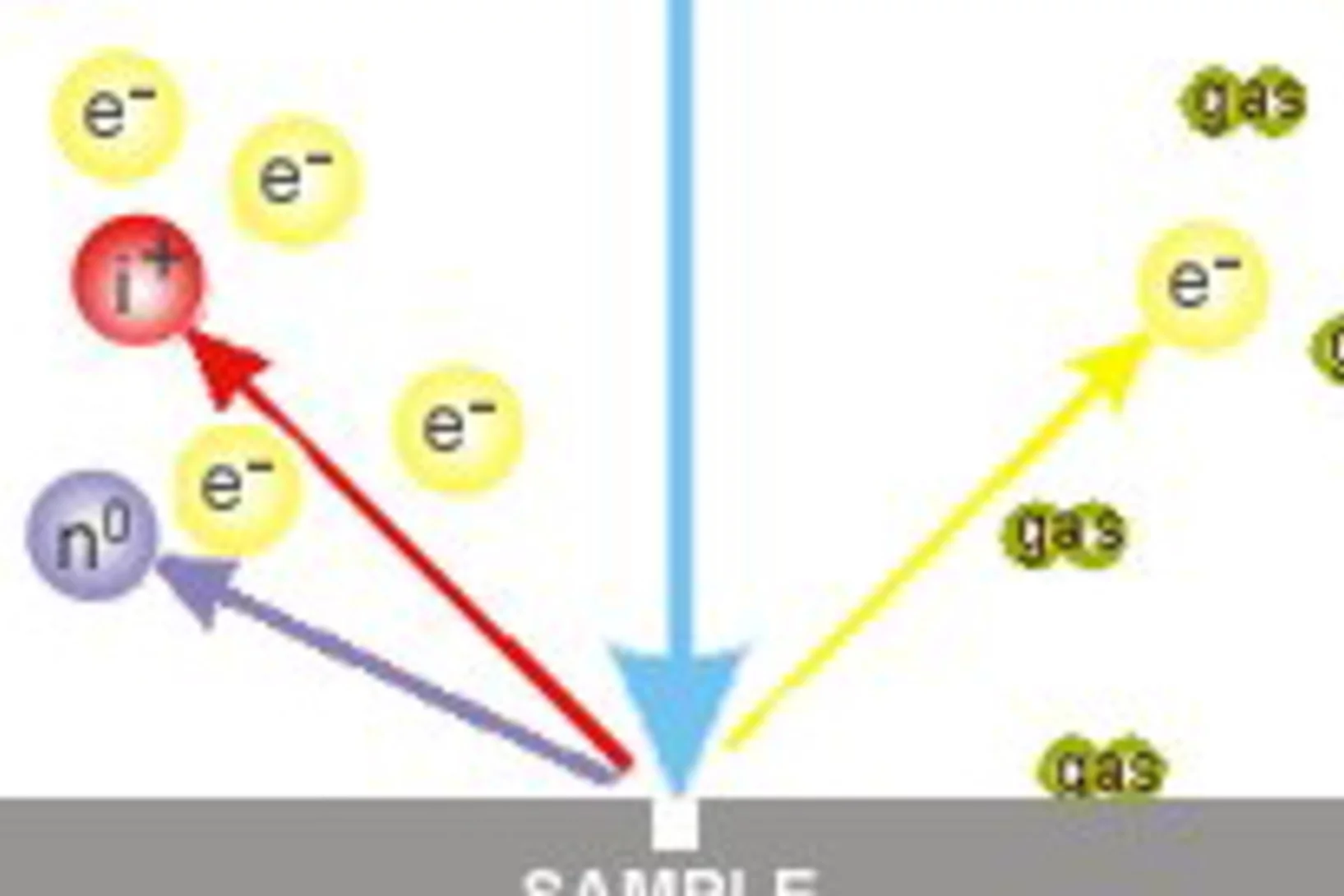
Am PSI widmen sich mehrere Projekte wichtigen Forschungsfragen rund um das Coronavirus Sars-CoV-2 und den daraus resultierenden Erkrankungen. Wir informieren über Aktivitäten und Vorhaben, zum Beispiel zu Untersuchungen von Lungengewebe, zur Produktion von Proteinen und Antikörpern oder über Ideen für neue Forschung zu Covid-19.
Nützliche Links
Petersen Investigator award in 2018 goes to the Center for Radiopharmaceutical Sciences at PSI
The Neuroendocrine Tumor Research Foundation (NETRF) is committed to funding the most promising research in order to discover cures and more effective treatments for carcinoid, pancreatic, and related neuroendocrine cancers. In January 2018 the Board of Directors has awarded a Petersen Investigator award to the team of Professor Roger Schibli for their research proposal titled, “Simultaneous Auger-Electron and β--Particle Therapy of Metastasized NET Using 161Tb-DOTATOC”. more info(link is external)
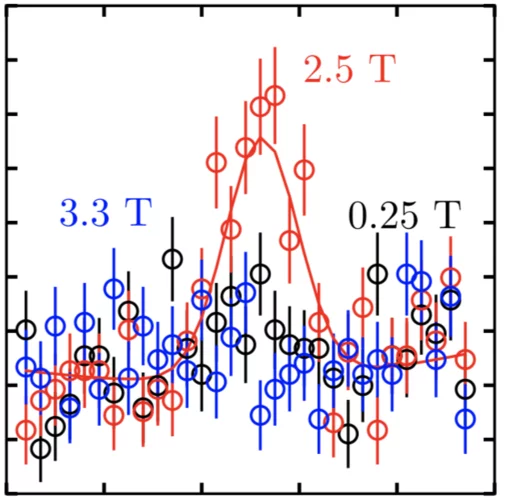
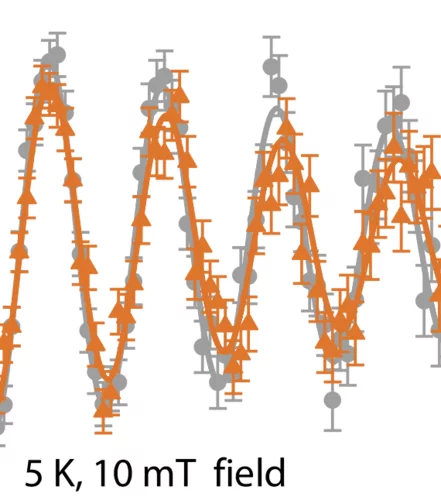
Multi-q Mesoscale Magnetism in CeAuSb2
We report the discovery of a field driven transition from a single-q to multi-q spin density wave (SDW) in the tetragonal heavy fermion compound CeAuSb2. Polarized along c, the sinusoidal SDW amplitude is 1.8(2)μB/Ce for T<N=6.25(10)K with a wave vector q1=(η,η,1/2) [η=0.136(2)]. For H || c, harmonics appearing at 2q1 evidence a striped magnetic texture below μ0H1=2.78(1) T.
