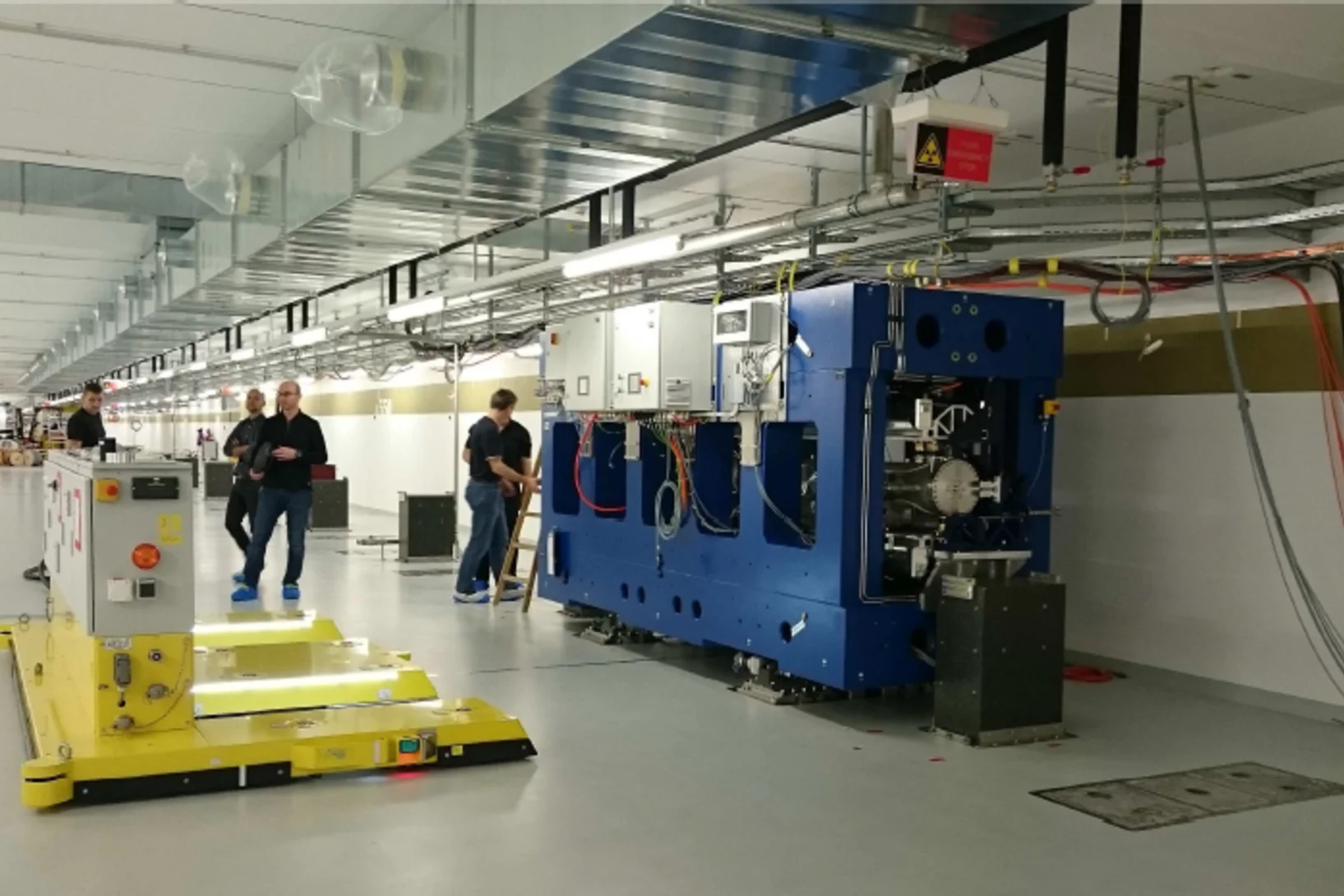
Installation progress of the SwissFEL Linac
The installation of the linear accelerator (Linac) progresses very well. This week, the last girder of the so-called “Linac 1” was installed in the SwissFEL tunnel. The entire C-band accelerator consists out of Linac 1, Linac 2, and Linac 3, and a total amount of 104 accelerating structures. Meanwhile, 38 accelerating structures are installed in the SwissFEL tunnel. The assembly work on the remaining Linac modules will take place until end of September of this year. By then it is planned to finish the installation of all Linac modules in the SwissFEL tunnel.
L'installation de recherche du Laboratoire chaud
Démarrage de l'enquête publique relative à une actualisation de l'autorisation d'exploitation de l'installation de recherche du Laboratoire chaud de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSILe Laboratoire chaud de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI est une installation au sein de laquelle des chercheurs et chercheuses étudient les matériaux hautement radioactifs dans des enceintes blindées spéciales, également baptisées cellules chaudes. Cette installation est unique en Suisse. Elle sert la recherche appliquée sur les matériaux en analysant des échantillons hautement radioactifs de barreaux de combustibles et de matériaux de structure provenant de centrales nucléaires, de réacteurs de recherche et de l'accélérateur de proton du PSI. Grâce aux travaux du Laboratoire chaud, l’Institut Paul Scherrer contribue ainsi à la sécurité des centrales nucléaires suisses. Près de 32 salariés travaillent au sein de l'infrastructure spécialisée dans les techniques de sécurité et d'analyses du Laboratoire chaud.
