Scientific Highlights from Research Division "Scientific Computing, Theory and Data" (SCD)
Scientific Highlights
Spin fluctuation induced Weyl semimetal state in the paramagnetic phase of EuCd2As2
Weyl fermions as emergent quasiparticles can arise in Weyl semimetals (WSMs) in which the energy bands are nondegenerate, resulting from inversion or time-reversal symmetry breaking. Nevertheless, experimental evidence for magnetically induced WSMs is scarce. Here, using photoemission spectroscopy, we observe that the degeneracy of Bloch bands is already lifted in the paramagnetic phase of EuCd2As2. We attribute this effect to the itinerant electrons experiencing quasi-static and quasi–long-range ferromagnetic fluctuations.
New material with magnetic shape memory
PSI researchers have developed a material whose shape memory is activated through magnetism. Application areas for this new kind of composite material include, for example, medicine, space flight, electronics, and robotics.
EPFL Adjunct Professorship to Christopher Mudry
Dr Christopher Mudry, who joined PSI in 1999 and is Research Group Leader of the Condensed Matter Theory Group at PSI since 2009, was awarded the title of Adjunct Professor at EPF Lausanne with the following citation. "Dr Christopher Mudry is a highly acclaimed theoretical physicist. He is regarded as one of the world’s leading experts on the quantum field theory of condensed matter and in the rapidly developing field of the topological properties of matter."
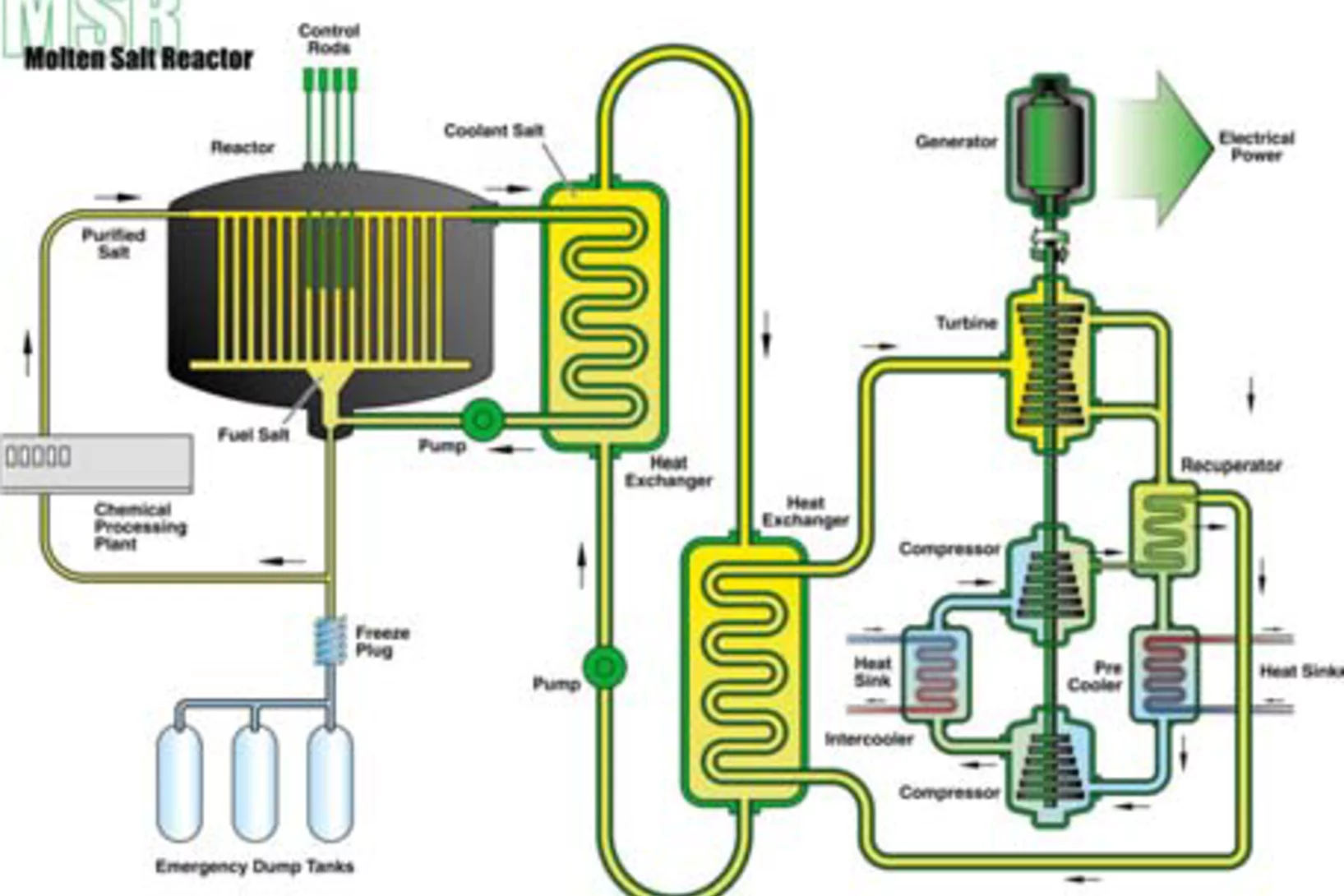