Lausanne-Villigen retour
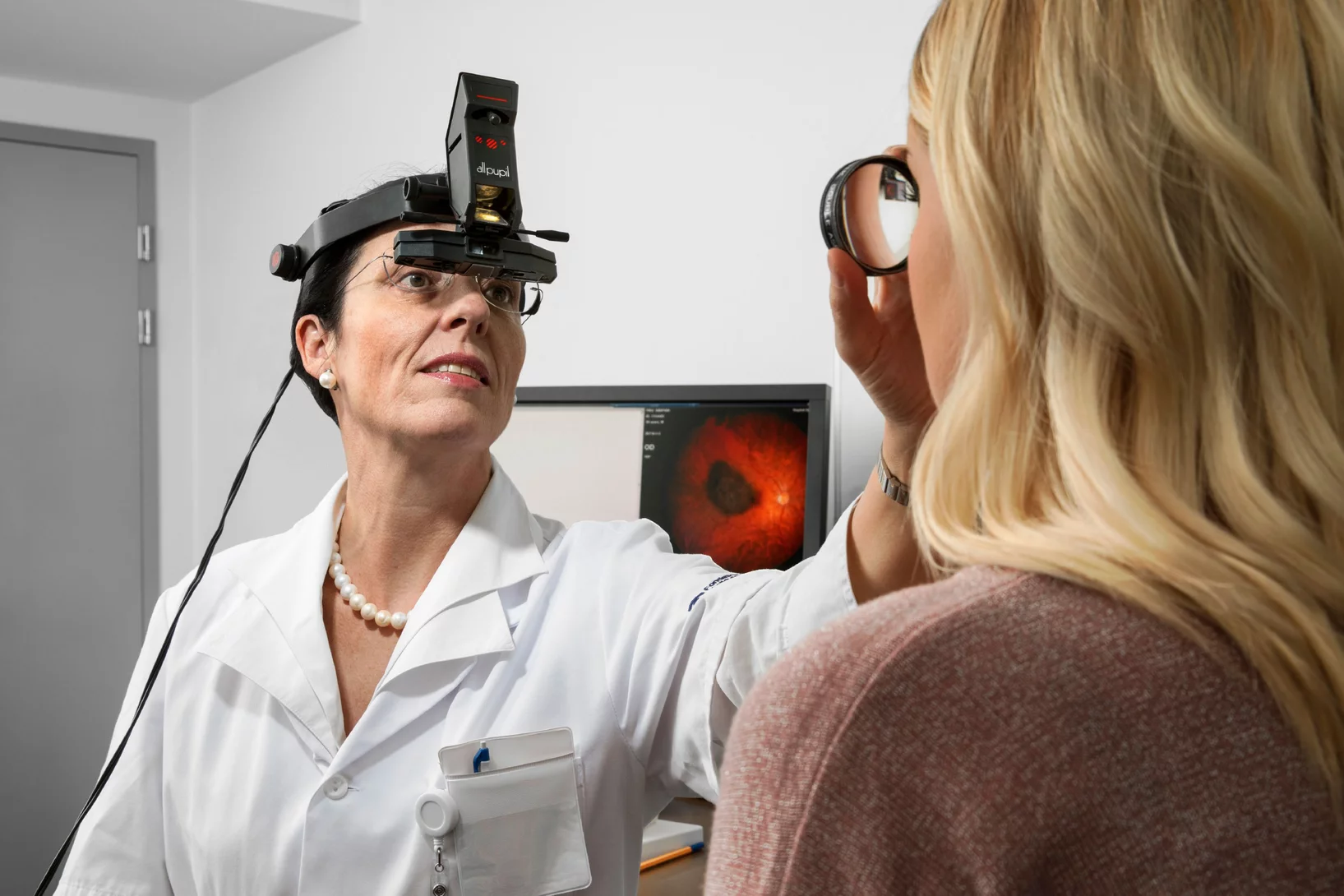
Nirgendwo auf der Welt wurden bereits so viele Augentumore mit Protonen bestrahlt wie am PSI. Doch bevor die betroffenen Patienten nach Villigen gehen, müssen sie nach Lausanne: zur Vorbehandlung bei Ann Schalenbourg in der Jules-Gonin-Augenklinik. Die seit mehr als dreissig Jahren bestehende Zusammenarbeit zwischen der Klinik und dem PSI ist einzigartig und rettet den meisten Patienten ihr krankes Auge.
