Am PSI widmen sich mehrere Projekte wichtigen Forschungsfragen rund um das Coronavirus Sars-CoV-2 und den daraus resultierenden Erkrankungen. Wir informieren über Aktivitäten und Vorhaben, zum Beispiel zu Untersuchungen von Lungengewebe, zur Produktion von Proteinen und Antikörpern oder über Ideen für neue Forschung zu Covid-19.
Nützliche Links
Neue Betriebsbewilligung
Am 21. Februar 2019 erteilte das Eidgenössische Departement für Umwelt, Verkehr, Energie und Kommunikation (UVEK) die neue Betriebsbewilligung für die Anlage PSI Hotlabor
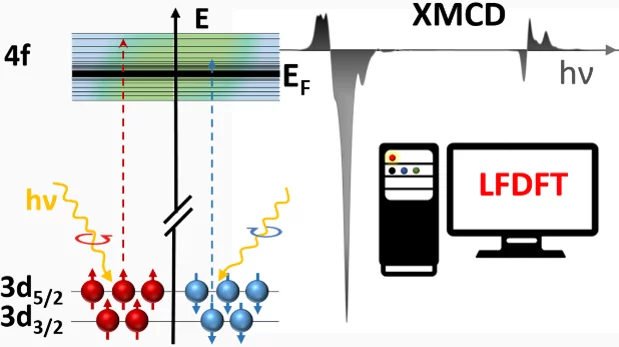
New Method for Calculating Soft X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism Spectra
Scientists have demonstrated in a combined theoretical and experimental effort that the new ligand-field density functional theory method (LF-DFT) can be used to calculate the X-ray absorption spectra (XAS) and X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) of lanthanide compounds from purely structural input.
Horizon 2020 project SAMOSAFER granted
The EU Horizon 2020 program granted 3.5 million Euros to the research and innovation project SAMOSAFER, where PSI is one of the 14 project partners. The total budget of the project, inclusive own and in-kind contributions, is 4.5 million Euros. The aim of SAMOSAFER project is to develop and demonstrate new safety barriers and a more controlled behaviour in severe accidents of the Molten Salt Reactor (MSR). Three groups at PSI will be involved in the project: the LSM groups for Advanced Nuclear Systems (ANS) and Multiscale Materials Modelling (MMM) and the Severe Accidents Research group (Sacre) of LRT, focusing on redistribution of the source term in the fuel treatment unit of MSR and assessment and reduction of radionuclide mobility during accidental conditions.
Negative flat band magnetism in a spin–orbit-coupled correlated kagome magnet
Electronic systems with flat bands are predicted to be a fertile ground for hosting emergent phenomena including unconven- tional magnetism and superconductivity, but materials that manifest this feature are rare. Here, we use scanning tunnelling microscopy to elucidate the atomically resolved electronic states and their magnetic response in the kagome magnet Co3Sn2S2.
How the methyl group position influences the ultrafast deactivation in aromatic radicals
The resonantly stabilized xylyl radicals (C8H9•) distinctively influence the combustion chemistry and, therefore, ultimately determine the performance of combustion engines. At that, the three different isomers (methyl group in ortho, para or meta position) exhibit notable differences at elevated temperatures. We have tracked down these dynamics on a femtosecond timescale by monitoring the response to preparation of a well-defined electronic and vibrational state.
Elektronen zuschauen und Bits anknipsen
Kleiner, schneller und vor allem energieeffizienter soll die Elektronik werden. Auch in mehreren Forschungsgruppen am PSI sind diese Themen präsent. Von schrittweisen Verbesserungen bis zum kompletten Umdenken – wer tüftelt derzeit woran?
