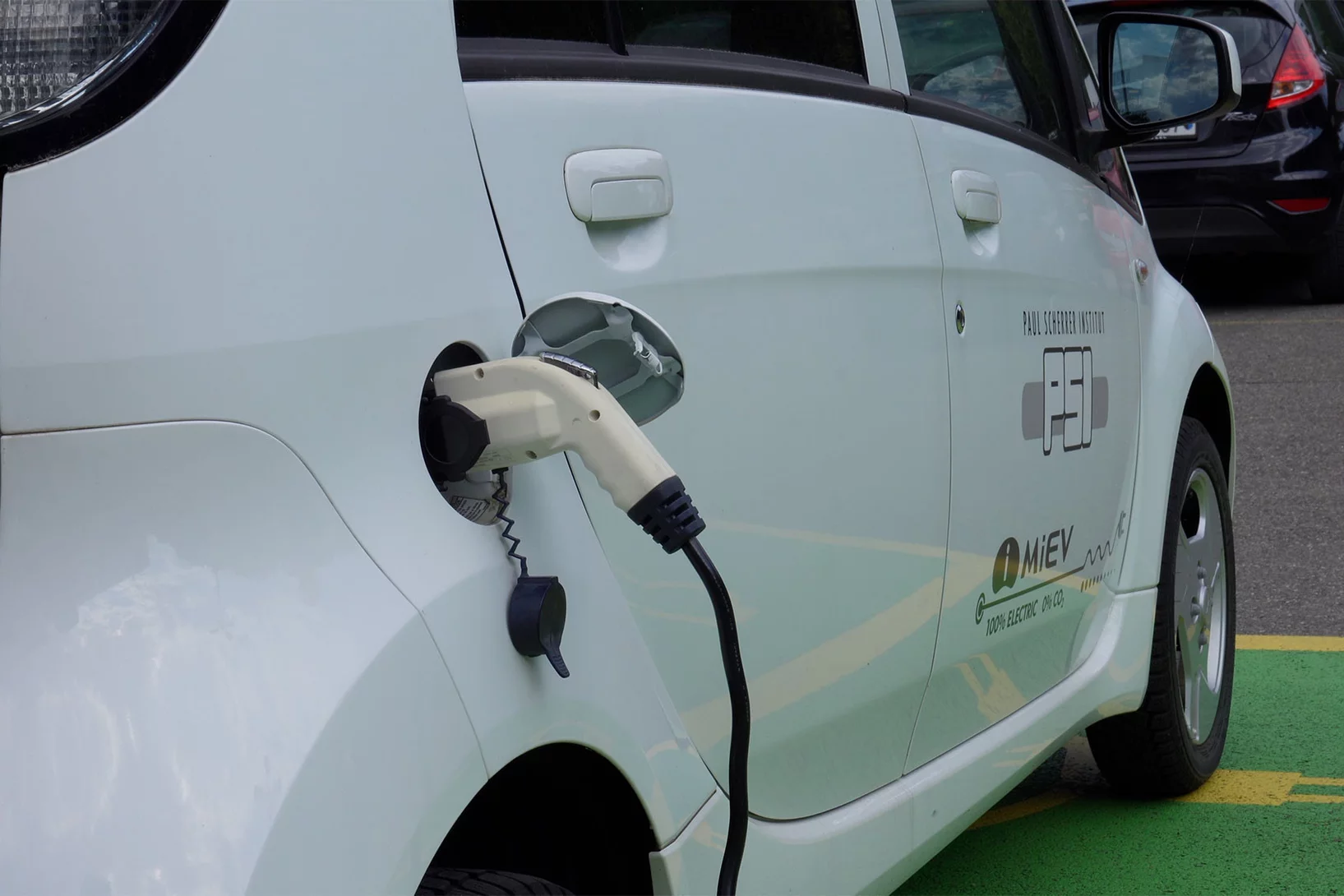
Wie lässt sich Kobalt in E-Auto-Batterien reduzieren?
Die Elektrifizierung des Verkehrs nimmt zu. Dafür braucht es mehr Batterien. Einige dieser Batterien enthalten jedoch einen äusserst problematischen Rohstoff: Kobalt. Das PSI forscht an Alternativen.
Wie kommt es, dass du deine Professur aufgegeben hast?
Diese Frage landete vor ein paar Tagen in meiner LinkedIn inbox. Völlig unerwartet kam sie von einer Person, mit der ich vor 10 Jahren zusammengearbeitet, und danach keinen Kontakt mehr gehabt hatte. Offensichtlich hat mein Entscheid, mich aus der akademischen Forschung zu verabschieden, Spuren hinterlassen. Aber was genau waren denn jetzt die Gründe?
Welcome to LXN Gabriel Weber
Herzlich Willkommen Gabriel Weberin LXN!
Eine bereichernde Partnerschaft für Forschung und Praxis
Die Forschungsinstitute des ETH-Bereichs verstärken ihre Kooperation in strategischen Bereichen.
Thank You SLS
Our beamline scientists look back on 22 years of brilliant science made possible by the Swiss Light Source SLS.
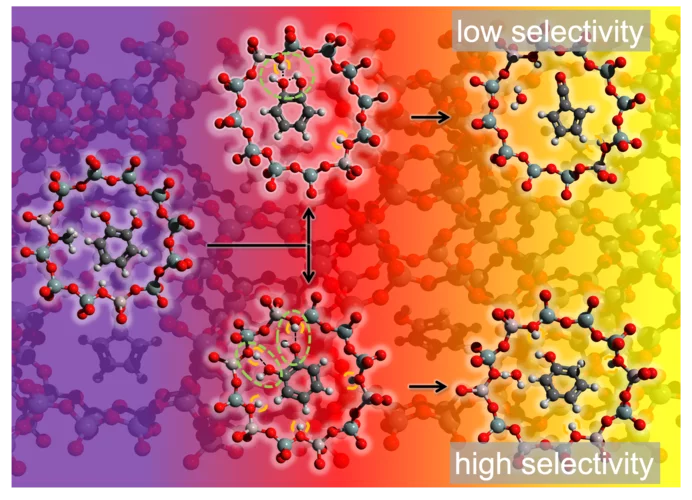
Unveiling the reaction mechanism shines light on the selectivity increase in catalytic processes
Increasing the selectivity of a chemical process through rational catalyst design is the Holy Grail of heterogeneous catalysis. Researchers at PSI and ETH Zürich showcase how revealing hidden steps in reaction pathways can steer processes towards preferred products, as demonstrated in a study focused on biomass valorization.