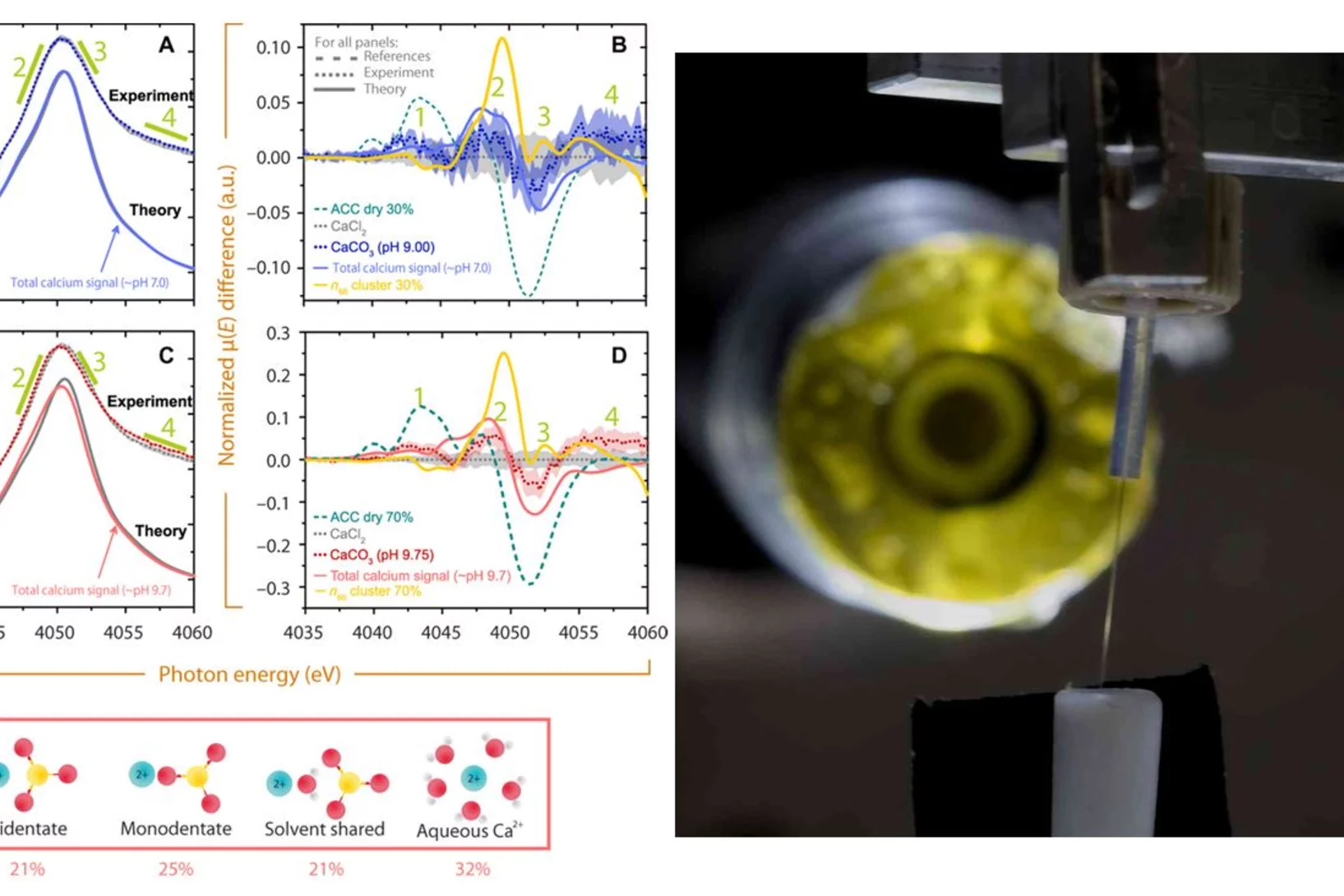
Are supersaturated calcium carbonate solutions classical or non-classical ?
Classical theory predicts that supersaturated carbonate solutions consist mostly of ions and ion pairs, with a small number of larger clusters present in the solution. The population of the different sized clusters in a solution is solely defined by the cluster’s size dependent Free Energy. If clusters are large enough they serve as nucleation germs for a new solid phase. The nucleation occurs once the surface free energy barrier posed by the new solid-liquid interface is overcome by the free energy win from bulk phase growth.
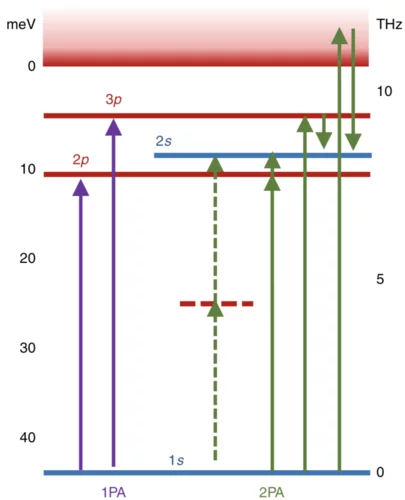
Giant multiphoton absorption points towards new methods for THz quantum control
In findings recently published in Nature Photonics, a team including researchers from the UK, the Netherlands and Photon Sciences division head Gabriel Aeppli have investigated multi-photon THz absorption in Si:P. Their studies, using the THz free-electron laser FELIX, discovered a two photon absorption cross-section ten orders of magnitude higher than that of a natural hydrogen atom and may enable new methods in quantum control. In addition to the original publication their findings are also discussed in a 'News and Views' article.
Quasistatic antiferromagnetism in the quantum wells of SmTiO3/SrTiO3 heterostructures
High carrier density quantum wells embedded within a Mott insulating matrix present a rich arena for exploring unconventional electronic phase behavior ranging from non-Fermi-liquid transport and signatures of quantum criticality to pseudogap formation. Probing the proposed connection between unconventional magnetotransport and incipient electronic order within these quantum wells has however remained an enduring challenge due to the ultra-thin layer thicknesses required.
Crystal-to-Crystal Transition of Ultrasoft Colloids under Shear
Ultrasoft colloids typically do not spontaneously crystallize, but rather vitrify, at high concentrations. Combining in situ rheo–small-angle-neutron-scattering experiments and numerical simulations we show that shear facilitates crystallization of colloidal star polymers in the vicinity of their glass transition. With increasing shear rate well beyond rheological yielding, a transition is found from an initial bcc-dominated structure to an fcc-dominated one.
