Endlagersuche: Viele 100'000 Jahre sicher im Ton
Obwohl die Schweiz aus der Kernenergie aussteigt, muss sie eine Lösung für das in den Kernkraftwerken, aber auch in Medizin, Industrie und Forschung entstandene, radioaktive Material finden. Daher stellt sie sich einer aussergewöhnlichen, verantwortungsvollen Aufgabe: Sie sucht einen Ort, an dem sie ihre radioaktiven Abfälle mehrere hunderttausend Jahre lang sicher lagern kann. So lange, bis sie von selbst die Radioaktivität natürlicher Gesteine erreicht haben.
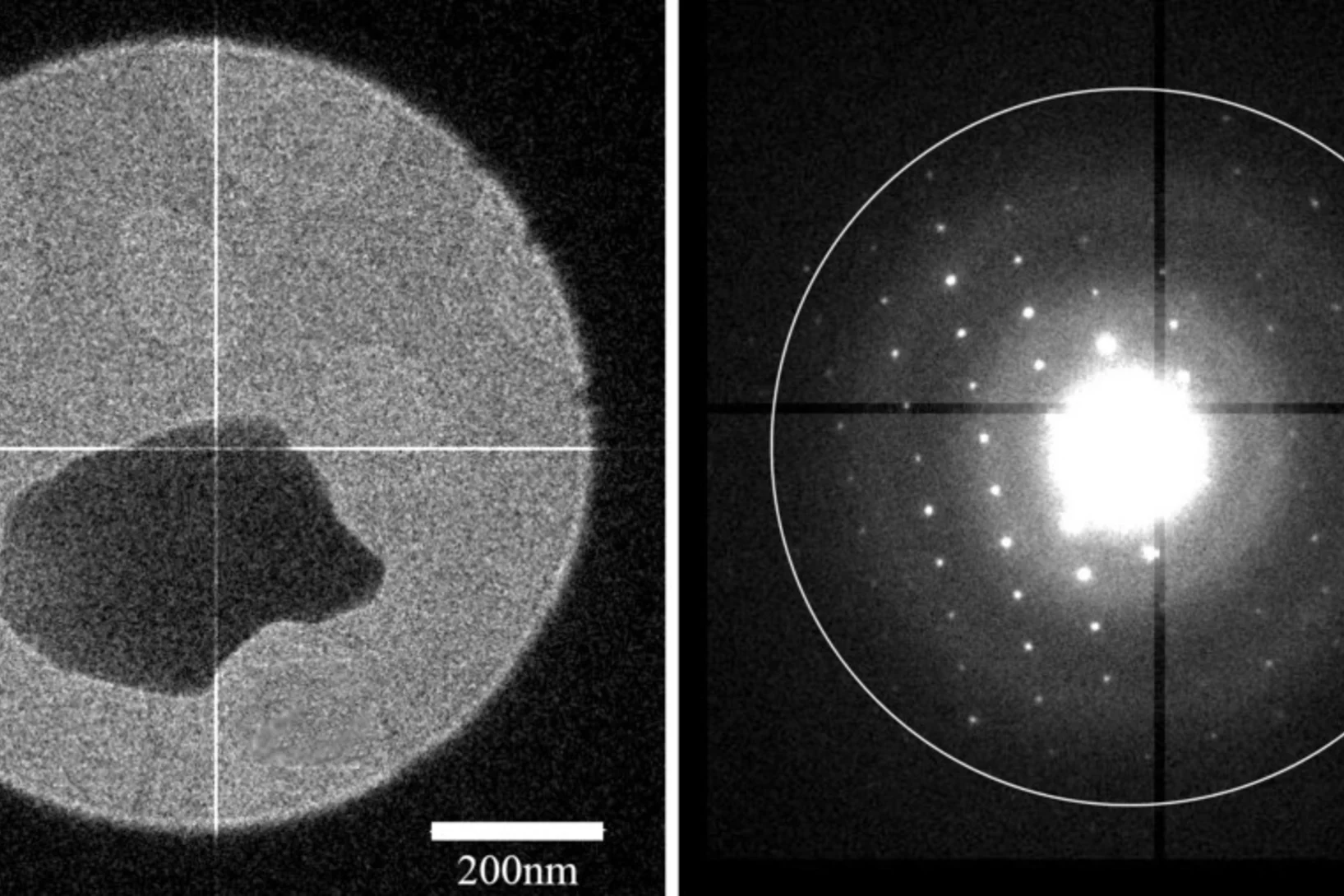
Determining the structures of nanocrystalline pharmaceuticals by electron diffraction
A new type of detector developed by Dr. van Genderen enables the structure determination of pharmaceutical compounds with electron diffraction at room temperature. The group concentrate on expanding this new technique to macromolecular compounds.
