Am PSI widmen sich mehrere Projekte wichtigen Forschungsfragen rund um das Coronavirus Sars-CoV-2 und den daraus resultierenden Erkrankungen. Wir informieren über Aktivitäten und Vorhaben, zum Beispiel zu Untersuchungen von Lungengewebe, zur Produktion von Proteinen und Antikörpern oder über Ideen für neue Forschung zu Covid-19.
Nützliche Links
Swiss BIC of CERN Technologies calls for innovative ideas – deadline 30th April
For the third time, Switzerland Innovation Park Innovaare in Villigen/AG is hosting the call for proposals for high-tech business ideas that incorporate accelerator technologies into their products.
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
Batteries under the neutron stroboscope
The first application of stroboscopic neutron diffraction to studying lithium-ion batteries during operation establishes a new approach to unravelling the complex processes playing out in energy-storage materials.
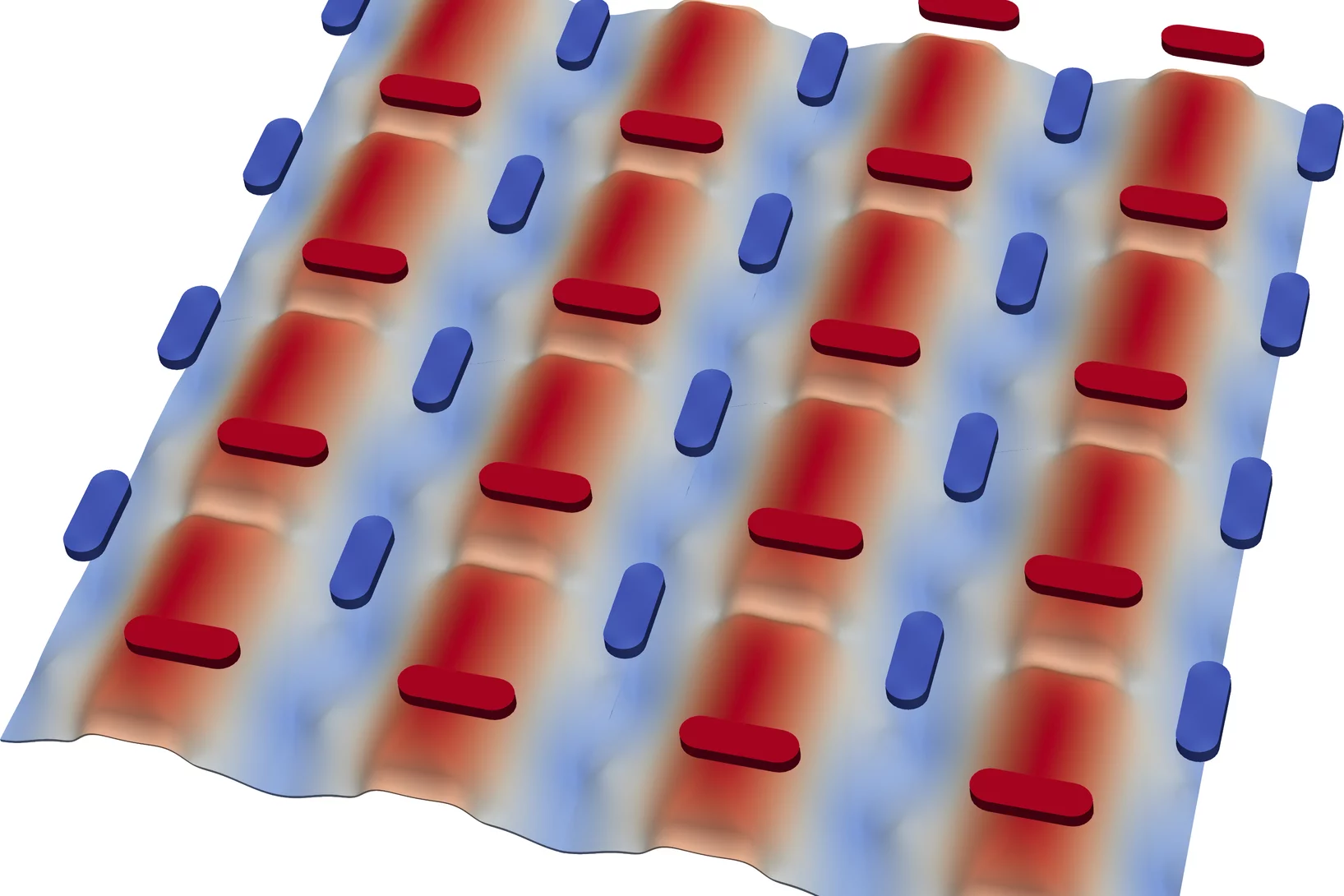
Tailoring Spin-Wave Channels in an Artificial Spin Ice
Magnonic crystals are periodic magnetic structures, which are attracting great interest because of their potential use in low-power information technology based on spin waves, or magnons. Artificial spin ices have been recently studied as reconfigurable magnonic crystals, but achieving the required combination of magnetic state reconfigurability and desired magnon dispersions remains challenging. Here, researchers propose a hybrid system that makes use of a magnetic thin film underlayer to couple and strengthen the interaction between the artificial spin ice’s nanoelements though spin waves. Moreover, the magnetic state of the artificial spin ice gives rise to directional spin wave channels in the underlayer. This hybrid system opens a new direction for band structure engineering in reconfigurable magnonic crystals.