Welcome to LXN Céline Hensky
Herzlich Willkommen Céline Hensky in LXN!
Lehrabschlussfeier 2023
Am Freitag, 18. August durften wir stolz und mit viel Freude 29 neue Berufsleute feiern. Sie schlossen ihrer Berufslehre mit einem tollen Noten-Durchschnitt von 5.1 ab. Im Kreise ihrer Eltern, den Berufsbildnerinnen und Berufsbildnern, den Fachbetreuerinnen und Fachbetreuer erlebten wir einen feierlichen, schönen und unterhaltsamen Abend.
Revolutionizing Renewable Processes: Ambizione Grant Winner Emanuele Moioli
Emanuele Moioli is one of the recipients of the prestigious Ambizione Grant awarded by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) on a yearly basis. With the great news of his award having arrived in August 2022, Moioli embarks on the journey of his groundbreaking project titled “Moving catalyst vs. Multi-catalyst: determination of the best reactor for the processing of unconventional feedstock,” set to commence this August 2023.
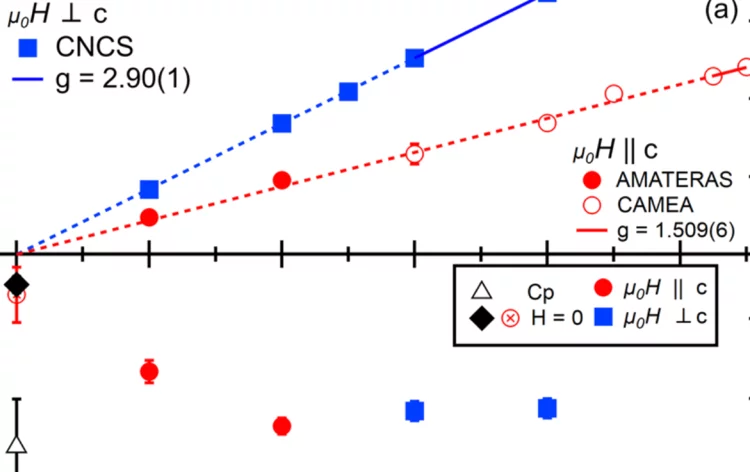
Field-tuned quantum renormalization of spin dynamics in the honeycomb lattice Heisenberg antiferromagnet YbCl3
The basis for our understanding of quantum magnetism has been the study of elegantly simple model systems. However, even for the antiferromagnetic honeycomb lattice with isotropic spin interactions – one of the simplest model systems – a detailed understanding of quantum effects is still lacking. Here, using inelastic neutron scattering measurements of the honeycomb lattice material YbCl3, we elucidate how quantum effects renormalize ...
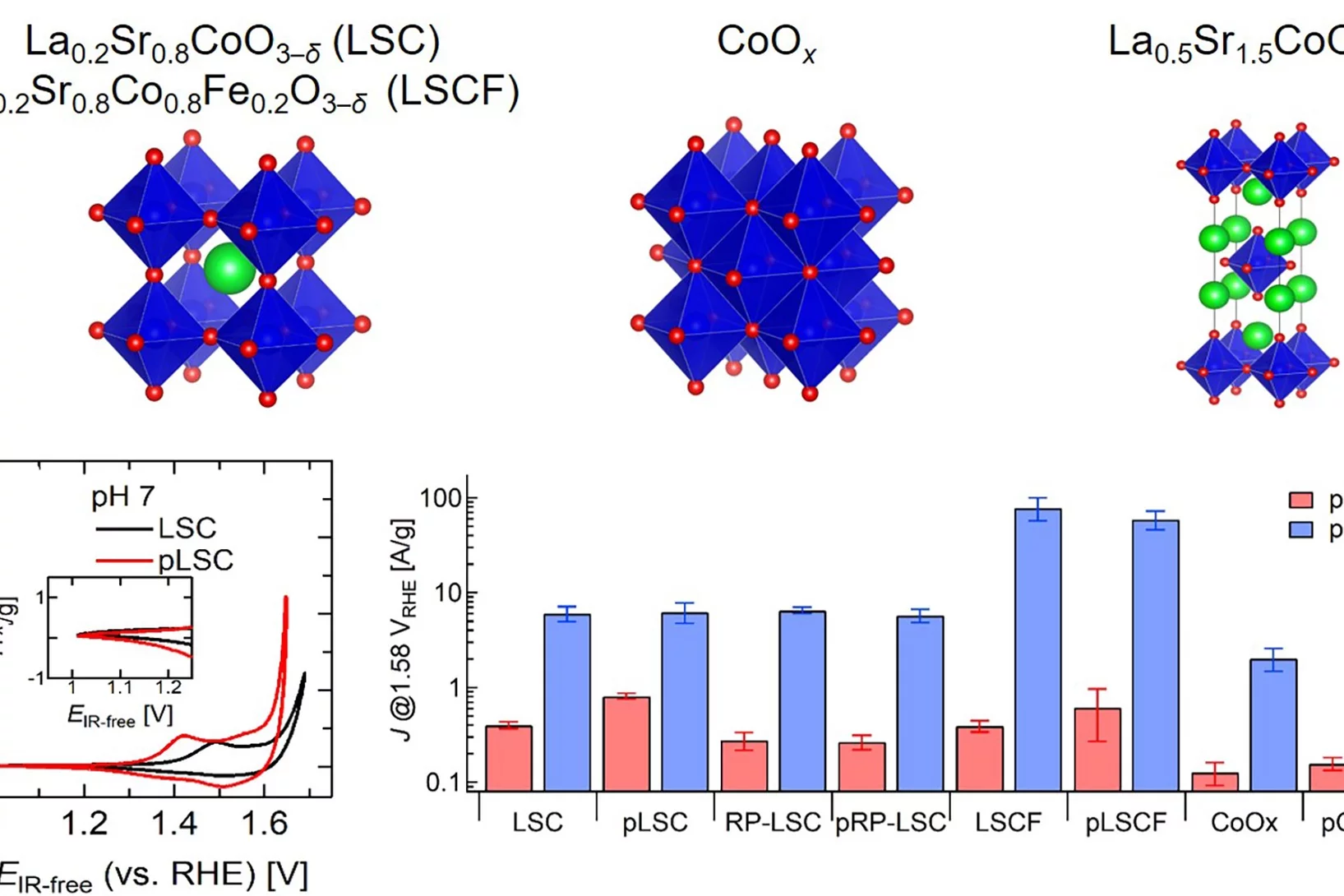
Improving the oxygen evolution reaction activity of Co-based oxides by phosphate functionalization
Our findings disclose that P-functionalization successfully enhances the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) activity of different cobalt-based catalysts (namely, La0.2Sr0.8CoO3–δ, La0.2Sr0.8Co0.8Fe0.2O3–δ, and CoOx) at near-neutral pHs and that both phosphate ion assistance in the OER mechanism and catalyst Co oxidation state can play a role in the enhanced OER activity.
