Abkehr von der Kernenergie, Ausbau von Solar- und Windkraft, Energiegewinnung aus Biomasse, Senkung des Energieverbrauchs. Bis 2050 soll die Schweiz klimaneutral werden. Ein ehrgeiziges Ziel, welches durch die zunehmend herausfordernde geopolitische Lage dringlicher denn je geworden ist. Wie lässt sich in den nächsten Jahren eine nachhaltige und widerstandsfähige Energieversorgung für die Schweiz aufbauen? Wie können erneuerbare Energien optimal genutzt werden? Welche neuen Technologien sind besonders vielversprechend? Am PSI suchen Forschende nach Antworten auf diese entscheidenden Fragen.
Christian Bauer interviewed on Electric Cars at the program Einstein by SRF
Christian Bauer, a scientist at PSI's Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis who specialises in life cycle and sustainability analyses, interviewed at the program Einstein by SRF on Electric Cars
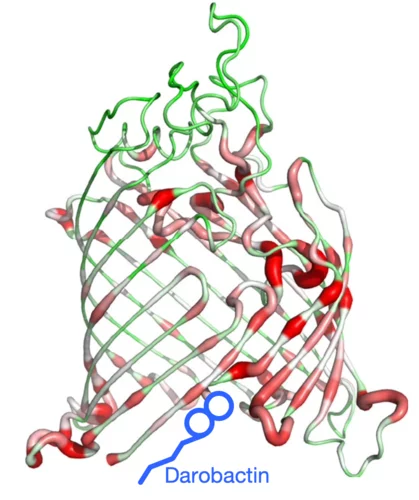
Combating antimicrobial resistance
In a study addressing the global health threat of drug resistance, researchers at the Biozentrum, University of Basel, have revealed how a new antibiotic, Darobactin, binds to the external membrane of gram-negative bacteria.
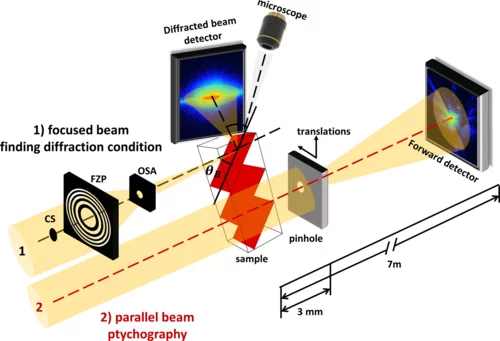
X-ray ptychographic topography: A robust nondestructive tool for strain imaging
We present x-ray ptychographic topography, a method for strain imaging, and demonstrate its use on an InSb micropillar after microcompression, where the strained region is visualized with a spatial resolution of 30 nm.
Das Zellskelett als Ziel für neue Wirkstoffe
Mit einer Kombination aus Computersimulation und Laborexperiment haben PSI-Forschende neue Bindungsstellen für Medikamente an dem lebenswichtigen Protein Tubulin identifiziert.
