Abkehr von der Kernenergie, Ausbau von Solar- und Windkraft, Energiegewinnung aus Biomasse, Senkung des Energieverbrauchs. Bis 2050 soll die Schweiz klimaneutral werden. Ein ehrgeiziges Ziel, welches durch die zunehmend herausfordernde geopolitische Lage dringlicher denn je geworden ist. Wie lässt sich in den nächsten Jahren eine nachhaltige und widerstandsfähige Energieversorgung für die Schweiz aufbauen? Wie können erneuerbare Energien optimal genutzt werden? Welche neuen Technologien sind besonders vielversprechend? Am PSI suchen Forschende nach Antworten auf diese entscheidenden Fragen.
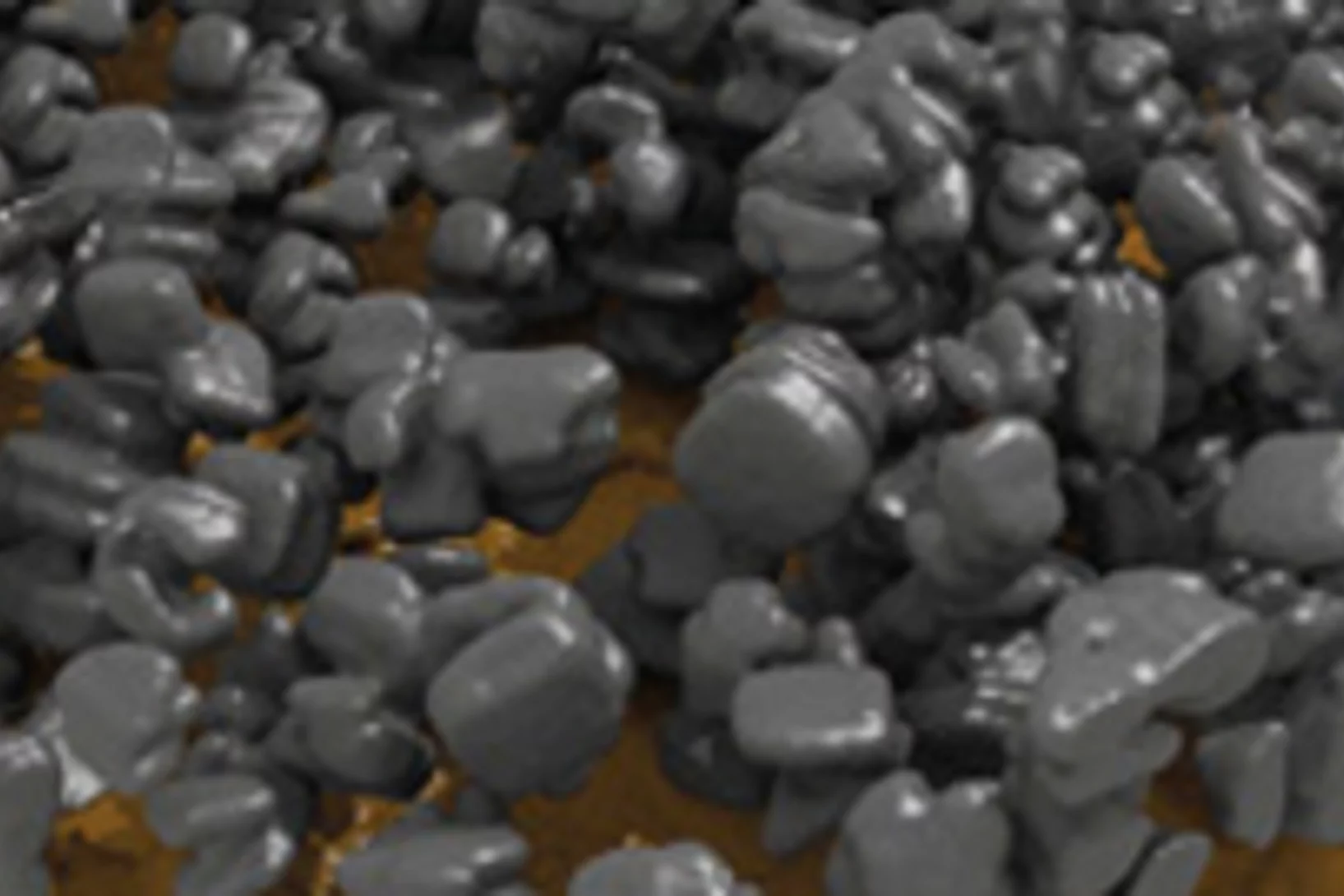
Wie Gesteinsporen im Tiefenlager zuwachsen
Chemische Reaktionen, so viel steht fest, werden die Beschaffenheit des Tiefenlagers sowie des umliegenden Gesteins (Tongestein) verändern. Aber in welchem Ausmass und mit welchen Auswirkungen auf die Sicherheit? Forscher des Paul Scherrer Instituts versuchen diese Frage mit Hilfe einer Kombination von Experimenten und Computersimulationen zu beantworten.
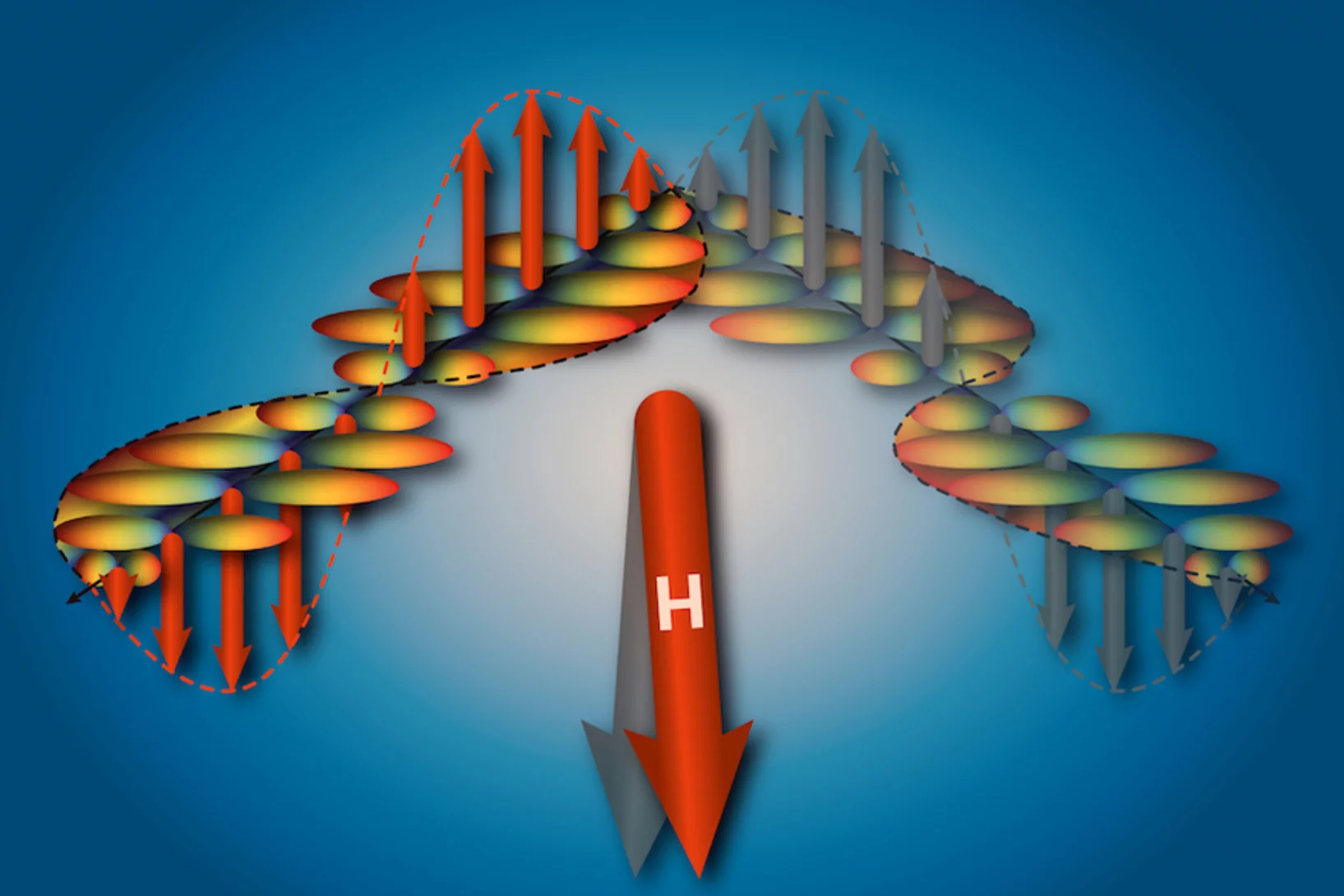
Switching of magnetic domains reveals spatially inhomogeneous superconductivity
The interplay of magnetic and charge fluctuations can lead to quantum phases with exceptional electronic properties. A case in point is magnetically-driven superconductivity, where magnetic correlations fundamentally affect the underlying symmetry and generate new physical properties. The superconducting wavefunction in most known magnetic superconductors does not break translational symmetry.