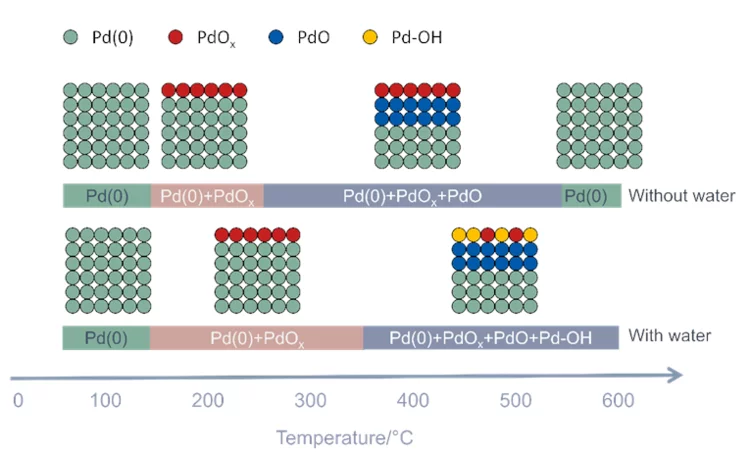
Role of water on the structure of palladium for methane complete oxidation
The mechanism of methane oxidation in the presence of water has been investigated in situ by means of APXPS.
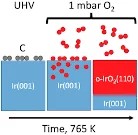
Kinetics of the Thermal Oxidation of Ir(100) Studied by APXPS
The thermal oxidation of single-crystalline Ir(100) films toward rutile IrO2(110) has been investigated in situ by means of APXPS.
Brennstoffzellenexponat im PSI forum
Anfang dieses Jahres haben die Physiklaboranten des 3. Lehrjahres das Brennstoffzellen Exponat im PSI forum repariert und auf den neusten Stand gebracht.
Warum Covid-19 ältere Menschen besonders hart trifft
Je älter man ist, desto höher ist die Gefahr, an einer Infektion mit dem Coronavirus zu sterben. G. V. Shivashankar, Gruppenleiter am PSI und Professor an der ETH Zürich, stellt in einer Veröffentlichung in «Nature Reviews» nun eine aussergewöhnliche These vor: Die Steifheit von Zellen soll für den Krankheitsverlauf eine entscheidende Rolle spielen. Im Interview erklärt er wieso.
«Im Kampf gegen das Virus zählt jeder Tag»
Die Forschungspraxis am PSI hat sich seit Ausbruch der Corona-Pandemie zwar verändert, steht aber nicht still. Gabriel Aeppli, Leiter des PSI-Forschungsbereichs für Photonenforschung, spricht über die besondere Bedrohung, die Covid-19 darstellt, und darüber, wie PSI-Forschende an der SLS und womöglich bald auch am SwissFEL dieses neue Virus untersuchen.