Profitabel für beide Seiten
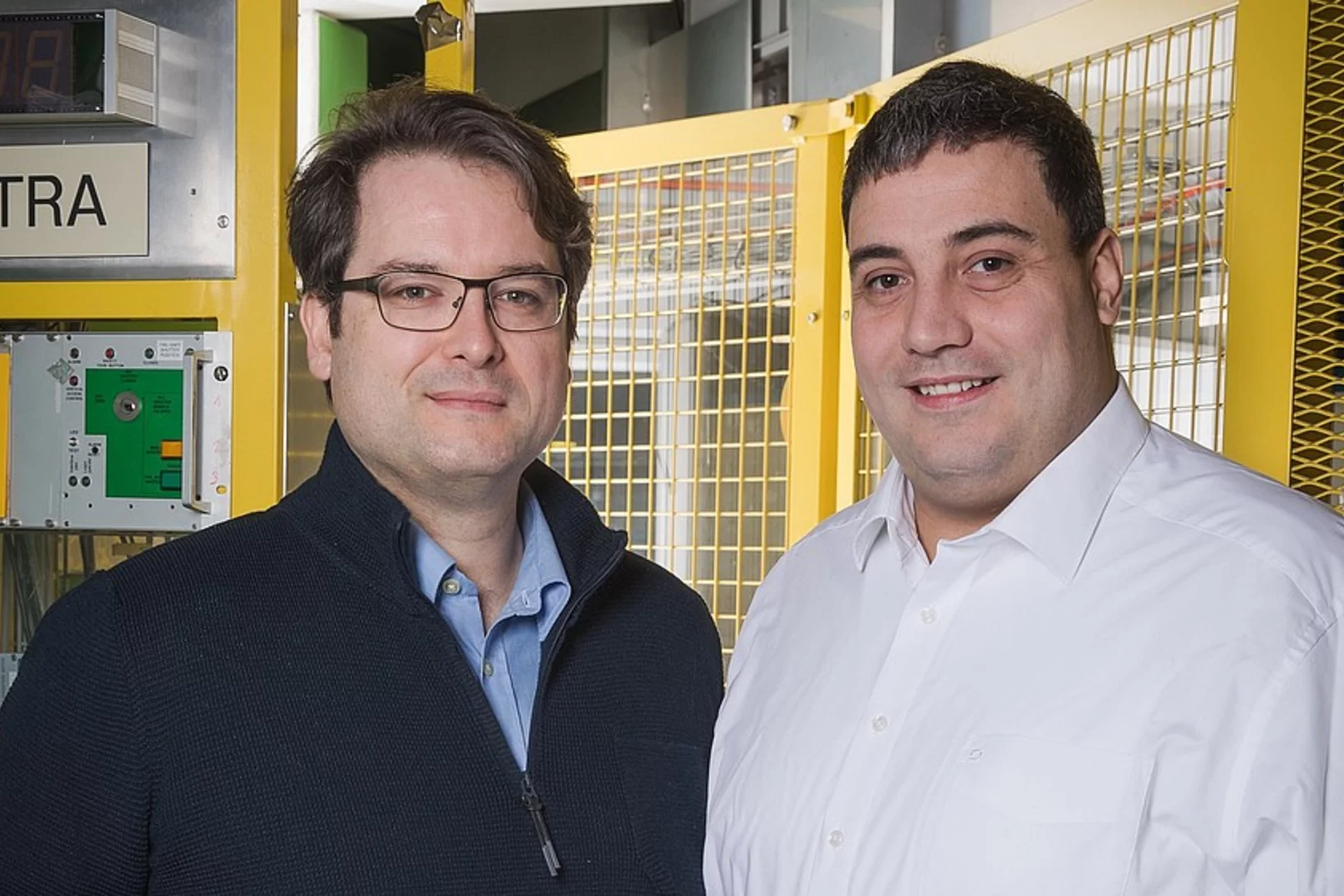
In Freiburg sitzt das junge Unternehmen Swiss Hydrogen. Hier wird an konkurrenzfähigen Hochleistungs-Brennstoffzellen getüftelt, die sich in umweltfreundlichen Fahrzeugen oder stationär als Stromerzeuger einsetzen lassen. Von der Zusammenarbeit mit dem PSI profitieren beide Seiten, erzählt Geschäftsführer Alexandre Closset im Interview.
Review of Mu3e at PSI
Mu3e has passed a detailed review at the PSI proton accelerator users meeting. Beam time in 2018 was granted for tests of the timing and pixel detectors as well as for further development of the compact muon beam line (CMBL).
Bildgebung am Paul Scherrer Institut hilft Aargauer ABB-Standort bei der Produktionssteigerung
Konkrete Empfehlungen zur Produktionssteigerung von Keramikbauteilen erhielt der ABB-Standort Wettingen. Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI hatten die Bauteile mittels Neutronen-Bildgebung untersucht. Anhand der Aufnahmen konnten die ABB-Mitarbeitenden sehen, wo es noch Potenzial für eine Prozessoptimierung gibt. Diese Machbarkeitsstudie wurde vom Hightech Zentrum Aargau gefördert.
Eine Technologie im Praxistest
Das Unternehmen Energie 360° mit Sitz in Zürich liefert schweizweit Erdgas, Biogas und Holzpellets. Jetzt hat es mit dem Paul Scherrer Institut PSI eine neue Power-to-Gas-Technik erfolgreich getestet, die im Bereich der Biogas-Herstellung eingesetzt wird. Das Gemeinschaftsprojekt wurde mit dem Schweizer Energiepreis Watt d’Or 2018 ausgezeichnet. Bereichsleiter Peter Dietiker erzählt im Interview von der Zusammenarbeit mit dem PSI.