Horizon 2020 project SAMOSAFER granted
The EU Horizon 2020 program granted 3.5 million Euros to the research and innovation project SAMOSAFER, where PSI is one of the 14 project partners. The total budget of the project, inclusive own and in-kind contributions, is 4.5 million Euros. The aim of SAMOSAFER project is to develop and demonstrate new safety barriers and a more controlled behaviour in severe accidents of the Molten Salt Reactor (MSR). Three groups at PSI will be involved in the project: the LSM groups for Advanced Nuclear Systems (ANS) and Multiscale Materials Modelling (MMM) and the Severe Accidents Research group (Sacre) of LRT, focusing on redistribution of the source term in the fuel treatment unit of MSR and assessment and reduction of radionuclide mobility during accidental conditions.
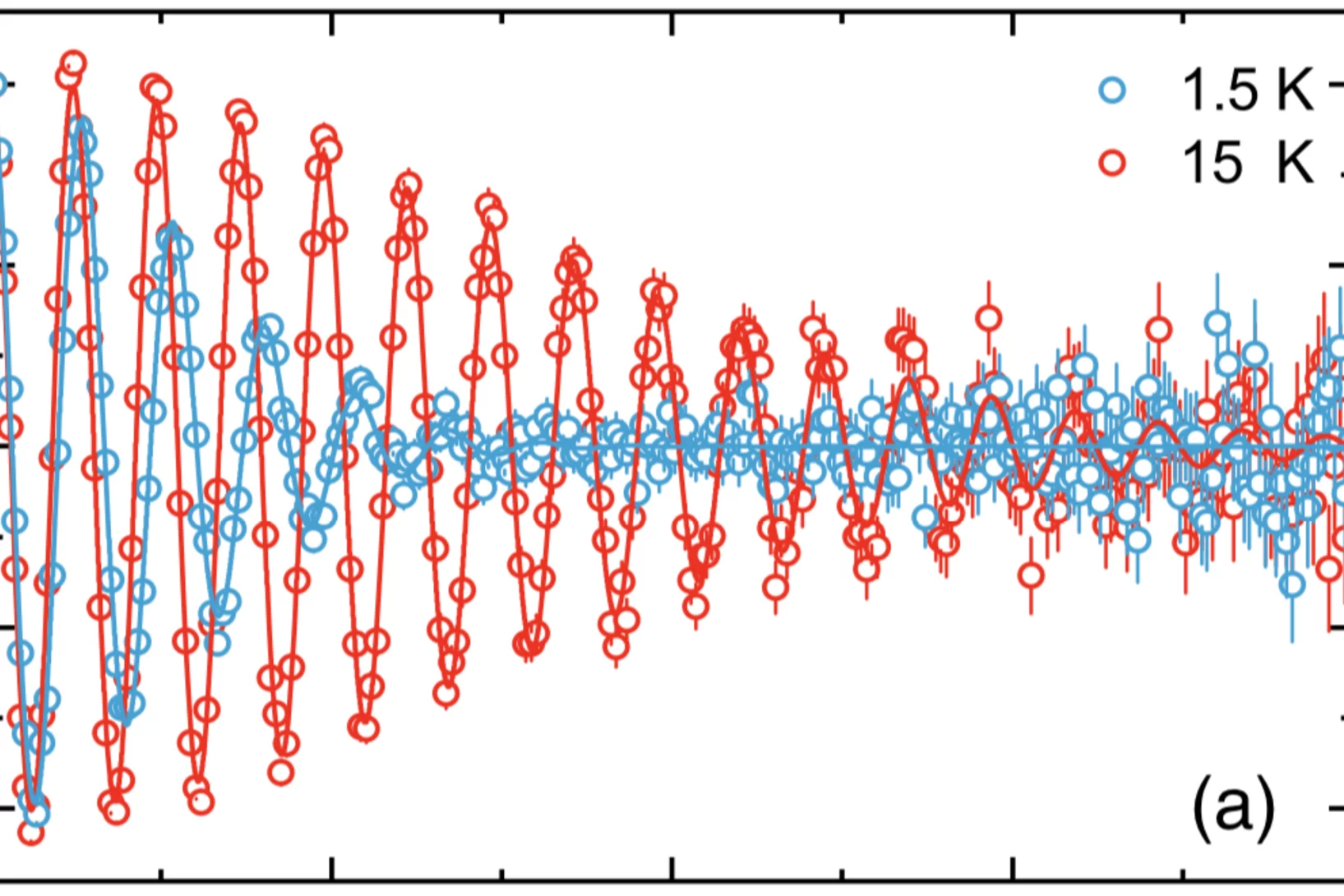
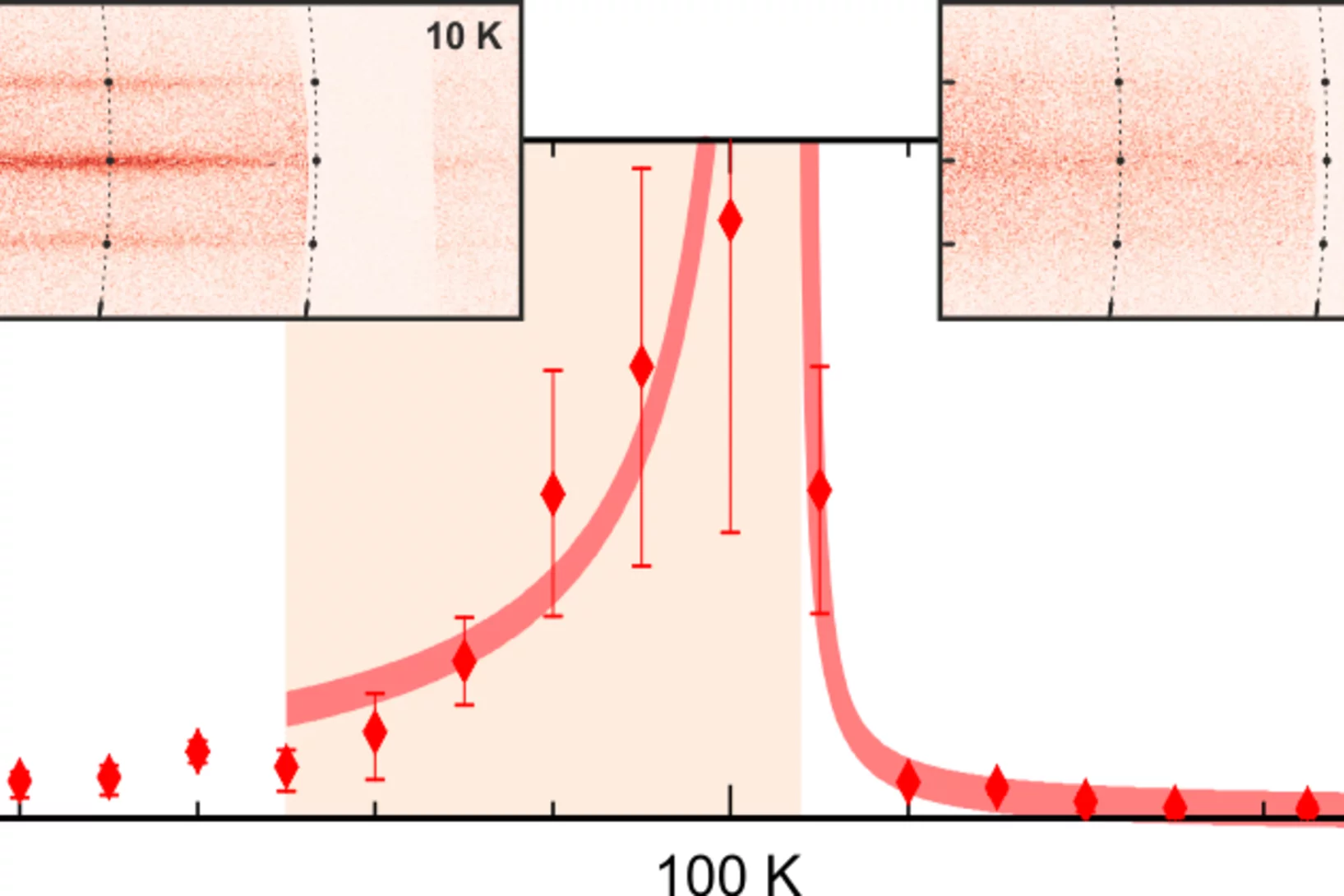
Time-Reversal Symmetry Breaking in Re-Based Superconductors
To trace the origin of time-reversal symmetry breaking (TRSB) in Re-based superconductors, we performed comparative muon-spin rotation and relaxation (μSR) studies of superconducting noncentro-symmetric Re0.82Nb0.18 (Tc=8.8 K) and centrosymmetric Re (Tc=2.7 K).
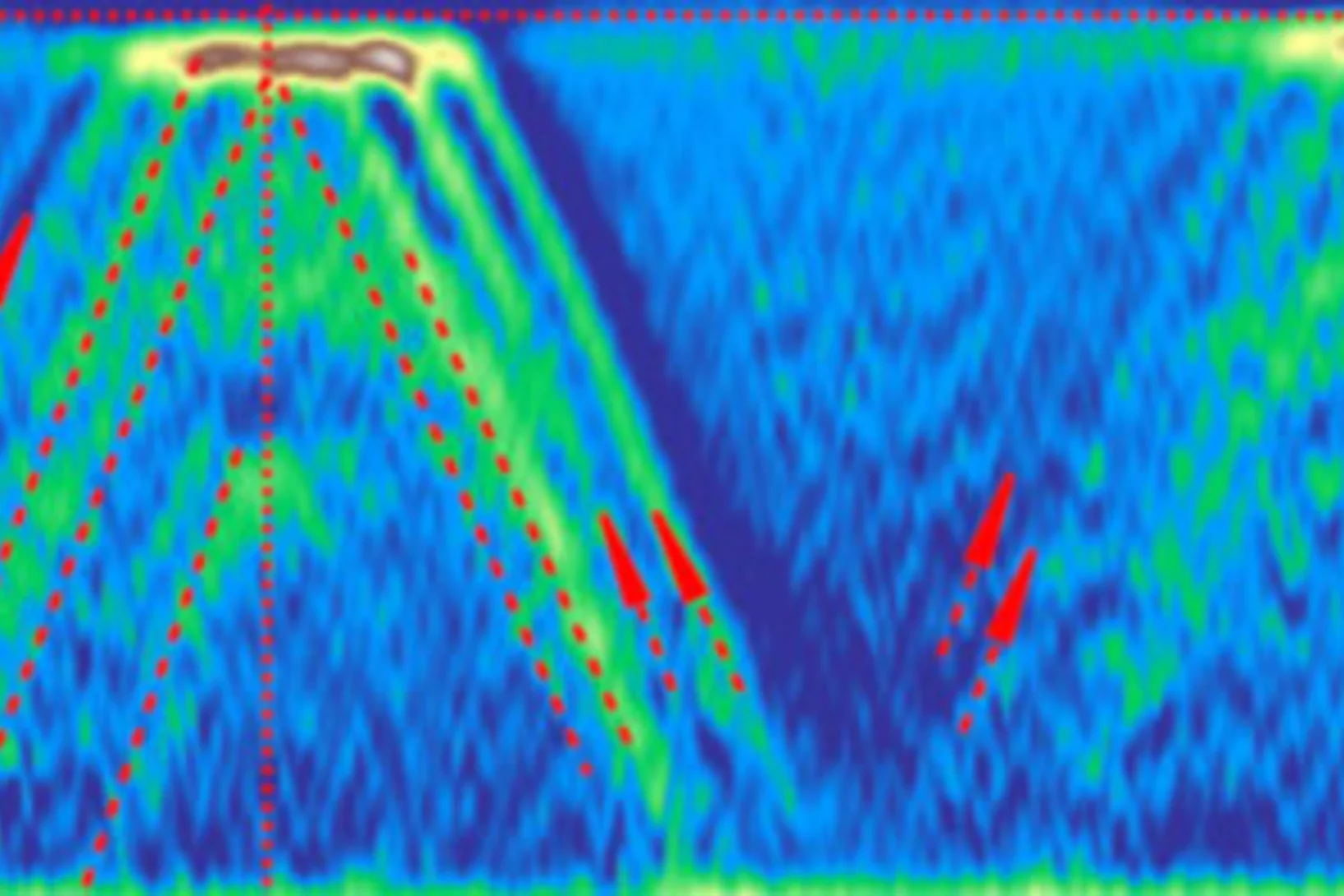
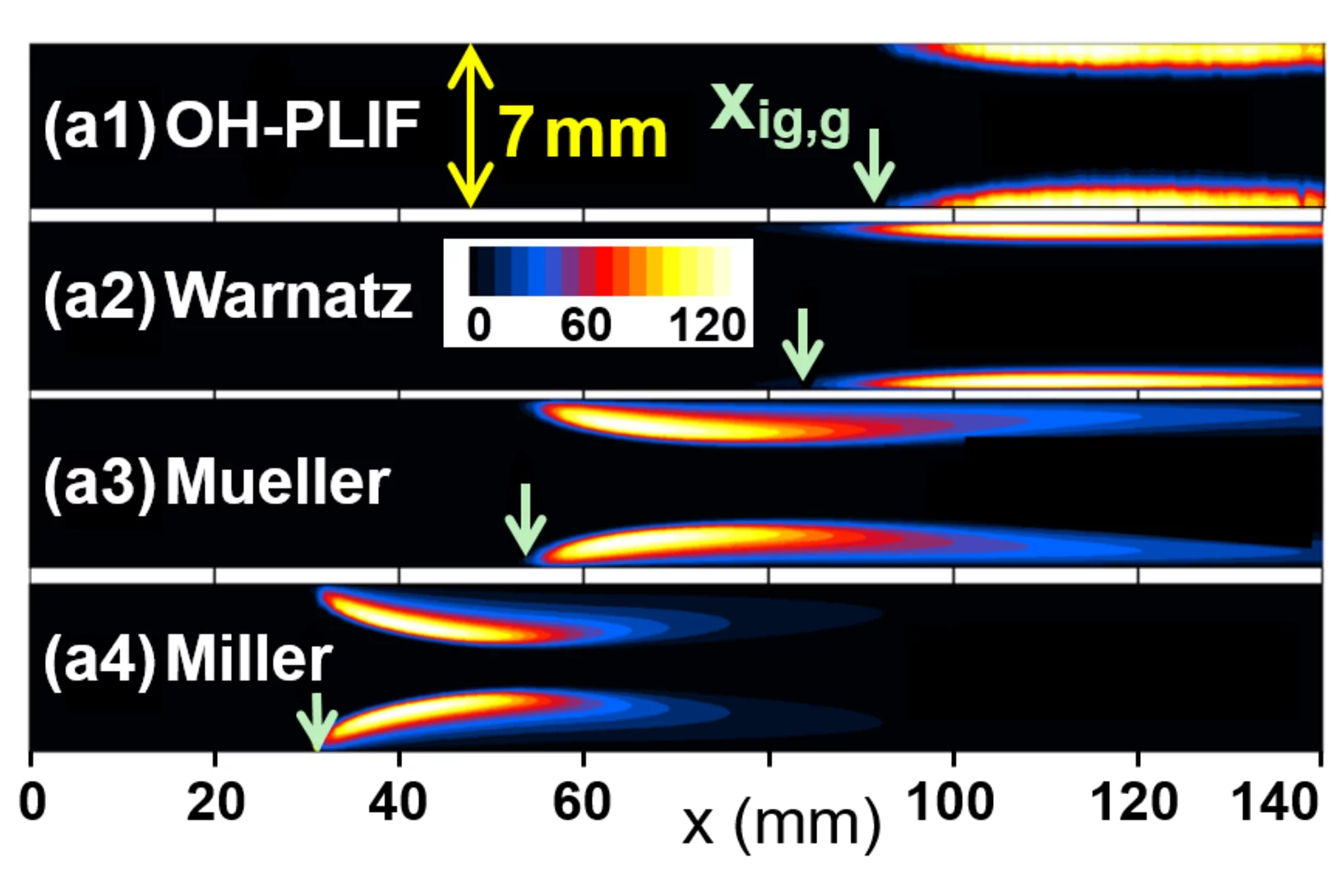
Progress in non intrusive laser based measurements of gas-phase thermoscalars and supporting modeling near catalytically reacting interfaces