Prioritäre Forschung geht weiter
Das Paul Scherrer Institut PSI befindet sich aufgrund der Covid-19-Pandemie im eingeschränkten Betrieb, und die meisten Mitarbeiter arbeiten entsprechend den Vorgaben des Bundesrates aus dem Home-Office. Unentbehrliche Forschungsanlagen und -projekte laufen unter Massgabe aller gebotenen Sicherheitsvorkehrungen aber weiter.
«Wir wollen verstehen, wie dieses Virus funktioniert»
Die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS am PSI ist trotz der Covid-19-Pandemie weiter in Betrieb – und wird möglicherweise gerade in diesen schwierigen Zeiten dringend benötigt. Oliver Bunk, Leiter des Labors für Makromoleküle und Bioimaging, erklärt wieso.
«Strategie und Vernetzung sind enorm wichtig»
Gebhard Schertler, Leiter des Bereichs Biologie und Chemie am PSI und gleichzeitig Professor für Strukturbiologie an der ETH Zürich, erklärt, welche Forschung zum Corona-Virus am PSI stattfindet und welche Bedeutung die Kooperation mit Forschenden anderer Institutionen dabei hat.
«Die SLS ist derzeit europaweit etwas ganz Besonderes»
Die Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS ist eine von nur wenigen Anlagen ihrer Art, die in Europa zu Pandemiezeiten noch in Betrieb ist. Mirjam van Daalen, Stabschefin des Forschungsbereichs Photonenforschung betont im Interview, wie wichtig gerade in diesen Tagen die internationale Zusammenarbeit ist.
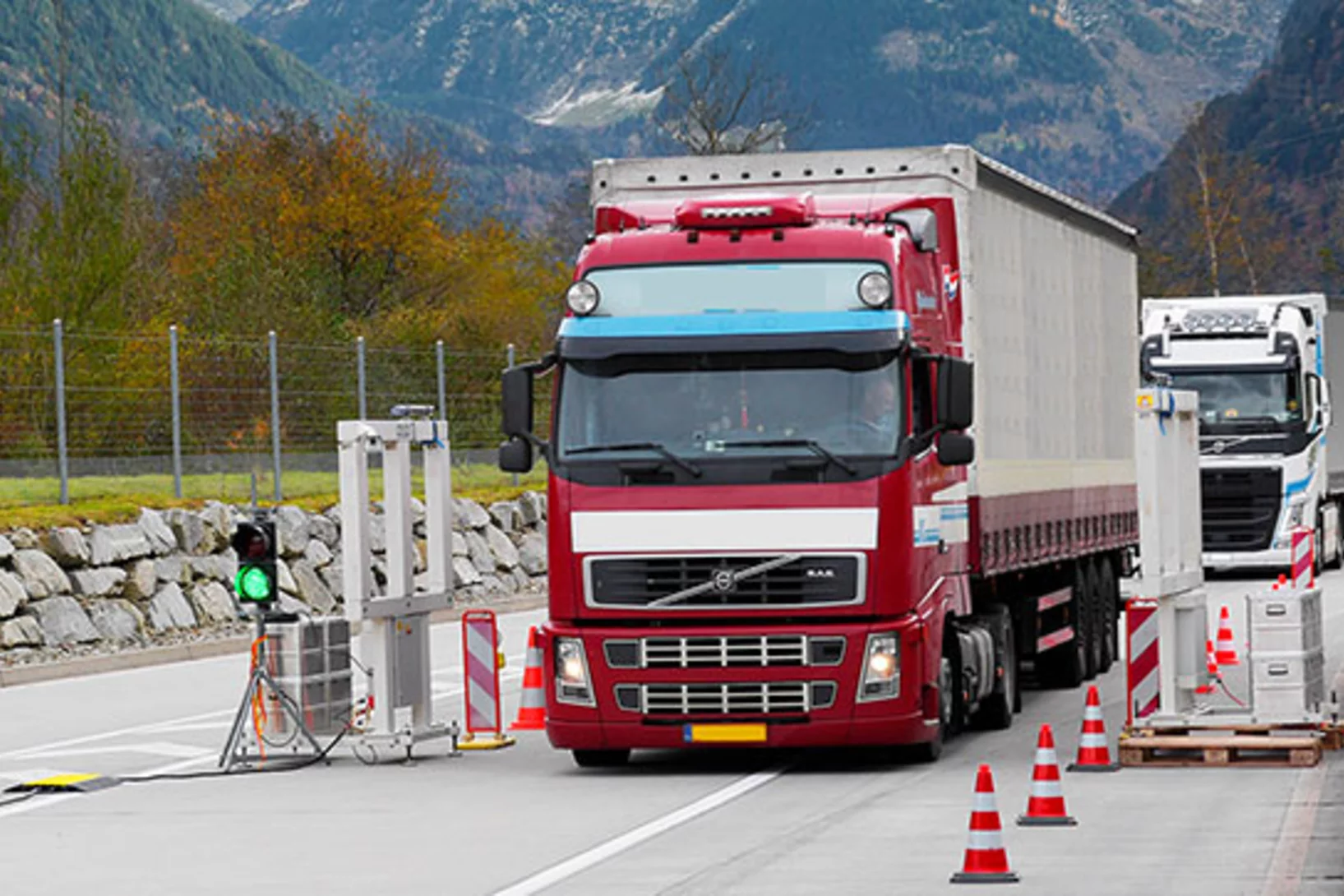
Radioaktive Stoffe im Güterverkehr aufspüren
Mit einem mobilen Messportal führt das PSI regelmässig Radioaktivitätskontrollen bei Lastwagen durch. Im Auftrag des Bundesamts für Gesundheit sollen so herrenlose Strahlenquellen entdeckt werden.