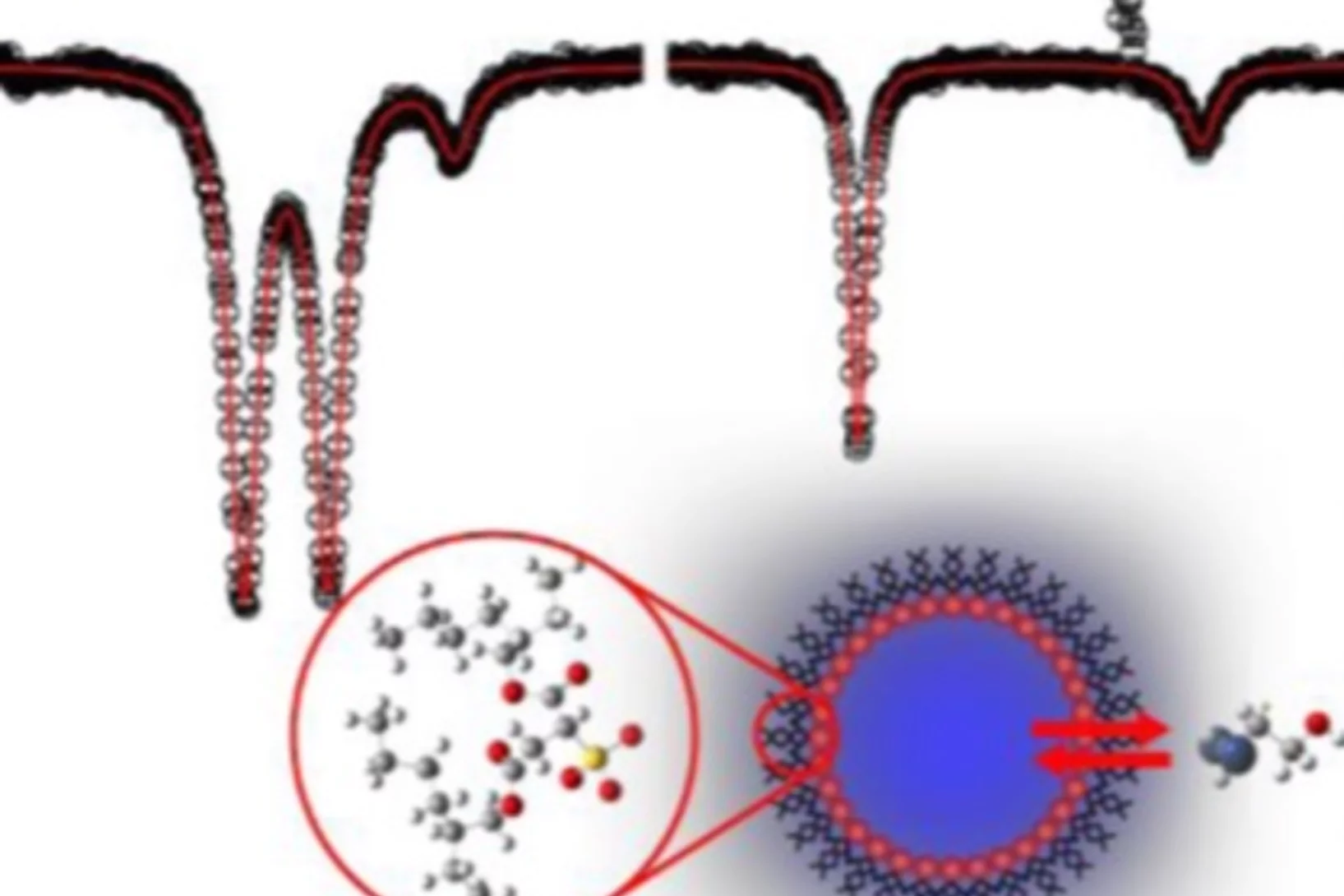
Rate of Molecular Transfer of Allyl Alcohol across an AOT Surfactant Layer Using Muon Spin Spectroscopy
The transfer rate of a probe molecule across the interfacial layer of a water-in-oil (w/o) microemulsion was investigated using a combination of transverse field muon spin rotation (TF-μSR), avoided level crossing muon spin resonance (ALC-μSR), and Monte Carlo simulations. Reverse micro-emulsions consist of nanometer-sized water droplets dispersed in an apolar solvent separated by a surfactant monolayer.
Ab in den Strahlkanal
Seit Herbst 2015 füllt sich der SwissFEL-Strahlkanal mit den Maschinenkomponenten für die neue PSI-Grossforschungsanlage. Stück für Stück werden die vormontierten Komponenten an ihren endgültigen Standort gebracht.
