Abkehr von der Kernenergie, Ausbau von Solar- und Windkraft, Energiegewinnung aus Biomasse, Senkung des Energieverbrauchs. Bis 2050 soll die Schweiz klimaneutral werden. Ein ehrgeiziges Ziel, welches durch die zunehmend herausfordernde geopolitische Lage dringlicher denn je geworden ist. Wie lässt sich in den nächsten Jahren eine nachhaltige und widerstandsfähige Energieversorgung für die Schweiz aufbauen? Wie können erneuerbare Energien optimal genutzt werden? Welche neuen Technologien sind besonders vielversprechend? Am PSI suchen Forschende nach Antworten auf diese entscheidenden Fragen.
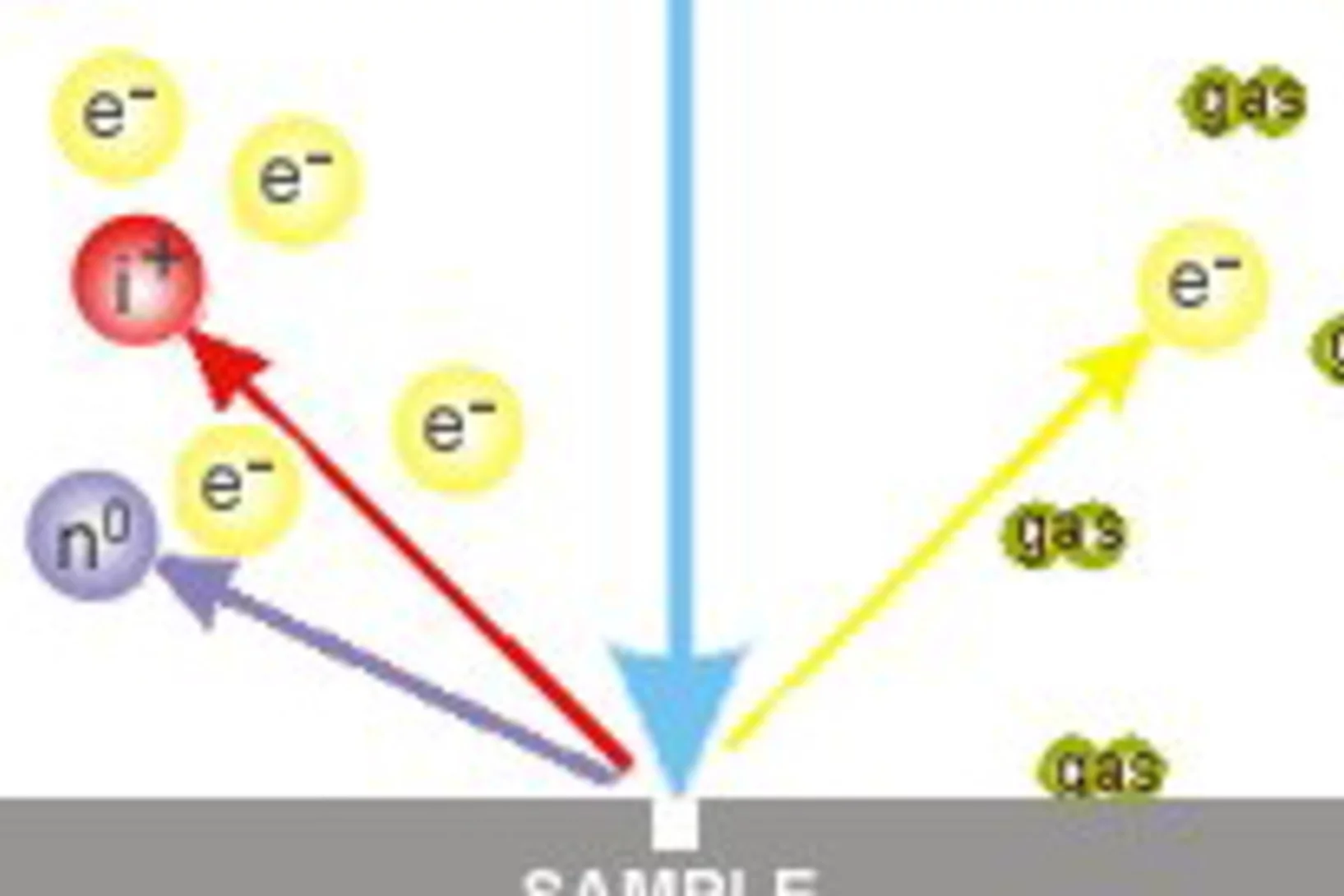
New Focused Ion Beam (FIB) in the Hot Laboratory
The implementation of Focused Ion Beam instruments in material research laboratories during the last decade has not only strongly improved the preparation of very thin specimens for the Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM), in particular at interfaces, but also led to the development of new analysis methods inside the instrument itself. It became a powerful instrument for the analyses of highly radioactive materials, because it allows for the production and analysis of very small specimens that can be then analyzed with very sensitive detectors without strong interference from the radiation field of the specimen itself.
UO2 fuel behavior at very high burnup
The investigation of the nuclear fuel at very high burnup is critical for evaluating the safety margin for the evaluated fuel in normal as well as in accidental conditions. PSI is one of the very few hot laboratories which possess access to irradiated UO2 fuel with very high burnup from commercial reactors. The application of relevant tools for the investigation, handling and analysis of those highly irradiated materials emphasize the necessary expertise.
Johannes Ihli's article makes it into ESRF Highlights
ESRF Highlights 2017 features work of researchers from the Laboratory of Catalysis and Sustainable Chemistry, the Photon Science Division at Paul Scherrer Institut and the ESRF, Grenoble, France.
Welcome Anthony Boucly
Join me in welcoming Anthony, our new postdoc, jointly affiliated with Markus Ammann’s Surface Chemistry group (Surface Chemistry) and within the Electrochemistry Laboratory (Laboratory of Electrochemistry), the group for Electrocatalysis and Interface headed by Prof. Thomas Schmidt under the supervision of Emiliana Fabbri.