Heterogeneous and combined hetero/homogeneous chemical processes have attracted increased attention in many energy conversion systems, which include large scale power generation, microreactors for portable power generation, household burners, fuel processing technologies and automotive exhaust gas aftertreatment. Progress in such systems crucially depends on the development of catalysts with enhanced activity and thermal stability and on the comprehensive understanding of the fundamental processes occurring near gas solid reacting interfaces.
Molten Salt Reactor research at LSM/NES
MSR research at LSM has 3 main justifications:
1. education purpose (2 PhD & 8 MSc internal students, 3 PhD & 4 other guests)
2. technology monitoring (it is the most revolutionary GIV system)
3. novel research topics (liquid phase of the fuel introduces many challenges)
Two major research objectives in NES:
1. safety: evaluate system behavior in nominal and transient conditions (tight multi‐physics coupling / H2020 SAMOFAR project)
2. sustainability: evaluate if the concept can use legacy nuclear waste as initial fuel, insure a high resource utilization (high burning)
Collective magnetism in an artificial 2D XY spin system
Two-dimensional magnetic systems with continuous spin degrees of freedom exhibit a rich spectrum of thermal behaviour due to the strong competition between fluctuations and correlations. When such systems incorporate coupling via the anisotropic dipolar interaction, a discrete symmetry emerges, which can be spontaneously broken leading to a low-temperature ordered phase.
