Abkehr von der Kernenergie, Ausbau von Solar- und Windkraft, Energiegewinnung aus Biomasse, Senkung des Energieverbrauchs. Bis 2050 soll die Schweiz klimaneutral werden. Ein ehrgeiziges Ziel, welches durch die zunehmend herausfordernde geopolitische Lage dringlicher denn je geworden ist. Wie lässt sich in den nächsten Jahren eine nachhaltige und widerstandsfähige Energieversorgung für die Schweiz aufbauen? Wie können erneuerbare Energien optimal genutzt werden? Welche neuen Technologien sind besonders vielversprechend? Am PSI suchen Forschende nach Antworten auf diese entscheidenden Fragen.
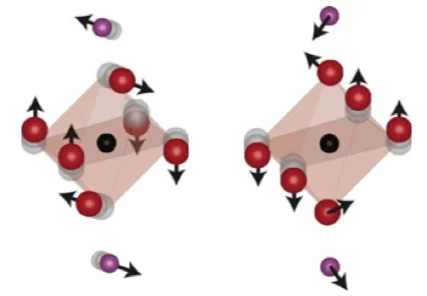
Electron–phonon-driven three-dimensional metallicity in an insulating cuprate
Elucidating the role of different degrees of freedom in a phase transition is crucial in the comprehension of complex materi- als. A phase transformation that attracts significant interest is the insulator-to-metal transition of Mott insulators, in which the electrons are thought to play the dominant role. Here, we use ultrafast laser spectroscopy and theoretical calculations ....
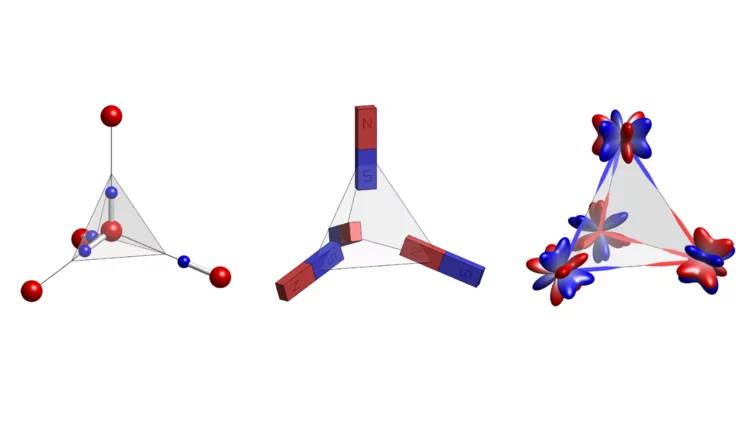
Spin ice expands to higher orders
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
Spin ice expands to higher orders
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
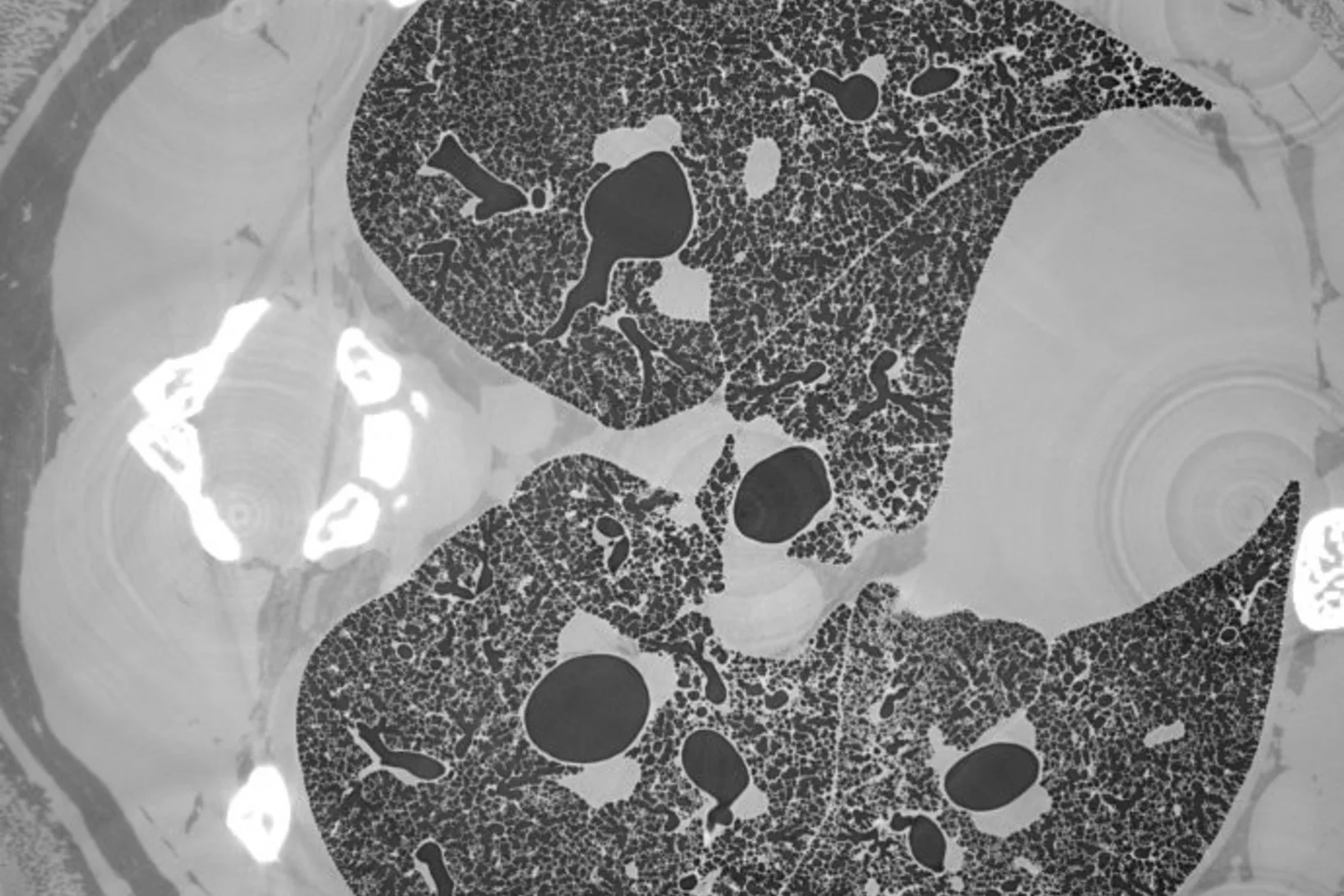
X-ray Imaging for Biomedicine: Imaging Large Volumes of Fresh Tissue at High Resolution
The TOMCAT beamline at the Swiss Light Source specializes in rapid high-resolution 3-dimensional tomographic microscopy measurements with a strong focus on biomedical imaging. The team has recently developed a technique to acquire micrometer-scale resolution datasets on the entire lung structure of a juvenile rat in its fresh natural state within the animal’s body and without the need for any fixation, staining or other alteration that would affect the observed structure (E. Borisova et al., 2020, Histochem Cell Biol).
A quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles on the pyrochlore lattice
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
15th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation postponed to 2021
Because of the coronavirus situation, the 15th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation and Resonance (µSR2020) has been postponed to 2021. More details will be announced in due time.
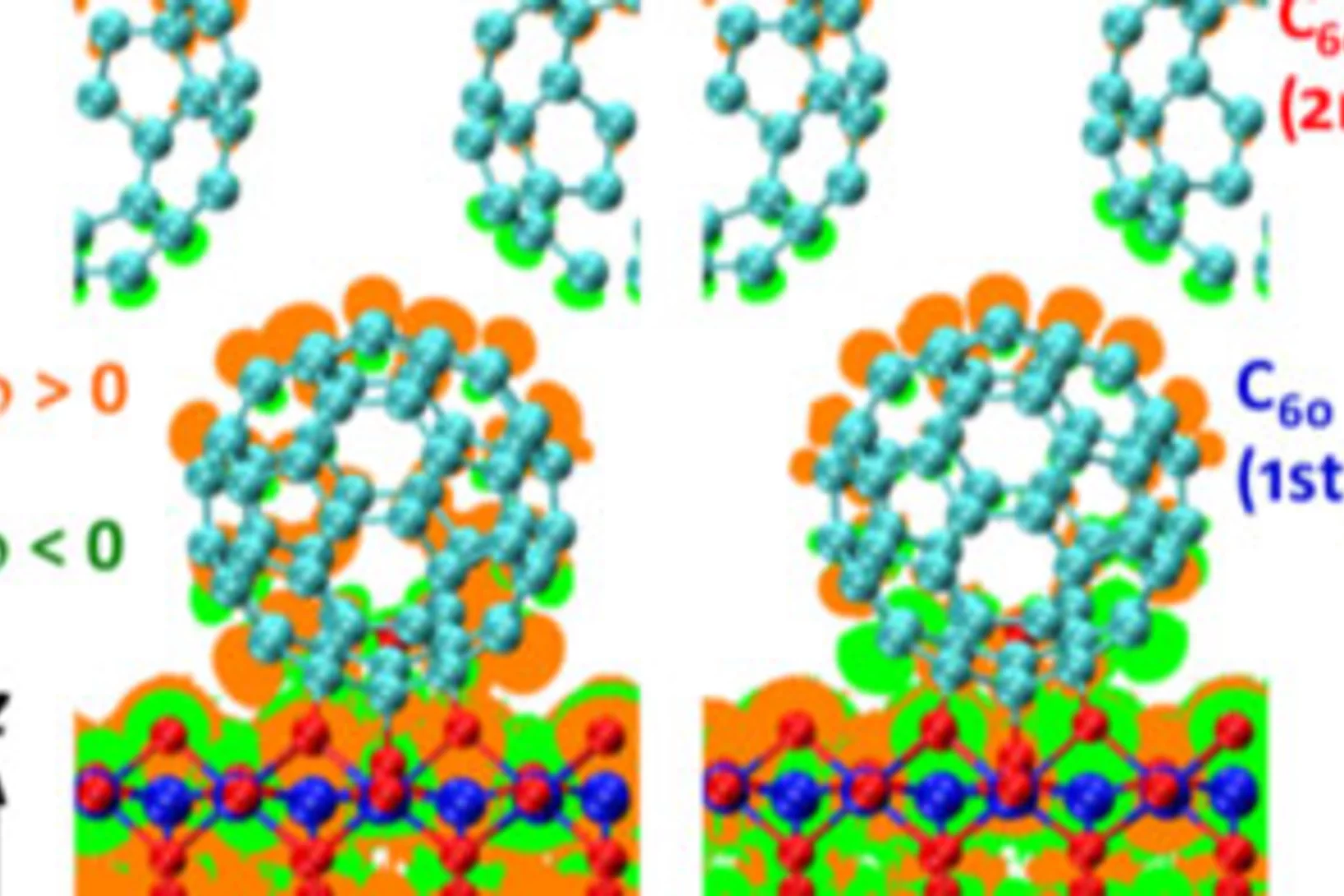
Reversible spin storage in metal oxide - fullerene heterojunctions
We show that hybrid MnOx/C60 heterojunctions can be used to design a storage device for spin-polarized charge: a spin capacitor. Hybridization at the carbon-metal oxide interface leads to spin-polarized charge trapping after an applied voltage or photocurrent. Strong electronic structure changes, including a 1-eV energy shift and spin polarization in the C60 lowest unoccupied molecular orbital, are then revealed by x-ray absorption spectroscopy, in agreement with density functional theory simulations.