Forensics: Quantitative tracing of Silicon in CRUD
Chalk River Unidentified Deposits (CRUD) are dissolved and suspended solids, product of the corrosion of structural elements in water circuits of nuclear reactors.
The chemical composition of CRUD is variable as it depends on the composition of the reactor’s structural material, as well as the types of refueling cycles. Recent internal investigations have found unexpected but significant Si-amount in CRUD. The chemical composition of CRUD holds key information for an improved understanding of CRUD formation and possible impact in fuel reliability and contamination prevention.
The standard analytical methods available in the hot laboratory did not allow an easy quantitative determination of the Si-amount in CRUD. A new innovative procedure has been developed and tested with synthetic CRUD name Syntcrud.
The adapted flex-fusion digestion method presented here is able to provide reliable concentrations of several elements within CRUD, including Si, which was not possible in methods used previously for ICPMS measurement.
Unveiling ultra-thin electron liquids in silicon
Soft X-rays enable scientists to visualise non-invasively the electronic properties of ultra-thin dopant layers buried within semiconductor wafers.
Swiss precision optics in Sweden
PSI has finalized the precision Selene neutron optics for the ESTIA instrument. The complex state-of-the-art guide was installed at the European Spallation Source as a Swiss in-kind delivery.
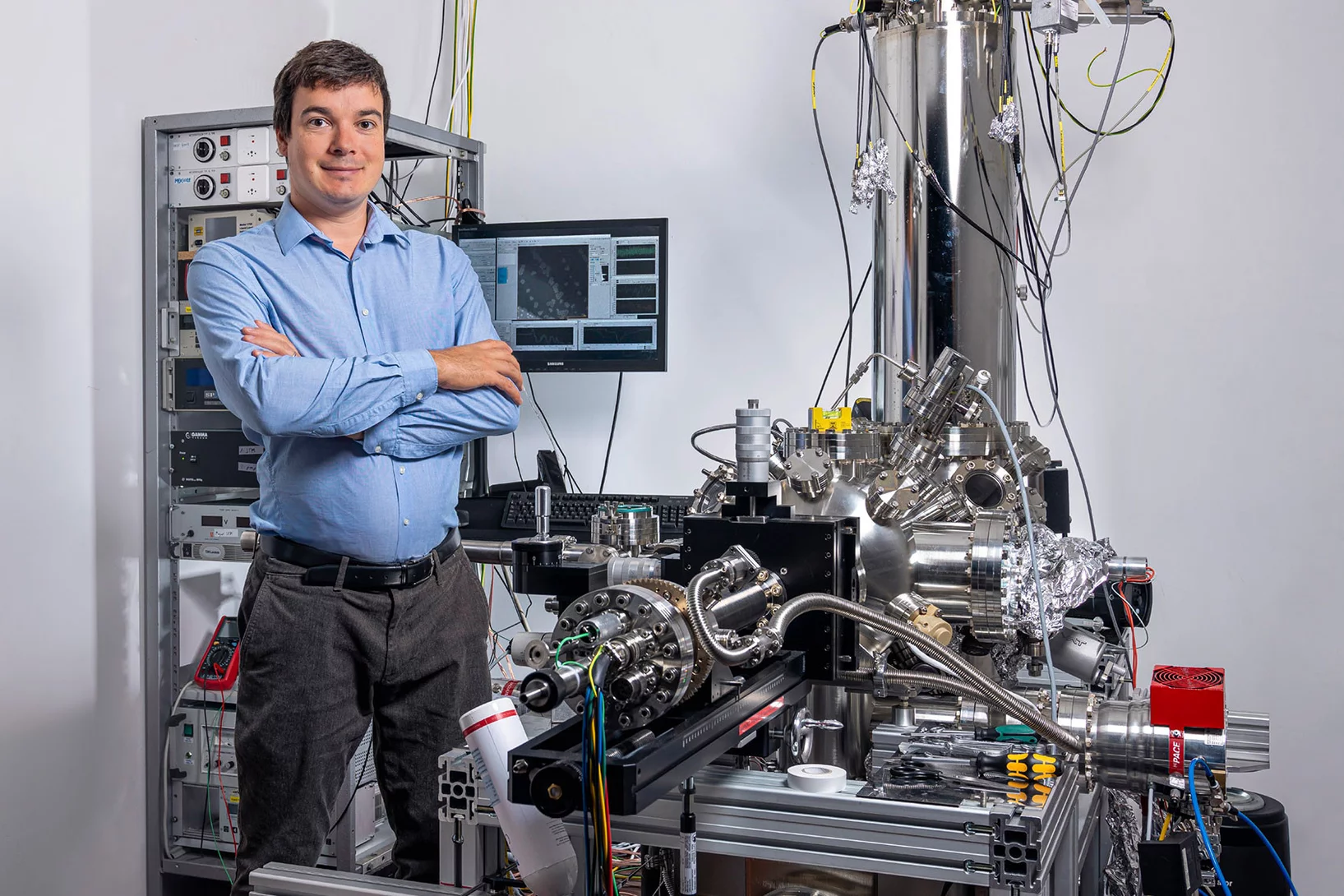
«Molekülketten könnten interessant sein für die Elektronik der Zukunft»
Christian Wäckerlin spricht über Grundlagenforschung an aussergewöhnlichen Nanodrähten – und über mögliche Anwendungen.