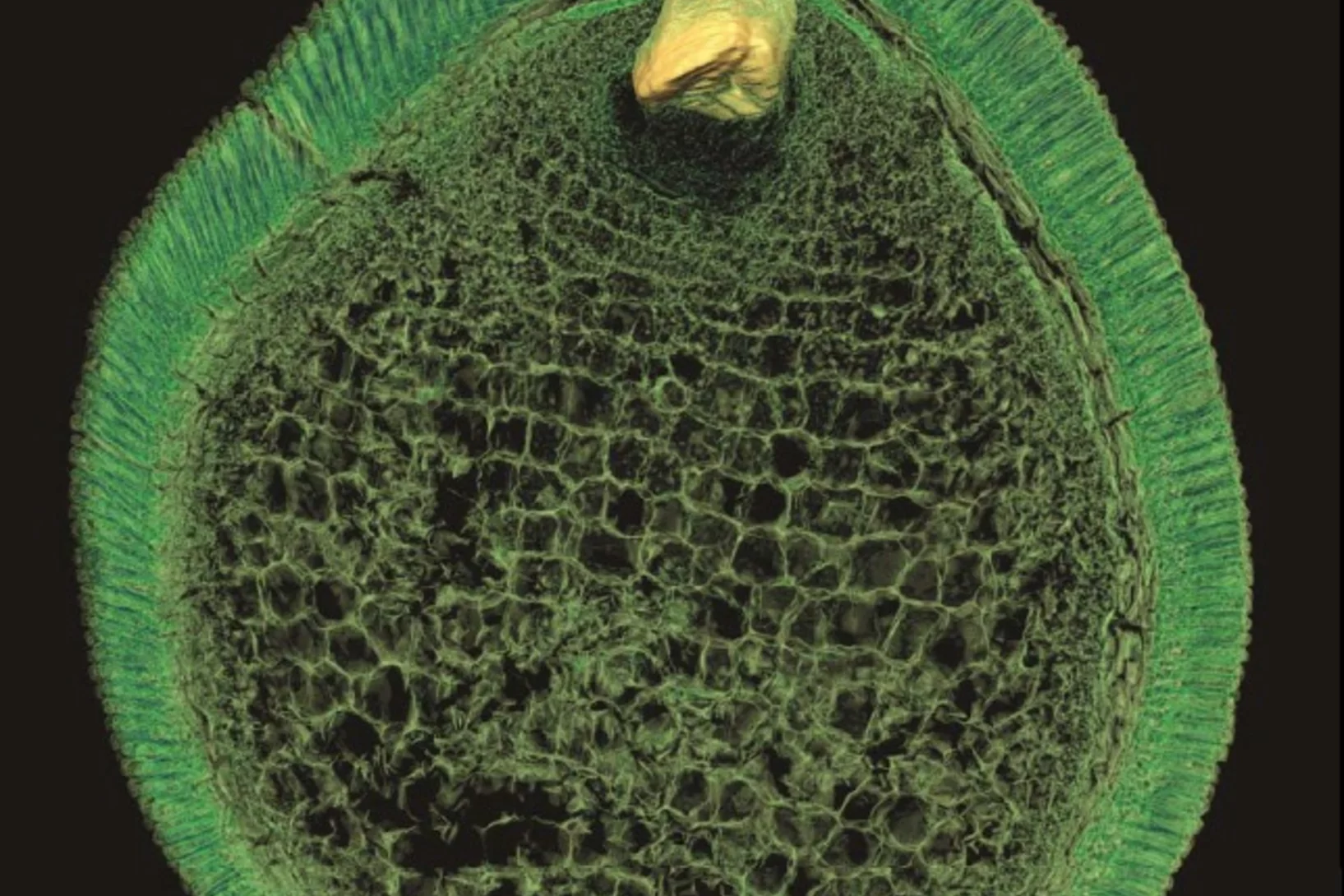
Preserved Embryos Illustrate Seed Dormancy in Early Angiosperms
The discovery of exceptionally well-preserved, tiny fossil seeds dating back to the Early Cretaceous corroborates that flowering plants were small opportunistic colonizers at that time, according to a new Yale-led study.
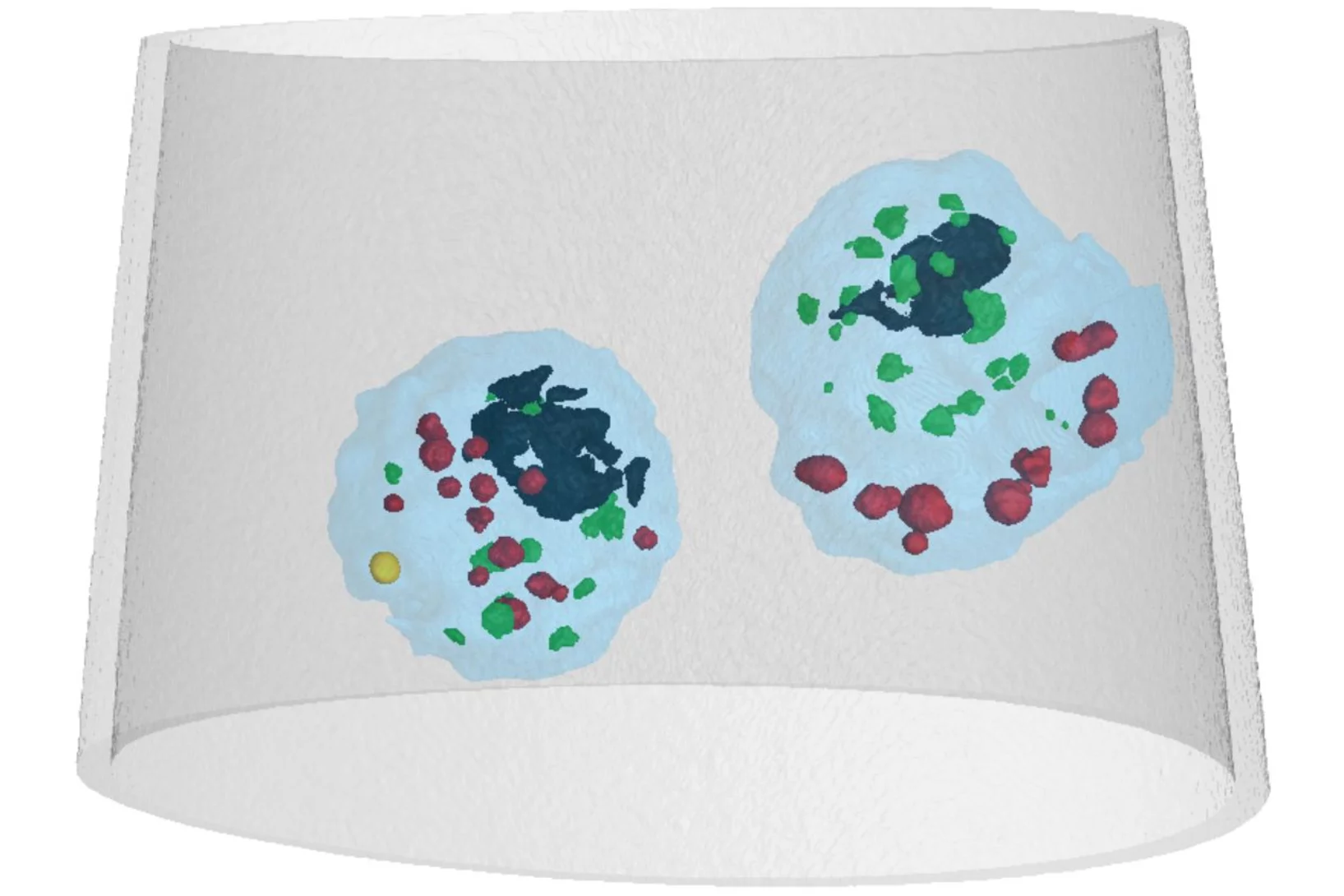
Mass density distribution of intact cell ultrastructure
The determination of the mass density of cellular compartments is one of the many analytical tools that biologists need to unravel the extremely complex structure of biological systems. Cryo X-ray nanotomography reveals absolute mass density maps of frozen hydrated cells in three dimensions.