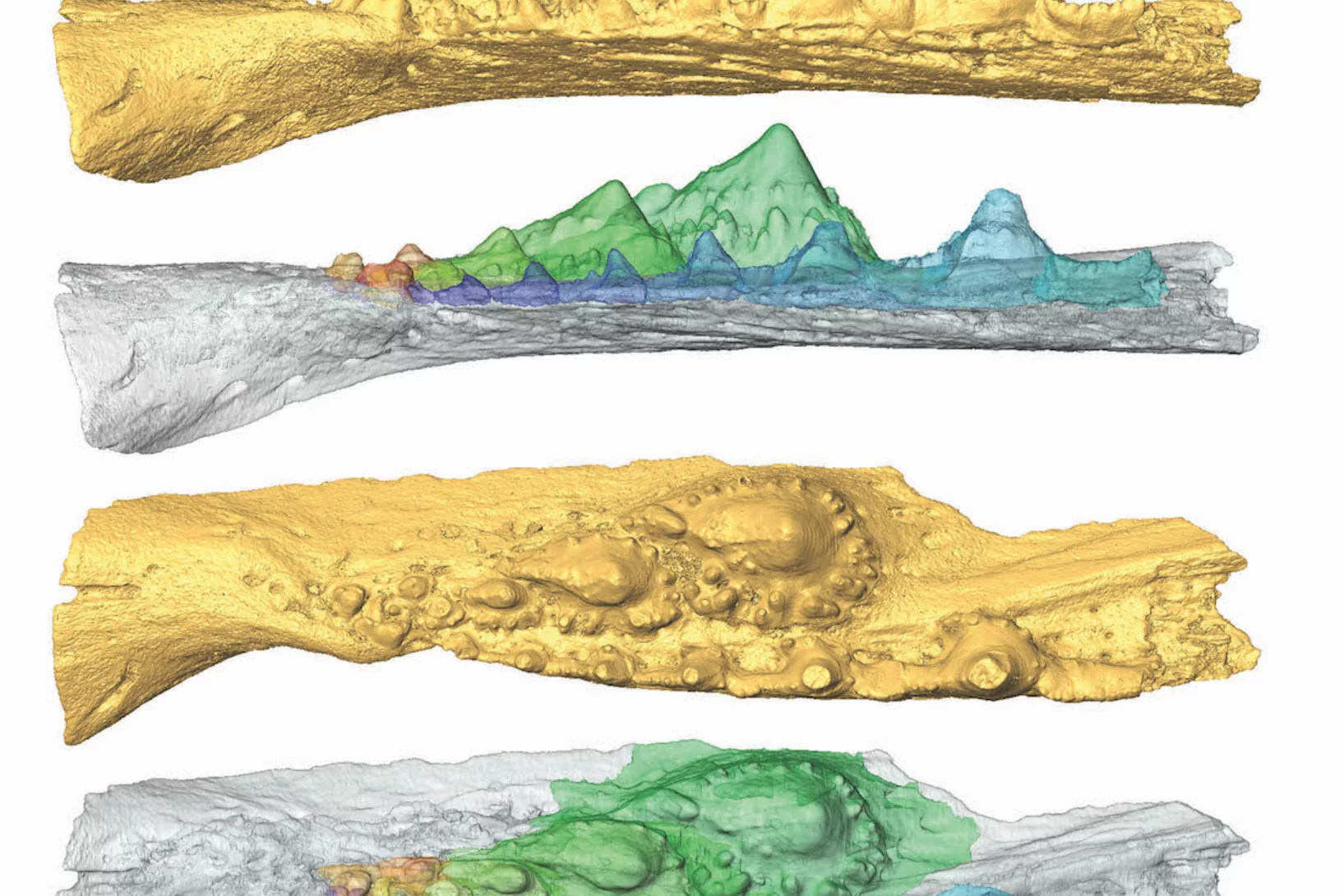
Deep evolutionary origins of the human smile
Detailed characterization of the tooth and jaw structure and development among shark ancestors by synchrotron based X-ray tomographic microscopy at TOMCAT led an international team of researchers from the Naturalis Biodiversity Center in Leiden and the University of Bristol to the discovery that while teeth evolved once, complex dentitions have been gained and lost many times in evolutionary history.
Coordination-Driven Monolayer-to-Bilayer Transition in Two-Dimensional Metal–Organic Networks
Scientists at LMN and the University of Basel have discovered a nucleation and growth mechanism of metal-organic coordination networks in Langmuir Blodgett films floating on water.
New record photon pulse energies at SwissFEL
The very large number of coherent photons produced by free-electron lasers is one of the key qualities of such facilities, attracting users from numerous research fields including chemistry, biology and materials science. Recently, the two branches of PSI's free-electron laser SwissFEL each have reached new record pulse energies, packing more photons than ever before into ultrashort X-ray pulses delivered at rates of 100 Hz to the users of both beamlines.