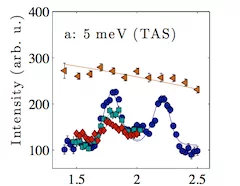
Magnetoelastic Excitations in the Pyrochlore Spin Liquid Tb2Ti2O7
Tb2Ti2O7 is often referred to as a spin liquid as it does indeed remain in a magnetically disordered phase with spin dynamics down to 0.05 K, but this itself is a surprise since there are strong expectations of magnetic order and/or a structural distortion. However, throughout the spin liquid regime there are also strong signs of magnetoelastic coupling, leading to the suggestion that both spin and structural degrees of freedom are frustrated.
Supervolcano eruptions driven by melt buoyancy in large silicic magma chambers
Super-eruptions that dwarf all historical volcanic episodes in erupted volume and environmental impact are abundant in the geological record. Such eruptions of silica-rich magmas form large calderas. The mechanisms that trigger these supereruptions are elusive because the processes occurring in conventional volcanic systems cannot simply be scaled up to the much larger magma chambers beneath super volcanoes.
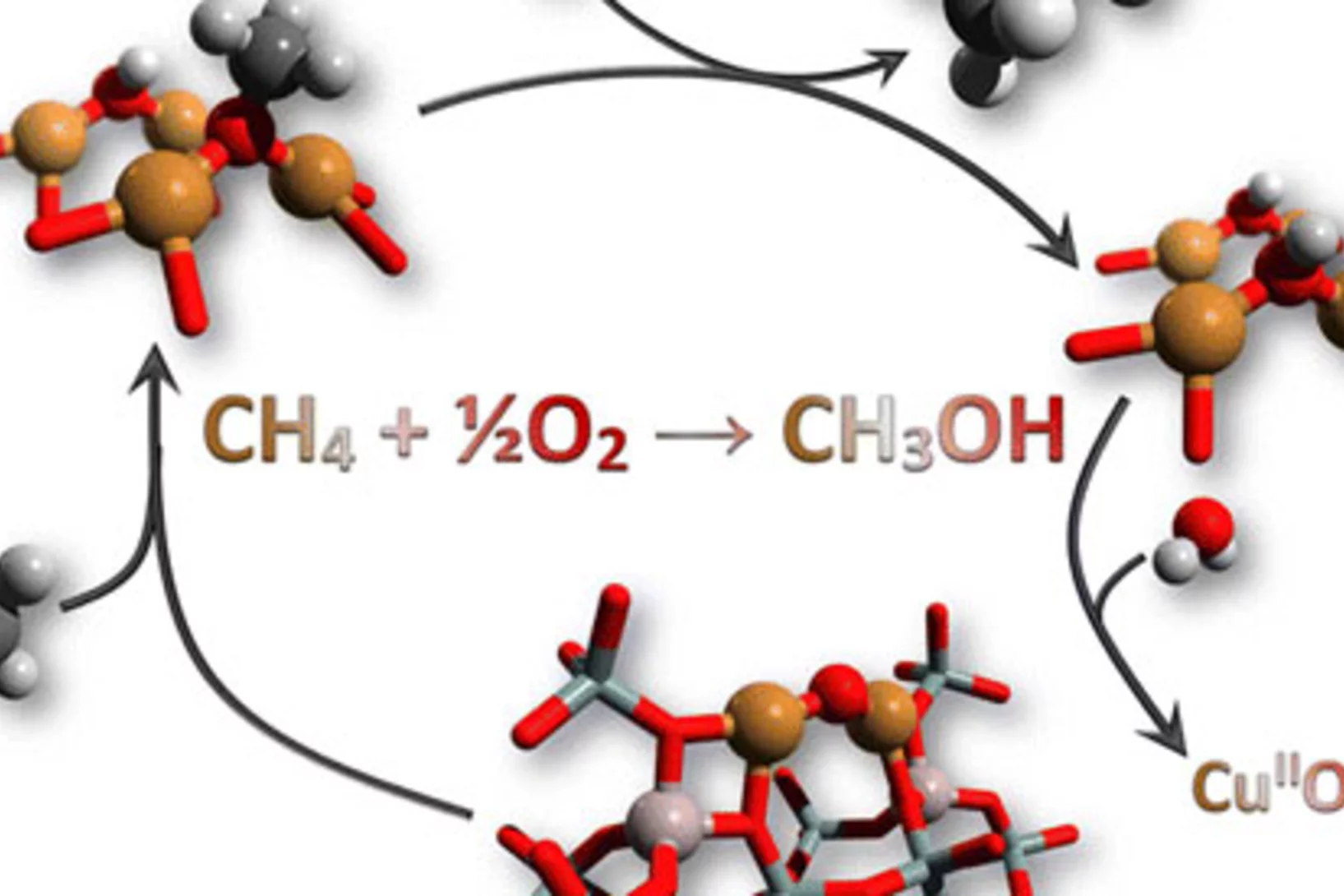
Reaction Conditions of Methane-to-Methanol Conversion Affect the Structure of Active Copper Sites
Determining the structure of the active Cu sites, which are associated with the methane conversion intermediate during stepwise, low-temperature, methane-to-methanol conversion, represents an important step for the upgrade of this reaction route to a viable process. Quick X-ray absorption spectroscopy allowed us to follow the electronic and structural changes to the active Cu sites during reaction with methane and during desorption of the activated intermediate. A large fraction (41%) of the oxygen-activated CuII reacted with methane and underwent reduction to CuI.
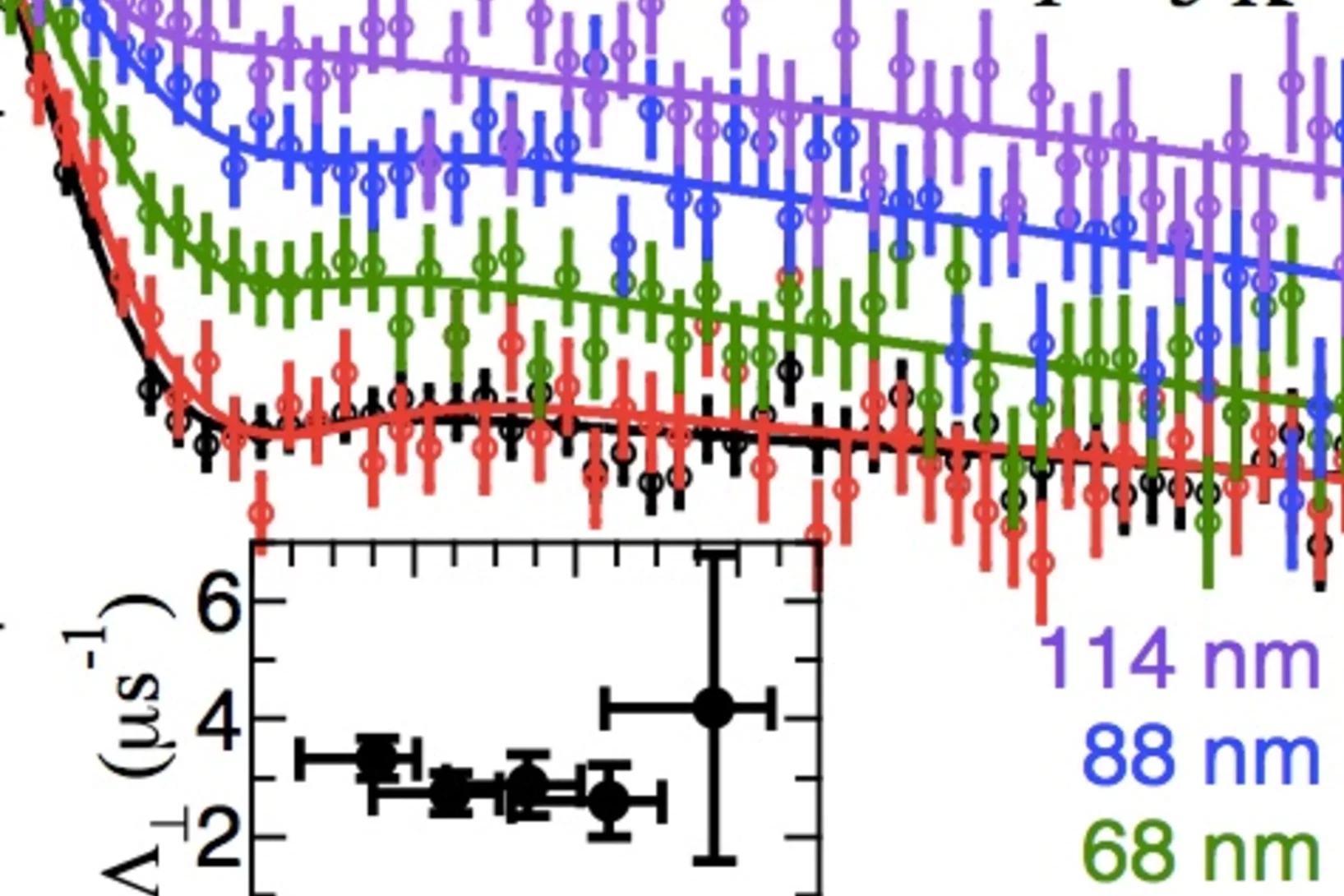
Bulk superconductivity in undoped T'-La1.9Y0.1CuO4 probed by muon spin rotation
The Meissner effect has been directly demonstrated by depth-resolved muon spin rotation measurements in high-quality thin films of the T'-structured cup rate, T'-La1.9Y0.1CuO4, to confirm bulk superconductivity (Tc ≈ 21 K) in its undoped state. The gradual expelling of an external magnetic field is observed over a depth range of ∼ 100 nm in films with a thickness of 275(15) nm, from which the penetration depth is deduced to be 466(22) nm. Based on this result, we argue that the true ground state of the “parent” compound of the n-type cuprates is not a Mott insulator but a strongly correlated metal with colossal sensitivity to apical oxygen impurities.