Die Vermessung der Gleichzeitigkeit
Was macht ein Physiker, wenn sein Experiment eine hochgenaue Zeiterfassung benötigt? So genau, dass bestehende Elektronik kaum weiterhilft? Ein Forscher des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI hat sich kurzerhand entschlossen, selbst eine Lösung zu entwickeln. Die heisst DRS4 und ist ein hochpräziser Elektronikchip, der die Physik unseres gesamten Universums entschlüsseln könnte. Nebenbei hilft der Chip schon heute Ärzten, Hirntumore genauestens zu lokalisieren.
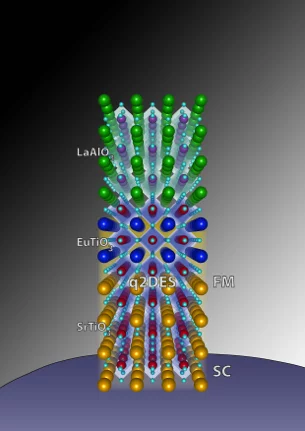
Tunable spin polarization and superconductivity in engineered oxide interfaces
A new kind of 2DEG is found by inserting two atomic layers of the antiferromagnetic and insulating compound EuTiO3 between LaAlO3 and SrTiO3. The 2DEG is found to exhibit besides a superconducting ground state, a strong spin-polarization. The magnetism of Eu and Ti was studied by XMCD at the X-Treme beamline in SLS.
Kohlendioxid: Das Klimaproblem im Untergrund entsorgen?
Allen Warnungen vor den Folgen des Klimawandels zum Trotz und unbeeindruckt von politischen Absichtserklärungen: Die weltweiten Kohlendioxidemissionen steigen und steigen. Hauptverantwortlich dafür sind Kohle- und Gaskraftwerke, die den zunehmenden Strombedarf decken. Könnte man deren Kohlendioxidemissionen dauerhaft im Boden speichern, anstatt damit Atmosphäre und Klima zu belasten? Und wäre das auch für die Schweiz interessant? Diese Fragen beleuchtet der neueste Energie-Spiegel des PSI.
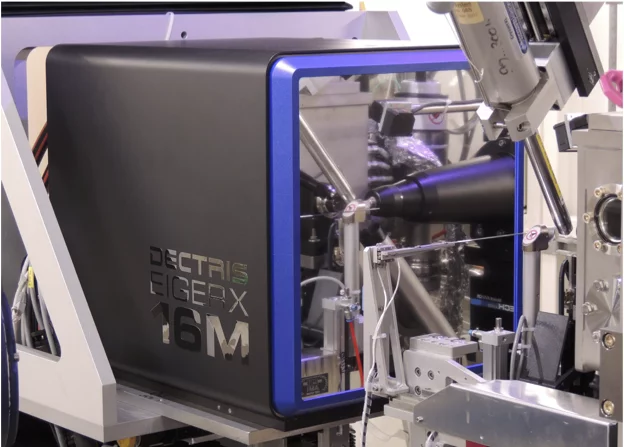
First EIGER X 16M in operation at the Swiss Light Source
The macromolecular crystallography beamline X06SA at the Swiss Light Source, a synchrotron operated by Paul Scherrer Institute, is the first one in the world to upgrade its detector to an EIGER X 16M.
The flip-over effect in pulsed laser deposition: Is it relevant at high background gas pressures?
In pulsed laser deposition the use of a rectangular or elliptical beam spot with a non 1:1 aspect ratio leads to the so called flip-over effect. Here, the longest dimension of the laser spot results in the shortest direction of plasma plume expansion.
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