He obtained his PhD from the University of Pierre et Marie Curie in Paris, in the Laboratory of Chemical Physics – Materials and Radiation. The title of his dissertation was “Catalytical Reactions and Environmnetal Chemistry Modifications as seen by Synchrotron Radiation NAP-XPS”. He is trained in surface chemistry and surface analysis methods.
At PSI, Anthony Boucly will be studying the electrochemical interaction between electrolytes and metal oxides relevant for electrochemical applications and for the weathering of mineral dust particles in the atmosphere with X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy at the Near Ambient Pressure Photoemission (NAPP) endstation at SLS.
Refurbishment of HZ6
The hot cell 6 is dedicated to the storage and conditioning of high level solid waste. This cell has been completely refurbished in the period 2015 – 2017. This include the complete dismantling and conditioning of the highly fuel contaminated old infrastructure, the cleaning of the cell and the installation and test of the new improved infrastructure.
Strom aus Nanomagneten
Oles Sendetskyi, Gewinner eines Founder Fellowships am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI, will die Umpolung von Nanomagneten nutzen, um eine nachhaltige Stromquelle für Kleingeräte zu entwickeln.
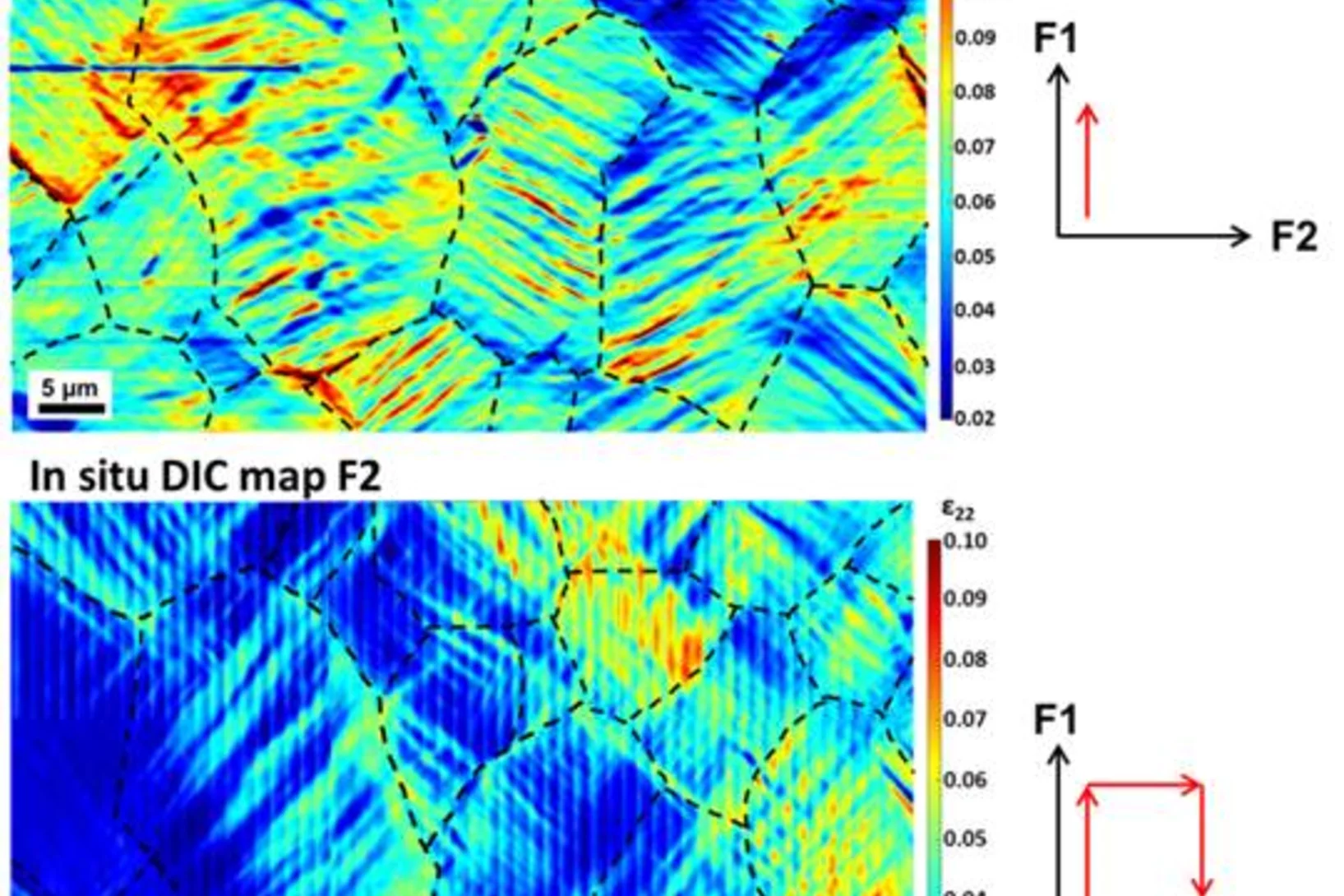
Martensitic transformation under multiaxial deformation
Researchers at PSI have established a link between the martensitic transformation, microstructural evolution and the mechanical behavior under multiaxial deformation in a NiTi alloy by using a unique combination of in situ high-resolution Digital Image Correlation (DIC), in situ X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy characterization.