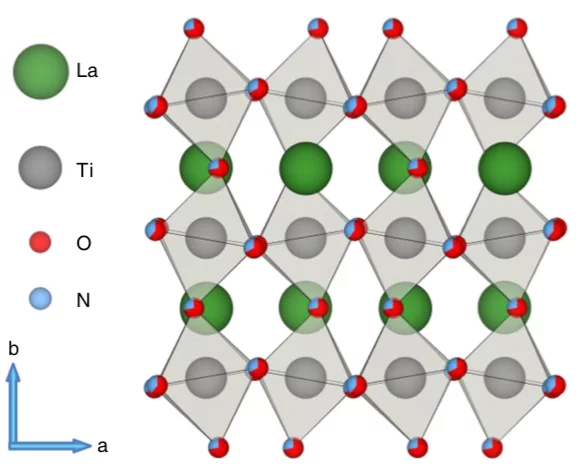
Examining the surface evolution of LaTiOxNy an oxynitride solar water splitting photocatalyst
LaTiOxNy oxynitride thin films are employed to study the surface modifications at the solid- liquid interface that occur during photoelectrocatalytic water splitting. Neutron reflectometry and grazing incidence x-ray absorption spectroscopy were utilised to distinguish between the surface and bulk signals, with a surface sensitivity of 3 nm.
Microcalcifications in breast tissue: Paving the way for future diagnostic solutions?
Microcalcifications are a common sign in mammography. For example, in 90% of ductal carcinoma in situ microcalcifications are the first and unique sign indicating the presence of the lesion. Nevertheless, up to around 50% of the resulting biopsies reveal a benign lesion, a 'false positive'. Researchers were able to show now that breast microcalcifications detected in tumors have specific chemical and crystalline features different from those observed in benign samples. Moreover, microcalcifications detected in tumors but located outside the lesion show malignant features too. This indicates that cancer influences the surrounding tissue even if it exhibits apparently healthy morphological features. These results indicate that the biochemical differences between benign and malignant microcalcifications can be potentially identified by light-based tools, able to investigate microcalcifications inside the breast without performing biopsies.