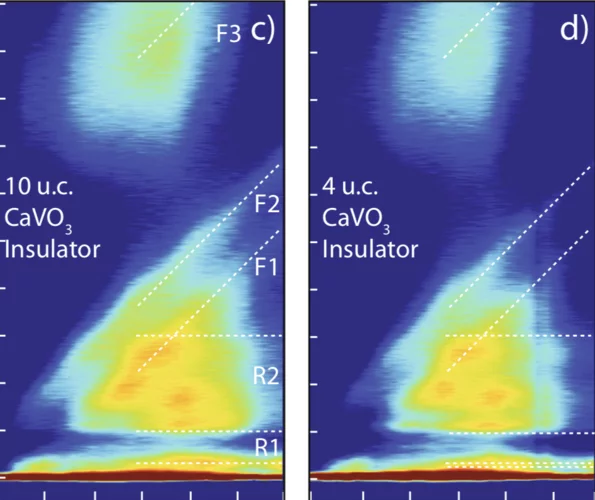
Electronic localization in CaVO3 films via bandwidth control
Understanding and controlling the electronic structure of thin layers of quantum materials is a crucial first step towards designing heterostructures where new phases and phenomena, including the metal-insulator transition (MIT), emerge. Here, we demonstrate control of the MIT via tuning electronic bandwidth and local site environment through selection of the number of atomic layers deposited.
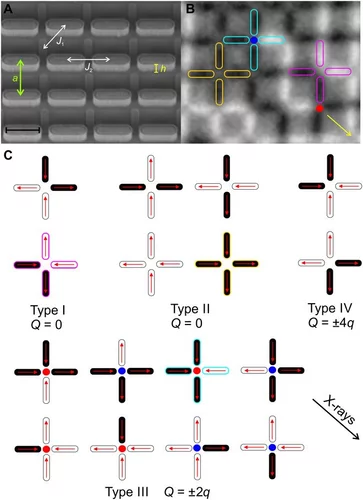
Emergent magnetic monopole dynamics in macroscopically degenerate artificial spin ice
Magnetic monopoles, proposed as elementary particles that act as isolated magnetic south and north poles, have long attracted research interest as magnetic analogs to electric charge. In solid-state physics, a classical analog to these elusive particles has emerged as topological excitations within pyrochlore spin ice systems. We present the first real-time imaging of emergent magnetic monopole motion in a macroscopically degenerate artificial spin ice system consisting of thermally activated Ising-type nanomagnets lithographically arranged onto a pre-etched silicon substrate. factors are observed.
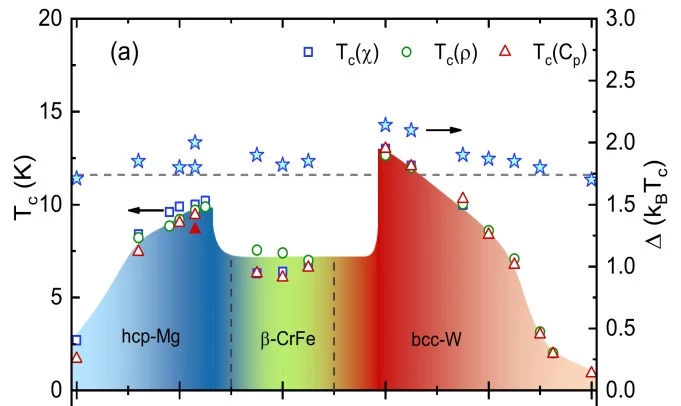
Structure and superconductivity in the binary Re1-xMox alloys
The binary Re1−xMox alloys, known to cover the full range of solid solutions, were successfully synthesized and their crystal structures and physical properties investigated via powder x-ray diffraction, electrical resistivity, magnetic susceptibility, and heat capacity. By varying the Re/Mo ratio, we explore the full Re1−xMox binary phase diagram, in all its four different solid phases: hcp-Mg (P63/mmc), α-Mn (I43m), β-CrFe (P42/mnm), and bcc-W (Im3m), of which the second is non-centrosymmetric with the rest being centrosymmetric. All Re1−xMox alloys are superconductors, whose critical temperatures exhibit a peculiar phase diagram, characterized by three different superconducting regions.
