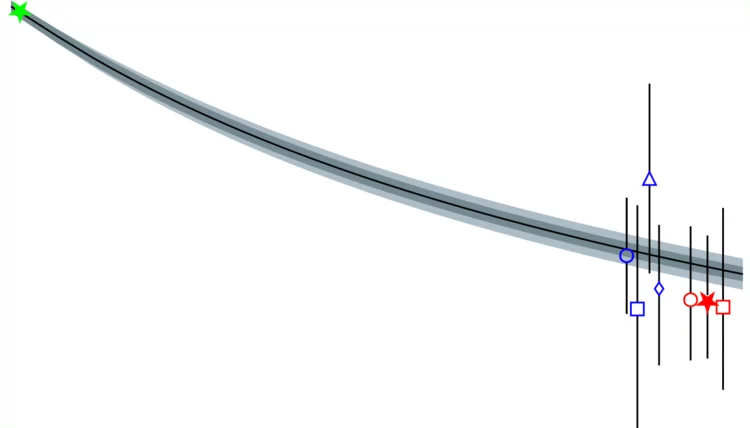
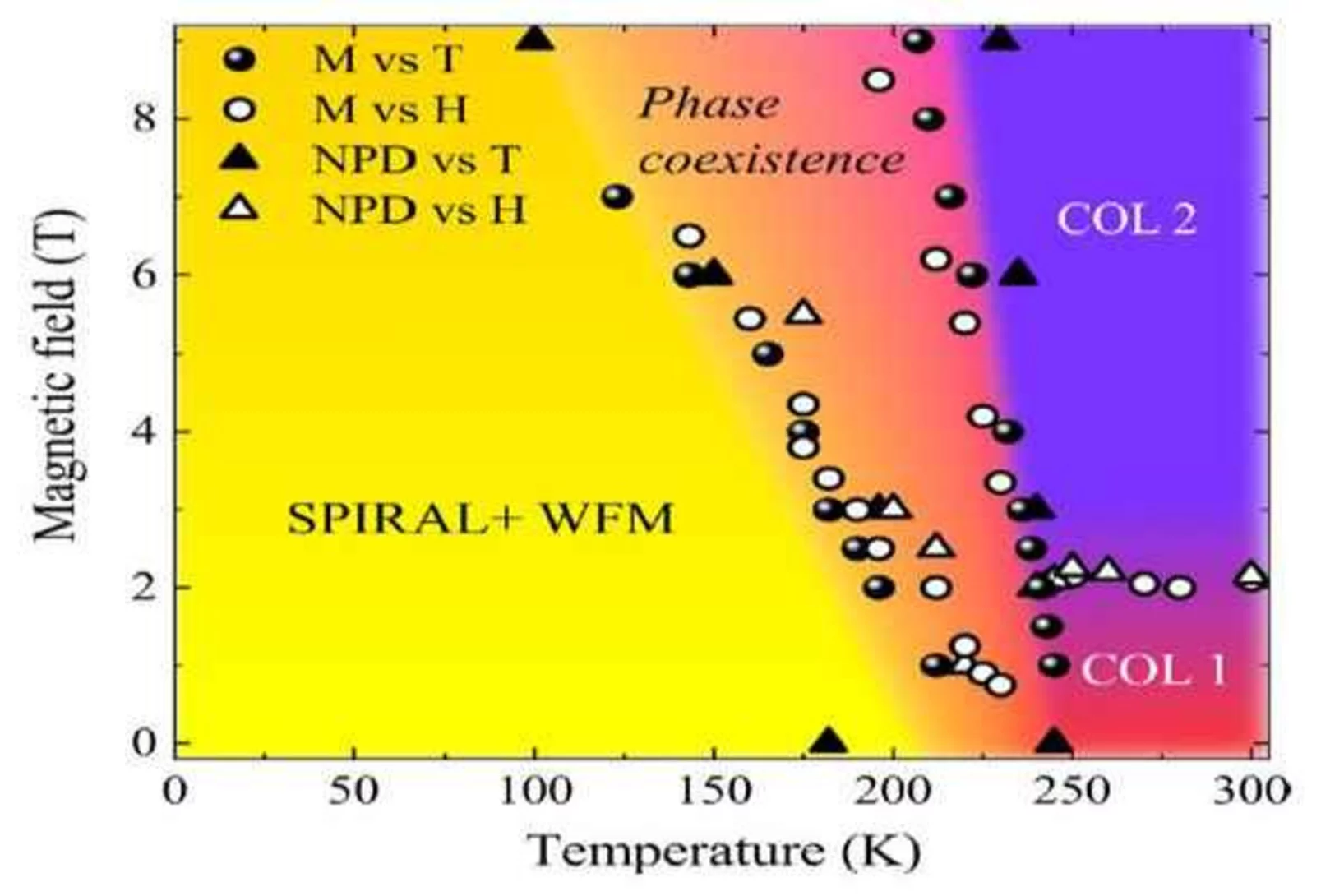
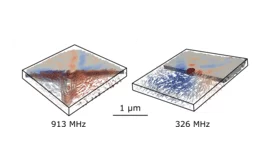
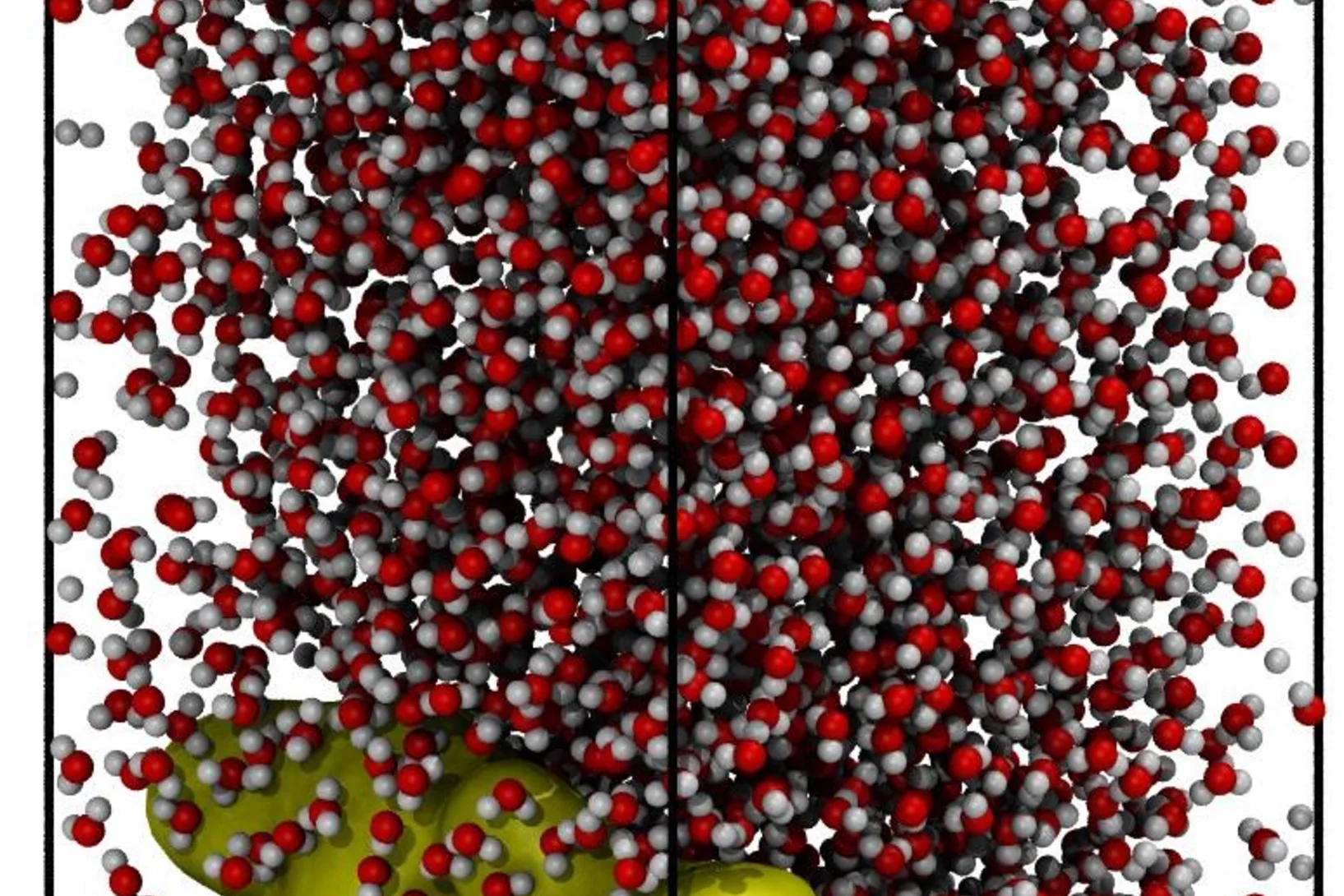
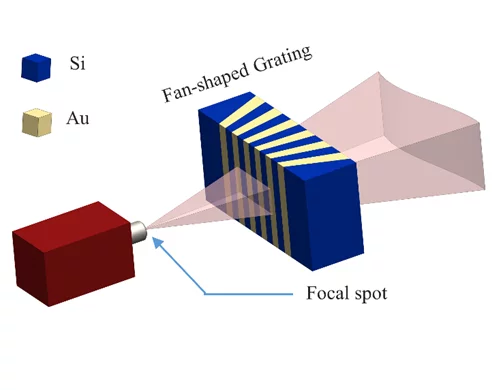
La recherche énergétique de l’Institut Paul Scherrer se concentre sur la recherche de procédés susceptibles d’être utilisés dans des technologies durables et sûres pour un approvisionnement en énergie si possible exempt d’émissions CO2. Les énergies renouvelables constituent un point fort important. A la plateforme ESI (Energy System Integration), la recherche et l’industrie peuvent tester des solutions d’intégration d’énergies renouvelables. Un autre point fort de ce domaine est l’utilisation sûre de l’énergie nucléaire. Ces activités sont complétées par des analyses d’évaluation globale des systèmes énergétiques. Le PSI mène également de la recherche climatique et environnementale sur les processus chimiques qui se jouent dans l’atmosphère.
Pour en savoir plus, reportez-vous à Aperçu Energie et climat