Supraleitung mit Magnetfeld eingeschaltet
Meist sieht man Supraleitung und Magnetfelder als Konkurrenten à sehr starke Magnetfelder zerstören in der Regel den supraleitenden Zustand. Physiker des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI haben nun gezeigt, dass in dem Material CeCoIn5 ein neuartiger supraleitender Zustand erst bei starken externen Magnetfeldern entsteht und dann durch Veränderung des Feldes manipuliert werden kann. Das Material ist auch schon bei schwächeren Feldern supraleitend, bei starken Feldern entsteht aber ein zusätzlicher zweiter supraleitender Zustand, so dass gleichzeitig im selben Material zwei unterschiedliche supraleitende Zustände existieren.
Experimente in der Wolke – Wie Russ das Klima beeinflusst
PSI-Forscher Martin Gysel erhält angesehene europäische Förderung (ERC Consolidator Grant) für Untersuchungen zur Rolle von Russ für Wolkenbildung und Atmosphärenerwärmung
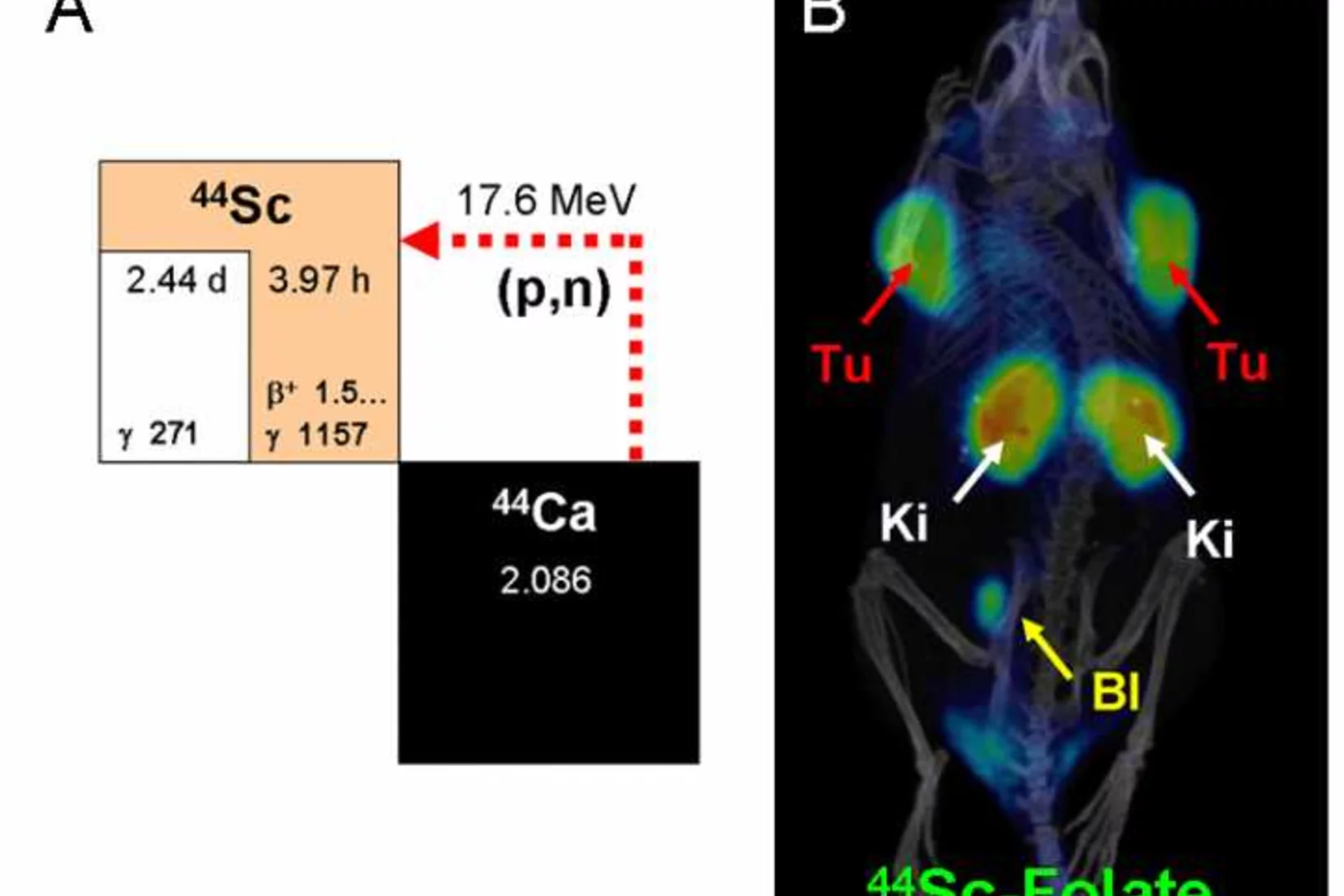
Promises of cyclotron-produced 44Sc as a diagnostic match for trivalent beta - emitters: In vitro and in vivo study of a 44Sc-DOTA-folate conjugate
Research Division Biology and Chemistry (BIO), Folate Receptor Targeting Group, Head Cristina Müller. In recent years, implementation of 68Ga-radiometalated peptides for PET imaging of cancer has attracted the attention of clinicians. Herein, we propose the use of 44Sc (half-life = 3.97 h, average β+ energy [Eβ+av] = 632 keV) as a valuable alternative to 68Ga (half-life = 68 min, Eβ+av = 830 keV) for imaging and dosimetry before 177Lu-based radionuclide therapy.
Das Paul Scherrer Institut leitet zwei der Energie-Kompetenzzentren des Bundes
Als Bestandteil der Energiestrategie 2050 haben Bund und Parlament eine verstärkte Förderung der Energieforschung in der Schweiz beschlossen. Dazu gehört die Einrichtung von sieben interuniversitär vernetzten Kompentenzzentren (Swiss Competence Centers in Energy Research SCCER). In den SCCER sollen sich Institutionen aus dem ETH-Bereich, den Universitäten und den Fachhochschulen gemeinsam mit Industriepartnern zusammenschliessen, um neue Kompetenzen und Lösungen in für die Energiewende entscheidenden Aktionsfeldern zu erarbeiten. In zwei SCCER à zu den Themen Speicherung und Biomasse à, die bereits den Zuschlag erhalten haben, ist das Paul Scherrer Institut PSI die federführende Institution. Die beiden Kompetenzzentren werden ihre Arbeit im Jahr 2014 aufnehmen.