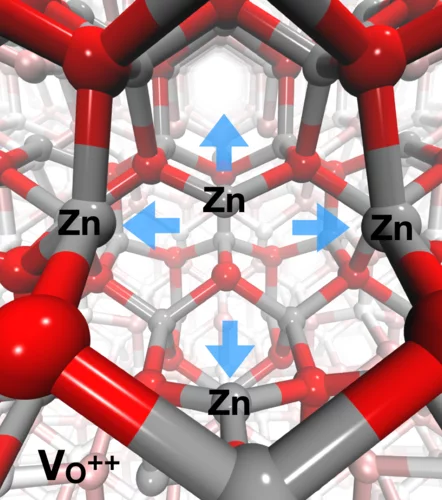
Identification of hole trapping sites in ZnO nanomaterials
Members of the Alvra group led an investigation into the fate of charge carrier dynamics in metal oxide semiconductor nanomaterials. The experiments were performed at the Advanced Photon Source (Argonne, IL, USA) and used a PSI-designed von Hamos geometry X-ray emission spectrometer that was constructed for the experiment to perform resonant XES measurements on a solution of 32 nm diameter ZnO nanoparticles photo-excited with 3.2 eV (355 nm) short laser pulses. The measurement showed that the hole-trapping takes place within less than 100 ps and the trapping site in the ZnO crystal lattice is at oxygen vacancies in the lattice. The trapping of the hole results in a local structural distortion, where the four neighbouring Zn atoms move away from the vacancy. The measurement demonstrated the strength of the RXES technique's ability to probe both the electronic and geometric structure of materials and the results were recently published in Nature Communications.
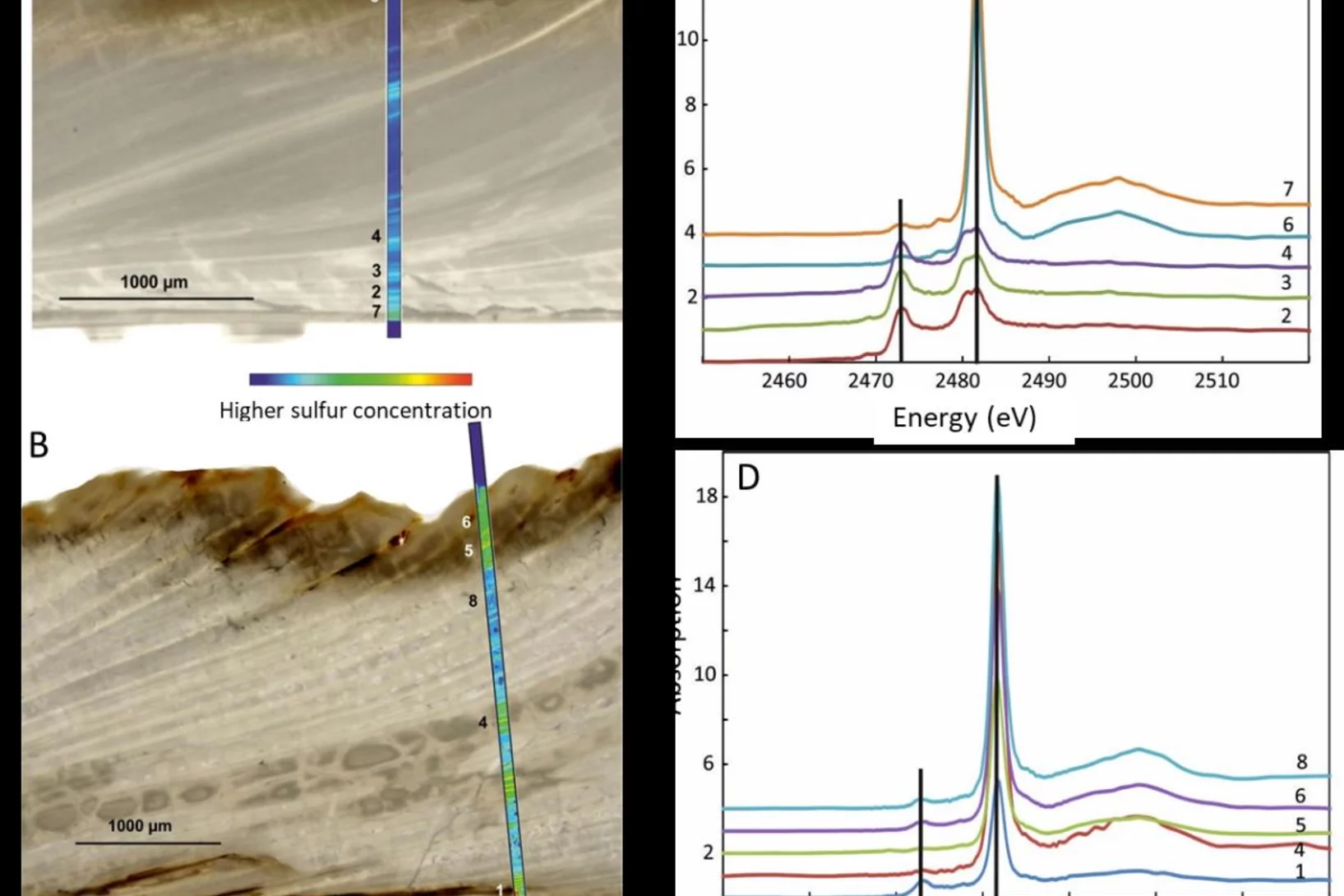
How is sulfur incorporated in biogenic carbonates and how is it affected by hydrothermal alteration?
Sulfate in biogenic carbonates is an important proxy for reconstructing the marine sulfur cycle. To investigate the exact location of carbonate associated sulfate (CAS) in biogenic carbonates and the effects of diagenetic alteration on sulfur in carbonates, shells of the marine bivalve Arctica islandica were artificially altered in modified seawater. Sulfur XANES analyses showed that CAS in A. islandica is indeed incorporated into the mineral part of the pristine shell, most likely as a hydrated or partly hydrated sulfate phase. The multi-analytical approach of XANES and µ-XRF analyses, sulfur isotope measurements, NanoSIMS analyses, and microstructural analysis on thin-sections of the shell samples further revealed that the different sulfur in a bivalve shell sensitively reacts to artificially induced hydrothermal alteration.