Spin-orbit driven superconducting proximity effects in Pt/Nb thin films
Manipulating the spin state of thin layers of superconducting material is a promising route to generate dissipationless spin currents in spintronic devices. Approaches typically focus on using thin ferromagnetic elements to perturb the spin state of the superconducting condensate to create spin-triplet correlations. We have investigated simple structures that generate spin-triplet correlations without using ferromagnetic elements.
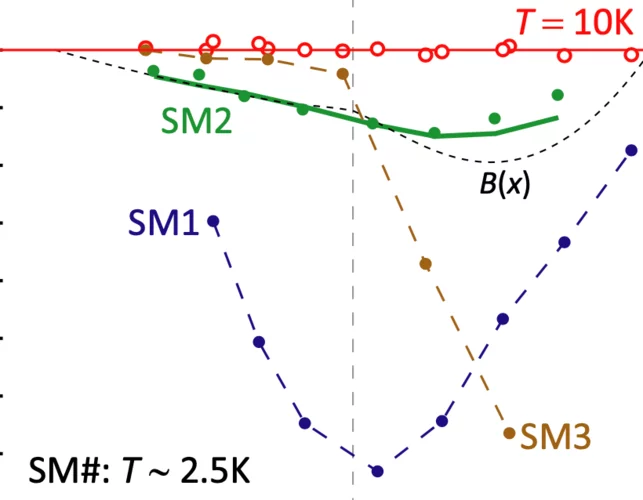
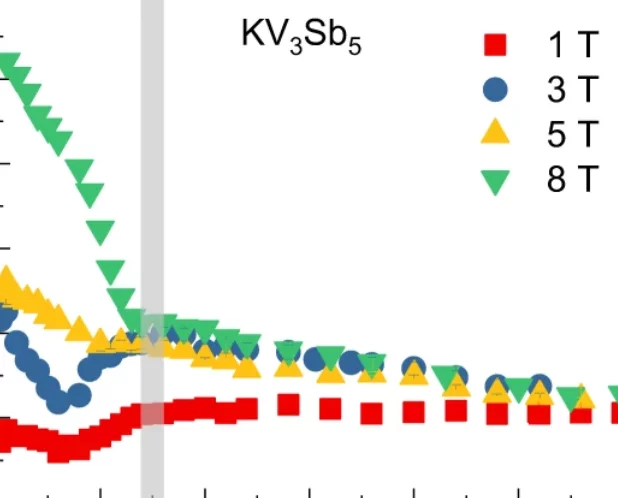
Unconventional charge order and superconductivity in kagome-lattice systems as seen by muon-spin rotation
Kagome lattices are intriguing and rich platforms for studying the intertwining of topology, electron correlation, and magnetism. These materials have been subject to tremendous experimental and theoretical studies not only due to their exciting physical properties but also as systems that may solve critical technological problems. We will review recent experimental progress on superconductivity and magnetic fingerprints of charge order in several kagome-lattice systems from the local-magnetic probe point of view by utilizing muon-spin rotation under extreme conditions, i.e., hydrostatic pressure, ultra low temperature and high magnetic field.
Strong phonon softening and avoided crossing in aliovalence-doped heavy-band thermoelectrics
Aliovalent doping is a way to optimize the electrical properties of semiconductors, but its impact on the phonon structure and propagation is seldom considered properly. Here we show that aliovalent doping can be much more effective in reducing the lattice thermal conductivity of thermoelectric semiconductors than the commonly employed isoelectronic alloying strategy. We demonstrate ...