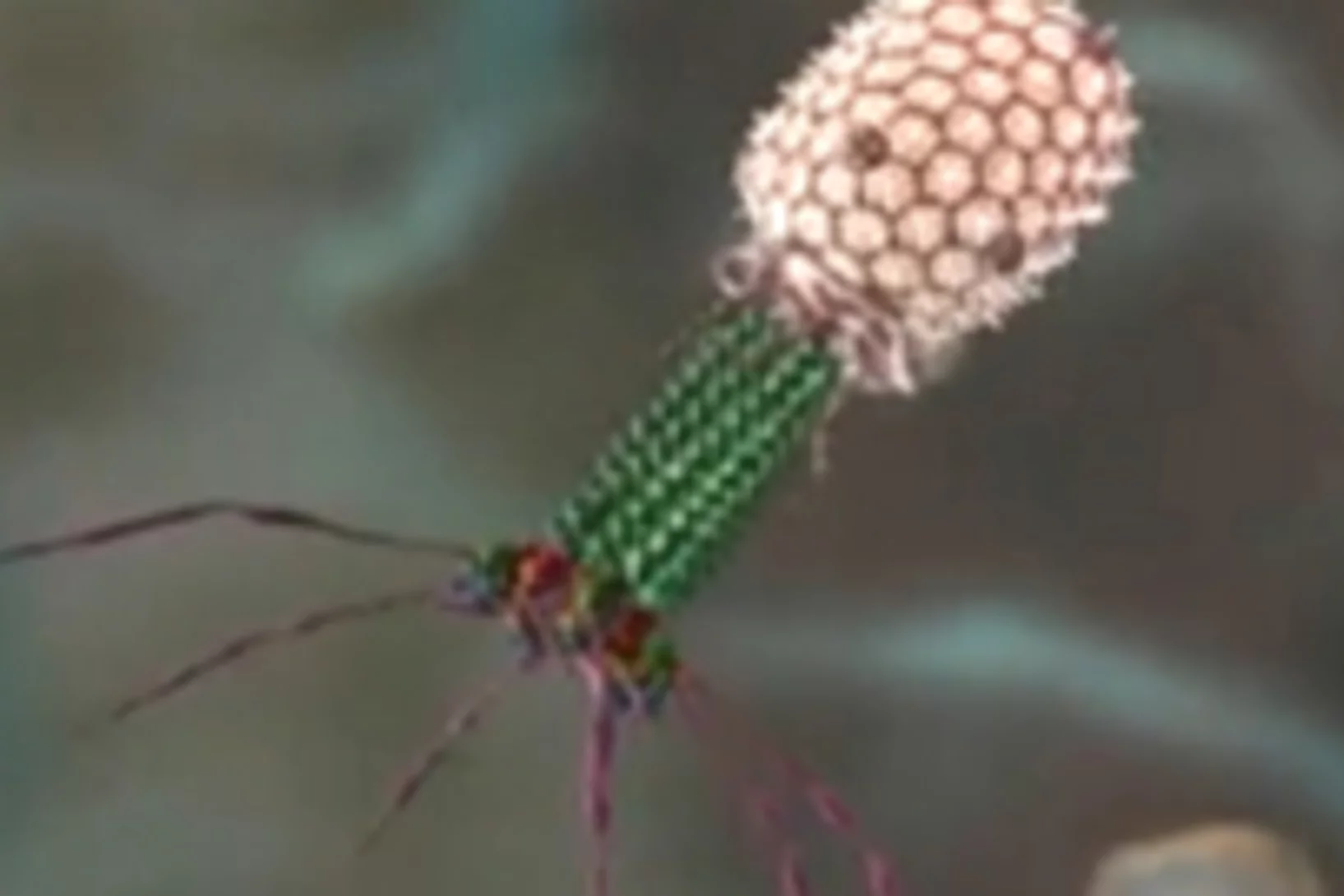
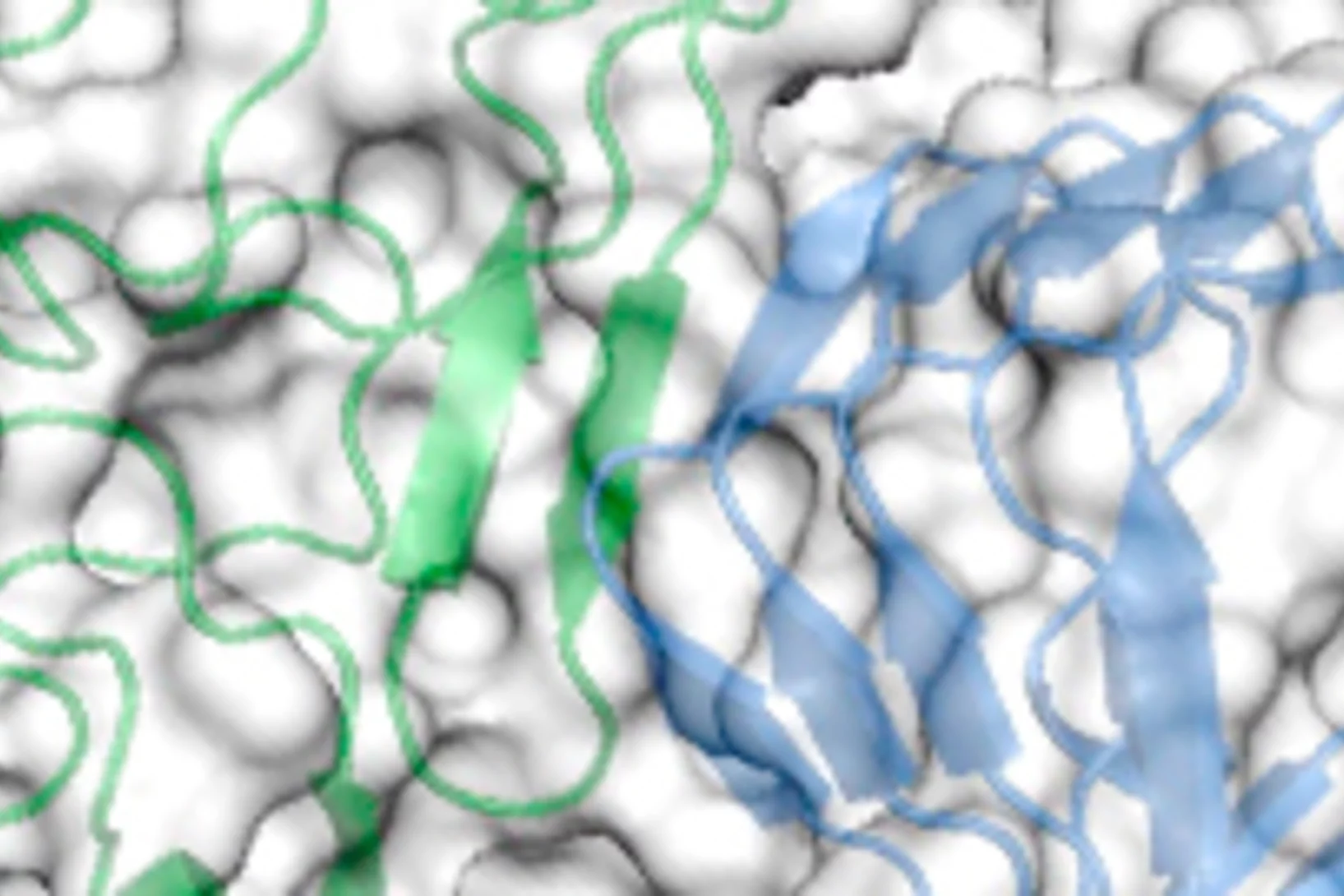
Ein Infektionswerkzeug mit metallischem Kern
Dank der Analyse von Proteinproben am PSI konnten Lausanner Forscher zeigen, mit welchem Instrument Bakterien Krankheiten übertragenForscher der ETH Lausanne EPFL haben mit bisher ungekannter Genauigkeit beschrieben, wie ein bestimmter Typ von Bakterien bei der Übertragung von Krankheiten vorgeht. Die Wissenschaftler um Petr Leiman, Assistenzprofessor am Labor für Strukturbiologie und Biophysik der EPFL, konnten zeigen, dass die Spitze des von den Bakterien benutzten Ansteckungswerkzeugs aus einem PAAR-Protein besteht, das ein Metallatom umgibt und spitz zuläuft. Grundlage der Erkenntnisse bilden Messungen an der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz SLS, einer der drei Grossforschungsanlagen des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI.