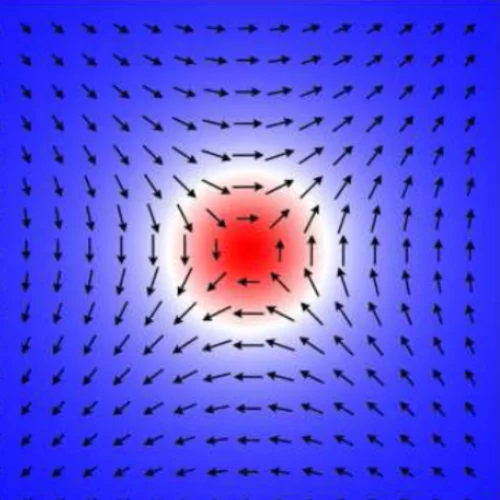
Three Dimensional Polarimetric Neutron Tomography of Magnetic Fields
Through the use of Time-of-Flight Three Dimensional Polarimetric Neutron Tomography (ToF 3DPNT) we have for the first time successfully demonstrated a technique capable of measuring and reconstructing three dimensional magnetic field strengths and directions unobtrusively and non-destructively with the potential to probe the interior of bulk samples which is not amenable otherwise.
Photoinduced transitions in magnetoresistive manganites: A comprehensive view
Using the FEMTO slicing source at SLS, we have studied the structural response during the photoinduced transition in a charge-ordered Pr1-xCaxMnO3 thin films. By investigating the dynamics of both superlattice reflections and regular Bragg peaks, we disentangle the different structural contributions and analyze their relevant time-scales. Comparing these results with studies of the charge order and magnetic dynamics, a comprehensive picture of the phase transition linked to a single critical fluence fc is proposed.
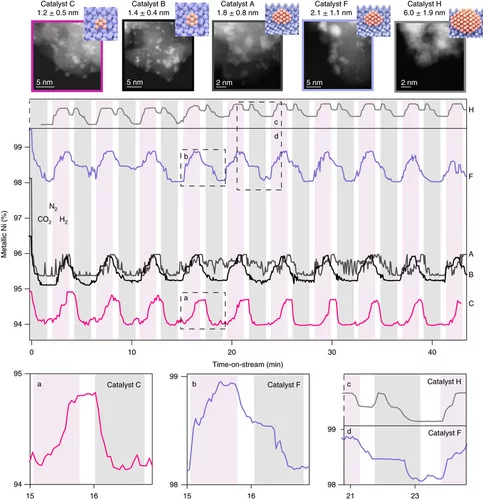
Unravelling structure sensitivity in CO2 hydrogenation over nickel
Using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (1–7 nm) and advanced characterization methods it was proved how structure sensitivity influences the mechanism of catalytic CO2 reduction, the nature of which has been long debated.
Nutzen, was da ist
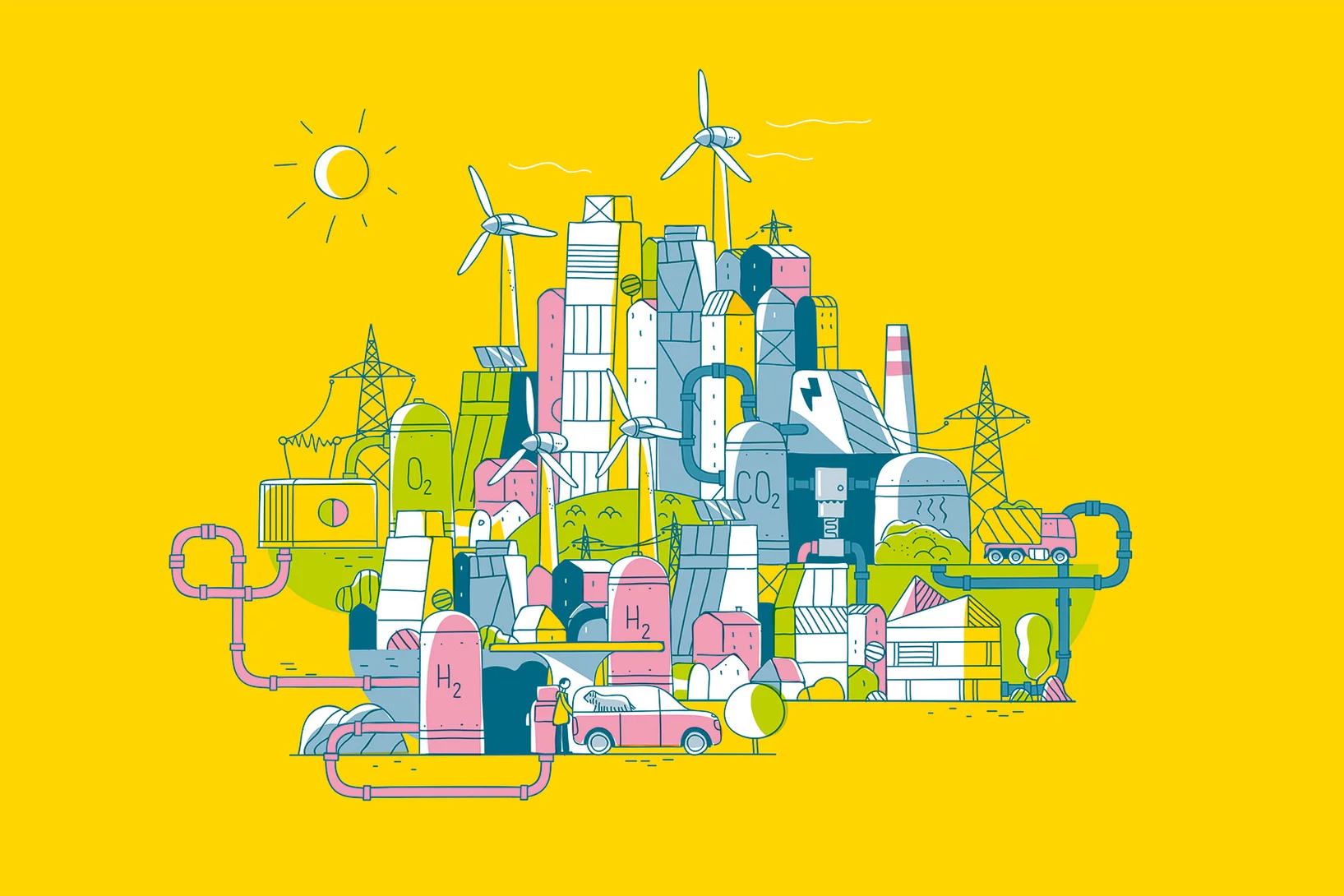
Am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI suchen Forschende nach Lösungen, wie man die Energie aus Sonne, Wind oder Biomasse effizient in das Schweizer Energiesystem integrieren kann.