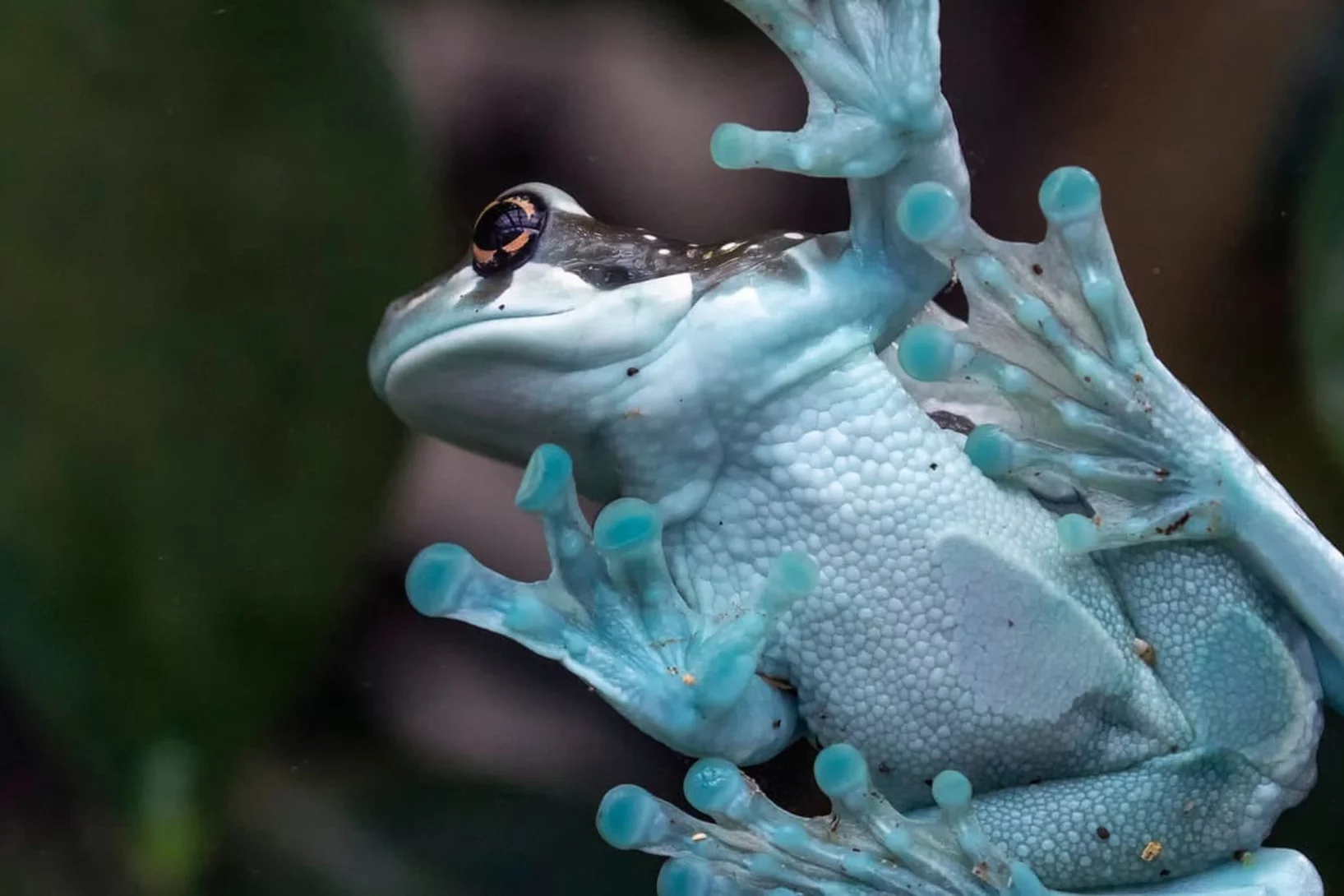
On the trail of blue bones
The bones of the tree hollow toad tree frog are turquoise blue. Our team is currently investigating the nanostructure of the bone and its significance for the frog.
Einführungswoche 2023
Am Montag, 7. August 2023 durften wir 30 neue Lernende und Praktikant*innen am PSI begrüssen. Wir wünschen