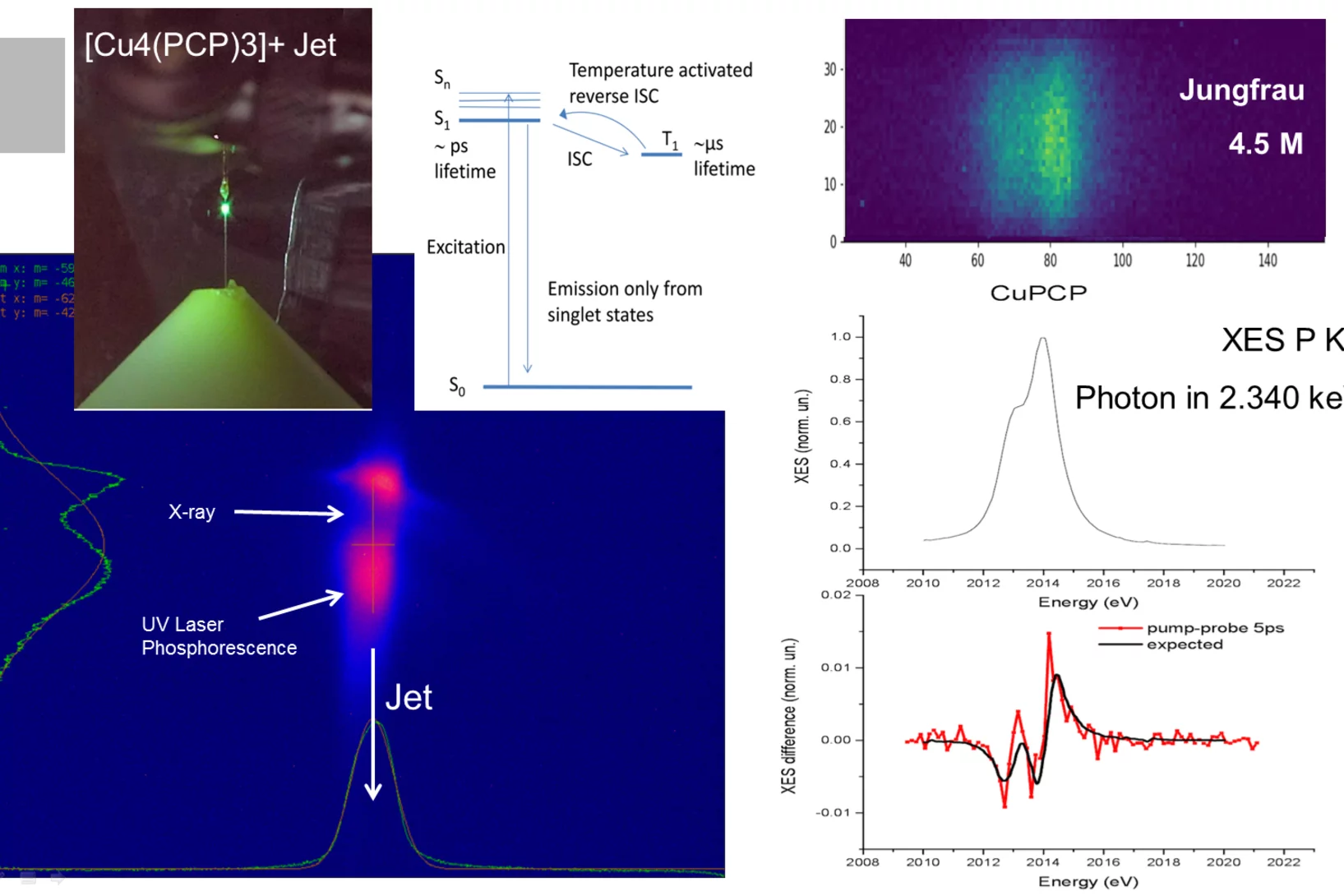
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra on UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Bremen, Krakow and PSI, led by Matthias Vogt (Univ. Bremen) and Chris Milne (PSI)in collaboration with J. Szlachetko, J. Czapla-Masztafiak, W. M. Kwiatek (Inst. of Nucl.Phys. PAN (Krakow), successfully did the first pilot experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra on UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system.
First Pilot Experiment at SwissFEL-Alvra: UV photo-induced charge transfer in OLED system
On the 17th of December 2017 SwissFEL saw its first pilot experiment in the Alvra experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline.
Wir starten mit 500 Millionen Myonen
Mit Myonen lassen sich Materialien für die Elektronik der Zukunft untersuchen. Die beiden PSI-Forscher Alex Amato und Thomas Prokscha erklären im Interview die Besonderheit dieser Elementarteilchen.
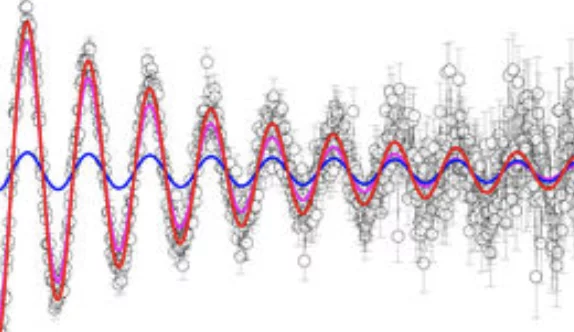
Macroscopic phase separation of superconductivity and ferromagnetism in Sr0.5Ce0.5FBiS2-xSex revealed by μSR
The compound Sr0.5Ce0.5FBiS2 belongs to the intensively studied family of layered BiS2 superconductors. It attracts special attention because superconductivity at Tsc = 2.8 K was found to coexist with local-moment ferromagnetic order with a Curie temperature TC = 7.5 K. Recently it was reported that upon replacing S by Se TC drops and ferromagnetism becomes of an itinerant nature.