If a ball is rolled up a hill with less kinetic energy than the potential energy at the top, it will return eventually, and stays bound in the valley. Tunnelling is a distinctly quantum mechanical phenomenon, in which such balls can magically cross the hill, and appear in the neighbouring valley, as if going through a tunnel. In order for this to happen with a non-negligible probability, the ball has to be small and the barrier, i.e. the hill, sharp.
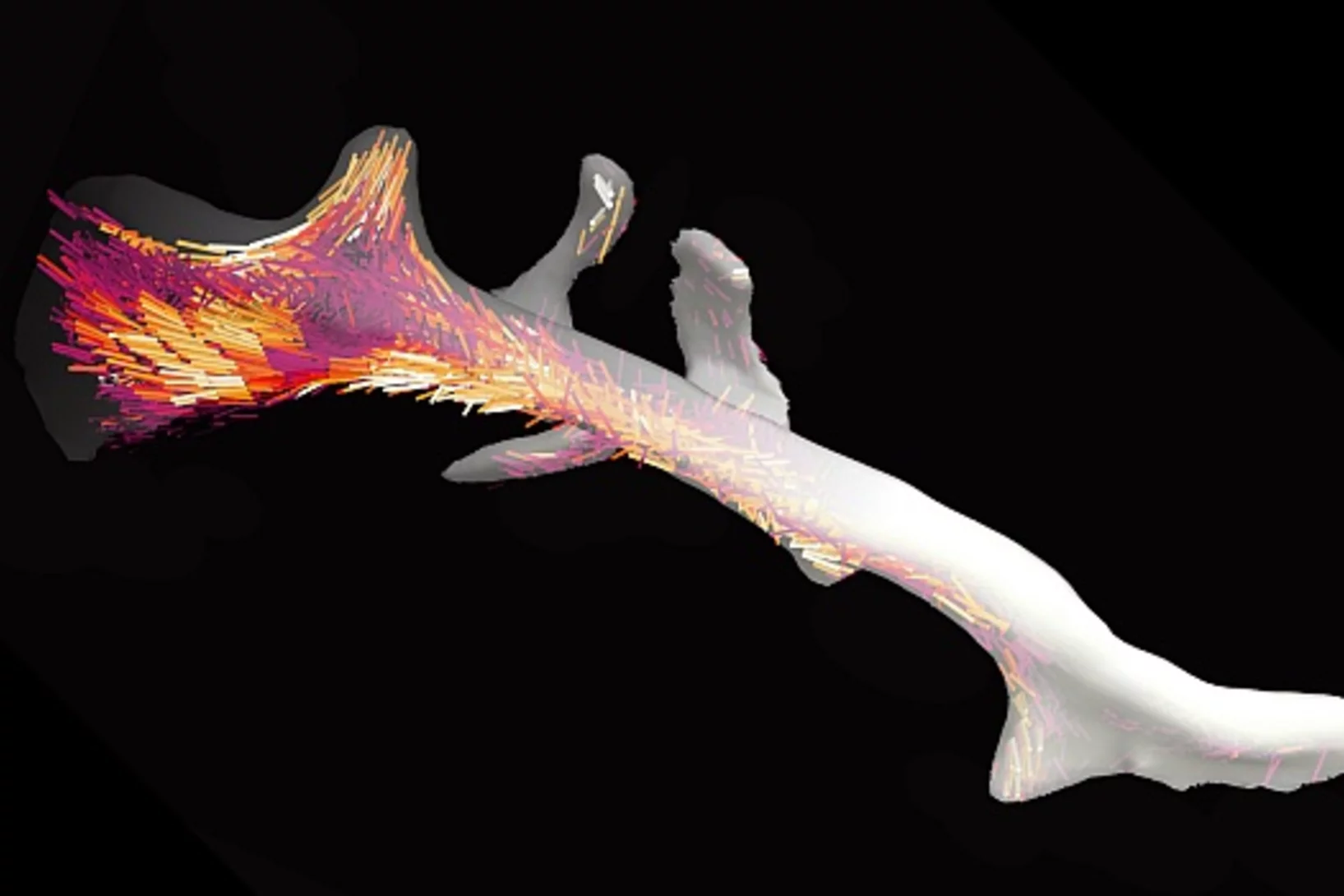
3-D-Nanostruktur eines Knochens sichtbar gemacht
Knochen bestehen aus winzigen Fasern, die etwa tausend Mal feiner sind als ein menschliches Haar. Mit einer neuartigen computerbasierten Auswertungsmethode konnten Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI zum ersten Mal die Anordnung dieser Nanostrukturen innerhalb eines gesamten Knochenstücks sichtbar machen.
Nanostructure surveys of macroscopic specimens by small-angle scattering tensor tomography
The mechanical properties of many materials are based on the macroscopic arrangement and orientation of their nanostructure. This nanostructure can be ordered over a range of length scales. In biology, the principle of hierarchical ordering is often used to maximize functionality, such as strength and robustness of the material, while minimizing weight and energy cost.
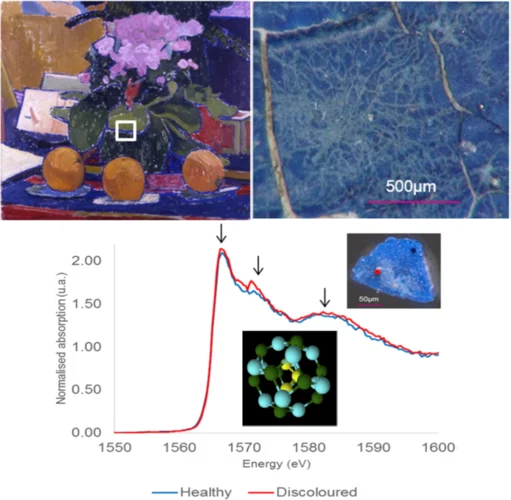
Aluminium X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy analysis of discoloured ultramarine blue in 20th century oil paintings
A specific case of synthetic ultramarine degradation was observed in three oil paintings from the early 20th century. Pigment particleswere found to have been discoloured, resulting in intricate patterns ofwhite lines, approximately 10 to 30 microns wide, criss-crossing the paint surface. Colour in ultramarine pigments comes from the encapsulated sulphur radical anions, chromophores, inside the cage framework built from SiO4 4 − and AlO4 5 −
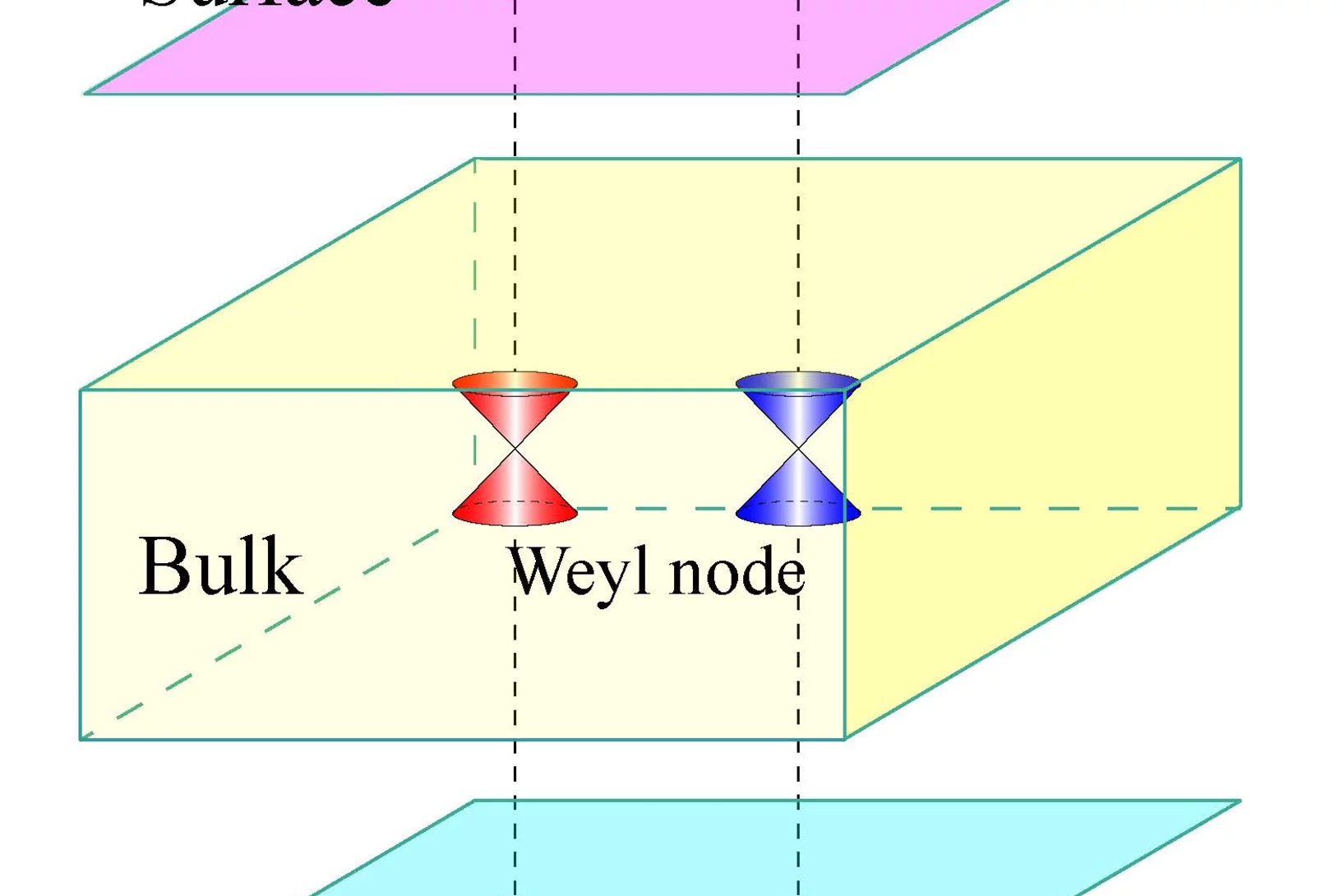
Observation of Fermi-Arc Spin Texture in TaAs