Mehr Widerstandskraft für die Schweizer Energieversorgung
Das Forschungsprojekt SURE startet.
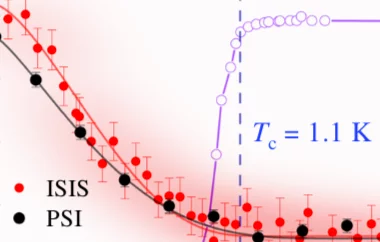
Chiral singlet superconductivity in the weakly correlated metal LaPt3P
Chiral superconductors are novel topological materials with finite angular momentum Cooper pairs circulating around a unique chiral axis, thereby spontaneously breaking time-reversal symmetry. They are rather scarce and usually feature triplet pairing: a canonical example is the chiral p-wave state realized in the A-phase of superfluid He3. Chiral triplet super- conductors are, however, topologically fragile with the corresponding gapless boundary modes only weakly protected against symmetry-preserving perturbations in contrast to their singlet counterparts. Using muon spin relaxation measurements ...
Die Informatiklernenden haben trotz aller Corona-Widrigkeiten ihre IPA erfolgreich abgeschlossen
Für die Lernenden am PSI waren die vergangenen Monate nicht leicht. Sie mussten während der Pandemie im Geschäft und auch in der Berufsschule weiterhin ihre Leistungen erbringen und auf einen erfolgreichen Lehrabschluss hinarbeiten. Die drei Informatik-Lernenden im vierten Lehrjahr haben diese Herausforderung bereits gemeistert und konnten in diesem Jahr Ihre Individuelle Pratktische Arbeit durchführen und abschliessen.
«Ziel ist ein experimenteller Quantencomputer im Kanton Aargau»
Die ETH Zürich und das PSI eröffnen gemeinsam einen «Quantum Computing Hub». Ein Interview mit Gabriel Aeppli und Christian Rüegg über das neue Forschungszentrum.