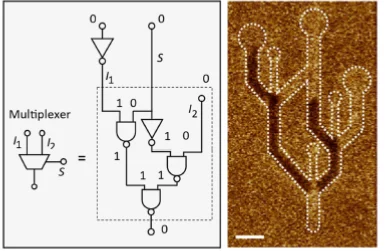
Logic operations with domain walls
A collaboration of scientists from the ETH Zürich and the Paul Scherrer Institute successfully demonstrated the all-electric operation of a magnetic domain-wall based NAND logic gate, paving the way towards the development of logic applications beyond the conventional metal-oxide semiconductor technology. The work has been published in the journal Nature.
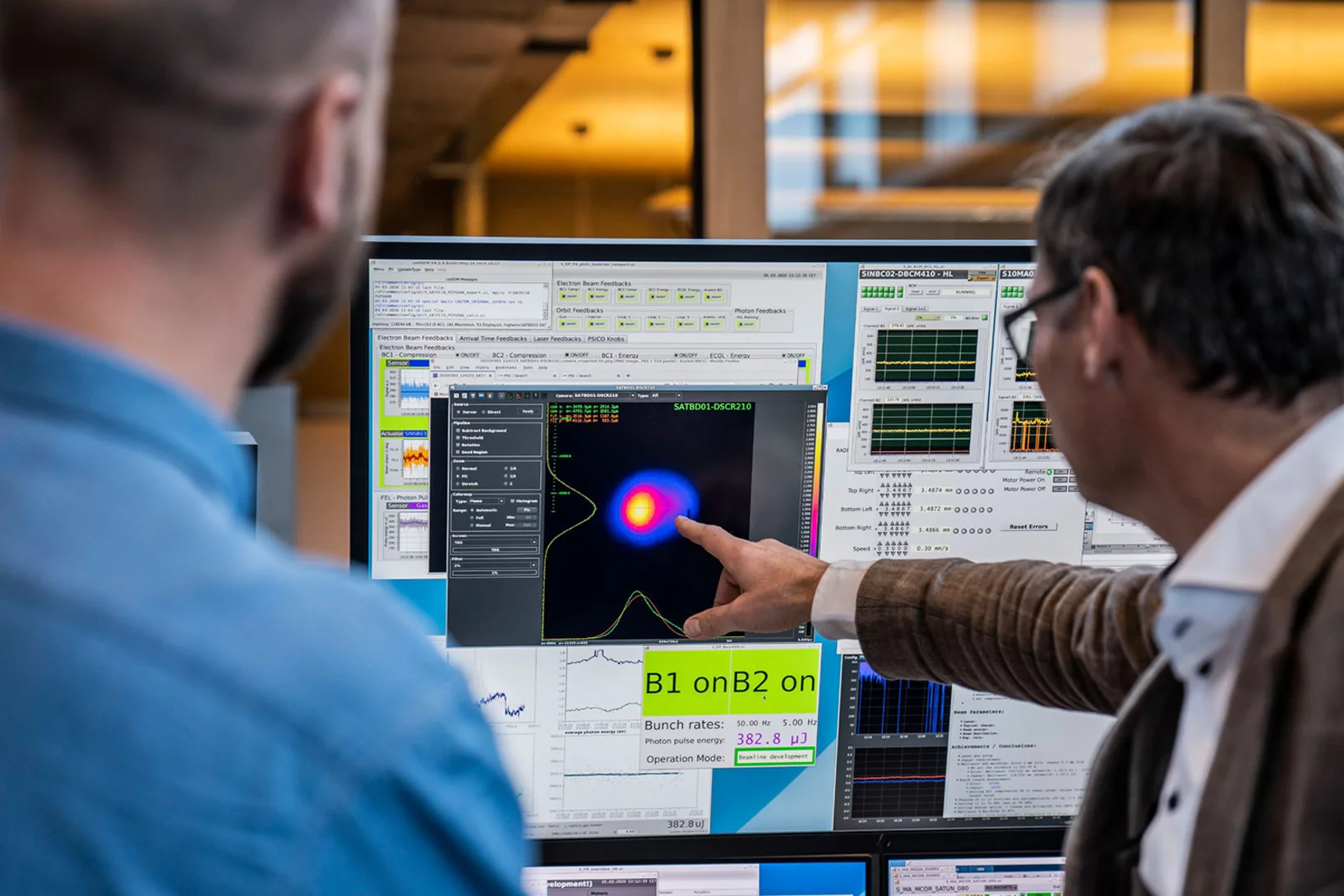
SwissFEL: «Athos» macht grosse Fortschritte
Die neue Strahllinie am Freie-Elektronen-Röntgenlaser SwissFEL des PSI ist schon bald einsatzbereit. Im Dezember lieferte «Athos» das erste Mal Laserlicht − zur Freude der Forschenden, die mit dem Aufbau betreut sind, sogar früher als erwartet.
Optics for spins
In this work, published on the front cover page of Advanced Materials, an international collaboration of Italian, American, and Swiss scientists demonstrated a novel concept for the generation and manipulation of spin waves, paving the way towards the development of magnonic nano-processors.