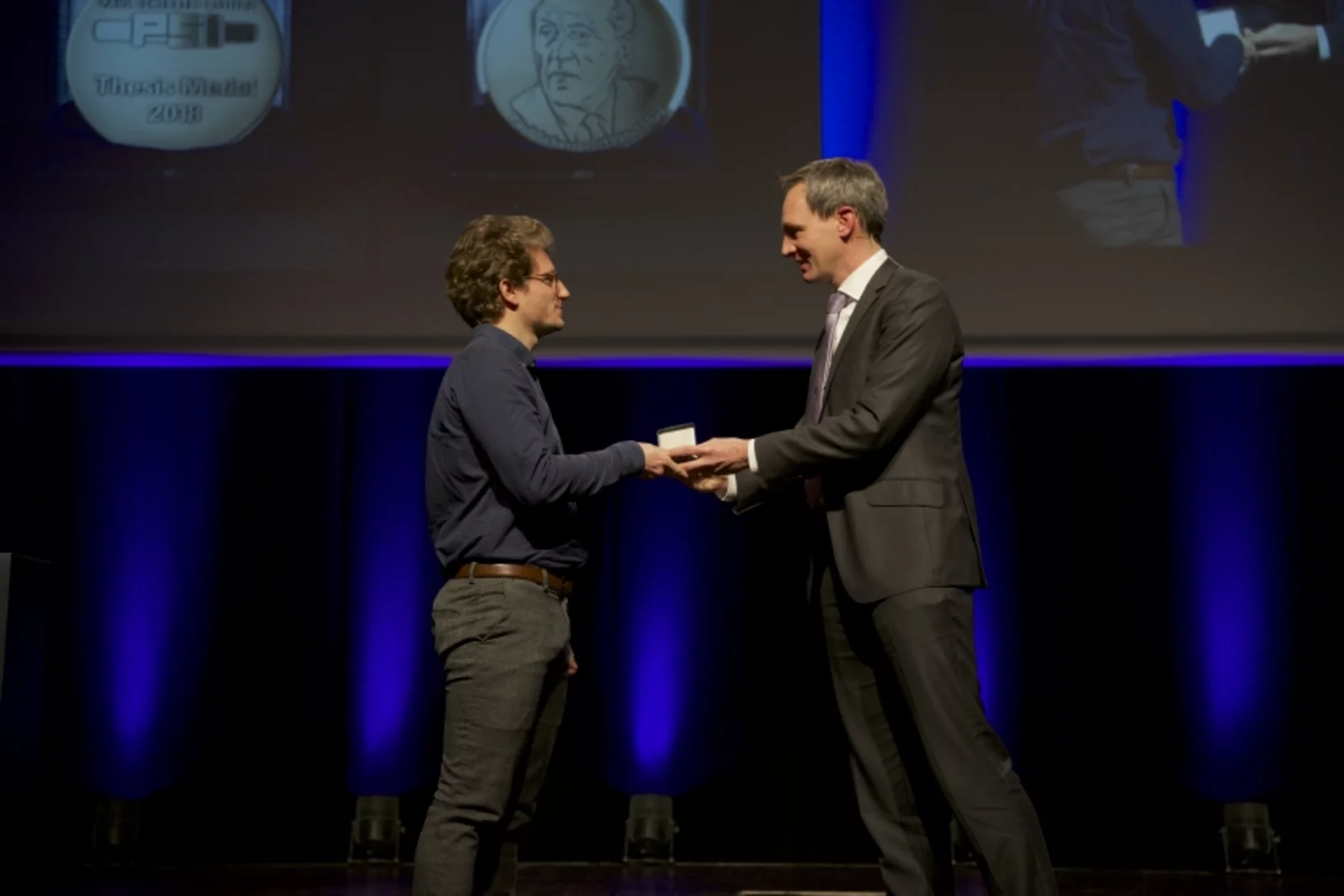
PSI Thesis Medal goes to Dr. Matias Kagias
The PSI Thesis Medal is awarded every second year to the best PhD thesis performed at the Paul Scherrer Institut. Matias received the prize for his excellent thesis entitled "Direct Self-Imaging Methods for X-ray Differential Phase and Scattering Imaging". Congratulations!
Wege der beruflichen Integration
In der Berufsschule Scala werden Lernende, die eine IV-unterstützte Berufsausbildung auf Stufe eidg. Berufsattest oder eidg. Fähigkeitszeugnis absolvieren, gezielt gefördert. Sehen Sie, wie die Vorbereitungs- und Förderkurse auch unserem Lernenden, Sacha R., beim Erreichen seiner Ziele geholfen haben.
Virtuelle Linse verbessert Röntgenmikroskopie
Eine von PSI-Forschenden neu entwickelte Methode macht Röntgenbilder von Materialien noch besser. Die Forschenden bewegten dafür eine optische Linse und nahmen dabei Einzelbilder auf. Mit Hilfe von Computeralgorithmen errechneten sie daraus ein Gesamtbild.