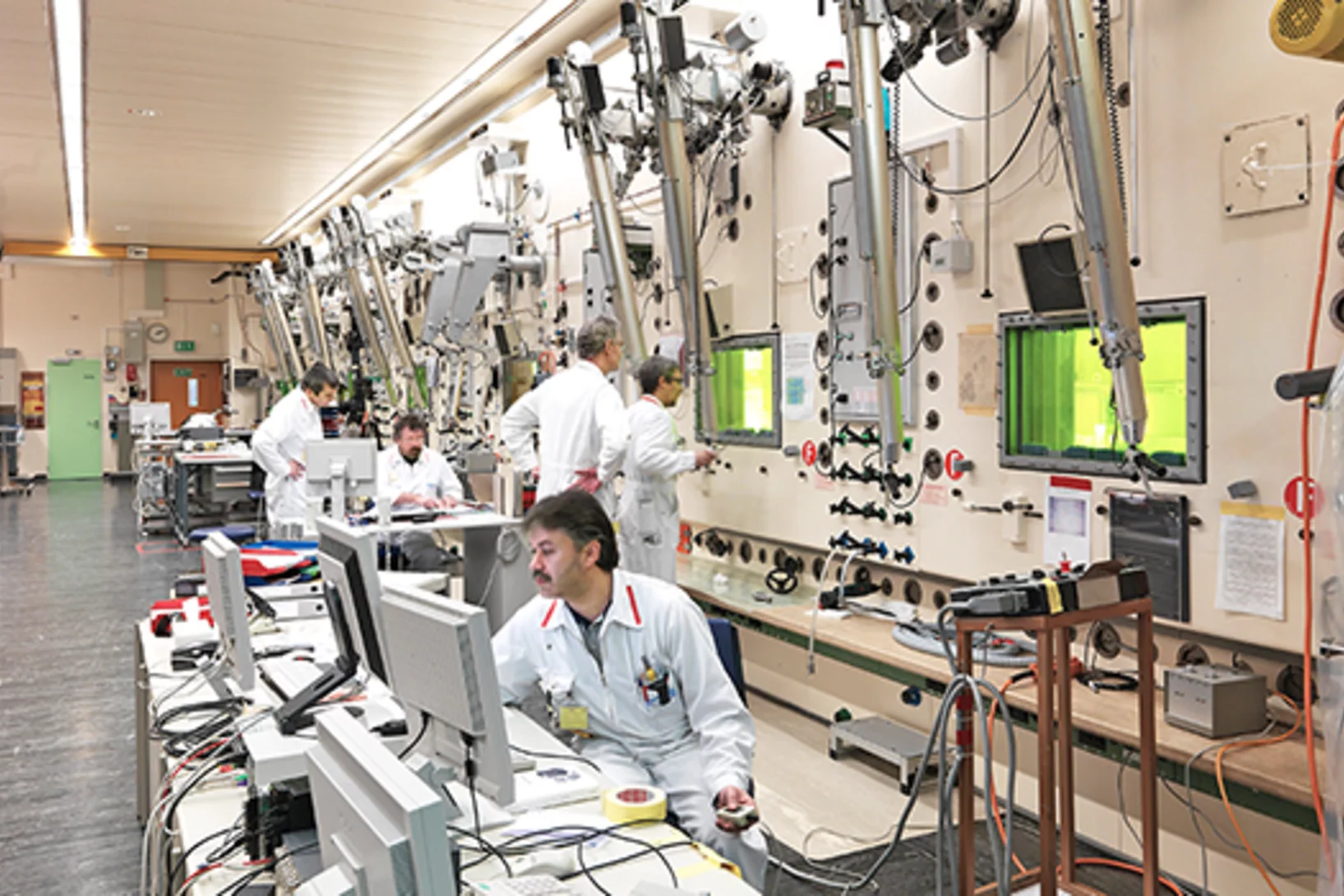
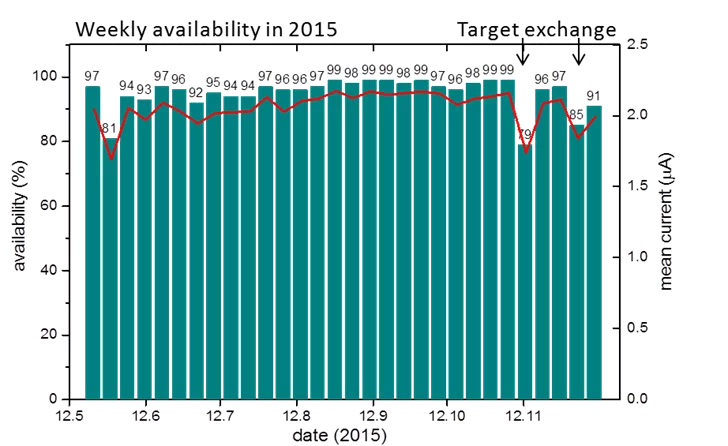
Proton Accelerator Operation Statistics 2015
For the first time in the history of the High Intensity Proton Accelerator the availability of the facility reached an outstanding value of 95% in 2015 with a record value of 99.3% in week 44. In comparison to the two previous years this corresponds to a reduction of the downtime by 50%. The user operation in 2015 was started as scheduled and already in the first week the machine was available 97% of the scheduled beam time. In addition to the smooth operation of the facility, high intensity beam experiments could regularly be performed with currents of up to 2.4 mA. nu