The study of nontrivial topological semimetals (TSM) is an emerging subject, providing a new frontier in topological aspects beyond insulators. Here, we have investigated the spin texture of surface Fermi arcs in the recently discovered Weyl semimetal TaAs using spin- and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. The experimental results demonstrate that the Fermi arcs are spin polarized. The measured spin texture fulfills the requirement of mirror and time-reversal symmetries and is well reproduced by our first-principles calculations, which gives strong evidence for the topologically nontrivial Weyl semimetal state in TaAs. The consistency between the experimental and calculated results further confirms the distribution of chirality of the Weyl nodes determined by first principles calculations.
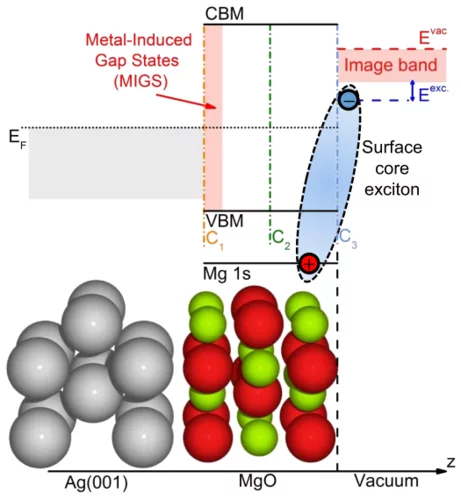
Excited states at interfaces of a metal-supported ultrathin oxide film
At the PEARL beamline, metal-supported ultrathin oxide films have been studied which are a class of materials of technological importance in various research fields such as catalysis, spintronics, or nanoelectronics.
Nationaler Zukunftstag 2015
Am Nationalen Zukunftstag 2015 durften wir 55 Mädchen und 56 Jungs am PSI begrüssen. Die 111 Kinder konnten aus den angebotenen 11 Stationen (Berech¬nungs-ingenieur, Chemieingenieure, Chemielaboranten, Elektroniker, Fachfrauen Betreuung, Metallographen, Physiker, Physiklaboranten, Strukturbiologen, Techn. Laborassistenten und iLab), jeweils zwei auswählen und diese beiden an einem halben Tag besichtigen.
Cousin des Elektrons nach 86 Jahren gefunden
Physiker des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI gemeinsam mit Kollegen aus China sowie von der ETH Zürich und der ETH Lausanne EPFL haben bei Versuchen an der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS ein Teilchen nachgewiesen, dessen Existenz bereits vor 86 Jahren vorausgesagt worden war. Es handelt sich um ein Mitglied der Teilchenfamilie, zu denen auch das Elektron, der Träger elektrischer Ströme, gehört. Anders als das Elektron hat das neue Teilchen aber keine Masse und es kommt nur in einer bestimmten Klasse von Materialien vor, die als Weyl-Halbmetalle bezeichnet werden.
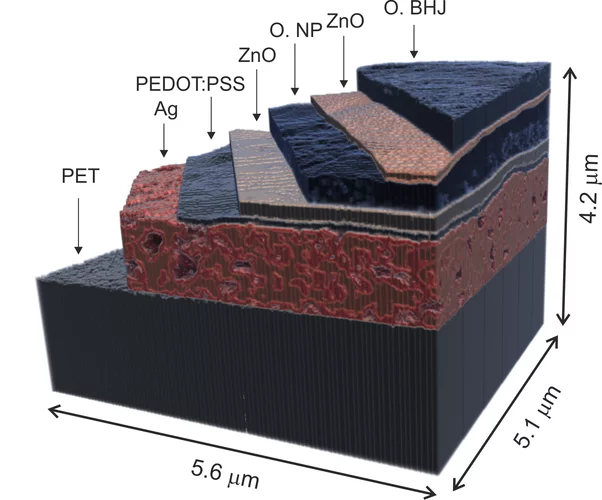
X-ray nanotomography aids the production of eco-friendly solar cells
Polymer solar cells are in the spotlight for sustainable energy production of the future. Characterization of these devices by X-ray nanotomography helps to improve their production using environmentally friendly materials.