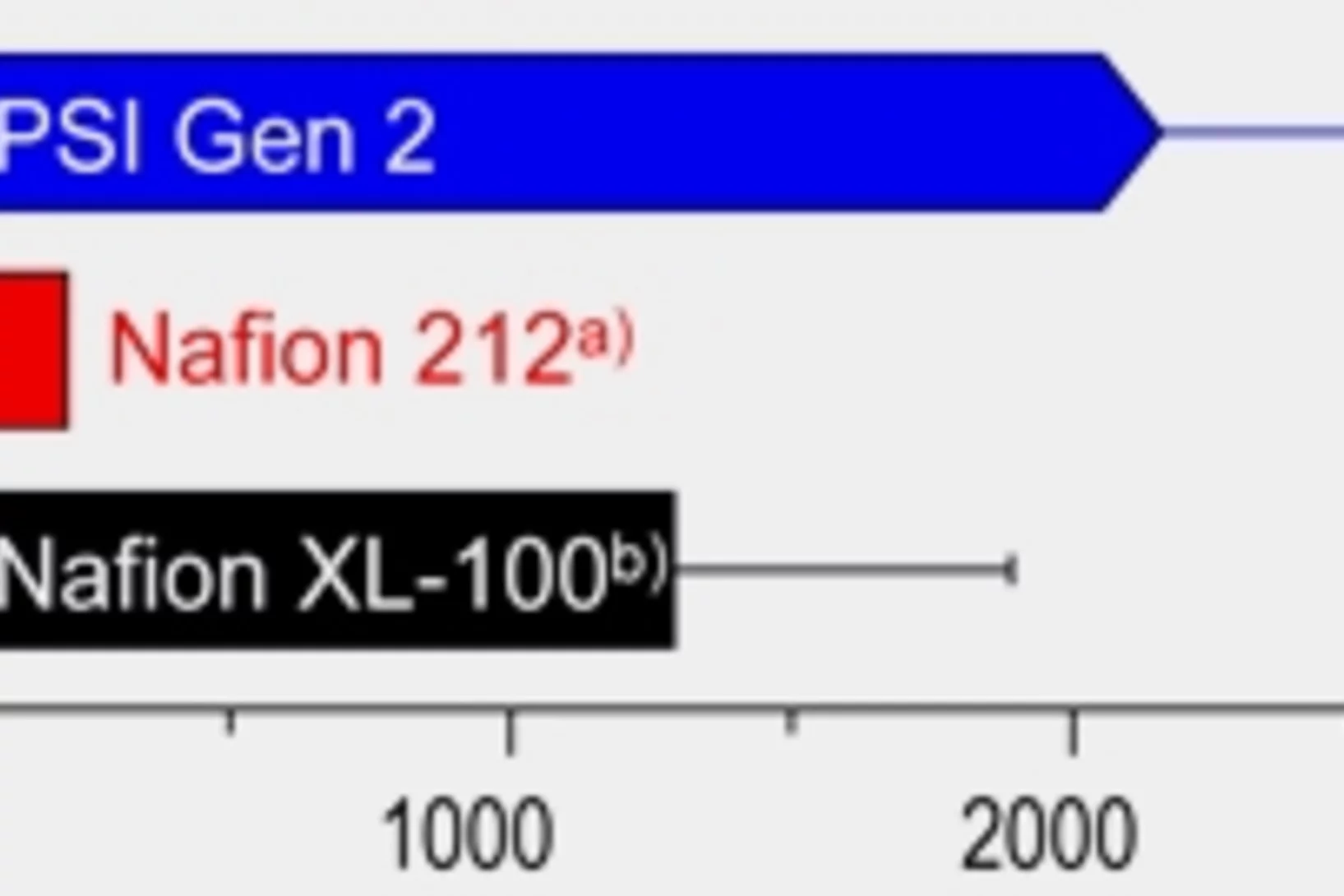
Brennstoffzellenmembran aus dem Paul Scherrer Institut besser als kommerzielle Pendants
Eine neuartige Polymermembran aus dem Paul Scherrer Institut PSI hat im Labortest eine längere Haltbarkeit als die besten kommerziell erhältlichen Pendants gezeigt. Der Durchbruch gelang dank Modifizierung eines preisgünstigen Kunststofffilmes durch Bestrahlung und anschliessendes Aufpfropfen funktioneller Komponenten. Der so veränderte Kunststoff hält nicht nur lange à er könnte die Herstellungskosten der Membran um 50 bis 80 Prozent senken. Anwendung finden könnte die Membran etwa in Wasserstoffbrennstoffzellen oder in Elektrolyseuren zur Wasserstoffherstellung aus Wasser.
Wie Botox an Nervenzellen bindet
Botox ist ein hochgefährliches Gift, das Lähmungen verursacht. In der Kosmetik wird es zur zeitweiligen Beseitigung von Falten und in der Medizin etwa als Mittel gegen Migräne oder zur Korrektur von Strabismus (Schielen) eingesetzt. Ein Forschungsteam hat nun bestimmt, wie das Toxinmolekül an die Nervenzelle bindet, deren Aktivität vom Gift blockiert wird. Die Ergebnisse können nützlich für die Entwicklung verbesserter Medikamente sein, bei denen die Gefahr einer Überdosierung geringer ist als bisher.
Schärferes Bild eines Katalysators mit Ecken und Kanten
Ein Katalysator aus dem Edelmetall Ruthenium auf einem Kohlenstoffträger wird industriell häufig eingesetzt. Ein prominentes Beispiel ist die Synthese von Ammoniak, welches unter anderem zur Herstellung von stickstoffhaltigen Düngemitteln dient. Diesen Katalysatortyp zu optimieren ist das Ziel vieler Forschungsgruppen weltweit, würde dies doch die Effizienz eines der ökonomisch bedeutendsten Industrieprozesse erhöhen. Doch das Verständnis dessen, wie es zum Aufbau der katalytisch aktiven Zentren im Katalysator kommt, ist bisher lückenhaft. Forscher des Paul Scherrer Instituts PSI bringen nun ein paar wichtige Erkenntnisse ans Licht.
Zukünftige Computerchips mit "elektronischem Blutkreislauf"
Im Rahmen des Sinergia-Programms fördert der Schweizerische Nationalfonds das dreijährige Forschungsvorhaben REPCOOL. Unter der Leitung von IBM Research à Zürich arbeiten in diesem Projekt Wissenschaftler der ETH Zürich, des Paul Scherrer Instituts in Villigen und der Università della Svizzera italiana in Lugano gemeinsam an der Erforschung eines elektronischen Blutkreislaufs für zukünftige 3D-Computerchips. Vom menschlichen Gehirn inspiriert, entwickeln die Forscher ein Mikrokanalsystem mit einer elektrochemischen Flussbatterie, die 3D-Chipstapel gleichzeitig kühlen und mit Energie versorgen. Ultimatives Ziel ist die Entwicklung eines Supercomputers in PC-Grösse.
Elektronen mit „gespaltener Persönlichkeit“
Im supraleitenden Material La1.77Sr0.23CuO4 verhält sich oberhalb der Übergangstemperatur ein Teil der Elektronen wie in einem konventionellen Metall, ein anderer Teile wie in einem unkonventionellen à je nach Bewegungsrichtung. Das zeigen Untersuchungen an der SLS. Die Entdeckung dieser Anisotropie liefert einen wesentlichen Beitrag zum Verständnis der Hochtemperatursupraleitung. Ausserdem wird man diesen Effekt in zukünftigen Experimenten und Theorien berücksichtigen müssen.
Die SwissFEL-Anlage: Laserlicht durch lawinenartige Verstärkung
Der SwissFEL wird Röntgenlicht mit Lasereigenschaften erzeugen. Die nötige Verstärkung des Lichts macht ein als Microbunching bekannter Prozess möglich – das Elektronenpaket teilt sich im Undulator in dünne Scheiben, sogenannte Microbunches auf, die das Licht in Phase abstrahlen. Zugleich wird an einem weiteren Verfahren – dem Seeding – geforscht, mit dem man die Eigenschaften des Lichts noch genauer wird festlegen können.
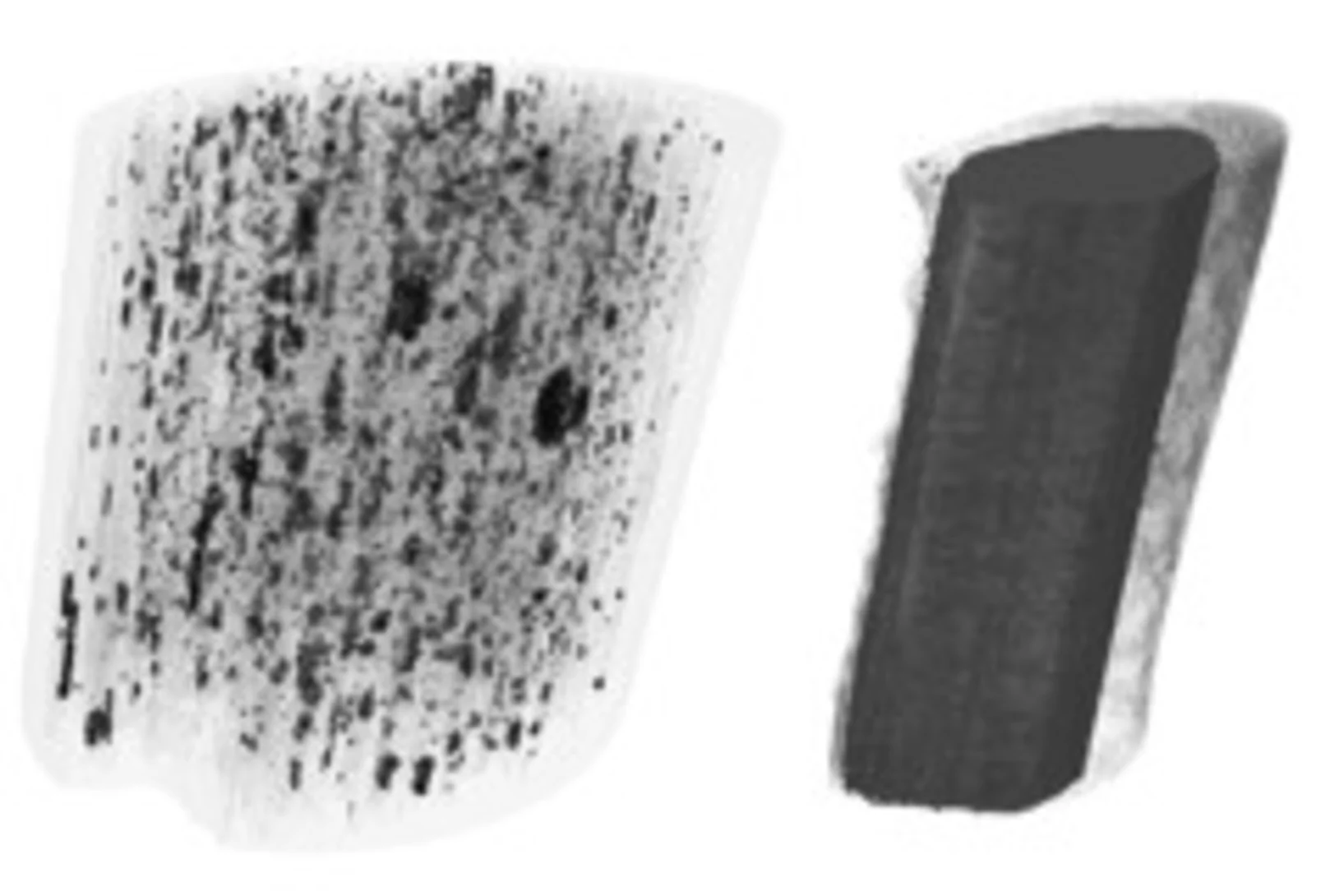
Unique insight into carbon fibers on the nanoscale
The investigation of the mechanical properties of carbon fibers benefits from highly resolved three-dimensional density maps within representative volumes, but such images are not easily obtained with standard methods. Scientists from the Paul Scherrer Institut in collaboration with Honda R&D in Germany have recently visualized density distributions on the sub-micrometer scale within entire carbon fiber sections, revealing surprising graphite distributions within the fibers. This capability will prove useful for the systematic characterization of fibers, contributing to the development of light and robust materials at lower costs.