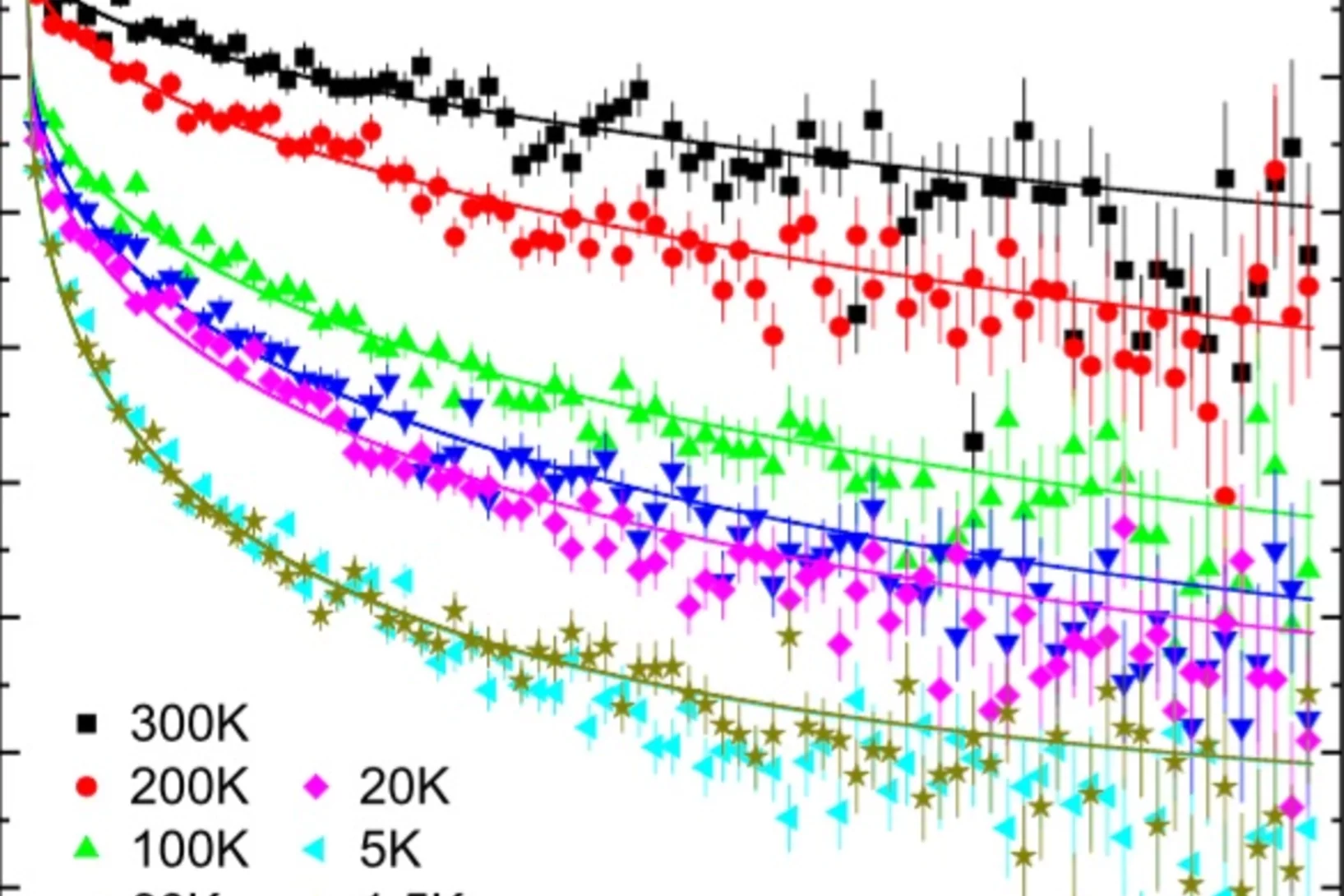
Coexistence of low-moment magnetism and superconductivity in tetragonal FeS and suppression of Tc under pressure
The family of iron-based superconductors has recently acquired a new member material, FeS. Theoretically, this compound has been shown to have electronic structure similar to that of the superconducting FeSe. However, contradictory ground states have been predicted for FeS. In this work, a collaboration of authors from Switzerland and Germany use muon spin rotation and relaxation to show that weak-moment magnetism microscopically coexists with bulk superconductivity.