ihnen einen guten Start in der Berufswelt und eine erfolgreiche Lehr- und Praktikumszeit.
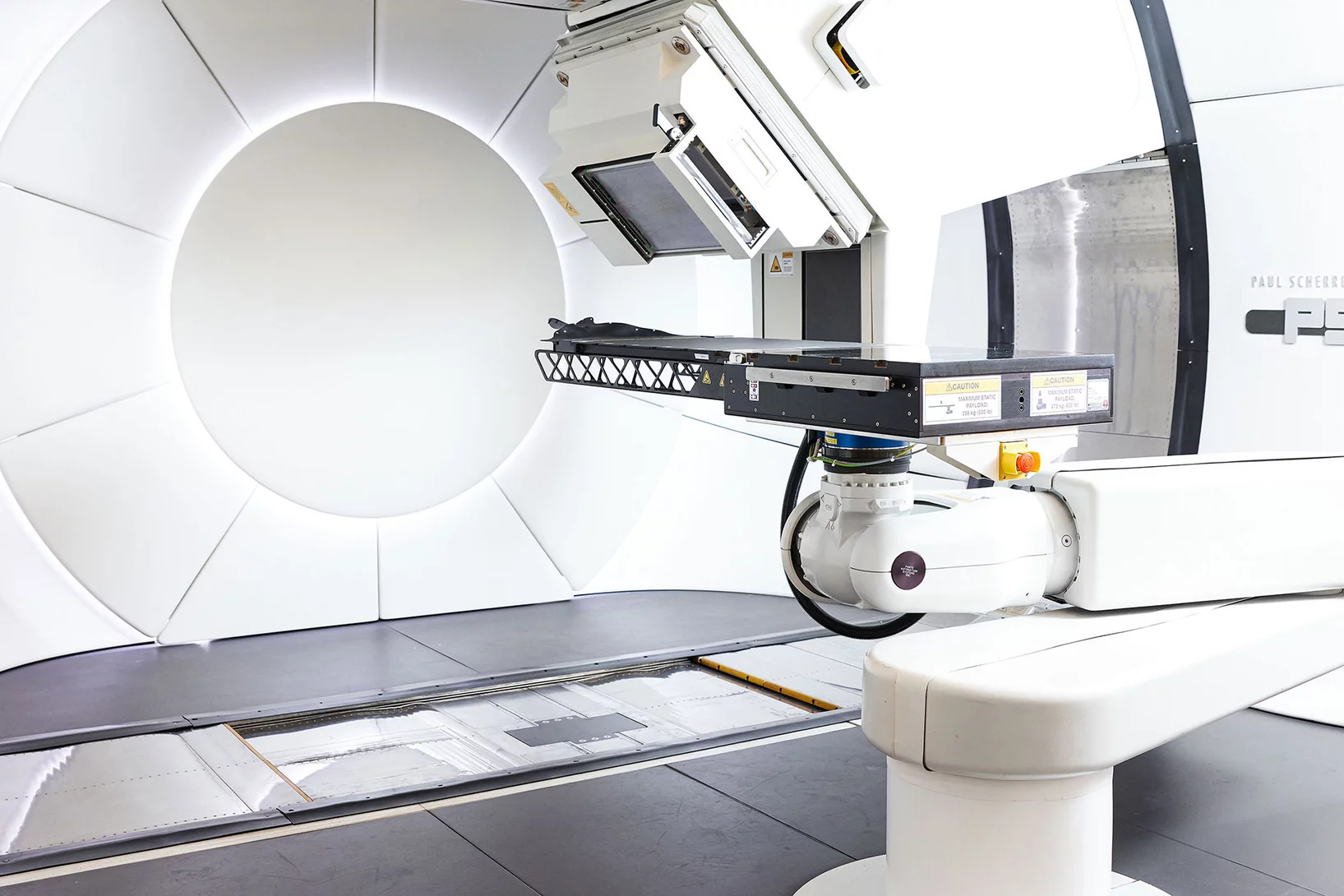
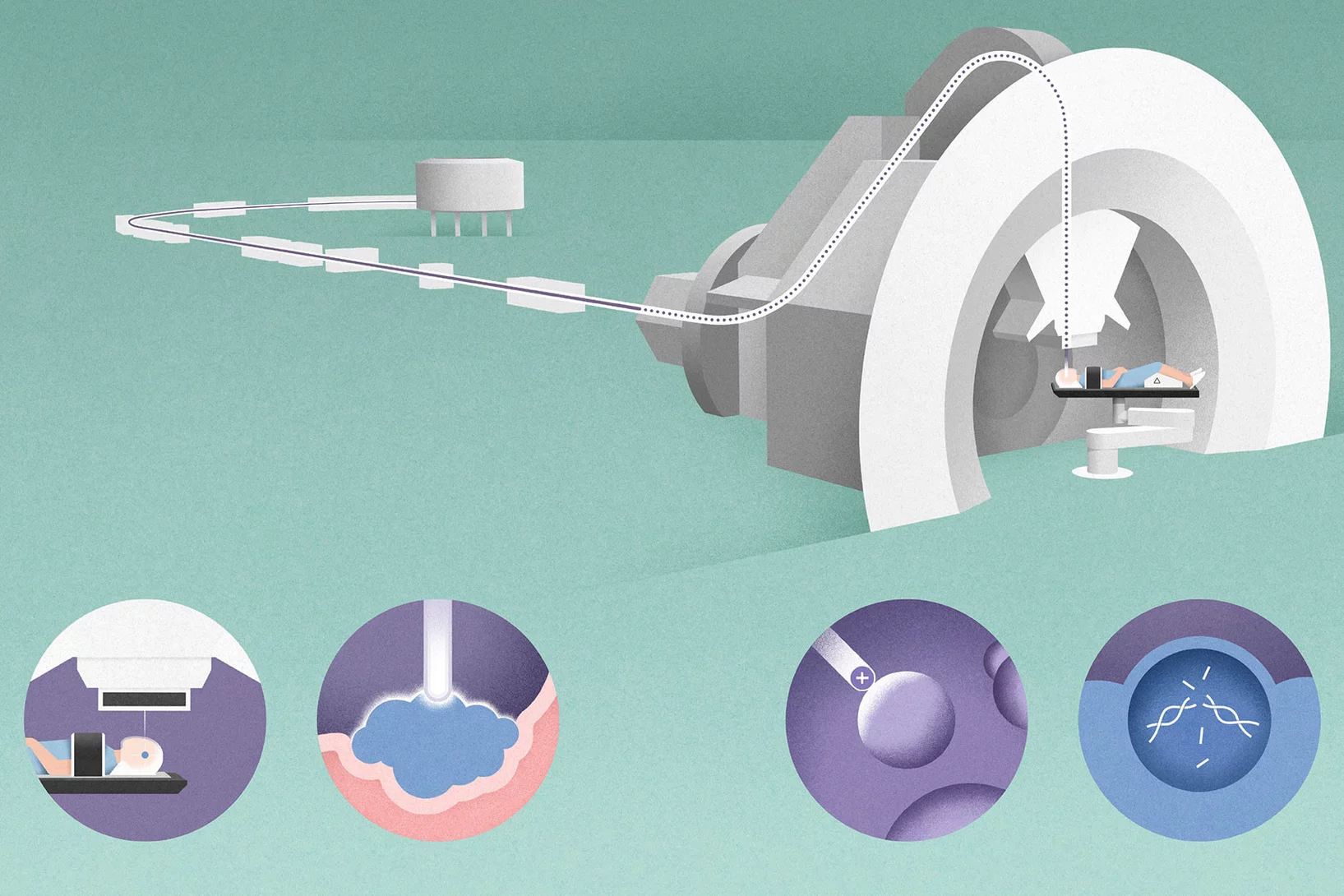
Premiere: Protonen gegen Speiseröhrenkrebs
Am 15. August 2023 wurde am PSI ein an Speiseröhrenkrebs erkrankter Patient mit Protonen bestrahlt – das erste Mal überhaupt in der Schweiz.