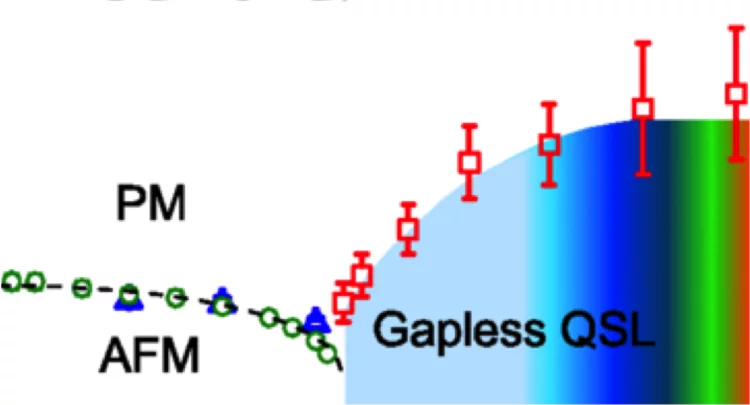
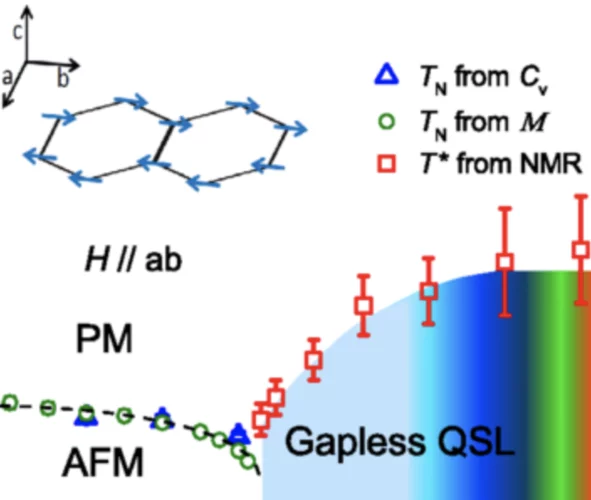
The field-induced quantum spin-liquid phase of α−RuCl3 is gapless
Throughout 2017, the material α−RuCl3 has continued to inspire and fascinate those interested in correlated condensed matter. New experimental data now provide unique insight, and pose fresh challenges.
Erstes Experiment am SwissFEL erfolgreich durchgeführt
Die Jahre des sorgsamen Planens und Aufbauens haben sich ausgezahlt: An der neuesten Grossforschungsanlage des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI – dem Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL – wurde das erste Experiment erfolgreich durchgeführt. Damit wurden zwei Ziele erreicht: Erstens gibt es schon gleich ein neues wissenschaftliches Ergebnis. Zweitens wird damit das Zusammenspiel der vielen Einzelkomponenten der hochkomplexen Anlage optimiert.
The Charpak-Ritz Prize 2018 is awarded to Roland Paul Horisberger
The Charpak-Ritz Prize 2018, jointly awarded by the French Physical Society and the Swiss Physical Society, has been bestowed to Roland Paul Horisberger for his numerous contributions to the development of precision silicon vertex detectors for particle physics experiments as well as for the application of these technologies in X-ray photon sciences.
Jean-Baptiste Mosset winner of PSI Founder Fellowship
Jean-Baptiste Mosset from the Laboratory of Particle Physics is the winner of a PSI Founder Fellowship and plans now to commercialise a neutron detector to spot plutonium and uranium. With his new technology, less expensive and more efficient neutron detectors could be developed. In the next 18 months, Mosset wants to further develop his prototype and find out if demand for this technology exists in industry.
Tuning Nanoparticle–Micelle Interactions and Resultant Phase Behavior
The evolution of the interaction between an anionic nanoparticle and a nonionic surfactant and their resultant phase behavior in aqueous solution in the presence of electrolyte and ionic surfactants have been studied. The mixed system of anionic silica nanoparticles (Ludox LS30) with nonionic surfactant decaethylene glycol monododecylether (C12E10) forms a highly stable clear phase over a wide concentration range of surfactant.
Arttu Miettinen joins the TOMCAT team as Post Doc
After his PhD at the University of Jyväskylä in Finnland in image analysis, Arttu will be working on the stitching and segmentation of large datasets in the framework of the Human Brain Project.
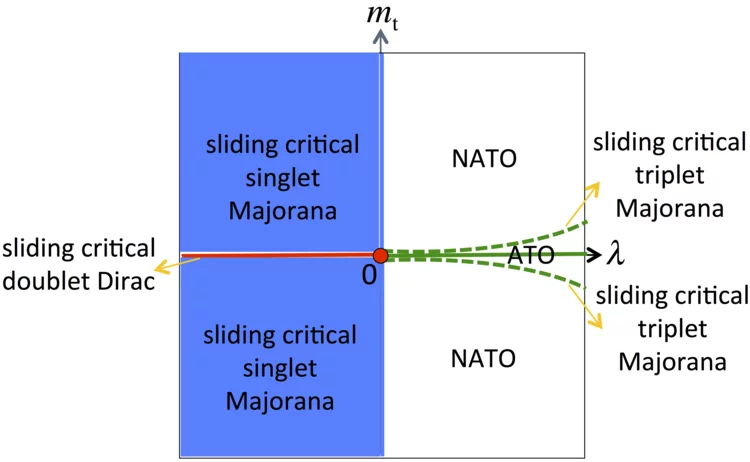
Coupled quantum wires realize Abelian and non-Abelian topological order in two-dimensional space
Christopher Mudry and his collaborators have shown theoretically how to construct strongly interacting phases of matter that realize topological order in two-dimensional space by strongly coupling quantum wire. Remarkably, their model supports both Abelian topological order (ATO) and non-Abelian topological order (NATO) with a continuous phase transition separating them. Read the full paper here
Gapless Spin Excitations in the Field-Induced Quantum Spin Liquid Phase of α-RuCl3
α-RuCl3 is a leading candidate material for the observation of physics related to the Kitaev quantum spin liquid (QSL). By combined susceptibility, specific-heat, and nuclear-magnetic-resonance measurements, we demonstrate that α-RuCl3 undergoes a quantum phase transition to a QSL in a magnetic field of 7.5 T applied in the ab plane. We show further that this high-field QSL phase has gapless spin excitations over a field range up to 16 T.