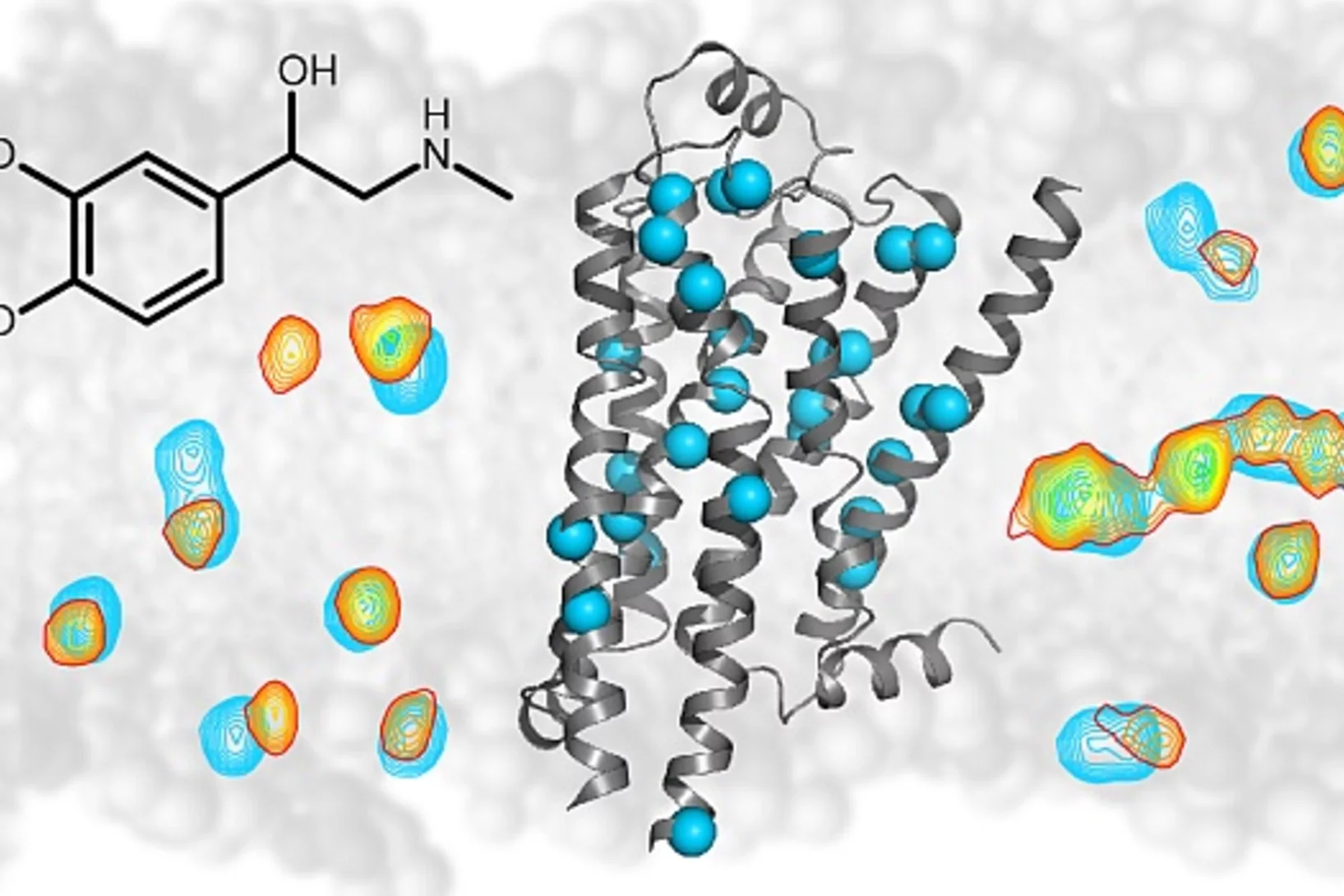
Pourquoi le cœur bat la chamade
Nouvel éclairage sur le mode de fonctionnement d’importants récepteurs, cibles de nombreux médicamentsCertains médicaments agissent sur des récepteurs situés au niveau de la membrane des cellules de notre organisme, autrement dit de leur enveloppe extérieure. L’adrénorécepteur béta-1, notamment responsable des palpitations cardiaques est l’un d’eux. La manière dont il transmet les signaux jusqu’à l’intérieur de la cellule a pu être élucidée ce qui devrait permettre de nettement mieux comprendre les mécanismes d’action de nombreux médicaments.
Porträt Jenna Poonoosamy: Die Vermesserin der Gesteinsporen
Drei Jahre in Folge hat Jenna Poonoosamy den Preis für die beste Präsentation am Doktorandentag im Bereich Nukleare Energie und Sicherheit (NES) am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI erhalten. Poonoosamy stammt ursprünglich von der Insel Mauritius im Indischen Ozean. Schon in der Schule interessierte sie sich vor allem für Chemie. «Die meisten meiner Freunde wollten in die Wirtschaft», erzählt sie. «Mich dagegen haben die Naturwissenschaften fasziniert.» Und so zog sie nach der Schule zum Chemie-Studium nach Paris. Und kam später für ihre Doktorarbeit ans PSI.