ETH Zürich und PSI gründen Quantum Computing Hub
Die ETH Zürich und das Paul Scherrer Institut PSI eröffnen ein gemeinsames Zentrum zur Entwicklung von Quantencomputern. Ziel ist es, die Realisierung von Quantencomputern sowohl auf Basis von Ionenfallen als auch von supraleitenden Bauteilen voranzutreiben.
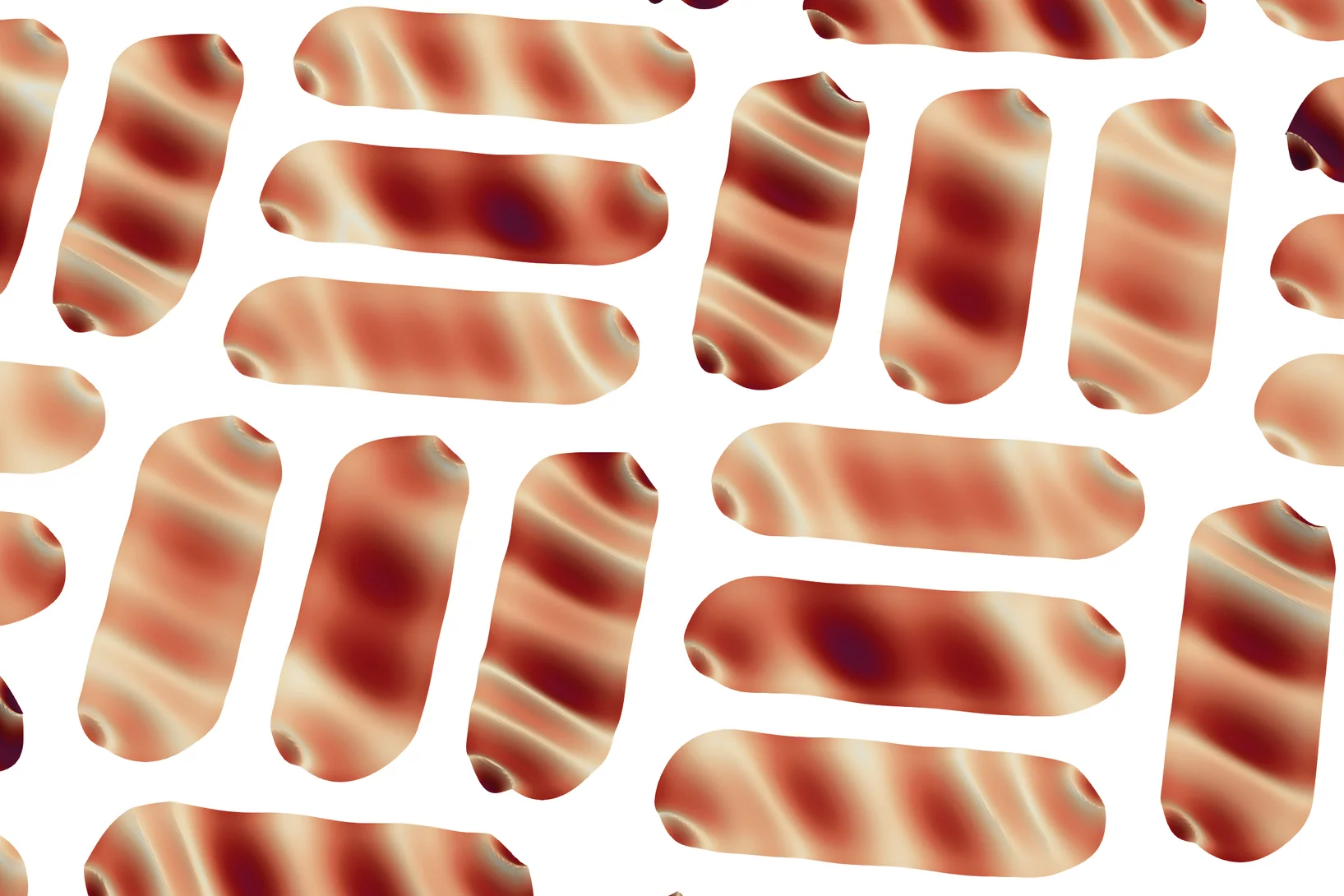
Spin-wave dynamics in a chiral artificial spin system
Artificial spin ices are periodic arrangements of interacting nanomagnets which allow investigating emergent phenomena in the presence of geometric frustration. Recently, it has been shown that artificial spin ices can be used as building blocks for creating functional materials, such as magnonic crystals. Scientists have now investigated the GHz dynamics in a spin ice with a chiral geometry. They found that the system possesses a rich spin-wave spectrum owing to the presence of anisotropic magnetostatic interactions. These results contribute to the understanding of GHz magnetization dynamics in spin ices and are relevant for the realization of reconfigurable magnonic crystals based on spin ices.
Fachkräftemangel: Neue Perspektiven für Nachwuchsforschende in der Industrie
Arbeitgeber sprechen von Fachkräftemangel, während Nachwuchsforschende häufig nicht so genau wissen, wo nach der nächsten beruflichen Herausforderung suchen. Die Verstärkung der Brücke zwischen Akademie und Industrie am PSI kann helfen, beiden Seiten neue Perspektiven zu eröffnen.