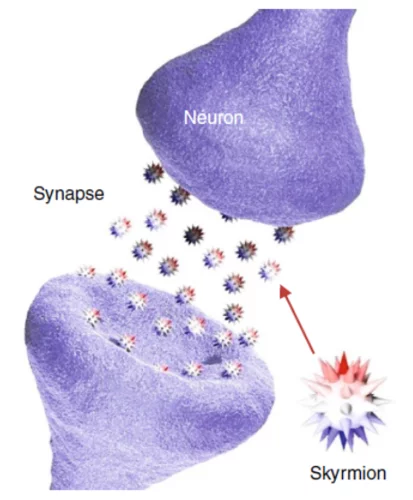
Can skyrmions read?
Can a skyrmion-based device be used to read a handwritten text? In this work, an international scientist collaboration led by the Korea Institute of Technology and the IBM Watson research center could provide a first answer to this question by fabricating a proof-of-principle single-neuron artificial neural network, using X-ray magnetic microscopy at the Swiss Light Source to investigate its performances.
Erstmals chemische Reaktionen direkt im Feinstaub nachgewiesen
Forschende am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI haben eine neue Methode entwickelt, um Feinstaub noch genauer als bislang zu analysieren. Mit ihrer Hilfe widerlegten sie die Lehrmeinung, dass Moleküle im Feinstaub keine chemischen Umwandlungen mehr eingehen, weil sie in Schwebepartikel eingebunden sind.
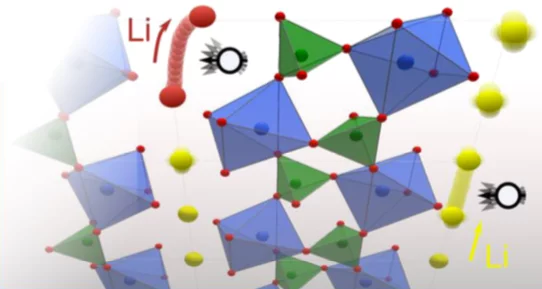
Quantifying Diffusion through Interfaces of Lithium-Ion Battery Active Materials
Detailed understanding of charge diffusion processes in a lithium-ion battery is crucial to enable its systematic improvement. Experimental investigation of diffusion at the interface between active particles and the electrolyte is challenging but warrants investigation as it can introduce resistances that, for example, limit the charge and discharge rates. Here, we show an approach to study diffusion at interfaces using muon spin spectroscopy.
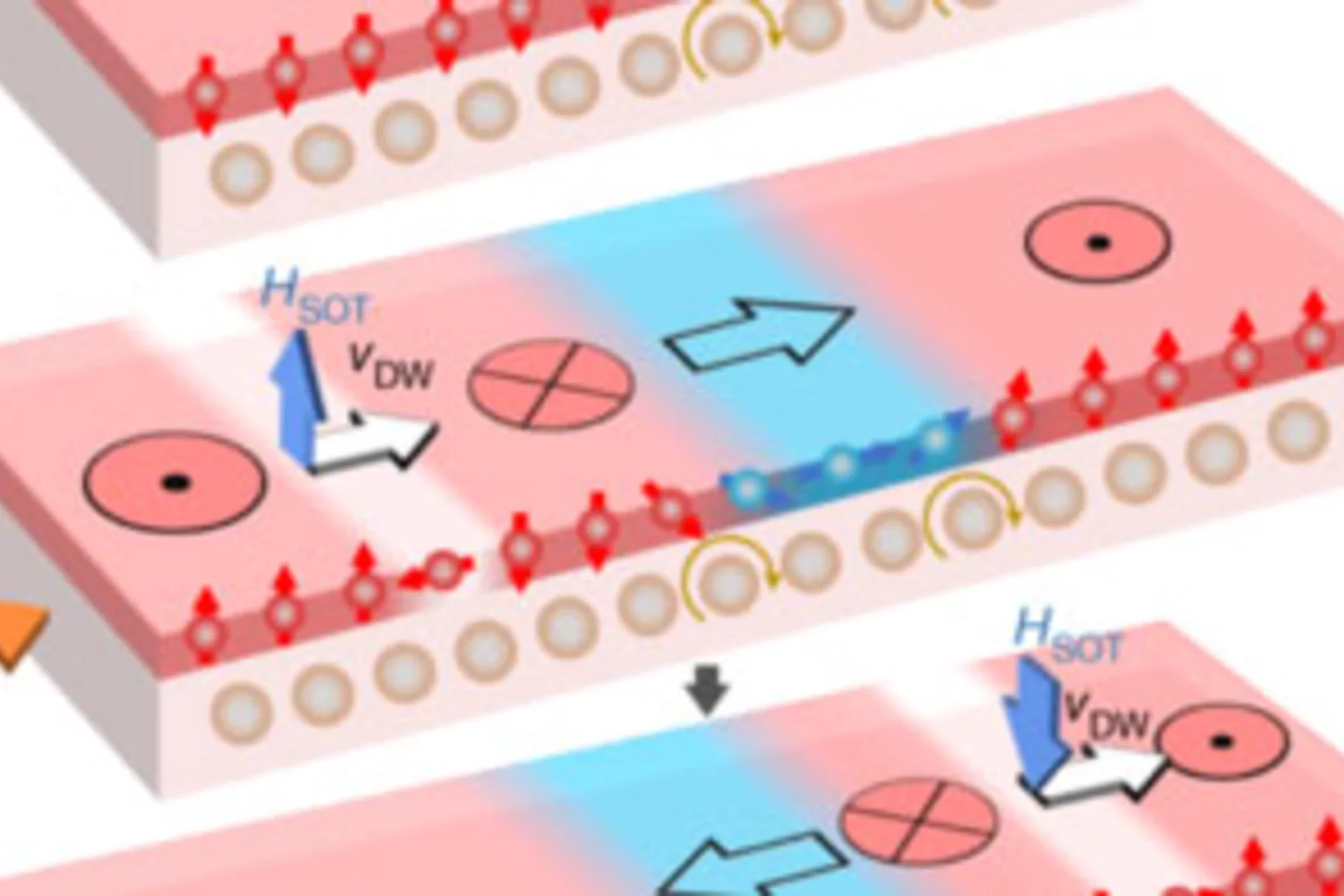
Current-driven magnetic domain-wall logic
Spin-based logic architectures provide nonvolatile data retention, near-zero leakage, and scalability, extending the technology roadmap beyond complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor logic. Architectures based on magnetic domain walls take advantage of the fast motion, high density, non-volatility and flexible design of domain walls to process and store information. Such schemes, however, rely on domain-wall manipulation and clocking using an external magnetic field, which limits their implementation in dense, large-scale chips.