Congratulations to Sven Avak
On 31 January 2019 Sven successfully defended his PhD entitled “Impact and Implications of Melting on the Preservation of Trace Elements in High-Alpine Snow and Glacier Ice" at the University of Bern. Congratulations! This thesis formed part of the collaborative project Microscale Distribution of Impurities in Snow and Glacier Ice (MiSo) in co-operation with LUC's Surface Chemistry research group and the WSL-SLF Davos. The project was funded by the Swiss National Science Foundation.
«Jetzt ist es Zeit für etwas Neues»
Macht man elektronische Bauteile kleiner, werden sie leider heisser. Auch ist bald die Grenze der technisch machbaren Verkleinerung erreicht. Am PSI arbeiten Gabriel Aeppli und Christian Rüegg an grundlegend neuen, physikalischen Lösungen für bessere Rechner und Datenspeicher.
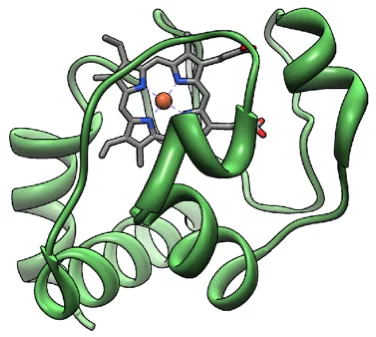
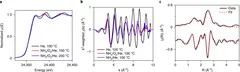
User operation at SwissFEL has begun
The first user experiment has taken place the the SwissFEL X-ray free electron laser, officially inaugurating it as the newest user facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute. The experiment, led by Camila Bacellar from EPFL, investigated ultrafast electron transfer dynamics in a protein to try to identify the charge density re-localization after the protein absorbs a photon of UV light. The experiment was performed using the Alvra Prime experimental station, taking advantage of the integrated von Hamos X-ray emission spectrometer to perform both X-ray absorption and emission measurements on the Fe atom, which is located at the centre of the protein.
Structural selectivity of supported Pd nanoparticles for catalytic NH3 oxidation resolved using combined operando spectroscopy
The link between Pd nanoparticle structure and surface reactivity for NH3 abatement was found using operando X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy, diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier-transformed spectroscopy and on-line mass spectrometry.
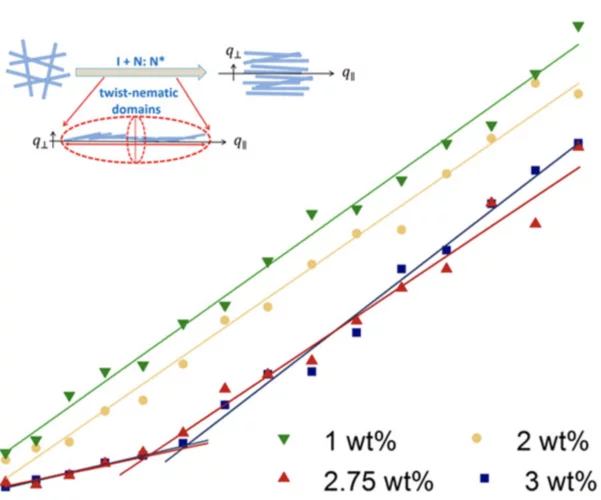
Anisotropic Diffusion and Phase Behavior of Cellulose Nanocrystal Suspensions
In this paper, we use dynamic light scattering in polarized and depolarized modes to determine the translational and rotational diffusion coefficients of concentrated rodlike cellulose nanocrystals in aqueous suspension. Within the range of studied concentrations (1–5 wt %), the suspension starts a phase transition from an isotropic to an anisotropic state as shown by polarized light microscopy and viscosity measurements.