A l'interface
Entretien avec Stefan Janssen, directeur du service aux utilisateurs
Stefan Janssen est directeur du service aux utilisateurs à l’Institut Paul Scherrer. Il explique dans l’entretien ci-après pourquoi les chercheurs externes apprécient autant les grands instruments de recherche du PSI, comment il s’y prend pour traiter les nombreuses demandes qui lui sont adressées et la manière dont il épaule les utilisateurs.
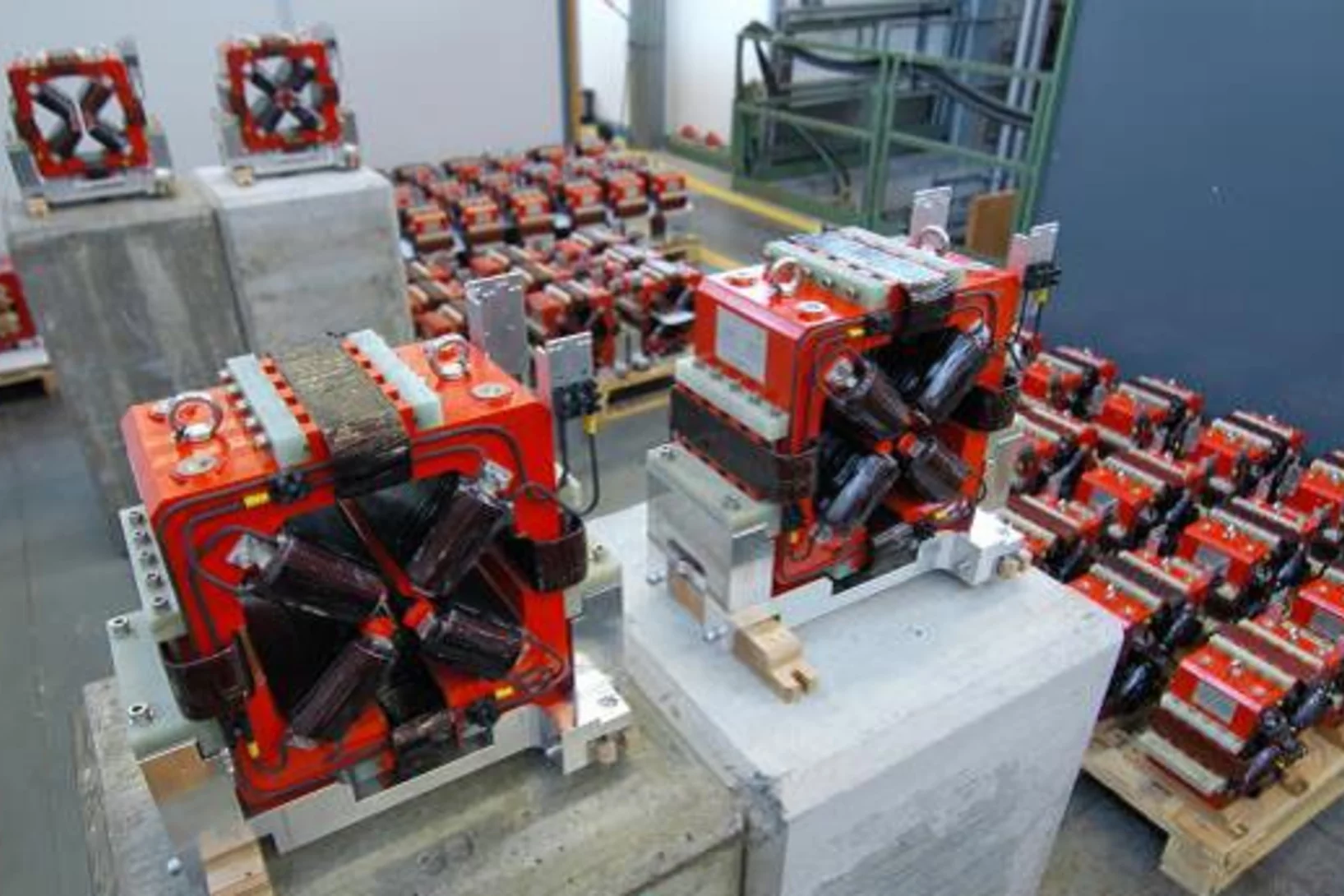
GFA delivers the SwissFEL magnets on schedule
The Paul Scherrer Institut is building an X-ray free electron laser (SwissFEL) providing a source of intense, ultra-short pulses of coherent radiation in the wavelength range of 0.1 nm to 0.7nm. For the hard X-ray beam line, the magnet section in GFA/ATK has the responsibility for the design, the procurement and the magnetic qualification of 267 electro-magnets of 22 different types. Several design studies were performed in an attempt to meet the required magnet specifications while optimizing construction and operation cost.