Magnetismus im Stress: Gleichzeitiger Anti- und Ferromagnetismus
Die gleichzeitige Existenz von Magnetismus und Ferroelektrizät in einem Material ist selten. Setzt sich dieser Magnetismus aus mehreren unabhängigen, magnetischen Grundzuständen zusammen, ist das ungewöhnlich. Einer schweizerisch-französischen Zusammenarbeit unter Leitung des Paul Scherrer Instituts ist es gelungen, mehrere magnetische Grundzustände in einem Material zu realisieren und detailliert zu untersuchen.
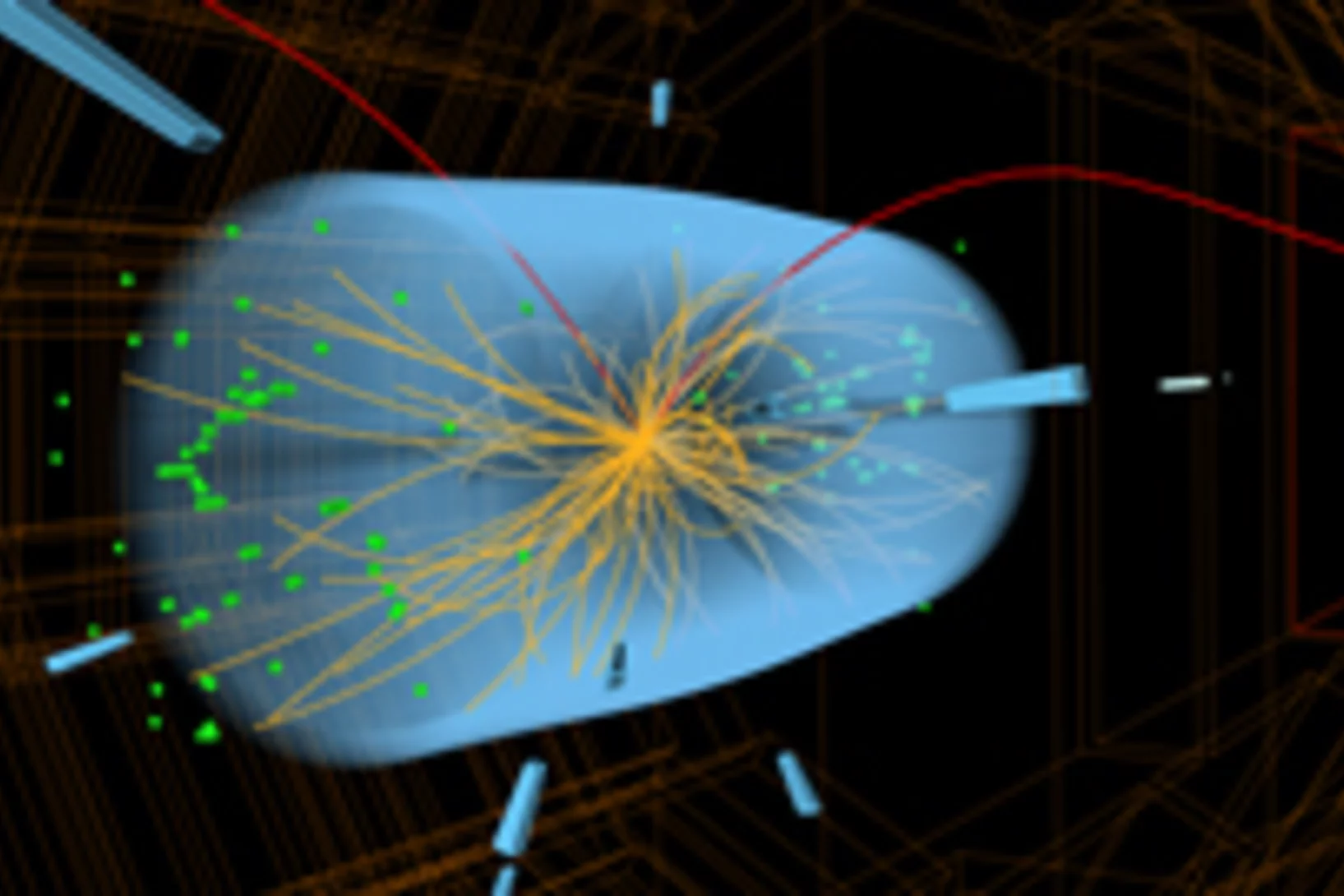
Seltene Teilchenzerfälle stützen Standardmodell
Forschende des Paul Scherrer Instituts haben aus den am CMS-Detektor am CERN gemessenen Daten erstmals den sehr seltenen Zerfall des Bs-Mesons in zwei Myonen mit hinreichender Sicherheit beobachtet und seine Häufigkeit bestimmt. Ihre Ergebnisse stimmen sehr gut mit den Voraussagen des Standardmodells der Teilchenphysik überein.
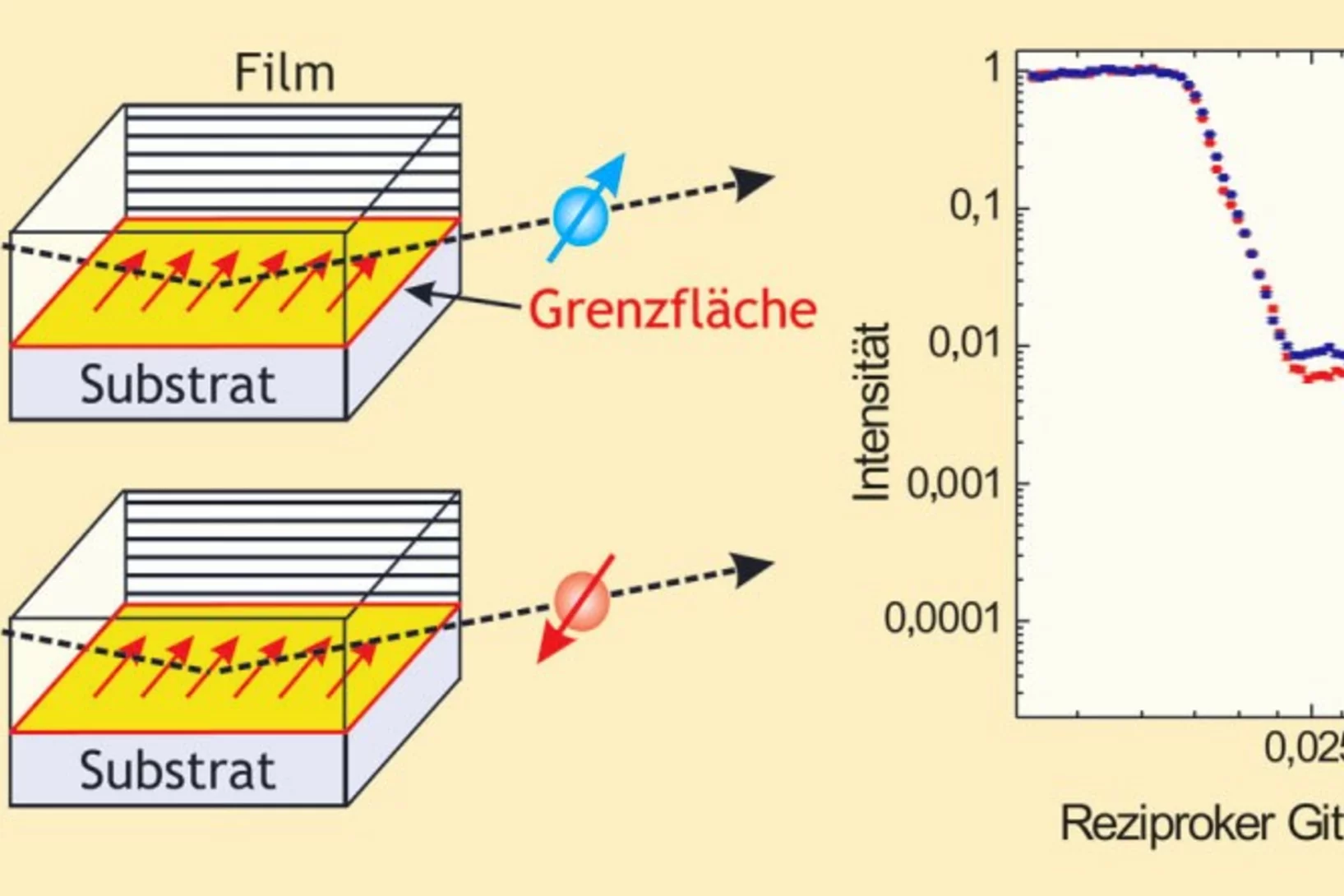
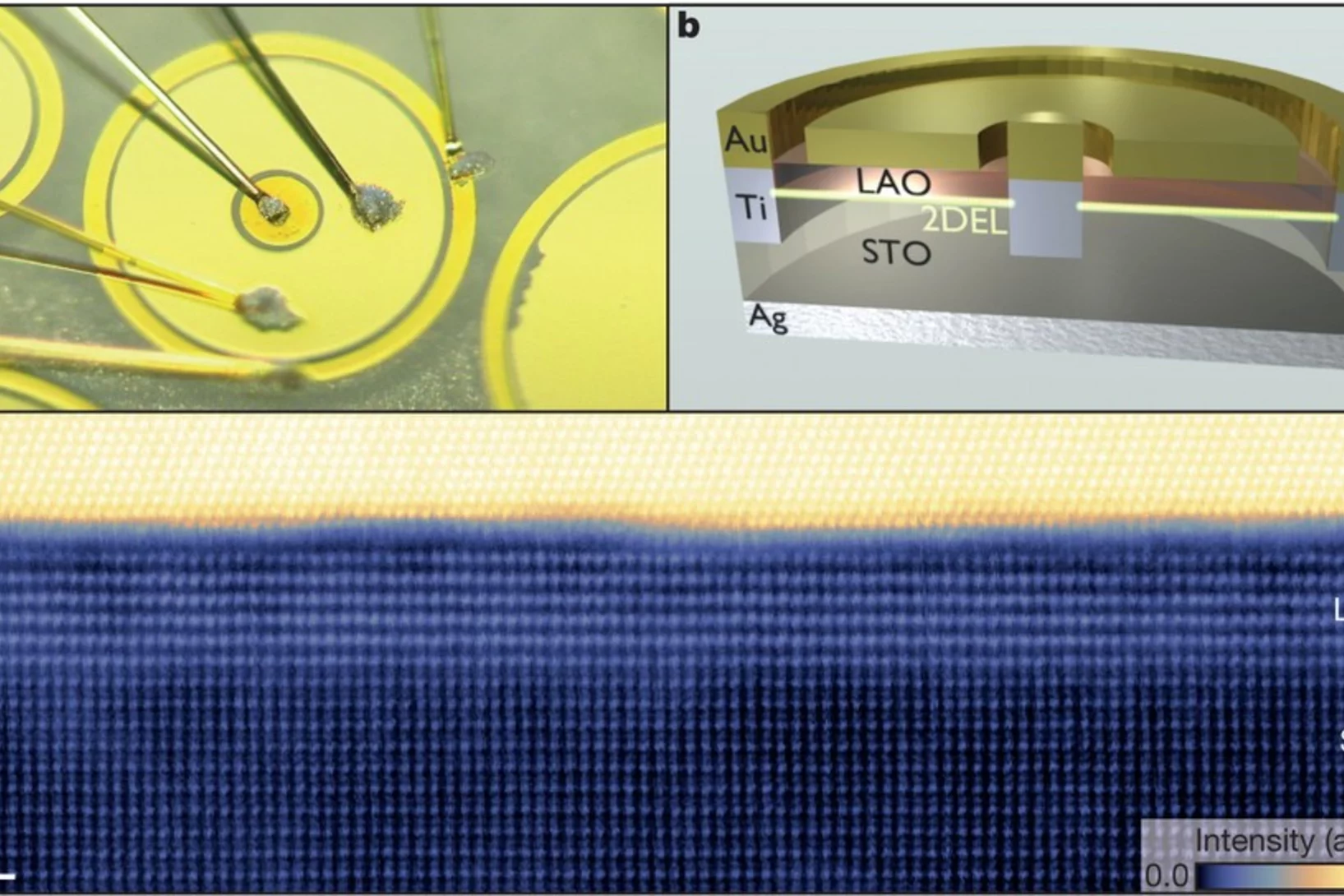
Interface superconductor with gap behaviour like a high-temperature superconductor