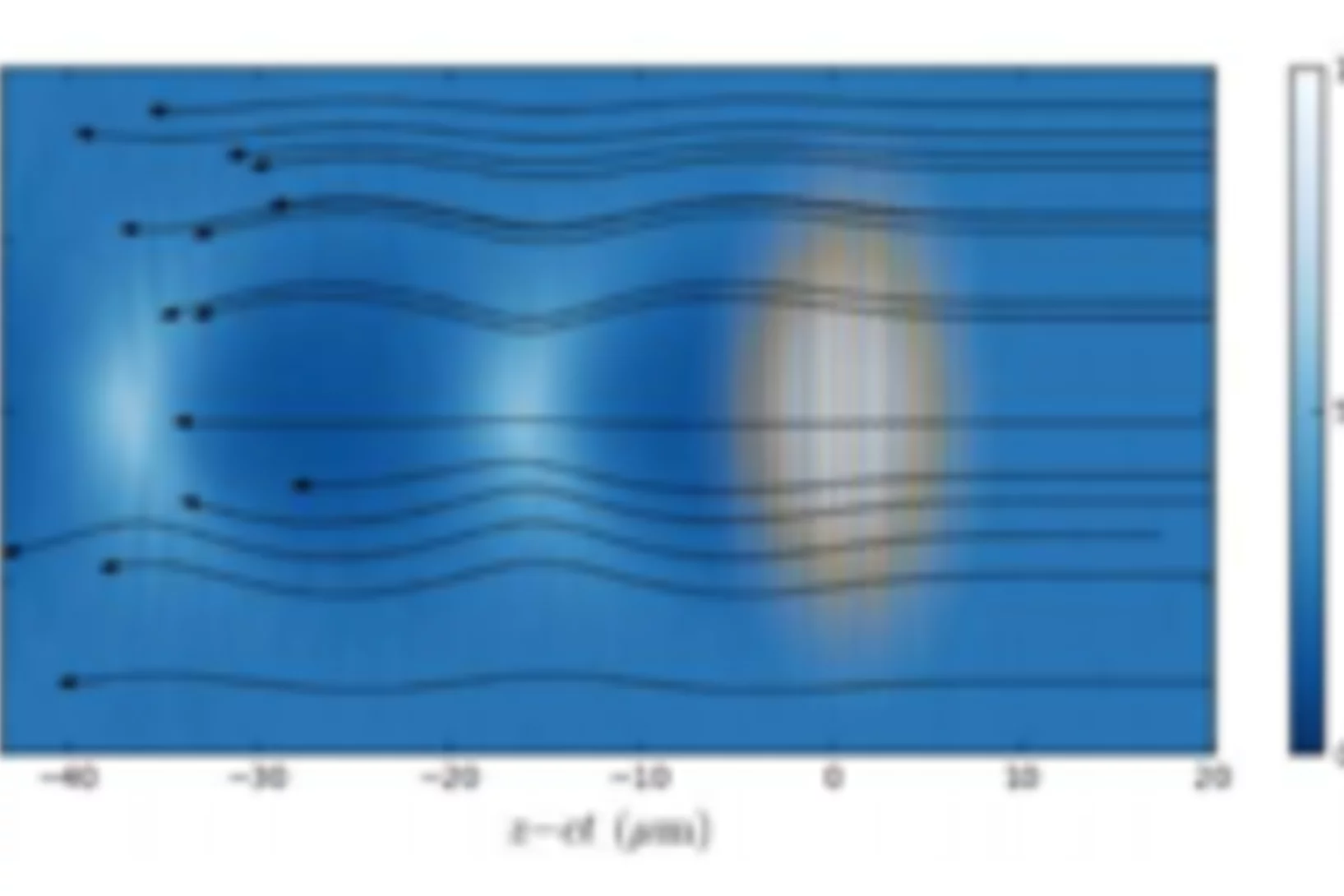
ETH Medal for outstanding MSc thesis
The characteristics of low energy electrons accelerated by a laser wakefield (Laser Wakefield Acceleration LWFA) has been studied. The work included understanding the acceleration process, setting up the experiment and measuring properties like charge, divergence and energy of the accelerated electrons. The experiment included diagnostics for the laser and the electrons. In order to make high-resolution energy distribution measurements with relative errors ∆E/E of below 10%, a tunable electron spectrometer has been designed, built and characterized. A tunable permanent magnet quadrupole triplet has been designed for stigmatic focusing in a range of 5 keV to 5 MeV.