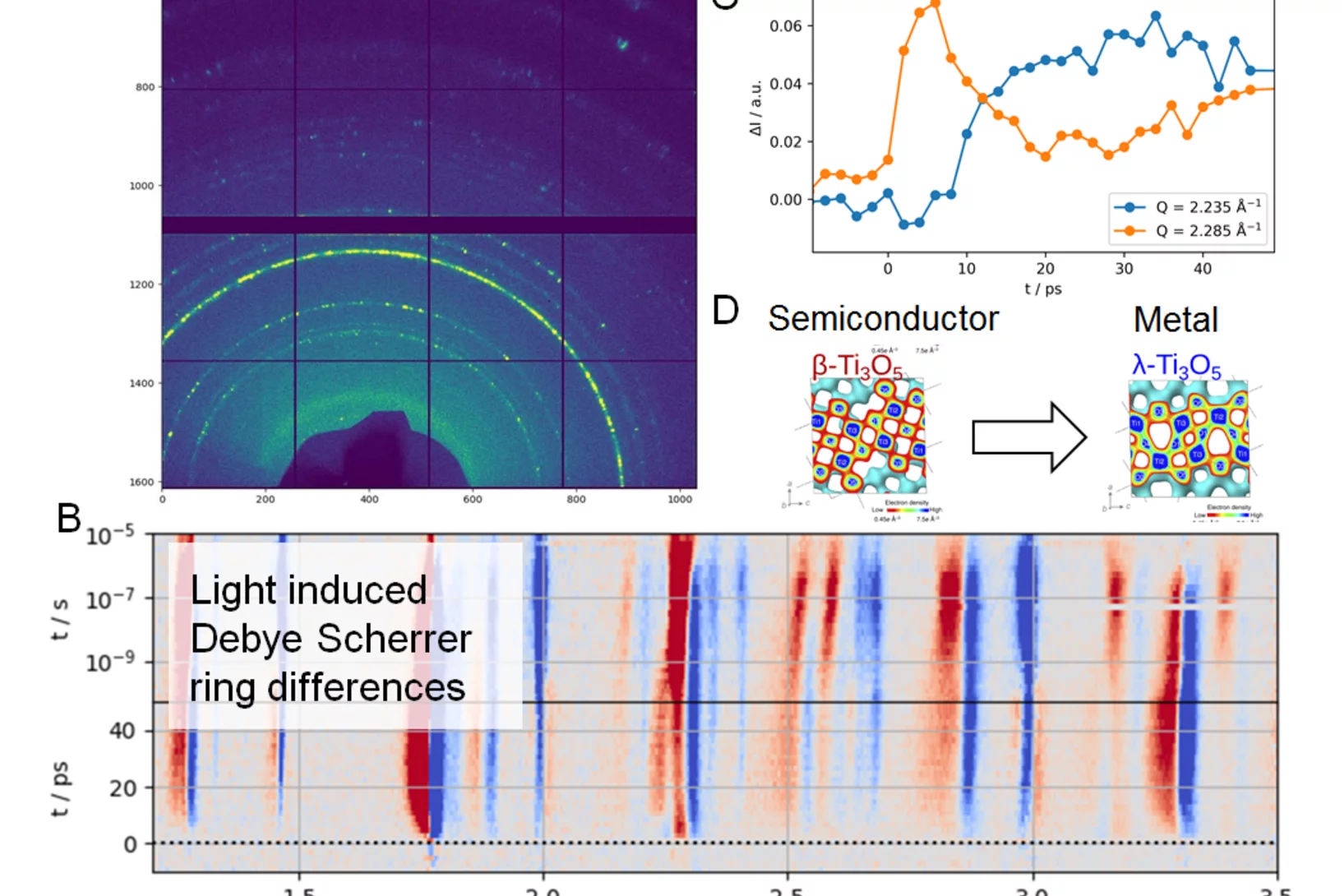
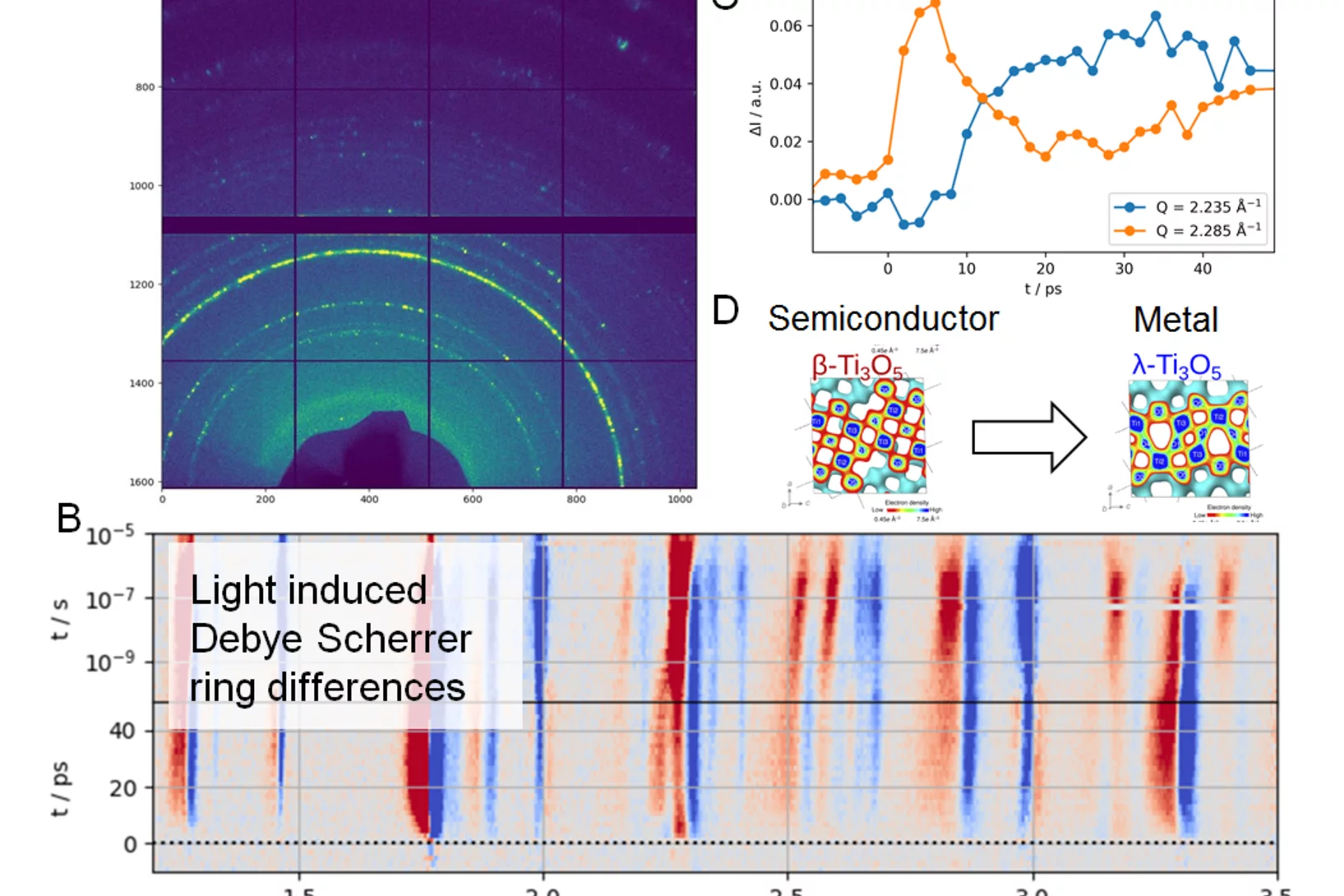
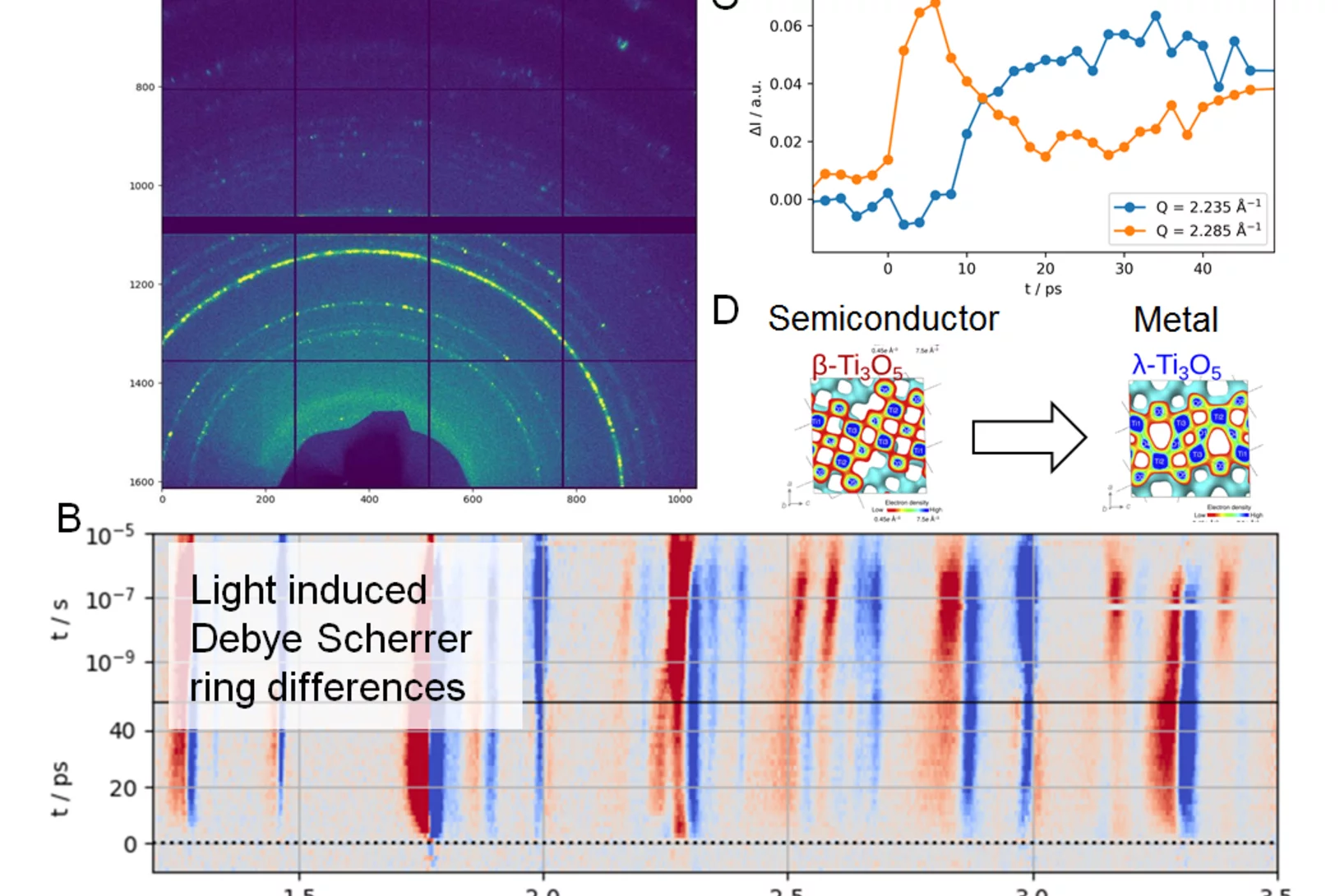
First time resolved Pilot Experiment by SwissFEL: Semiconductor to metal transition in Ti3O5 nanocrystals
On the 30th of November 2017 SwissFEL saw its first time resolved pilot experiment in the Bernina experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Rennes, ESRF and PSI, led by Marco Cammarata (Univ. Rennes) and Henrik Lemke (PSI), successfully started the experimental phase at SwissFEL. The goal was to study the picosecond dynamics of a light-induced phase transition from a semiconductor to metallic crystal structure in a Titanium Oxide (D).
First time resolved Pilot Experiment by SwissFEL: Semiconductor to metal transition in Ti3O5 nanocrystals
On the 30th of November 2017 SwissFEL saw its first time resolved pilot experiment in the Bernina experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Rennes, ESRF and PSI, led by Marco Cammarata (Univ. Rennes) and Henrik Lemke (PSI), successfully started the experimental phase at SwissFEL.