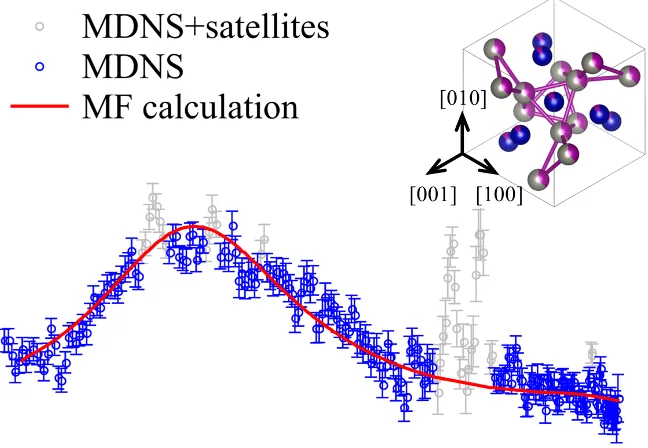
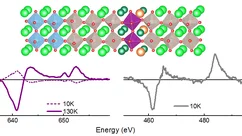
Charge Condensation and Lattice Coupling Drives Stripe Formation in Nickelates
Revealing the predominant driving force behind symmetry breaking in correlated materials is sometimes a formidable task due to the intertwined nature of different degrees of freedom. This is the case for La2−xSrxNiO4+δ, in which coupled incommensurate charge and spin stripes form at low temperatures. Here, we use resonant x-ray photon correlation spectroscopy to study the temporal stability and domain memory of the charge and spin stripes in La2−xSrxNiO4+δ.
Zuwachs bei den Datenwissenschaften
Am PSI wird ein weiterer Standort des Swiss Data Science Center entstehen. Der Ausbau soll den Datenwissenschaften in der Schweiz einen weiteren Schub verleihen.
New SSC Access rules
Due to the Corona pandemic starting 1. May 2021, new access rules to the SSC user facilites will apply. More details can be found at https://www.psi.ch/de/lmx-ssc/access-rules.
COVID-19: Test obligation for external PSI users
From May 1, 2021 on all external users of the PSI facilities SLS, SwissFEL, SINQ, SμS and CHRISP must present a certificate of a negative PCR test for SARS-CoV-2 (with the date of the result being not older than 72 hrs when arriving at PSI, NO self-testing). A full COVID-19 vaccination with the last dose received at least two weeks earlier than your arrival date at PSI as well as a full recovery from COVID-19 do replace a negative PCR test.
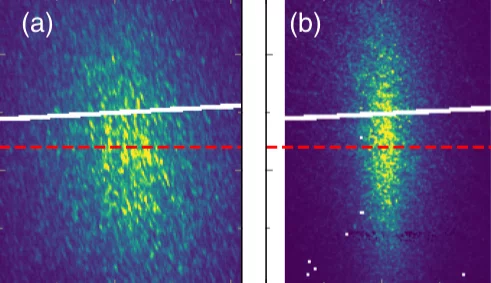
Frustration-driven magnetic fluctuations as the origin of the low-temperature skyrmion phase in Co7Zn7Mn6
Magnetic skyrmions in chiral cubic helimagnets, are stabilized by thermal fluctuations over a narrow region directly below the magnetic ordering temperature. Due to often being touted for use in applications, there is high demand to identify new mechanism that can expand the equilibrium skyrmion phases where these topological vortices may display an enhanced robustness against external perturbations, such as magnetic fields, due to a larger magnetic order parameter.