The physics of the superconducting state in two-dimensional (2D) electron systems is relevant to understanding the high-transition-temperature copper oxide superconductors and for the development of future superconductors based on interface electron systems. But it is not yet understood how fundamental superconducting parameters, such as the spectral density of states, change when these superconducting electron systems are depleted of charge carriers.
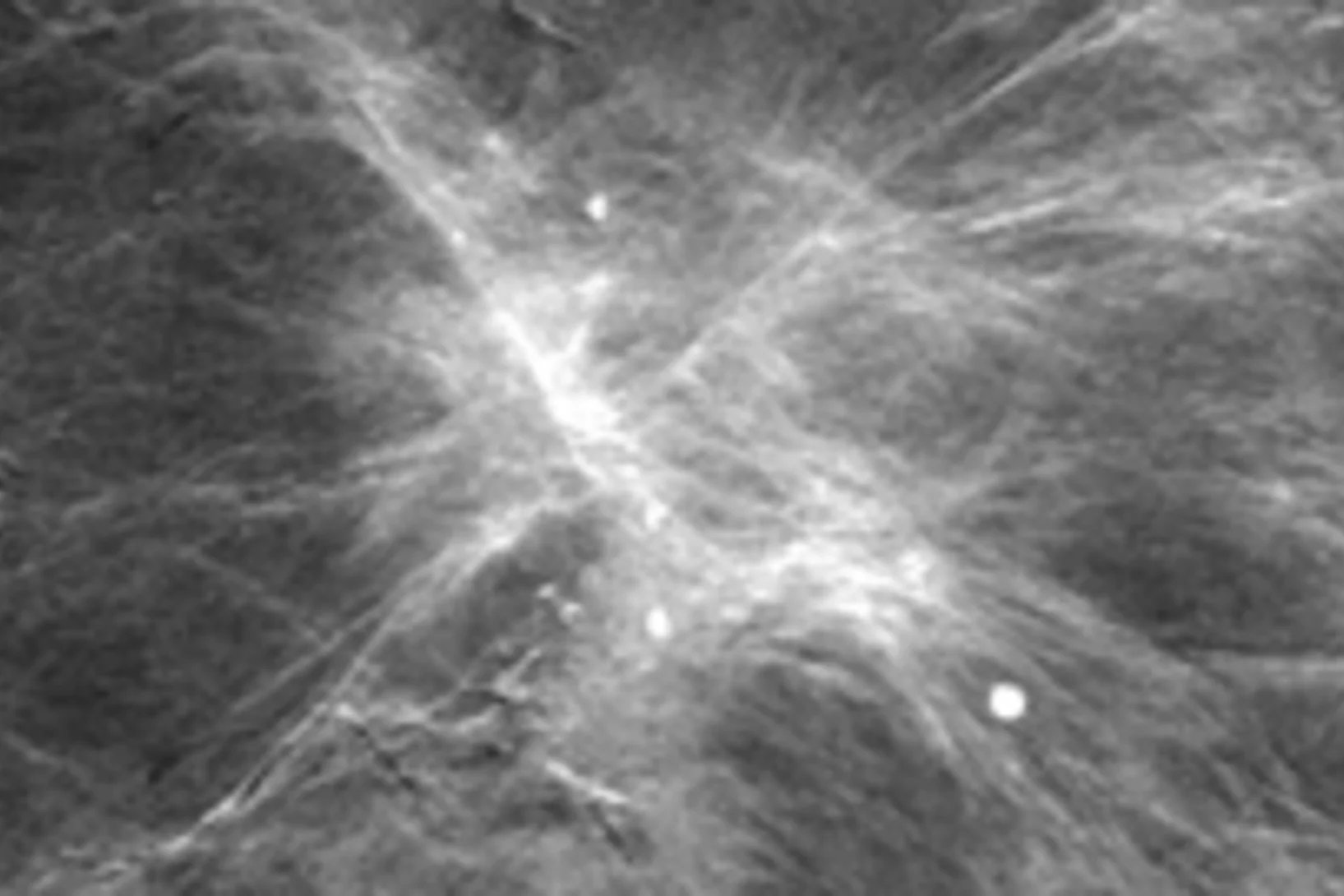
Neues Diagnoseverfahren bei Brustkrebs vielversprechend
Ein neues Mammografie-Verfahren könnte laut einer soeben veröffentlichten Studie einen deutlichen Mehrwert für die Diagnose von Brustkrebs in der medizinischen Praxis bringen. Die am PSI in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Brustzentrum des Kantonsspitals Baden und dem Industriepartner Philips entwickelte Methode macht bereits kleinste Gewebeveränderungen besser sichtbar. Dies könnte potenziell die Früherkennung von Brustkrebs verbessern. Zukünftig sollen Studien an Frauen mit einer Brustkrebserkrankung den Mehrwert der Methode endgültig belegen.