Nanowelten in 3-D
Tomogramme aus dem Inneren von Fossilien, Hirnzellen oder Computerchips liefern neue Erkenntnisse über feinste Strukturen. Die 3-D-Bilder gelingen mithilfe der Röntgenstrahlen der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS dank eigens entwickelter Detektoren und raffinierter Computeralgorithmen.
Broken time-reversal symmetry in the topological superconductor UPt3
Topological properties of materials are of fundamental as well as practical importance. Of particular interest are unconven- tional superconductors that break time-reversal symmetry, for which the superconducting state is protected topologically and vortices can host Majorana fermions with potential use in quantum computing. However, in striking contrast to the unconventional A phase of superfluid 3He where chiral symmetry was directly observed, .....
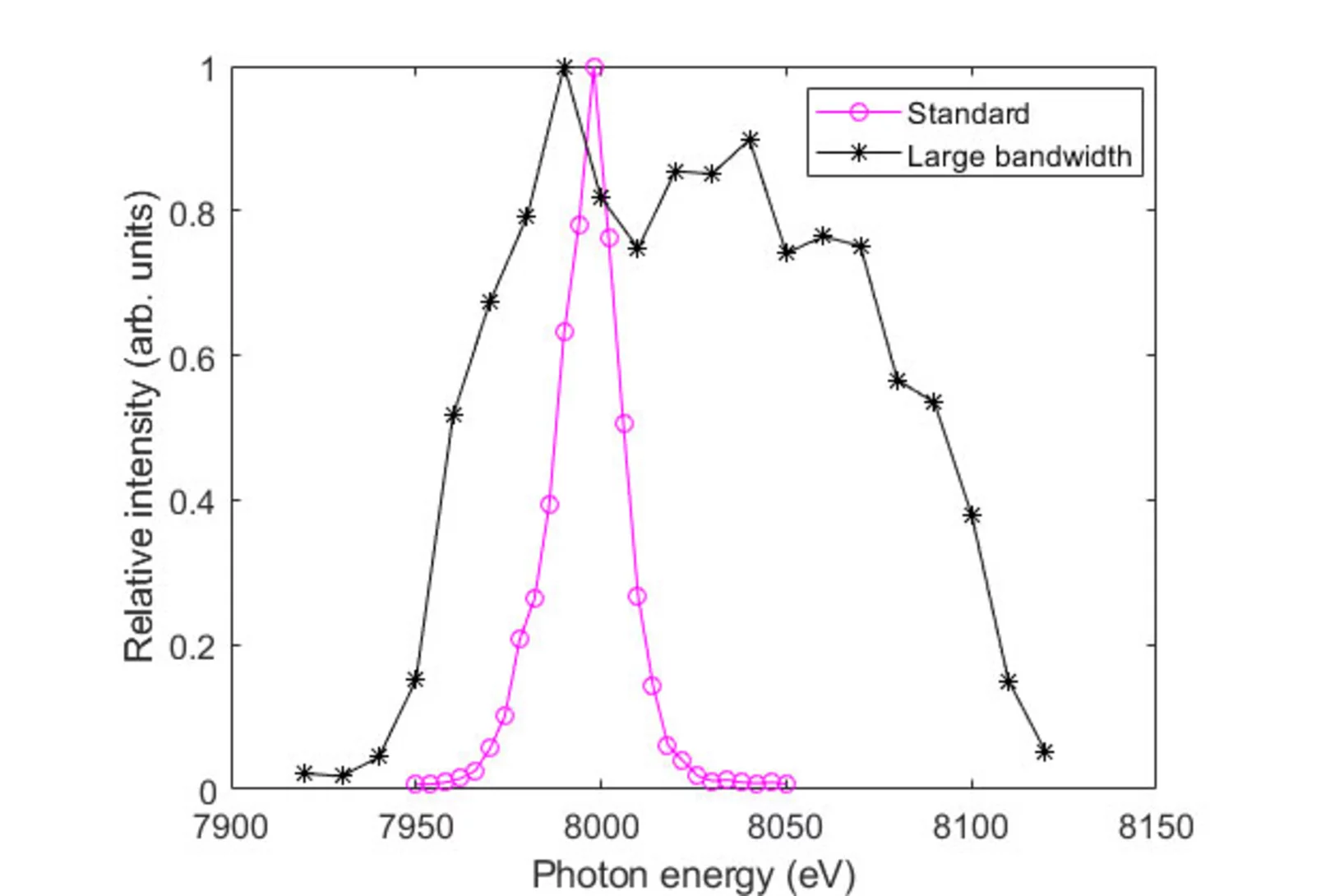
Demonstration of Large Bandwidth Hard X-Ray Free-Electron Laser Pulses at SwissFEL
We have produced hard x-ray free-electron laser (FEL) radiation with unprecedented large bandwidth tunable up to 2%. The experiments have been carried out at SwissFEL, the x-ray FEL facility at the Paul Scherrer Institute in Switzerland. The bandwidth is enhanced by maximizing the energy chirp of the electron beam, which is accomplished by optimizing the compression setup. We demonstrate continuous tunability of the bandwidth with a simple method only requiring a quadrupole magnet. The generation of such broadband FEL pulses will improve the efficiency of many techniques such as x-ray crystallography and spectroscopy, opening the door to significant progress in photon science. It has already been demonstrated that the broadband pulses of SwissFEL are beneficial to enhance the performance of crystallography, and further SwissFEL users plan to exploit this large bandwidth radiation to improve the efficiency of their measurement techniques.