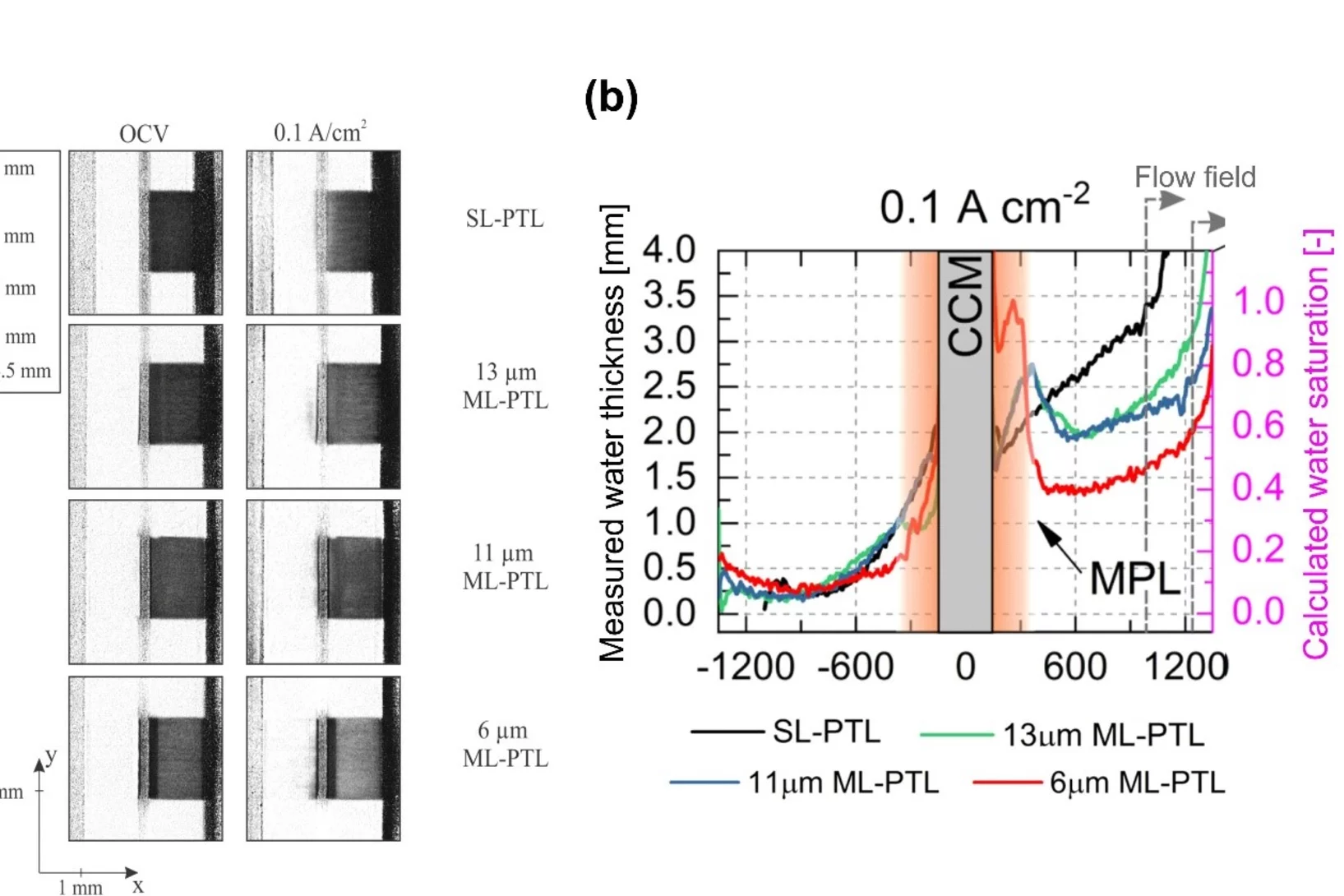
Impact of micro-porous layers (MPL) on two-phase flow in electrolyzers
Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolyzers (PEWE), due to their excellent dynamic characteristics, can provide an economical solution to the intermittent nature of new renewable sources, by converting the excess electricity into hydrogen. However, improvements in efficiency and in capital cost are still required for the large-scale deployment of this solution. In this context, we studied whether the efficiency improvements observed when using porous structures featuring a micro-porous layer (MPL) can be attributed to a better distribution of the water.
Einmalig scharfer Röntgenblick
Ein neues Verfahren des PSI erlaubt die quantenphysikalische Erforschung von Materialien mithilfe von Röntgenlasern.
Christian Bauer interviewed on Electric Cars at the program Treffpunkt by SRF
SRF interviewed Christian Bauer, a scientist at PSI's Laboratory for Energy Systems Analysis who specialises in life cycle and sustainability analyses, on Electric Cars
A time-domain phase diagram of metastable quantum states
Our collaborators at the Jozef Stefan Institute – the leading author, Jan Ravnik, is now a PSI Fellow at LMN – report a ‘dynamical’ phase diagram of metastable quantum states generated via photoexcitation of the prototypical dichalcogenide material 1T-TaS2.