Controlling tunnelling in methane loss from acetone ions by deuteration
At the imaging Photoelectron Photoion Coincidence (iPEPICO) endstation of the VUV beamline evidence of H-atom tunneling was shown.
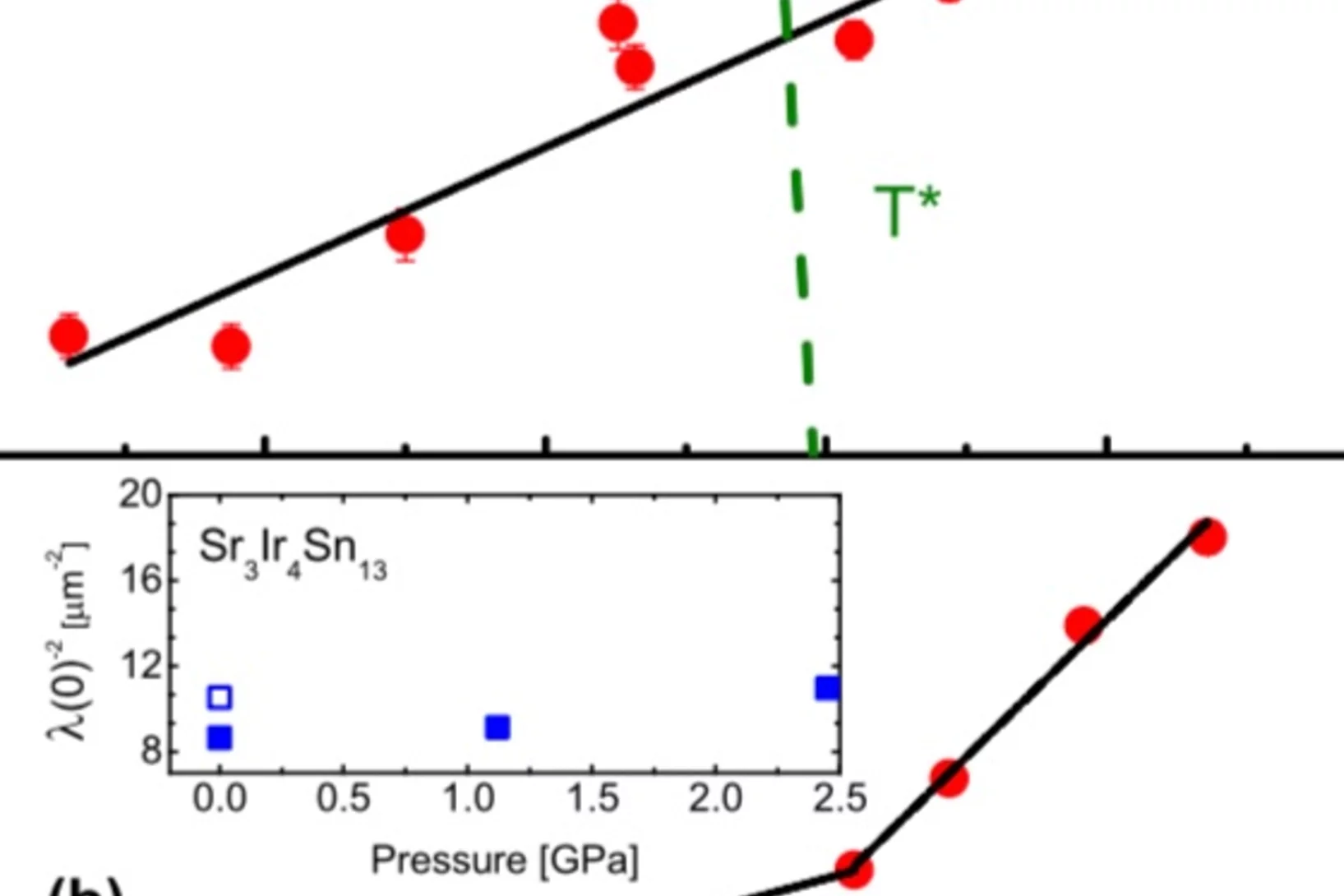
Strong enhancement of s-wave superconductivity near a quantum critical point of Ca3Ir4Sn13
We report microscopic studies by muon spin rotation/relaxation as a function of pressure of the Ca3Ir4Sn13 and Sr3Ir4Sn13 cubic compounds, which are members of the (Ca1−xSrx)3Ir4Sn13 system displaying superconductivity and a structural phase transition associated with the formation of a charge density wave (CDW).
Direct evidence for a pressure-induced nodal superconducting gap in the Ba0.65Rb0.35Fe2As2 superconductor
The superconducting gap structure in iron-based high-temperature superconductors (Fe-HTSs) is non-universal. In contrast to other unconventional superconductors, in the Fe-HTSs both d-wave and extended s-wave pairing symmetries are close in energy. Probing the proximity between these very different superconducting states and identifying experi- mental parameters that can tune them is of central interest.