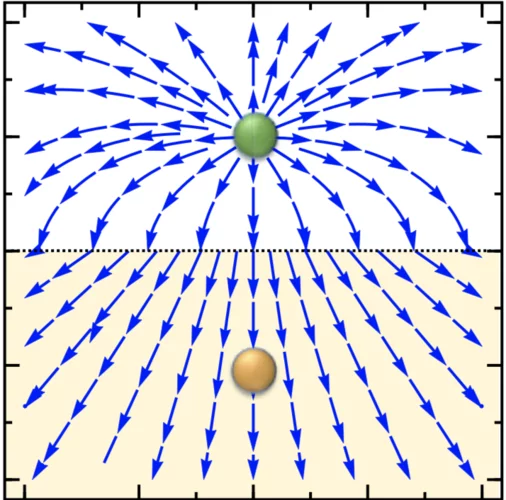
Search for the Magnetic Monopole at a Magnetoelectric Surface
We show, by solving Maxwell’s equations, that an electric charge on the surface of a slab of a linear magnetoelectric material generates an image magnetic monopole below the surface provided that the magnetoelectric has a diagonal component in its magnetoelectric response. The image monopole, in turn, generates an ideal monopolar magnetic field outside of the slab.
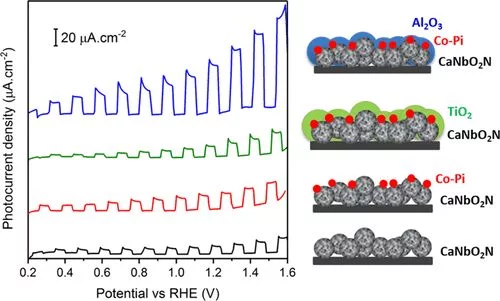
Improved Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting of CaNbO2N Photoanodes by CoPi Photodeposition and Surface Passivation
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) solar water splitting is a promising approach to convert solar energy into sustainable hydrogen fuel using semiconductor electrodes. Owing to their visible light absorption properties, oxynitrides have shown to be attractive photocatalysts for this application. In this study, the influence of the preparation method of CaNbO2N particles on their morphological and optical properties, and thereby their PEC performance, is investigated. The best performing CaNbO2N photoanode is produced by ammonolysis of Nb-enriched calcium niobium oxide.
Lehrvertragsunterzeichnung 2019
Am Mittwoch den 16. Januar durften wir während der Lehrvertragsunterzeichnung alle angehenden Lernenden, für das Jahr 2019, begrüssen. Die Schülerinnen und Schüler haben gemeinsam mit ihren Eltern die Lehr- und Praktikumsverträge unterschrieben. Nun sind sie ihrem Lehrbeginn, der am 5. August ist, bereits einen Schritt näher.
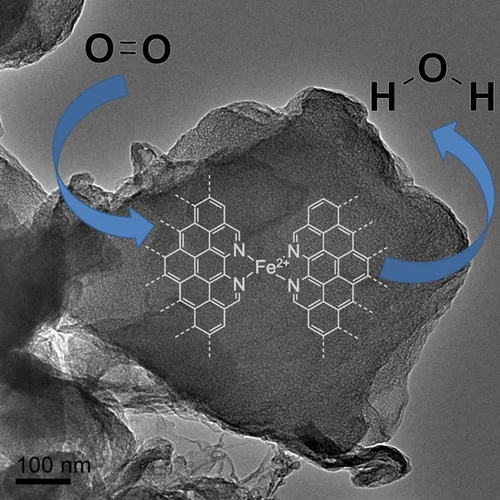
Fe-Based O2-Reduction Catalysts Synthesized Using Na2CO3 as a Pore-Inducing Agent
This work presents a new approach for synthesizing Fe-based oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts using sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) as an inexpensive but effective pore-inducing agent offering microporosity control.
15th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation
The 15th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation and Resonance (µSR2020) will be held in Parma, Italy, from 6-10th July, 2020.
The conference is organized by the University of Parma in conjunction with eth ISIS Muon and Neutron Source.
Vermessung von fünf Weltraum-Blitzen
Ein am PSI entwickelter Detektor namens POLAR hat von einer Weltraumstation aus Daten sogenannter Gammablitze gesammelt. Dies hilft nun, diese extrem energiereichen Lichtblitze besser zu verstehen.