Mit Röntgenstrahlen der Lebensdauer von Lithium-Ionen-Akkus auf der Spur
Mithilfe von Röntgen-Tomographie haben Forschende die Vorgänge in Materialien von Batterie-Elektroden detailliert untersuchen können. Anhand hochaufgelöster 3D-Filme zeigen sie auf, weshalb die Lebensdauer der Energiespeicher begrenzt ist.
PSI-Forscherin Helena Van Swygenhoven erhält angesehene Europäische Förderung (ERC Grant)
Helena Van Swygenhoven, Werkstoffforscherin am Paul Scherrer Institut und Professorin an der ETH Lausanne (EPFL), erhält einen ERC Advanced Grant. Diese angesehene Förderung des Europäischen Forschungsrates in Höhe von 2,5 Millionen Euro wird es ihr ermöglichen, das neues Forschungsprojekt MULTIAX zu begründen. In diesem Projekt wird sie Vorgänge bei der Verformung von metallischen Werkstoffen untersuchen, die zum Beispiel für die Herstellungsprozesse von Autoteilen wichtig sind. Zusätzlich werden in dem Projekt neuartige Verfahren zur Untersuchung von Werkstoffen entwickelt, die dann auch anderen Forschenden zur Verfügung stehen werden.
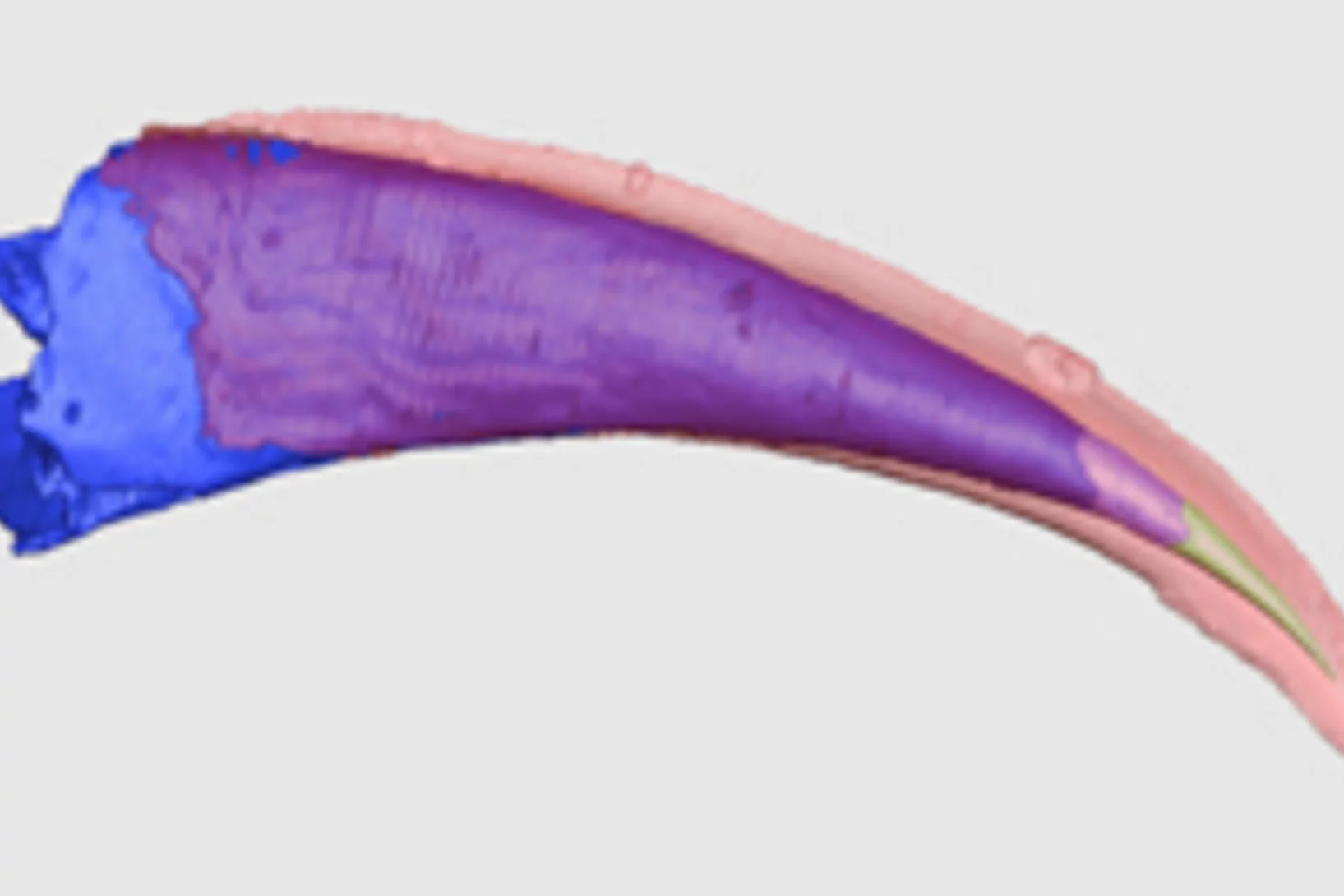
Die Ursprünge der ersten Fische mit Zähnen
Mit Hilfe von Röntgenlicht aus der Synchrotron Lichtquelle Schweiz des PSI ist es Paläontologen der Universität Bristol gelungen, ein Rätsel um den Ursprung der ersten Wirbeltiere mit harten Körperteilen zu lösen. Sie haben gezeigt, dass die Zähne altertümlicher Fische (der sogenannten Conodonten) unabhängig von den Zähnen und Kiefern heutiger Wirbeltiere entstanden sind. Die Zähne dieser Wirbeltiere haben sich vielmehr aus einem Panzer entwickelt, der dem Schutz vor den Conodonten, den ersten Raubtieren, diente.
Ein Blick in die Zukunft der globalen Energieversorgung
Wie wird sich die Welt im Jahr 2050 mit Energie versorgen und was werden die ökonomischen, ökologischen und sozialen Folgen verschiedener Entwicklungsziele und politischer Rahmenbedingungen sein? Diese Fragen beantworten Forscher des Paul Scherrer Institus PSI in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Weltenergierat WEC durch eine Untersuchung von zwei Szenarien, einem eher marktwirtschftlich und einem eher regulatorisch orientierten. Die Ergebnisse der nun abgeschlossenen Untersuchung werden vom 13. bis 17. Oktober am World Energy Congress des WEC in der südkoreanischen Stadt Daegu präsentiert werden
Mit Vitamin gegen Krebs
Cristina Müller vom Zentrum für Radiopharmazeutische Wissenschaften forscht an einer Therapie mit radioaktiv markierten Folsäure-Verbindungen. Diese gelangen wie ein Trojanisches Pferd ungehindert in die Zelle und töten diese dann mit ihrer Strahlung ab, erklärt sie.
Partikelbildung in der Atmosphäre
Wolken bestehen aus Wolkentröpfchen, die sich aus winzigen Partikeln bilden, die in der Atmosphäre schweben. Wie diese Partikel entstehen, ist in grossen Teilen noch nicht verstanden. Nun gelang erstmals die Beschreibung der Partikelbildung aus Aminen und Schwefelsäure. Ein Meilenstein in der Atmosphärenforschung.
Die Sicherheitskultur gestalten
Sabine Mayer leitet seit Anfang Jahr die Abteilung Strahlenschutz und Sicherheit ASI und ist somit zuständig für die Gewährleistung der Sicherheit am PSI von der Betriebsfeuerwehr über die Arbeitssicherheit bis zur radiologischen Überwachung. Doch die Bedeutung der Abteilung reicht über das PSI hinaus: die Schweizerischen Behörden vertrauen ihrem Pool an Fachleuten, so dass sie die Sicherheitskultur in der Schweiz mitprägt. Ein Interview.
Ein entscheidender Zerfall
Ein seltener Vorgang in der Natur soll darüber entscheiden, wie wir in Zukunft am besten unser Universum beschreiben. Es handelt sich um einen bestimmten Zerfall einer bestimmten Elementarteilchensorte: der Myonen. Diese Teilchen leben nicht lange und zerfallen in verschiedene andere Partikel. Doch ein ganz besonderer Zerfallsprozess ist laut den einen theoretischen Modellen praktisch verboten, laut den anderen aber erlaubt. Welche Theorie hat recht? Durch die genaueste Beobachtung von vielen hundert Billionen Teilchenzerfällen sind Physiker am Paul Scherrer Institut diesem Rätsel näher gekommen. Ihre Ergebnisse haben sie im Fachblatt Physical Review Letters veröffentlicht.