Ralentissement du flux électrique peut montrer la voie vers des ordinateurs économes en énergie
Les ordinateurs et les autres appareils électroniques représentent aujourd’hui une part considérable de la consommation d’énergie, une part dont il est pratiquement impossible de modifier l’importance avec les technologies actuellement utilisées. Les puces électroniques qui prendront place dans les appareils économes en énergie de demain devront donc être composées de matériaux innovants. De nouveaux résultats de recherche indiquent une voie possible comment on peut obtenir ces matériaux.
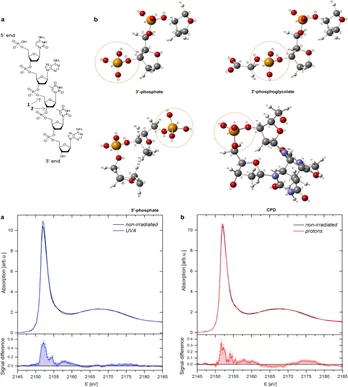
Biophysical effects of UV radiation on biological samples
The biological influence of radiation on living matter has been studied for years; however, several questions about the detailed mechanism of radiation damage formation remain largely unanswered. Among all biomolecules exposed to radiation, DNA plays an important role because any damage to its molecular structure can affect the whole cell and may lead to chromosomal rearrangements resulting in genomic instability or cell death.
Transport of first "completed" Undulator into the SwissFEL Tunnel
On the 25th of January, the first "completed" undulator has been transported to its final position in the SwissFEL tunnel. The 1064 permanent magnets of this undulator where shimmed to the sub-micrometer level and the magnetic profile has been carefully measured for the full gap range. Twelve of such undulators will be installed until October 2016!
Small-Angle Neutron Scattering Study of Interplay of Attractive and Repulsive Interactions in Nanoparticle-Polymer System
The phase behavior of nanoparticle (silica)−polymer (polyethylene glycol) system without and with an electrolyte (NaCl) has been studied. It is observed that nanoparticle−polymer system behaves very differently in the presence of electrolyte. In the absence of electrolyte, the nanoparticle−polymer system remains in one-phase even at very high polymer concentrations.
Georgian Order of Honor for Zurab Guguchia
Thomas Prokscha from Laboratory for the Muon Spin Spectroscopy LMU and Head of the LEM Group was invited to serve an additional year as a member of the INTC Committee (ISOLDE and Neutron Time-of-Flight Experiments Committee) at CERN.
The INTC evaluates proposals for experiments on the ISOLDE facility. In addition it reviews the experiments proposed for the neutron time-of-flight facility.
Reconduction des directeurs du PSI et du WSL
Sur proposition du Conseil des EPF, le Conseil fédéral a reconduit dans leurs fonctions, le 20 janvier 2016, Joël Mesot, directeur de l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI, et Konrad Steffen, directeur de l’Institut fédéral de recherches sur la forêt, la neige et le paysage WSL, pour une période de quatre ans. Joël Mesot entamera son troisième mandat le 1er août 2016 et Konrad Steffen son deuxième mandat le 1er juillet 2016.
Mechanically Enhanced Liquid Interfaces at Human Body Temperature Using Thermosensitive Methylated Nanocrystalline Cellulose
The mechanical performance of materials at oil/water interfaces after consumption is a key factor affecting hydrophobic drug release. In this study, we methylated the surface of nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC) by mercerization and dimethyl sulfate exposure to produce thermosensitive biopolymers. These methylated NCC (metNCC) were used to investigate interfacial thermogelation at air/water and medium-chain triglyceride (MCT)/water interfaces at body temperature.
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
If a ball is rolled up a hill with less kinetic energy than the potential energy at the top, it will return eventually, and stays bound in the valley. Tunnelling is a distinctly quantum mechanical phenomenon, in which such balls can magically cross the hill, and appear in the neighbouring valley, as if going through a tunnel. In order for this to happen with a non-negligible probability, the ball has to be small and the barrier, i.e. the hill, sharp.
Attaquer le cancer de manière ciblée
Il existe des tumeurs contre lesquelles, apparemment, rien ne marche: ni la chimiothérapie, ni la radiothérapie externe, ni la chirurgie. Souvent, elles ont déjà formé des métastases et ne peuvent plus être éliminées par des méthodes conventionnelles. La seule issue qui reste alors, c’est la radiothérapie interne avec des substances radioactives ciblées, que l’on introduit directement dans la tumeur. Vingt chercheurs spécialisés œuvrent dans ce but au Centre des sciences radiopharmaceutiques à l’Institut Paul Scherrer PSI, une institution commune du PSI, de l’EPF Zurich et de l’Hôpital universitaire de Zurich.