First time resolved Pilot Experiment by SwissFEL: Semiconductor to metal transition in Ti3O5 nanocrystals
On the 30th of November 2017 SwissFEL saw its first time resolved pilot experiment in the Bernina experimental station of the SwissFEL ARAMIS beamline. A team of scientists from the University of Rennes, ESRF and PSI, led by Marco Cammarata (Univ. Rennes) and Henrik Lemke (PSI), successfully started the experimental phase at SwissFEL. The goal was to study the picosecond dynamics of a light-induced phase transition from a semiconductor to metallic crystal structure in a Titanium Oxide (D).
Mehr als ein Prototyp
Jean-Baptiste Mosset, Gewinner eines Founder Fellowships am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI, will einen Neutronendetektor zur Erkennung von Plutonium und Uran kommerzialisieren.
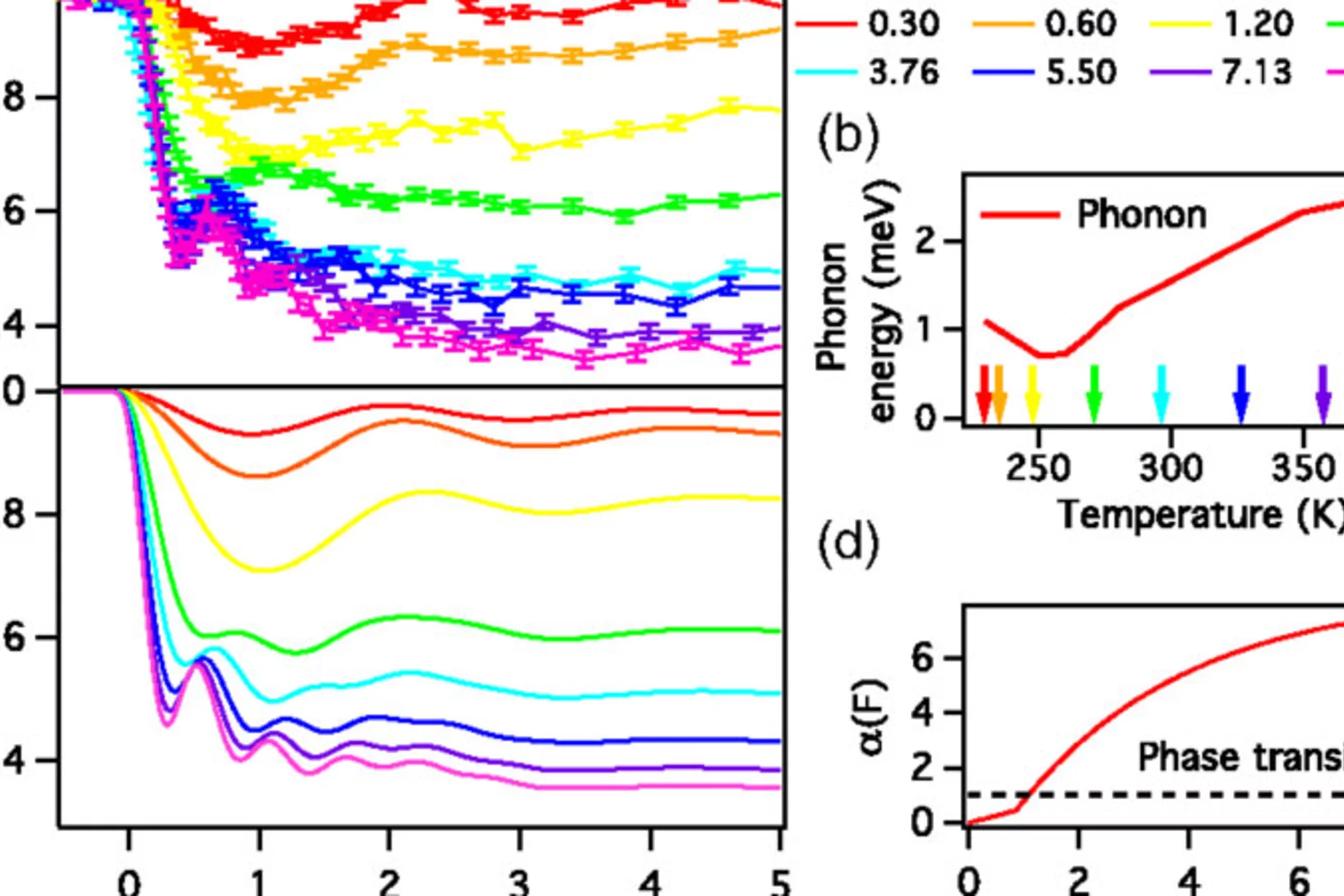
Coupling between a Charge Density Wave and Magnetism in an Heusler Material
The prototypical magnetic memory shape alloy Ni2MnGa undergoes various phase transitions as a function of the temperature, pressure, and doping. In the low-temperature phases below 260 K, an incommensurate structural modulation occurs along the [110] direction which is thought to arise from the softening of a phonon mode. It is not at present clear how this phenomenon is related, if at all, to the magnetic memory effect. Here we report time-resolved measurements which track both the structural and magnetic components of the phase transition from the modulated cubic phase as it is brought into the high-symmetry phase.
2017 Highly Cited Researchers
Two LAC researchers were highly cited in 2017.