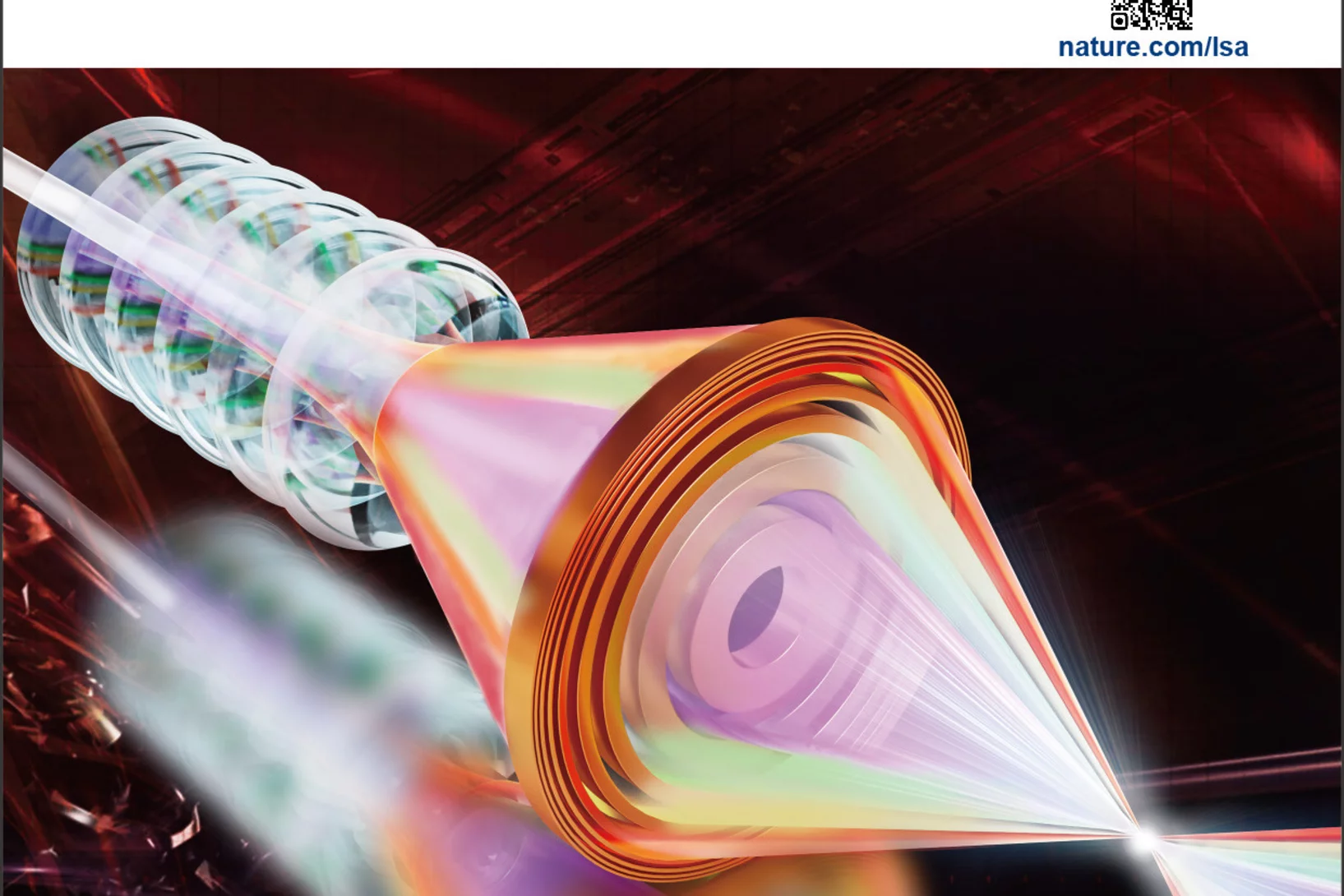
Apochromatic X-ray focusing as Editor's Highlight in Light: Science & Applications
Our recent work on the 1st demonstration of apochromatic X-ray lenses has been selected as an Editor's Highlight in Light: Science & Applications.
Sandra Mous received the ETH Medal for her dissertation at ETH Zurich
Sandra Mous received the ETH Medal for her dissertation at ETH Zurich under the supervision of Prof. Gebhard F.X. Schertler, Division Head of Biology and Chemistry at PSI. She captured the first molecular movie of an anion transported across the cell membrane by a protein pump. Congratulations!
Welcome to LXN Narmadha Devi
Herzlich Willkommen Narmadha Devi in LXN!
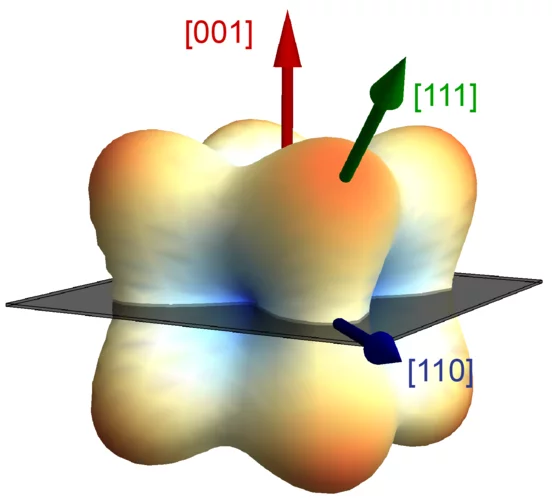
Direct observation of exchange anisotropy in the helimagnetic insulator Cu2OSeO3
The helical magnetic structures of cubic chiral systems are well explained by the competition among Heisen- berg exchange, Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, cubic anisotropy, and anisotropic exchange interaction (AEI). Recently, the role of the latter has been argued theoretically to be crucial for the low-temperature phase diagram of the cubic chiral magnet Cu2OSeO3, which features tilted conical and disordered skyrmion states for a specific orientation of the applied magnetic field (μ0H⃗ ∥ [001]). In this study ...
PSI Alumni Karrieren: Kathrin Ebner – von der Doktorandin bei ENE zur Risikoanalystin im Emerging Green Tech Solutions Team von Munich Re
Der PSI Career Blog stellt PSI Alumni und ihre Karrierewege vor, um die Vielseitigkeit der PSI-Gemeinschaft zu zeigen, und die nächste Generation zu inspirieren. Heute mit Kathrin Ebner, die uns über ihren Weg vom Doktorat am PSI zur Risikoanalystin bei Munich Re erzählt.