Neutron radiography of detrimental hydrogen in nuclear fuel claddings
Hydrogen is at the source of degradation mechanisms affecting mechanical properties of many structural metal materials. In nuclear power plants, zirconium alloy fuel cladding tubes take up a part of the hydrogen from coolant water due to oxidation. Because of the high mobility of hydrogen interstitial atoms down temperature and concentration gradients and up stress gradients, hydrogen distribution in fuel claddings can often be non-uniform, arising the risk for the integrity of spent fuel rods under mechanical load. At the Laboratory of Nuclear Materials (LNM) in collaboration with the Laboratory of Neutron Scattering and Imaging (LNS), hydrogen redistribution in zirconium alloys was quantified by neutron radiography using the state-of-the-art detector of PSI Neutron Microscope, and the concentration was computed based on thermodynamics, to predict hydrogen diffusion and precipitation for used nuclear fuel.
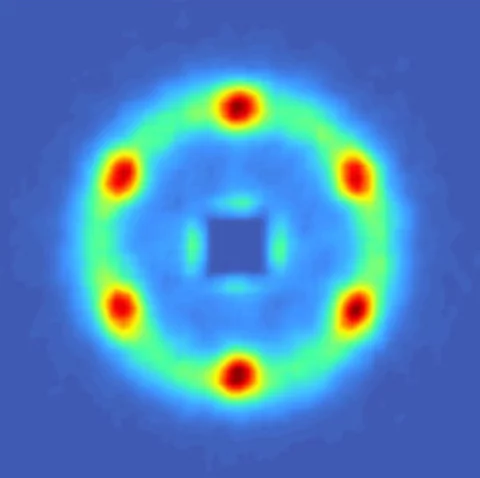
Low-Field Bi-Skyrmion Formation in a Noncentrosymmetric Chimney Ladder Ferromagnet
The real-space spin texture and the relevant magnetic parameters were investigated for an easy-axis non-centrosymmetric ferromagnet Cr11Ge19 with Nowotny chimney ladder structure. Using Lorentz transmission electron microscopy,we report the formation of bi-Skyrmions,i.e., pairs of spin vortices with opposite magnetic helicities.
PSI-Feriencamp 2018
Suchen Sie für Ihr Kind ein spannendes Angebot während den Sommerferien? Möchten Sie in ihm die Neugier und Begeisterung für naturwissenschaftlich-technische Themen wecken? Die Berufsbildung und das Komitee für Chancengleichheit führt dieses Jahr zum achten Mal das PSI-Feriencamp durch!
For the second time on the cover of Journal of Physical Chemistry
For the second time on the cover page of Journal of Physical Chemistry.
Effiziente Energie aus Bioabfällen – Watt d'Or für PSI und Energie 360°
Die Energie aus Bioabfällen effizient nutzen: Eine am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI entwickelte und gemeinsam mit dem Zürcher Energieversorger Energie 360° erfolgreich getestete Technologie macht das möglich. Sie holt deutlich mehr Biomethan aus den Abfällen heraus als herkömmliche Verfahren. Für diesen wichtigen Beitrag zu einer nachhaltigen Energieversorgung wurden das PSI und Energie 360° nun in der Kategorie Erneuerbare Energien mit dem Watt d’Or 2018 des Bundesamtes für Energie ausgezeichnet.
Successful PhD Defense
Anna Dal Farra successfully defended her PhD at the University of Bern, entitled "Effect of light-absorbing impurities on the albedo of the Alpine glacier Plaine Morte". The project was jointly funded by the University of Bern and the Paul Scherrer Institut.
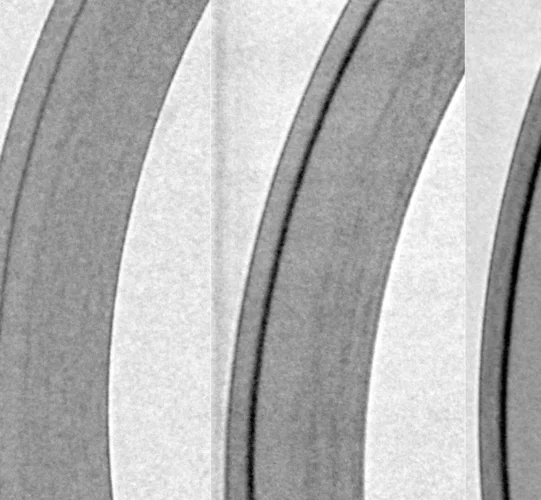
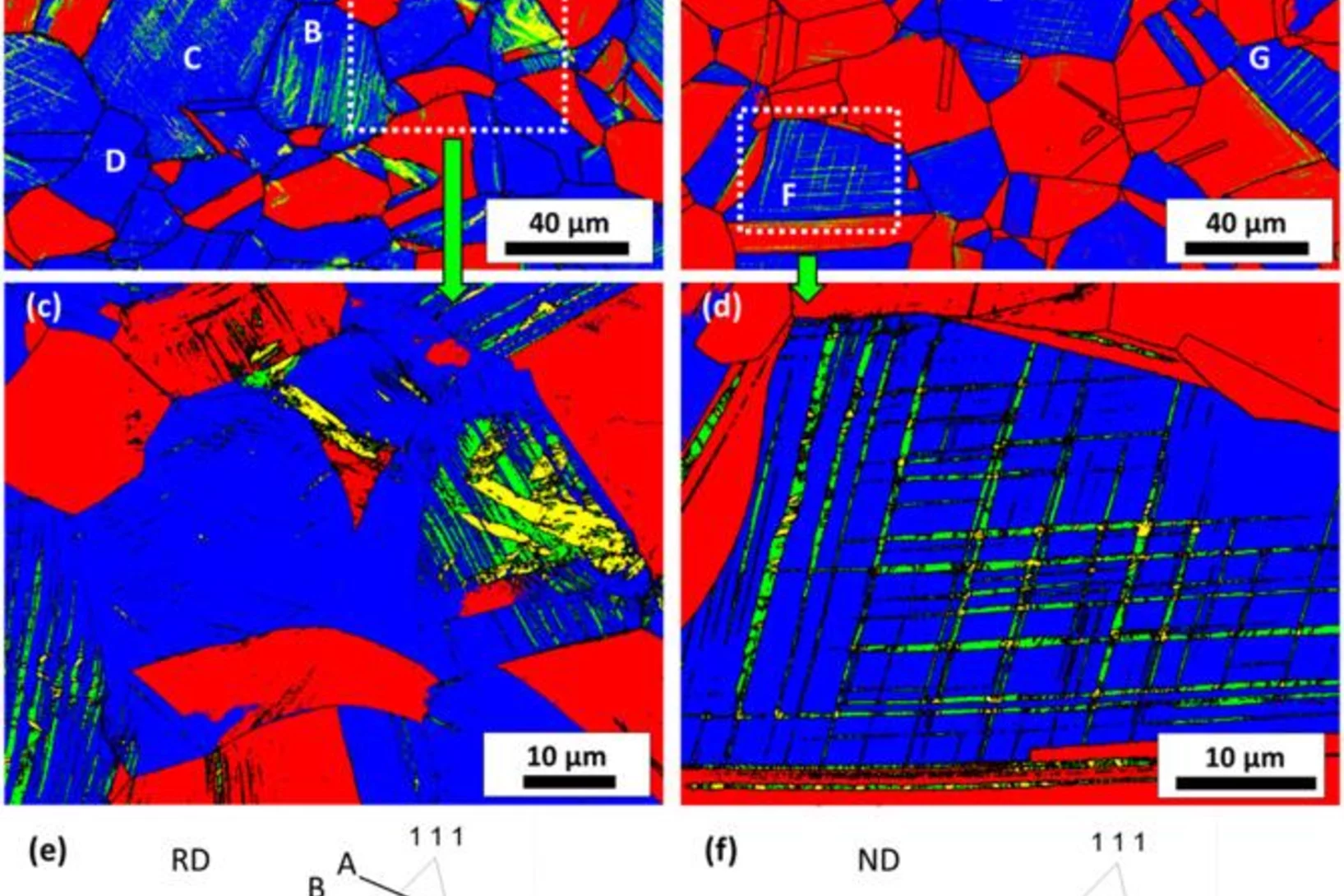
Suppressed martensitic transformation under biaxial loading in low stacking fault energy metastable austenitic steels
In-situ neutron diffraction studies performed on metastable 201 stainless steel combined with EBSD measurements confirm that ε-martensite is a precursor for α′-martensite during uniaxial and equibiaxial deformation at the same loading rate. In both loading states, the grains that contain martensite belong to orientations for which the leading partial dislocations have higher Schmid factor than the trailing partial dislocations. The martensitic transformation is suppressed during equibiaxial loading as a consequence of the different textures formed during deformation.