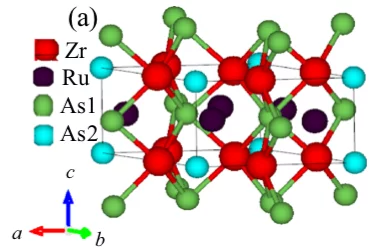
Probing the superconducting gap structure in the noncentrosymmetric topological superconductor ZrRuAs
The superconducting gap structure of the topological superconductor candidate ZrRuAs with a noncen- trosymmetric crystal structure has been investigated using muon-spin rotation/relaxation (μSR) measurements in transverse-field (TF) and zero-field (ZF) geometries. Magnetization, electrical resistivity, and heat capacity measurements reveal bulk superconductivity below a superconducting transition temperature Tc = 7.9(1) K.
Hindering the magnetic dead layer in manganites
The authors demonstrate the stability of ferromagnetic order of one unit cell thick optimally doped manganite (La0.7Ba0.3MnO3, LBMO) epitaxially grown between two layers of SrRuO3 (SRO). LBMO shows ferromagnetism even above SRO Tc. Density Functional Theory calculations help understand the reasons behind this interesting result.
New group member
Cornelius Hempel officially joins LMN as group leader "Ion Traps". We wish him every success for the future!
Was Wasser mit Quantenmagneten gemein hat
Bei hohem Druck verschmelzen flüssiges Wasser und Wasserdampf – die Phasengrenze verschwindet. Forschende haben jetzt ein ähnliches Verhalten in einem Quantenmagneten entdeckt.
A quantum magnetic analogue to the critical point of water
At the liquid–gas phase transition in water, the density has a discontinuity at atmospheric pressure; however, the line of these first-order transitions defined by increasing the applied pressure terminates at the critical point, a concept ubiquitous in statistical thermodynamics. In correlated quantum materials, it was predicted and then confirmed experimentally that a critical point terminates the line of Mott metal–insulator transitions, which are also first-order with a discontinuous charge carrier density. In quantum spin systems, continuous quantum phase transitions have been controlled by pressure, applied magnetic field and disorder, but discontinuous quantum phase transitions have received less attention.
Women in Engineering Materials highlights Dr. Lucia Romano's work
The paper "High aspect ratio grating microfabrication by Pt assisted chemical etching and Au electroplating” by Dr. Lucia Romano & coauthors has been highlighted in the "Women in Engineering Materials" Virtual Issue published on Advanced Engineering Materials. This Virtual Issue draws attention to outstanding works within Materials Science created under the lead of women as principal investigators.
Congratulations to Lucia and the x-ray optics design and fabrication team!
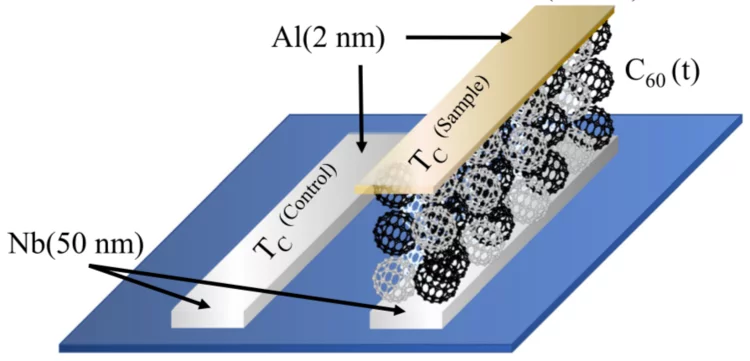
Spin-singlet to triplet Cooper pair converter interface
Combining magnetic and superconducting functionalities enables lower energy spin transfer and magnetic switching in quantum computing and information storage, owing to the dissipationless nature of quasi-particle mediated supercurrents. Here, we put forward a system where emergent spin-ordering and diffusion of Cooper pairs are achieved at a non-intrinsically magnetic nor superconducting metallo-molecular interface.