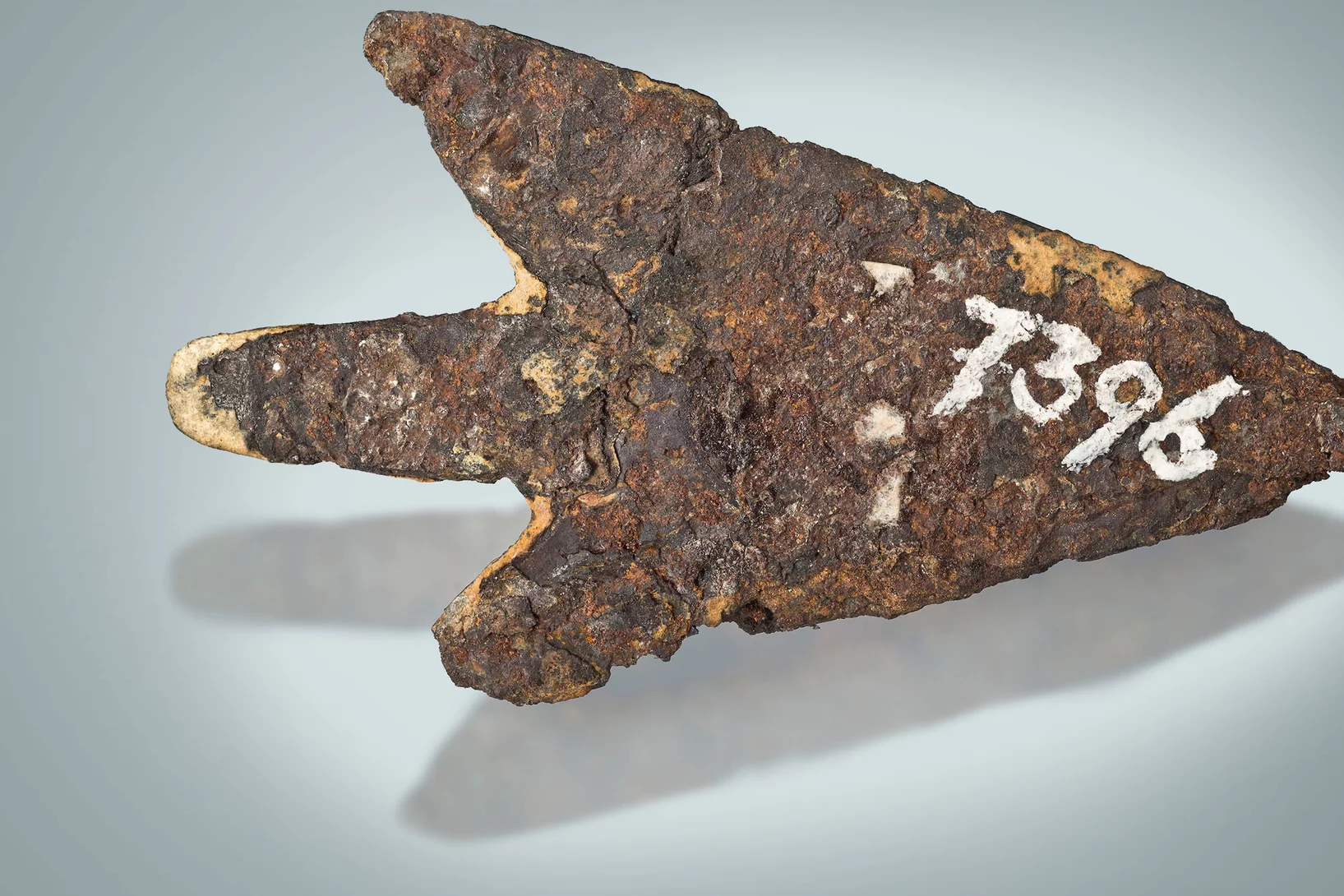
Bronzezeitliche Pfeilspitze stammt aus meteoritischem Eisen
Mithilfe von Myonen konnten PSI-Forschende die Materialherkunft einer Pfeilspitze bestimmen.
Welcome to LXN Bechir Braham
Herzlich Willkommen Bechir Braham in LXN!
Physics against Cancer: How PSI pioneered modern proton therapy
A recently published book tells the story of scientists and physicians at PSI developing a revolutionary technique to treat cancer.
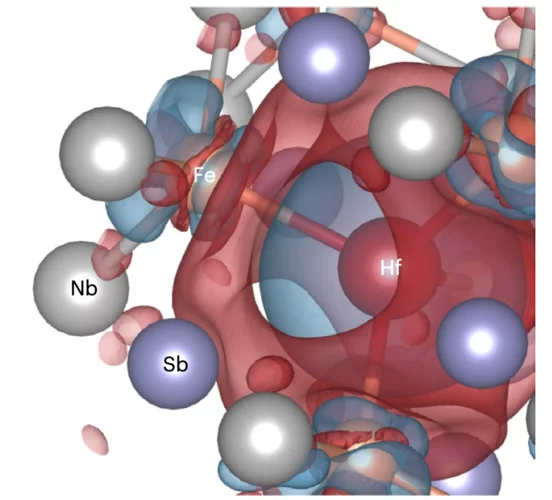
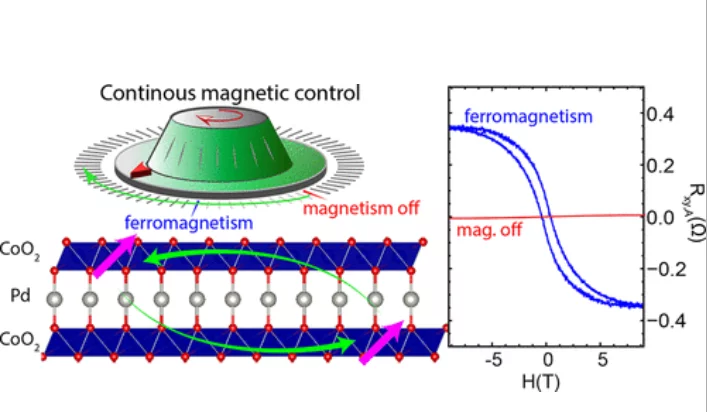
Emergent Magnetism with Continuous Control in the Ultrahigh-Conductivity Layered Oxide PdCoO2
The current challenge to realizing continuously tunable magnetism lies in our inability to systematically change properties, such as valence, spin, and orbital degrees of freedom, as well as crystallographic geometry. Here, we demonstrate that ferromagnetism can be externally turned on with the application of low-energy helium implantation and can be subsequently erased and returned to the pristine state via annealing.