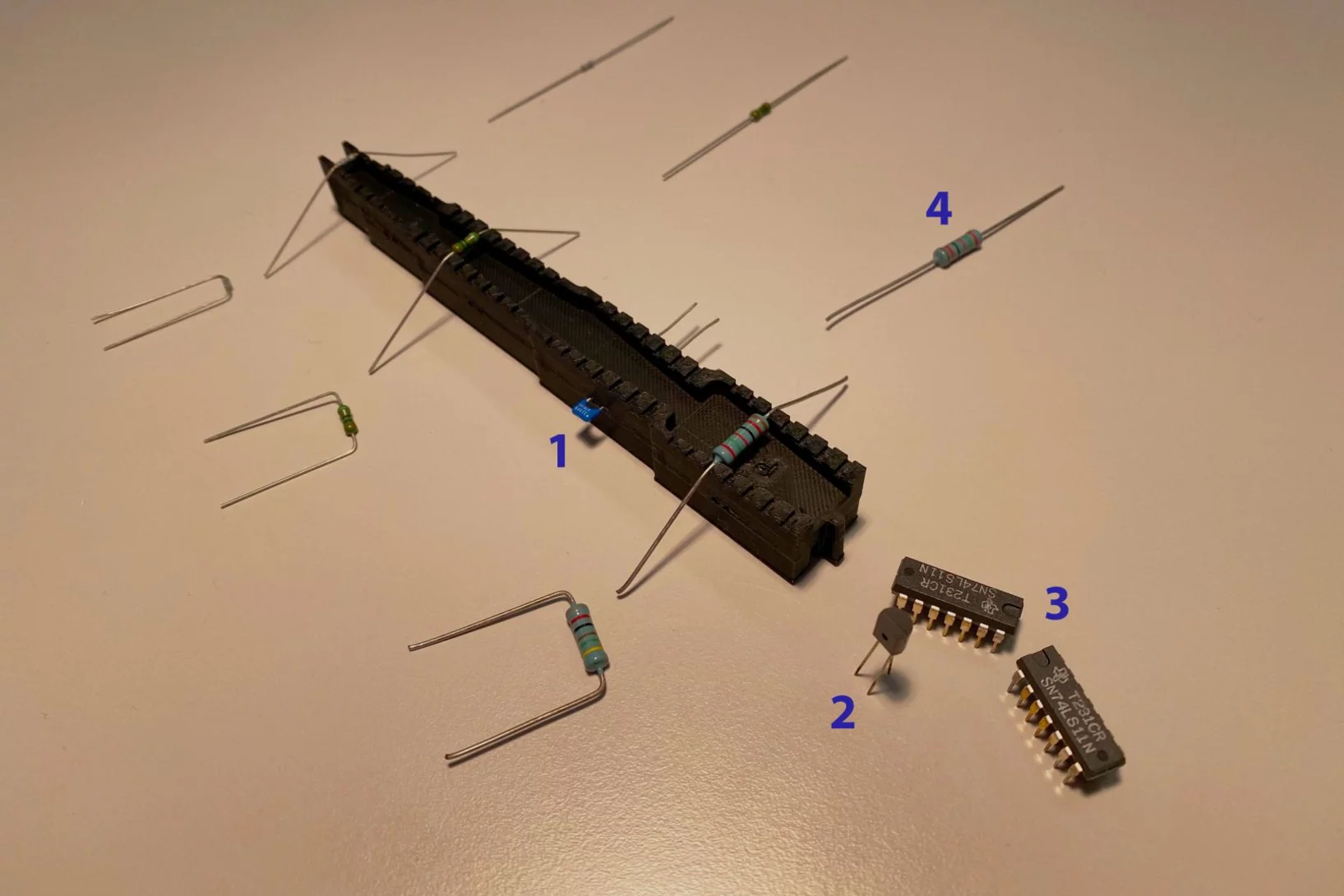
4-in-1 Biegebauklotz
Dank dem 4-in-1 Biegebauklotz erleichtern wir den Elektronikern die Arbeit am Arbeitsplatz!
«Schon heute ist Elektro die richtige Wahl»
Ein Interview über Fahrzeugantriebe mit Christian Bauer, Wissenschaftler am Labor für Energiesystemanalyse des PSI und spezialisiert auf Lebenszyklus- und Nachhaltigkeitsanalysen.
Symposium in memory of Jean-Pierre Blaser
Jean-Pierre Blaser (1923-2019) was one of the founders of the Swiss Institute for Nuclear Research SIN - one of the two institutions, which merged to the Paul Scherrer Institut in 1988. From 1988-1990 he was the first Director of the Paul Scherrer Institut. On the occasion of his first obit ETH Zurich and PSI organised a symposium to honour the lifetime achievement of this outstanding Swiss physicist.