Information for CHRISP users
Because of the present coronavirus situation, preparations for the startup of the proton accelerator HIPA are currently suspended since March 16. At that point in time, there were still about 8 weeks to finalize the shutdown work.
Home Office der Lernenden Chemielaboranten während Coronavirus
Mit den folgenden Beiträgen wollen wir Ihnen zeigen, welche Projekte die Chemielaboranten während dem Home Office erarbeitet haben. Zudem wollen wir Ihnen auch veranschaulichen, dass Chemie überall in unserem Alltag anzutreffen ist.
Professor Dr. Christian Rüegg neuer Direktor des Paul Scherrer Instituts
Der neue Direktor des Paul Scherrer Instituts tritt heute sein Amt an: Christian Rüegg will die Spitzenstellung der Grossforschungsanlagen des PSI weiter ausbauen und so den Forschungsstandort Schweiz stärken.
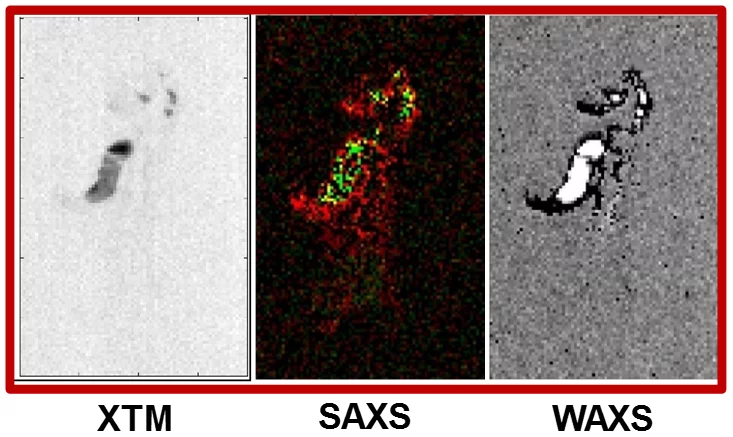
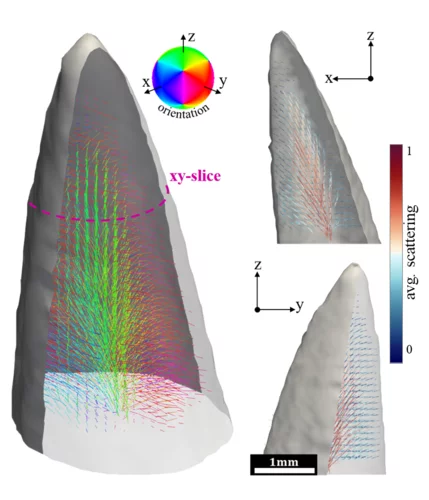
Rapid 3D directional small-angle scattering imaging achieved at TOMCAT
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline have developed a small-angle scattering tensor tomography method to visualize microscopic features within a macroscopic field of view with unprecedented data acquisition speed. The results of the study were published in Applied Physics Letters on April 1, 2020.
Rapid 3D directional small-angle scattering imaging achieved at TOMCAT
Researchers from the TOMCAT beamline have developed a small-angle scattering tensor tomography method to visualize microscopic features within a macroscopic field of view with unprecedented data acquisition speed. The results of the study were published in Applied Physics Letters on April 1, 2020.
SLS MX beamtime update
Update of the SLS MX beamline operation during the COVID-19 period
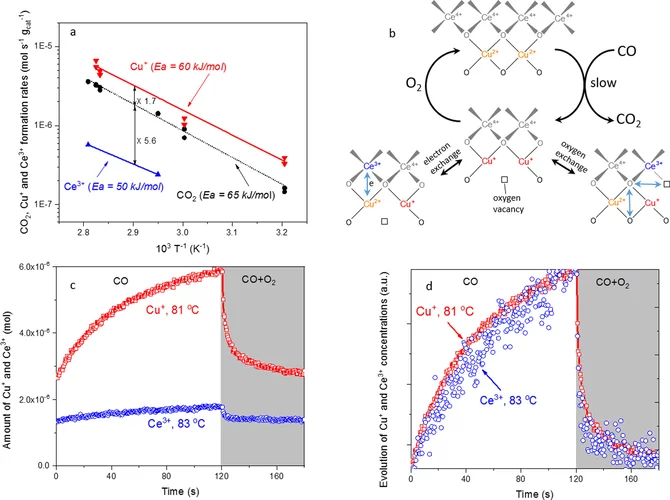
Elucidating the Oxygen Activation Mechanism on Ceria-Supported Copper-Oxo Species Using Time-Resolved X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy
We monitored the dynamic structure of the active sites in a catalyst containing highly dispersed copper-oxo species on ceria during low-temperature CO oxidation using time-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy. We quantitatively demonstrate that the CO oxidation mechanism below 90 °C involves an oxygen intermediate strongly bound to the active sites as well as the redox activity of Cu2+/Cu+ and Ce4+/Ce3+ couples.