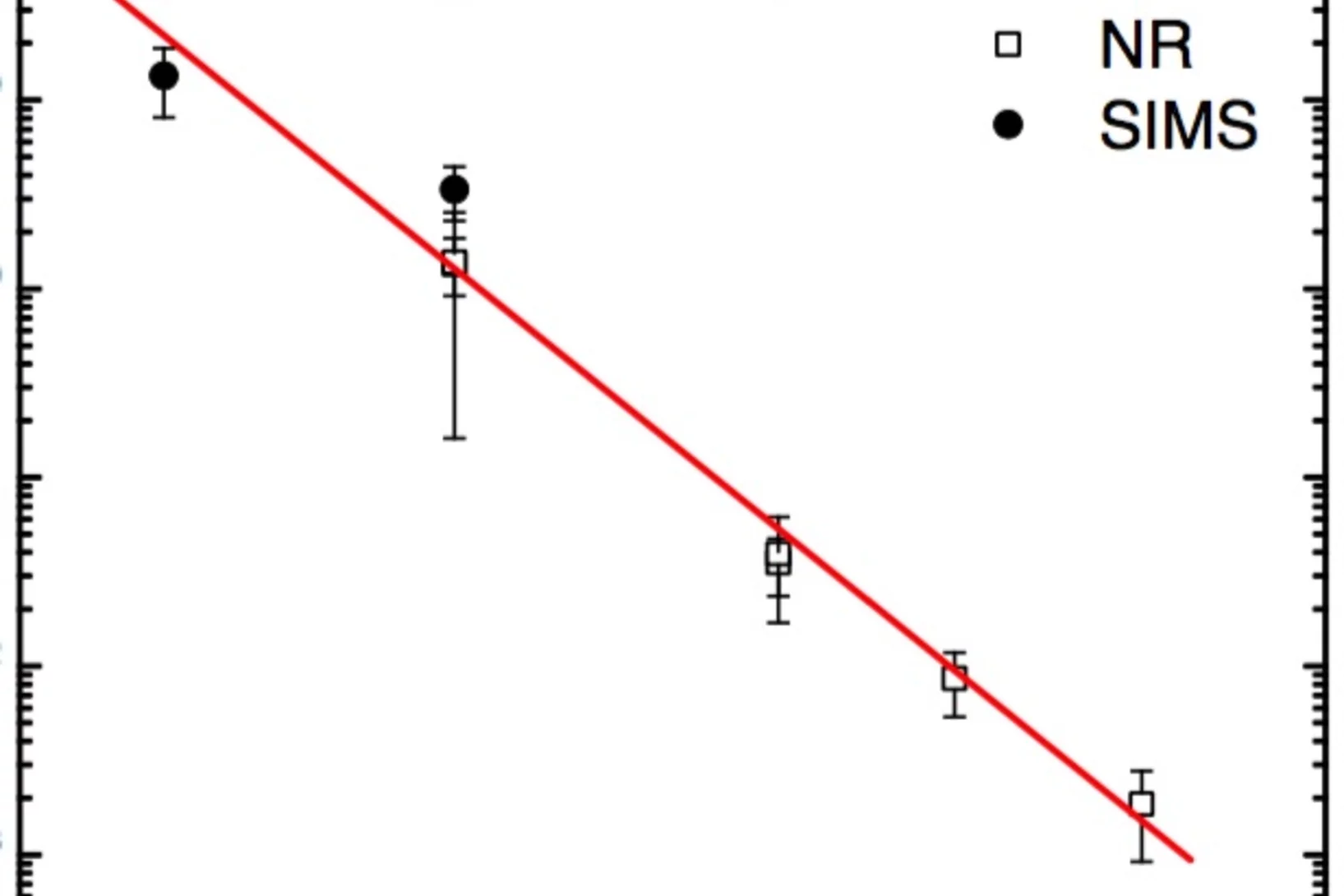
Self-Diffusion in Amorphous Silicon
The present Letter reports on self-diffusion in amorphous silicon. Experiments were done on 29Si/natSi heterostructures using neutron reflectometry and secondary ion mass spectrometry. The diffusivities follow the Arrhenius law in the temperature range between 550 and 700°C with an activation energy of (4.4 ± 0.3) eV.
Des neutrons mettent en évidence la répartition d’îlots de tubes de flux
Normalement, les supraconducteurs repoussent les champs magnétiques appliqués. Mais à l’intérieur des supraconducteurs de type II, il se forme de fins canaux appelés tubes de flux par lesquels passe le champ magnétique, alors que le reste du matériau reste sans champ et supraconducteur. Dans le niobium (un métal), les tubes de flux se regroupent en îlots et forment des schémas complexes, que l’on rencontre fréquemment dans la nature sous une forme analogue. Des chercheurs du PSI et de l’Université technique de Munich (Technische Universität München: TUM) sont les premiers à avoir mené des expériences avec des neutrons pour analyser ces structures dans le niobium. Ils ont réussi à visualiser en détail la répartition des îlots.