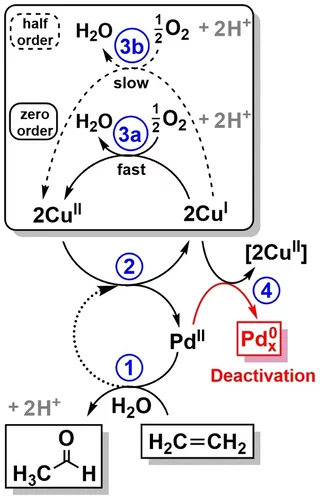
Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS
Unlike the homogeneous Wacker process, the understanding of the mechanism of the heterogeneous system has long remained to be superficial. Here the authors investigated the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y through transient XAS coupled with kinetic studies and chemometric analysis.
Dem Rätsel der Materie auf der Spur
Forschende haben an der Quelle für ultrakalte Neutronen des PSI eine Eigenschaft des Neutrons so genau wie noch nie vermessen: sein elektrisches Dipolmoment. Denn bis heute wird nach einer Erklärung gesucht, weshalb es nach dem Urknall mehr Materie als Antimaterie gab.
Plakatkampagne «Werde Wissenschaftlerin!» «Werde Ingenieurin!» «Werde Technikerin!»
Nur ungefähr jede vierte Stelle im naturwissenschaftlichen, technischen und im Ingenieur-Bereich in der Schweiz ist mit einer Frau besetzt.[1] Am PSI sieht das Verhältnis zwischen Frauen und Männern in diesen Bereichen nicht anders aus. Deshalb möchte das PSI ein Zeichen setzen und zum Internationalen Frauentag am 8. März weibliche Rollenvorbilder geben. Auf Plakaten in Baden, Brugg und Aarau zeigt das PSI Naturwissenschaftlerinnen, Technikerinnen und Ingenieurinnen, die darüber Auskunft geben, weshalb sie diesen Beruf gewählt haben und was sie an ihrer Arbeit fasziniert.
The work "Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by
The work "Elucidating the mechanism of heterogeneous Wacker oxidation over Pd-Cu/zeolite Y by transient XAS" of Jerick Imbao (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-14982-x), result of a collaboration with Dr. Maarten Nachtegaal of the Paul Scherrer Institut, was highlighted by the editors of Nature Communications.
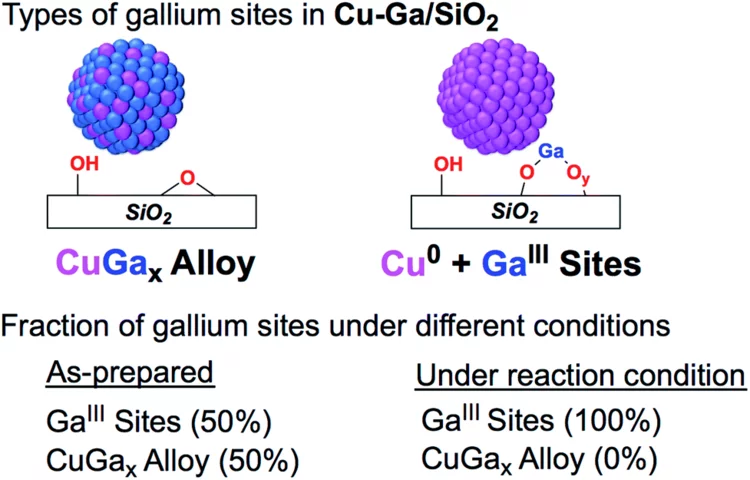
Enhanced CH3OH selectivity in CO2 hydrogenation using Cu-based catalysts generated via SOMC from GaIII single-sites
Small and narrowly distributed nanoparticles of copper alloyed with gallium supported on silica containing residual GaIII sites can be obtained via surface organometallic chemistry. This material is highly active and selective for CO2 hydrogenation to CH3OH. In situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy shows that gallium is oxidized under reaction conditions while copper remains as Cu0.
Kurzfilm eines magnetischen Nanowirbels
Mit einer neu entwickelten Untersuchungsmethode konnten Forschende die magnetische Struktur im Inneren eines Materials mit Nanometer-Auflösung abbilden. Ihnen gelang ein kurzer «Film» aus sieben Bildern, der erstmalig in 3-D zeigt, wie sich winzige Wirbel der Magnetisierung tief im Inneren eines Materials verändern.