SNF funds dynamic X-ray imaging of the human auditory system in motion
In collaboration with clinicians from the Inselspital and engineers of the University Hospital of Bern, the X-Ray Tomography Group will be part of a new SNF project entitled “The Human Auditory System in Motion: Direct Observation of the Microfunction of Sound Transmission using Dynamic Phase-contrast X-ray Imaging”.
Electron–phonon-driven three-dimensional metallicity in an insulating cuprate
Elucidating the role of different degrees of freedom in a phase transition is crucial in the comprehension of complex materi- als. A phase transformation that attracts significant interest is the insulator-to-metal transition of Mott insulators, in which the electrons are thought to play the dominant role. Here, we use ultrafast laser spectroscopy and theoretical calculations ....
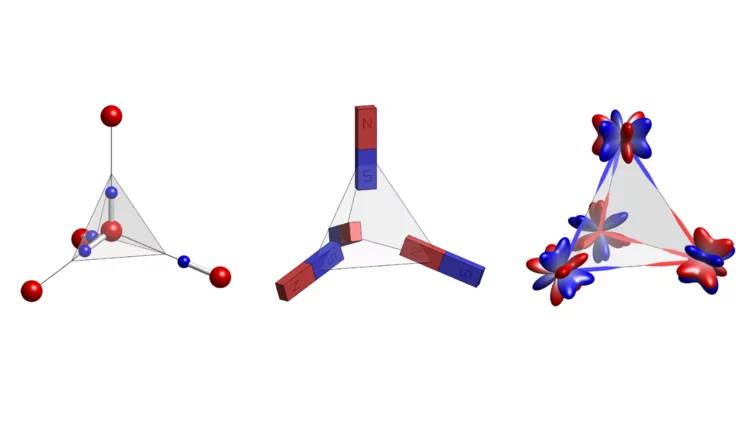
Spin ice expands to higher orders
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
Spin ice expands to higher orders
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
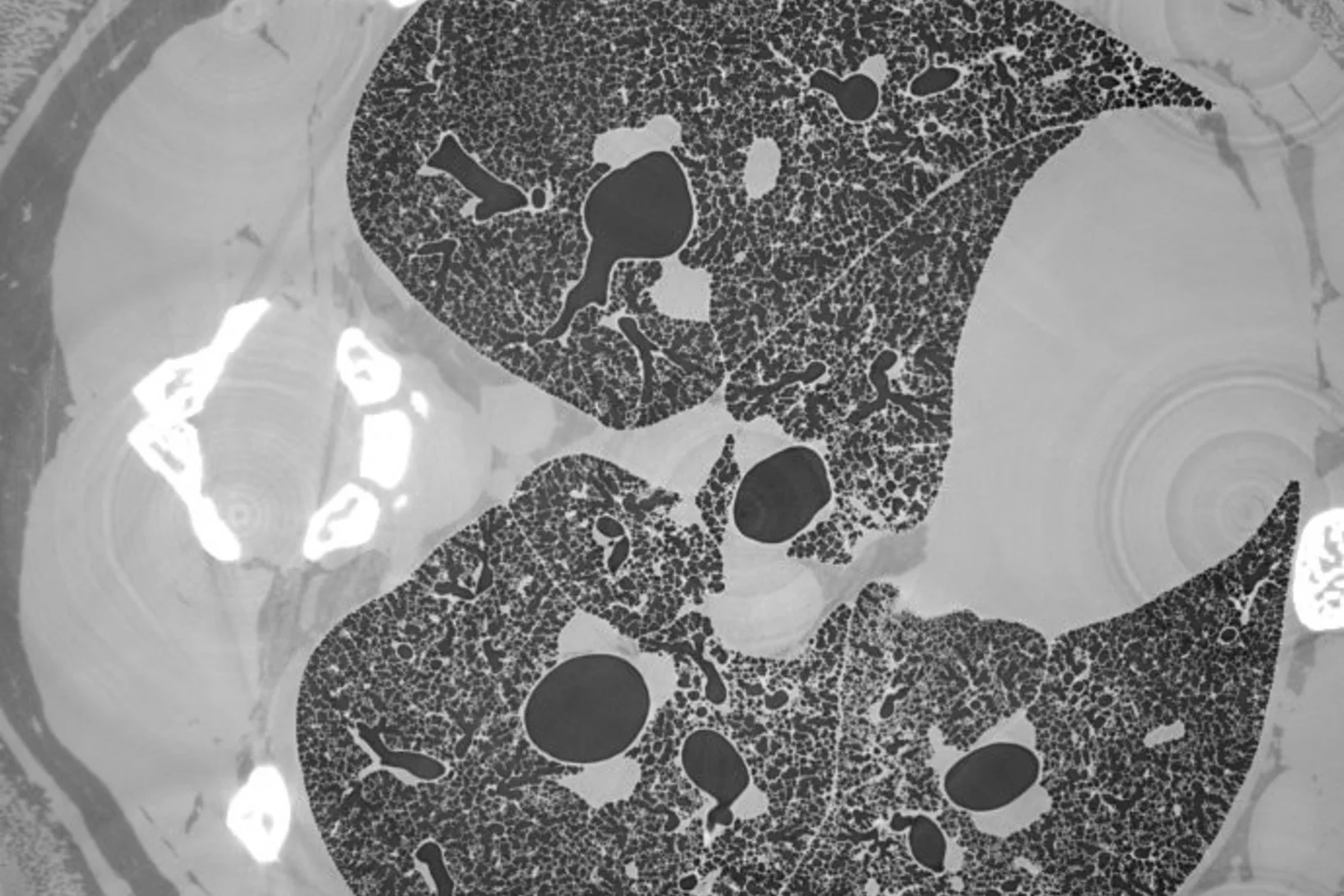
X-ray Imaging for Biomedicine: Imaging Large Volumes of Fresh Tissue at High Resolution