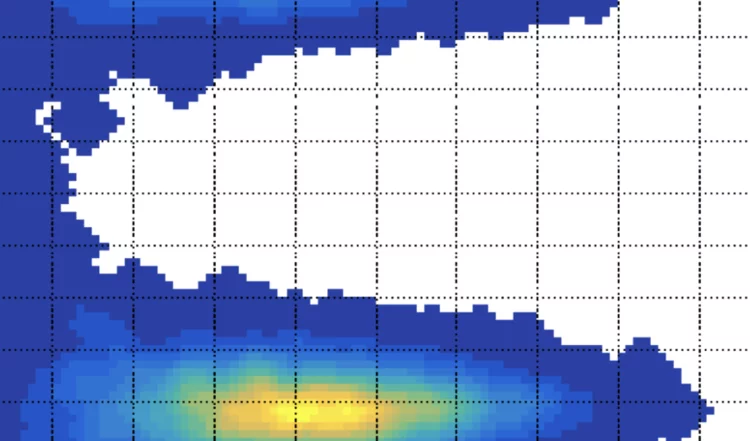
Detailed polarization measurements of the prompt emission of five gamma-ray bursts
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are the strongest explosions in the Universe since the Big Bang. They are believed to be produced either in the formation of black holes at the end of massive star evolution or the merging of compact objects.
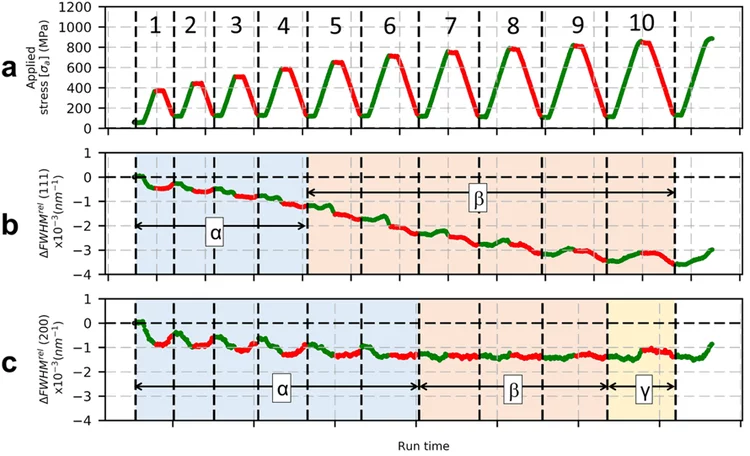
Revealing the role of microstructure architecture on strength and ductility of Ni microwires by in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction
The effect of diameter reduction on the mechanical properties of cold-drawn nickel microwires has been analyzed by a combination of in situ X-ray diffraction and electron backscatter diffraction observations.
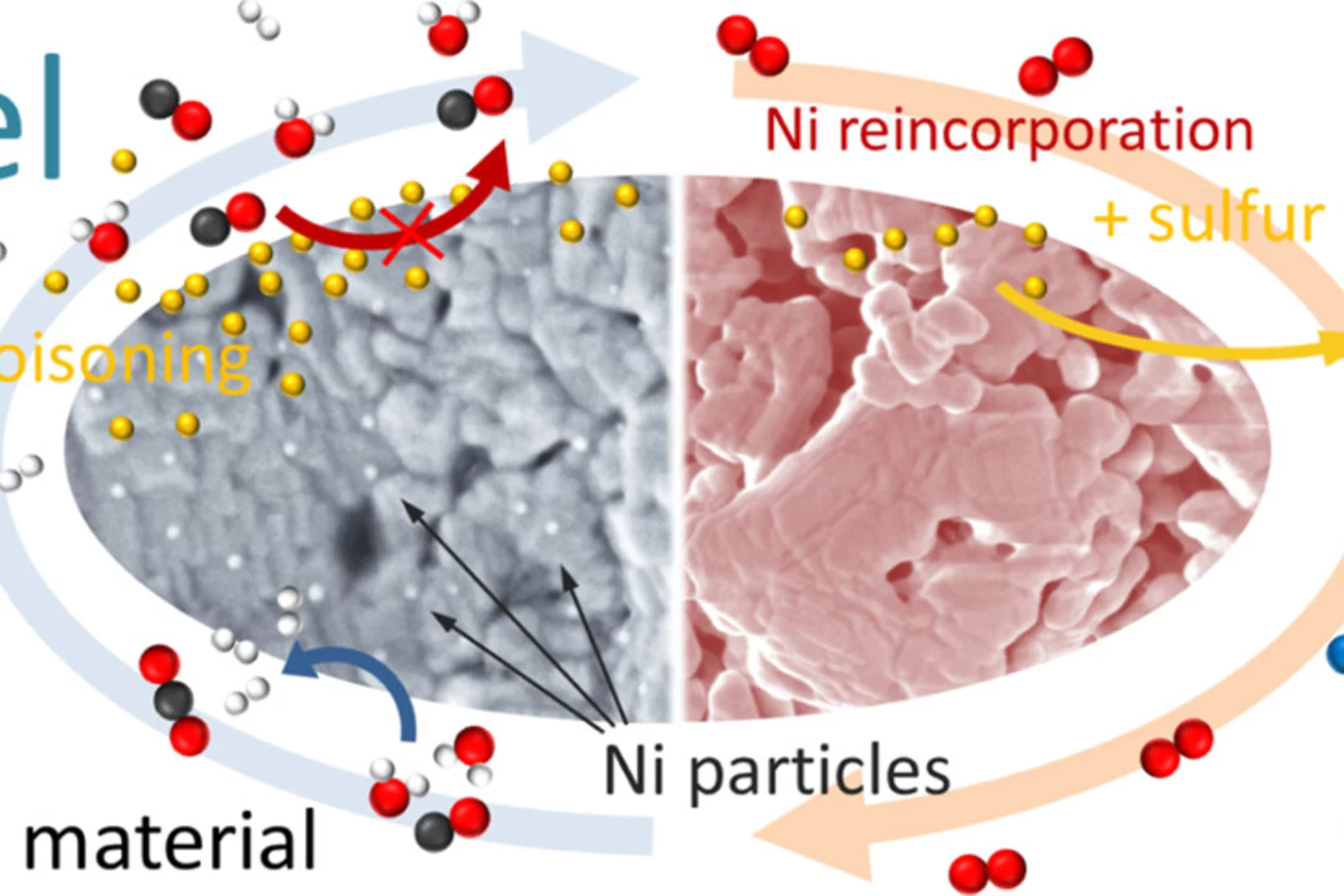
Sulfur poisoning recovery on a SOFC anode material through reversible segregation of Nickel
Exploitation of the self-regenerative property of perovskite-type oxides allowed to demonstrate recovery of La0.3Sr0.55Ti0.95Ni0.05O3 from sulfur poisoning by reversible segregation-incorporation of Ni at SOFC temperatures.
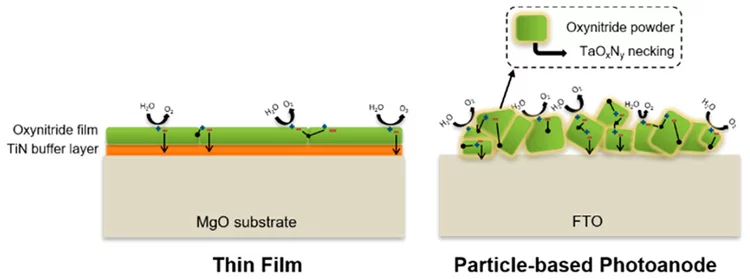
Oxynitride Thin Films versus Particle-Based Photoanodes: A Comparative Study for Photoelectrochemical Solar Water Splitting