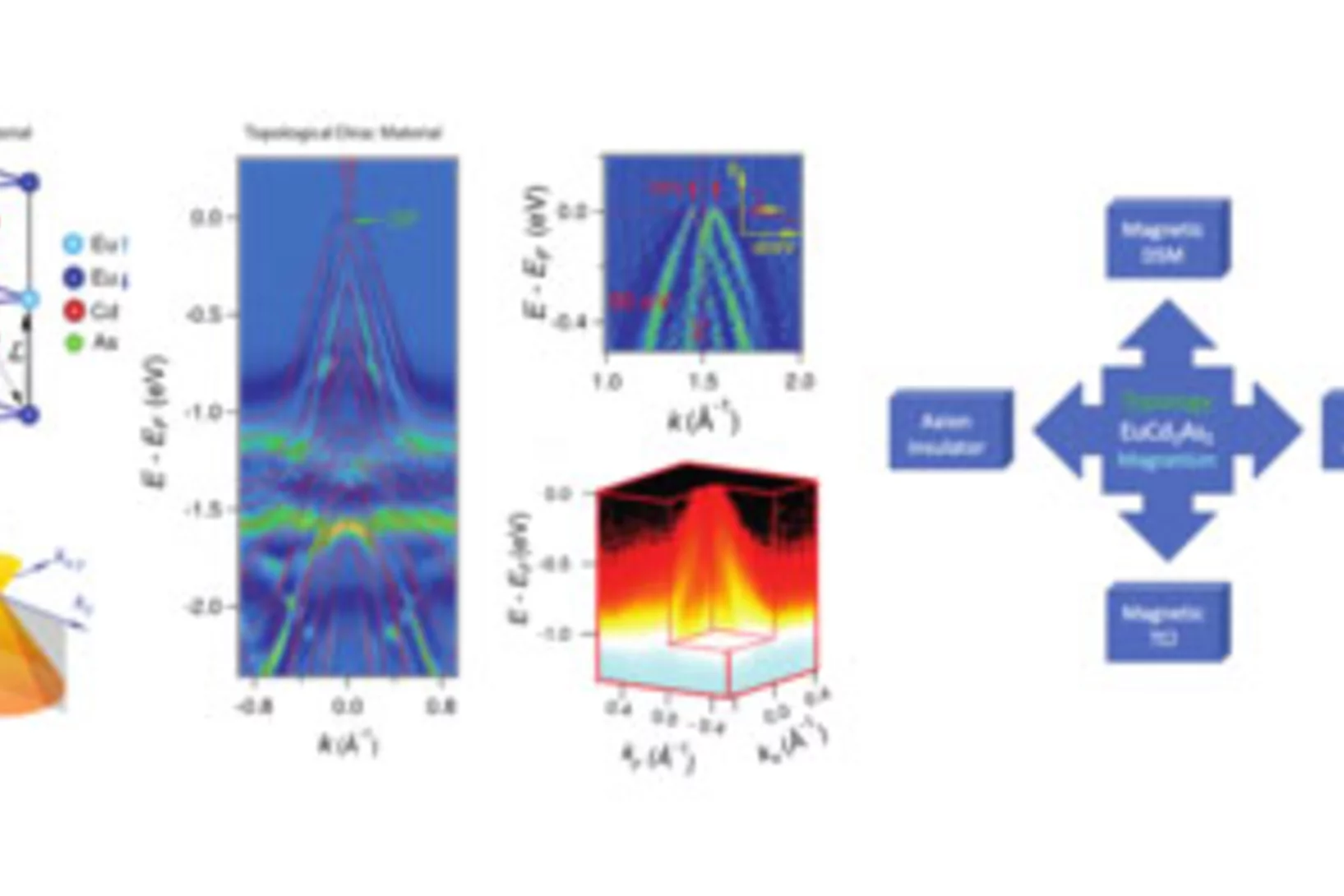
Emergence of Nontrivial Low-Energy Dirac Fermions in Antiferromagnet EuCd2As2
When magnetism meets topology, colorful novel states can emerge in condensed matter. It is widely believed that parity-time symmetry plays an essential role for the formation of Dirac states in Dirac semimetals. So far, all of the experimentally identified topological nontrivial Dirac semimetals possess both parity and time reversal symmetry. Since the magnetism will break time-reversal symmetry, only in special cases the Dirac states can be protected in a magnetic system. Thus, the realization of magnetic topological Dirac materials remains a major issue in the research of topological physics. In this work, the authors ascertained that the ground state of EuCd2As2 is a good candidate for magnetic topological Dirac semimetal when the spins point in the out-of-plane direction in the A-type antiferromagnetic phase. The Dirac state is protected by the combination of parity-time symmetry with additional translation operation. Moreover, when the spins deviate from out-of-plane direction, the bulk Dirac cone will open a gap, and the system develops into a novel state containing axion insulator, antiferromagnetic topological crystalline insulator, and higher order topological insulator.
Emergence of Nontrivial Low-Energy Dirac Fermions in Antiferromagnet EuCd2As2
When magnetism meets topology, colorful novel states can emerge in condensed matter. It is widely believed that parity-time symmetry plays an essential role for the formation of Dirac states in Dirac semimetals. So far, all of the experimentally identified topological nontrivial Dirac semimetals possess both parity and time reversal symmetry. Since the magnetism will break time-reversal symmetry, only in special cases the Dirac states can be protected in a magnetic system. Thus, the realization of magnetic topological Dirac materials remains a major issue in the research of topological physics. In this work, the authors ascertained that the ground state of EuCd2As2 is a good candidate for magnetic topological Dirac semimetal when the spins point in the out-of-plane direction in the A-type antiferromagnetic phase. The Dirac state is protected by the combination of parity-time symmetry with additional translation operation. Moreover, when the spins deviate from out-of-plane direction, the bulk Dirac cone will open a gap, and the system develops into a novel state containing axion insulator, antiferromagnetic topological crystalline insulator, and higher order topological insulator.
First beam test with all Mu3e subdetectors integrated
During a week of beam tests at DESY, Hamburg, we for the first time took data with the pixel, fibre and tile detectors running in a common data acquisition setup. The lessons learned are key to completion and comissioning of the complete detector readout.
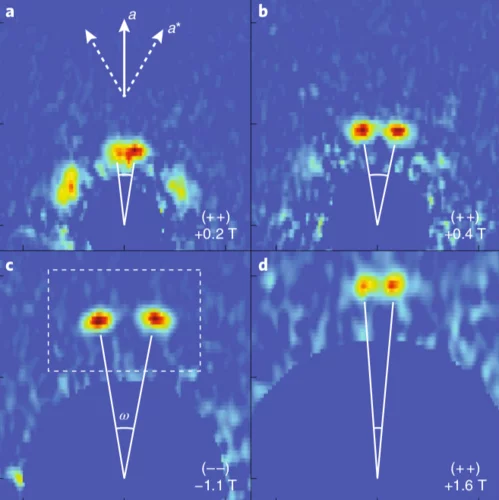
Many skyrmions, one angle
Employing a tailored multilayered magnetic film, optimized for the zero-field stabilization of magnetic skyrmions, researchers have investigated the influence of the skyrmion diameter on its current-induced sideways motion, uncovering mechanisms that allow for this topological property to be controlled.