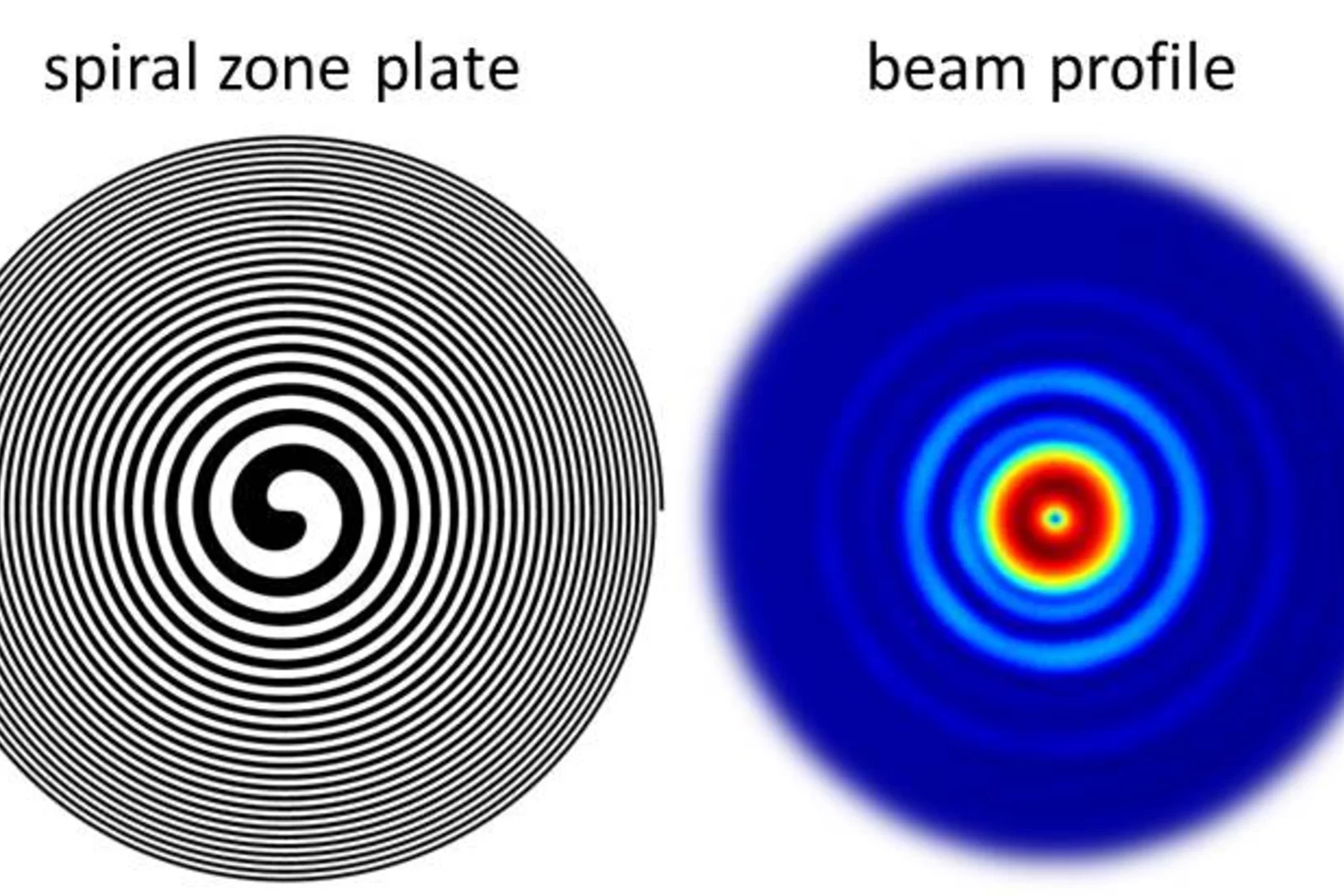
Extreme Ultraviolet Vortices at Free Electron Lasers
PSI scientists have developed tailored diffractive X-ray optics for a free electron laser that induces an optical vortex in extreme ultraviolet radiation. The experiment facilitates the first demonstration of orbital angular momentum in radiation created by a free electron laser in the extreme ultraviolet regime, with an extraordinary clean and defined wavefront. In a collaborative effort with researchers from the FERMI free electron laser in Trieste, Italy and from the University of Nova Gorica in Slovenia, the wavefront of the intense beams carrying an orbtial angular momentum was characterized. Furthermore, a method to characterize the footprint of a focused beam from a free electron laser was refined based on ablation imprints in polymers and subsequent treatment with organic solvents. In this way, the sensitivity of the imprint method could be enhanced to a dynamic range of three orders of magnitude in a single shot.
Mit Blaulicht in die Gefahrenzone
Die Strahlenwehr des PSI ist nicht nur für Einsätze im Institut, sondern im ganzen Kanton Aargau zuständig. Viermal im Jahr übt sie den Ernstfall.
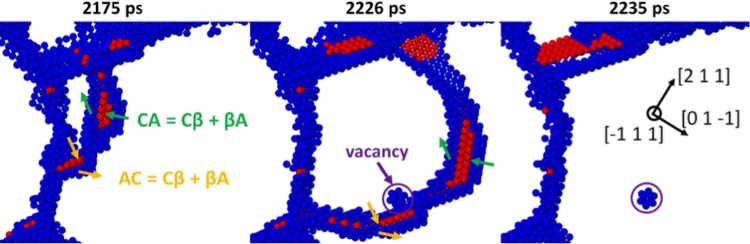
Dislocation interactions at reduced strain rates in atomistic simulations of nanocrystalline Al
Molecular dynamics simulations of transient stress drops have been carried out in different regimes on a nanocrystalline Aluminum sample with average grain size of 12 nm. Besides confirming the interpretation of experimental results obtained during in situ X-ray diffraction, the creep simulations performed at 2 or 3 orders of magnitude lower strain rates than usual reveal deformation mechanisms that have not been observed previously.
PSI-Spin-off GratXray
gewinnt Swiss Technology Award 2017
Ein Spin-off aus dem PSI hat den diesjährigen Swiss Technology Award erhalten: Das junge Unternehmen “GratXray” entwickelt eine neue Methode zur Früherkennung von Brustkrebs.
Noch keine Spur von Dunkler Materie
Keine Hinweise auf Dunkle Materie aus Axionen – Ergebnis eines Experiments am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI schränkt Theorien zur Natur Dunkler Materie weiter ein.