The solar water splitting process assisted by semiconductor photocatalysts attracts growing research interests worldwide for the production of hydrogen as a clean and sustainable energy carrier. Because of their optical and electrical properties, several oxynitride materials show great promise for the fabrication of efficient photocatalysts for solar water splitting. This study reports a comparative investigation of particle- and thin-film-based photocatalysts using three different oxynitride materials.
Dr Yasin Ekinci elected as Fellow of SPIE
Dr. Yasin Ekinci, Head of the Advanced Lithography and Metrology Group and ad interim Head of the Laboratory for Micro and Nanotechnology, has been elected to the grade of Fellow of The International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE).
Dr Mirjam van Daalen appointed as Swiss ESFRI delegate
Dr. Mirjam van Daalen Chief of staff of the Photon Science Division, was mandated on the 1st of January 2019, by the State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation SERI as a member of the Swiss Delegation to the European Science Forum on Research Infrastructures ESFRI https://www.esfri.eu/.
SESAME beamline for tomography project (BEATS) is launched
On 1st January 2019, the European Horizon 2020 project BEAmline for Tomography at SESAME (BEATS) was launched with the objective to design, procure, construct and commission a beamline for hard X-ray full-field tomography at the SESAME synchrotron in Jordan. The European grant is worth 6 million euros and will span a four-year period from beginning 2019 to end 2022.