The TOMCAT beamline at the Swiss Light Source specializes in rapid high-resolution 3-dimensional tomographic microscopy measurements with a strong focus on biomedical imaging. The team has recently developed a technique to acquire micrometer-scale resolution datasets on the entire lung structure of a juvenile rat in its fresh natural state within the animal’s body and without the need for any fixation, staining or other alteration that would affect the observed structure (E. Borisova et al., 2020, Histochem Cell Biol).
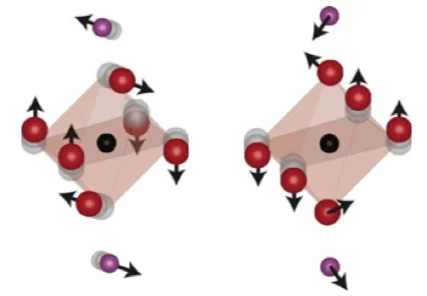
A quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles on the pyrochlore lattice
With experimental work demonstrating that the correlated ground state of the pyrochlore system Ce2Sn2O7 is a quantum liquid of magnetic octupoles, an international team led by PSI researcher Romain Sibille establishes a fundamentally new state of matter: higher-rank multipole ice.
15th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation postponed to 2021
Because of the coronavirus situation, the 15th International Conference on Muon Spin Rotation, Relaxation and Resonance (µSR2020) has been postponed to 2021. More details will be announced in due time.