UO2 fuel behavior at very high burnup
The investigation of the nuclear fuel at very high burnup is critical for evaluating the safety margin for the evaluated fuel in normal as well as in accidental conditions. PSI is one of the very few hot laboratories which possess access to irradiated UO2 fuel with very high burnup from commercial reactors. The application of relevant tools for the investigation, handling and analysis of those highly irradiated materials emphasize the necessary expertise.
New Focused Ion Beam (FIB) in the Hot Laboratory
The implementation of Focused Ion Beam instruments in material research laboratories during the last decade has not only strongly improved the preparation of very thin specimens for the Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM), in particular at interfaces, but also led to the development of new analysis methods inside the instrument itself. It became a powerful instrument for the analyses of highly radioactive materials, because it allows for the production and analysis of very small specimens that can be then analyzed with very sensitive detectors without strong interference from the radiation field of the specimen itself.
Johannes Ihli's article makes it into ESRF Highlights
ESRF Highlights 2017 features work of researchers from the Laboratory of Catalysis and Sustainable Chemistry, the Photon Science Division at Paul Scherrer Institut and the ESRF, Grenoble, France.
Welcome Anthony Boucly
Join me in welcoming Anthony, our new postdoc, jointly affiliated with Markus Ammann’s Surface Chemistry group (Surface Chemistry) and within the Electrochemistry Laboratory (Laboratory of Electrochemistry), the group for Electrocatalysis and Interface headed by Prof. Thomas Schmidt under the supervision of Emiliana Fabbri.
He obtained his PhD from the University of Pierre et Marie Curie in Paris, in the Laboratory of Chemical Physics – Materials and Radiation. The title of his dissertation was “Catalytical Reactions and Environmnetal Chemistry Modifications as seen by Synchrotron Radiation NAP-XPS”. He is trained in surface chemistry and surface analysis methods.
At PSI, Anthony Boucly will be studying the electrochemical interaction between electrolytes and metal oxides relevant for electrochemical applications and for the weathering of mineral dust particles in the atmosphere with X-Ray photoelectron spectroscopy at the Near Ambient Pressure Photoemission (NAPP) endstation at SLS.
Refurbishment of HZ6
The hot cell 6 is dedicated to the storage and conditioning of high level solid waste. This cell has been completely refurbished in the period 2015 – 2017. This include the complete dismantling and conditioning of the highly fuel contaminated old infrastructure, the cleaning of the cell and the installation and test of the new improved infrastructure.
Strom aus Nanomagneten
Oles Sendetskyi, Gewinner eines Founder Fellowships am Paul Scherrer Institut PSI, will die Umpolung von Nanomagneten nutzen, um eine nachhaltige Stromquelle für Kleingeräte zu entwickeln.