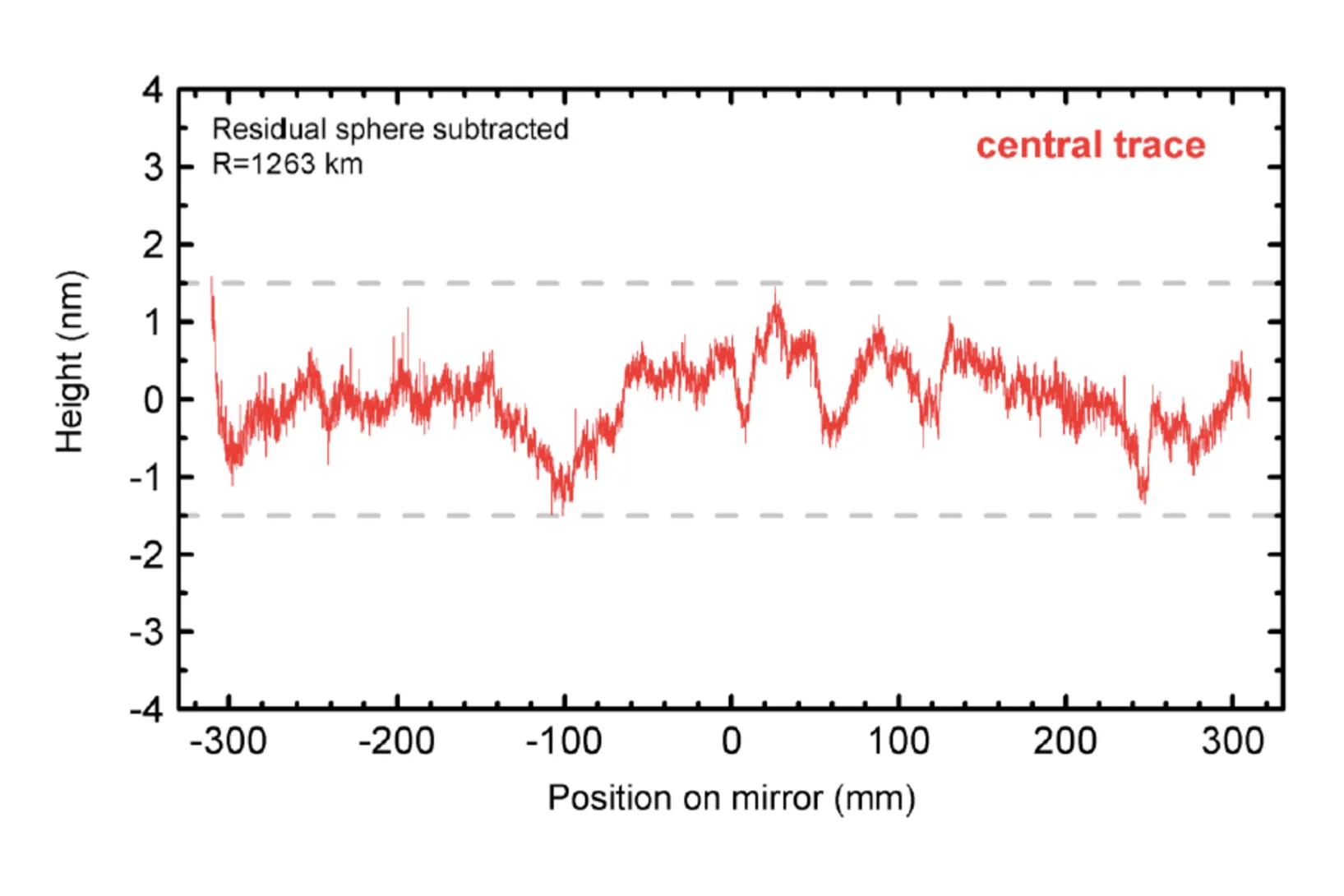
First ultraprecise mirror for SwissFEL arrived at PSI
Mirrors are key elements to distribute and shape the Xray beam generated by the undulators of the SwissFEL facility. They are essential tools to guide and focus the light according to the specific users requirements and should do this without noticeable effects on the beam quality. A quantitative measure is the quality of the beam wavefront. The wavefront must be conserved by the optical elements in the SwissFEL beamlines within a fraction of the wavelength which can be as short as one Angstrom in the case of Aramis. There are only few companies in the world, who are able to fabricated such ultraprecise mirrors.
In-situ visualization of stress-dependent bulk magnetic domain formation by neutron grating interferometry
The performance and degree of efficiency of industrial transformers are directly influenced by the magnetic properties of high-permeability steel laminations (HPSLs). Industrial transformer cores are built of stacks of single HPSLs. While the insulating coating on each HPSL reduces eddy-current losses in the transformer core, the coating also induces favorable inter-granular tensile stresses that significantly influence the underlying magnetic domain structure.
First ultraprecise mirror for SwissFEL arrived at PSI
Mirrors are key elements to distribute and shape the Xray beam generated by the undulators of the SwissFEL facility. They are essential tools to guide and focus the light according to the specific users requirements and should do this without noticeable effects on the beam quality. A quantitative measure is the quality of the beam wavefront.