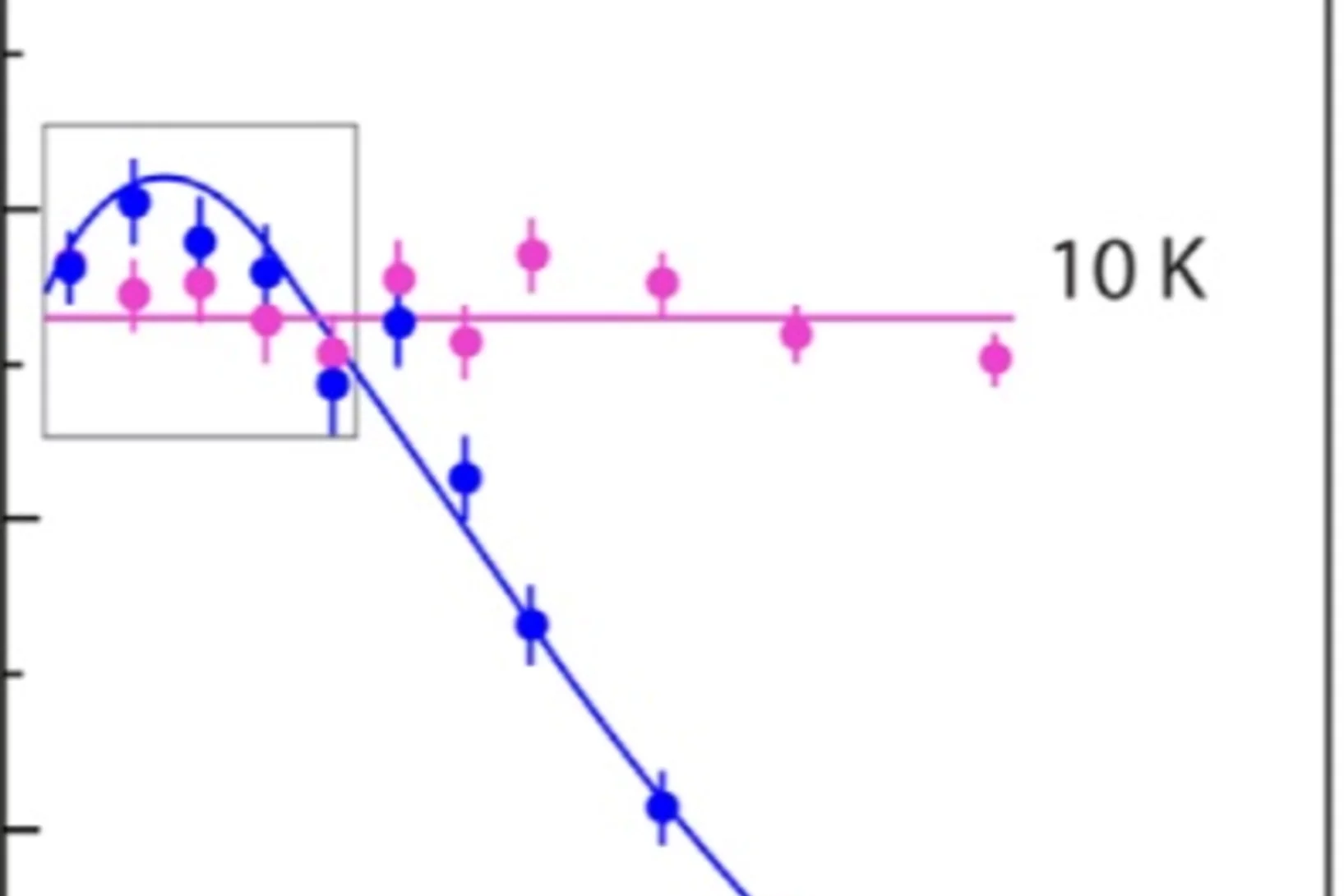
Intrinsic Paramagnetic Meissner Effect Due to s-Wave Odd-Frequency Superconductivity
In 1933, Meissner and Ochsenfeld reported the expulsion of magnetic flux - the diamagnetic Meissner effect - from the interior of superconducting lead. This discovery was crucial in formulating the Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) theory of superconductivity. In exotic superconducting systems BCS theory does not strictly apply.
Struktur der Betonkrankheit
entschlüsselt
Wenn Brücken, Staumauern und andere Bauwerke aus Beton nach einigen Jahrzehnten von dunklen Rissen durchzogen sind, dann ist die sogenannte Betonkrankheit die Ursache. Wie das Material, das in diesen Rissen entsteht, auf der Ebene einzelner Atome aufgebaut ist, haben jetzt Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI und der Empa entschlüsselt - und dabei eine bislang unbekannte kristalline Anordnung der Atome entdeckt.
New EU project: Guiding light for the world's brightest light sources
EUCALL will build bridges between major laser and X-ray research centres: For the past half-century, two special kinds of light have changed the landscape of research. Advanced visible-spectrum optical lasers have propelled studies into ultrafast processes, new materials, telecommunications, and many other fields, while intense X-rays produced at synchrotrons have helped image tiny structures and otherwise invisible parts of matter, enabling huge leaps in biochemistry, pharmacology, and materials science. New developments have enhanced the generation of X-rays at optical-laser and accelerator facilities, resulting in the creation of large international research centres. The European Union is now funding a 7 million-euro effort to bring these research centres together through the European Cluster of Advanced Laser Light Sources (EUCALL) project.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
Visualizing the morphology of vortex lattice domains in a bulk type-II superconductor
Alike materials in the solid state, the phase diagram of type-II superconductors exhibit crystalline, amorphous, liquid and spatially inhomogeneous phases. The multitude of different phases of vortex matter has thence proven to act as almost ideal model system for the study of both the underlying properties of superconductivity but also of general phenomena such as domain nucleation and morphology.
Röntgenforschung im Ufo
Die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS fällt zuerst durch ihr markantes Gebäude auf. Innen beeindruckt sie mit Spitzenforschung. Ein Streifzug durch die Welt, in der Elektronen Slalomkurse einlegen und Röntgenstrahlen Proteine entschlüsseln.
Put in perspective
Researchers from the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded in using commercially available camera technology to visualise terahertz light. In doing so, they are enabling a low-cost alternative to the procedure available to date, whilst simultaneously increasing the comparative image resolution by a factor of 25. The special properties of terahertz light make it potentially advantageous for many applications, from safety technology to medical diagnostics.